Strain Energy Induced Rotary Speed Acceleration in a Light-Driven Molecular Motor
Kai Lan
College of Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Green Chemistry and Technology of Ministry of Education, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, 610064 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShilong Zhang
SCNU-UG International Joint Laboratory of Molecular Science and Displays, National Center for International Research on Green Optoelectronics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, 510006 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYi Lu
Department of Chemistry and Shenzhen Grubbs Institute, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Peiyuan Yu
Department of Chemistry and Shenzhen Grubbs Institute, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Email: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Jiawen Chen
SCNU-UG International Joint Laboratory of Molecular Science and Displays, National Center for International Research on Green Optoelectronics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, 510006 China
Email: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Chuyang Cheng
College of Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Green Chemistry and Technology of Ministry of Education, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, 610064 China
Email: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorKai Lan
College of Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Green Chemistry and Technology of Ministry of Education, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, 610064 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorShilong Zhang
SCNU-UG International Joint Laboratory of Molecular Science and Displays, National Center for International Research on Green Optoelectronics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, 510006 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYi Lu
Department of Chemistry and Shenzhen Grubbs Institute, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Peiyuan Yu
Department of Chemistry and Shenzhen Grubbs Institute, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, 518055 China
Email: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Jiawen Chen
SCNU-UG International Joint Laboratory of Molecular Science and Displays, National Center for International Research on Green Optoelectronics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, 510006 China
Email: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Chuyang Cheng
College of Chemistry, Key Laboratory of Green Chemistry and Technology of Ministry of Education, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan, 610064 China
Email: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorIn memory of Sir Fraser Stoddart
Graphical Abstract
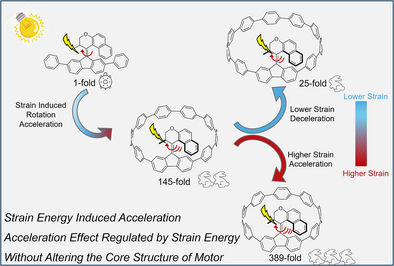
A new strategy accelerates rotary speed in overcrowded alkene-based molecular motors by tuning cycloparaphenylene loop size, preserving core structures. Strain energy variations drive hierarchical acceleration up to 389-fold. This study systematically reveals motor behavior under strain, offering new avenues for engineering light-driven nanomachines.
Abstract
Light-driven molecular motors based on overcrowded alkenes represent a major type of molecular machines that are able to rotate unidirectionally. The regulation of the rotary speed without altering the core structure of a motor is crucial and remains a major challenge. In the present study, we reported that the rotary speed of molecular motors can be significantly enhanced by harnessing the strain energy of cycloparaphenylene (CPP). A series of molecular motors incorporated in CPP with varying sizes were synthesized, and their photochemical and thermal isomerization behaviors were meticulously examined using UV–vis and 1H NMR spectroscopy. The remarkable increase of the acceleration effect of the rotary speed with decreasing macrocycle sizes, up to 389-fold, can be attributed to the strain energy induced bending in the stator part, which reduces steric hindrance in the “fjord region” of the molecule, supported by a detailed computational study employing density functional theory. This work provides systematic insight into the behavior of molecular motors under strain energy, thereby paving the way for the application of motor-incorporating CPPs as a general strategy to accelerate the rotary speed of molecular motors.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202507487-sup-0001-SupMat.pdf10.9 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1C. J. Bruns, J. F. Stoddart, The Nature of the Mechanical Bond: From Molecules to Machines, Wiley, New York, NY 2016.
10.1002/9781119044123 Google Scholar
- 2S. Kassem, T. van Leeuwen, A. S. Lubbe, M. R. Wilson, B. L. Feringa, D. A. Leigh, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2592–2621.
- 3R. D. Vale, R. A. Milligan, Science 2000, 288, 88–95.
- 4V. Ramakrishnan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4355–4380.
- 5J. E. Walker, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2308–2319.
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980918)37:17<2308::AID-ANIE2308>3.0.CO;2-W CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 6R. Eelkema, M. M. Pollard, J. Vicario, N. Katsonis, B. S. Ramon, C. W. M. Bastiaansen, D. J. Broer, B. L. Feringa, Nature 2006, 440, 163–163.
- 7A. Coskun, M. Banaszak, R. D. Astumian, J. F. Stoddart, B. A. Grzybowski, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 19–30.
- 8J. Zhang, Y. Fu, H.-H. Han, Y. Zang, J. Li, X.-P. He, B. L. Feringa, H. Tian, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 987.
- 9N. Koumura, R. W. J. Zijlstra, R. A. van Delden, N. Harada, B. L. Feringa, Nature 1999, 401, 152–155.
- 10F. Lancia, A. Ryabchun, N. Katsonis, Nat. Rev. Chem 2019, 3, 536–551.
- 11D. R. S. Pooler, A. S. Lubbe, S. Crespi, B. L. Feringa, Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 14964–14986.
- 12S. Erbas-Cakmak, D. A. Leigh, C. T. McTernan, A. L. Nussbaumer, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10081–10206.
- 13R. D. Astumian, Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 840–845.
- 14V. García-López, D. Liu, J. M. Tour, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 79–124.
- 15E. Moulin, L. Faour, C. C. Carmona-Vargas, N. Giuseppone, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906036.
- 16J. Wang, B. L. Feringa, Science 2011, 331, 1429–1432.
- 17J.-J. Yu, Z.-Q. Cao, Q. Zhang, S. Yang, D.-H. Qu, H. Tian, Chem. Comm. 2016, 52, 12056–12059.
- 18J. Li, S. Xie, J. Meng, Y. Liu, Q. Zhan, Y. Zhang, L. Shui, G. Zhou, B. L. Feringa, J. Chen, CCS Chem 2024, 6, 427–438.
- 19J. Vicario, A. Meetsma, B. L. Feringa, Chem. Comm. 2005, 5910.
- 20D. Pijper, R. A. van Delden, A. Meetsma, B. L. Feringa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17612–17613.
- 21J. Vicario, M. Walko, A. Meetsma, B. L. Feringa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5127–5135.
- 22T. Fernández Landaluce, G. London, M. M. Pollard, P. Rudolf, B. L. Feringa, J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 5323–5325.
- 23S. J. Wezenberg, K.-Y. Chen, B. L. Feringa, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11457–11461.
- 24A. Faulkner, T. van Leeuwen, B. L. Feringa, S. J. Wezenberg, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13597–13603.
- 25R. Dorel, C. Miró, Y. Wei, S. J. Wezenberg, B. L. Feringa, Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3715–3718.
- 26D. Roke, S. J. Wezenberg, B. L. Feringa, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2018, 115, 9423–9431.
- 27M. Klok, N. Boyle, M. T. Pryce, A. Meetsma, W. R. Browne, B. L. Feringa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10484–10485.
- 28B. P. Corbet, A. S. Lubbe, S. Crespi, B. L. Feringa, in Molecular Photoswitches, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ 2022, pp. 213–251.
10.1002/9783527827626.ch11 Google Scholar
- 29R. Jasti, J. Bhattacharjee, J. B. Neaton, C. R. Bertozzi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 17646–17647.
- 30H. Takaba, H. Omachi, Y. Yamamoto, J. Bouffard, K. Itami, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6112–6116.
- 31S. Yamago, Y. Watanabe, T. Iwamoto, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 757–759.
- 32H. Omachi, Y. Segawa, K. Itami, Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1378–1389.
- 33E. R. Darzi, R. Jasti, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6401–6410.
- 34E. J. Leonhardt, R. Jasti, Nat. Rev. Chem 2019, 3, 672–686.
- 35Y. Tsuchido, R. Abe, T. Ide, K. Osakada, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22928–22932.
- 36K. Senthilkumar, M. Kondratowicz, T. Lis, P. J. Chmielewski, J. Cybińska, J. L. Zafra, J. Casado, T. Vives, J. Crassous, L. Favereau, M. Stępień, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7421–7427.
- 37B. Hou, K. Li, H. He, J. Hu, Z. Xu, Q. Xiang, P. Wang, X. Chen, Z. Sun, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202301046.
- 38P. Fang, Z. Cheng, W. Peng, J. Xu, X. Zhang, F. Zhang, G. Zhuang, P. Du, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202407078.
- 39Y. Xu, M.-Y. Leung, L. Yan, Z. Chen, P. Li, Y.-H. Cheng, M. H.-Y. Chan, V. W.-W. Yam, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 13226–13235.
- 40F. Schwer, S. Zank, M. Freiberger, F. M. Steudel, N. Geue, L. Ye, P. E. Barran, T. Drewello, D. M. Guldi, M. von Delius, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2024, 64, e202413404.
- 41Y. Yang, O. Blacque, S. Sato, M. Juríček, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13529–13535.
- 42H. Kwon, B. S. Newell, C. J. Bruns, Nanoscale 2022, 14, 14276–14285.
- 43Y. Fan, J. He, L. Liu, G. Liu, S. Guo, Z. Lian, X. Li, W. Guo, X. Chen, Y. Wang, H. Jiang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304623.
- 44M. Zhu, Q. Zhou, H. Cheng, Y. Sha, V. I. Bregadze, H. Yan, Z. Sun, X. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202213470.
- 45X.-W. Chen, Q.-S. Deng, B.-H. Zheng, J.-F. Xing, H.-R. Pan, X.-J. Zhao, Y.-Z. Tan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 31665–31670.
- 46L. Zhu, J. Xu, B. Lan, X. Chen, H. Kono, H. Xu, J. Yan, W. Li, A. Yagi, Y. Yuan, K. Itami, Y. Li, Org. Chem. Front. 2024, 11, 5130–5137.
- 47G. Li, L.-L. Mao, J.-N. Gao, X. Shi, Z.-Y. Huo, J. Yang, W. Zhou, H. Li, H.-B. Yang, C.-H. Tung, L.-Z. Wu, H. Cong, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. e202419435.
- 48J. Chen, J. Vachon, B. L. Feringa, J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 6025–6034.
- 49M. K. J. ter Wiel, J. Vicario, S. G. Davey, A. Meetsma, B. L. Feringa, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 28.
- 50E. R. Darzi, T. J. Sisto, R. Jasti, J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 6624–6628.
- 51J. Wang, H. Shi, S. Wang, X. Zhang, P. Fang, Y. Zhou, G.-L. Zhuang, X. Shao, P. Du, Chem. - Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202103828.
- 52X. Zhang, K. Lan, C. Cheng, Org. Lett. 2024, 26, 7853–7857.
- 53V. K. Patel, E. Kayahara, S. Yamago, Chem. - Eur. J. 2015, 21, 5742–5749.
- 54T. A. Schaub, J. T. Margraf, L. Zakharov, K. Reuter, R. Jasti, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16348–16353.
- 55J. M. Fehr, N. Myrthil, A. L. Garrison, T. W. Price, S. A. Lopez, R. Jasti, Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 2839–2848.
- 56E. Kayahara, T. Hayashi, K. Takeuchi, F. Ozawa, K. Ashida, S. Ogoshi, S. Yamago, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11418–11421.
- 57M. M. Pollard, P. V. Wesenhagen, D. Pijper, B. L. Feringa, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 1605.
- 58M. Kathan, S. Crespi, N. O. Thiel, D. L. Stares, D. Morsa, J. de Boer, G. Pacella, T. van den Enk, P. Kobauri, G. Portale, C. A. Schalley, B. L. Feringa, Nat. Nanotechnol 2022, 17, 159–165.
- 59M. Kathan, S. Crespi, A. Troncossi, C. N. Stindt, R. Toyoda, B. L. Feringa, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202205801.