Journal list menu
Hot Papers
Hot Papers are chosen by the Editors for their importance in a rapidly evolving field of high current interest. Many of the "Very Important Papers" (VIPs) would certainly qualify to be included here, but such a duplication is avoided.
Nanovaccine
Atorvastatin-Loaded Mineralized Vaccine Reprograms Endosomal Trafficking to Amplify STING-Driven Cancer Immunotherapy
Yuhan Yang, Wei Long, Xiangyu Pei, Shangfei Li, Bowen Fu, Hao Zhai, Xiaoyi Zhang, Ying Wan, Prof. Yayun Peng, Ting Cai
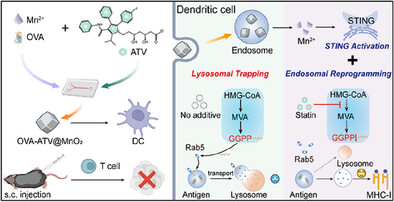
A biomineralized nanovaccine (OVA-ATV@MnO₂) spatiotemporally co-delivers and releases tumor antigen, atorvastatin, and Mn adjuvants in dendritic cells. Atorvastatin reprograms endosomal trafficking to delay lysosomal degradation, enhancing antigen cross-presentation via MHC-I, while Mn2+ activates the cGAS-STING pathway, amplifying dendritic cell maturation and antitumor T-cell responses. This dual-action strategy achieves potent tumor regression, suppresses metastasis, and establishes durable anticancer immunity.
Atomic Precision
Hydrogen-Bonding-Assisted Assembly of Stable High-Nuclearity Copper(I)-Alkyne Nanoclusters for X-Ray Scintillation
Bao-Liang Han, Fahri Alkan, Zhi-Rui Yuan, Paritosh Mahato, Zhi Wang, Chen-Ho Tung, Di Sun
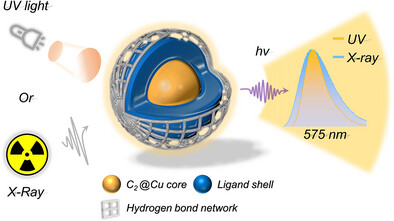
A novel hydrogen-bonding-assisted assembly strategy has been developed for the construction of high-nuclearity copper nanoclusters. Furthermore, the X-ray scintillation properties of the high-nuclearity nanocluster are investigated for the first time, demonstrating their potential for advanced radiation detection applications.
Electrochemical C─H Chlorination
Alkali Metal Cations Impact the Selectivity of Radical-Mediated Electrochemical C─H Chlorination
Bo Wu, Ruihu Lu, Tenghui Yuan, Beijing Cai, Bingqing Wang, Bote Zhao, Shibo Xi, Ziyun Wang, Yanwei Lum
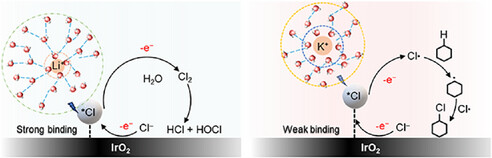
In this work, we found that alkali metal cations in the electrolyte can impact the *Cl binding energy, which controls selectivity between radical-mediated electrochemical C─H chlorination and competing Cl2 formation.
CO2 Hydrogenation
Establishing 3d-4d Orbital Hybridization for Efficient Photothermal Catalytic CO2 Hydrogenation
Yisi Yang, Dr. Fengliang Wang, Wenyuan Lyu, Dawang Tang, Datong Chen, Dr. Xin Zhao, Prof. Ruiqi Fang, Prof. Yingwei Li
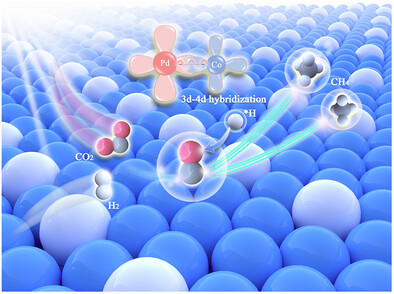
The d-d hybridization between 3d and 4d metals can induce the modulation of the affinity of *CO intermediate, thereby accelerating the *CO hydrogenation process in photothermal CO2 methanation.
Porous Organic Salts
Constructing Water-Stable Porous Organic Salts via Suppressed Proton Integration Using Fluorinated Tetrazole Tectons
Dr. Errui Li, Dr. Xian Suo, Yujing Tong, Dr. Phattananawee Nalaoh, Dr. David M. Jenkins, Dr. Carlos Alberto Steren, Dr. Lilin He, Alexander S. Ivanov, Dr. Leighanne C. Gallington, Dr. Victoria Cooley, Dr. Bo Li, Dr. Xin Wang, Dr. Kai Li, Dr. Juntian Fan, Dr. Liqi Qiu, Dr. De-en Jiang, Dr. Katherine R. Johnson, Dr. Takeshi Kobayashi, Dr. Murillo L. Martins, Dr. Shannon M. Mahurin, Dr. Zhenzhen Yang, Dr. Sheng Dai
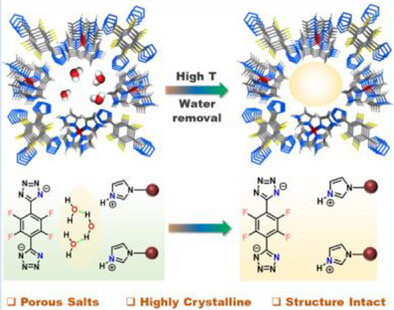
Porous organic salts featuring hydrophobic channels and minimal hydrogen bonding were constructed using a fluorinated tetrazole as a weak acid tecton and a tetra-substituted imidazole precursor lacking active protons as the base. These materials exhibited exceptional robustness and structural integrity under both aqueous and water-lean conditions, maintaining their stacking mode and crystal structure even at elevated temperatures.
Fluoroalkenes
Platinum-Catalysed Hydrofluorination of Alkynes at Room Temperature Promoted by a Fluoride Shuttle
Ouchan He, Dr. Froze Jameel, Hannah Flammang, Smrithi Suresh Babu, Prof. Dr. Martin Kaupp, Prof. Dr. Thomas Braun
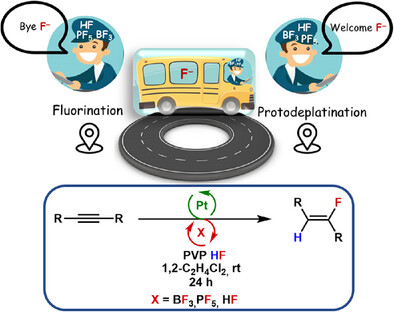
This work presents an air and moisture tolerant platinum-catalysed hydrofluorination system that gives selectively (Z)-fluoroalkenes. Experimental and computational investigation on the mechanism allowed for the identification of catalytic species. The hydrofluorination is mediated by complexes between the fluorinated anion and HF, resulting into BF3, PF5 and HF serving as fluoride shuttles.
Heterometallic Complex
C(sp2)─H Bond Activation with a Heterometallic Nickel-Aluminium Complex
Joseph A. Zurakowski, Dr. Benedek Stadler, Prof. Dr. Marcus W. Drover, Prof. Dr. Mark R. Crimmin
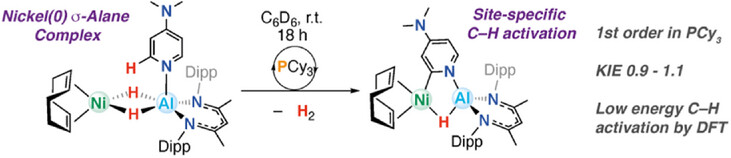
Despite the prevalence of Ni/Al catalysts for pyridine C─H functionalization, mechanistic details of such systems remain scarce. Herein, we present the discovery of PCy3-catalyzed bond-breaking and making processes that occur in the coordination sphere of a novel Ni─Al heterometallic complex. The reaction is 1st order in PCy3 and proceeds with a low KIE of 0.9-1.1. These data suggest that both C─H activation and H2 reductive elimination steps in this system are low energy, are readily accessible, and are not rate limiting.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Scalable Hyperpolarized MRI Enabled by Ace-SABRE of [1-13C]Pyruvate
Stephen J. McBride, Megan Pike, Erica Curran, Alexander Zavriyev, Bukola Adebesin, Luke Tucker, Jared M. Harzan, Ishani M. Senanayake, Mustapha Abdulmojeed, Franziska Theiss, Sheng Shen, Thomas Boele, Simon B. Duckett, Boyd M. Goodson, Matthew S. Rosen, Eduard Y. Chekmenev, Hong Yuan, Carlos Dedesma, Terence Gade, Stephen Kadlecek, Thomas Theis, Patrick TomHon
![Scalable Hyperpolarized MRI Enabled by Ace-SABRE of [1-13C]Pyruvate Scalable Hyperpolarized MRI Enabled by Ace-SABRE of [1-13C]Pyruvate](/cms/asset/a4ca10b9-8aea-4c04-96dc-96341ec02b2a/anie202501231-gra-0001-m.jpg)
Ace-SABRE overcomes previous biocompatibility challenges associated with the Signal Amplification By Reversible Exchange (SABRE) hyperpolarization technique. The employed acetone-water mixtures greatly simplify separation of the hyperpolarized compound (e.g., pyruvate) from solvents and catalysts delivering a biocompatible injectable. Ace-SABRE retains high polarization during processing and enables effective metabolic characterization in vivo.
Multisite Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer
Multisite Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer Facilitates Oxidative Photocatalysis in a Molecular Zr-Based Coordination Compound
Mercedes Moreno-Albarracín, Alvaro M. Rodriguez-Jimenez, Omar Nuñez, Pablo Garrido-Barros
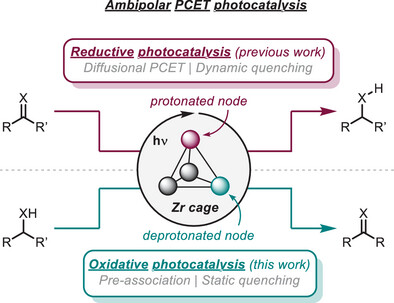
Deprotonation of the hydroxy ligand in the Zr3(O)(OH)3 nodes of a molecular cage unlocks photo-oxidative catalysis via multisite proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET), complementing previous findings in the reductive counterpart. This platform offers valuable insights into the excited-state reactivity of photoredox catalysts and stands as a promising tool with unprecedented ambipolar reactivity for solar-to-chemical conversion.
Radicals
Feedstock-Derived Thiophene Radical Anions Exhibiting Redox Stability at Extreme Potentials
Aurelio C. Gasser, Daniel Käch, Prof. Dr. Máté J. Bezdek
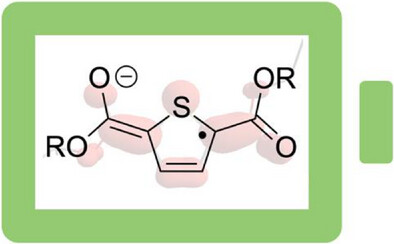
Although organic redox systems are emerging as next-generation energy storage media, stability at high cell voltage is often achieved at the expense of synthetic accessibility. Here, we isolate and characterize a feedstock-derived thiophene radical anion bearing simple ester groups. Despite a minimalist design, the radical and its derivatives are stable at extreme potentials, enabling their use as readily accessible electrolytes for electron storage.
Triarylmethyl Radicals
Chloromethoxytrityls: Tuning the SOMO Level of Stable Luminescent Radicals
Hannah E. Hackney, Cory Ruchlin, Emil Stahle, Dmytro F. Perepichka
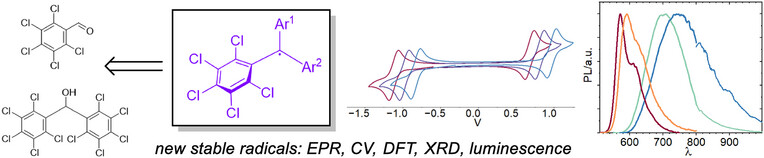
In this work, we use chlorine and methoxy groups to control the singly occupied molecular orbital level of triarylmethyl radicals within a wide range of 1.8 eV and establish structure-properties relationships between the substituents and photophysical properties of triarylmethyl radicals.
Vibrational Strong Coupling
The Diels-Alder Reaction as a Mechanistic Probe for Vibrational Strong Coupling
Dr. Cyprien Muller, Dr. Maciej Piejko, Sinan Bascil, Prof. Dr. Joseph Moran
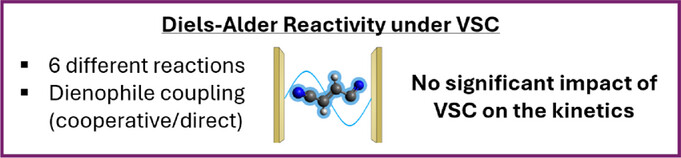
Vibrational Strong Coupling (VSC) was recently shown to modify chemical reactivity, but it is unclear why. We introduce the Diels-Alder (DA) reaction as a mechanistic probe for some of the most popular hypotheses and provide the first experimental investigation of the DA reaction under VSC by measuring the kinetics of six different DA reactions under various coupling conditions. No significant change in kinetics was observed.
Perovskite Solar Cells
Monodisperse Regulation of Self-Assembled Monolayer Via Dipole Molecules for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells
Zhinan Zhang, Yinghao Xu, Sifan Chen, Wenbo Li, Shaofu Wang, Chuan Peng, Shengjie Du, Sixiong Li, Xingzhong Zhao, Ti Wang, Zhenhua Yu
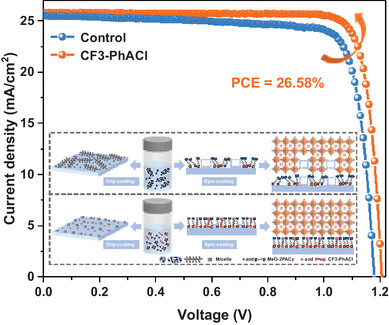
Strong dipole molecules are employed to regulate the monodispersity of self-assembled monolayer (SAM) micelles and coverage distribution of the resulting SAM films, achieving an efficiency of 26.58%.
Total Synthesis
Ligand Type Guided Keto-Arylation Enables Modular Total Synthesis of Polycyclic CBS Xanthones
Jonas W. Meringdal, Vivienne Prangenberg, Tim Treiber, Andreas J. Schneider, Leon Honsdorf, Dirk Menche
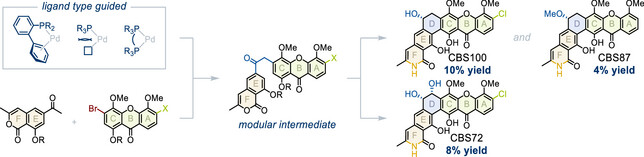
A ligand type concept guided a central aromatic keto-arylation in the first total syntheses of CBS72, CBS87 and CBS100. Davis oxidation with catalytic base and late-stage aminolysis completed the route. This strategy provides modular, concise and high-yielding access to uncharted polycyclic xanthones. Meanwhile, ligand types emerge as a powerful design tool in sophisticated cross couplings.
Thermoelectrics
Conduction Band Convergence and Modular Nanostructures: Driving High Thermoelectric Performance in n-Type PbSe
Indrajit Haldar, Vaishali Taneja, Naveen Goyal, Mohammad Ubaid, Debattam Sarkar, Dinesh Kumar Kedia, Kumar Saurabh, Surjeet Singh, Koushik Pal, N. Ravishankar, Kanishka Biswas
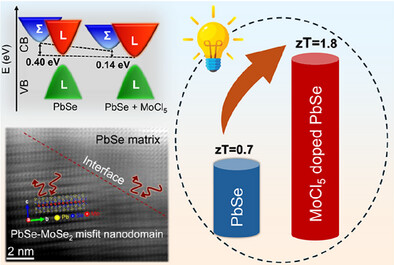
Mo 4d orbital hybridized with the Se 4p-Pb 6p to provide conduction band convergence, and PbSe-MoSe2 modular nanostructures lead to high thermoelectric performance in MoCl5 doped n-type PbSe.
Tip-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Angularly Resolved Tip-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Felix Schneider, Tim Parker, Dr. Liangxuan Wang, Michel Rebmann, Yang Zhao, Eric Juriatti, Prof. Heiko Peisert, Prof. Alfred J. Meixner, Dr. Johannes Gierschner, Prof. Lingyan Meng, Prof. Dai Zhang
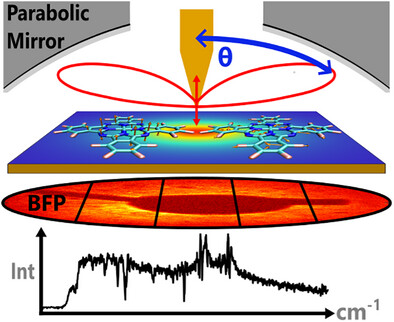
We find that the tip-enhanced Raman signal (TERS) is angularly distributed and vibrational mode specific. The radiation pattern in the back focal plane (BFP) of vertical or parallel Raman dipoles is strongly influenced by the near-field in the TERS nanogap, while the emission is guided into the far-field with high directionality by the tip-sample antenna; however, with significant differences in the emission angle, intensity, and the divergency..
Facet-Dependent Photocatalytic HER
Crystal Facet-Dependent Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution From Ultra-Stable Cu-Zr/Hf Heterobimetallic Metal-Organic Frameworks
Hang Lei, Dr. Jieping Zhang, Zhiyuan Wu, Yangxingyu Ye, Dr. Zhijia Li, Yunfang Zhao, Prof. Lian Chen, Prof. Yongsheng Liu, Prof. Maochun Hong
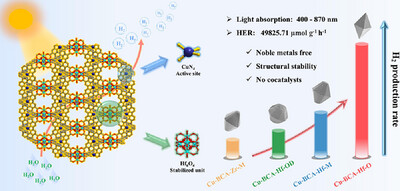
Crystal engineering and facet engineering were concurrently employed to develop a series of precious-metal-free heterobimetallic MOFs (M-BCA-M', M = Cu+, M' = Zr4+ or Hf4+) for record-high photocatalytic hydrogen production in pristine MOFs. The high performance and crystal-facet dependent behaviors were investigated to provide molecular-level insights into the coordination regulation and morphology control of pristine MOFs for efficient photocatalysis.
Perovskite Solar Cells
Antisolvent-Bathing Strategy with Ultra-Wide Processing Window for Making High-efficiency Perovskite Solar Cells in Ambient Air
Lixiu Zhang, Chuantian Zuo, Mei Zhang, Ruihao Chen, Xiangyu Chen, Ke Jin, Feng Hao, Keyou Yan, Zuo Xiao, Congcong Wu, Jingjing Chang, Yong Ding, Liming Ding
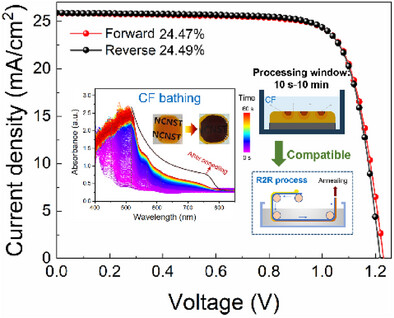
Antisolvent bathing strategy with ultra-wide processing window (10 s-10 min) is proposed to achieve high-performance perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The bathing process is in situ monitored via time-resolved UV-Vis spectroscopy, systematically unrevealing the crystallization kinetics for different antisolvents. The PCE of CF-bathed device achieves 24.49% in ambient air, representing the record for antisolvent bathing method.
Organosilicon Chemistry
Nickel-Catalyzed Sila-Cycloaddition of Dichlorodisilanes: Selective Si─Cl Activation for Cyclic Disilanes and Enantioenriched Synthesis
Dr. Liangliang Qi, Shaojie Xu, Prof. Xiaobo Pang, Yu-Ke Wu, Prof. Xiaotai Wang, Prof. Xing-Zhong Shu
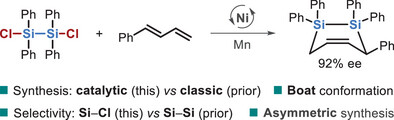
A nickel-catalyzed [4 + 2] sila-cycloaddition between dichlorodisilanes and 1,3-dienes enables efficient access to diverse cyclic disilanes via selective Si─Cl activation. The method tolerates broad diene scope, offers an enantioselective variant, and reveals a unique Ni⁰-mediated SN2-type activation pathway.
Circularly Polarized Luminescence
Chiral Tin-Oxo Cluster Matrices with Fluorophore Embedment for Multichromatic Circularly Polarized Luminescence
Gui-Xin Yan, Dr. Er-Xia Chen, Dr. Jin-Xia Yang, Prof. Jian Zhang, Prof. Qipu Lin
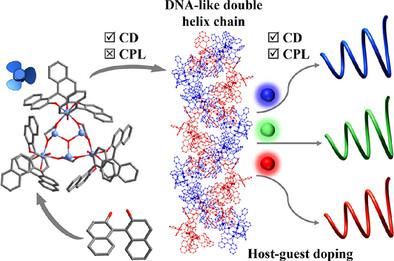
Enantiomeric tin-oxo clusters form helical supramolecular matrices through directional intermolecular interactions, enabling efficient transfer of optical handedness to encapsulated non-chiral fluorophores via spatial confinement. These assemblies exhibit tunable circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) emissions.
CO2 Reduction
Ordered Copper Triangular Atomic Sites for Industrial-Grade Electromethanation of CO2 via Self-Regulated Adsorption of Reactants
Dr. Fanglei Yao, Dr. Yuntong Sun, Long Nie, Dr. Cheng Zhang, Dr. Hongwei Shou, Zhiming Li, Prof. Xiaoping Gao, Prof. Jin Wang
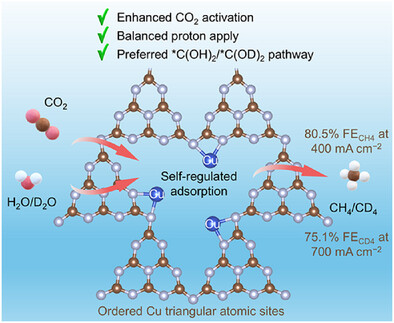
Ordered copper triangular atomic site motifs loaded on poly(heptazine imide) (Cu TAS/PHI) were synthesized via a precise ion exchange strategy. Cu TAS/PHI enables enhanced CO2 coverage and activation with balanced proton supply through self-regulated adsorption of reactants, as well as unlocks an energetically favorable *C(OH)2 pathway, achieving an FECH4 of 80.5% at 400 mA cm−2 and an FECD4 of 75.1% at 700 mA cm−2.
Cobalt Catalysis
A Homobimetallic Frustrated Lewis Pair Cobalt Catalyst for the Methanolysis of Hydrosilanes
Dr. Ana Luque-Gómez, Daniel Barrena-Espés, Dr. Pilar García-Orduña, Andrea Pérez-García, Miguel A. Casado, Dr. Julen Munarriz, Dr. Manuel Iglesias
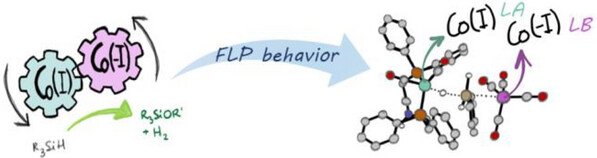
The bimetallic Co(I)/Co(-I) complex [Co(CO)2(κ3-P,N,P-PNHP)][Co(CO)4] shows excellent activities in the methanolysis of hydrosilanes, reaching TOF values of ca. 50 000 h−1. This behavior can be ascribed to the presence of the [Co(CO)4]- anion, which allows for a frustrated Lewis pair mechanism, resulting in a low energy pathway for the heterolytic splitting of the Si─H bond, as substantiated by DFT calculations.
Homichiral Ferroelectric
Mathematical Double-Matrix Switchable Homochiral Ferroelectric
Dr. Xian-Jiang Song, Dr. Yan Qin, Prof. Yong Ai, Dr. Xiao-Gang Chen, Dr. Yan-Ran Weng, Dr. Hang Peng, Dr. Hui-Peng Lv, Dr. Ren-Gen Xiong, Dr. Wei-Qiang Liao
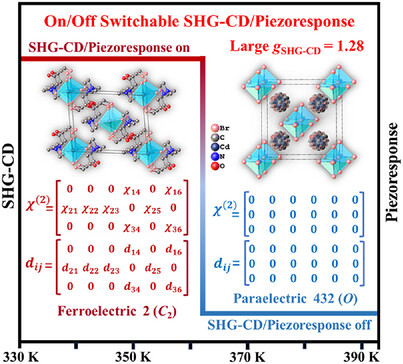
We reported the first homochiral metal halide ferroelectrics showing on/off switchable second-harmonic generation circular dichroism (SHG-CD) response. They exhibit strong SHG-CD with the anisotropy factor (gSHG-CD) up to 1.28 and a 432F2 ferroelectric phase transition, enabling the unprecedented on/off switching of both SHG-CD and piezoelectric response between the SHG-CD/piezoelectric active and SHG-CD/piezoelectric inactive states.
Phototheranostics
Doping Bulky Fluorinated Organic Anion to Construct Highly Efficient Anion-π+ Type Photosensitizers for Cancer Phototheranostics
Lingxiu Liu, Jianye Gong, Xue Wang, Prof. Guoyu Jiang, Prof. Ben Zhong Tang, Prof. Jianguo Wang
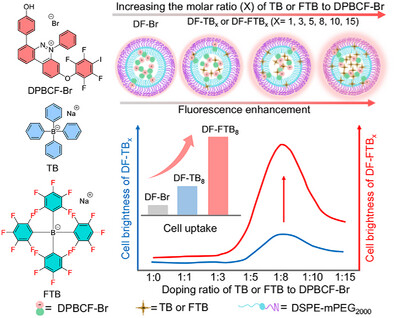
A facile strategy to enhance the fluorescence intensity and to modulate cellular uptake of anion-π+ AIE PSs by doping bulky fluorinated anions tetrakis(pentafluorophenyl)borate (FTB) into nanoparticles was proposed. The optimized DF-FTB8 (FTB:DPBCF-Br = 8:1) exhibited superior cellular uptake, outstanding imaging capabilities and high intracellular reactive oxygen species generation level, enabling efficient cancer photodynamic therapy.
Gold(0) Complexes
Dinuclear Au(0) Complex Supported by Tridentate P-Mg-P Ligands
Yafei Li, Tianze Xu, Xinggao Ji, Jie Zeng, Jin Xie, Jing Ma, Congqing Zhu, Qin Zhu
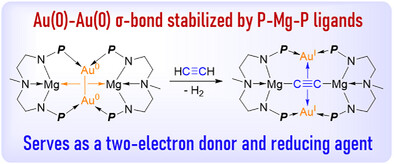
A complex featuring an Au(0)-Au(0) σ-bond is stabilized by tridentate P-Mg-P ligands, with the σ-bond serving as a two-electron donor to the Mg centers and enabling two-electron reductions of various substrates. This work highlights the significance of ligand design for stabilizing low-valent Au center and provides new cases to explore the properties of dinuclear Au(0) complexes.
CO2 Electroreduction
Enhanced Active Hydrogen Absorption and Stabilized Cu(I) Species Over Cu-O-Ce Bridges Boosting Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to Ethylene
Zhenwei Zhao, Yu Zhang, Junjun Li, Bingqing Yao, Hui Zhang, Zhicheng Zhang
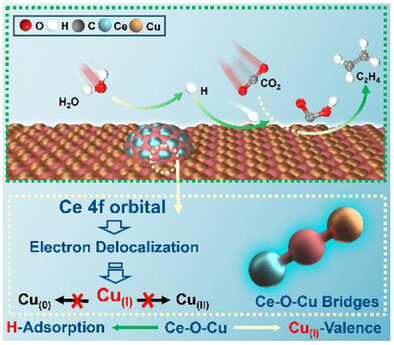
The as-synthesized CuxO-CeO2 composites exhibit enhanced Faradaic efficiency and partial current density of C2H4 compared with Cu2O cubes. In situ spectroscopies and theoretical calculations confirm that the Cu-O-Ce bridges in CuxO-CeO2 composite can effectively enhance *H absorption and stabilize Cu(I) species, facilitating subsequent C-C coupling and further protonation into the key *COCHO intermediate of C2H4.
Supramolecular Polymers
Mechanically Tunable Slide-Ring Polymers via Photo-Regulated Topological Control
Xiaoqing Wang, Chenjuan Yu, Maolin Wang, Shiyu Zhao, Qimo Mao, Prof. Yuping Wang
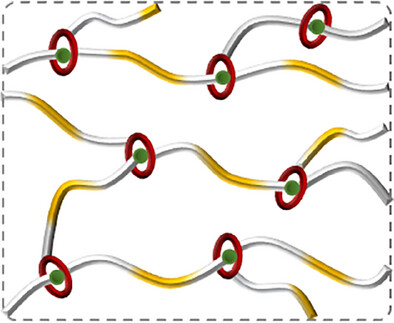
We developed light-responsive slide-ring polymer networks whose mechanical properties can be tuned through photoisomerization of the incorporated azobenzene units. The trans-state permits unhindered macrocycle sliding, yielding ductile materials, while UV-induced cis-configuration restricts macrocycle mobility to double Young's modulus. Furthermore, the azobenzene linkage confers controlled degradability under mild conditions.
Anion Channels
Dual-Function Tetrabenzylphosphonium Groups as Mitochondria-Targeting Artificial Anion Channels
Dr. Fei Gou, Xinlei Huangfu, Qiuting Wang, Zihong Yang, Xiyu Yuan, Dr. Wenju Chang, Prof. Dr. Jie Shen, Prof. Dr. Wen-Xiong Zhang, Prof. Dr. Huaqiang Zeng
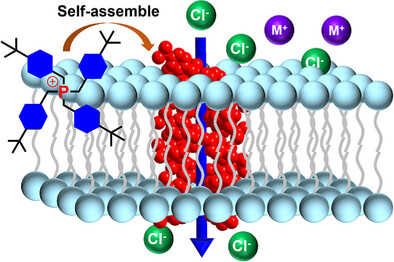
A series of mitochondriotropic artificial anion channels have been constructed from a self-assembled tetrabenzylphosphonium framework with an inherent ability to autonomously target mitochondria. Anion transport is mediated by multiple intermolecular C─H⋯anion H─bonds and electrostatic ion pair interactions. The highly efficient transmembrane anion transport is demonstrated by low micromolar anticancer activity against three cancer cell lines.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Macromolecule-Driven Supramolecular Polymerization Induced by Crowding Effects
Dr. Joost J. B. v. d. Tol, Magda M. J. Dekker, Ádám Müller, Puck Springintveld, Prof. Dr. E. W. Meijer, Prof. Dr. Ghislaine Vantomme
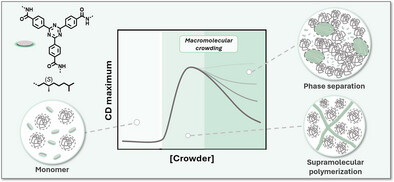
A systematic study is presented that investigates the influence of the excluded volume effect by macromolecules on supramolecular polymerizations in organic media. Upon crowding, the discotic supramolecular monomers sequentially assemble into polymers and higher-order aggregates (HOAs), affected by the macromolecule's concentration, size and polarity. The proven tunability and general applicability of this entropically driven assembly open new avenues for applying macromolecular crowding beyond aqueous systems.
Organic Photovoltaics
Prolonging Exciton Diffusion Length via Modulating Aggregation Structures for Binary Organic Photovoltaics Approaching 20% Certified Efficiency
Jiayou Zhang, Fang Fang, Bending Zhang, Dr. Lifu Zhang, Houdong Mao, Lin Wen, Dr. Dou Luo, Chongbin Yu, Prof. Zhen Yang, Prof. Yiwang Chen
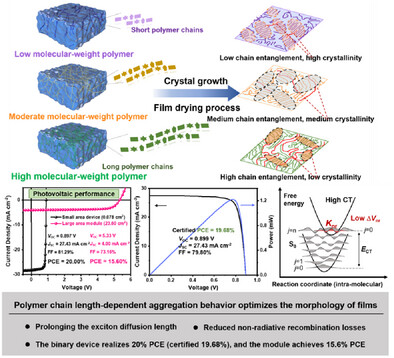
The exciton diffusion length (LD) and fluid mechanics were effectively optimized by modulating the polymer aggregation structure. The printing PPHJ flexible OPVs exhibits more than 18% efficiency, and the flexible device maintained 90.4% of the initial PCE after 2000 bending cycles, showing excellent mechanical stability. Meanwhile, the rigid device exhibits 20% efficiency (certified19.68%, the highest value for the eco-friendly solvent system). Notably, the fabricated 23.60 cm2 large-area module was 15.60% PCE.
Photocages
Unveiling the Power of Dark State Photocages: An Efficient Pathway to Triplet State Under Near-Infrared Light Irradiation
Qiao Hu, Prof. Jianjun Du, Syed Ali Abbas Abedi, Prof. Xiaogang Liu, Saran Long, Prof. Wen Sun, Prof. Jiangli Fan, Prof. Xiaojun Peng
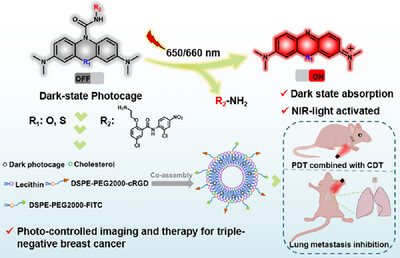
The concept of a dark state photocage was proposed based on near-infrared light-activated leuco dyes. The dark state enhances triplet-state formation, enabling the release of dyes and functional molecules under red light irradiation. This platform exhibited excellent “OFF”-to-“ON” tumor imaging contrast and effective tumor inhibition against triple-negative breast cancer and lung metastases.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Tailoring Tubular Supramolecular Polymers with Polar Lumens to Host Hydrophilic Dye Molecules
Irene Sancho-Casado, Dr. Fátima Aparicio, Dr. Marina González-Sánchez, Dr. Raquel Chamorro, Dr. Víctor Vega-Mayoral, Dr. Juan Cabanillas-González, Prof. David González-Rodríguez
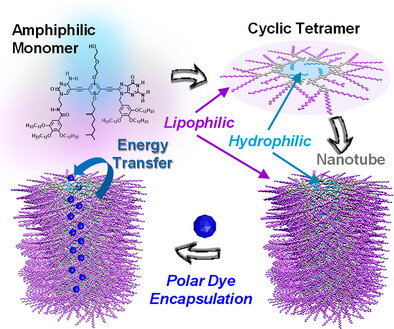
A unique class of tubular polymer structures that are soluble in apolar organic solvents but are endowed with polar pores has been created through the rational design of the monomer units, which self-assemble in amphiphilic cyclic entities that then stack into tubular architectures. These tailored assemblies are able to selectively host hydrophilic dye molecules that are complementary in size and chemical affinity for the pore coating, providing containers for the study of energy transfer processes.
InP QD-LEDs
Dual-Mode Strain Relief via Zinc Acetate Enables High-Efficiency InP Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes
Changwei Yuan, Prof. Qun Wan, Xinrong Liao, Mengda He, Canan Li, Prof. Zhemin Shen, Prof. Baoquan Sun, Prof. Zan Qu, Prof. Long Kong, Prof. Liang Li
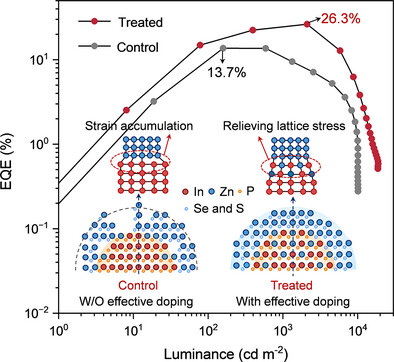
This study presents a novel strain engineering strategy that enables stress relief and uniform shell growth at the InP quantum dot coreshell interface using a small-molecule Zn(Ac)2 precursor. This approach significantly reduces interfacial strain and boosts the PLQY to nearly 100%. The resulting QLEDs demonstrate enhanced charge injection and energy level alignment, achieving an external quantum efficiency of up to 26.3%, offering a scalable platform for advanced quantum dot and device development.
Urea Electrosynthesis
Atomic-Scale Mott-Schottky Analogy in SnCu Nanoalloy Promote High-Efficiency Urea Electrosynthesis at Ultralow Potential
Pingyi Feng, Buqi Ke, Shao Wang, Yanxu Chen, Mingyu Cheng, Zechuan Dai, Bocheng Zhang, Yifan Li, Prof. Genqiang Zhang
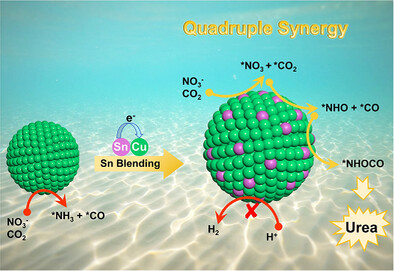
Electron-enriched Cu active sites arising from an atomic-scale Mott-Schottky analogy in SnCu nanoalloy catalyst, exhibited quadruple synergism: enhanced CO2 and NO3− co-adsorption, elevated *CO surface coverage, accelerated *NHO-*CO coupling, and concurrent HER suppression, collectively achieving a twofold enhancement in urea yield compared to pristine Cu.
Photocatalysis
Light-Induced Fe-LMCT Catalysis for Redox-Coupled Conversion of NOx and SO2 Mixture
Ruimin Chen, Jielin Wang, Taobo Huang, Chunling Zhang, Xiuping Zhu, Jieyuan Li, Fan Dong

A light-induced Fe-LMCT (ligand-to-metal charge transfer) catalytic system is demonstrated, whereby continuous conversion of NO to N2 and SO2 to SO42− is achieved, with the formation of N2O byproducts suppressed via LMCT-driven spatial segregation of redox pathways.
ZrO2/Ni Inverse Catalysts
Spontaneous Nano-ZrO2 Exsolution from Ni-Zr-O Mixed Oxides Enables Facile Fabrication of ZrO2/Ni Inverse Catalysts for Efficient COx Methanation
Xin Tang, Yuanchang Wang, Jinrong Zhang, Cheng Yu, Mengyao Cheng, Shiqing Yang, Xuguang Yang, Liangwei Liu, Lili Han, Yao Xu, Chuqiao Song, Lili Lin
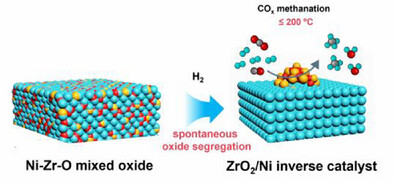
A spontaneous nano-oxide exsolution strategy was reported as a facile engineering of ZrO2/Ni inverse catalyst, involving the one-step co-precipitation synthesis of Ni-Zr-O mixed oxide with monodispersed Zr species followed by H₂-induced in situ oxide segregation. The prepared ZrO2/Ni inverse catalyst was demonstrated to exhibit near-thermodynamic-equilibrium COx conversions at 200 °C, while maintaining robust stability under complex simulated syngas conditions.
Small Molecule Activation
Cooperative Activation of CO and Pyridine by an Aluminum(I) Complex Ligated with a Silylene-Borane Ligand
Jinghuang Lv, Xiao Fang, Fanshu Cao, Prof. Dr. Zhenbo Mo
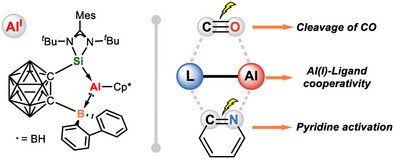
A silylene-borane-ligated aluminum(I) complex featuring Si(II)→Al(I) and Al(I)→B(III) donor-acceptor interactions were synthesized and structurally characterized. The ambiphilic ligand- aluminum cooperation enables C≡O bond cleavage and pyridine dearomatization, uncovering new avenues in low-valent aluminum chemistry.
Rotaxanes
Logic-Gated Release of a Dual Payload from a β-Lactam Mechanophore with a Rotaxane Actuator
Dr. Lei Chen, Prof. Dr. Guillaume De Bo
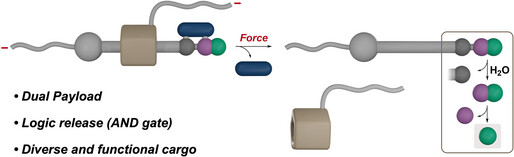
A rotaxane device operates as a logic AND gate to release a single or dual cargo payload upon application of force in the absence or the presence of water, respectively. This concept was demonstrated with the release of a ketene and varied drugs, paving the way for precision release applications.
Ferroptosis
EDTA-Mg Nano-Chelators Amplify Ferroptosis by Artificially Simulating the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Process and Endogenous Iron Deprivation
Yulin Xie, Tengfei Jiang, Junrong Wang, Yanrong Qian, Wencheng Xu, Guanghui Zhao, Prof. Haidong Gao, Prof. Chunxia Li
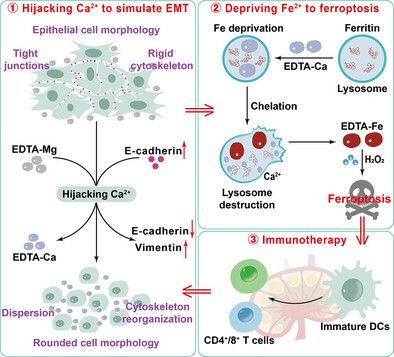
Based on metal chelation therapy, we utilize the chelation performance of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) for different divalent metal ions to achieve the precise regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process in tumors and simultaneously synergize ferroptosis and immunotherapy to effectively inhibit the growth and metastasis of tumors.
Batteries
Amorphous Nitride-chloride Solid-State Electrolytes for High Performance All-Solid-State Lithium Batteries
Ting-Ting Wu, Dr. Si-Jie Guo, Dr. Hong-Shen Zhang, Yue Jiang, Jun Wang, Jiacheng Zhu, Dr. Xusheng Zhang, Dr. Pengfei Wei, Dr. Ziyang Hu, Rongzhi Gao, Prof. GuanHua Chen, Prof. Rui Wen, Prof. Xuefeng Wang, Prof. An-Min Cao
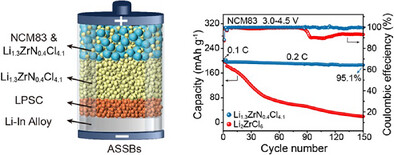
An amorphous nitrogenchloride dual-anion solid-state electrolyte (Li1.3ZrN0.4Cl4.1) with high ionic conductivity (3.01 mS cm−1 at 25 °C) and broad electrochemical stability is developed. When paired with LiNi0.83Co0.06Mn0.11O2, it enables all-solid-state batteries (ASSBs) with high capacity (200.1 mAh g−1 at 4.5 V), excellent cycle retention (95.1% after 150 cycles), and long-term durability (3,000 cycles at 3 C). The electrolyte remains stable under extreme conditions, operating at 4.8 V and 50 °C, demonstrating strong potential for high-energy, long-life ASSBs.
Pt-Based Hydrogen Oxidation
Site-Blocking Strategy Boosts H2S Tolerance in Platinum-Based Hydrogen Oxidation Catalysts
Wei Kang, Dr. Tao Shen, Ying Wang, Jilong Xu, Chuansheng Ma, Yue Wang, Dr. Yue-Jiao Zhang, Prof. Jia-Bo Le, Prof. Yifan Ye, Prof. Jian-Feng Li, Prof. Jin-Chao Dong
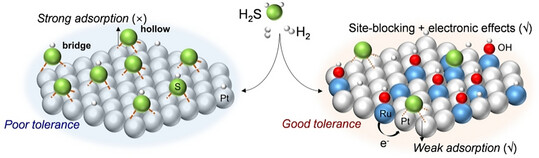
The in situ Raman spectroscopy reveals that the S-contained poisoning intermediates formed on pure Pt could be limited on PtRu alloy to enhance the H2S tolerance in hydrogen-oxygen fuel cells, which originates from the site-blocking effect and electronic tuning effect induced by Ru.
Bioorthogonal Reactions
Tuning Encodable Tetrazine Chemistry for Site-Specific Protein Bioorthogonal Ligations
Subhashis Jana, Alex J. Eddins, Yogesh M. Gangarde, P. Andrew Karplus, Ryan A. Mehl
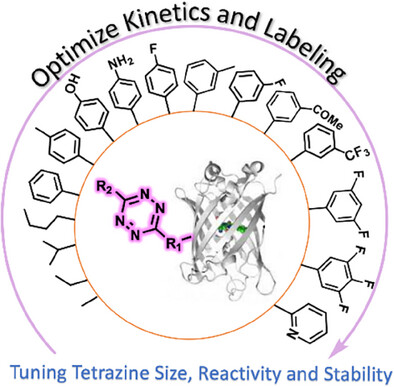
We expand the bioorthogonal chemistry toolkit by synthesizing and characterizing 29 tetrazine ncAAs and evaluating their genetic encoding into proteins. Site-specific incorporation was achieved, and tools to assess efficiency, fidelity, stability, and reactivity were applied. This roadmap enabled the design of tunable tetrazines and the fastest quantitative labeling at 10⁶ M⁻¹s⁻¹ without compromising stability.
Polymer Chemistry
Catalytic Polymerization of n-Doped Poly(benzodifurandione) (n-PBDF) Using Parts Per Million (ppm) Levels of Molybdenum Trioxide
Dr. Guangchao Liu, Uttam Pal, Dr. Sanket Samal, Michael F. Espenship, Dr. Yuanhe Li, Dr. Won-June Lee, Lawal Adewale Ogunfowora, Dr. Liyan You, Prof. Julia Laskin, Prof. Jianguo Mei
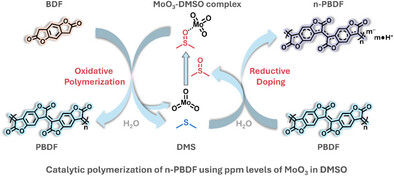
An efficient, scalable, and cost-effective catalytic polymerization of n-PBDF using ppm levels of MoO3 was developed in this study. Kinetic studies reveal that this polymerization demonstrates chain-growth characteristics, enabling the preparation of high-quality n-PBDF polymers. Mechanistic investigations reveal that MoO3 mediates an oxidative pathway involving dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), with dimethyl sulfide (DMS) identified as the reduction product. This method eliminates the need for purification process, demonstrating the potential for large-scale production of high-quality n-PBDF ink.
Room-Temperature Phosphorescence
Molecular Engineering of Plant Polyphenols Into Amorphous Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Materials
Guobin Yang, Yajing Zhang, Chuang Lei, Dr. Yunxiang He, Yizhen Wang, Prof. Huijing Li, Prof. Yanchao Wu, Prof. Junling Guo
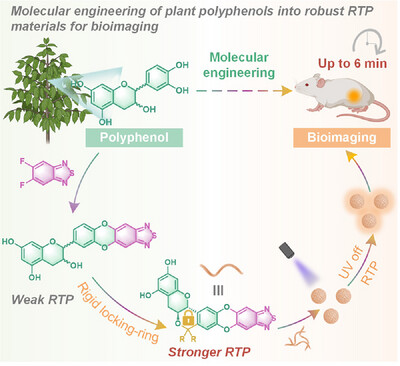
A phenolic-mediated molecular splicing and ring-locking strategy enables the fabrication of amorphous RTP systems with lifetimes up to 124 ms. The resulting phosphorescent nanoparticles exhibit exceptional biocompatibility, enabling high-contrast, time-resolved luminescence imaging, offering a sustainable approach for biomedical RTP applications.
Organic Materials
Chiral Co-Assembled Liquid Crystal Polymer Network Enabled by In-Situ Photopolymerization for High-Performance CP-OLEDs
Chunya Fu, Dong Li, Chao Liu, Yu Zhang, Junsheng Zhang, Yixiang Cheng
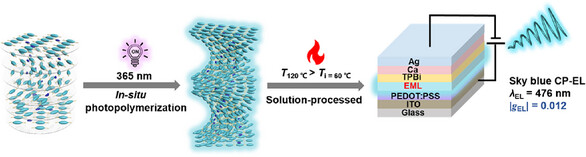
This work developed a facile in situ photopolymerization approach to construct rigid cholesteric liquid crystal polymer network (ChLC-PN) as the emitting layers (EML) for CP-OLEDs through chiral co-assembly strategy in cholesteric liquid crystal matrices.
DNAzyme
Framework Nucleic Acid-Mediated DNAzyme Chaperoning for Sensitive Trace Metal Ion Mapping on Live Neuronal Cell Membranes
Tianqi Xu, Fan Li, Yichao Jin, Feng Jia, Yu Wang, Tao Lv, Yueyue Zhang, Min Li, Chunhai Fan, Mingqiang Li, Xiaohua Zhang, Shaopeng Wang, Xiaolei Zuo
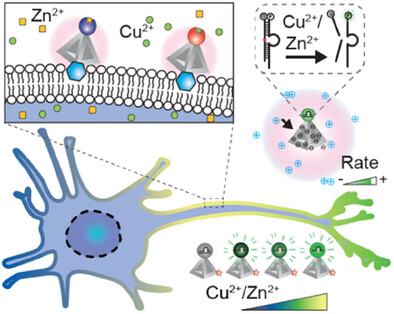
Inspired by the beneficial effects of molecular chaperones on the stability and functionality of proteins, we present in this study the development of tetrahedral DNA frameworks (TDF) as chaperones for DNAzymes. Integration of TDF with DNAzymes significantly improves sensitivity and stability, facilitating precise and quantitative mapping of local trace metal ion concentrations on live neuronal cell membranes. This adaptable approach sets a foundation for developing sensitive nanodevices based on DNAzymes.
Sustainable Carbon Sequestration
Long-Range Electronically Polarized Fe-N5 Catalysts Redirect Polymerization-Driven Phenolic Pollutant Removal Toward Sustainable Carbon Sequestration
Yanchun Deng, Prof. Yingtang Zhou, Dr. Zilong Song, Prof. Xin Yang
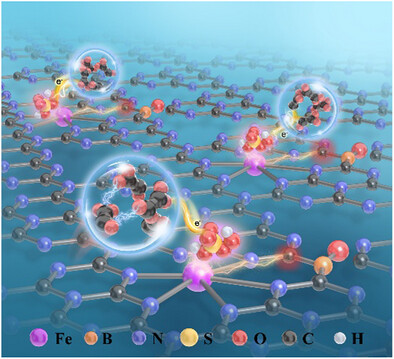
A long-range electronically polarized Fe-N5 catalyst is developed, enabling specific and efficient peroxymonosulfate (PMS)-catalyst complex generation. BPA removal is redirected by tailored PMS complexes from conventional radical-mediated mineralization pathways to interfacial polymerization. A 4-668 times higher total organic carbon (TOC) removal than reported for iron-based single-atom catalysts (Fe-SACs) is achieved, with sustainable practical wastewater treatment and carbon sequestration observed (>1700 h operation).
Direct X-ray Detectors
Solution-Processed Amorphous Zero-Dimensional Organic Metal Halide Hybrid Films for Direct X-Ray Detectors
Oluwadara J Olasupo, Abiodun M. Adewolu, Mohammad Khizr, Tarannuma F. Manny, He Liu, Tunde B. Shonde, Md S. Islam, Sahel Moslemi, Ethan Kim, J.S. Raaj V Winfred, Thilina N.D.D. Gamaralalage, Yan-Yan Hu, Ranjan Das, Biwu Ma
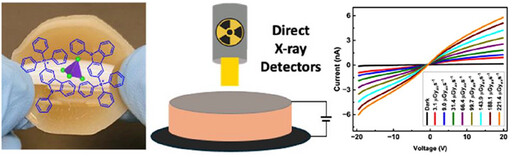
The use of solution-processed amorphous zero-dimensional organic metal halide hybrid (TPPCarz)2ZnBr4 films for direct X-ray detection is demonstrated. The amorphous films exhibit efficient molecular sensitization, with ZnBr42− species serving as X-ray absorbers and TPPCarz⁺ moieties as charge transporters. The resulting detectors achieve a detection sensitivity of 2165 µC Gyair−1cm−2 at 20 V mm−1 and a detection limit of 6.01 nGyair s−1.
Batteries
Local Electric Field Microenvironment-Induced Dynamic Spatial Confinement to Stabilize I+ Toward High-Mass-Loading and Stable Zinc-Iodine Batteries
Liting Chen, Song Huang, Zhenfeng Feng, Zhenxin Lin, Haolong Huang, Minghui Ye, Yufei Zhang, Zhipeng Wen, Yongchao Tang, Xiaoqing Liu, Cheng Chao Li
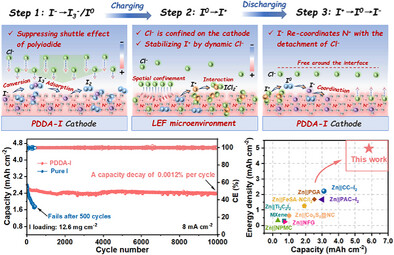
A local electric field (LEF) microenvironment is induced by the abundant polyquaternary ammonium cations in polydimethylammonium iodide (PDDA-I), which effectively spatially confine nucleophilic species (Cl−) on the cathode.This design dynamically coordinates the dense ligand sites around I+, ensuring the stable conversion of I+ ion even under high iodine mass loading conditions.
Metal Clusters for Catalysis
Photocatalytic Reduction of CO2 to CO in 100%: The Synergistic Effect of Nickel and Europium in Heterometallic Clusters
Kai-Peng Bai, Dr. Wei-Peng Chen, Meng-Di Cui, Prof. Yan-Zhen Zheng
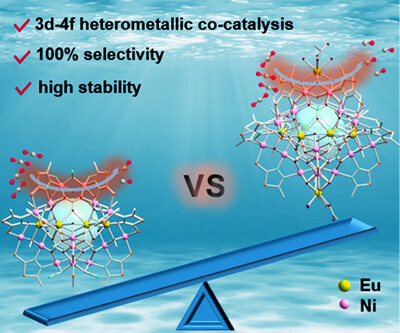
Two series of 3d-4f nanoclusters with analogous structures were synthesized, and the {Ni24Eu10} cluster demonstrates high stability and exceptional performance in the photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO, which can be attributed to the synergistic interaction between the Ni(II) and Eu(III) metal centers within its [Ni4Eu] assembly units.
Electrophilic Functionalization
Reductive N2 Cleavage and Nitride Insertion Reactivity at Molybdenum Complexes Supported by a Rigid PNP Pincer
Minjun Kim, Jeewhan Oh, Sanha Park, Hankyul Lee, Prof. Dr. Zee Hwan Kim, Prof. Dr. Jin Kim, Dr. Heui Beom Lee, Prof. Dr. Jonghoon Choi, Prof. Dr. Yunho Lee
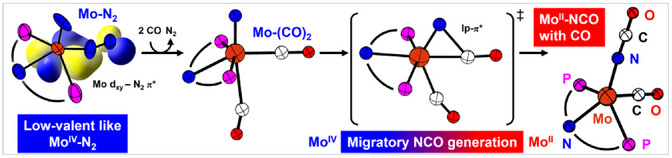
Reductive N2 cleavage at an acridane PNP pincer-supported Mo center leads to the first crystallographically characterized example of an unusual Mo(IV) nitride species featuring a bridging N2 coordination stabilized via Mo-N2 dπ-pπ backbonding interactions. Nitride functionalization with CO leads to Mo(II) isocyanate species.
Batteries
Symmetry Breaking Enabled Stable Oxygen Redox in Li-Rich Cathodes via π-Type Interaction
Dr. Fu-Da Yu, Zhe-Jian Yi, Hai-Nan Wang, Jia-Zhen Zhao, Yang-Qian Zhang, Prof. Yang Ren, Dr. Ji-Gang Zhou, Prof. Ji-Huai Wu, Prof. Zhang Lan, Prof. Yi-Ming Xie, Dr. Lan-Fang Que, Dr. Yun-Shan Jiang, Prof. Zhen-Bo Wang
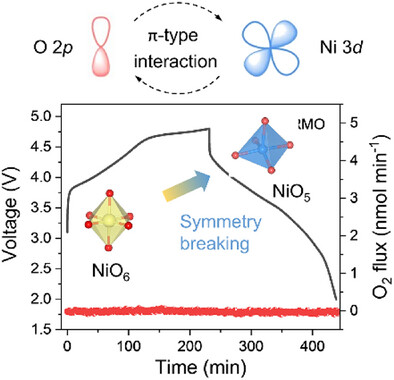
Interfacial Li/Ni disordered via hydrothermal treatment is achieved in Li-rich cathode materials to trigger a robust π-type interaction between metal and ligand. The reductive coupling (charge transfer from O 2p to Ni t2g) and induced symmetry breaking of NiO6 is confirmed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and theoretical calculations, which avoids excessive irreversible oxygen release from non-bonding O 2p state.
Batteries
Nuclear Quantum Confinement Enables Robust Deuterium Bonds for Highly Reversible Aluminum Anodes
Hao Cheng, Yao Lu, Zheng Li, Zibo Chen, Chao Chen, Xinyi Li, Hailin Yu, Adham Hashibon, Zhongliang Tian, Guanjie He
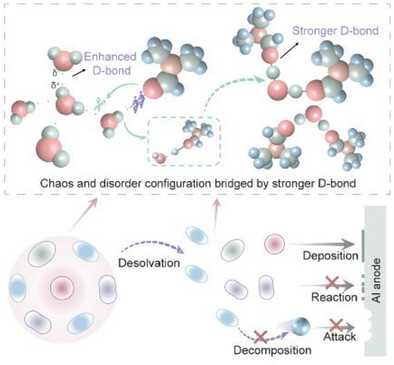
Quantum confinement by leveraging D as a quantum bridge is engineered to tailor stronger intra- and intermolecular D-bonds, effectively suppressing water reactivity and achieving exceptional HER inhibition. The induced Al3+ solvation structures further inhibit the decomposition of water at the interface and improve Al redox reversibility.
Graphene Nanoribbons
Engineering Graphene Nanoribbons via Periodically Embedding Oxygen Atoms
Dr. Yan Zhao, Dr. Li-Xia Kang, Yi-Jun Wang, Yi Wu, Guang-Yan Xing, Dr. Shi-Wen Li, Dr. Jinliang Pan, Nie-Wei Wang, Dr. Yin-Ti Ren, Ying Wang, Dr. Ya-Cheng Zhu, Prof. Xing-Qiang Shi, Dr. Mengxi Liu, Prof. Xiaohui Qiu, Prof. Pei-Nian Liu, Prof. Deng-Yuan Li
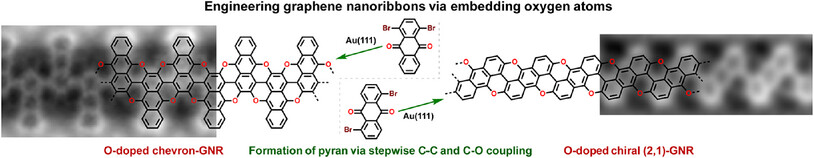
Two types of oxygen-doped graphene nanoribbons (O-doped chevron-GNR and O-doped chiral (2,1)-GNR) were synthesized on Au(111) via in situ formation of pyrans. Both O-doped GNRs are direct bandgap semiconductors but exhibit different sensitivities to oxygen dopants, which is attributed to the difference in the density of states near the Fermi level between the substituted intrinsic carbon atoms and their pristine counterparts.
Vibrational Strong Coupling
A Phenomenological Symmetry Rule for Chemical Reactivity Under Vibrational Strong Coupling
A. Jayachandran, B. Patrahau, J. G. Ricca, M. K. Mahato, Y. Pang, K. Nagarajan, A. Thomas, C. Genet, T. W. Ebbesen
A general symmetry rule emerges from the study of charge transfer complexes in cavities that points to an underlying framework to the predict the outcome of chemical reactivity under vibrational strong coupling.
Wastewater Treatment
Electron-Delocalized Cu2+ Activates Spin Channels in Spinel Oxides to Selectively Produce 1O2 for Wastewater Treatment
Le-Yang Hao, Zi-Jun Tang, Chu-Yi Cai, Yu-Chen Zhao, Dr. Lei Tian, Prof. Nan Li, Prof. Zhao-Qing Liu
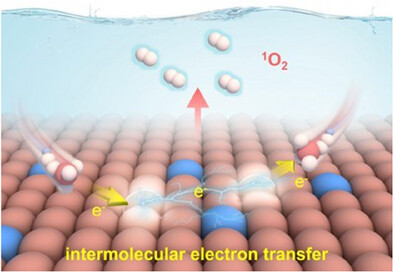
This work proposes an electron-delocalized strategy to unlock FeTd2+─O─FeOh3+ spin channel, inducing intermolecular electron transfer of two PMS for selective 1O2 generation. The directed electron transfer behavior not only maintains the catalyst stability, but also immensely reduces the 1O2 generation energy barrier and improves the PMS utilization.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Tunable Endo/Exo Selectivity in Direct Catalytic Asymmetric 1,3-Dipolar Cycloadditions with Polyfunctional Lewis Acid / Azolium-Aryloxide Catalysts
Adrian Bürstner, Patrick M. Becker, Alexander Allgaier, Lucca Pfitzer, Dr. Daniel M. Wanner, Johanna Dollinger, Dr. Felix Willig, Justin Herrmann, Dr. Vukoslava Miskov-Pajic, Dr. Andreas C. Hans, Dr. Wolfgang Frey, Prof. Dr. Joris van Slageren, Prof. Dr. Johannes Kästner, Prof. Dr. René Peters
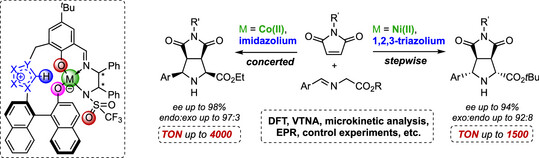
A novel concept for catalytic asymmetric 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions with iminoesters employs modular polyfunctional Lewis acid/azolium-aryloxide betaine catalysts, controlling endo- and exo-selectivity through adjustments of metal center, azolium, and sterics. DFT studies reveal an almost perfect spatial fit of functional sites, enabling precise orchestration of the catalytically relevant moieties involved—reminiscent of enzymatic catalysis.
Raman Scattering
Transfer Learning-Assisted SERS: Predicting Molecular Identity and Concentration in Mixtures Using Pure Compound Spectra
Dr. Emily Xi Tan, Jaslyn Ru Ting Chen, Desmond Wei Cheng Pang, Prof. Nguan Soon Tan, Prof. In Yee Phang, Prof. Xing Yi Ling

Transfer learning-driven SERS to elucidate mixtures with unknown composition and ratios.
Helicenes
Spring-Like Behavior in [8]Helicene Diimides: How Helical Pitch Governs Optical Anisotropy and Electronic Conjugation
Fridolin Saal, Vincenzo Brancaccio, Dr. Krzysztof Radacki, Dr. Holger Braunschweig, Dr. Prince Ravat
![Spring-Like Behavior in [8]Helicene Diimides: How Helical Pitch Governs Optical Anisotropy and Electronic Conjugation Spring-Like Behavior in [8]Helicene Diimides: How Helical Pitch Governs Optical Anisotropy and Electronic Conjugation](/cms/asset/0d0004f8-c0e4-41b7-8d32-bec940933d34/anie202508779-gra-0001-m.jpg)
Bridging the imide nitrogen atoms of [8]helicene diimides with different alkyl chains allows for precise control over the helical pitch of their backbones. This has a profound impact on the molecular packing, chiroptical properties, and through-space electronic conjugation of the molecules. As a result, this approach enables fine-tuning of the properties of this new class of materials with enhanced optical anisotropy and electronic communication.
Oxygen Reduction Reaction
A Dual-Atom La2 Catalyst for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Jingru Sun, Tianmi Tang, Siying Zhang, Siyu Chen, Yingying Duan, Xue Bai, Xiaoqin Xu, Xiaodi Niu, Zhenlu Wang, Jingqi Guan
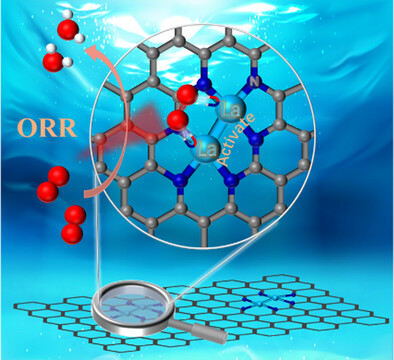
Using an ultra-fast printing technology, we have successfully embedded diatomic lanthanum sites onto a graphene framework, which shows excellent ORR performance. The La2-N6 configuration structure can effectively reduce the reaction barrier of RDS and promote effective charge transfer, thus enhancing the catalytic process, on which the intermediates and structural evolution were well uncovered by combining advanced characterizations and theoretical calculations.
Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Ultrathin PtSe2 Nanowires in Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
Nan Si, Rui Wang, Xianyu Hu, Yide Chang, Qingyuan He, Yang Wang, Yakui Mu, Yanming Wang, Siyu Liu, Qinglin Yuan
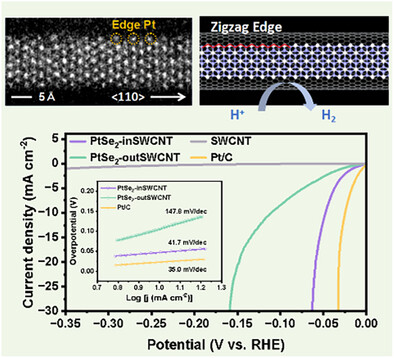
PtSe2 NWs grow anisotropically along the <110> direction inside the SWCNTs, and expose abundant zigzag edges, which contribute to the higher catalytic activity for HER. The as-prepared PtSe2 NWs exhibit excellent HER activity at extremely low Pt loading of 4.684 wt%, with an overpotential of 47 mV@10 mA cm−2 and a Tafel slope of 41.7 mV dec−1.
DNA Nanotechnology
Complex Donuts: Small Variations in DNA Sequence Dictate Pathway Complexity in DNA Nanotoroids
Muhammad Ghufran Rafique, Yihao Wu, Yutong Shi, Quentin Laurent, Abdelrahman Elmanzalawy, Christopher Saab, Yu Shi, Dmytro F. Perepichka, Jianing Li, Hanadi F. Sleiman
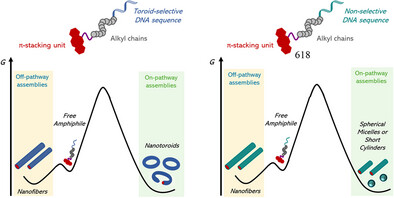
Chemical information encoded in the sequence of DNA amphiphiles enables the selective formation of kinetically trapped DNA nanotoroids through a complex self-assembly pathway. The toroids are formed as on-pathway structures via a competitive mechanism only when a toroid-selective DNA sequence is used.
Aluminium Compounds
Intriguing Reactivity of a 1,2-Dihydrodialumane Towards Organic Azides - From a Terminal Diazido-Dialumane to Pendulum-Clock-Like Azide Bridging
Xiaobai Wang, Dr. Franziska Traeger, Raphael F. Ligorio, Dr. Nico Graw, Dr. Regine Herbst-Irmer, Prof. Dr. Anna Krawczuk, Prof. Dr. Malte Fischer, Prof. Dr. Dietmar Stalke
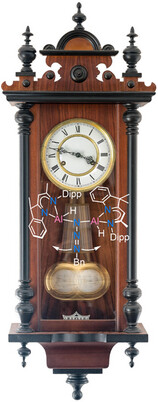
The reaction of a dihydro-dialane supported by a hybrid ligand (DNI) with organic azides yields structurally diverse aluminium species, including the first example of low oxidation state aluminium azide complex, a diazido-dialane, along with an aluminium-tetrazole, and azide alumination. Spectroscopic studies reveal dynamic behaviour in solution, featuring a pendulum-clock-like motion of the benzyl azide and Nα oscillation within the complex.
Ammonia Production
Ru Single Atoms Anchored in Metal Borides Enable Hydrogen Spillover for Superior Electrochemical Ammonia Production
Yuanguo Chen, Dr. Haoyun Bai, Dr. Jiao Lan, Dr. Cheng-Wei Kao, Dr. Feng Xie, Dr. Linghu Meng, Dr. Jilong Li, Dr. Ying-Rui Lu, Dr. Ming Peng, Prof. Hui Pan, Prof. Yongwen Tan
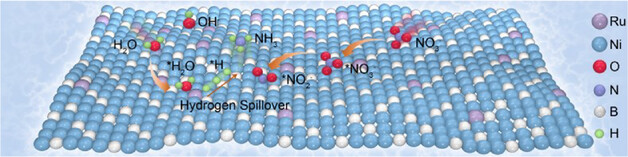
Single-atom Ru-decorated nanoporous metal borides are developed as high-performance electrochemical nitrate reduction electrocatalysts utilizing an atomic-scale hydrogen spillover effect. This strategy facilitates dissociation of water into *H and promotes the *H spillover for increasing *H coverage on the surface, thereby synergistically reducing the hydrogenation energy barrier for converting nitrate into valuable ammonia products.
Siloxane Electrolytes
Origin of Anion-Rich Solvation Structures in Siloxane Electrolytes
Yao-Peng Chen, Yi-Lin Niu, Dr. Zhao Zheng, Dr. Xiang Chen, Yu-Chen Gao, Nan Yao, Dr. Rui Zhang, Prof. Qiang Zhang
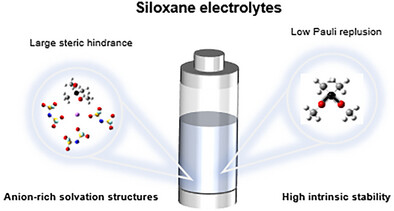
Siloxane electrolytes exhibit anion-rich solvation structures due to their large steric hindrance. The lower Pauli repulsion of Si─O bond compared to C─O bond leads to higher intrinsic stability than corresponding ethers.
Fuel Cells
Copper-Tailored Molybdenum-Nickel Catalyst Boosts Hydrogen Oxidation and Suppresses Parasitic Oxygen Reduction for Durable Fuel Cells
Lei Zhu, Xiao-Long Zhang, Yu Yang, Ye-Cheng Li, Ye-Hua Wang, Hui-Kun Yan, Fei-Yue Gao, Yu-Cai Zhang, Zhi-Zheng Wu, Shu-Ping Sun, Pu-Gan Lu, Wanjie Song, Prof. Xiaolin Ge, Prof. Tongwen Xu, Prof. Kai-Bin Tang, Prof. Min-Rui Gao
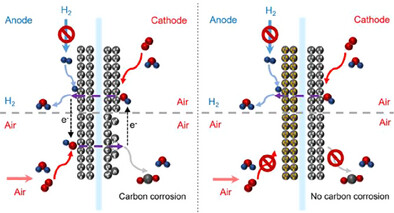
A copper-tailored MoNi4 alloyed catalyst (MoNi3.6Cu0.4) showing high hydrogen oxidation activity but low oxygen reduction activity in alkali has been developed. Such dual functionality tackles the issue of reverse-current decay—the harmful potential jump from parasitic anodic oxygen reduction during startup/shutdown events. When integrating into an anion-exchange membrane fuel cell, this catalyst demonstrates superior corrosion resistance and durability compared with the Pt/C counterpart over repeated startup/shutdown cycles.
Electrocatalysis
Catalyst-Engineered Proton Transfer Pathways for Selective Hydrogen Peroxide Electrosynthesis in Solid-State Electrolytes
Jun Wang, Dr. Junheng Huang, Chunguang Jia, Wenxing Chen, Junxiang Chen, Shengjian Lin, Yangjie Liu, Kai Chen, Yiqi Liang, Dr. Suqin Ci, Prof. Zhenhai Wen
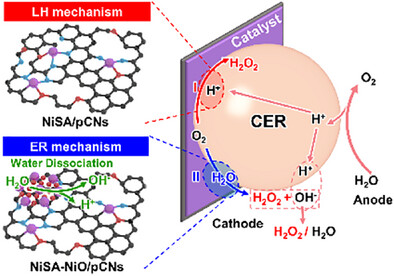
We developed a rationally designed catalyst integrating Ni single atoms and NiO nanoclusters on porous carbon nanosheets for electrochemical H2O2 synthesis in solid electrolytes. This catalyst achieves 97% Faradaic efficiency and 356 mA cm−2 partial current density for pure H2O2 production. The study addresses a critical gap in elucidating proton transfer pathways in solid electrolytes during two-electron oxygen reduction reaction.
COFs for Gold Recovery
Stable Acrylamide-Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks via Mannich Polymerization for Efficient Gold Recovery from Complex E-Waste Leachates
Rui Zhang, Cheng-Peng Niu, Nai-Huai Dong, Prof. Ru-Ping Liang, Li-Ling Chen, Yun-Peng Wu, Ying-Ying Xiao, Ying-Ao Wang, Xiao-Xing Wang, Zhi-Hai Peng, Prof. Jian-Ding Qiu
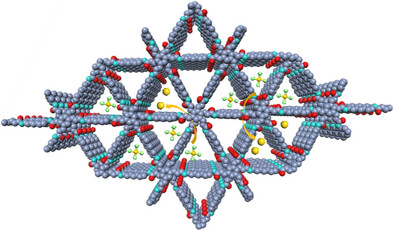
Acrylamide-linked covalent organic frameworks (COFs) were synthesized through a one-step Mannich-type three-component polymerization. The resulting frameworks feature irreversible linkages, extended π-conjugation, and dual C═O/N─H coordination sites, enabling exceptional stability and highly selective gold recovery from complex electronic waste leachates.
Photoswitches
Conditional Stabilization of the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor HIF1α— Photoswitchable Stapled Peptides Prevent Elongin BC-Mediated Degradation
Dr. Van Tuan Trinh, Dr. Sabrina Fischer, Dr. Lei Zhang, Dr. Heiko Geisler, Belen Pardo, Dr. Robert Liefke, Dr. Frank Abendroth, Prof. Dr. Olalla Vázquez
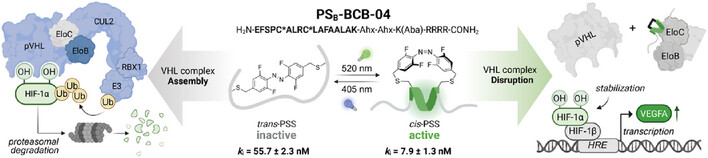
Visible-light photoswitchable peptides enable the stabilization of the hydroxylated hypoxia transcription factor 1α (HIF1α—OH) by targeting the pVHL-EloBC interaction. Significant differences in conformation, binding, and transcription of HIF-targeted genes between the photostationary states (PSS) were demonstrated.
Organocatalysis
A Bioinspired Diazafluorenone Catalytic System for Aerobic Oxidative Deamination of Primary Amines
Sheng Gong, Wenhu Zhang, Yongchang Song, Jianfeng Chen, Baoguo Zhao
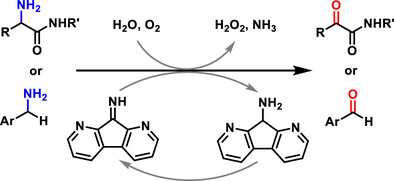
A highly efficient biomimetic aerobic oxidation of α-amino amides and benzylamines into α-keto amides and aromatic aldehydes is enabled by 1,8-diazafluoren-9-one (DFO), a new organocatalyst with a simple structure, high robustness, and strong electrophilicity.
MOFs for Upconversion
Upconversion Lanthanide-Based 2D Metal-Organic Frameworks for Multimode Information Encryption
Jiabo Chen, Yao Xie, Wanjun Yang, Renrui Sun, Prof. Feifei Xing, Gabrielle A. Mandl, Prof. John A. Capobianco, Prof. Lining Sun
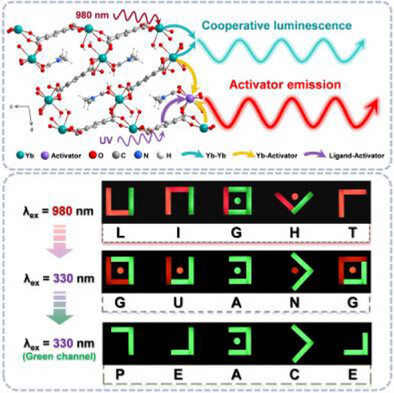
A novel 2D Yb-PMA MOFs were synthesized, and upconversion luminescence under 980 nm excitation was successfully achieved by introducing Ho3+, Tb3+, or Eu3+ as the luminescence center and using Yb3+ as the sensitizer. The upconversion/down-shifting luminescent lanthanide-based 2D MOFs designed in this work show good potential for application in the field of information encryption.
Photoredox Catalysis
Counterintuitive Photochemistry of an Isolated Acridinyl Radical: ConPET via Preassembly, Solvated Electrons or a Long-Lived Excited State?
Dr. Samuel J. Horsewill, Katherine M. M. Sharrock, Dr. Péter P. Fehér, Dr. Jack M. Woolley, Dr. Imre Pápai, Dr. Daniel J. Scott
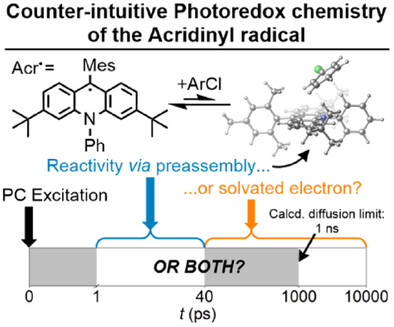
In this paper, we isolate the reduced form of a commonly used acridinium photocatalyst (acridinyl, Acr•) and investigate its photochemistry using transient absorption, analysed alongside TD-DFT calculations. We show that despite the apparent long lifetime of the fluorescent state of Acr•, it is not relevant to reactivity. Instead, reactivity occurs through counterintuitive preassembly and solvated electron-based mechanisms.
Photochemistry
Dynamic Regulation of Radical Photochromism and Photoluminescence via Polymer Polarity
Quanchi Tian, Qiuyue Ding, Chao Xu, Dr. Lunjun Qu, Dr. Kaiti Wang, Prof. Dr. Chaolong Yang, Prof. Yanli Zhao
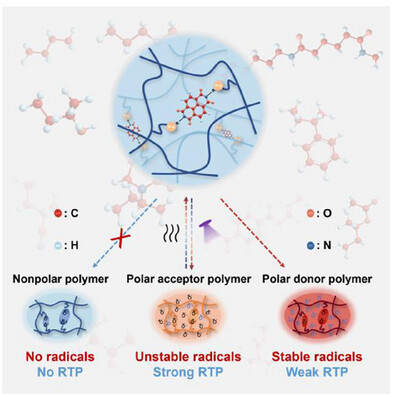
The polarity of polymer matrices not only plays a crucial role in inducing room-temperature phosphorescence by protecting the naphthalene diimide core structure from quenching by oxygen and moisture, but also facilitates the generation of stable anion radicals through photoinduced electron transfer, even in the absence of UV irradiation.
Mechanically Interlocked Molecules
Is the Smallest Molecular Trefoil Knot Actually the Tightest One?
Wei-Tao Xu, Chenxing Guo, Yefei Jiang, Wei-Jian Li, Xiao-Qin Xu, Xue Li, Siqi Luo, Prof. Dr. Lianrui Hu, Prof. Dr. Xiujun Yu, Prof. Dr. Xiaopeng Li, Prof. Dr. Hai-Bo Yang, Prof. Dr. Wei Wang

The use of a modular self-assembly strategy has enabled the successful synthesis of a new family of molecular trefoil knots with varied backbone-atom numbers. An interesting odd-even effect of alkyl chain linkers on their tightness was demonstrated, which not only provides key insights into size-tightness relationships but also guides further development of knotted, woven, and entangled molecules and materials.
Room-Temperature Phosphorescence
N─B─N Isomer Induced Room Temperature Phosphorescence: Expression, Mechanistic Insights, and Multi-Level Anti-Counterfeiting Applications
Dr. Jianhua Liu, Junxiong Yao, Ruping Mu, Xinyi Mao, Haihua Li, Prof. Jianqi Sun, Jifeng Huang, Dr. Qiang Feng, Prof. Xiaohua Cao, Prof. Jianguo Wang, Prof. Huanan Huang

This study introduces an N─B─N unit-based strategy to enhance room temperature phosphorescence (RTP), highlighting that 1,1-DB shows strong RTP property, unlike its isomer 1,2-DB. The contrast in their performance aids in understanding the relationship between molecular structure and phosphorescence, offering insights for designing and optimizing RTP materials.
Nanomotors
Communicative Nanomotors Reprogram Cancer Cell Death via Pyroptosis
Mingchen Sun, Luc van Oss, Chenxuan Wan, Daniela A. Wilson
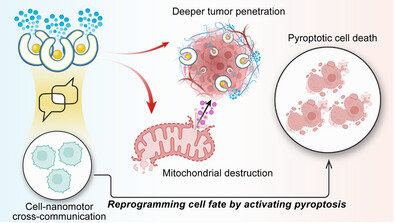
Communicative nanomotors respond to elevated ROS in the tumor microenvironment, enabling active communication and selective mitochondrial targeting through non-covalent surface engineering. Their precise interaction with cells induces mitochondrial damage, cytochrome c release, and pyroptotic cell death, while chemotactic motility ensures deeper tumor penetration, advancing intelligent cancer therapeutics.
MXenes for Fenton-like Catalysis
Confining Asymmetrically Coordinated Cobalt Single-Atoms/Clusters on Holey MXene for Ultrafast Fenton-Like Catalysis
Xin Guo, Hao Zhang, Yunlong Wang, Yiyuan Yao, Chengming Xiao, Kechen Gu, Junwen Qi, Yujun Zhou, Yue Yang, Zhigao Zhu, Prof. Dr. Jiansheng Li
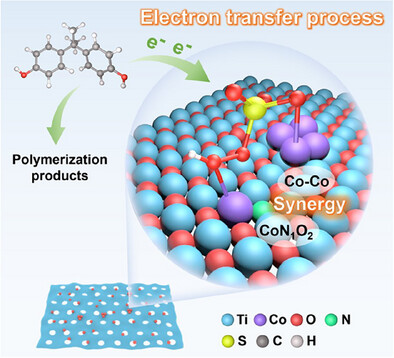
Through a dual-coordination microenvironment strategy, CoN1O2 single atoms and Co nanoclusters (NCs) were confined within highly graphitized carbon layers supported on holey MXene nanosheets. The Co NCs optimized the electronic structure of Co active centers, synergistically enhancing peroxymonosulfate adsorption and electron transfer efficiency. A nonradical electron transfer mechanism was proposed to drive the polymerization of bisphenol A.
Microcrystals
Probing Multilevel Chiroptical Activity in Organic Supramolecular Microcrystals for High-Performance Circularly Polarized Lasing
Shizhe Ren, Zheng-Fei Liu, Penghao Li, Prof. Kang Wang, Prof. Jiannian Yao, Prof. Qing-Zheng Yang, Prof. Yong Sheng Zhao, Prof. Haiyun Dong
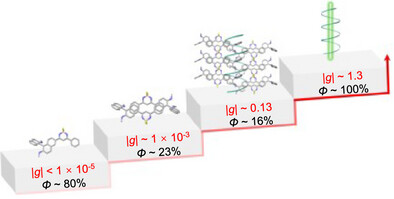
The evolution of chiroptical activity from chiral molecular monomers to dimers to supramolecular helices is tracked for exploring high-performance organic circularly polarized lasers. By virtue of the efficient coupling of multilevel chiroptical activity with high optical gain, the chiral organic supramolecular microcrystals exhibit circularly polarized laser outputs with dissymmetry factors up to ∼1.3 and quantum yields close to 100%.
Analytical Biochemistry
Simple and Rapid Tumor EV Enrichment Enabled by Long DNA Probe-Guided Entanglement
Dr. Yuanjie Liu, Dr. Yunpeng Fan, Prof. Xiaoqiang Li, Prof. Gang Tian, Prof. Bo Shen, Dr. Menghan Li, Dr. Kai Su, Dr. Xuhuai Fu, Dr. Mengxuan Zhang, Prof. Yonghong Wang, Prof. Xinyu Li, Prof. Xinmin Li, Prof. Shijia Ding
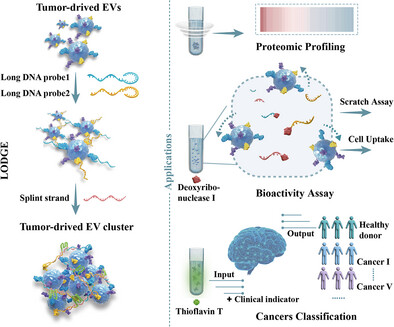
The selective isolation of extracellular vesicle (EV) subpopulations is essential for their biomedical applications. We present a simple, rapid, and versatile strategy termed LODGE (Long DNA Probe-Guided EV Entanglement) for the enrichment of tumor-derived EVs (tEVs) from biofluids. LODGE facilitates the application of tEVs in biomarker discovery, therapeutic agents, and disease diagnosis, as evidenced by proteomic profiling, bioactivity assays, and cancer classification.
Zinc-Ion Batteries
High-Capacity and Long-Life Cathode Constructed Solely by Carbon Dots for Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries
Dr. Tian-Bing Song, Qian-Li Ma, Bao-Juan Wang, Xi-Rong Zhang, Prof. Yong-Gang Wang, Prof. Huan-Ming Xiong
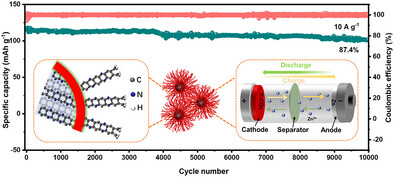
Carbon dots are solely applied as the active cathode material in aqueous zinc-ion batteries for the first time, which exhibit decent cycling performance, excellent capacity retention, and ultrahigh ion diffusion ability.
CO2 Reduction
Mechanistic Promiscuity in Cobalt-Mediated CO2 Reduction Reaction: One- Versus Two-Electron Reduction Process
Ayan Bera, Dr. Sarah Bimmermann, Dr. Philipp Gerschel, Dibya Jyoti Barman, Leon Gerndt, Dr. Thomas Lohmiller, Dr. Kaltum Abdiaziz, Dr. Alexander Schnegg, Dr. Maylis Orio, Prof. Dr. Dennis G. H. Hetterscheid, Prof. Dr. Kara L. Bren, Prof. Dr. Michael Roemelt, Prof. Dr. Ulf-Peter Apfel, Prof. Dr. Kallol Ray

The cobalt complexes [(Hbbpya)CoII]2⁺, and [(Mebbpya)CoII]2⁺ show contrasting CO₂ reduction behaviors. [(Hbbpya)CoII]2⁺ selectively forms CO via a fast, two-electron pathway aided by a -NH proton relay, while [(Mebbpya)CoII]2⁺ favours hydrogen evolution due to a slower, competitive one-electron mechanism. Stopped-flow studies reveal a reactive CO₂ radical anion, offering insights into their distinct catalytic pathways.
Sodium Metal Batteries
Electrolytes with Tailored Solvent-Solvent Interactions for Flame-Retardant Stable Sodium-Metal Batteries.
Zhangbin Cheng, Zehui Zhang, Mingtian Wu, Prof. Min Jia, Xinyi Du, Zheng Gao, Shuai Tong, Tao Wang, Prof. Xiaohong Yan, Prof. Xiaoyu Zhang, Prof. Haoshen Zhou
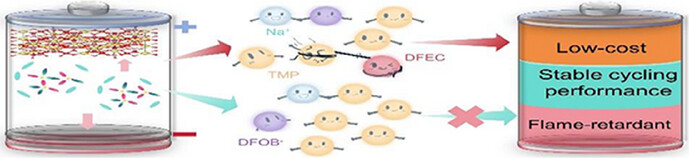
This work, by introducing solvent-solvent interactions, achieves an ion-aggregate-rich solvation structure at low concentrations, promoting the formation of an inorganic-rich SEI, effectively suppressing the reaction between trimethyl phosphate and the sodium metal anode, thereby enabling stable cycling of Na||Na3V2(PO4)3 battery.
Bioimaging
Location-Differentiated DNA Hierarchical Cyclic Construction Demarcating Identical Biomolecules Across Cell Membrane Microenvironments
Zhu Li, Xinyin Li, Mengying Ye, Wenjing Shu, Yan He, Haotian Li, Feng Chen, Yongxi Zhao
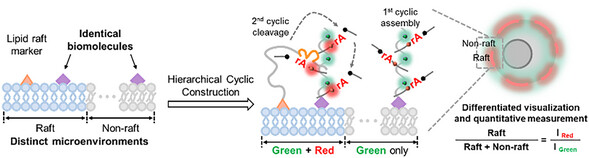
Spatial demarcation of identical biomolecules across distinct cell membrane microenvironments has not been well determined. Here we report location-differentiated DNA hierarchical cyclic construction for lipid raft-differentiated spatial profiling in living cells. It can differentially visualize identical biomolecules inside and outside lipid rafts, and quantitatively measures molecule distribution rate (lipid raft to the whole cell membrane).
Nitrate Reduction
Fast Seawater Desalination Driven by Efficient Nitrate Reduction via Bimetallic Iron/Zinc Polyphthalocyanine Frameworks
Minzhang Li, Wei Wang, Man Liang, Qingjie Yang, Yirong Wang, Lu Guo, Zixun Yu, Fuming Chen, Yuan Chen
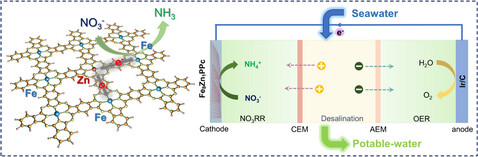
Bimetallic Fe/Zn polyphthalocyanine frameworks enable highly efficient and selective electrochemical reduction of nitrate to ammonia. When integrated into an electrocatalytic desalination device, this reaction facilitates rapid salt ion mass transfer, allowing the conversion of natural seawater into drinkable water and simultaneously converting nitrate contaminants into a useful chemical.
Polymer Brushes
Highly Oxygen-Tolerant and Self-Adaptive Surface-Initiated Bimetal-Mediated Controlled Radical Polymerization
Menglu Chen, Wei Li, Shuai You, Wenbo Sheng, Feng Zhou
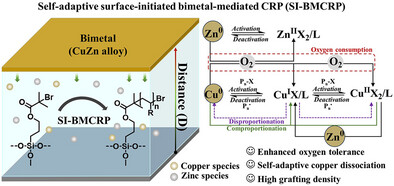
We report a novel and versatile self-adaptive surface-initiated bimetal-mediated controlled radical polymerization strategy for the fabrication of multifunctional polymer brushes under ambient conditions with exceptional oxygen tolerance. By introducing a bimetal CuZn alloy, the system self-adaptively regulates the dissociation of copper species, ensuring robust and controllable polymer brush growth across a wide range of distances between the bimetallic alloy and the initiator-modified substrate.
Alkyne Cyclotrimerization
Ligand-Controlled Chemoselectivity in the Rhodium-Catalyzed Synthesis of Pentafulvenes via (2 + 2 + 1) Alkyne Cyclotrimerization
Belinda Español-Sánchez, Jesús Moradell, Dr. María Galiana-Cameo, Eduardo Barrenas, Prof. Jesús J. Pérez-Torrente, Dr. Vincenzo Passarelli, Dr. Ricardo Castarlenas
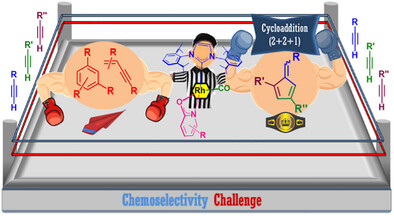
Chemoselectivity Challenge: A precise catalyst design allows for chemoselectivity control over alkyne reactivity to yield pentafulvenes via (2 + 2 + 1) cyclotrimerization. Operative mechanism has been elucidated by means of stoichiometric and deuteration experiments, as well as DFT calculations.
Solar Energy Conversion
Nature of Anti-Dissipative High-Energy Excited States in Quaterpyridine-Bridged Ruthenium Complexes
Noémie Chantry, Agustina Cotic, Simon De Kreijger, Riccardo Di Forti, Benjamin Elias, Ludovic Troian-Gautier, Alejandro Cadranel
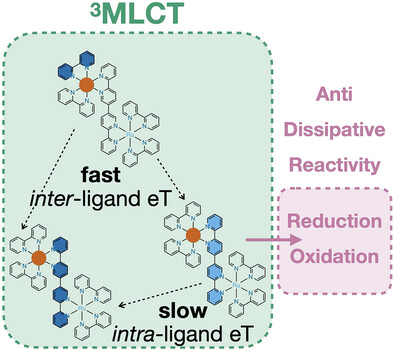
Upon photoexcitation, meta-connected quaterpyridine-bridged Ru complexes undergo fast inter-ligand electron transfer like typical chromophores, but unusually slow intra-ligand electron transfer within bridge-centered MLCT states. The energy saved was exploited for photoreductions and photooxidations with model electron donors and acceptors, respectively. Design guidelines involving ancillary-ligand substitution and bridge topology were derived.
Batteries
Ultralong-Cycling Lithium Storage of SrGe2O4S Anode Enabled by In Situ Formed Oxysulfide Matrix
A.P. Chenlong Dong, A.P. Ruiqi Wang, Yuanxia Zhang, Dr. Qiang Fu, Dr. Siwei Zhao, A.P. Guobao Li, Prof. Zhiyong Mao, Prof. Fuqiang Huang
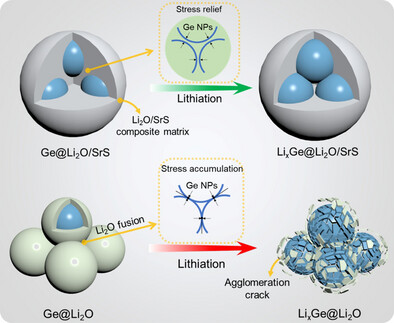
A novel SrGe2O4S anode demonstrates ultralong cycling stability. In situ formed Li2O/SrS oxysulfide matrix in SrGe2O4S effectively prevents agglomeration of Ge nanodots during cycling, facilitated by pinning effect of Sr2+ and the enhanced polarity of S2−.
Molecular Ratchets
Light-Driven Ratchet Mechanism Accelerates Regioselective Metal-Cation Exchange in a Heterobimetallic Helicate
Maximilian J. Notheis, Dr. Gregor Schnakenburg, Dr. Larissa K. S. von Krbek
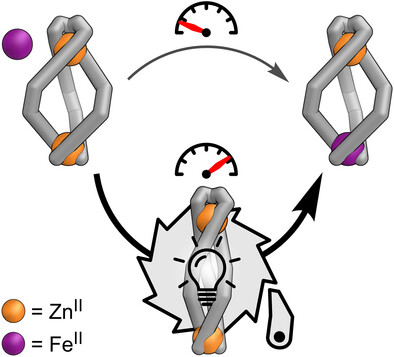
Photoswitchable homo- and heterobimetallic helicates form with high diastereo- and regioselectivity via single-step self-assembly or self-sorting. White-light exposure autonomously operates one helicate as a molecular ratchet, promoting the selective formation of an out-of-equilibrium structure. This ratchet mechanism furthermore accelerates regioselective metal-cation exchange from a homometallic to a heterometallic helicate.
Photocatalytic Oxygen Reduction
Si/Carbon-dots with Surface N-C Sites Promoting Proton and Electron Transfers in Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Yankun Wang, Mingxian Zhang, Haihua Wu, Meirong Huang, Prof. Yuanxing Fang, Prof. Masakazu Anpo, Prof. Xinchen Wang
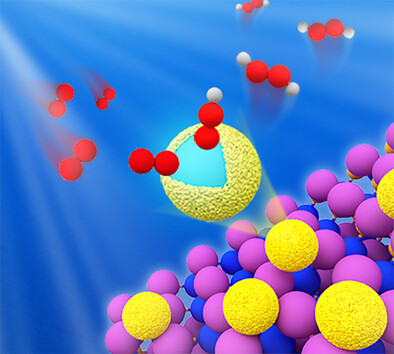
The *O2⁻ + H⁺ → *OOH step is considered the rate-determining step in the oxygen reduction reaction. Silane chain-grafted carbon dots with N-C active sites help overcome the energy barrier through promoting proton and electron transfers, thereby enhancing H2O2 production in photocatalytic oxygen reduction reactions.
Desymmetrization
Modular Access to P(V)-Stereogenic Compounds via Cu-Catalyzed Desymmetrization of (Thio)Phosphonic Dichlorides
Hong-Qing Yao, Yue-Ming Cai, Tian Xie, Ji-Yuan Lv, Shuai-Shuai Fang, Ming-Hong Li, Prof. Dr. Ming Shang
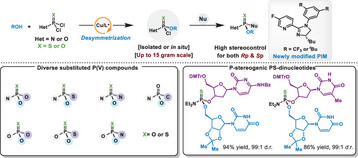
A Cu-catalyzed desymmetrization strategy using newly modified chiral PIM ligands enables modular access to diverse P(V)-stereogenic compounds with high stereocontrol. This approach tolerates broad functionality, constructs challenging P═S motifs, and enables late-stage nucleoside derivatization, providing a versatile platform for drug and nucleic acid-based therapeutic development.
Renal Clearable Nanoparticles
Blood Retention and Kidney Clearance of Renal-Clearable Gold Nanoparticles Strongly Correlate with Renal Injury Biomarkers
Samira Ahrari, Yi Luo, Xuhui Ning, Qi Cai, Nilum Rajora, Ramesh Saxena, Mengxiao Yu, Jie Zheng
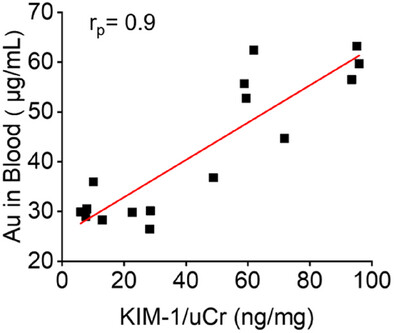
In a doxorubicin-induced acute kidney injury model, proximal tubular injury—rather than glomerular leakage—predominantly determines the renal clearance of gold nanoclusters. The blood retention of Au₂₅(SG)₁₈ strongly correlates with proximal tubular injury biomarker KIM-1, highlighting its potential as a sensitive exogenous blood marker for proximal tubular injury.
Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Transforming Single-Atom Site to Dual-Atom Site in Fe-N-C Catalysts: A Universal Strategy for Enhancing Durability in Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
Ruguang Wang, Dr. Jiaxin Guo, Jisi Li, Quanlu Wang, Zheng Lv, Prof. Cairong Gong, Prof. Caofeng Pan, Prof. Tao Ling
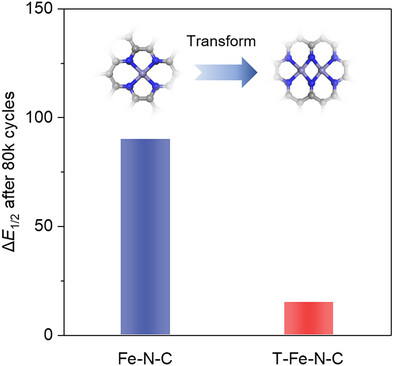
This work develops a general strategy to transform FeN4 single-atom sites to Fe2N6 dual-atom sites in Fe-N-C catalysts with various carbon substrates. Experimental evidence demonstrates that the transformed Fe-N-C catalyst exhibits highly active, selective, and strong H2O2 decomposition capability for proton-exchange membrane fuel cells.
Photochemistry
Merging One- and Multi-Photon Processes in Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Frameworks for Enhanced NIR Light-Driven Photothermal and Photochemical Conversions
Chen-Hui Liu, Zhong-Hao Wang, Yin-Hui Huang, Yu-Lin Lu, Shao-Ping Zheng, Xiao-Dong Zhang, Prof. Kai Wu, Prof. Cheng-Xia Chen, Prof. Hai-Sen Xu, Prof. Mei Pan, Prof. Cheng-Yong Su
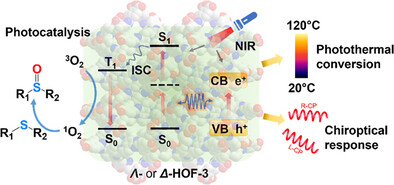
This work demonstrates a paradigm for the development of highly stable and multifunctional HOF materials to enable the full-spectrum utilization of sunlight, which is achieved through a dual-process mechanism involving one-photon and two-photon excitations, facilitated by direct absorption of NIR light within a single HOF platform, for synergistically enhanced performance in photothermal, photochemical, and chiroptical applications.
Chiral Metal Halides
First Chiral Catalan Solid Based on Molybdenum Halide with Efficient Circularly Polarized Luminescence in the Deep-Red Region
Sehrish Gull, Wenkai Zhao, Zhaoyu Wang, Yunxin Zhang, Haolin Lu, Xinyi Niu, Tianjiao Qiao, Hebin Wang, Tianyin Shao, Wenting Liu, Prof. Bing Sun, Prof. Hao-Li Zhang, Prof. Yongsheng Chen, Prof. Guankui Long
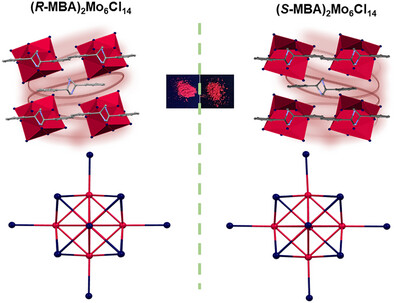
The first chiral molybdenum halide tetrakis hexahedra was successfully synthesized via a solvothermal method. This unique Catalan solid structure exhibits efficient deep-red circularly polarized emission, enhanced stability, and improved photoluminescence quantum yield. The proposed system provides a novel platform for advancing the research on chiral metal halides and paves the way for their application toward chiral optoelectronics.
Homogeneous Catalysis
Stable Yet Strongly Lewis-Acidic Anions Enabling Cooperative Catalysis with Cationic Transition-Metal Complexes
Ryo Mandai, Prof. Dr. Takanori Iwasaki, Prof. Dr. Kyoko Nozaki
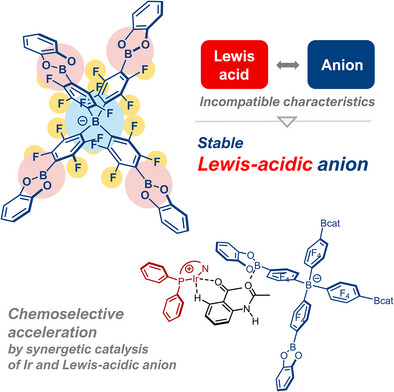
A stable tetraarylborate anion, BBcat, possessing strong Lewis acidity was synthesized. BBcat serves as a weakly coordinating counteranion for the cationic transition-metal complex, and its Ir complex exhibited up to 8.2-fold higher reaction rate than the common counteranion BArF in the hydrogen isotope exchange of 1,2-disubstituted arenes by cooperative catalysis of the cationic transition-metal complex and the Lewis-acidic counteranion.
Organic Acids at TiO2 Interfaces
Effect of Ambient Organic Acids on the Water Structure at Interfaces
Abhinav S. Raman, Annabella Selloni
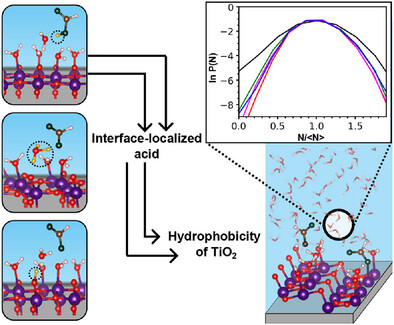
Ambient organic acids such as formic acid tend to localize in the interfacial water layers close to surfaces, facilitated by the interaction and exchange of the acid proton with a surface oxygen. These localized acids make the anatase surface hydrophobic, which is offset by the larger fraction of dissociated water on rutile. Thus, the wettability of is largely controlled by acid-base chemistry rather than chemisorption.
Germanium Chemistry
Reactivity of a Methylene-Bridged 1,3-Bis(germylene) in Dynamic Equilibrium with Its Dimer
Daichi Uchida, Prof. Dr. Mariko Yukimoto, Prof. Dr. Norihiro Tokitoh, Prof. Dr. Mitsuaki Yamauchi, Dr. Hiroko Yamada, Prof. Dr. Yoshiyuki Mizuhata
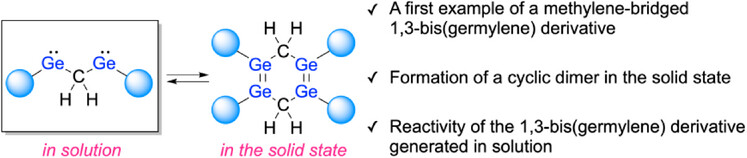
We report the properties and reactivity of an unprecedented methylene-bridged 1,3-bis(germylene) derivative. In the solid state, the 1,3-bis(germylene) derivative undergoes dimerization to afford a 1,2,4,5-tetragermacyclohexa-1,4-diene (Ge4CHD) derivative. Moreover, the reactivity revealed that the Ge4CHD derivative dissociated into the methylene-bridged 1,3-bis(germylene) derivative in solution.
Catalyst Design
“Outside-in” Design of Single-Atom Catalysts: Linking Specific Peripheral Geometry to Defined CO2 Reduction Performance
Jia Zhao, Yang Chen, Di Liu, Weng Fai Ip, Jian Lin, Xiaodong Wang, Sen Lin, Xianzhi Fu, Tao Zhang
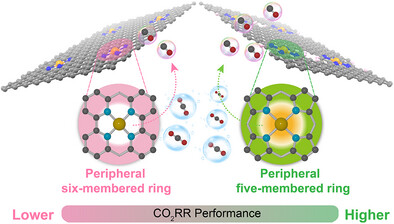
This work proposes an “outside-in” strategy for the design of NC-supported Fe and Ni SACs for CO2RR. Combined DFT calculations and experimental studies show that incorporating specific six- or five-membered rings into the outer shell retrofit the electronic property of coordination N atoms in the inner shell, thereby precisely controlling the catalytic performance of the metal center.
Covalent Organic Frameworks
Stepwise Post-Modification of Pyridine-Imine COFs for Enhanced Hydrolytic Stability and Proton Conductivity
Hongfei Wang, Wen-Na Jiao, Wei-De Zhu, Si Huang, Xiao-Chun Lin, Ting Chen, Yanan Fan, Fangzheng Chen, Prof. Hai-Sen Xu, Prof. Mei Pan, Prof. Cheng-Yong Su
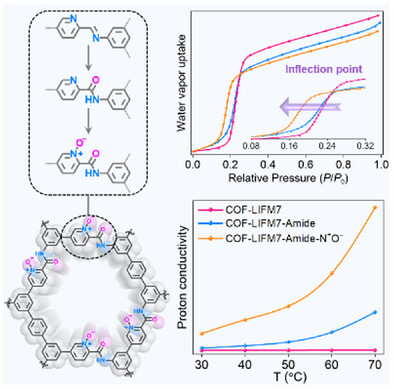
The self-condensation reaction of bifunctional monomers containing both amino and acetal groups yielded COF-LIFM7. Via subsequent amidation and N-oxidation modifications, the pore polarity and hydrophilicity of the post-modified COFs were progressively enhanced, consequently leading to a significant increase in proton conductivity.
Biosynthesis
Sequential Reconstruction of Calicheamicin γ1I Iodo-Thiobenzoate by Selective Carrier Protein Trapping Reveals a Flavin-Dependent Iodinase
Dr. Fang Pang, Prof. Craig A. Townsend
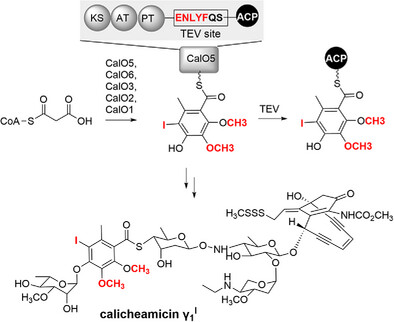
Enzymatic synthesis of the iodo-thiobenzoate of calicheamicin γ1I was reconstituted in vitro from malonyl-CoA, involving the orsellinate biosynthesis by CalO5 and subsequent modifications by CalO6, CalO3, CalO2, and CalO1. A TEV site was introduced into CalO5, enabling the successful detection of the intermediate or product attached to the ACP domain through intact-protein mass spectrometric analysis.
Perovskite Solar Cells
Synergistic Dual-Interface Engineering in Perovskite Solar Cells via Chloramine Hydrochloride Molecular Bridges
Feiyi Zhou, Xu Zhang, Runze Dai, Qingyue Guo, Dr. Yi Dong, Fanxiang Meng, Jun Wan, Zeyu Wang, Huajie Lyu, Prof. Chenghang Zheng, Prof. Qingquan He, Prof. Rui Wang, Prof. Peng Liu, Prof. Jun Pan, Prof. Xiang Gao
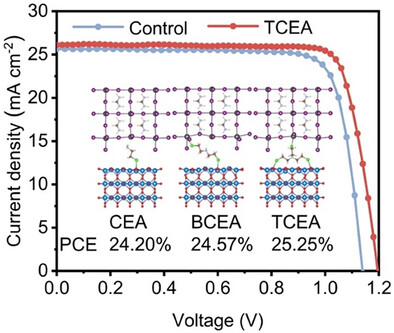
Here, 2-Chloroethylamine Hydrochloride (CEA), Bis(2-chloroethyl)amine Hydrochloride (BCEA), and Tris(2-Chloroethyl)Amine Hydrochloride (TCEA) act as bifunctional molecular bridges to simultaneously passivate defects at both SnO2 and perovskite interfaces while controlling crystallization. TCEA accelerates α-FAPbI3 formation, promotes grain size, and minimizes grain boundary defects. This improves electron extraction efficiency, prolongs hot-carrier cooling, and achieves a champion power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 25.25%, with a PCE retention rate of 90% after 1000 h.
Heterogeneous Catalysis
Three-Dimensional Porphyrin and Phthalocyanine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks for Boosting Urea Oxidation
Dr. Guanyu Qiao, Dr. Bolun Wang, Ziyi Zhao, Hongde Yu, Jingyang Lin, Yunyu Guo, Jiahuan Wang, Dr. Lin Li, Thomas Heine, Prof. Donghai Mei, Prof. Enquan Jin

A series of three-dimensional (3D COFs) was developed with a cyt topology, facilitating the uniform dispersion and full exposure of distinct metal sites. The resulting TAPP-OFPc-COFs demonstrate exceptional electrocatalytic performance in urea oxidation. The Fe-Ni bimetallic sites synergistically ensure high efficiency and cycle stability.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Enantioselective Nickel-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of α-Alkylidene Succinimides Enabled by Weak Noncovalent Interactions
Xinhong Cai, Yicong Luo, Dr. Jianzhong Chen, Prof. Dr. Wanbin Zhang
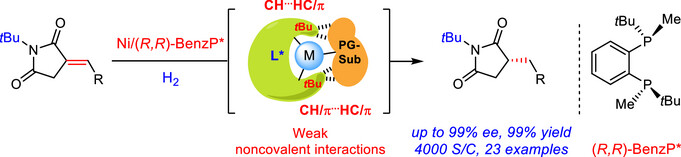
A positive correlation between weak noncovalent interactions and the activity of asymmetric hydrogenation was explored through both DFT calculations and experimental studies by modifying the protecting group of the substrate. Based on these findings, an Earth-abundant nickel catalytic system was developed for the asymmetric hydrogenation of α-alkylene succinimide, demonstrating superior efficiency (4000 S/C, substrate/catalyst) compared to rare metal catalysts (2000 S/C). This system delivered excellent results, achieving up to 99% enantiomeric excess (ee) and 99% yield.






































