Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover
Front Cover: Development of Organoautocatalyzed Double s-Bond C(sp2)-N Transamination Metathesis Reaction (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 28/2025)
- First Published: 26 June 2025

Organoautocatalyzed transamination metathesis of challenging cyclic tertiary amines is reported. In their Research Article (e202505275), Svetlana B. Tsogoeva and co-workers demonstrate the use of an in situ-formed pyrrolidinium salt as an efficient organoautocatalyst, enabling double C(sp2)-N bond metathesis at room temperature via a domino reaction mechanism. This metal- and additive-free transformation advances green, waste-reducing, and sustainable approaches in organic synthesis.
Inside Front Cover: Hierarchically Self-Assembled Anion-Coordination-Driven Gels for Guest Segregation and Electrical Sensing (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 28/2025)
- First Published: 02 June 2025

The phase separation of self-assembled hosts in a gel from liquid guests is a convenient approach for heterogeneous encapsulation. In their Communication (e202504207), Dong Yang and co-workers report a class of gels formed through hierarchical self-assembly of “aniono” helicates, which can be utilized as filling material in columns and show the ability to selectively encapsulate and release choline. This study introduces the concept of flowing a solution containing guests through a host-containing gel for effective guest separation. The process of guest binding could be also monitored in real time via electrical characterization.
Inside Back Cover: A Simple Quinoid Building Block for Polymer Semiconductors with Tunable Polarity and High n-Type Thermoelectric Performance (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 28/2025)
- First Published: 28 May 2025

Developing high-performance n-type polymers relies on simple, easily accessible building blocks with minimal steric hindrance and strong electron deficiency. Xugang Guo and co-workers report a quinoid building block, thieno[3,2-b]thiophene-2,5-dione (TTD), in their Research Article (e202501196). The TTD-based polymers exhibit tunable charge carrier polarity from p-type to ambipolar and ultimately to n-type upon thermal annealing, along with outstanding n-type thermoelectric performance.
Outside Back Cover: Polyphosphorus Ligand Complexes of Coinage Metals for Multiple Capturing of Intact P4 Tetrahedra (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 28/2025)
- First Published: 30 May 2025

Like attracts like, they say; however, decades elapsed before mixed polyphosphorus ligand complexes were finally self-assembled. In their Research Article (e202503614), Eugenia Peresypkina, Manfred Scheer et al. demonstrate that reactive white phosphorus molecules can be captured by a polynuclear silver complex based on pentaphosphaferrocene and controllably released in solution. The cover image plays around the concept of high loading of intact tetrahedral P4 molecules within the carrier complex.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Whole-Cell Lysosome SMLM Imaging as Indicators for Functional Diagnostics with a Low-Phototoxic Spontaneously Blinking Probe
- First Published: 07 July 2025

Aze-HMSiR, a near-infrared spontaneously blinking fluorophore, enables long-term SMLM imaging of lysosomes with minimal phototoxicity, as reported by Xiaogang Liu et al. in their Research Article (e202503177). Combining pH responsiveness and high photostability, it reveals critical lysosomal features—distribution, size, and lumen pH—under different anticancer treatments. This whole-cell imaging approach provides a powerful new tool for visualizing lysosomal dynamics and serves as a sensitive indicator for functional diagnostics in live-cell environments.
Frontispiece: Cost-Effective and Low-Carbon Scalable Recycling of Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate Through Bio-Based Guaiacol-Enhanced Methanolysis
- First Published: 07 July 2025

A low-cost, scalable polyethylene terephthalate (PET) recycling method, detailed by Qingqing Mei et al. (e202503469), utilizes bio-based guaiacol and potassium bicarbonate to efficiently convert waste PET into high-value DMT. The artwork features a stylized tree intertwined with PET waste including bottles and textiles, symbolizing the connection between nature and science, while cyclical arrows emphasize PET recycling and sustainability.
Introducing…
Viewpoint Article
History of Science
Theodor Förster: Life and FRET from 1933 to 1951. A Viewpoint from the Archives
- First Published: 17 June 2025
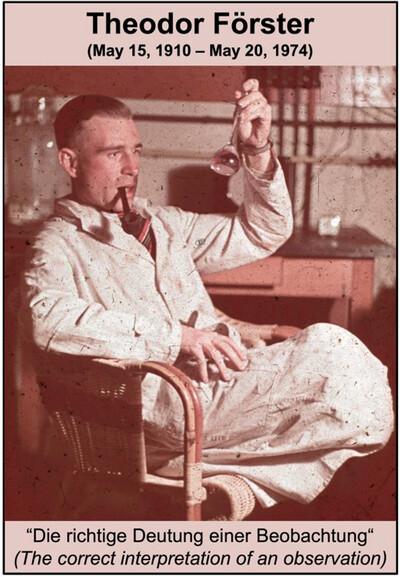

Theodor Förster's name is forever linked to FRET (Förster resonance energy transfer) and while his development of FRET theory is well known and recognized, only few is documented about his scientific career and life from 1933 to 1951. By reviewing documents from different archives, this Viewpoint Article discusses Förster's life and career before, during, and after National Socialism in Germany.
Minireview
Organic Molecular Crystals
Red and Near-Infrared Emissive Organic Crystals: Molecular Design and Optoelectronic Applications
- First Published: 04 June 2025
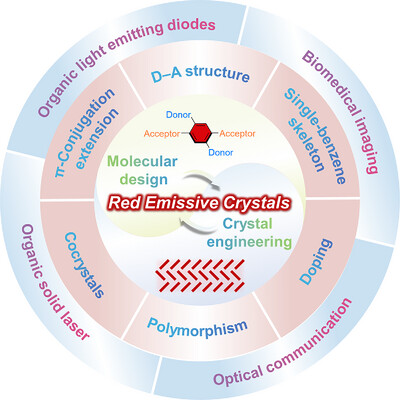
Over the past decade, red-emissive organic molecular crystals have advanced through molecular design (donor-acceptor structures, π-conjugation) and crystal engineering to overcome aggregation-caused quenching and energy gap limitations. Featuring high quantum yields, tunable deep-red/NIR emission, and flexibility, they enable applications in flexible waveguides, lasers, and bio-integrated optoelectronics.
Organic Cocrystals
From Binary to Higher-Order Organic Cocrystals: Design Principles and Performance Optimization
- First Published: 05 June 2025
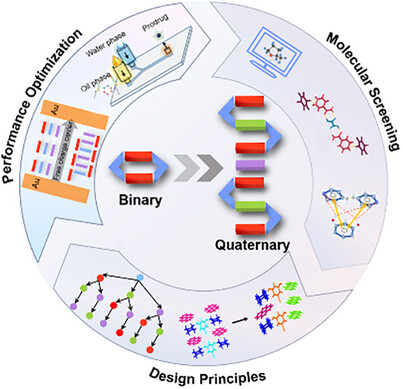
From binary to higher-order organic cocrystals: strategic design principles, precision synthesis, and multifunctional applications. The emergence of ternary and higher-order cocrystalline systems, comprising three or more components, has revolutionized the paradigm of material design by significantly expanding both structural diversity and functional potential. These advanced architectures not only exhibit enhanced design versatility through synergistic molecular engineering but also enable unprecedented modulation of physicochemical properties, thereby introducing novel optoelectronic, mechanical, and stimuli-responsive functionalities.
Review
Aerogels
Data-Driven Review on Aerogels and Polymeric Aerogels
- First Published: 31 March 2025

A review goes to data-driven. An exhaustive literature survey provides an overview of research status on aerogels, a category of highly porous solids with unique physicochemical properties. Statistical/data-driven analysis tells us positive/negative aspects; aerogels have a promising potential to contribute to emerging energy/environmental issues, while they are causing an academic fever with irresponsible exaggerations and a flood of unreliable data.
Electrocatalysis
Mechanistic Insights into Cation Effects in Electrolytes for Electrocatalysis
- First Published: 17 April 2025
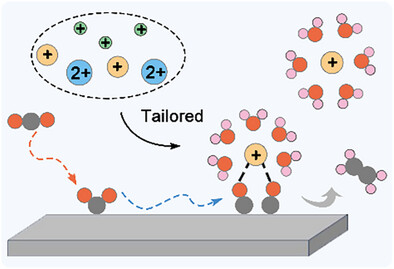
Cations play a pivotal role in controlling electrocatalytic reaction pathways, selectivity, and kinetics. A deeper mechanistic understanding of cation effects offers opportunities to overcome the activity–selectivity trade-off in electrocatalytic reactions, enabling the rational design of more efficient electrolyte systems.
Li–S Batteries
Design Strategies Based on Electronic Interactions for Effective Catalysts in Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
- First Published: 30 April 2025
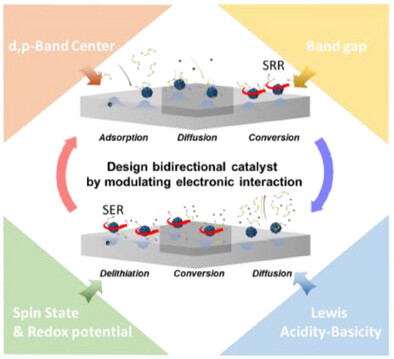
Design of effective bidirectional electrocatalyst focused on electronic interactions in lithium–sulfur batteries. Development of effective bidirectional catalyst is essential for high-energy density and long-life lithium–sulfur batteries. The catalytic activity of catalyst is directly related to the degree of the interaction between the catalysts and adsorbates. In the review, we introduce the design strategy for catalysts with high catalytic activity focused on the electronic structure and properties of catalysts and reactants.
Nanomedicine
Nanoparticle-Mediated Targeted Protein Degradation: An Emerging Therapeutics Technology
- First Published: 05 May 2025
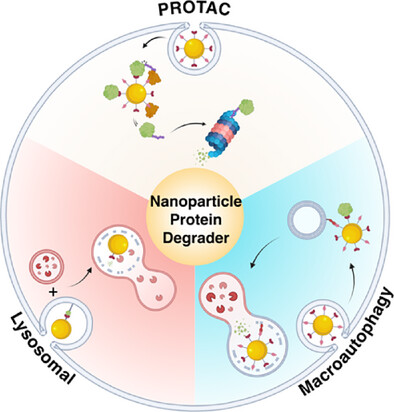
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) has emerged as a powerful therapeutic approach, with numerous candidates molecules now advancing into clinical development. Recent innovations have incorporated nanoparticles to facilitate and enhance these degradation processes, yielding synergistic effects. This work provides a comprehensive overview of the current landscape of nanoparticle-mediated targeted degradation, outlining recent advances, key challenges, and future opportunities to guide progress in this rapidly evolving field.
Research Article
NIR Molecular Probes
Whole-Cell Lysosome SMLM Imaging as Indicators for Functional Diagnostics with a Low-Phototoxic Spontaneously Blinking Probe
- First Published: 27 February 2025
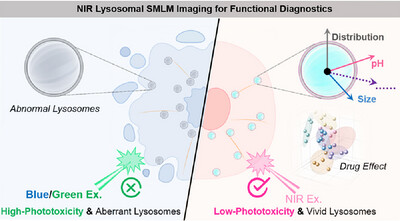
An NIR spontaneously blinking fluorophore, Aze-HMSiR, optimized for long-term SMLM imaging of lysosomes is developed. It exhibits superior photostability, pH responsiveness, and minimal phototoxicity. Aze-HMSiR can reveal key lysosomal characteristics, including distribution, size, and lumen pH, in response to various anticancer agents. Such whole-cell lysosome SMLM imaging serves as a valuable indicator for lysosomal functional diagnostics.
Autocatalysis
Development of an Organoautocatalyzed Double σ-Bond C(sp2)-N Transamination Metathesis Reaction
- First Published: 24 April 2025
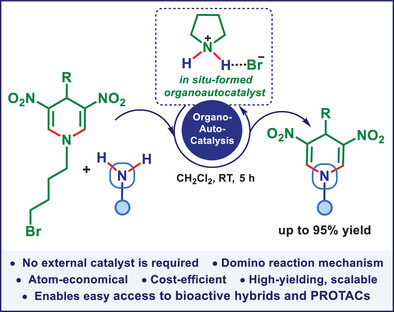
Organoautocatalyzed transamination metathesis of cyclic tertiary amines is disclosed as a high-yielding, scalable reaction that proceeds under mild, catalyst-free conditions. It operates via a multi-step domino reaction mechanism, where an in situ-formed pyrrolidinium salt functions as a HBD organoautocatalyst. The reaction opens the door for the efficient synthesis of novel N-substituted DNDHPs of interest in both life and materials sciences.
Polymer Semiconductors | Hot Paper
A Simple Quinoid Building Block for Polymer Semiconductors with Tunable Polarity and High n-Type Thermoelectric Performance
- First Published: 10 April 2025

A simple quinoid building block TTD, featuring small steric hindrance and high electron deficiency, was obtained via a one-step synthesis. Unexpectedly, the TTD-based polymers showed tunable charge carrier polarity from p-type to ambipolar and ultimately to n-type upon thermal annealing, and the n-doped polymers attained remarkable thermoelectric performance with a power factor of 36.7 µW m−1 K−2.
White Phosphorus | Hot Paper
Polyphosphorus Ligand Complexes of Coinage Metals for Multiple Capturing of Intact P4 Tetrahedra
- First Published: 22 April 2025
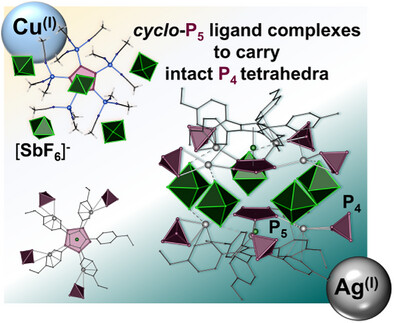
Self-assembly reactions of [CpRFe(η5-P5)] (CpR = C5(CH3)5 and C5(4-EtC6H4)5) with coinage metal salts and white phosphorus afforded an unprecedented novel class of mixed polyphosphorus ligand complexes in which metal ions multiply coordinate intact P4 tetrahedra. The bulkiness of the used CpR ligand and the right choice of the solvent tune the structure and the content of P4 in the coordination products that can release P4 upon decomplexation.
Nucleic Acids
Aptamer as a Molecular Tethering Agent Induces PrPC Aggregation and Degradation to Inhibit Melanoma Proliferation
- First Published: 30 April 2025
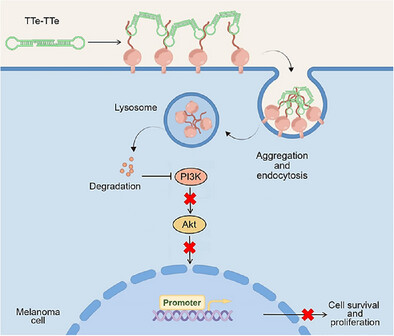
We developed a molecular tethering agent, TTe-TTe, that binds to the octapeptide repeat region of glycosylated PrPC. TTe-TTe suppresses malignant melanoma proliferation by triggering PrPC to aggregate on the cell membrane surface, followed by its degradation. This versatile platform technology opens up new avenues for targeted protein degradation in a wide range of therapeutic applications, potentially advancing the field of drug discovery.
3D COF
High-Performance Perovskite Solar Cells via 3D Covalent Organic Frameworks: Enhanced Efficiency Through Precision Interface Engineering
- First Published: 29 April 2025
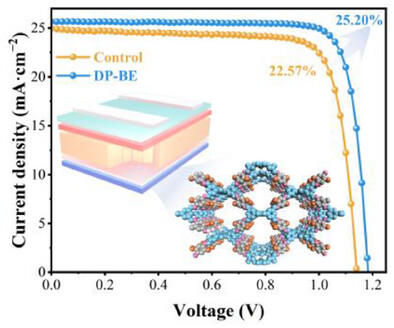
Two donor-acceptor 3D COFs synthesized via Schiff base reactions were integrated into perovskite solar cells’ SAMs. Their architecture enabled efficient charge separation, stable interfacial anchoring, and optimized energy alignment, enhancing hole transport and perovskite quality and reduced defect density. This achieving PCEs up to 25.20%, demonstrating COFs' potential in advancing PSC efficiency.
Hydrogen Production
Energy-Efficient Hydrogen Generation via Peroxide-Mediated Electrocatalytic Pathways
- First Published: 29 April 2025
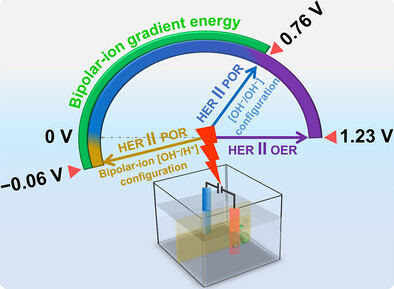
The advantages of peroxide redox chemistry are explored for green hydrogen production. Peroxide redox electrocatalysts enable efficient and selective peroxide production and oxidation, facilitating on-site hydrogen generation while achieving a nearly 50% reduction in applied potential compared to conventional water-splitting methods. An integrated bipolar-ion gradient system further reduces energy requirements to nearly one-third of traditional electrolysis.
Hydroarylation
Modular Access to Arylethylamines Enabled by Ni-Catalyzed Markovnikov-Selective Hydroarylation of Allylic Amines
- First Published: 29 April 2025
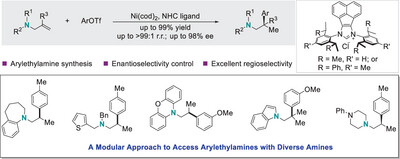
We describe a modular and efficient nickel-catalyzed Markovnikov-selective hydroarylation of readily available allylic amines, affording various valuable arylethylamines with exclusive regiocontrol. The use of NHC─Ni catalyst was crucial to achieve high efficiency and selectivity. In particular, with bulky chiral NHC ligands, enantioenriched arylethylamines were prepared in high efficiency with excellent regio- and enantioselectivities.
Photocatalytic H2O2 Production
Production of H2O2 via Energy Transfer Photocatalysis by Coupling with Furfuryl Alcohol Conversion over an Amide-Functionalized Heptazine Framework
- First Published: 30 April 2025

Traditional charge-carrier-based photocatalysis can be switched to a novel energy transfer route for efficient and selective 1O2 generation through amide functionalization to modulate the electronic structure of the photocatalyst, thus providing a promising approach for simultaneous synthesis of H2O2 and conversion of a biomass derivative.
Ionic Liquids
Revealing the Nature of Non-Covalent Interactions in Ionic Liquids by Combined Pulse EPR and 19F NMR Spectroscopy
- First Published: 29 April 2025
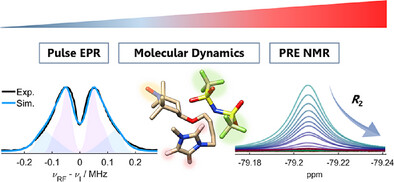
Ionic liquids have been proposed as alternatives to molecular solvents. Here, spin probes and spin-labelled ILs are studied by pulse electron paramagnetic resonance, paramagnetic relaxation enhancement NMR, molecular dynamics, and density functional theory, revealing the IL interaction sphere. The results challenge previous interpretations of nitroxide-solvent nanostructuring in ILs.
Fenton Chemistry | Hot Paper
Bromide as Noninnocent Ligand to Iron Tames Fenton Chemistry for Chemoselective Nondegrading Oxidation
- First Published: 30 April 2025
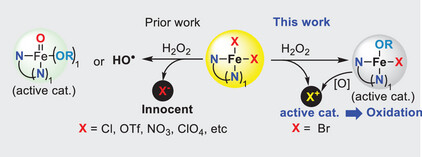
We report for the first time that the bromide ion, acting as a non-N-ligand in iron complexes with the tridentate N-ligand bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (BMPA), which is traditionally used in Fenton chemistry to degrade organic compounds, tames Fenton chemistry and enables chemo-selective, nondegrading oxidation reactions. This discovery of the bromide effect bridges the gap between Fenton chemistry and haloperoxidase-catalyzed halogenation, potentially inspiring further investigation into the “innocent” ligands of iron complexes for new reactivity and applications. The overlooked inorganic anion may be exploited in other catalytic systems.
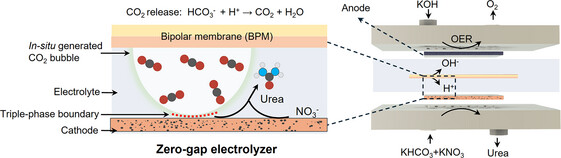
Zero-Gap Electrolyzer
Triple-Phase Boundaries Enable Selective Urea Production From Simulated Flue Gas in a Zero-Gap Electrolyzer
- First Published: 30 April 2025
Carbon Dots | Hot Paper
Visible Light Excited Time-Dependent Phosphorescence Color Tuning in Carbon Dots via Charge Transfer
- First Published: 29 April 2025
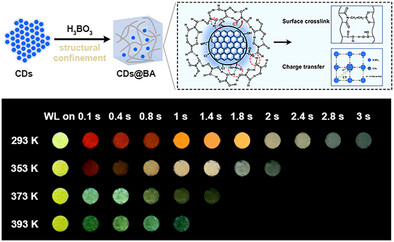
We reported the discovery of confining carbon dots (CDs) into boric acid matrix realizing the precise regulation of color from red to white with delay time increase under white light (WL) excitation. And composites can emit persistent afterglow at high temperatures up to 393 K under WL excitation. Its time-dependent phosphorescence color (TDPC) and high stability lay a solid foundation for higher-order cryptographic and anticounterfeiting.
Photoswitches
Harnessing Negative Photochromism in Styryl Cyanines for Light-Modulated Proton Transport
- First Published: 02 May 2025
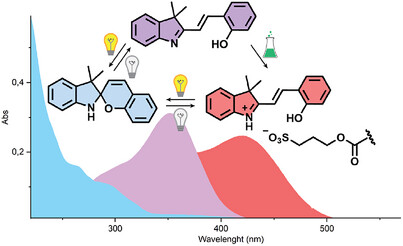
We show how photo switchable styryl cyanines undergo an extremely efficient photochemical ring-closing reaction upon irradiation. Furthermore, substituents on the ring and the nature of their surroundings can be used to tune their chemistry, kinetics, and photochemical properties. Finally, we demonstrate how these molecules can be used as smart dopants to control proton transport using light in a polymeric matrix.
CO2 Electroreduction
Beyond Second Coordination Shell: Long-Range π-Electrons Delocalization Engineering in Single-Atom Catalysts for CO2 Electroreduction
- First Published: 30 April 2025
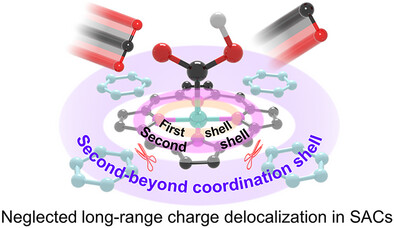
Single-atom catalysts (SACs) depend on hierarchical coordination environments, yet higher-order shells (>2nd) critically influence electronic structures via long-range charge delocalization. This study pioneers long-range interaction engineering in single-atom catalysts (SACs) for CO2 electroreduction. By tailoring pyrolysis of NiTPP to preserve Ni-N4 coordination shell (first and second) while eliminating peripheral π-delocalization, the catalyst achieves a 29-fold CO efficiency boost (85.9% at −1.4 V) and 98.3% selectivity at 500 mA cm−2.
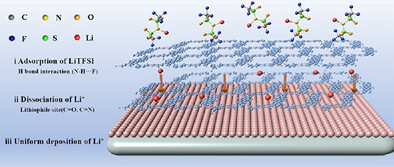
Lithium Metal Batteries
Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Framework with Desolventization and Lithium-Rich Sites for High-Performance Lithium Metal Anodes
- First Published: 01 May 2025
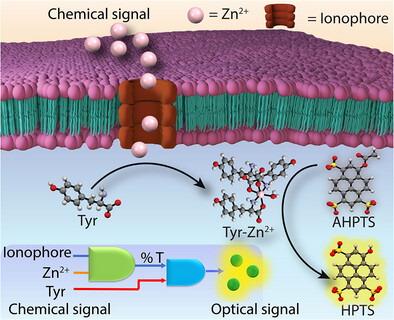
Transmembrane Ion Transport
Supramolecular Ion Channels to Engineer Zn2+ Ion Transport Mediated Chemical-to-Optical Signal Transduction
- First Published: 29 April 2025
Protein-Protein Interactions | Hot Paper
Multiple and Alternative Sites Make Tau Protein an Adaptable Sticky Surface for the SH3 Domain of Fyn Kinase
- First Published: 05 May 2025
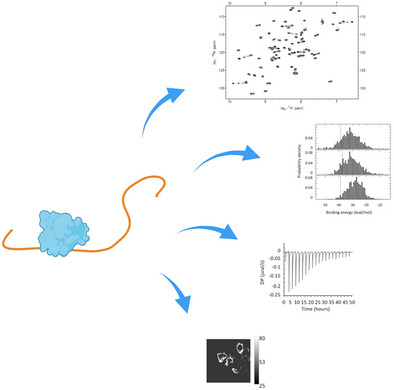
An NMR-based study, combined with computational, calorimetric and in-cell FRET methods, sheds light on the complex recognition mechanism between the intrinsically disordered protein Tau and the SH3 domain of Fyn kinase, highlighting how the multiple binding sites present in Tau make the protein an adaptable recognition surface that can function even when single consensus motifs are eliminated.
Spirobipyridine Synthesis
Chiral Spirobipyridine Synthesis by Cobalt-Catalyzed Enantioselective Double [2 + 2 + 2] Cycloaddition
- First Published: 30 April 2025
Biocatalysis
Covalent Organic Framework Nanosheets for the Assembly of Efficient Membrane Bioreactors
- First Published: 30 April 2025
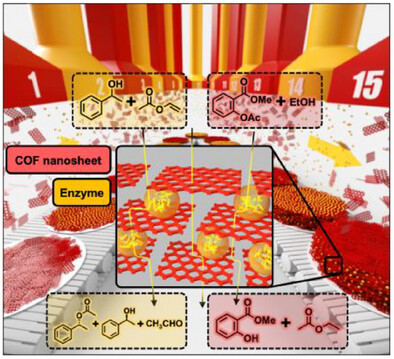
We present a layer-by-layer assembly method to trap enzymes between covalent organic framework (COF) nanosheets instead for the construction of membrane bioreactors. This design boosts mass transfer, shields enzymes from harmful by-products, and enables rapid substrate conversion (complete in 7.95 s)—achieving 1018× higher activity than free enzymes. The reactor maintains stability under continuous use and works with diverse enzymes/COFs, offering a versatile platform for high-performance biocatalysts.
Conjugated Oligoelectrolytes | Hot Paper
Mechanosensitive Conjugated Oligoelectrolytes for Visualizing Temporal Changes in Live Cells
- First Published: 05 May 2025
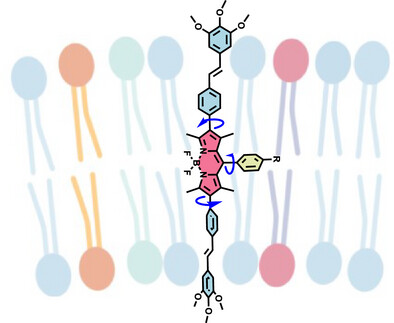
Mechanosensitive conjugated oligoelectrolytes (COEs) with integrated twistable bonds enable real-time imaging of membrane tension in lipid bilayers. Using fluorescence lifetime analysis, COE-BY probes reveal vesicle rigidity changes during endocytosis, providing insights into membrane mechanics at the subcellular level.
Organic Solar Cells | Hot Paper
Multiple-Asymmetric Molecular Engineering Enables Regioregular Selenium-Substituted Acceptor with High Efficiency and Ultra-low Energy Loss in Binary Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 04 May 2025
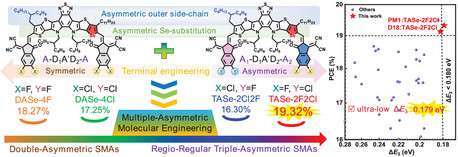
The synergistic strategies of the double asymmetric core and symmetric/asymmetric terminal engineering are applied to develop multiple-asymmetric acceptors. By delicately tuning the number and position of peripheral F and Cl atoms, the regioregular triple-asymmetric TASe-2F2Cl-based binary OSCs yield the first-class efficiency of 19.32% and ultralow nonradiative recombination energy loss (ΔE3) among selenium-substituted acceptors.
Lipid Nanoparticles
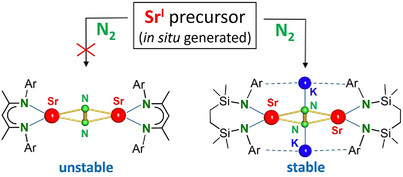
N2 Activation | Hot Paper
Molecular Motors
Strain Energy Induced Rotary Speed Acceleration in a Light-Driven Molecular Motor
- First Published: 30 April 2025
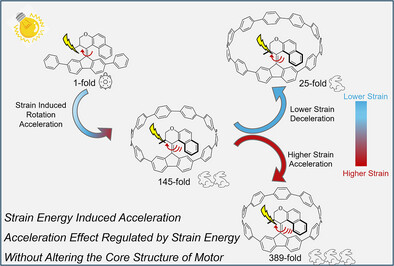
A new strategy accelerates rotary speed in overcrowded alkene-based molecular motors by tuning cycloparaphenylene loop size, preserving core structures. Strain energy variations drive hierarchical acceleration up to 389-fold. This study systematically reveals motor behavior under strain, offering new avenues for engineering light-driven nanomachines.
Anode-Free Batteries | Very Important Paper
Preparation of Cyclic Olefin Polymers via Group Transfer Radical Cyclopolymerization for High Performance in Anode-Free Batteries
- First Published: 30 April 2025
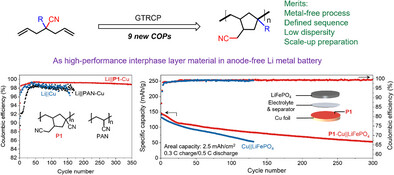
An innovative group transfer radical cyclopolymerization (GTRCP) method has been developed for the precise synthesis of functionalized cyclic olefin polymers (COPs) using non-conjugated diene monomers. Through rational monomer design, various polar groups are incorporated into the COP backbones. The resulting polymers exhibit high molecular weights, low dispersities, controllable chain sequences, and high structural diversity. The polymer can function as a robust interphase layer, enhancing the reversibility of lithium plating/stripping in anode-free lithium metal batteries.
Composite Polymer Electrolytes
Regulating Ion Transport Through Direct Coordination in Composite Gel Polymer Electrolytes Toward High-Voltage and High-Loading Quasi-Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries
- First Published: 02 May 2025
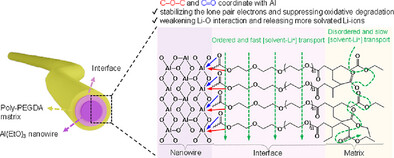
Polyether monomers coordinate with aluminum ethoxide nanowires via in situ ultraviolet curing, stabilizing the lone pair electrons of ethereal oxygen atoms and suppressing oxidative degradation. This coordination also forms abundant and tight interfaces as the predominant lithium-ion conduction pathways, contributing to ordered lithium-ion fluxes. The composite gel polymer electrolyte facilitates high-performance Li||LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cell.
Covalent Inhibitors
Lysine-Targeting, Covalent Inhibitors of Bromodomain BD1 of BET Proteins in Live Cells and Animals
- First Published: 01 May 2025
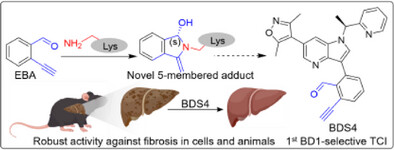
We successfully developed the first BD1-targted covalent inhibitor (TCI), BDS4, by utilizing 2-ethynylbenzaldehyde (EBA). Importantly, BDS4 retained robust activity against fibrosis in cells and animals when compared to the marginal effects of BD2 inhibitor RVX-208. Our developed tool showed clear advantages of long-lasting domain-selective TCI in delineating the district function of BD1 and BD2.
Drug Discovery
The ATM Kinase Inhibitor AZD0156 Is a Potent Inhibitor of Plasmodium Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase (PI4Kβ) and Is an Attractive Candidate for Medicinal Chemistry Optimization Against Malaria
- First Published: 03 May 2025
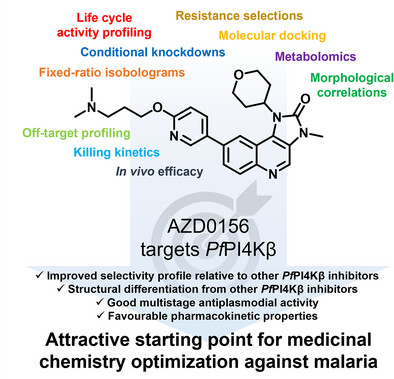
AZD0156, an ATM kinase inhibitor in clinical development, shows promising multistage antiplasmodial activity by targeting Plasmodium falciparum phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase (PfPI4Kβ). With an improved specificity profile relative to other PfPI4Kβ inhibitors and moderate efficacy in a P. berghei disease model, AZD0156 is an attractive candidate for medicinal chemistry optimization against malaria.
Topological Heterostructures | Very Important Paper
Noncovalent Synthesis of Topological Heterostructures Using a Site-Selective Electrostatic Co-Assembly Strategy
- First Published: 07 May 2025
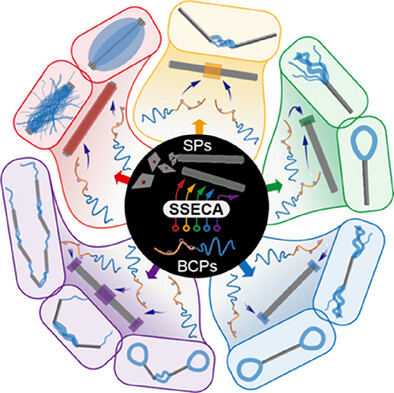
A site-selective electrostatic co-assembly (SSECA) strategy was developed to fabricate a variety of topological heterostructures (THSs) with unprecedented architectures from two-component systems of organometallic complexes and block copolymers. The THSs are composed of rigid parts of closely stacked organometallic complexes and flexible segments formed from electrostatic co-assembly of BCPs and the complexes originally in the SPs.
Anti-Tumor Agents
Tumor-Specific On-Site Activation of Cisplatin via Cascade Catalytic-Redox Reactions for Highly Efficient Chemo-Immunotherapy
- First Published: 04 May 2025
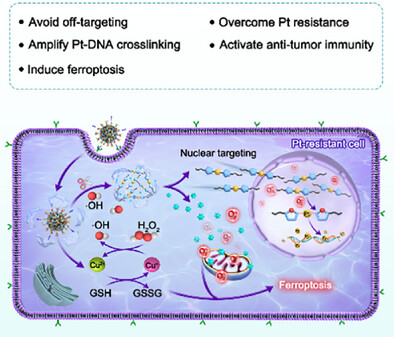
A double-lock protected PtII nanomedicine has been developed, which performs cascade unlocking of cisplatin (cDDP) via catalytic-redox reactions, thus achieving tumor-specific “on-site” activation of cDDP in the nucleus accompanied with substantial induction of ferroptosis for highly efficient chemo-immunotherapy.
Circularly Polarized Luminescence
Supramolecular Charge-Transfer Approach for Tunable and Efficient Circularly Polarized Delayed Fluorescence and Phosphorescence
- First Published: 02 May 2025
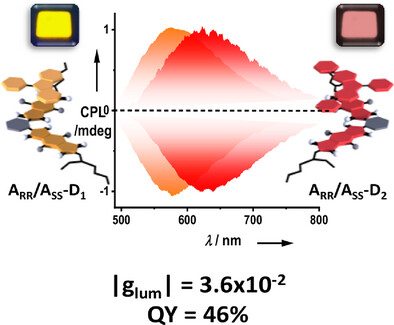
The non-covalent supramolecular and intermolecular charge-transfer (CT) strategy, employing bis-chromophoric pyromellitic diimides (PmDIs) and judicious choice of donors, enabled tunable circularly polarized delayed luminescence in the red region with a high quantum yield of ∼46% and a significant |glum| value of up to ∼3.6 × 10⁻2.
Zinc-Sulfur Batteries
High-Entropy Sulfides Catalyze Rate-Determining Redox in Fast-Charging Aqueous Zinc–Sulfur Batteries
- First Published: 04 May 2025
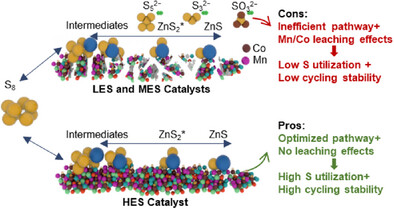
This work reveals how entropy regulates sulfur utilization and cycling stability in aqueous Zn–S batteries. High-entropy (HES) catalysts enable optimized Zn–S redox pathways and structural integrity, achieving high sulfur utilization and stable cycling. In contrast, low- (LES) and medium-entropy (MES) catalysts show inefficient reactions with by-product formation and Mn/Co leaching, degrading performance. Practical validation demonstrates HES-based pouch cells maintain exceptional stability over 400 cycles at 4 C with merely 0.06% capacity decay per cycle, establishing entropy engineering as a practical design strategy.
Host-Guest Systems
Phenacetin[3]Arenes: Mannich-Type Macrocyclization, Unique Structure, Versatile Functionalization, and Strong Allosteric Binding
- First Published: 02 May 2025
![Phenacetin[3]Arenes: Mannich-Type Macrocyclization, Unique Structure, Versatile Functionalization, and Strong Allosteric Binding](/cms/asset/57413a48-00ca-4d21-a09f-e7d5b7bc7e06/anie202504211-gra-0001-m.jpg)
The one-step acid-catalyzed condensation of phenacetin and its analogues with paraformaldehyde provides a facile route to hourglass-shaped phenacetin[3]arenes with distinct functionalized rims in good yields. These novel macrocyclic arene show excellent binding properties and offer the potential for chirality sensing.
Photoelectrocatalysis | Hot Paper
Photoelectrocatalytic Activation of C─H Bond in Toluene by Titanium Dioxide-Supported Subnanometric PtOx Clusters
- First Published: 04 May 2025
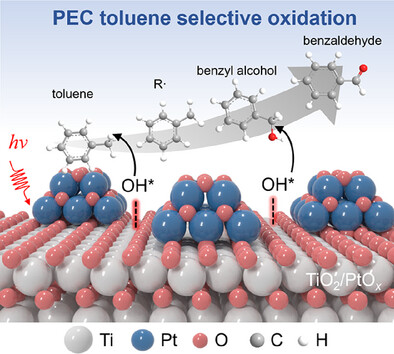
Photoelectrocatalytic activation of C(sp3)─H bonds in hydrocarbon molecules to produce valuable oxygenates still suffers from the limited generation of reactive species and the weak adsorption of reactants. This study achieved the selective oxidation of toluene using a TiO2 supported subnanometric PtOx cluster (PtOx/TiO2) photoanode via an electrophilic OH*-mediated pathway. The modification of PtOx cluster can facilitate toluene adsorption and OH* generation, leading to the high efficiency of toluene oxidation.
Liquid Crystals
On the Mechanism of Soft Self-Assembly from Melt: The Ubiquitous Heat Capacity Hump and Spontaneous Melt Chirality
- First Published: 02 May 2025
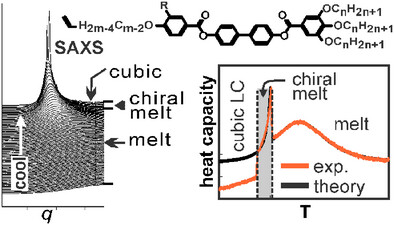
Phase transition from melt to most complex liquid crystal (LC) phases is weak 1st order but is preceded by a large heat capacity maximum. In addition, a chiral liquid forms through another transition before that to the LC, despite the compounds being achiral. We investigate these poorly understood phenomena experimentally and develop a statistical theory that fits the experiments remarkably well, giving new insights into the mechanism of self-assembly and pre-assembly.
Composite Crystals
Spatially Engineering the Internal Microstructure of a Single Crystal via Nanoparticle Occlusion
- First Published: 02 May 2025
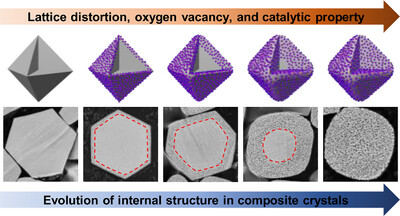
The spatially controlled occlusion of polymeric nanoparticles into cuprous oxide (Cu2O) systematically alters lattice distortion, oxygen vacancy content, and catalytic efficiency in the resulting composite crystals, offering a robust framework for the development of advanced functional composite materials.
Sodium Batteries
P-type Cathode Material Design Guided by Material Descriptors for High-Energy Density Sodium Batteries
- First Published: 02 May 2025
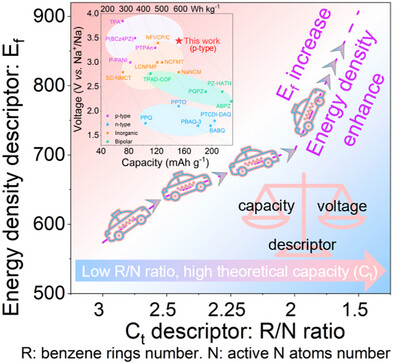
The material descriptors are first proposed to guide the design and screening of high-energy density p-type organic cathode materials. Triphenylamine and synthesized p-PZA POP proved the rationality of these descriptors. Na||p-PZA POP batteries exhibit a surprisingly high energy density of 524.6 Wh kg−1 at 1 A g−1 and excellent wide-temperature electrochemical performance.
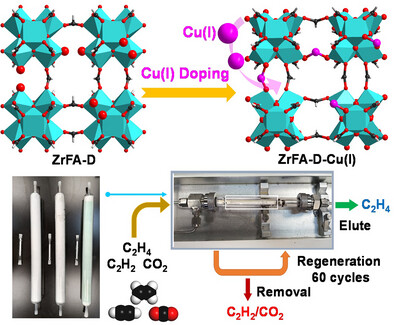
Metal-Organic Frameworks | Very Important Paper
Synthesis and Modification of Formate Zr-MOF (ZrFA) Toward Scalable and Cost-Cutting Gas Separation
- First Published: 02 May 2025
Electrochemiluminescence | Hot Paper
p–π Conjugation-Promoted Electrochemiluminescence of Halogenated Covalent Organic Framework Nanoemitters
- First Published: 02 May 2025
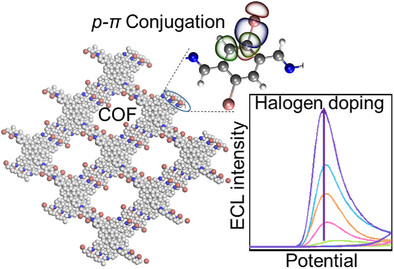
We design a series of halogenated COF nanoemitters via a covalent halogenation predesign strategy. The introduction of halogen atoms facilitates p–π conjugation within COF skeleton, leading to a 49-fold ECL enhancement compared to nonhalogenated COF. Furthermore, the performance of four partially brominated COFs establishes a positive correlation between the degree of Br doping and ECL intensity.
Mechanoluminescent Materials | Hot Paper
Solar-Blind UV Organic Mechanoluminescent Materials
- First Published: 02 May 2025
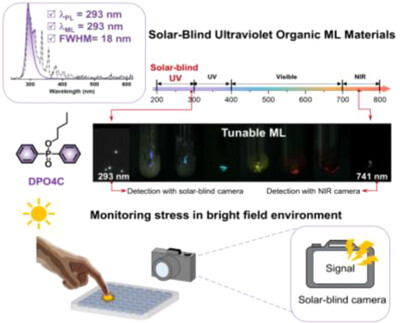
A new strategy to achieve solar-blind UV mechanoluminescent (ML) materials through strategically breaking the molecular conjugation and adjusting the packing mode. DPO3C and DPO4C exhibited solar-blind UV emission with the maxima at ca. 293 nm, with wide-range color-tunable ML emissions from 293 to 741 nm via host–guest doping. This study also paves the way for advancements in bright-field stress visualization.
H2O2 Photosynthesis | Hot Paper
Unlocking One-Step Two-Electron Oxygen Reduction via Metalloid Boron-Modified Zn3In2S6 for Efficient H2O2 Photosynthesis
- First Published: 02 May 2025
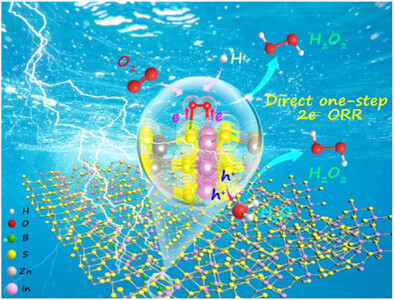
A boron-modified Zn3In2S6 photocatalyst is engineered, featuring In-B dual-active sites that establish dual-channel carrier transfer pathways and substantially prolong photogenerated carrier lifetimes five-fold. These synergistic effects enable direct one-step 2e− ORR for efficient H2O2 production from O2 in pure water, achieving a record apparent quantum yield of 49.8% at 365 nm among inorganic semiconductor photocatalysts.
Organic Solar Cells | Very Important Paper
Design of Intrinsically Stable Hole-Selective Self-Assembled Monolayers by Introducing Fused-Ring Intramolecular Donor–Acceptor Interactions
- First Published: 05 May 2025
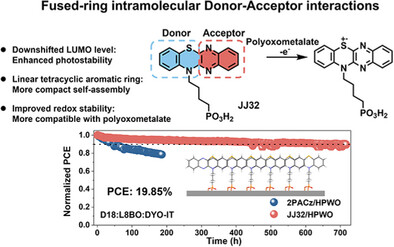
Herein, we develop a novel SAM molecular design strategy by introducing fused-ring intramolecular donor–acceptor (D–A) interactions. The designed molecule, JJ32, features a benzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline skeleton, where strong D–A interactions enhance charge delocalization and downshift the LUMO energy level. This leads to enhanced photostability, redox stability, and intermolecular interactions. Moreover, the improved redox stability benefits the promising polyoxometalate/SAM composite HSL, allowing the JJ32/HPWO-based OSC to reach 19.85% efficiency with improved stability.
C─H Activation | Very Important Paper
Effective Hole Utilization for Atomically Dispersed Low-Coordination Molybdenum Accelerating Photocatalytic C─H Activation
- First Published: 02 May 2025
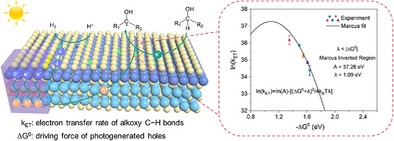
Atomically dispersed low-coordination Mo on ultrathin ZnIn2S4 nanosheets has been successfully developed for acceptorless dehydrogenation of alcohols. The isolated Mo sites optimize the driving force of photogenerated holes, which greatly accelerates the electron transfer rate of the alkoxy C─H bonds, resulting in the formation of high-concentration alkyl radicals.
Solid State Li Batteries | Hot Paper
Constructing Ionic Transport Network via Supramolecular Composite Binder in Cathode for All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries
- First Published: 02 May 2025
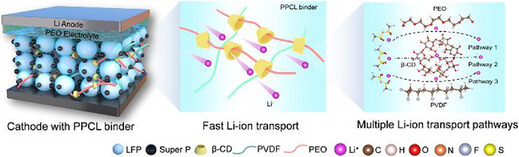
A simple and effective composite binder strategy is proposed to establish multiple and highly efficient Li+ transport channels within the LiFePO4 cathode, which significantly improves the Li+ transport efficiency and achieves high-performance all-solid-state lithium batteries at high cathode active loading.
Organic Solar Cells | Hot Paper
Construction of Shamrock-Shaped Giant Molecule Acceptors for Efficient Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 02 May 2025
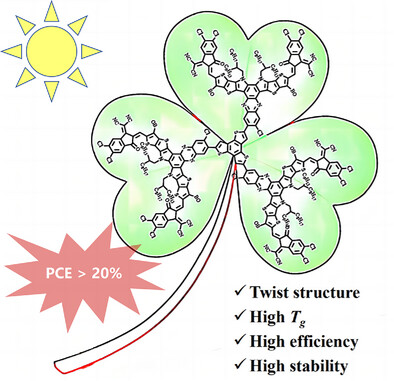
Based on the highly efficient Qx series of small molecules, we have synthesized T-Qxs, which are shamrock-shaped giant molecules with high glass transition temperature. The miscibility with the polymer donor PM6 was fine-tuned by modulation of the central and terminal atoms, thereby altering the molecular distortion angle. Organic solar cells (OSCs) based on the fully chlorine-substituted T-Qx-15Cl achieve both high power conversion efficiency (PCE) and high thermal stability.
Liquid Crystals | Hot Paper
Intrinsically Luminescent Nematic Liquid Crystals Enabling High-Brightness Full-Color and White Circularly Polarized Luminescence via Chiral Coassembly
- First Published: 02 May 2025
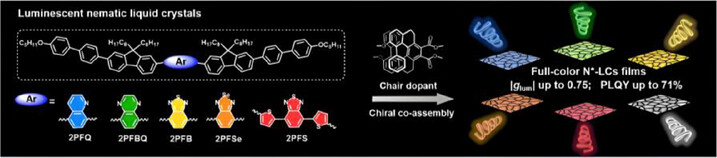
A novel class of luminescent nematic liquid crystals (N-LCs) exhibiting full-color emission was developed. Through coassembly with chiral dopants, these N-LCs enabled the fabrication of high-brightness full-color and white circularly polarized luminescent (CPL) films with simultaneously enhanced glum (up to 0.75) and photoluminescence quantum yield (up to 71%), representing the best performance to date among all intrinsically luminescent CPL materials.
CO2 Photoreduction
Dopant and Exfoliation Induced Simultaneous Modification of Charge Density and C─C Coupling Sites for Efficient CO2 Photoreduction to Ethylene
- First Published: 05 May 2025
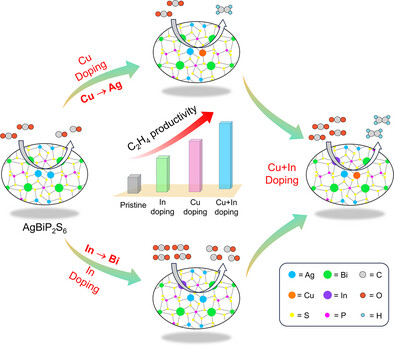
The photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into higher carbon products demands precise catalyst engineering. In this study, we implemented a dual doping strategy in AgBiP₂S₆ to optimize charge density and enhance active sites for C─C coupling. This approach successfully enabled the synthesis of ethylene through the photoreduction of CO2, showcasing the effectiveness of the modified catalyst design.
Homogeneous Catalysis
Iron-Catalyzed Radical Allylic Substitution of Unprotected Allylic Alcohols
- First Published: 05 May 2025
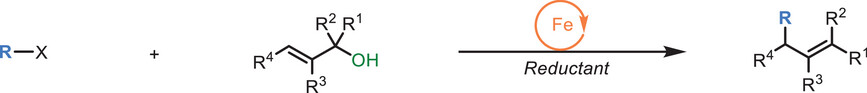
We report an iron-catalyzed radical allylic substitution method that directly functionalizes unprotected allylic alcohols, eliminating the need for prefunctionalization and toxic reagents. Utilizing iron's unique redox and oxophilic properties, this approach offers a step-economic and sustainable pathway to allylic functionalization. This method expands the synthetic toolbox and demonstrates the versatility of outer-sphere mechanisms in radical-based reactions, facilitating the efficient synthesis of diverse molecular architectures.
Li-Rich Mn-based Cathodes | Hot Paper
Boosting Initial Coulombic Efficiency in Li-Rich Mn-based Cathodes by Tuning Orbital Hybridization
- First Published: 06 May 2025
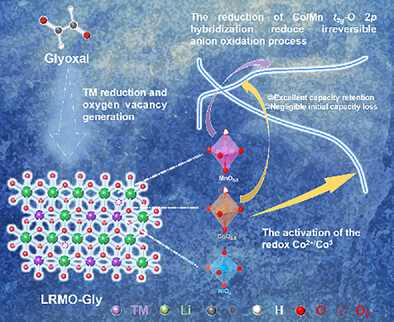
In this study, we investigated the potential of Li-rich manganese-based oxides as promising cathode materials for next-generation lithium-ion batteries, highlighting the critical challenges posed by low initial coulombic efficiency and irreversible oxygen release. We introduce a novel treatment method using Glyoxal, which facilitates the integration of transition metal 3d and oxygen 2p orbital hybridization, aimed at optimizing the electrochemical performance of LRMO. Our results demonstrate a significant improvement in ICE, increasing from 85.3% to 102.5%. Additionally, the treated LRMO achieves a high specific capacity of 291.2 mAh g−1 at 0.1 C, surpassing untreated samples, and exhibits excellent cycling stability with retention rates of 90.1% after 150 cycles and 76.5% after 250 cycles at 0.5 C.
Batteries | Hot Paper
Dihydrophenazine Derived Pd6L12 Cage: Self-Assembly, Polyradical Cations, and Lithium Battery Cathode Application
- First Published: 05 May 2025
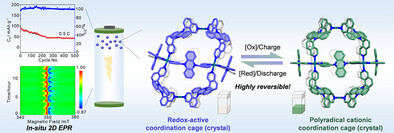
In this study, we synthesized a dihydrophenazine-based Pd6L12 coordination cage (Cage 1) with excellent redox activity. It can reversibly transform into its radical cation form (112•+) via electrochemical or chemical oxidation/reduction. Both forms' structures were determined by X-ray diffraction. In situ spectroelectrochemical techniques verified their redox reversibility and electrochromic behavior. Cage 1 was also used as a lithium battery cathode, with its redox behavior studied by in situ 2D EPR.
Furfural-Nitrate System
Manipulation of Hydrogen Transfer Behaviors by RhCu Alloying Enables an All-in-one Sustainable “Furfural-Nitrate” System
- First Published: 06 May 2025
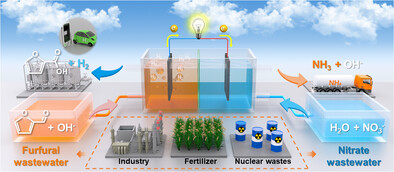
We report an all-in-one electrochemical energy system by coupling the rational conversions from nitrogen-oxysalts and biomass-derived-aldehydes (industrial/agricultural wastes). The poor reaction kinetics are efficaciously optimized by RhCu alloy electrocatalyst with dual-directional H*-modulation properties. So, nitrate and furfural can be simultaneously converted into multiple non-mixed valuable products (NH3, H2, etc.) with electricity output.
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
Site-Specific Spin State Modulation in Spinel Oxides for Enhanced Nonradical Oxidation
- First Published: 05 May 2025

This work highlights a strategy that leverages site-specific spin state modulation in spinel oxides, which optimizes site-specific functionalities and enhances the overall nonradical oxidation reaction kinetics by 22-fold. XAS, magnetism characterization combined with theoretical calculation unveil the establishment of a QSEI that facilitates spin channel for charge transfer and the RDS desorption with a lower-ICOHP in fine-tuned spin states.
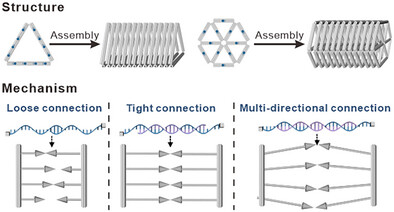
Nanomaterials | Hot Paper
Programming One-Dimensional Open-Channel Superlattices with Edge-Bonding of Meta-DNA
- First Published: 07 May 2025
Oxygen Reduction Reaction | Very Important Paper
Defect-Triggered Orbital Hybridization in FeMn Dual-Atom Catalysts Toward Sabatier-Optimized Oxygen Reduction
- First Published: 06 May 2025
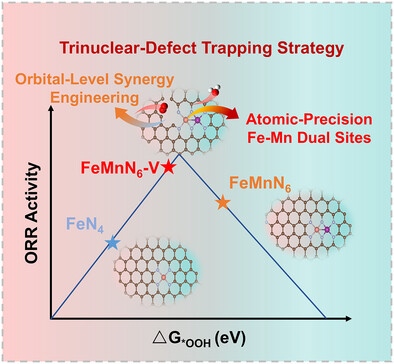
A defect-engineered heteronuclear FeMn dual-atom catalyst on a porous N-doped carbon matrix is synthesized via a customized trinuclear-defect trapping strategy. The defect-mediated coordination strengthens Fe 3dz2 with O 2p orbital hybridization, optimizing adsorption energy toward Sabatier optimality. The catalyst delivers a 0.921 V half-wave potential for alkaline oxygen reduction and excellent Zn-air battery performance.
Cancer Therapy
Evoking Simultaneous Ferroptosis and Apoptosis by a Dual-Locked Platinum (IV) Prodrug for Synergistic Chemo-immunotherapy
- First Published: 05 May 2025
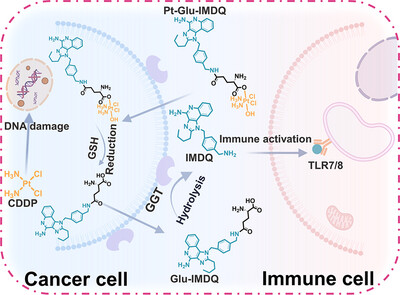
A dual-locked Pt(IV) prodrug combines a TLR7/8 agonist (IMDQ) with a GGT-responsive moiety. Reduction to Pt(II) triggers GGT-mediated cleavage of axial ligands, releasing IMDQ to activate immunity. TLR7/8 signaling boosts T-cell infiltration into tumors and stimulates tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and dendritic cells (DCs). Synergy between platinum chemotherapy and immune activation achieves potent antitumor efficacy.
Water Electrolysis | Very Important Paper
Activating Surface Oxygen in Ce/Mo-Doped Ni Oxyhydroxide for Synergistically Enhancing Furfural Oxidation and Hydrogen Evolution at Ampere-Level Current Densities
- First Published: 07 May 2025
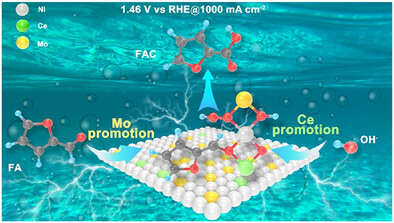
A Mo/Ce co-doped Ni oxyhydroxide was prepared for the electrochemical oxidation of furfural coupled with hydrogen evolution. Mo promotes the adsorption of furfural while Ce promotes the formation of OOH, and the synergistic effect of Ce and Mo leads to an industrial current density of 1000 mA cm−2 at only 1.46 V versus RHE.
Organic Materials | Hot Paper
Interweaving Covalent Organic Polymer Chains Into Two-Dimensional Networks: Synthesis, Single Crystal Structure, and Application for Stabilizing Lithium Metal Anode
- First Published: 05 May 2025

A woven two-dimensional (2D) covalent organic polymer network (CityU-46) was designed, fabricated, and structurally resolved through single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis, which revealed a unique, well-defined two-over, two-under interweaving pattern at the molecular level. CityU-46, serving as an artificial organic solid-electrolyte interphase layer on the surface of Li metal anodes, demonstrated excellent electrochemical performance in practical lithium metal cells.
Organogermanes
Nucleophilic Germylation of Stable π Bonds via Ge─Ge Bond Heterolysis
- First Published: 05 May 2025
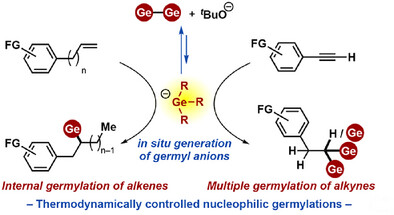
A thermodynamically controlled nucleophilic germylation of stable π bonds was achieved by germyl anion generated in situ via heterolytic cleavage of the Ge─Ge bond in the presence of KOtBu. This methodology enables unprecedented multiple germylation of alkynes and internally selective germylation of alkenes, affording 1-alkyl-1-germylalkanes, 1,1-digermylalkanes, and 1,1,1-trigermylalkanes.
Decarboxylative Acylation of α-Hydroxy Acids
Enantioselective Decarboxylative Acylation of α-Hydroxy Acids with Carboxylic Acids via Photoredox/Nickel Dual Catalysis
- First Published: 05 May 2025
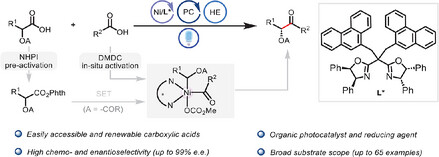
A photoredox/nickel dual-catalyzed enantioselective decarboxylative acylation of α-hydroxy acid derivatives with carboxylic acids has been developed, enabling efficient access to enantioenriched α-oxygenated ketones. This method exhibits a broad substrate scope, good functional group tolerance, high chemoselectivity, and excellent enantioselectivity.
Photodegradation of Organic Pollutants
Asymmetric Coordination in Cobalt Single-Atom Catalysts Enables Fast Charge Dynamics and Hierarchical Active Sites for Two-Stage Kinetics in Photodegradation of Organic Pollutants
- First Published: 06 May 2025
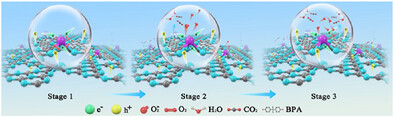
This investigation demonstrates an efficient synthetic methodology for the fabrication of atomically dispersed cobalt species anchored on carbon nitride substrate, featuring distinctive asymmetric Co─C2N3 coordination environments and hierarchical active sites. The unique electronic structure of this single-atom catalyst exhibits strengthened driving force and boosted charge carrier transport properties, manifesting in two-stage reaction kinetics during the photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A contaminants in wastewater.
Aromaticity | Hot Paper
Valence Tautomerism and Alkaline Properties of Global Aromatic Imine- and Methine-Bridged all-Benzenoid Macrocyclic Superpyrazine and Supertriazine
- First Published: 06 May 2025
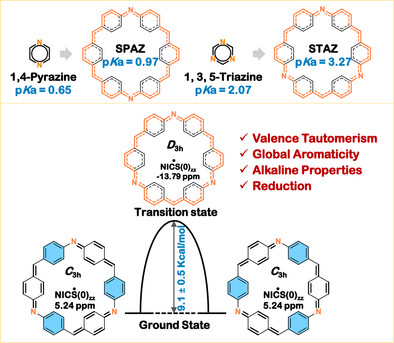
We prepared two imine macrocycles, SPAZ and STAZ, as analogues of 1,4-pyrazine and 1,3,5-triazine, respectively. SPAZ and STAZ exhibit Brønsted basicity with pKa values of 0.97 and 3.27, respectively. Notably, we elucidate their unprecedented valence tautomerism between “super-Kekulé” benzenoid/quinoidal structures and a “super-sextet” transient structure, facilitated by aza[30]annulene pathways.
Propane Dehydrogenation
Tri-Coordinated Boron Species in Confined Boron Oxide Catalysts for Enhanced Low-Temperature Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Propane
- First Published: 05 May 2025
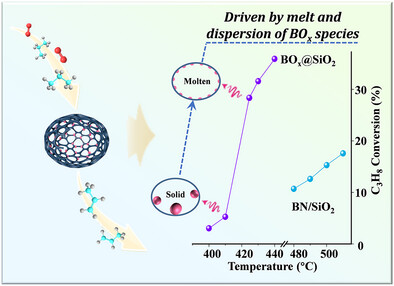
The confined BOx@SiO2 with highly dispersed BOx species was synthesized by the in situ transformation of BN@SiO2, which showed a remarkable activity of a unique C3H8 conversion uprush increasing from 5.3% at 410 °C to 28.4% at 424.6 °C for oxidative dehydrogenation of propane. The key for the efficient C3H8 activation was the increased amount of tri-coordinated B─OH derived from the dispersion of molten BOx species within spatially confined SiO2.
Ammonia Production | Very Important Paper
Interfacial Water Structure Modulation on Unconventional Phase Non-Precious Metal Alloy Nanostructures for Efficient Nitrate Electroreduction to Ammonia in Neutral Media
- First Published: 05 May 2025
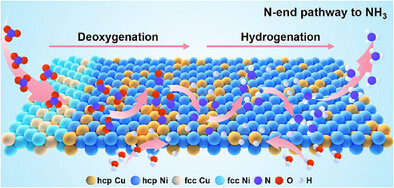
The controlled synthesis of noble metal-free CuNi alloy nanostructures with unconventional hcp/fcc heterophase has been successfully achieved. Notably, hcp/fcc CuNi nanoalloys demonstrate much superior catalytic performance toward ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate than the common fcc CuNi counterparts. Mechanism studies reveal that the hcp/fcc CuNi alloys facilitate the formation of K+–H2O, enhance the interfacial water dissociation, and create high *H coverage, thereby boosting the ammonia synthesis.
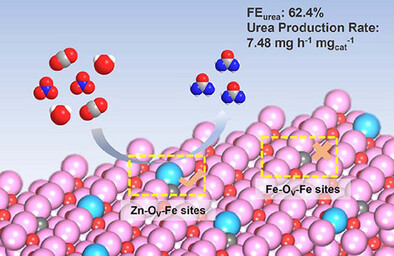
Electrocatalysis
Boosting Urea Electrosynthesis via Asymmetric Oxygen Vacancies in Zn-Doped Fe2O3 Catalysts
- First Published: 06 May 2025
Aldehyde Oxidation
High-Performance Cu6Sn5 Alloy Electrocatalysts for Formaldehyde Oxidative Dehydrogenation and Bipolar Hydrogen Production
- First Published: 06 May 2025
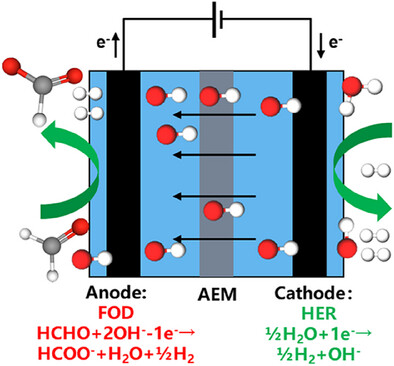
The Cu₆Sn₅ alloy was developed as a high-performance, noble-metal-free electrocatalyst for the anodic formaldehyde oxidative dehydrogenation (FOD) reaction. When paired with the cathodic hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), it enables a formaldehyde-assisted water electrolyzer, facilitating energy-efficient bipolar hydrogen production and the generation of value-added formate.
Hybrid Perovskites | Hot Paper
High-Security and High-Efficiency Information Encryption/Decryption Based on 2D Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Perovskites via Delicate Organic-Cation Engineering
- First Published: 06 May 2025

We develop a unique strategy of information encryption/decryption based on stimuli-responsive luminescence of 2D hybrid organic–inorganic perovskites via delicate organic-cation engineering. The facile triple-key implementation working in multiple switching modes (featuring high contrast and quick response) allows us to achieve high security and readout efficiency, opening a new door to information security based on optical encryption.
Enzyme Catalysis
Cytochrome P450 Mediated Cyclohexane Ring Formation in Forazoline Biosynthesis
- First Published: 06 May 2025
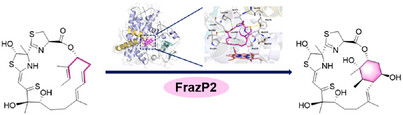
FrazP2, a cytochrome P450, catalyzes cyclohexane ring formation in forazoline A, a marine-derived antifungal from Actinomadura sp. WMMB-499. Structural and mechanistic studies have uncovered a radical-mediated cyclization, unlocking opportunities to engineer P450s for the generation of novel antifungal forazoline analogues.
Photocatalytic CO2 Fixation | Hot Paper
Regulated Second-sphere Coordination in Amorphous Metal-organic Framework for Efficient CO2 Fixation
- First Published: 07 May 2025
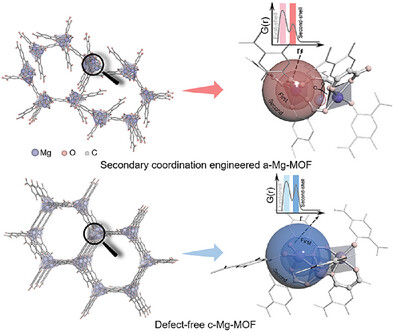
Second-sphere coordination regulation strategy is employed by atomically tailoring the metal–metal coordination of the secondary building unit (SBU), with efforts to trigger more orbital interactions with guest molecules. Amorphous metal-organic framework (a-MOF) is chosen to transform rigid trinuclear nodes into flexible dinuclear motifs. Such architecture with clear and unique second-sphere interaction can open spatial proximity to access the guest molecule and optimize s–π* overlap by enabling orbital reorientation.
Synthetic Methods | Hot Paper
Metal-Free Divergent Hydroboration/Multiboration of Terminal Alkynes via Markovnikov Pathway
- First Published: 06 May 2025
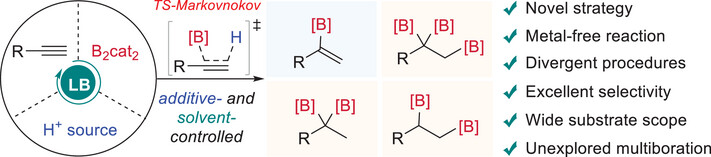
A metal-free and Markovnikov-type process for divergent hydroboration/multiboration of terminal alkynes has been achieved, enabling the transformation of diverse aryl and alkyl alkynes into valuable but previously inaccessible α-alkenylboronate, 2,2-diborylalkane, 1,2,2-triborylalkane, and 1,2-diborylalkane with excellent regio- and chemoselectivities by simply modulating the proton additive and solvent.
CO Electroreduction | Very Important Paper
Selective CO Electroreduction to Multicarbon Oxygenates Over Atomically Dispersed Cu–Ag Sites in Alkaline Membrane Electrode Assembly Electrolyzer
- First Published: 07 May 2025
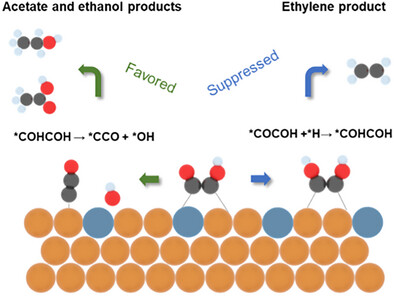
Atomically dispersed Cu–Ag sites on the catalyst surface promote the *OH cleavage of *COCOH toward *COO, thereby enhancing the selectivity of C2+ oxygenates from CO electroreduction. CO electrolysis over the optimized CuAg catalyst achieves a Faradaic efficiency of 71.4% for C2+ oxygenates at a current density of 2.5 A cm−2 in alkaline membrane electrode assembly electrolyzer.
Organic Light-Emitting Diodes
Equalized Dual Emissions from Copper Complexes via Multichannel Balanced Intersystem Crossing: Toward 100% Quantum Efficiencies
- First Published: 06 May 2025
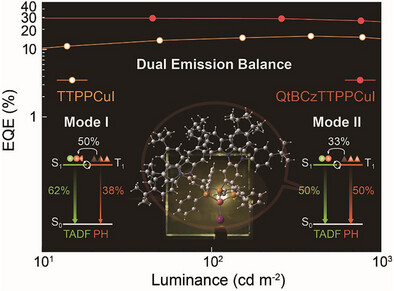
Dual emissions containing equalized thermally activated delayed fluorescence and phosphorescence are achieved by a copper iodide complex QtBCzTTPPCuI, which exhibits ∼100% photoluminescence quantum efficiencies and record-high twofold increased external quantum efficiencies of ∼30% among pure-yellow spin-coated organic light-emitting diodes, owing to the contributions of high-lying ligand-centered charge transfer excited states to intersystem crossing.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Enantioselective Divergent Cyclization of Amide-Type 1,6-Enynes Enabled by H–[Pd]–CN Catalysis
- First Published: 06 May 2025
![Enantioselective Divergent Cyclization of Amide-Type 1,6-Enynes Enabled by H–[Pd]–CN Catalysis](/cms/asset/aa6626f9-e2cf-49b8-806a-42465e55b5e9/anie202508702-gra-0001-m.jpg)
Three distinctive asymmetric 1,6-enyne cyclization strategies, namely, hydrocyanative cyclization, cyclization/Heck reaction, and cyclization/Heck/hydrocyanation, have been developed, providing a modular synthetic platform for various chiral γ-lactams bearing a quaternary stereogenic center. Furthermore, preliminary mechanistic studies, including DFT calculations, are also conducted.
Hydrogenation
Silylchromium-Catalyzed Selective Semihydrogenation of Undirected Allenes by Sila-Metalation and β-Silyl Elimination
- First Published: 07 May 2025
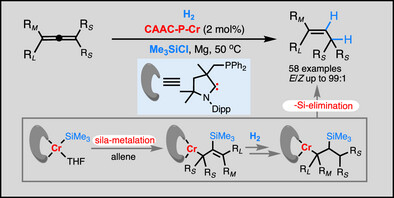
Substituted allenes without a directing group underwent chromium-catalyzed chemo-, stereo-, and regioselective semihydrogenation with an (alkyl)(amino)carbene-phosphine ligand and a chlorosilane additive. The silylchromium complex formed in situ promotes semihydrogenation through a pathway involving sila-metalation of the allene and β-silyl elimination, with the silyl group acting as a noninnocent ligand to give E-alkene products selectively.
Hydrogenation Reactions
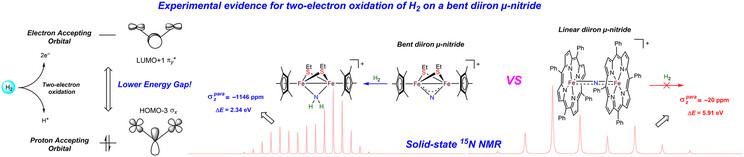
Electronic Structure Origins of Distinct Hydrogenation Activities Observed for Linear and Bent Bimetallic μ-Nitrides
- First Published: 07 May 2025
NOx Reduction
Unexpected Redox Role of WO3 in V2O5-WO3/TiO2 Catalysts for Selective Reduction of NO by Forming V–W Dinuclear Sites
- First Published: 08 May 2025
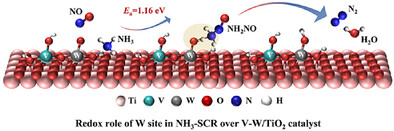
In the NH3-SCR reaction over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst, WO3 not only serves as an acidic promoter and structural regulator, but also plays a redox role. The WO3 directly participates in the oxidative activation of NH3, and hence explicitly exerts a redox effect by forming V–W dinuclear sites with V2O5.
Zinc Anode | Very Important Paper
Unveiling Zinc Stripping and Molecular Engineering for High-Performance Zinc Anode
- First Published: 07 May 2025
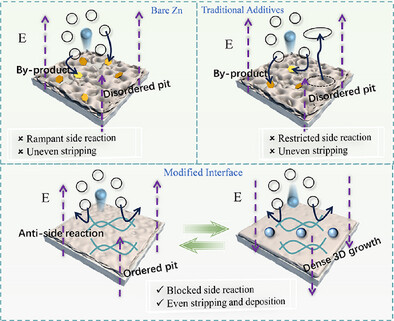
It is found that the zinc stripping process is more prone to cause severe side reactions than the deposition process, resulting in the formation of dendrites and “dead zinc.” In this regard, a dynamic molecular protection strategy is proposed to regulate the zinc stripping and deposition processes simultaneously, achieving long-lasting protection of the zinc anodes.
Gene Editing
Light-Triggered CRISPR/Cas12a for Genomic Editing and Tumor Regression
- First Published: 07 May 2025

A photo-triggered CRISPR/Cas12a machinery for gene editing is introduced. The machinery is applied for endogenous DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) gene editing and for in vitro disruption of the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) gene. The machinery is used for in vivo knockout and disruption of the HGF gene in HepG2 tumors, resulting in effective apoptosis and necrosis of the tumor tissues.
Sustainable Polymers
Dynamic Exchange Reactions as Self-Blowing Agents for the Production of Reprocessable Foams
- First Published: 08 May 2025
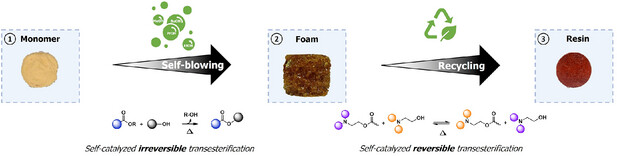
This study introduces an innovative approach to designing self-blown foams by leveraging the irreversible and self-catalyzed transesterification of alkylester which release alcohol gas as blowing agents. The morphology and thermo-mechanical properties of these foams can be precisely tailored by modifying the precursor structure. Remarkably, they can be reprocessed as rigid resins through reversible self-catalyzed transesterification reactions.
Porous Materials
Turing-Structured Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for Fast and Precise Peptide Separations
- First Published: 07 May 2025
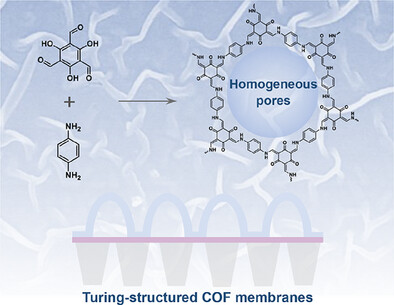
A Turing-structured COF membrane with externally striped and internally cavitated architectures is created via the modulation based on metal-polyphenol chemistry. The resulting COF membrane exhibits simultaneously enhanced water permeation and molecular sieving properties, demonstrating its great potential in the separation of high-value pharmaceuticals.
H2O2 Electrosynthesis | Hot Paper
Tuning Local Proton Concentration and *OOH Intermediate Generation for Efficient Acidic H2O2 Electrosynthesis at Ampere-Level Current Density
- First Published: 07 May 2025
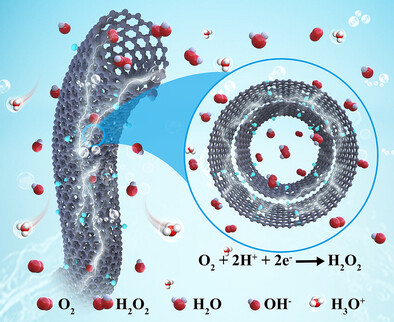
Efficient acidic H2O2 electrosynthesis was achieved on F-CNTs with Faradaic efficiency of 95.6% at 1.0 A cm−2. F-doping regulated the electronic structure, enhanced nanoconfinement effect and oxygen mass transfer of CNTs, leading to a local alkaline microenvironment and promoted *OOH generation for acidic H2O2 electrosynthesis.
Peptide Inhibitors
Antiparallel β-Sheet as a Key Motif of Amyloid-β Inhibitor Designed via Topological Peptide Reprogramming
- First Published: 09 May 2025
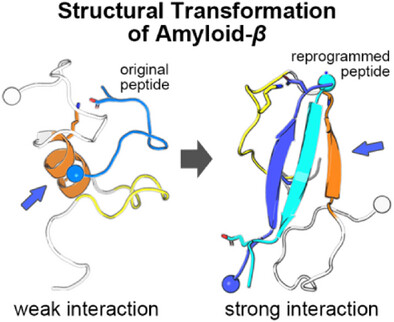
Targeting Amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation requires a peptide-based approach that accounts for the structural heterogeneity of Aβ. Here, we employ topological reprogramming via disulfide bonds to stabilize antiparallel β-sheets within the dimeric peptide. This strategy overcomes limitations of linear peptides by creating structured complexes that resist aggregation, offering a novel tactic for tackling AD-related protein aggregation.
C─O Functionalization | Hot Paper
Rhodium/Indium Heterobimetallic Alloy as an Effective Catalyst for Reductive C(sp3)─O Silylation of Ethers with Chlorosilanes
- First Published: 07 May 2025
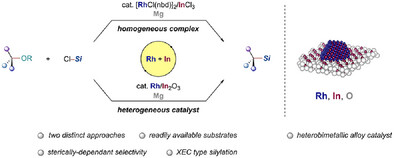
Here, we describe the reductive C(sp3)─O bond silylation of ethers with chlorosilanes and magnesium reductants by cooperative rhodium and indium catalysis. This methodology allows the incorporation of silyl moieties into the C(sp3)─O bond of various unactivated cyclic and acyclic alkyl ethers using chlorotriorganosilanes. Not only the mixture of rhodium complex with indium reagent but also rhodium nanoparticles supported on indium oxide showed high catalytic activity, indicating a remarkable cooperative effect by the two metals. Notably, in both cases, the generation of rhodium/indium heterobimetallic alloy nanoparticles was revealed by mechanistic studies including XRD, XAS, and TEM imaging.
Photodetectors
Nucleophilic Covalent Ligands Enable Simultaneous Surface Reconstruction and Passivation of Colloidal InSb Quantum Dots for Stable Short-Wave Infrared Photodetectors
- First Published: 08 May 2025
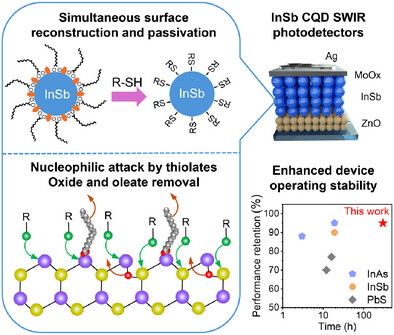
A simultaneous surface reconstruction and passivation strategy is designed for indium antimonide (InSb) colloidal quantum dots (CQDs) using sulfur-based nucleophilic covalent ligands. This leads to stable CQD inks and 1450 nm-operating InSb CQD photodetectors with 28% external quantum efficiency and 300 h operating lifetime.
Cage Compounds
Modulation of Photoluminescence of BODIHY Dye Using Water-Soluble Coordination Cages With Different Shapes
- First Published: 07 May 2025
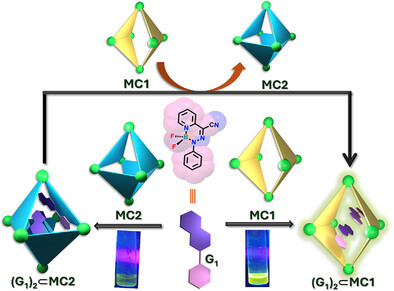
The fluorescence of Boron difluoride hydrazone (BODIHY) (G1) dye was effectively controlled through confinement within coordination cages of different shapes. The encapsulation of G1 within a double-square cage (MC1) resulted in a highly emissive solution, whereas similar confinement within an octahedral cage (MC2) exhibited a weak emission. Moreover, we achieved turn-on emission of G1 through the displacement of G1 from MC2 to MC1.
C─H Functionalization | Very Important Paper
Machine Learning Reveals In-Cavity Versus Surface Activity for Selective C─H Borylation by Metal-Organic Framework Catalysts
- First Published: 06 May 2025
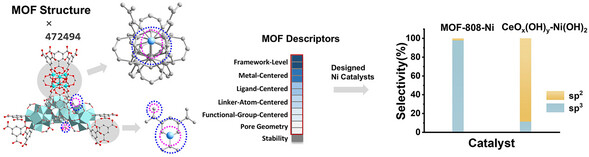
A set of 45 general descriptors was developed to capture the diverse structural features of a wide range of MOFs, enabling the study of MOF-supported nickel (Ni) catalysts for C─H borylation. This analysis revealed key factors that govern sp3 versus sp2 selectivity, allowing for the rational design of Ni catalysts with up to 97.8% sp3 selectivity and 88.7% sp2 selectivity.
Photoluminescence | Hot Paper
Local Atomic Off-Centering Mediated Efficient Self-Trapped Excitonic Emission in Cs5Cu3Cl6I2 Nanoplates
- First Published: 07 May 2025
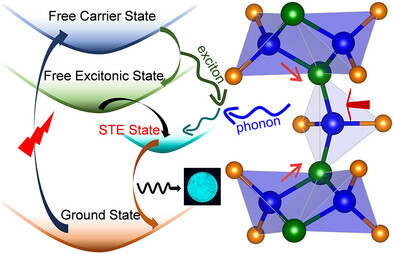
Cs5Cu3Cl6I2 nanoplates exhibit reasonably photostable and intense broadband sky-blue emission, originating from self-trapped excitons. The self-trapping of excitons occurs due to strong electron-phonon coupling, which is created by elastic structural distortion on the atomic scale. Synchrotron X-ray total scattering studies reveal the local structural distortion to be crafted by off-centering the copper atom.
Conjugated Microporous Polymers
Chloromethylation Modified Pyranonitrile-Based Conjugated Microporous Polymers for Selective One-Step Two-Electron O2 Reduction to H2O2
- First Published: 07 May 2025
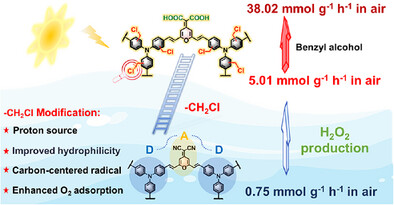
A post-modification strategy employing a chloromethylation reaction was proposed to enhance H2O2 production of covalent microporous polymers (CMPs). The H2O2 production rate of the chloromethylated CMP namely DCM-TPA-Cl reached 5.01 mmol g−1 h−1 in air, which is 6.7 times greater than that of the unmodified photocatalyst. An exceptional 38.02 mmol g−1 h−1 rate was further achieved in water/benzyl alcohol mixtures, exceeding that of most reported polymer photocatalysts.
Host–Guest Complexes | Very Important Paper
Supramolecular TADF Materials from Calix[3]Acridan and Guest-Linked Polymers for Rapid and Visual Detection of Trace Benzene
- First Published: 07 May 2025
![Supramolecular TADF Materials from Calix[3]Acridan and Guest-Linked Polymers for Rapid and Visual Detection of Trace Benzene](/cms/asset/e6db3b6a-ebd0-4dd6-a31b-86bd8b6172fb/anie202508987-gra-0001-m.jpg)
A new strategy for the rapid and visual detection of trace benzene was reported by utilizing supramolecular thermally activated delayed fluorescence polymeric materials GPs@C[3]A based on luminescence color change mechanism, and the limit of detection concentration for benzene vapor reached 3.5 mg L−1. Moreover, GP1@C[3]A was fabricated into a visualized and convenient paper-based sensor strip for detecting benzene in cyclohexane.
Communication
Low-Cost Scalable PET Recycling | Hot Paper
Cost-Effective and Low-Carbon Scalable Recycling of Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate Through Bio-Based Guaiacol-Enhanced Methanolysis
- First Published: 28 April 2025
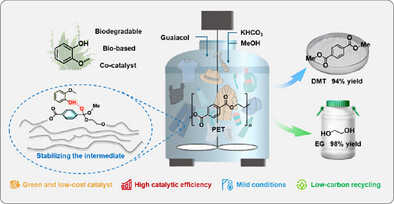
A cost-effective and low-carbon PET recycling strategy is developed using bio-based guaiacol to promote methanolysis through an intermediate stabilizing mechanism. Under mild conditions (120 °C, 0.6 MPa), the system achieves complete PET conversion within 2 h, producing dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) and ethylene glycol (EG) at yields of 94% and 98%, respectively.
Gels | Hot Paper
Hierarchically Self-Assembled Anion-Coordination-Driven Gels for Guest Segregation and Electrical Sensing
- First Published: 16 April 2025
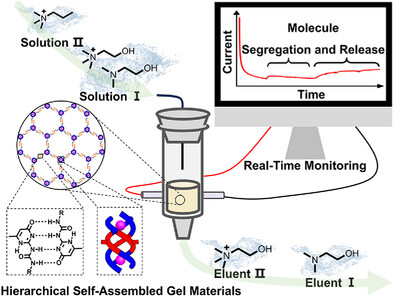
A class of gels formed through hierarchical self-assembly of “aniono” helicates were developed that can be utilized as filling material in columns and showed the ability to selectively encapsulate and release choline. The host-guest properties could also be monitored in real time by electrical characterization. This study introduces the concept of flowing a solution containing guests through a host-containing gel for effective guest separation.
On-surface Synthesis
On-Surface Synthesis of Nanographenes Through Domino Cyclization Reactions
- First Published: 30 April 2025
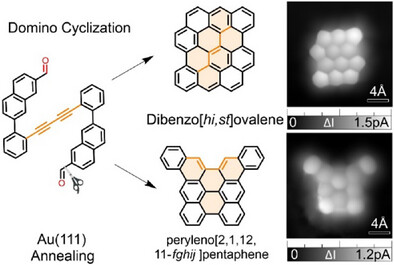
On-surface synthesis enables nanographene fabrication but with limited reactions. Here, bis{2-(7-formylnaphthalen-2-yl)phenyl}diacetylene undergoes domino cyclization via cycloisomerization, cyclodehydrogenation, and formyl cyclization, yielding dibenzo[hi,st]ovalene and peryleno[2,1,12,11-fghij]pentaphene. STM, STS, and DFT analyses reveal their structures and properties, advancing carbon nanostructure synthesis.
Chirality
Induced Chirality and Vibrational Optical Activity in an Ionic-Liquid Anion
- First Published: 01 May 2025
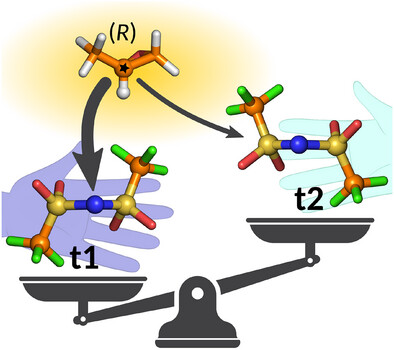
Chirality can be induced in an ionic liquid anion. Normally, the enantiomeric conformers are equally populated, and no optical activity is observed. However, if a chiral probe molecule (e.g., propylene oxide) is added, a non-symmetric redistribution of the conformers occurs, chirally imprinting the ionic liquid.
Crystallography
Comparative Study of Solvatomorphs of Stryker's Reagent Using MicroED and Quantum Mechanics
- First Published: 05 May 2025
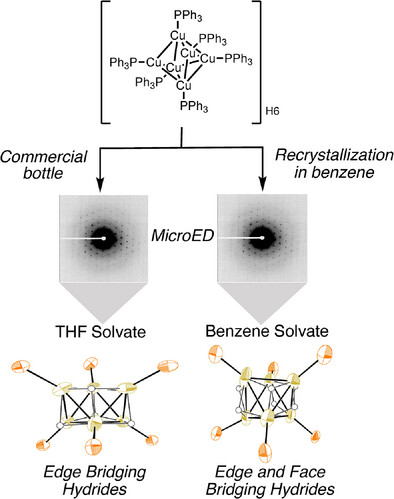
A new solvate form of Stryker's reagent was crystallized from benzene which has regular octahedra with equivalent Cu–Cu interatomic distances. Quantum crystallography approach HAR led to reliable position of hydrides in both the forms. The reported THF solvate form has edge bridging hydrides while the newly discovered form may have both edge and face bridging hydrides supported by structural and topological analysis.
Organocatalysis
Stereocontrol in Conformationally Stable C(sp2)─C(sp3) Atropisomers
- First Published: 24 May 2025
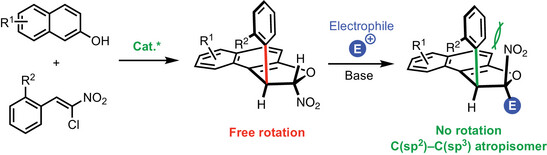
Building in our expertize in the synthesis of trans-dihydrobenzofurans via organocatalyzed domino Michael/O-cyclization between β-naphthols and nitroalkenes, we developed an efficient strategy to access a new family of atropisomers bearing a conformationally stable C(sp2)─C(sp3) bond and two stereogenic centers through simple and highly diastereoselective alkylation of dihydrofurans with structurally diverse electrophiles. This crucial step places the nitro group in a relative cis-configuration with respect to the aromatic moiety, effectively increasing the barrier to diastereomerization and stabilizing the molecular conformation.
Transition-Metal Catalysis
Iridium-Catalyzed Asymmetric β-Selective Hydroamination of Enamides for the Synthesis of 1,2-Diamines
- First Published: 30 April 2025
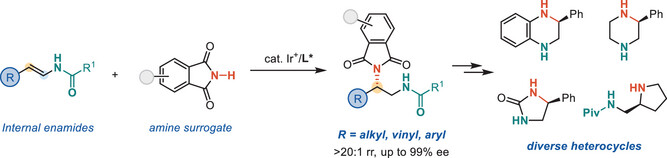
Internal enamides were found to undergo enantioselective hydroamination catalyzed by a cationic iridium complex. An amide group effectively directs the catalyst to achieve unconventional β-regioselectivity with up to 99% ee. This coordination assistance strategy creates an efficient pathway for synthesizing valuable enantioenriched 1,2-diamine derivatives.
Photochemistry
Xanthopinacol Boronate: A Robust, Photochemically Assembled and Cleavable Boronic Ester for Orthogonal Chemistry
- First Published: 29 April 2025
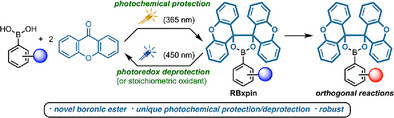
Xanthopinacol (xpin) boronates are a conceptually new class of masked boronic acids designed to alleviate many of the disadvantages of pinacol esters and other popular adducts. They can be formed directly from xanthone and UV light, undergo orthogonal transformations, and are cleavable under photoredox catalysis or oxidative conditions that recycle xanthone to prevent the re-esterification and facilitate the isolation of the boronic acid.
Synthetic Methods
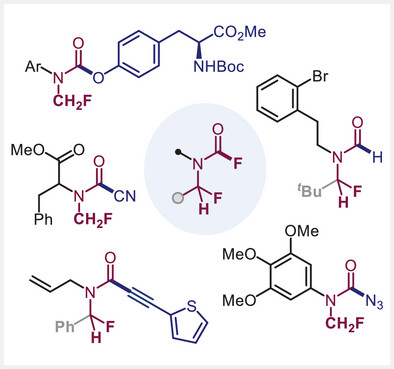
Access to N-Monofluoromethylated (Thio)Carbamates, Formamides, Alkynamides, and Related Derivatives
- First Published: 01 May 2025
Bioorthogonal Chemistry
On-Demand Ligate and Release Strategy Based on Photoclick Reaction in Tandem with Pd-Mediated Deallylation
- First Published: 03 May 2025
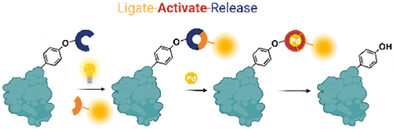
A consecutive, controllable, and revertible new-to-nature ligation and cleavage strategy has been rationally devised to selectively visualize and manipulate biomolecules of interest. The photoclick cycloaddition between allenyl phenyl ether motifs and 9,10-phenanthrenequinone analogues installed a terminal allyl handle at the exocyclic site, thereby enabling on-demand Pd-mediated deallylation to release phenolic payloads (copyright permission obtained from BioRender).
Heterocyclic Carbenes
Phosphinoisocyanide/Alkyne Cycloaddition: Generation of Azaphospholylidene (NPHC) Ligands
- First Published: 08 May 2025
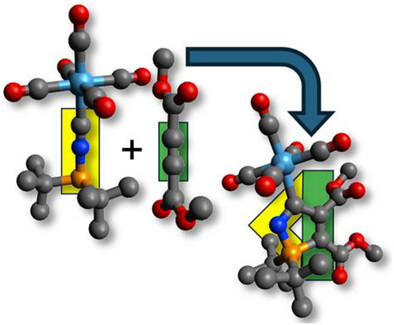
Rare examples of nitrogen phosphorus heterocyclic carbene (NPHC) complexes of group 6 and 7 metals arise from a facile [3 + 2] cycloaddition of phosphinoisocyanides (LnM-CNPR2) with activated alkynes. The NPHC ligands are shown to be comparatively π-acidic and the group 6 examples undergo facile transfer of the intact carbene to gold(I) centres.
Enantioselectivity | Very Important Paper
Enantioselective Palladium-Catalyzed α-Arylation of Acyclic Esters
- First Published: 05 May 2025
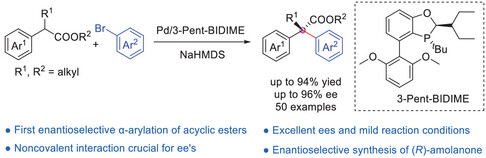
A Pd-catalyzed enantioselective α-arylation of α,α-disubstituted esters with aryl bromides is established for the first time by employing P-chiral monophosphorus ligand 3-Pent-BIDIME as a chiral ligand, leading to a series of enantioenriched α,α-diaryl esters possessing quaternary carbon stereocenters in moderate to good yields and high enantioselectivities. The method features a broad substrate scope, mild conditions, excellent functional group compatibility, and low Pd loadings (as low as 1 mol%). Its synthetic utilities are exemplified by the efficient preparation of a chiral α,α-diaryl substituted γ-lactone and the asymmetric synthesis of (R)-amolanone.
Stereodivergent Synthesis | Hot Paper
Ternary Aldehyde–Copper–Iridium Catalysis Enables Stereodivergent Allylation via α-C-H Functionalization of Primary Amines
- First Published: 05 May 2025
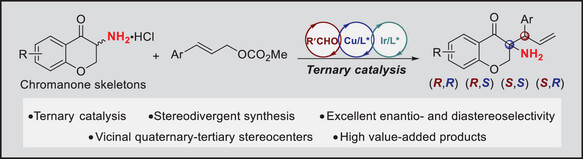
A direct enantio- and diastereodivergent α-allylation of unprotected primary amines has been developed using aldehyde/Cu/Ir ternary catalysis. This catalytic system enables the synthesis of α-tertiary primary amines bearing vicinal stereocenters in high yields with excellent stereoselectivities. Notably, this method establishes a sophisticated asymmetric induction model for asymmetric α-C-H functionalization of unprotected primary amines.
Corrigendum
Correction to “Carbodicarbene-Stibenium Ion-Mediated Functionalization of C(sp3)−H and C(sp)−H Bonds”
- First Published: 18 June 2025







![Chiral Spirobipyridine Synthesis by Cobalt-Catalyzed Enantioselective Double [2 + 2 + 2] Cycloaddition](/cms/asset/ab7206e6-2dae-4597-80e8-836abfa6a7b8/anie202504831-gra-0001-m.jpg)