Als DIE Zeitschrift für Verfahrensingenieure, technische Chemiker, Apparatebauer und Biotechnologen, gilt die Chemie Ingenieur Technik (CIT), Fachorgan von DECHEMA, GDCh und VDI-GVC, als das unverzichtbare Forum für den Erfahrungsaustausch zwischen Forschern und Anwendern aus Industrie, Forschung und Entwicklung. Wissenschaftlicher Fortschritt und Praxisnähe: eine Kombination, die es nur in der CITgibt!
Journal Metrics
- 3.3CiteScore
- 1.6Journal Impact Factor
- 81%Acceptance rate
- 105 days Submission to first decision
Titel-Beiträge
Articles
Review on CO2 Activation via Catalytic Reverse Water-Gas Shift Reaction
- 16 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
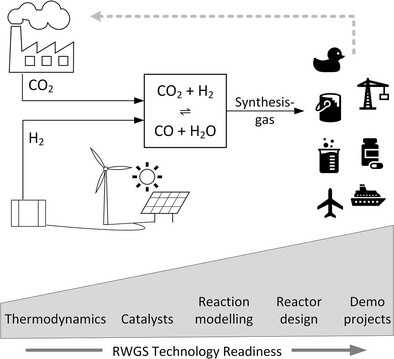
For turning CO₂ into valuable chemicals, the reverse water-gas shift (RWGS) reaction offers a promising solution by converting CO₂ and H₂ into CO and H₂O. Thermodynamic challenges, catalytic mechanisms, and an overview of the technological readiness of various RWGS implementation approaches across different scales are presented and discussed.
Von Radikal‐Chemie bis Bioplastik: GDCh‐Preisträger auf dem Science Forum Chemistry 2025
- 672-673
- 10 July 2025
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
Physical Adsorption Characterization of Nanoporous Materials
- 1059-1073
- 25 June 2010
Graphical Abstract
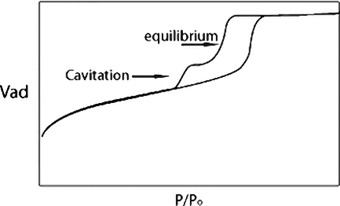
Major progress in the understanding of the adsorption, pore condensation and hysteresis behavior of fluids in novel ordered nanoporous materials with well defined pore structure has led to major advances in the structural characterization by physical adsorption, also because of the development and availability of advanced theoretical procedures based on statistical mechanics which allows to describe adsorption and phase behavior of fluids in pores on a molecular level.
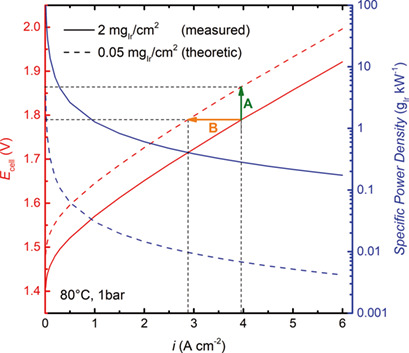
Current Challenges in Catalyst Development for PEM Water Electrolyzers
- 31-39
- 20 November 2019
Graphical Abstract
Overview of Surrogate Modeling in Chemical Process Engineering
- 228-239
- 3 January 2019
Graphical Abstract
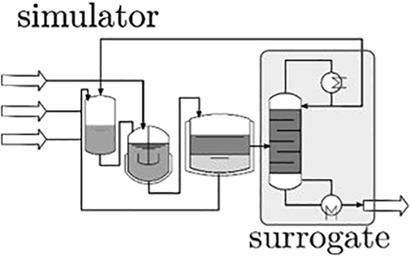
This article summarizes recent use of surrogate modeling in the chemical process engineering field and presents several examples found in the literature. Through the use of these mathematically simpler representations of complex functions or process simulations, the computational effort of optimization or study has simplified considerably.
Methane Pyrolysis for CO2-Free H2 Production: A Green Process to Overcome Renewable Energies Unsteadiness
- 1596-1609
- 25 August 2020
Graphical Abstract
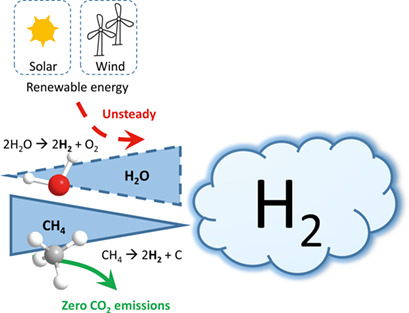
The conversion of exhaust gases from the steel industry into methanol is a promising way to reduce the carbon footprint via CO2 hydrogenation. Due to the unsteadiness of renewable energies for the required H2 production, other hydrogen sources must be found. Methane pyrolysis appears as a green alternative to meet the hydrogen demand since it provides CO2-free H2.
Latest news
Recent issues
- Volume 97, Issue 7
Special Issue: Membrantechnik
665-771July 2025Guest Editor(s):
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Membrantechnik