Cytochrome P450 Mediated Cyclohexane Ring Formation in Forazoline Biosynthesis
Xinru Chen
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYujie Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-Carbon Manufacturing, Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tianjin, 300308 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 A Yuguan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShiqi Li
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Search for more papers by this authorWeiting Liao
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Weixin Tao
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zixin Deng
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tim S Bugni
Pharmaceutical Sciences Division, University of Wisconsin–Madison, Madison, WI, 53705 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hao Su
State Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-Carbon Manufacturing, Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tianjin, 300308 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 A Yuguan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Fan Zhang
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorXinru Chen
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYujie Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-Carbon Manufacturing, Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tianjin, 300308 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 A Yuguan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShiqi Li
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Search for more papers by this authorWeiting Liao
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Weixin Tao
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zixin Deng
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tim S Bugni
Pharmaceutical Sciences Division, University of Wisconsin–Madison, Madison, WI, 53705 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hao Su
State Key Laboratory of Engineering Biology for Low-Carbon Manufacturing, Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tianjin, 300308 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 A Yuguan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Fan Zhang
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, TaiKang Center for Life and Medical Sciences, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430071 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
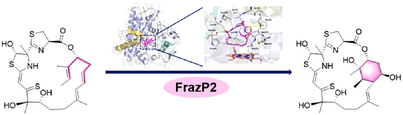
FrazP2, a cytochrome P450, catalyzes cyclohexane ring formation in forazoline A, a marine-derived antifungal from Actinomadura sp. WMMB-499. Structural and mechanistic studies have uncovered a radical-mediated cyclization, unlocking opportunities to engineer P450s for the generation of novel antifungal forazoline analogues.
Abstract
Forazoline A, produced by the marine actinomycete Actinomadura sp. WMMB-499, is a unique PK/NRP hybrid macrolactone with promising antifungal in vivo efficacy through a previously unreported mechanism. Although a PKS/NRPS gene cluster was identified as a candidate for forazoline production, the precise biosynthetic pathway and the functions of the tailoring enzymes remain unclear. In this work, the functions of three cytochrome P450 mono-oxygenases (FrazP1P2P3) were characterized. Notably, FrazP2 was found to mediate cyclohexane ring formation from an 1,3,6-triene precursor during forazoline A biosynthesis, as confirmed by genetic and biochemical analysis. To gain structural and mechanistic insight into the activity of FrazP2, the crystal structure of a FrazP2-substrate complex has been solved at 2.3 Å resolution. The molecular dynamics simulations and DFT calculations revealed an unprecedented enzyme-catalyzed oxidative cyclization reaction by FrazP2. These findings expand our understanding of the catalytic diversity of cytochrome P450s, contributing to the diversification of natural products and enabling the creation of unnatural derivatives with increased antifungal potency.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202504925-sup-0001-SuppMat.pdf16 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1C. D. Fage, E. A. Isiorho, Y. Liu, D. T. Wagner, H. W. Liu, A. T. Keatinge-Clay, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 256–258.
- 2Q. Zhang, H. Li, S. Li, Y. Zhu, G. Zhang, H. Zhang, W. Zhang, R. Shi, C. Zhang, Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 6142–6145.
- 3Y. Pan, G. Li, R. Liu, J. Guo, Y. Liu, M. Liu, X. Zhang, L. Chi, K. Xu, R. Wu, Y. Zhang, Y. Li, X. Gao, S. Li, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1669.
- 4M. Ma, T. Kwong, S. K. Lim, J. Ju, J. R. Lohman, B. Shen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2489–2492.
- 5P. Jiang, H. Jin, G. Zhang, W. Zhang, W. Liu, Y. Zhu, C. Zhang, L. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310728.
- 6G. Sun, C. Hu, Q. Mei, M. Luo, X. Chen, Z. Li, Y. Liu, Z. Deng, Z. Zhang, Y. Sun, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4501.
- 7A. J. Devine, A. E. Parnell, C. R. Back, N. R. Lees, S. T. Johns, A. Z. Zulkepli, R. Barringer, K. Zorn, J. E. M. Stach, M. P. Crump, M. A. Hayes, M. W. van der Kamp, P. R. Race, C. L. Willis, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202213053.
- 8Z. Yunt, K. Reinhardt, A. Li, M. Engeser, H. M. Dahse, M. Gütschow, T. Bruhn, G. Bringmann, J. Piel, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2297–2305.
- 9W. Tao, M. E. Yurkovich, S. Wen, K. E. Lebe, M. Samborskyy, Y. Liu, A. Yang, Y. Liu, Y. Ju, Z. Deng, M. Tosin, Y. Sun, P. F. Leadlay, Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 376–385.
- 10L. C. Montemiglio, G. Parisi, A. Scaglione, G. Sciara, C. Savino, B. Vallone, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 465–475.
- 11M. K. Kharel, S. E. Nybo, M. D. Shepherd, J. Rohr, ChemBioChem 2010, 11, 523–532.
- 12S. Li, S. Ni, L. Wu, L. Li, B. Jiang, H. Wang, G. Sun, M. Gan, J. Li, W. He, L. Lin, Y. Wang, S. Bai, S. Si, J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 969–973.
- 13T. Liu, M. K. Kharel, C. Fischer, A. McCormick, J. Rohr, ChemBioChem 2006, 7, 1070–1077.
- 14J. D. Rudolf, L. B. Dong, K. Manoogian, B. Shen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16711–16721.
- 15Y. Sun, X. Zhou, G. Tu, Z. Deng, Arch. Microbiol. 2003, 180, 101–107.
- 16Y. He, Y. Sun, T. Liu, X. Zhou, L. Bai, Z. Deng, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3283–3292.
- 17Y. Wang, J. Wang, S. Yu, F. Wang, H. Ma, C. Yue, M. Liu, Z. Deng, Y. Huang, X. Qu, ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 799–803.
- 18Y. Shi, Z. Jiang, X. Hu, X. Hu, R. Gu, B. Jiang, L. Zuo, X. Li, H. Sun, C. Zhang, L. Wang, L. Wu, B. Hong, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 15399–15404.
- 19H. Zhang, J. Chen, H. Wang, Y. Xie, J. Ju, Y. Yan, H. Zhang, FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 1675–1680.
- 20H. Onaka, S. Asamizu, Y. Igarashi, R. Yoshida, T. Furumai, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 1753–1759.
- 21A. Greule, T. Izoré, D. Iftime, J. Tailhades, M. Schoppet, Y. Zhao, M. Peschke, I. Ahmed, A. Kulik, M. Adamek, R. J. A. Goode, R. B. Schittenhelm, J. A. Kaczmarski, C. J. Jackson, N. Ziemert, E. H. Krenske, J. J. de Voss, E. Stegmann, M. J. Cryle, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2613.
- 22L. E. Zetzsche, S. Chakrabarty, A. R. H. Narayan, ACS Chem. Biol. 2022, 17, 2986–2992.
- 23C. Fang, L. Zhang, Y. Wang, W. Xiong, Z. Yan, W. Zhang, Q. Zhang, B. Wang, Y. Zhu, C. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 16478–16489.
- 24L. E. Zetzsche, J. A. Yazarians, S. Chakrabarty, M. E. Hinze, L. A. M. Murray, A. L. Lukowski, L. A. Joyce, A. R. H. Narayan, Nature 2022, 603, 79–85.
- 25H. Nam, J. S. An, J. Lee, Y. Yun, H. Lee, H. Park, Y. Jung, K. B. Oh, D. C. Oh, S. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 22047–22057.
- 26M. Makino, H. Sugimoto, Y. Shiro, S. Asamizu, H. Onaka, S. Nagano, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2007, 104, 11591–11596.
- 27Y. Wang, H. Chen, M. Makino, Y. Shiro, S. Nagano, S. Asamizu, H. Onaka, S. Shaik, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6748–6762.
- 28Q. Cheng, D. C. Lamb, S. L. Kelly, L. Lei, F. P. Guengerich, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15173–15175.
- 29Y. M. Yang, E. J. Zhao, W. Wei, Z. F. Xu, J. Shi, X. Wu, B. Zhang, Y. Igarashi, R. H. Jiao, Y. Liang, R. X. Tan, H. M. Ge, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214026.
- 30Y. H. Chooi, Y. J. Hong, R. A. Cacho, D. J. Tantillo, Y. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16805–16808.
- 31T. P. Wyche, J. S. Piotrowski, Y. Hou, D. Braun, R. Deshpande, S. McIlwain, I. M. Ong, C. L. Myers, I. A. Guzei, W. M. Westler, D. R. Andes, T. S. Bugni, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11583–11586.
- 32F. Zhang, T. P. Wyche, Y. Zhu, D. R. Braun, J. X. Yan, S. Chanana, Y. Ge, I. A. Guzei, M. G. Chevrette, C. R. Currie, M. G. Thomas, S. R. Rajski, T. S. Bugni, Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 1275–1279.
- 33K. Räty, T. Kunnari, J. Hakala, P. Mäntsälä, K. Ylihonko, Gen. Genet. 2000, 264, 164–172.
- 34W. Lu, C. Leimkuhler, G. J. Gatto, R. G. Kruger, M. Oberthür, D. Kahne, C. T. Walsh, Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 527–534.
- 35S. Malla, N. P. Niraula, K. Liou, J. K. Sohng, J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 108, 92–98.
- 36S. A. Borisova, C. Zhang, H. Takahashi, H. Zhang, A. W. Wong, J. S. Thorson, H. W. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2748–2753.
- 37L. M. Garrido, F. Lombó, I. Baig, M. Nur-E-Alam, R. L. Furlan, C. C. Borda, A. Braña, C. Méndez, J. A. Salas, J. Rohr, G. Padilla, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 122–131.
- 38C. Olano, A. M. Rodriguez, J. M. Michel, C. Méndez, M. C. Raynal, J. A. Salas, Mol. Gen. Genet. 1998, 259, 299–308.
- 39X. L. Tang, P. Dai, H. Gao, C. X. Wang, G. D. Chen, K. Hong, D. Hu, X. S. Yao, ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 1241–1249.
- 40M. C. Moncrieffe, M. J. Fernandez, D. Spiteller, H. Matsumura, N. J. Gay, B. F. Luisi, P. F. Leadlay, J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 415, 92–101.
- 41W. Tian, C. Sun, M. Zheng, J. R. Harmer, M. Yu, Y. Zhang, H. Peng, D. Zhu, Z. Deng, S. L. Chen, M. Mobli, X. Jia, X. Qu, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4428.
- 42X. Liu, F. Li, T. Sun, J. Guo, X. Zhang, X. Zheng, L. Du, W. Zhang, L. Ma, S. Li, Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 791.
- 43J. D. Rudolf, C. Y. Chang, M. Ma, B. Shen, Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 1141–1172.
- 44L. Holm, Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 5326–5327.
- 45R. Nagel, L. E. Alexander, C. E. Stewart Jr., R. J. Peters, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2023, 120, e2221549120.
- 46G. Zocher, M. E. Richter, U. Mueller, C. Hertweck, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2292–2302.
- 47M. Zhao, J. Ma, M. Li, Y. Zhang, B. Jiang, X. Zhao, C. Huai, L. Shen, N. Zhang, L. He, S. Qin, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12808.
- 48I. G. Denisov, S. G. Sligar, Activation of Molecular Oxygen in Cytochromes P450, Springer, Berlin, Germany 2015.
10.1007/978-3-319-12108-6_3 Google Scholar
- 49J. Sambrook, D. W. Russell, Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 2001.
- 50S. E. Nybo, M. D. Shepherd, M. A. Bosserman, J. Rohr, Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2010, 19, 10E.4.1–10E.4.5.
10.1002/9780471729259.mc10e03s19 Google Scholar
- 51S. Huang, N. Li, J. Zhou, J. He, Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2012, 52, 30–37.
- 52B. Gust, G. L. Challis, K. Fowler, T. Kieser, K. F. Chater, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1541–1546.
- 53W. Kabsch, Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 125–132.
- 54A. J. McCoy, R. W. Grosse-Kunstleve, P. D. Adams, M. D. Winn, L. C. Storoni, R. J. Read, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674.
- 55P. D. Adams, N. W. Moriarty, R. D. Oeffner, B. K. Poon, M. G. Prisant, R. J. Read, J. S. Richardson, D. C. Richardson, M. D. Sammito, O. V. Sobolev, D. H. Stockwell, T. C. Terwilliger, A. G. Urzhumtsev, L. L. Videau, C. J. Williams, Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2019, 75, 861–877.
- 56 Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4 Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1994, 50, 760–763.
- 57J. Jumper, R. Evans, A. Pritzel, J. Adler, T. Back, D. Hassabis, Nature 2021, 596, 583–589.
- 58G. N. Murshudov, A. A. Vagin, E. J. Dodson, Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1997, 53, 240–255.
- 59P. Emsley, K. Cowtan, Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132.
- 60N. Eswar, D. Eramian, B. Webb, M.-Y. Shen, A. Sali, Structural Proteomics: High-Throughput Methods 2008, 145–159.
10.1007/978-1-60327-058-8_8 Google Scholar
- 61C. R. Søndergaard, M. H. Olsson, M. Rostkowski, J. H. Jensen, J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 2284–2295.
- 62P. Li, K. M. Merz Jr., MCPB.py: A Python-Based Metal Center Parameter Builder, ACS Publications, Washington, DC 2016.
- 63J. Wang, R. M. Wolf, J. W. Caldwell, P. A. Kollman, D. A. Case, J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174.
- 64C. I. Bayly, P. Cieplak, W. Cornell, P. A. Kollman, J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 10269–10280.
- 65M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, G. A. Petersson, H. Nakatsuji, X. Li, M. Caricato, A. V. Marenich, J. Bloino, B. G. Janesko, R. Gomperts, B. Mennucci, H. P. Hratchian, J. V. Ortiz, A. F. Izmaylov, J. L. Sonnenberg, D. Williams-Young, F. Ding, F. Lipparini, F. Egidi, J. Goings, B. Peng, A. Petrone, T. Henderson, D. Ranasinghe, et al., Gaussian 16, Revision C.01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT 2016.
- 66D. A. Case, K. Belfon, I. Ben-Shalom, S. R. Brozell, D. Cerutti, T. Cheatham, V. W. D. Cruzeiro, T. Darden, R. E. Duke, G. Giambasu, M. Gilson, H. Gohlke, A. Götz, R. Harris, S. Izadi, S. A. Izmaylov, K. Kasavajhala, A. Kovalenko, R. Krasny, T. Kurtzman, T. Lee, S. LeGrand, P. Li, C. Lin, J. Liu, T. Luchko, R. Luo, V. Man, K. M. Merz, Y. Miao, et al., AMBER 2020, University of California, San Francisco, CA 2020.
- 67A. D. MacKerell, D. Bashford, M. Bellott, R. L. Dunbrack, J. D. Evanseck, M. J. Field, S. Fischer, J. Gao, H. Guo, S. Ha, D. Joseph-McCarthy, L. Kuchnir, K. Kuczera, F. T. Lau, C. Mattos, S. Michnick, T. Ngo, D. T. Nguyen, B. Prodhom, W. E. Reiher, B. Roux, M. Schlenkrich, J. C. Smith, R. Stote, J. Straub, M. Watanabe, J. Wiórkiewicz-Kuczera, D. Yin, M. Karplus, J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3586–3616.
- 68W. L. Jorgensen, J. Chandrasekhar, J. D. Madura, R. W. Impey, M. L. Klein, J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935.
- 69J. A. Izaguirre, D. P. Catarello, J. M. Wozniak, R. D. Skeel, J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 2090–2098.
- 70H. J. Berendsen, J. V. Postma, W. F. van Gunsteren, A. DiNola, J. R. Haak, J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690.
- 71T. Darden, D. York, L. Pedersen, J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092.
- 72J.-P. Ryckaert, G. Ciccotti, H. J. Berendsen, J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341.
- 73B. R. Miller 3rd, T. D. McGee Jr., J. M. Swails, N. Homeyer, H. Gohlke, A. E. Roitberg, J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3314–3321.
- 74A. D. Becke, Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100.
- 75A. D. Becke, J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652.
- 76C. Lee, W. Yang, R. G. Parr, Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789.
- 77S. Shaik, S. Cohen, Y. Wang, H. Chen, D. Kumar, W. Thiel, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 949–1017.
- 78W. Peng, S. Yan, X. Zhang, L. Liao, J. Zhang, S. Shaik, B. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 20484–20494.
- 79J. Chen, S. Dong, W. Fang, Y. Jiang, Z. Chen, X. Qin, C. Wang, H. Zhou, L. Jin, Y. Feng, B. Wang, Z. Cong, Angew. Chem. 2023, 135, e202215088.
- 80X. Zhang, Y. Jiang, Q. Chen, S. Dong, Y. Feng, Z. Cong, S. Shaik, B. Wang, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 8774–8785.
- 81A. Li, Q. Wang, X. Song, X. Zhang, J.-W. Huang, C.-C. Chen, R.-T. Guo, B. Wang, M. T. Reetz, Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 47, 191–199.
- 82F. G. Cantú Reinhard, Y.-T. Lin, A. Stańczak, S. P. de Visser, Molecules 2020, 25, 2675.
- 83Y.-T. Lin, S. P. de Visser, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7172.
- 84T. Mokkawes, T. de Visser, Y. Cao, S. P. de Visser, Molecules 2023, 28, 6961.
- 85F. Weigend, R. Ahlrichs, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297.
- 86S. Grimme, J. Comput. Chem. 2006, 27, 1787–1799.
- 87S. Grimme, J. Antony, S. Ehrlich, H. Krieg, J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104.
- 88S. Grimme, S. Ehrlich, L. Goerigk, J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465.
- 89S. P. de Visser, S. C. Porro, G. M. Quesne, A. M. Sainna, W. A. Munro, Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 2218–2232.
- 90J. Wei, Y. Liu, J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3638–3648.
- 91H. Chen, A. Zhou, D. Sun, Y. Zhao, Y. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 8419–8430.
- 92S. Louka, S. M. Barry, D. J. Heyes, M. Q. E. Mubarak, H. S. Ali, L. M. Alkhalaf, A. W. Munro, N. S. Scrutton, G. L. Challis, S. P. de Visser, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15764–15779.
- 93T. P. Zhou, J. Feng, Y. Wang, S. Li, B. Wang, JACS Au 2024, 4, 1591–1604.
- 94 CLSI, Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts; Approved Standard—Third edition, CLSI document M27-A3, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA 2008.
- 95H. Wang, Z. Li, R. Jia, Y. Hou, J. Yin, X. Bian, A. Li, R. Müller, A. F. Stewart, J. Fu, Y. Zhang, Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1175–1190.
- 96F. Flett, V. Mersinias, C. P. Smith, FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1997, 155, 223–229.
- 97K. F. Chater, L. C. Wilde, J. Gen. Microbiol. 1980, 116, 323–334.