Journal list menu
Highlights
Highlights describe very important recent results of original research, by a third person, with a view to instruct and to highlight the significance of the findings.
HF‐Free Manufacturing of Fluorochemicals from Fluorspar
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition
- 20 May 2025
Graphical Abstract

The hazardous production of HF poses a major chemical and societal challenge. How to incorporate fluorine (F) atoms into organic molecules, circumventing HF generation? Recently, Gouverneur and co-workers reported an innovative method to activate fluorspar (CaF2), mitigating the environmental impact of the fluorination process.
Photoexcited Structural Diversification of Carboxylic Acids with Phosphorus Promoter
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition
- 17 March 2025
Graphical Abstract

This article showcases recent breakthroughs by Scheidt and co-workers in the photoexcited structural reconstruction of carboxylic acids. By leveraging hydrogen-atom transfer and cyclization sequences, the generated diradicals facilitate the synthesis of valuable α-hydroxyl and amino phosphonates in a highly efficient and sustainable manner.
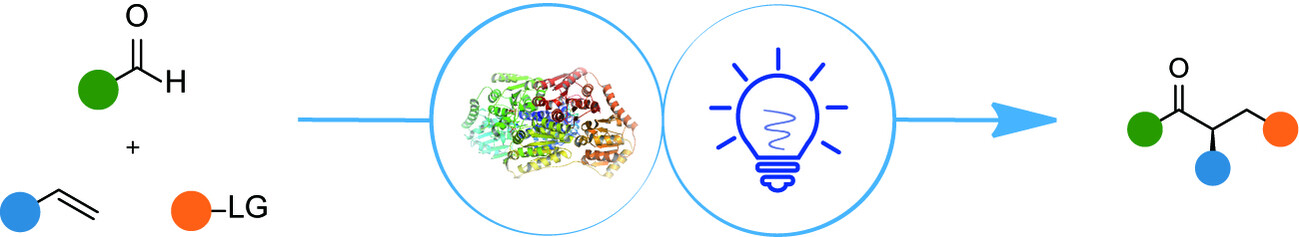
Photobiocatalytic Reaction: From Single Component to Triple Components
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition
- 26 February 2025
Synergistic Cancer Photoimmunotherapy by Harnessing Near‐Infrared‐Activated Nanoparticles Containing Charge Transfer Complexes
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition
- 27 January 2025
Graphical Abstract
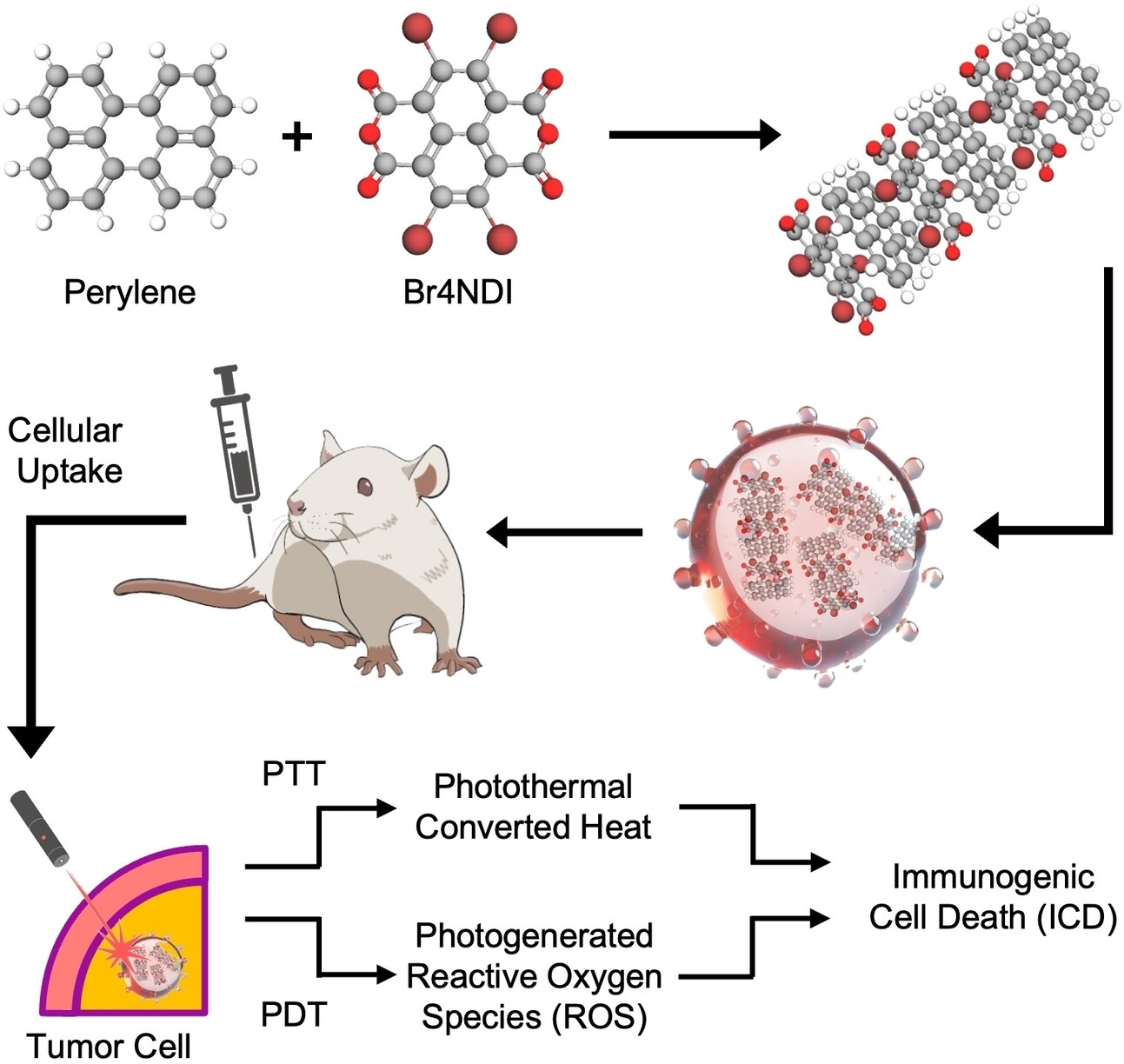
C. Wang et al. recently developed a near-infrared-activated charge transfer complex-based nanoparticle with donor- acceptor (D–A) units, which enhances photothermal conversion and generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) synergistically combines photothermal and photodynamic therapies (PTT/PDT). Preclinical experiments have shown a strong immunotherapeutic effect by integrating programmed cell death protein 1 antibody combination therapy. While the use of D–A units in nanosystems for photoimmunotherapy is still emerging, it holds great potential to revolutionize cancer treatment.
Giant Polyketide Synthases Biosynthesize a Marine Polyether Biotoxin
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition
- 5 December 2024
Graphical Abstract
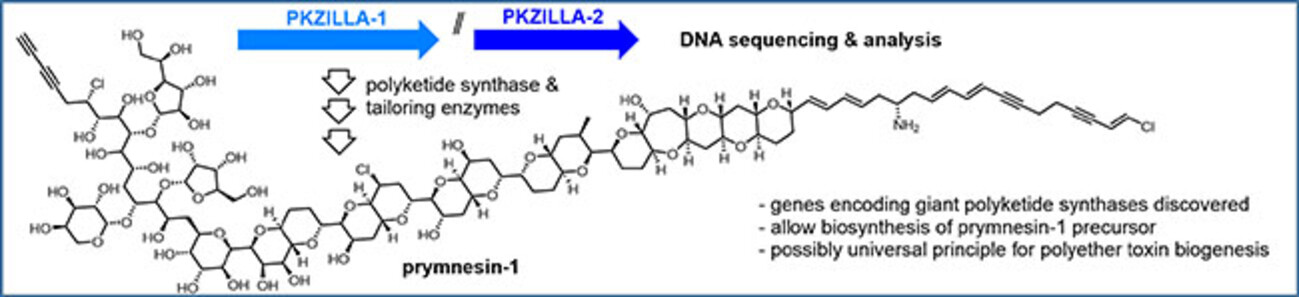
Fallon, Shende, Moore, and co-workers have identified for the first time genes encoding giant type I polyketide synthases (PKZILLA-1 & 2) in the “golden alga” Prymnesium parvum for the biosynthesis of the polyether toxin prymnesin-1, corroborating long-held biosynthetic postulates. The authors’ approach may serve as a blueprint for the future discovery of the biosynthetic machineries underlying other polyether toxins.