Engineering Graphene Nanoribbons via Periodically Embedding Oxygen Atoms
Dr. Yan Zhao
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Li-Xia Kang
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYi-Jun Wang
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
Search for more papers by this authorYi Wu
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
Search for more papers by this authorGuang-Yan Xing
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shi-Wen Li
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jinliang Pan
CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
Search for more papers by this authorNie-Wei Wang
College of Physics Science and Technology, Hebei University, Baoding, 071002 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yin-Ti Ren
College of Physics Science and Technology, Hebei University, Baoding, 071002 China
Search for more papers by this authorYing Wang
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ya-Cheng Zhu
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xing-Qiang Shi
College of Physics Science and Technology, Hebei University, Baoding, 071002 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Mengxi Liu
CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xiaohui Qiu
CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Pei-Nian Liu
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Deng-Yuan Li
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yan Zhao
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Li-Xia Kang
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYi-Jun Wang
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
Search for more papers by this authorYi Wu
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
Search for more papers by this authorGuang-Yan Xing
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shi-Wen Li
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jinliang Pan
CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
Search for more papers by this authorNie-Wei Wang
College of Physics Science and Technology, Hebei University, Baoding, 071002 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yin-Ti Ren
College of Physics Science and Technology, Hebei University, Baoding, 071002 China
Search for more papers by this authorYing Wang
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ya-Cheng Zhu
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xing-Qiang Shi
College of Physics Science and Technology, Hebei University, Baoding, 071002 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Mengxi Liu
CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xiaohui Qiu
CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Pei-Nian Liu
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai, 200237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Deng-Yuan Li
State Key Laboratory of Natural Medicines, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, 211198 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
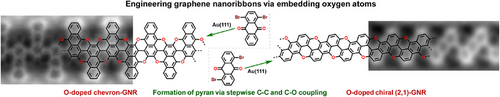
Two types of oxygen-doped graphene nanoribbons (O-doped chevron-GNR and O-doped chiral (2,1)-GNR) were synthesized on Au(111) via in situ formation of pyrans. Both O-doped GNRs are direct bandgap semiconductors but exhibit different sensitivities to oxygen dopants, which is attributed to the difference in the density of states near the Fermi level between the substituted intrinsic carbon atoms and their pristine counterparts.
Abstract
Heteroatom doping is an important method for engineering graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) because of its ability to modify electronic properties by introducing extra electrons or vacancies. However, precisely integrating oxygen atoms into the lattice of GNRs is unexplored, and the resulting electronic properties remain elusive. Here, we achieve the precise embedding of oxygen atoms into the lattice of GNRs via in situ formation of pyrans, synthesizing two types of oxygen-doped GNRs (O-doped chevron-GNR and O-doped chiral (2,1)-GNR). Using scanning tunneling microscopy, noncontact atomic force microscopy, and density functional theory calculations, the atomic structures and electronic properties of O-doped GNRs are determined, demonstrating that both GNRs are direct bandgap semiconductors with different sensitivities to oxygen dopants. Oxygen dopants have a minor impact on the bandgap of chevron-GNR but a significant effect on the bandgap of chiral (2,1)-GNR, which is attributed to the difference in density of states near the Fermi level between substituted intrinsic carbon atoms and their pristine counterparts. Compared with the pristine chiral (2,1)-GNR, the band structure of O-doped chiral (2,1)-GNR exhibits unexpected band edges transition, which is ascribed to sp2-hybridized oxygen atoms which introduces additional electrons to the conduction band of chiral (2,1)-GNR, leading to the upward shift of Fermi surface.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202500490-sup-0001-SuppMat.pdf3.6 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1Y.-W. Son, M. L. Cohen, S. G. Louie, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 216803.
- 2W. Han, R. K. Kawakami, M. Gmitra, J. Fabian, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 794–807.
- 3F. Bonaccorso, Z. Sun, T. Hasan, A. C. Ferrari, Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 611–622.
- 4Z. Chen, A. Narita, K. Müllen, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001893.
- 5D. J. Rizzo, G. Veber, T. Cao, C. Bronner, T. Chen, F. Zhao, H. Rodriguez, S. G. Louie, M. F. Crommie, F. R. Fischer, Nature 2018, 560, 204–208.
- 6O. Gröning, S. Wang, X. Yao, C. A. Pignedoli, G. Borin Barin, C. Daniels, A. Cupo, V. Meunier, X. Feng, A. Narita, K. Müllen, P. Ruffieux, R. Fasel, Nature 2018, 560, 209–213.
- 7D. J. Rizzo, G. Veber, J. Jiang, R. McCurdy, T. Cao, C. Bronner, T. Chen, S. G. Louie, F. R. Fischer, M. F. Crommie, Science 2020, 369, 1597–1603.
- 8S. Mishra, G. Catarina, F. Wu, R. Ortiz, D. Jacob, K. Eimre, J. Ma, C. A. Pignedoli, X. Feng, P. Ruffieux, J. Fernández-Rossier, R. Fasel, Nature 2021, 598, 287–292.
- 9M. Ezawa, Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 045432.
- 10L. Yang, C.-H. Park, Y.-W. Son, M. L. Cohen, S. G. Louie, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 186801.
- 11T. Wassmann, A. P. Seitsonen, A. M. Saitta, M. Lazzeri, F. Mauri, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3440–3451.
- 12Y.-W. Son, M. L. Cohen, S. G. Louie, Nature 2006, 444, 347–349.
- 13T. Wang, S. Sanz, J. Castro-Esteban, J. Lawrence, A. Berdonces-Layunta, M. S. G. Mohammed, M. Vilas-Varela, M. Corso, D. Peña, T. Frederiksen, D. G. De Oteyza, Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 164–171.
- 14P. Ruffieux, S. Wang, B. Yang, C. Sánchez-Sánchez, J. Liu, T. Dienel, L. Talirz, P. Shinde, C. A. Pignedoli, D. Passerone, T. Dumslaff, X. Feng, K. Müllen, R. Fasel, Nature 2016, 531, 489–492.
- 15L. Talirz, H. Söde, J. Cai, P. Ruffieux, S. Blankenburg, R. Jafaar, R. Berger, X. Feng, K. Müllen, D. Passerone, R. Fasel, C. A. Pignedoli, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2060–2063.
- 16H. Sakaguchi, S. Song, T. Kojima, T. Nakae, Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 57–63.
- 17N. Merino-Díez, J. Li, A. Garcia-Lekue, G. Vasseur, M. Vilas-Varela, E. Carbonell-Sanromà, M. Corso, J. E. Ortega, D. Peña, J. I. Pascual, D. G. De Oteyza, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 25–30.
- 18O. V. Yazyev, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2319–2328.
- 19W. Niu, J. Ma, X. Feng, Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 3322–3333.
- 20N. Gorjizadeh, A. A. Farajian, K. Esfarjani, Y. Kawazoe, Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 155427.
- 21E. Cruz-Silva, Z. M. Barnett, B. G. Sumpter, V. Meunier, Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 155445.
- 22B. Biel, F. Triozon, X. Blase, S. Roche, Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2725–2729.
- 23M. Ali, S. Khan, F. Awwad, N. Tit, Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 514, 145866.
- 24Z. Wang, J. Xiao, X. Li, Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 64–67.
- 25T. Liao, C. Sun, Z. Sun, A. Du, D. Hulicova-Jurcakova, S. C. Smith, J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 13751.
- 26F. N. Ajeel, M. H. Mohammed, A. M. Khudhair, Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostr. 2019, 105, 105–115.
- 27L. Talirz, P. Ruffieux, R. Fasel, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6222–6231.
- 28X.-Y. Wang, X. Yao, A. Narita, K. Müllen, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2491–2505.
- 29R. Yin, Z. Wang, S. Tan, C. Ma, B. Wang, ACS Nano 2023, 17, 17610–17623.
- 30R. R. Cloke, T. Marangoni, G. D. Nguyen, T. Joshi, D. J. Rizzo, C. Bronner, T. Cao, S. G. Louie, M. F. Crommie, F. R. Fischer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8872–8875.
- 31N. Friedrich, P. Brandimarte, J. Li, S. Saito, S. Yamaguchi, I. Pozo, D. Peña, T. Frederiksen, A. Garcia-Lekue, D. Sánchez-Portal, J. I. Pascual, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 146801.
- 32S. Kawai, S. Saito, S. Osumi, S. Yamaguchi, A. S. Foster, P. Spijker, E. Meyer, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8098.
- 33Z. Pedramrazi, C. Chen, F. Zhao, T. Cao, G. D. Nguyen, A. A. Omrani, H.-Z. Tsai, R. R. Cloke, T. Marangoni, D. J. Rizzo, T. Joshi, C. Bronner, W.-W. Choi, F. R. Fischer, S. G. Louie, M. F. Crommie, Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3550–3556.
- 34N. Friedrich, R. E. Menchón, I. Pozo, J. Hieulle, A. Vegliante, J. Li, D. Sánchez-Portal, D. Peña, A. Garcia-Lekue, J. I. Pascual, ACS Nano 2022, 16, 14819–14826.
- 35Y. Gao, L. Huang, Y. Cao, M. Richter, J. Qi, Q. Zheng, H. Yang, J. Ma, X. Chang, X. Fu, C.-A. Palma, H. Lu, Y.-Y. Zhang, Z. Cheng, X. Lin, M. Ouyang, X. Feng, S. Du, H.-J. Gao, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6146.
- 36R. E. Blackwell, F. Zhao, E. Brooks, J. Zhu, I. Piskun, S. Wang, A. Delgado, Y.-L. Lee, S. G. Louie, F. R. Fischer, Nature 2021, 600, 647–652.
- 37T. H. Vo, U. G. E. Perera, M. Shekhirev, M. Mehdi Pour, D. A. Kunkel, H. Lu, A. Gruverman, E. Sutter, M. Cotlet, D. Nykypanchuk, P. Zahl, A. Enders, A. Sinitskii, P. Sutter, Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 5770–5777.
- 38C. Bronner, S. Stremlau, M. Gille, F. Brauße, A. Haase, S. Hecht, P. Tegeder, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4422–4425.
- 39E. C. H. Wen, P. H. Jacobse, J. Jiang, Z. Wang, S. G. Louie, M. F. Crommie, F. R. Fischer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 19338–19346.
- 40E. C. H. Wen, P. H. Jacobse, J. Jiang, Z. Wang, R. D. McCurdy, S. G. öLouie, M. F. Crommie, F. R. Fischer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 13696–13703.
- 41N. Bassi, X. Xu, F. Xiang, N. Krane, C. A. Pignedoli, A. Narita, R. Fasel, P. Ruffieux, Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 274.
- 42G. D. Nguyen, H.-Z. Tsai, A. A. Omrani, T. Marabgoni, M. Wu, D. J. Rizzo, G. F. Rodgers, R. R. Cloke, R. A. Durr, Y. Sakai, F. Liou, A. S. Aikawa, J. R. Chelikowsky, S. G. Louie, F. R. Fischer, M. F. Crommie, Nat. Nanotech. 2017, 12, 1077–1082.
- 43R. A. Durr, D. Haberer, Y.-L. Lee, R. Blackwell, A. M. Kalayjian, T. Marangoni, J. Ihm, S. G. Louie, F. R. Fischer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 807–813.
- 44G. D. Nguyen, F. M. Toma, T. Cao, Z. Pedramrazi, C. Chen, D. J. Rizzo, T. Joshi, C. Bronner, Y.-C. Chen, M. Favaro, S. G. Louie, F. R. Fischer, M. F. Crommie, J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 2684–2687.
- 45Y.-F. Zhang, Y. Zhang, G. Li, J. Lu, Y. Que, H. Chen, R. Berger, X. Feng, K. Müllen, X. Lin, Y.-Y. Zhang, S. Du, S. T. Pantelides, H.-J. Gao, Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3377–3384.
- 46S. Kawai, S. Nakatsuka, T. Hatakeyama, R. Pawlak, T. Meier, J. Tracey, E. Meyer, A. S. Foster, Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar7181.
- 47Y. Fu, H. Yang, Y. Gao, L. Huang, R. Berger, J. Liu, H. Lu, Z. Cheng, S. Du, H. Gao, X. Feng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8873–8879.
- 48X. Chang, L. Huang, Y. Gao, Y. Fu, J. Ma, H. Yang, J. Liu, X. Fu, X. Lin, X. Feng, S. Du, H.-J. Gao, Nano Res. 2023, 16, 10436–10442.
- 49X.-Y. Wang, T. Dienel, M. Di Giovannantonio, G. B. Barin, N. Kharche, O. Deniz, J. I. Urgel, R. Widmer, S. Stolz, L. H. De Lima, M. Muntwiler, M. Tommasini, V. Meunier, P. Ruffieux, X. Feng, R. Fasel, K. Müllen, A. Narita, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4671–4674.
- 50X.-Y. Wang, J. I. Urgel, G. B. Barin, K. Eimre, M. Di Giovannantonio, A. Milani, M. Tommasini, C. A. Pignedoli, P. Ruffieux, X. Feng, R. Fasel, K. Müllen, A. Narita, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 9104–9107.
- 51J. Zhang, J. Ma, X. Feng, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2023, 224, 2200232.
- 52A. S. Da Costa Azevêdo, A. Saraiva-Souza, V. Meunier, E. C. Girão, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 13204–13215.
- 53F. Cervantes-Sodi, G. Csányi, S. Piscanec, A. C. Ferrari, Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 165427.
- 54A. Berdonces-Layunta, J. Lawrence, S. Edalatmanesh, J. Castro-Esteban, T. Wang, M. S. G. Mohammed, L. Colazzo, D. Peña, P. Jelínek, D. G. De Oteyza, ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5610–5617.
- 55L. Gross, F. Mohn, N. Moll, G. Meyer, R. Ebel, W. M. Abdel-Mageed, M. Jaspars, Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 821–825.
- 56G. Heimel, in The WSPC Reference on Organic Electronics: Organic Semiconductors, (Eds: J. L. Bredas, S. R. Marder), World Scientific Publishing, Singapore 2016 pp 131–158.
10.1142/9789813148598_0005 Google Scholar
- 57G. Giovannetti, P. A. Khomyakov, G. Brocks, V. M. Karpan, J. van den Brink, P. J. Kelly, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 026803.
- 58A. Nagoya, H. Tetsuka, N. Ohba, J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 17756–17763.
- 59C. A. Hunter, H. L. Anderson, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7488–7499.
- 60S. Blankenburg, J. Cai, P. Ruffieux, R. Jaafar, D. Passerone, X. Feng, K. Müllen, R. Fasel, C. A. Pignedoli, ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2020–2025.
- 61J. Björk, S. Stafström, F. Hanke, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14884–14887.
- 62J. Kohout, Molecules 2021, 26, 7162.