Unveiling Zinc Stripping and Molecular Engineering for High-Performance Zinc Anode
Zeping Liu
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorGuangning Xu
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu Zhang
Department of Chemistry, Stockholm University, Stockholm, 10691 Sweden
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Li
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoran Li
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiachi Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Hu
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tiesong Lin
State Key Laboratory of Precision Welding & Joining of Materials and Structures, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Naiqing Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorZeping Liu
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorGuangning Xu
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu Zhang
Department of Chemistry, Stockholm University, Stockholm, 10691 Sweden
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Li
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoran Li
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiachi Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Hu
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tiesong Lin
State Key Laboratory of Precision Welding & Joining of Materials and Structures, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Naiqing Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Urban-rural Water Resources and Environment, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
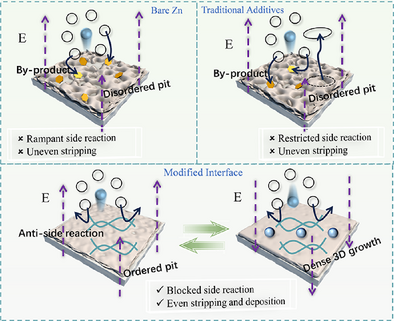
It is found that the zinc stripping process is more prone to cause severe side reactions than the deposition process, resulting in the formation of dendrites and “dead zinc.” In this regard, a dynamic molecular protection strategy is proposed to regulate the zinc stripping and deposition processes simultaneously, achieving long-lasting protection of the zinc anodes.
Abstract
The unstable zinc anode is a key challenge limiting the cycle life of rechargeable zinc-ion batteries. The current research primarily focuses on the zinc plating process, with strategies to induce uniform zinc deposition for a stable zinc anode. Here, we demonstrate that the zinc stripping process has a more significant impact on the subsequent zinc deposition, which exacerbates the formation of by-products, dendrites, and “dead zinc.” Therefore, we propose using aspartyl-phenylalanine methyl ester (APM) molecules to regulate the zinc stripping, achieving uniform stripping of the zinc anode by increasing the stripping overpotential across high-energy barriers. Simultaneously, its localized hydrophobic functional groups effectively inhibit the byproducts triggered by solvated water molecules. The experimental results show that the Zn-APM symmetric cell exhibits excellent cycling stability, with stable cycling over 6500 h (>9 months) at 1 mA cm−2 for 1 mAh cm−2 and 700 h at 70% zinc utilization with 10 µm zinc. In addition, the Zn-APM||Zn0.58V2O5·H2O full cell exhibits 80% capacity retention after 500 cycles at a loading of 8.1 mg cm−2.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202501960-supp-0001-SuppMat.docx50.6 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1L. Jiang, D. Li, X. Xie, D. Ji, L. Li, L. Li, Z. He, B. Lu, S. Liang, J. Zhou, Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 62, 102932.
- 2H.-B. Chen, H. Meng, T.-R. Zhang, Q. Ran, J. Liu, H. Shi, G.-F. Han, T.-H. Wang, Z. Wen, X.-Y. Lang, Q. Jiang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202402327.
- 3Q. Li, A. Chen, D. Wang, Y. Zhao, X. Wang, X. Jin, B. Xiong, C. Zhi, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3699.
- 4Q. Ma, R. Gao, Y. Liu, H. Dou, Y. Zheng, T. Or, L. Yang, Q. Li, Q. Cu, R. Feng, Z. Zhang, Y. Nie, B. Ren, D. Luo, X. Wang, A. Yu, Z. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2207344.
- 5D. Wang, S. Hu, T. Li, C. Chang, S. Li, S. Guo, H. Li, Q. Liu, J. Gong, J. Zhou, C. Han, Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 259.
- 6Z. Guo, Z. Liu, P. Wang, C. Zhao, X. Lu, Y. Zhang, N. Zhang, Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 14656–14662.
- 7X. Yang, Y. Lu, Z. Liu, H. Ji, Z. Chen, J. Peng, Y. Su, Y. Zou, C. Wu, S. Dou, P. Gao, Z. Guo, J. Sun, Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 5563–5575.
- 8Y. Ai, C. Yang, Z. Yin, T. Wang, T. Gai, J. Feng, K. Li, W. Zhang, Y. Li, F. Wang, D. Chao, Y. Wang, D. Zhao, W. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 15496–15505.
- 9A. Chen, C. Zhao, J. Gao, Z. Guo, X. Lu, J. Zhang, Z. Liu, M. Wang, N. Liu, L. Fan, Y. Zhang, N. Zhang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 275–284.
- 10Z. Zhang, X. Yang, P. Li, Y. Wang, X. Zhao, J. Safaei, H. Tian, D. Zhou, B. Li, F. Kang, G. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2206970.
- 11J. Zhou, F. Wu, Y. Mei, Y. Hao, L. Li, M. Xie, R. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200782.
- 12X. Liao, S. Chen, J. Chen, Y. Li, W. Wang, T. Lu, Z. Chen, L. Cao, Y. Wang, R. Huang, X. Sun, R. Lv, H. Wang, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2317796121.
- 13D. Wang, H. Peng, S. Zhang, H. Liu, N. Wang, J. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202315834.
- 14Y. Wang, T. Wang, S. Bu, J. Zhu, Y. Wang, R. Zhang, H. Hong, W. Zhang, J. Fan, C. Zhi, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1828.
- 15L. Yao, G. Wang, F. Zhang, X. Chi, Y. Liu, Sci. 2023, 16, 4432.
- 16Y. Zhao, S. Guo, M. Chen, B. Lu, X. Zhang, S. Liang, J. Zhou, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7080.
- 17Y. Mu, Z. Li, B.-k. Wu, H. Huang, F. Wu, Y. Chu, L. Zou, M. Yang, J. He, L. Ye, M. Han, T. Zhao, L. Zeng, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4205.
- 18X. Wang, L. Liu, Z. Hu, C. Han, X. Xu, S. Dou, W. Li, Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 17348–17361.
- 19S. Zhang, Y. Wu, J. Gao, Y. Song, B. Jin, M. Shao, Small 2024, 20, 2402489.
- 20Z. Yang, Q. Zhang, C. Xie, Y. Li, W. Li, T. Wu, Y. Tang, H. Wang, Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 47, 319–326.
- 21Z. Liu, Z. Guo, L. Fan, C. Zhao, A. Chen, M. Wang, M. Li, X. Lu, J. Zhang, Y.u Zhang, N. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2305988.
- 22H. Gan, H. Li, M. Xu, C. Han, H.-M. Cheng, Joule 2024, 8, 3054–3071.
- 23L. Liu, X. Wang, Z. Hu, X. Wang, Q. Zheng, C. Han, J. Xu, X. Xu, H.-K. Liu, S.-X. Dou, W. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202405209.
- 24M. Yang, J. Zhu, S. Bi, R. Wang, H. Wang, F. Yue, Z. Niu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202400337.
- 25M. Qiu, P. Sun, Y. Wang, L. Ma, C. Zhi, W. Mai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202210979.
- 26Q. Chen, K. Ouyang, Y. Wang, M. Chen, H. Mi, J. Chen, C. He, H. Li, D. Ma, P. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2406386.
- 27J. Huang, Y. Zhong, H. Fu, Y. Zhao, S. Li, Y. Xie, H. Zhang, B. Lu, L. Chen, S. Liang, J. Zhou, Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2406257.
- 28Y. Liu, Y. Ding, Z. Liu, X. Li, S. Tian, L. Fan, J. Xie, L. Xu, J. Lee, J. Li, L. Yang, PhotoniX. 2024, 5, 6.
- 29M. Liu, W. Yuan, X. Qu, X. Ru, X. Li, T. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, N. Zhang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 9611–9622.
- 30D. Li, Y. Zhong, X. Xu, D. Zhou, Y. Tang, L. Wang, S. Liang, B. Lu, Y. Liu, J. Zhou, Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 8855–8865.
- 31Y. Zhang, X. Li, L. Fan, Y. Shuai, N. Zhang, Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100824.
- 32R. Wang, M. Yao, M. Yang, J. Zhu, J. Chen, Z. Niu, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2221980120.
- 33P. Sun, L. Ma, W. Zhou, M. Qiu, Z. Wang, D. Chao, W. Mai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 18247–18255.
- 34X. Yu, M. Chen, Z. Li, X. Tan, H. Zhang, J. Wang, Y. Tang, J. Xu, W. Yin, Y. Yang, D. Chao, F. Wang, Y. Zou, G. Feng, Y. Qiao, H. Zhou, S.-G. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 17103–17113.
- 35S. Zhou, X. Meng, Y. Chen, J. Li, S. Lin, C. Han, X. Ji, Z. Chang, A. Pan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202403050.
- 36J.-L. Yang, T. Xiao, T. Xiao, J. Li, Z. Yu, K. Liu, P. Yang, H. J. Fan, Mater. 2024, 36, 2313610.
- 37J. Zhou, L. Zhang, M. Peng, X. Zhou, Y. Cao, J. Liu, X. Shen, C. Yan, T. Qian, Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200131.
- 38H. Li, Y. Ren, Y. Zhu, J. Tian, X. Sun, C. Sheng, P. He, S. Guo, H. Zhou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310143.
- 39Y. Hu, P. Wang, M. Li, Z. Liu, S. Liang, G. Fang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 8078–8093.
- 40Z. Liu, B. Sun, Y. Zhang, Q. Zhang, L. Fan, Prog Polym Sci. 2024, 152, 101817.
- 41Y. Zhang, Z. Liu, X. Li, L. Fan, Y. Shuai, N. Zhang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2302126.
- 42D. Han, C. Cui, K. Zhang, Z. Wang, J. Gao, Y. Guo, Z. Zhang, S. Wu, L. Yin, Z. Weng, F. Kang, Q.-H. Yang, Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 205–213.
- 43H. Wang, H. Li, Y. Tang, Z. Xu, K. Wang, Q. Li, B. He, Y. Liu, M. Ge, S. Chen, T. Hao, G. Xing, Y. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207898.
- 44C. Chang, S. Hu, T. Li, F. Zeng, D. Wang, S. Guo, M. Xu, G. Liang, Y. Tang, H. Li, C. Han, H.-M. Cheng, Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 680–694.