Synthesis and Modification of Formate Zr-MOF (ZrFA) Toward Scalable and Cost-Cutting Gas Separation
Dr. Xiao-Hong Xiong
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Key Laboratory for Preparation and Application of Ordered Structural Materials of Guangdong Province, Shantou University, Shantou, 515063 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLiang Song
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWei Wang
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Yan Zhu
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorLiu-Li Meng
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui-Ting Zheng
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zhang-Wen Wei
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Li-Lin Tan
Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Guangdong Laboratory, Guangzhou, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Xiao-Chun Huang
Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Key Laboratory for Preparation and Application of Ordered Structural Materials of Guangdong Province, Shantou University, Shantou, 515063 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Cheng-Yong Su
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xiao-Hong Xiong
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Key Laboratory for Preparation and Application of Ordered Structural Materials of Guangdong Province, Shantou University, Shantou, 515063 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLiang Song
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWei Wang
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Yan Zhu
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorLiu-Li Meng
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui-Ting Zheng
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zhang-Wen Wei
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Li-Lin Tan
Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Guangdong Laboratory, Guangzhou, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Xiao-Chun Huang
Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Key Laboratory for Preparation and Application of Ordered Structural Materials of Guangdong Province, Shantou University, Shantou, 515063 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Cheng-Yong Su
MOE Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, LIFM, IGCME, School of Chemistry, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
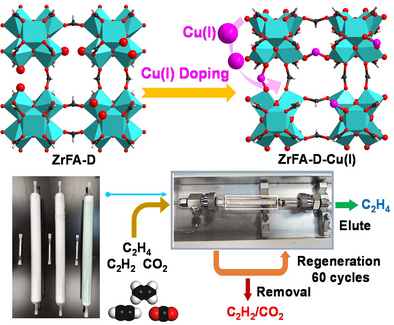
The mass production of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with affordable cost is highly demanding yet limited for commercial applications, e.g., purification of polymer-grade ethylene (C2H4) via acetylene (C2H2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) removal faces the challenge of developing low-cost and large-scale physisorbents with efficiency and recyclability. Herein, we developed a viable synthetic protocol to scale-up a series of ultramicroporous Zr-MOFs (ZrFA/ZrFA-D/ZrFA-D-Cu(I)) with the simplest monocarboxylate, formate (FA), through consecutive production by recycling solvent/modulator. Besides a size-exclusion effect disfavoring C2H4 adsorption, introduction of defective and Cu(I) sites was found to enhance gas affinity and uptake capacity. A comprehensive evaluation of C2H4 separation and economic efficiency has been proposed, suggesting the improvement of C2H2 uptake capacity is effective for the binary C2H2/C2H4 separation, while the separation process of the ternary C2H2/CO2/C2H4 mixtures depends on subtle tradeoff of complex factors and limited by challenging CO2/C2H4 separating. Notably, the large-scale separation has been testified to significantly improve separation efficiency, and the low-cost preparation benefits high economic efficiency. The distinct C2H2/C2H4/CO2 adsorption mechanism in ZrFA/ZrFA-D/ZrFA-D-Cu(I) has been elucidated by the theoretical calculations. This work may shed a light on the future C2H4 purification technology by pushing MOF-syntheses toward low-cost, scale-up, and recyclable production.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the Supporting Information of this article. Deposition Numbers 2127436 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge via the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC) and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202505978-supp-0001-SuppMat.pdf3.2 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1K. Adil, Y. Belmabkhout, R. S. Pillai, A. Cadiau, P. M. Bhatt, A. H. Assen, G. Maurin, M. Eddaoudi, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3402–3430.
- 2Q. Dong, X. Zhang, S. Liu, R.-B. Lin, Y. Guo, Y. Ma, A. Yonezu, R. Krishna, G. Liu, J. Duan, R. Matsuda, W. Jin, B. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22756–22762.
- 3K.-J. Chen, D. G. Madden, S. Mukherjee, T. Pham, K. A. Forrest, A. Kumar, B. Space, J. Kong, Q.-Y. Zhang, M. J. Zaworotko, Science 2019, 366, 241–246.
- 4H. Zeng, X.-J. Xie, T. Wang, M. Xie, Y. Wang, R.-J. Wei, W. Lu, D. Li, Nat. Chem. Eng. 2024, 1, 108–115.
10.1038/s44286-023-00004-2 Google Scholar
- 5K. Sumida, D. L. Rogow, J. A. Mason, T. M. McDonald, E. D. Bloch, Z. R. Herm, T.-H. Bae, J. R. Long, Chem. Rev.2012, 112, 724–781.
- 6H. Zeng, M. Xie, T. Wang, R.-J. Wei, X.-J. Xie, Y. Zhao, W. Lu, D. Li, Nature 2021, 595, 542–548.
- 7J. Cui, Z. Zhang, L. Yang, J. Hu, A. Jin, Z. Yang, Y. Zhao, B. Meng, Y. Zhou, J. Wang, Y. Su, J. Wang, X. Cui, H. Xing, Science 2024, 383, 179–183.
- 8L. Li, R.-B. Lin, R. Krishna, H. Li, S. Xiang, H. Wu, J. Li, W. Zhou, B. Chen, Science 2018, 362, 443–446.
- 9P.-Q. Liao, N.-Y. Huang, W.-X. Zhang, J.-P. Zhang, X.-M. Chen, Science 2017, 356, 1193–1196.
- 10W.-G. Cui, T.-L. Hu, X.-H. Bu, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1806445.
- 11X. Zhu, T. Ke, P. Han, Z. Zhang, Z. Bao, Y. Yang, Q. Ren, Q. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024;
- 12X. Zhang, Y.-L. Zhao, X.-Y. Li, X. Bai, Q. Chen, J.-R. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 19303–19309.
- 13S.-M. Wang, X.-T. Mu, H.-R. Liu, S.-T. Zheng, Q.-Y. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202207066.
- 14S. Tu, J. Yao, S. Zhao, D. Lin, L. Yu, X. Zhou, H. Wang, Y. Wu, Q. Xia, Small 2024, 20, 2307990.
- 15Y. Ye, S. Xian, H. Cui, K. Tan, L. Gong, B. Liang, T. Pham, H. Pandey, R. Krishna, P. C. Lan, K. A. Forrest, B. Space, T. Thonhauser, J. Li, S. Ma, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1681–1689.
- 16J. Pang, Z. Di, J.-S. Qin, S. Yuan, C. T. Lollar, J. Li, P. Zhang, M. Wu, D. Yuan, M. Hong, H.-C. Zhou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15020–15026.
- 17G. Huang, L. Yang, Q. Yin, Z.-B. Fang, X.-J. Hu, A.-A. Zhang, J. Jiang, T.-F. Liu, R. Cao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4385–4390.
- 18E. A. Dolgopolova, A. M. Rice, C. R. Martin, N. B. Shustova, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4710–4728.
- 19I. Abánades Lázaro, R. S. Forgan, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 380, 230–259.
- 20J. A. Mason, J. Oktawiec, M. K. Taylor, M. R. Hudson, J. Rodriguez, J. E. Bachman, M. I. Gonzalez, A. Cervellino, A. Guagliardi, C. M. Brown, P. L. Llewellyn, N. Masciocchi, J. R. Long, Nature 2015, 527, 357–361.
- 21Z. Chen, S. L. Hanna, L. R. Redfern, D. Alezi, T. Islamoglu, O. K. Farha, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 386, 32–49.
- 22B. Li, X. Cui, D. O'Nolan, H.-M. Wen, M. Jiang, R. Krishna, H. Wu, R.-B. Lin, Y.-S. Chen, D. Yuan, H. Xing, W. Zhou, Q. Ren, G. Qian, M. J. Zaworotko, B. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1704210.
- 23R.-B. Lin, L. Li, H.-L. Zhou, H. Wu, C. He, S. Li, R. Krishna, J. Li, W. Zhou, B. Chen, Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 1128–1133.
- 24F. Xiang, H. Zhang, Y. Yang, L. Li, Z. Que, L. Chen, Z. Yuan, S. Chen, Z. Yao, J. Fu, S. Xiang, B. Chen, Z. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202300638.
- 25Y. Peng, Z.-J. Guan, K.-K. Liu, D. Zhang, Y. Zhao, M. Jin, S. Wang, Y.u Fang, CCS Chem 2024, 0, 1–19.
- 26S.-Y. Li, S.-C. Fan, P. Zhang, W.-Y. Yuan, Y. Wang, Q.-G. Zhai, Chem 2024, 10, 2761–2775.
- 27Y.-Y. Xiong, C.-X. Chen, T. Pham, Z.-W. Wei, K. A. Forrest, M. Pan, C.-Y. Su, CCS Chem 2024, 6, 241–254.
- 28H. Sun, F. Chen, R. Chen, J. Li, L. Guo, Y. Liu, F. Shen, Q. Yang, Z. Zhang, Q. Ren, Z. Bao, Small 2023, 19, 2208182.
- 29Y. Wang, M. Fu, S. Zhou, H. Liu, X. Wang, W. Fan, Z. Liu, Z. Wang, D. Li, H. Hao, X. Lu, S. Hu, D. Sun, Chem 2022, 8, 3263–3274.
- 30S. Yang, A. J. Ramirez-Cuesta, R. Newby, V. Garcia-Sakai, P. Manuel, S. K. Callear, S. I. Campbell, C. C. Tang, M. Schröder, Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 121–129.
- 31Z. Xu, X. Xiong, J. Xiong, R. Krishna, L. Li, Y. Fan, F. Luo, B. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3163.
- 32Q. Dong, Y. Huang, K. Hyeon-Deuk, I.-Y. Chang, J. Wan, C. Chen, J. Duan, W. Jin, S. Kitagawa, Adv. Fun. Mater. 2022, 32, 2203745.
- 33Y. Jiang, Y. Hu, B. Luan, L. Wang, R. Krishna, H. Ni, X. Hu, Y. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 401.
- 34S. Mukherjee, N. Kumar, A. A. Bezrukov, K. Tan, T. Pham, K. A. Forrest, K. A. Oyekan, O. T. Qazvini, D. G. Madden, B. Space, M. J. Zaworotko, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 10902–10909.
- 35X. Li, Q. Ding, J. Liu, L. Dong, X. Qin, L. Zhou, Z. Zhao, H. Ji, S. Zhang, K. Chai, Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 4463–4469.
- 36L. Wang, Y. Zhang, P. Zhang, X. Liu, H. Xiong, R. Krishna, J. Liu, H. Shuai, P. Wang, Z. Zhou, J. Chen, S. Chen, S. Deng, J. Wang, AIChE J. 2024. 70, e18396.
- 37J.-W. Cao, S. Mukherjee, T. Pham, Y. Wang, T. Wang, T. Zhang, X. Jiang, H.-J. Tang, K. A. Forrest, B. Space, M. J. Zaworotko, K.-J. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6507.
- 38B. Wang, X.-L. Lv, D. Feng, L.-H. Xie, J. Zhang, M. Li, Y. Xie, J.-R. Li, H.-C. Zhou, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6204–6216.
- 39X.-H. Xiong, Z.-W. Wei, W. Wang, L.-L. Meng, C.-Y. Su, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 14354–14364.
- 40T. Devic, C. Serre, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6097–6115.
- 41W. Liang, R. Babarao, M. J. Murphy, D. M. D'Alessandro, Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 1516–1519.
- 42Y. Shi, Y. Xie, T. Alshahrani, B. Chen, CrystEngComm 2023, 25, 1643–1647.
- 43L. Sarkisov, A. Harrison, Mol. Simulat 2011, 37, 1248–1257.
- 44J.-R. Li, R. J. Kuppler, H.-C. Zhou, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1477.
- 45L. Zhang, K. Jiang, L. Yang, L. Li, E. Hu, L. Yang, K. Shao, H. Xing, Y. Cui, Y. Yang, B. Li, B. Chen, G. Qian, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 15995–16002.
- 46Z. Fang, B. Bueken, D. E. de Vos, R. A. Fischer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7234–7254.
- 47A. M. Abdel-Mageed, B. Rungtaweevoranit, M. Parlinska-Wojtan, X. Pei, O. M. Yaghi, R. J. Behm, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5201–5210.
- 48Y. Zhou, J. Zhang, L. Wang, X. Cui, X. Liu, S. S. Wong, H. An, N. Yan, J. Xie, C. Yu, P. Zhang, Y. Du, S. Xi, L. Zheng, X. Cao, Y. Wu, Y. Wang, C. Wang, H. Wen, L. Chen, H. Xing, J. Wang, Science 2021, 373, 315–320.
- 49Accelrys, Materials Studio Release Notes, Release 5.5.1, Accelrys Software, Inc., San Diego, 2010;
- 50L. Valenzano, B. Civalleri, S. Chavan, S. Bordiga, M. H. Nilsen, S. Jakobsen, K. P. Lillerud, C. Lamberti, Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 1700–1718.
- 51G. Gong, F. Xie, L. Wang, J. Wang, S. Chen, Synlett 2022, 34, 423–428;
- 52M. Fischer, F. Hoffmann, M. Fröba, ChemPhysChem 2010, 11, 2220–2229.