Probing Multilevel Chiroptical Activity in Organic Supramolecular Microcrystals for High-Performance Circularly Polarized Lasing
Shizhe Ren
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Both the authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZheng-Fei Liu
Key Laboratory of Radiopharmaceuticals, Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875 China
Both the authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorPenghao Li
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Kang Wang
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Jiannian Yao
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Qing-Zheng Yang
Key Laboratory of Radiopharmaceuticals, Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yong Sheng Zhao
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Haiyun Dong
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorShizhe Ren
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Both the authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZheng-Fei Liu
Key Laboratory of Radiopharmaceuticals, Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875 China
Both the authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorPenghao Li
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Kang Wang
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Jiannian Yao
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Qing-Zheng Yang
Key Laboratory of Radiopharmaceuticals, Ministry of Education, College of Chemistry, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, 100875 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yong Sheng Zhao
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Haiyun Dong
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
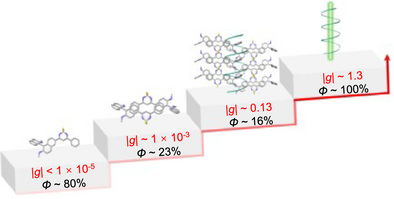
The evolution of chiroptical activity from chiral molecular monomers to dimers to supramolecular helices is tracked for exploring high-performance organic circularly polarized lasers. By virtue of the efficient coupling of multilevel chiroptical activity with high optical gain, the chiral organic supramolecular microcrystals exhibit circularly polarized laser outputs with dissymmetry factors up to ∼1.3 and quantum yields close to 100%.
Abstract
Chiral organic materials are rapidly emerging as a promising platform for circularly polarized lasing. However, the lag in mechanistic research has severely hindered the development of organic circularly polarized lasers. Here, we attempt to probe multilevel chiroptical activity in organic supramolecular microcrystals for exploring high-performance circularly polarized lasing. The evolution of chiroptical activity is tracked spanning from chiral molecular monomers to dimers to supramolecular helices. The crucial roles of excimers and supramolecular helices in achieving high optical gain and large chiroptical activity are revealed. Accordingly, circularly polarized lasing with low thresholds and large dissymmetry factors is realized in the organic supramolecular microcrystals. Our work marks the beginning of mechanistic research on chirality induced circularly polarized lasing, which will initiate the rational design of chiral organic materials for circularly polarized lasing.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202512072-sup-0001-SuppMat.pdf2.4 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1M. Liu, L. Zhang, T. Wang, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7304–7397.
- 2R. Naaman, Y. Paltiel, D. H. Waldeck, Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019, 3, 250–260.
- 3D. G. Blackmond, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 4831–4847.
- 4S.-H. Yang, R. Naaman, Y. Paltiel, S. S. P. Parkin, Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021, 3, 328–343.
- 5J. Lu, Y. Xue, K. Bernardino, N.-N. Zhang, W. R. Gomes, N. S. Ramesar, S. Liu, Z. Hu, T. Sun, A. F. de Moura, N. A. Kotov, K. Liu, Science 2021, 371, 1368–1374.
- 6X. Zhang, Y. Liu, J. Han, Y. Kivshar, Q. Song, Science 2022, 377, 1215–1218.
- 7L. Xu, X. Wang, W. Wang, M. Sun, W. J. Choi, J.-Y. Kim, C. Hao, S. Li, A. Qu, M. Lu, X. Wu, F. M. Colombari, W. R. Gomes, A. L. Blanco, A. F. de Moura, X. Guo, H. Kuang, N. A. Kotov, C. Xu, Nature 2022, 601, 366–373.
- 8I. Song, J. Ahn, H. Ahn, S. H. Lee, J. Mei, N. A. Kotov, J. H. Oh, Nature 2023, 617, 92–99.
- 9M. Lu, P. Li, X. Dong, Z. Jiang, S. Ren, J. Yao, H. Dong, Y. S. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202408619.
- 10X. Tang, J. Zha, X. Wu, J. Tong, Q. Gu, K. Zhang, Y. Zhang, S. Zheng, J. Fan, W. Zhang, Q. Zhang, C. Tan, S. Cai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202413675.
- 11R. Carr, N. H. Evans, D. Parker, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7673–7686.
- 12P. Lodahl, S. Mahmoodian, S. Stobbe, A. Rauschenbeutel, P. Schneeweiss, J. Volz, H. Pichler, P. Zoller, Nature 2017, 541, 473–480.
- 13J. S. Kang, S. Kang, J.-M. Suh, S. M. Park, D. K. Yoon, M. H. Lim, W. Y. Kim, M. Seo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2657–2666.
- 14D.-W. Zhang, M. Li, C.-F. Chen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1331–1343.
- 15L. Zhang, H.-X. Wang, S. Li, M. Liu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 9095–9120.
- 16C.-L. Sun, J. Li, Q.-W. Song, Y. Ma, Z.-Q. Zhang, J.-B. De, Q. Liao, H. Fu, J. Yao, H.-L. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11080–11086.
- 17R. Vattikunta, M. Annadhasan, R. Jada, M. D. Prasad, N. Mitetelo, K. Zhdanova, E. Mamonov, K. Müllen, T. Murzina, R. Chandrasekar, Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 2000431.
- 18Z.-L. Gong, X. Zhu, Z. Zhou, S.-W. Zhang, D. Yang, B. Zhao, Y.-P. Zhang, J. Deng, Y. Cheng, Y.-X. Zheng, S.-Q. Zang, H. Kuang, P. Duan, M. Yuan, C.-F. Chen, Y. S. Zhao, Y.-W. Zhong, B. Z. Tang, M. Liu, Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 2060–2104.
- 19Z. Huang, Z. He, B. Ding, H. Tian, X. Ma, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7841.
- 20D. Liu, W.-J. Wang, P. Alam, Z. Yang, K. Wu, L. Zhu, Y. Xiong, S. Chang, Y. Liu, B. Wu, Q. Wu, Z. Qiu, Z. Zhao, B. Z. Tang, Nat. Photonics 2024, 18, 1276–1284.
- 21Z.-F. Liu, X.-Y. Ye, L. Chen, L.-Y. Niu, W. J. Jin, S. Zhang, Q.-Z. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202318856.
- 22J. P. Riehl, F. S. Richardson, Chem. Rev. 1986, 86, 1–16.
- 23Z. Yuan, Y. Zhou, Z. Qiao, C. Eng Aik, W.-C. Tu, X. Wu, Y.-C. Chen, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 8965–8975.
- 24Z.-F. Liu, J. Ren, P. Li, L.-Y. Niu, Q. Liao, S. Zhang, Q.-Z. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214211.
- 25D. Zhu, Z. Wang, X. Xu, W. Du, W. Huang, Y. Kuai, B. Yu, J. Zheng, Z. Hu, S. Li, Photonics Res. 2024, 12, 1654–1664.
- 26S. Ren, Z.-F. Liu, P. Li, H. Liu, M. Lu, K. Wang, J. Yao, H. Dong, Q.-Z. Yang, Y. S. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202415092.
- 27H. Zhu, Y. Fu, F. Meng, X. Wu, Z. Gong, Q. Ding, M. V. Gustafsson, M. T. Trinh, S. Jin, X. Y. Zhu, Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 636–642.
- 28D. Venkatakrishnarao, C. Sahoo, E. A. Mamonov, V. B. Novikov, N. V. Mitetelo, S. R. G. Naraharisetty, T. V. Murzina, R. Chandrasekar, J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 12349–12353.
- 29N. V. Mitetelo, M. E. Popov, E. A. Mamonov, A. I. Maydykovskiy, D. Venkatakrishnarao, J. Ravi, R. Chandrasekar, T. V. Murzina, Laser Phys. Lett. 2020, 17, 036201.
- 30Y.-X. Yuan, J.-H. Jia, Y.-P. Song, F.-Y. Ye, Y.-S. Zheng, S.-Q. Zang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5389–5399.
- 31Z.-F. Liu, X.-X. Liu, H. Zhang, L. Zeng, L.-Y. Niu, P.-Z. Chen, W.-H. Fang, X. Peng, G. Cui, Q.-Z. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202407135.
- 32C. Shang, G. Wang, K. Liu, Q. Jiang, F. Liu, P.-T. Chou, Y. Fang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8579–8585.
- 33J. R. Hamza, J. K. Sharma, P. A. Karr, A. van der Est, F. D'Souza, P. K. Poddutoori, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 25403–25408.
- 34L. Meng, Z.-Q. Li, K. Tang, J.-Y. Shao, Z. Chen, Y.-W. Zhong, J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 676–684.
- 35C.-W. Ju, B. Li, L. Li, W. Yan, C. Cui, X. Ma, D. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 5903–5916.
- 36K.-F. Zhang, N. Saleh, M. Swierczewski, A. Rosspeintner, F. Zinna, G. Pescitelli, C. Besnard, L. Guénée, T. Bürgi, J. Lacour, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304075.
- 37W. Jiang, Y. Shen, Y. Ge, C. Zhou, Y. Wen, H. Liu, H. Liu, S. Zhang, P. Lu, B. Yang, J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 3367–3373.
- 38X. Zhang, S. Wang, Z. Fu, C. Wang, Z. Yang, Y. Gao, H. Liu, S.-T. Zhang, C. Gu, B. Yang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301228.
- 39X. Bai, Y. Sun, Y. Jiang, G. Zhao, J. Jiang, C. Yuan, M. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3745–3751.
- 40L.-T. Bao, R.-H. Zhang, X. Yuan, X. Wang, P. Wu, X.-Q. Wang, J. Chen, A. Zhu, H.-B. Yang, W. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202500472.
- 41H. Shigemitsu, K. Kawakami, Y. Nagata, R. Kajiwara, S. Yamada, T. Mori, T. Kida, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114700.
- 42K. Takaishi, S. Murakami, F. Yoshinami, T. Ema, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202204609.
- 43X. Cui, Y. Hao, W. Guan, L. Liu, W. Shi, C. Lu, Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 2000125.
- 44Z. Xie, D. Liu, Z. Zhao, C. Gao, P. Wang, C. Jiang, X. Liu, X. Zhang, Z. Ren, S. Yan, W. Hu, H. Dong, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202319380.
- 45Y. Jiang, Y.-Y. Liu, X. Liu, H. Lin, K. Gao, W.-Y. Lai, W. Huang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5885–5944.
- 46C. Wei, M. Gao, F. Hu, J. Yao, Y. S. Zhao, Adv. Opt. Mater. 2016, 4, 1009–1014.
- 47J.-J. Wu, X.-D. Wang, L.-S. Liao, Laser Photonics Rev. 2022, 16, 2200366.
- 48H. Liu, Z. Lu, Z. Zhang, Y. Wang, H. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8448–8452.
- 49X. Wang, M. Shoaib, X. Wang, X. Zhang, M. He, Z. Luo, W. Zheng, H. Li, T. Yang, X. Zhu, L. Ma, A. Pan, ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6170–6178.
- 50N. Mitetelo, D. Venkatakrishnarao, J. Ravi, M. Popov, E. Mamonov, T. V. Murzina, R. Chandrasekar, Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1801775.
- 51L. N. Quan, J. Kang, C.-Z. Ning, P. Yang, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 9153–9169.
- 52Q. Liao, X. G. Wang, S. Lv, Z. Xu, Y. Zhang, H. Fu, ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5359–5367.
- 53J. L. Greenfield, J. Wade, J. R. Brandt, X. Shi, T. J. Penfold, M. J. Fuchter, Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 8589–8602.
- 54S. Wang, D. Hu, X. Guan, S. Cai, G. Shi, Z. Shuai, J. Zhang, Q. Peng, X. Wan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 21918–21926.
- 55M. Hu, F.-Y. Ye, C. Du, W. Wang, T.-T. Zhou, M.-L. Gao, M. Liu, Y.-S. Zheng, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16673–16682.
- 56J. Han, Y. Shi, X. Jin, X. Yang, P. Duan, Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 6074–6080.
- 57Y. Shi, J. Han, C. Li, T. Zhao, X. Jin, P. Duan, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6123.
- 58M. Annadhasan, D. P. Karothu, R. Chinnasamy, L. Catalano, E. Ahmed, S. Ghosh, P. Naumov, R. Chandrasekar, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13821–13830.
- 59J.-J. Wu, M.-P. Zhuo, R. Lai, S.-N. Zou, C.-C. Yan, Y. Yuan, S.-Y. Yang, G.-Q. Wei, X.-D. Wang, L.-S. Liao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 9114–9119.
- 60H. Dong, C. N. Saggau, M. Zhu, J. Liang, S. Duan, X. Wang, H. Tang, Y. Yin, X. Wang, J. Wang, C. Zhang, Y. S. Zhao, L. Ma, O. G. Schmidt, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2109080.
- 61Q. Liang, X. Ma, T. Long, J. Yao, Q. Liao, H. Fu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202213229.
- 62C. Zhang, F.-J. Shu, C.-L. Zou, H. Dong, J. Yao, Y. S. Zhao, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300054.
- 63R. Su, C. Diederichs, J. Wang, T. C. H. Liew, J. Zhao, S. Liu, W. Xu, Z. Chen, Q. Xiong, Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 3982–3988.
- 64P. Li, Z. Zhou, G. Ran, T. Zhang, Z. Jiang, H. Liu, W. Zhang, Y. Yan, J. Yao, H. Dong, Y. S. Zhao, Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10880.
- 65P. H. Schippers, A. v. d. Buekel, H. P. J. M. Dekkers, J. Phys. E 1982, 15, 945.