Design of Intrinsically Stable Hole-Selective Self-Assembled Monolayers by Introducing Fused-Ring Intramolecular Donor–Acceptor Interactions
Graphical Abstract
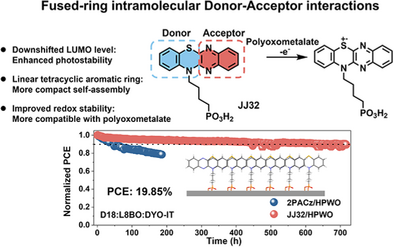
Herein, we develop a novel SAM molecular design strategy by introducing fused-ring intramolecular donor–acceptor (D–A) interactions. The designed molecule, JJ32, features a benzo[5,6][1,4]thiazino[2,3-b]quinoxaline skeleton, where strong D–A interactions enhance charge delocalization and downshift the LUMO energy level. This leads to enhanced photostability, redox stability, and intermolecular interactions. Moreover, the improved redox stability benefits the promising polyoxometalate/SAM composite HSL, allowing the JJ32/HPWO-based OSC to reach 19.85% efficiency with improved stability.
Abstract
Hole-selective self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) incorporating electron-donating conjugated units as head groups have witnessed remarkable success in helping achieve high-performance organic solar cells (OSCs). However, these molecules frequently exhibit a shallow lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) level, rendering them prone to photodegradation. To tackle this problem, we introduce fused-ring intramolecular donor–acceptor (D–A) interactions into the design of SAM molecules to downshift the LUMO level. The resultant molecule, JJ32, shows both enhanced photostability and intermolecular interactions. Furthermore, the fused-ring intramolecular D–A interactions also help stabilize the radical cation state of JJ32 to result in significantly improved redox stability. This enables them to be included in polyoxometalate (POM)-based composite hole-selective layers (HSLs), resulting in an impressive efficiency of 19.85% alongside significantly enhanced stability in corresponding OSCs. This study not only validates the concept of using fused-ring D–A-structure SAMs to improve the efficiency and stability of OSCs but also elucidates the relationship between SAM structures and POM doping behaviors to provide an effective strategy in designing intrinsically stable SAM molecules for high-performance OSCs.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article.