Dopant and Exfoliation Induced Simultaneous Modification of Charge Density and C─C Coupling Sites for Efficient CO2 Photoreduction to Ethylene
Dr. Kousik Das
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorSubhajit Chakraborty
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Siddhi Kediya
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ashutosh Kumar Singh
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Risov Das
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Soumi Mondal
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Mohd Riyaz
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Devender Goud
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorNilutpal Dutta
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Chathakudath P. Vinod
Catalysis and Inorganic Chemistry Division, CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Pune, 410008 India
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Sebastian C. Peter
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Kousik Das
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorSubhajit Chakraborty
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Siddhi Kediya
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ashutosh Kumar Singh
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Chemistry and Physics of Materials Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Risov Das
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Soumi Mondal
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Mohd Riyaz
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Devender Goud
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorNilutpal Dutta
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Chathakudath P. Vinod
Catalysis and Inorganic Chemistry Division, CSIR-National Chemical Laboratory, Dr. Homi Bhabha Road, Pune, 410008 India
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Sebastian C. Peter
New Chemistry Unit, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
School of Advanced Materials, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Jakkur, Bangalore, 560064 India
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
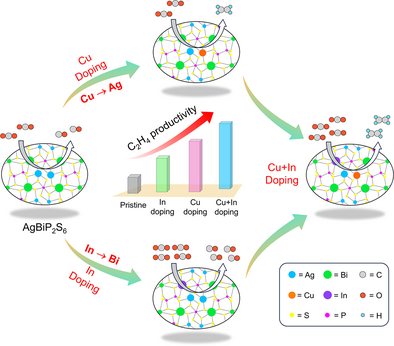
The photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into higher carbon products demands precise catalyst engineering. In this study, we implemented a dual doping strategy in AgBiP₂S₆ to optimize charge density and enhance active sites for C─C coupling. This approach successfully enabled the synthesis of ethylene through the photoreduction of CO2, showcasing the effectiveness of the modified catalyst design.
Abstract
The photochemical conversion of CO2 into C2+ products has emerged as an attractive method for synthesizing valuable chemicals and fuels using abundant solar energy. However, the challenge lies in enhancing the efficiency and selectivity of C2+ product formation. In this study, we employed a heteroatom doping strategy to optimize the photocatalytic parameters and achieve excellent efficiency and selectivity in the photocatalytic CO2 reduction to C2+ product formation. Our experimental analysis revealed that the local electronic structure of the catalyst, modified by In-doping, enables enhanced efficiency. Additionally, the incorporation of Cu facilitates the coupling of C1 intermediates, resulting in excellent selectivity towards C2+ products. The CO2 reduction performance is further enhanced through exfoliation, which increases the exposure of active sites and extends the charge carrier lifetime by reducing the charge diffusion length. We report that the rate of formation of C2H4 reached 54.3 µmol·h−1·g−1 with an outstanding selectivity of 91% over the exfoliated CuIn-doped AgBiP2S6 catalyst. By elucidating the role of heteroatom doping and exfoliation in enhancing both the efficiency and selectivity of C2+ product formation, our study contributes to advancing the development of sustainable and efficient photocatalytic CO2 conversion technologies.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202423471-sup-0001-SuppMat.docx32.3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1Z. Jiang, X. Xu, Y. Ma, H. S. Cho, D. Ding, C. Wang, J. Wu, P. Oleynikov, M. Jia, J. Cheng, Y. Zhou, O. Terasaki, T. Peng, L. Zan, H. Deng, Nature 2020, 586, 549–554.
- 2W. H. Lee, C. W. Lee, G. D. Cha, B.-H. Lee, J. H. Jeong, H. Park, J. Heo, M. S. Bootharaju, S.-H. Sunwoo, J. H. Kim, K. H. Ahn, D.-H. Kim, T. Hyeon, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 754–762.
- 3H. Jung, C. Kim, H.-W. Yoo, J. You, J. S. Kim, A. Jamal, I. Gereige, J. W. Ager, H.-T. Jung, Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 2869–2878.
- 4X. Wu, Y. Li, G. Zhang, H. Chen, J. Li, K. Wang, Y. Pan, Y. Zhao, Y. Sun, Y. Xie, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5267–5274.
- 5J. Li, H. Huang, W. Xue, K. Sun, X. Song, C. Wu, L. Nie, Y. Li, C. Liu, Y. Pan, Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 719–729.
- 6Y. Shi, G. Zhan, H. Li, X. Wang, X. Liu, L. Shi, K. Wei, C. Ling, Z. Li, H. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100143.
- 7K. Das, R. Das, M. Riyaz, A. Parui, D. Bagchi, A. K. Singh, A. K. Singh, C. P. Vinod, S. C. Peter, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2205994.
- 8R. Wang, J. Huang, X. Zhang, J. Han, Z. Zhang, T. Gao, L. Xu, S. Liu, P. Xu, B. Song, ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3593–3603.
- 9B. Song, K. Li, Y. Yin, T. Wu, L. Dang, M. Cabán-Acevedo, J. Han, T. Gao, X. Wang, Z. Zhang, J. R. Schmidt, P. Xu, S. Jin, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8549–8557.
- 10N. Wang, P. Ou, R. K. Miao, Y. Chang, Z. Wang, S.-F. Hung, J. Abed, A. Ozden, H.-Y. Chen, H.-L. Wu, J. E. Huang, D. Zhou, W. Ni, L. Fan, Y. Yan, T. Peng, D. Sinton, Y. Liu, H. Liang, E. H. Sargent, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 7829–7836.
- 11Y. Zhou, F. Che, M. Liu, C. Zou, Z. Liang, P. De Luna, H. Yuan, J. Li, Z. Wang, H. Xie, H. Li, P. Chen, E. Bladt, R. Quintero-Bermudez, T.-K. Sham, S. Bals, J. Hofkens, D. Sinton, G. Chen, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 974–980.
- 12L. Wang, B. Zhao, C. Wang, M. Sun, Y. Yu, B. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 10175–10179.
- 13F. Yu, X. Jing, Y. Wang, M. Sun, C. Duan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 24849–24853.
- 14X. Jiao, K. Zheng, L. Liang, X. Li, Y. Sun, Y. Xie, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6592–6604.
- 15W. Wang, C. Deng, S. Xie, Y. Li, W. Zhang, H. Sheng, C. Chen, J. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2984–2993.
- 16T. Wang, L. Chen, C. Chen, M. Huang, Y. Huang, S. Liu, B. Li, ACS Nano 2022, 16, 2306–2318.
- 17W. Xie, K. Li, X.-H. Liu, X. Zhang, H. Huang, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2208132.
- 18S. Chakraborty, R. Das, M. Riyaz, K. Das, A. K. Singh, D. Bagchi, C. P. Vinod, S. C. Peter, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202216613.
- 19E. L. Clark, C. Hahn, T. F. Jaramillo, A. T. Bell, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15848–15857.
- 20C. G. Morales-Guio, E. R. Cave, S. A. Nitopi, J. T. Feaster, L. Wang, K. P. Kuhl, A. Jackson, N. C. Johnson, D. N. Abram, T. Hatsukade, C. Hahn, T. F. Jaramillo, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 764–771.
- 21D. Ren, B. S.-H. Ang, B. S. Yeo, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 8239–8247.
- 22R. Xu, D.-H. Si, S.-S. Zhao, Q.-J. Wu, X.-S. Wang, T.-F. Liu, H. Zhao, R. Cao, Y.-B. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 8261–8270.
- 23R. Das, K. Das, B. Ray, C. P. Vinod, S. C. Peter, Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 1967–1976.
- 24M. A. Susner, M. Chyasnavichyus, M. A. McGuire, P. Ganesh, P. Maksymovych, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1602852.
- 25Q. Zhao, Z. Cao, X. Wang, H. Chen, Y. Shi, Z. Cheng, Y. Guo, B. Li, Y. Gong, Z. Du, S. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 21242–21252.
- 26T. V. Misuryaev, T. V. Murzina, O. A. Aktsipetrov, N. E. Sherstyuk, V. B. Cajipe, X. Bourdon, Solid State Commun. 2000, 115, 605–608.
- 27R. Gusmão, Z. Sofer, M. Pumera, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9326–9337.
- 28M. A. Gave, D. Bilc, S. Mahanti, J. D. Breshears, M. G. Kanatzidis, Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 5293–5303.
- 29L. Ju, J. Shang, X. Tang, L. Kou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 1492–1500.
- 30R. A. Wheeler, P. P. Kumar, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 4776–4784.
- 31T. J. McCarthy, M. G. Kanatzidis, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1994, 1089–1090.
- 32X. Wang, K. Du, W. Liu, P. Hu, X. Lu, W. Xu, C. Kloc, Q. Xiong, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 123103.
- 33W. Gao, S. Li, H. He, X. Li, Z. Cheng, Y. Yang, J. Wang, Q. Shen, X. Wang, Y. Xiong, Y. Zhou, Z. Zou, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4747.
- 34H. Wang, Y. Jiao, B. Wu, D. Wang, Y. Hu, F. Liang, C. Shen, A. Knauer, D. Ren, H. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202217253.
- 35M. A. Gave, D. Bilc, S. D. Mahanti, J. D. Breshears, M. G. Kanatzidis, Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 5293–5303.
- 36P. Jiang, J. C. Neuefeind, M. Avdeev, Q. Huang, M. Yue, X. Yang, R. Cong, T. Yang, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1303.
- 37Y. M. Vysochanskii, V. Stephanovich, A. Molnar, V. Cajipe, X. Bourdon, Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 9119–9124.
- 38C. Sourisseau, J. P. Forgerit, Y. Mathey, J. Solid State Chem. 1983, 49, 134–149.
- 39D. Çakır, C. Sevik, F. M. Peeters, Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 165406.
- 40B. Su, Y. Kong, S. Wang, S. Zuo, W. Lin, Y. Fang, Y. Hou, G. Zhang, H. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 27415–27423.
- 41M. Kou, W. Liu, Y. Wang, J. Huang, Y. Chen, Y. Zhou, Y. Chen, M. Ma, K. Lei, H. Xie, P. K. Wong, L. Ye, Appl. Catal., B 2021, 291, 120146.
- 42K. Yan, D. Wu, T. Wang, C. Chen, S. Liu, Y. Hu, C. Gao, H. Chen, B. Li, ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 2302–2312.
- 43F. Guo, R.-X. Li, S. Yang, X.-Y. Zhang, H. Yu, J. J. Urban, W.-Y. Sun, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202216232.
- 44Y. Wu, Q. Chen, J. Zhu, K. Zheng, M. Wu, M. Fan, W. Yan, J. Hu, J. Zhu, Y. Pan, X. Jiao, Y. Sun, Y. Xie, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301075.
- 45W. Gao, S. Li, H. He, X. Li, Z. Cheng, Y. Yang, J. Wang, Q. Shen, X. Wang, Y. Xiong, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–8.
- 46S. Qiao, Y. Chen, Y. Tang, J. Yuan, J. Shen, D. Zhang, Y. Du, Z. Li, D. Yuan, H. Tang, C. Liu, Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140321.
- 47R. Das, R. Paul, A. Parui, A. Shrotri, C. Atzori, K. A. Lomachenko, A. K. Singh, J. Mondal, S. C. Peter, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 422–435.
- 48W. Gao, L. Shi, W. Hou, C. Ding, Q. Liu, R. Long, H. Chi, Y. Zhang, X. Xu, X. Ma, Z. Tang, Y. Yang, X. Wang, Q. Shen, Y. Xiong, J. Wang, Z. Zou, Y. Zhou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, e202317852.
- 49S. W. Gaarenstroom, N. Winograd, J. Chem. Phys. 1977, 67, 3500–3506.
- 50K. Das, S. Lohkna, G. Yang, P. Ghosh, S. Roy, J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 21721–21734
- 51C. Pu, J. Ma, H. Qin, M. Yan, T. Fu, Y. Niu, X. Yang, Y. Huang, F. Zhao, X. Peng, ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 32–39.
- 52C. C. Stoumpos, L. Frazer, D. J. Clark, Y. S. Kim, S. H. Rhim, A. J. Freeman, J. B. Ketterson, J. I. Jang, M. G. Kanatzidis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6804–6819.
- 53F. Chen, T. Ma, T. Zhang, Y. Zhang, H. Huang, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005256.
- 54I. Shown, S. Samireddi, Y.-C. Chang, R. Putikam, P.-H. Chang, A. Sabbah, F.-Y. Fu, W.-F. Chen, C.-I. Wu, T.-Y. Yu, P.-W. Chung, M. C. Lin, L.-C. Chen, K.-H. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 169.
- 55X. Zu, Y. Zhao, X. Li, R. Chen, W. Shao, L. Li, P. Qiao, W. Yan, Y. Pan, Q. Xu, J. Zhu, Y. Sun, Y. Xie, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215247.
- 56J. Xu, Z. Ju, W. Zhang, Y. Pan, J. Zhu, J. Mao, X. Zheng, H. Fu, M. Yuan, H. Chen, R. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 8705–8709.
- 57W. Xia, Y. Xie, S. Jia, S. Han, R. Qi, T. Chen, X. Xing, T. Yao, D. Zhou, X. Dong, J. Zhai, J. Li, J. He, D. Jiang, Y. Yamauchi, M. He, H. Wu, B. Han, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 17253–17264.
- 58H. Wan, Y. Jiao, A. Bagger, J. Rossmeisl, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 533–541.
- 59Y. Kim, S. Park, S.-J. Shin, W. Choi, B. K. Min, H. Kim, W. Kim, Y. J. Hwang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4301–4311.
- 60D. Devasia, A. J. Wilson, J. Heo, V. Mohan, P. K. Jain, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2612.
- 61G. Kresse, J. Furthmüller, Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186.
- 62G. Kresse, J. Furthmüller, Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50.
- 63V. Wang, N. Xu, J.-C. Liu, G. Tang, W.-T. Geng, Comput. Phys. Commun. 2021, 267, 108033.
- 64J. P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868.
- 65P. E. Blöchl, Phys. Rev. B 1994, 50, 17953–17979.
- 66H. J. Monkhorst, J. D. Pack, Phys. Rev. B 1976, 13, 5188–5192.
- 67Y. Wu, C. Liu, C. Wang, Y. Yu, Y. Shi, B. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3881.
- 68J. K. Nørskov, J. Rossmeisl, A. Logadottir, L. Lindqvist, J. R. Kitchin, T. Bligaard, H. Jonsson, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17886–17892.
- 69S. Trasatti, Pure Appl. Chem. 1986, 58, 955–966.