Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
FROM THE BENCH
Osteogenic differentiation of preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with lipopolysaccharide on modified poly-l-lactic-acid nanofibers
- Pages: 5343-5353
- First Published: 04 December 2018
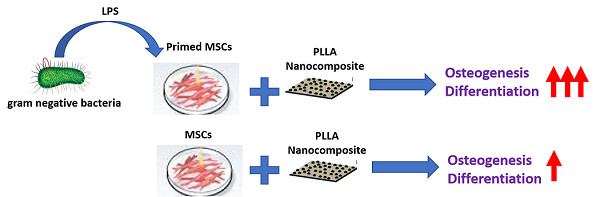
rimed mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on poly-l-lactic-acid nanoscaffold significantly enhanced MSCs proliferation and osteogenesis. Also the combination of LPS and electrospun nanofibers can provide a new and suitable matrix to support stem cells differentiation for bone tissue engineering.
RAPID COMMUNICATIONS
Invasiveness-triggered state transition in malignant melanoma cells
- Pages: 5354-5361
- First Published: 27 November 2018
Proinflammatory macrophages promote degenerative phenotypes in rat nucleus pulpous cells partly through ERK and JNK signaling
- Pages: 5362-5371
- First Published: 26 October 2018
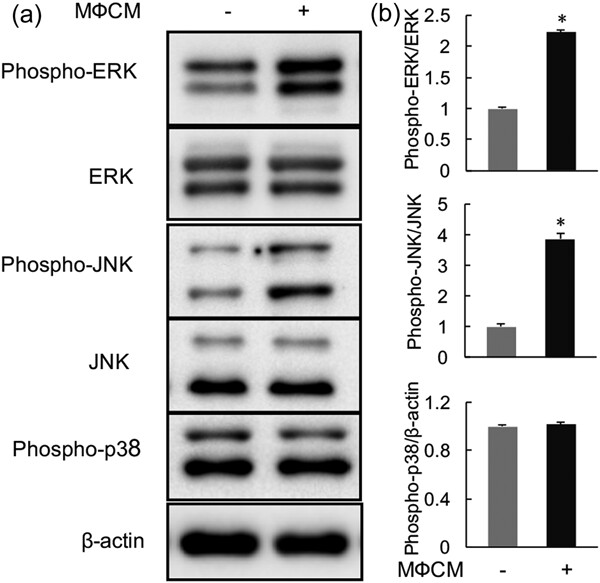
Proinflammatory macrophages inhibited the expression of matrix anabolic genes, but increased the expression of inflammation-related genes as well as matrix catabolic genes, in rat nucleus pulposus (rNP) cells. Proinflammatory macrophages promoted the degenerative phenotypes in rNP cells in part through activating ERK and JNK signaling. Targeting ERK and JNK pathways may serve as a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment of intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration.
MINI-REVIEWS
Melatonin and pancreatic cancer: Current knowledge and future perspectives
- Pages: 5372-5378
- First Published: 19 September 2018
Tumor suppressors BTG1 and BTG2: Beyond growth control
- Pages: 5379-5389
- First Published: 23 October 2018
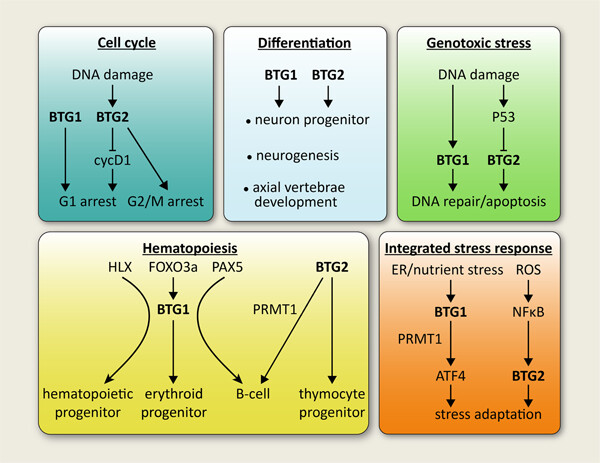
Members of the B-cell translocation gene (BTG) protein family are important regulators of cellular differentiation and maintenance of homeostasis under conditions of cellular stress. This review describes these and other cellular functions, and highlights their emerging roles as potential tumor suppressors.
Inflammation and pericarditis: Are neutrophils actors behind the scenes?
- Pages: 5390-5398
- First Published: 11 November 2018
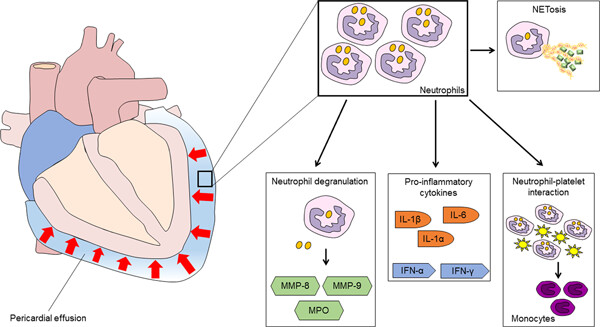
The morbidity of acute pericarditis is increasing overtime. Apart the known impairment of the adaptive immunity, recently a large body evidence indicated the central role of the innate immune system in the pathogenesis of recurrent pericarditis, starting from similarities with autoinflammatory diseases, with the “inflammasome” playing an important role. The role of the adaptive immune system in pericarditis cannot be reduced to a black or white issue as these mechanisms often overlap and new therapeutic strategies should be investigated in this direction.
The role of microRNAs regulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in breast cancer development, progression, and metastasis
- Pages: 5399-5412
- First Published: 22 November 2018

MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate several biological and physiological processes in mammalian cells, including cellular proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and metabolism. Recent studies have confirmed the alteration of them during the cancer development. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), belonging to the large family of proteases, have also been demonstrated to play crucial roles in tissue remodeling, and to support cancer progression and metastasis. There are several known miRNAs which regulate the MMP family and their expression. The expression profiles of miRNAs involved in MMP regulation, change during cancer progression and metastasis.
Real-time detection of breast cancer at the cellular level
- Pages: 5413-5419
- First Published: 26 October 2018
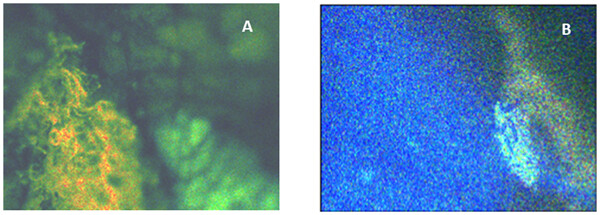
Novel optoelectronic instrumentation has been developed for the multispectral imaging of autofluorescence emitted by metabolic fluorophores. The images resolve individual cells while spectra are collected for each pixel in the images. To date, the system has been applied to fresh, ex vivo, human surgical specimens and has distinguished breast cancer (A) from benign tissue (B).
Osteochondral tissue cultures: Between limits and sparks, the next step for advanced in vitro models
- Pages: 5420-5435
- First Published: 26 October 2018
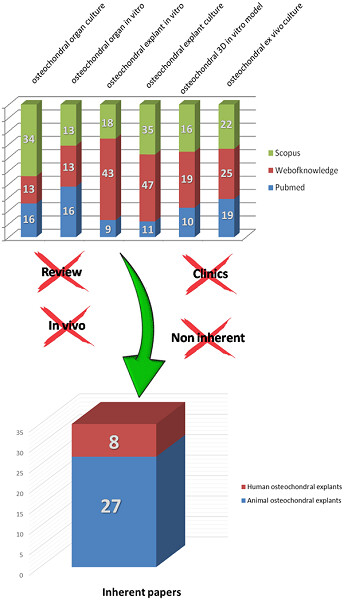
The development of innovative in vitro models is a growing need in the field of orthopedics and regenerative medicine. The present review aimed at critically revising the existing literature on osteochondral tissue culture models to identify a reference experimental set-up, applicable to the study of osteochondral lesions.
Exogenous nanoparticles and endogenous crystalline molecules as danger signals for the NLRP3 inflammasomes
- Pages: 5436-5450
- First Published: 28 October 2018
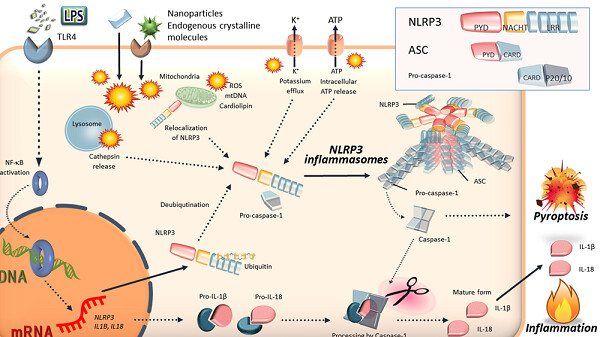
Inflammasome mechanisms are involved as some of the pathways of sterile inflammation. Nanoparticle-associated molecular patterns (NAMPs), which are mediated by synthetic materials, including nanomaterials and nanoparticles, are proposed to be new danger signals of NLRP3 inflammasomes. NLRP3: nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-, leucine-rich repeat-, and pyrin domain-containing 3
An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods
- Pages: 5451-5465
- First Published: 23 November 2018
REVIEW ARTICLES
Neural regulation of bone remodeling: Identifying novel neural molecules and pathways between brain and bone
- Pages: 5466-5477
- First Published: 27 January 2018
The role of DEAD-box RNA helicase p68 (DDX5) in the development and treatment of breast cancer
- Pages: 5478-5487
- First Published: 11 November 2018
The novel relationship between Sirt3 and autophagy in myocardial ischemia–reperfusion
- Pages: 5488-5495
- First Published: 28 November 2018
The miR-15a/16 gene cluster in human cancer: A systematic review
- Pages: 5496-5506
- First Published: 24 September 2018
Interferon-stimulated gene 15 enters posttranslational modifications of p53
- Pages: 5507-5518
- First Published: 14 October 2018
The genetic factors contributing to hypospadias and their clinical utility in its diagnosis
- Pages: 5519-5523
- First Published: 21 September 2018
Mutant p53R248Q downregulates oxidative phosphorylation and upregulates glycolysis under normoxia and hypoxia in human cervix cancer cells
- Pages: 5524-5536
- First Published: 10 September 2018
Curcumin nanofibers for the purpose of wound healing
- Pages: 5537-5554
- First Published: 28 October 2018
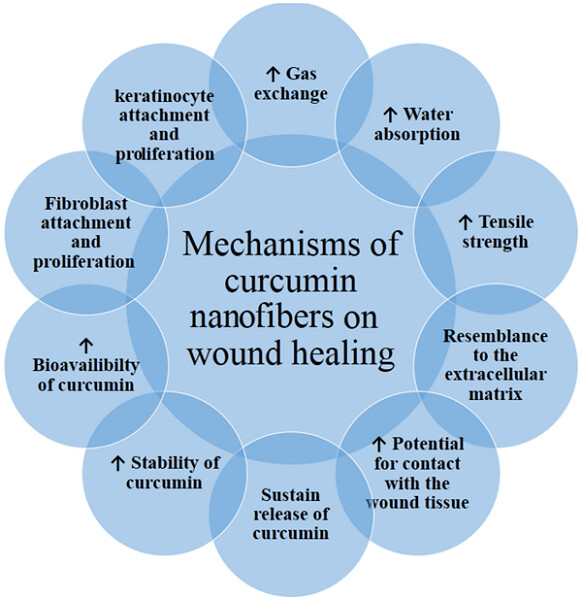
Curcumin is a phytochemical with diverse biological properties that could contribute to accelerated wound healing. Formulation of curcumin into nanofibers created using electrospinning process has been suggested as a promising strategy to improve the delivery of curcumin to wound tissue. Here, we review the extant evidence on the use of synthesized curcumin nanofibers for the purpose of wound healing.
Prognostic value of pretreatment systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with gastrointestinal cancers
- Pages: 5555-5563
- First Published: 23 October 2018
The mechanisms of DIRAS family members in role of tumor suppressor
- Pages: 5564-5577
- First Published: 14 October 2018
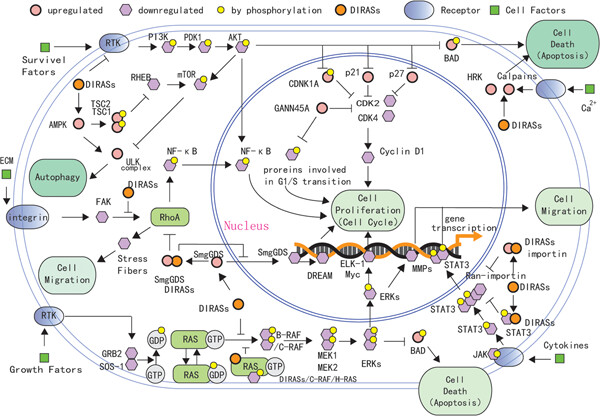
This review focuses on the latest research regarding the roles and mechanisms of the DIRAS family members in regulating Ras function, cancer development, assessing potential challenges, and providing insights into the possibility of targeting them for therapeutic use. Ingenuity signaling pathway analysis of cellular physiology (cell proliferation, migration, apoptosis, autophagy) by induction of DIRAS family members. DIRAS family members mainly regulate the PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK, NF-κB, and JAK/STAT signaling pathways to inhibit cell proliferation and migration (light green ellipse) and induce apoptosis and autophagy (dark green ellipse). (Orange round represent DIRAS family members, pink round represent molecular upregulated by DIRAS family members, purple hexagon represent molecular downregulated by DIRAS family members, small yellow round represent molecular by phosphorylation, blue oval represent transmembrane receptor, and green square represent extracellular factor).
Genetics and rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Iran
- Pages: 5578-5587
- First Published: 21 September 2018
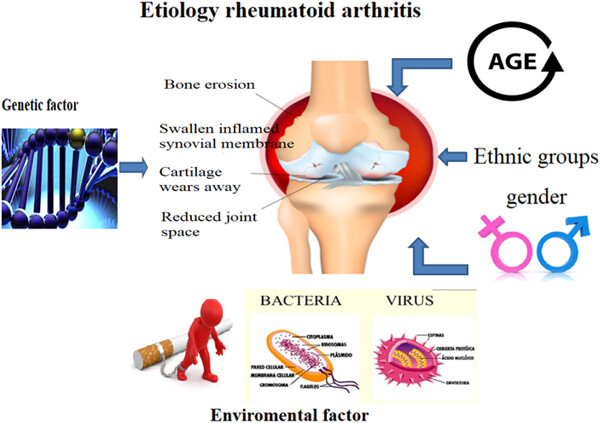
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disorder with a number of risk factors, including both genetic and environmental, and a number of RA risk associated genomic loci has been identified. In this review, we summarize the association of genetic factors with RA reported in population studies in Iran; no significant association was found between the majority of genetic factors identified in other populations and risk for RA in the Iranian subjects. This conflicting result could be due to the ethnic differences and diversity that are present in Iran and we conclude that there is a need to investigate larger groups of Iranian subjects, encompassing different regions of Iran, to either prove or refute these initial findings.
Circular RNA in cardiovascular disease
- Pages: 5588-5600
- First Published: 20 October 2018
Strategies to target energy metabolism in consensus molecular subtype 3 along with Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog mutations for colorectal cancer therapy
- Pages: 5601-5612
- First Published: 20 October 2018
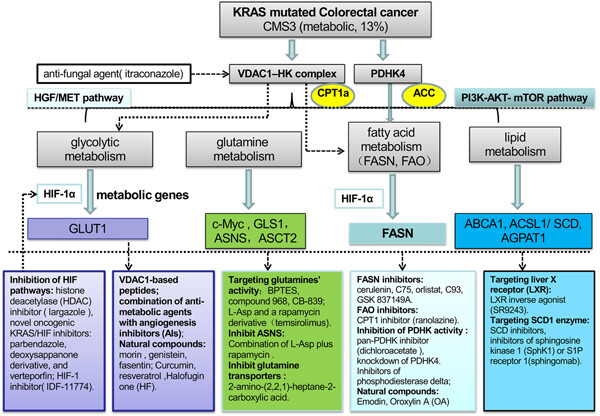
The interactions and mutational profile of metabolic oncoregulators with energy metabolism in mutated Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (KRAS) colorectal cancer.
Selective inhibitors or agents against metabolic targets or KRAS signaling may be clinically useful for consensus molecular subtype 3 tumor treatment through a cancer-patient-personalized approach.
Melatonin and cancer: From the promotion of genomic stability to use in cancer treatment
- Pages: 5613-5627
- First Published: 21 September 2018
Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer therapy: Strategies, challenges, and successes
- Pages: 5628-5642
- First Published: 27 November 2018
Curcumin: A naturally occurring autophagy modulator
- Pages: 5643-5654
- First Published: 21 September 2018
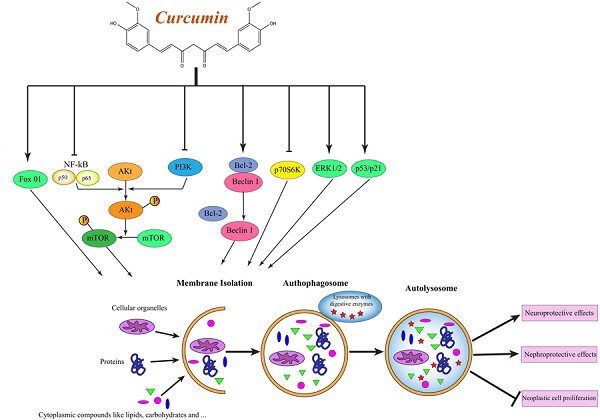
Autophagy is a self-degradative process that plays a pivotal role in several medical conditions associated with infection, cancer, neurodegeneration, aging, and metabolic disorders. Curcumin, as a hydrophobic polyphenol compound extracted from the known spice turmeric, is capable of triggering autophagy in several cancer cells.
Challenges facing antiangiogenesis therapy: The significant role of hypoxia-inducible factor and MET in development of resistance to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapies
- Pages: 5655-5663
- First Published: 04 December 2018
The role of microRNAs involved in PI3-kinase signaling pathway in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 5664-5673
- First Published: 29 November 2018
Interleukin-18 and diabetic nephropathy: A review
- Pages: 5674-5682
- First Published: 11 November 2018
Cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer: A review
- Pages: 5683-5699
- First Published: 20 October 2018
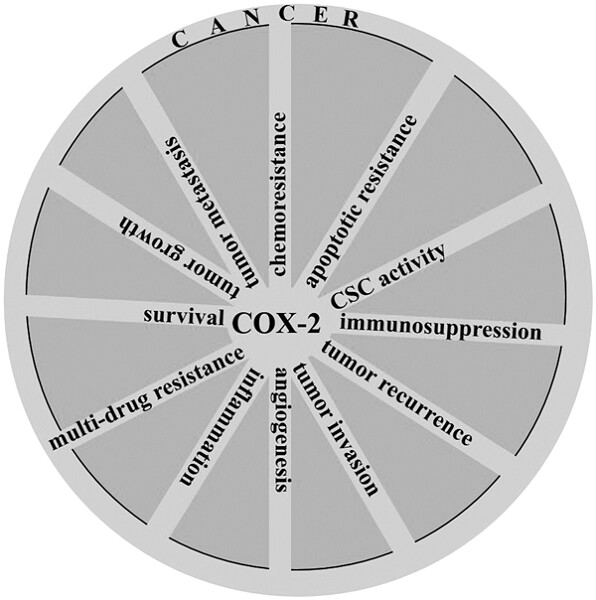
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is frequently expressed in many types of cancers exerting a pleiotropic and multifaceted role in genesis or promotion of carcinogenesis and cancer cell resistance to chemo- and radiotherapy. COX-2 is released by cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), macrophage type 2 (M2) cells, and cancer cells to the tumor microenvironment (TME). COX-2 induces cancer stem cell (CSC)-like activity and promotes apoptotic resistance, proliferation, angiogenesis, inflammation, invasion, and metastasis of cancer cells.
Tumor microenvironment: Interactions and therapy
- Pages: 5700-5721
- First Published: 30 October 2018
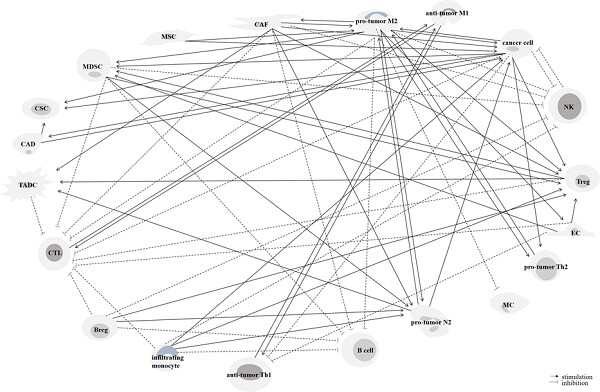
Cross-talks between various cells in the stroma of tumor microenvironment (TME) in favor of or against of tumor progression. Release of a variety of proteins, transcription factors, cytokines, chemokines, and so forth from cells inside the TME direct the fate of cancer. Concentration of these TME components along with temperature, circadian rhythm, and pH inside this microenvironment determine the fate of signaling. Complexity of the TME is a reason for failure of most of the conventional therapies against cancer.
Between an ugly truth and a perfect lie: Wiping off fearful memories using beta-adrenergic receptors antagonists
- Pages: 5722-5727
- First Published: 11 November 2018
Curcumin as an anti-inflammatory agent: Implications to radiotherapy and chemotherapy
- Pages: 5728-5740
- First Published: 14 October 2018
Hereditary breast cancer; Genetic penetrance and current status with BRCA
- Pages: 5741-5750
- First Published: 14 December 2018
CRISPR–Cas9 in genome editing: Its function and medical applications
- Pages: 5751-5761
- First Published: 26 October 2018
Immunological biomarkers of tolerance in human kidney transplantation: An updated literature review
- Pages: 5762-5774
- First Published: 26 October 2018
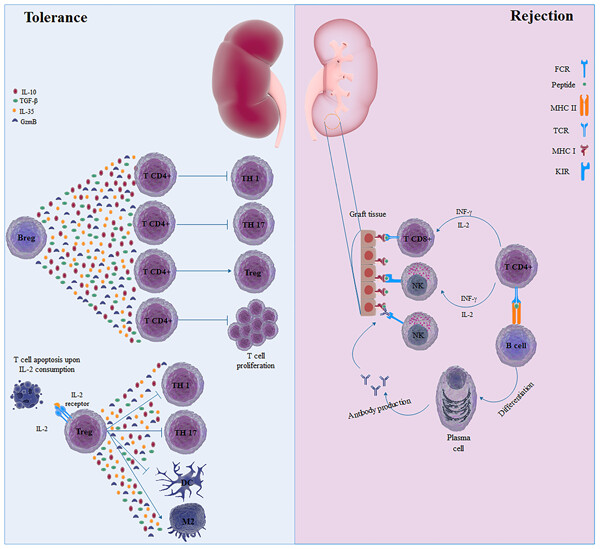
The half-life of transplanted kidneys is <10 years. Acute or chronic rejections have a negative impact on the transplant outcome. Therefore, achieving to allograft tolerance for improving long-term transplant outcome is a desirable goal of the transplantation field. The main reason for allograft loss is the immunological responses. In the present study, we are going to review and discuss the immunological characteristics of renal transplant recipients with rejection and compare them with tolerant subjects.
MicroRNAs and signaling networks involved in epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Pages: 5775-5785
- First Published: 11 November 2018
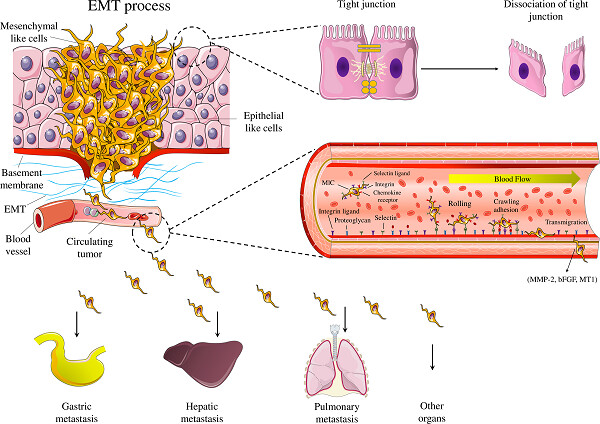
In nature, MT participates in many physiological and pathological processes including embryonic development, organogenesis, wound healing, and cancer metastasis. Many aspects regulate EMT including: transcription factors, gene expression patterns, and signaling pathway crosstalk. MicroRNAs as noncoding genes play a distinct role in the progression or suppression of EMT.
Narrative review of the effects of antidiabetic drugs on albuminuria
- Pages: 5786-5797
- First Published: 26 October 2018
Chronic myeloid leukemia with complex karyotypes: Prognosis and therapeutic approaches
- Pages: 5798-5806
- First Published: 14 November 2018
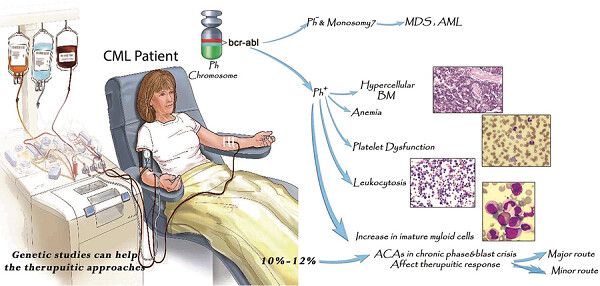
-
Additional chromosomal aberrations may cause different features on chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients according to Philadelphia translocation pattern.
-
Karyotype analysis in CML patients with complex karyotype shows unrandom pattern.
-
Incidence of additional chromosome and variant translocation is higher in blast crisis of CML.
Metabolic syndrome, Mediterranean diet, and polyphenols: Evidence and perspectives
- Pages: 5807-5826
- First Published: 14 October 2018
Predictive and therapeutic biomarkers in chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy: A clinical perspective
- Pages: 5827-5841
- First Published: 14 October 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Eucalyptol protects lungs against bacterial invasion through attenuating ciliated cell damage and suppressing MUC5AC expression
- Pages: 5842-5850
- First Published: 07 December 2017
Effects of shRNA-mediated silencing of PSMA7 on cell proliferation and vascular endothelial growth factor expression via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in cervical cancer
- Pages: 5851-5862
- First Published: 16 December 2017
Differential mechanisms of adenosine- and ATPγS-induced microvascular endothelial barrier strengthening
- Pages: 5863-5879
- First Published: 22 December 2017
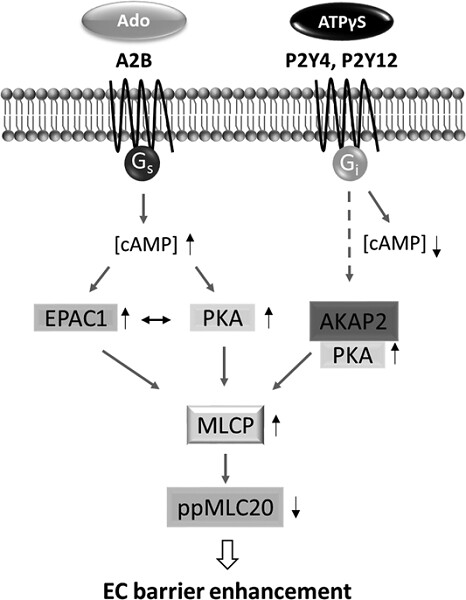
In the present study we define and compare the molecular mechanisms linking adenosine- and ATPγ-induced purinergic receptor activation and barrier strengthening in HLMVECs. We found that ATPγS-induced EC barrier enhancement is EPAC1-independent and is instead mediated by activation of PKA which is then guided by AKAP2, in a cAMP-independent mechanism, to activate MLCP and dephosphorylate MLC20 resulting in reduced EC contraction.
HIV-1 increases extracellular amyloid-beta levels through neprilysin regulation in primary cultures of human astrocytes
- Pages: 5880-5887
- First Published: 11 January 2018
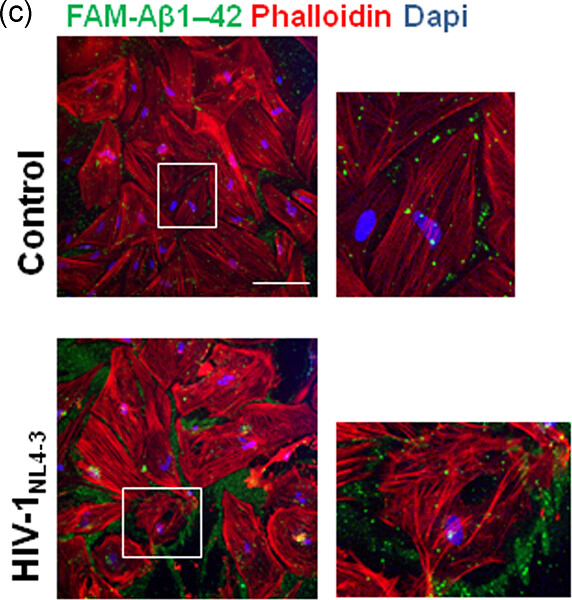
The increased life expectancy of HIV-1 infected people is accompanied by a higher prevalence of HIV-1 associated neurocognitive disorders. HIV-1 infection increases extracellular deposits of amyloid beta protein in primary cutures of human astrocytes. The presence of HIV-1 in the brain could contribute to the increase of the total burden of cerebral Aβ.
Inhibition of glycolytic metabolism in glioblastoma cells by Pt3glc combinated with PI3K inhibitor via SIRT3-mediated mitochondrial and PI3K/Akt–MAPK pathway
- Pages: 5888-5903
- First Published: 16 January 2018
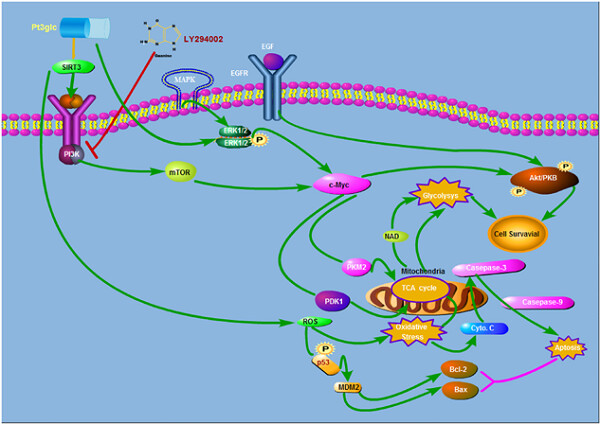
The possible interactions between different signaling pathways in glioblastoma cells treated with Pt3glc, which inhibited glioblastoma cell proliferation and promote apoptosis by regulating the expression of SIRT3 and down-regulating the p53 through ROS/p53-mediated mitochondrial pathway via SIRT3. The combination of Pt3glc with LY294002 could produce the synergistic effect to inhibit the SIRT3-mediated glycolytic as well as regulation of mTOR/Akt pathway. Pt3glc appears to play a central role in regulating SIRT3 for glioblastoma cell death, thus qualifies as a potential target for anti-cancer treatment.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: Effect of PLK1 inhibition on cisplatin-resistant gastric cancer cells
- Pages: 5904-5914
- First Published: 29 November 2018
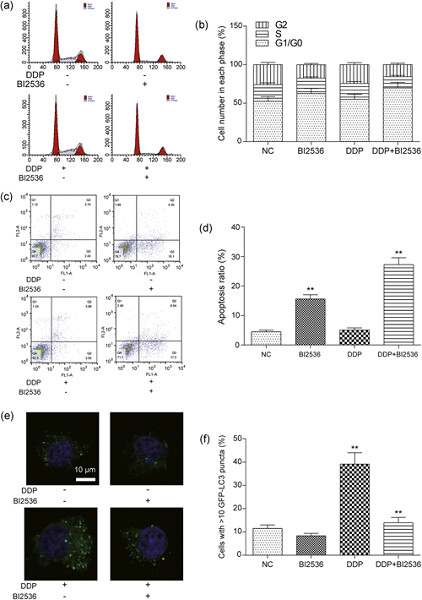
This study aims to investigate the effect of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibition on cisplatin (DDP)-resistant gastric cancer (GC) cells. Together, our experimental results illustrated that the DDP resistance of GC cells might be associated with the aberrant overexpression of PLK1. PLK1 inhibition, including si-PLK1 and BI2536 treatment, could restore the chemosensitivity of drug-resistant SGC-7901/DDP cells and enhance the efficacy of DDP, revealing the potential value of PLK1 inhibition in GC chemotherapy.
Retracted: MicroRNA-21 contributes to high glucose–induced fibrosis in peritoneal mesothelial cells in rat models by activation of the Ras–MAPK signaling pathway via Sprouty-1
- Pages: 5915-5925
- First Published: 04 December 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Purple sweet potato color attenuated NLRP3 inflammasome by inducing autophagy to delay endothelial senescence
- Pages: 5926-5939
- First Published: 26 December 2018
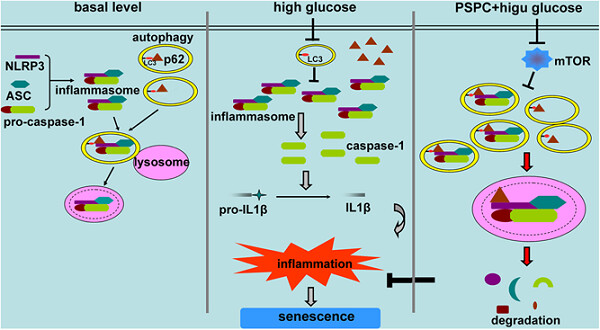
Purple sweet potato color (PSPC) delays endothelial senescence by promoting autophagy. Autophagy receptor colocalizes with nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine rich repeat and pyrin domain containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. Autophagosomes induced by PSPC target the NLRP3 inflammasome and deliver it to the lysosome for degradation.
Membrane-tethered Notch1 exhibits oncogenic property via activation of EGFR–PI3K–AKT pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 5940-5952
- First Published: 04 December 2018
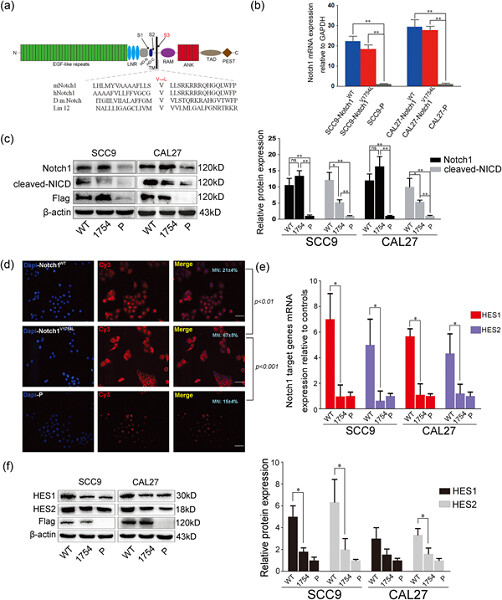
This was the first time that we clearly simulated the Notch1 activities by blocking its processing and determined the ability of unprocessed Notch1 to signal. These data emphasized the significant role of epidermal growth factor receptor–phosphoinositide 3-kinase–protein kinase B signaling in Notch1-mediated oncogenesis and could explain the potential mechanism underlying membrane-tethered Notch1-related phenotypic alterations.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: TNF-α–TNFR signal pathway inhibits autophagy and promotes apoptosis of alveolar macrophages in coal worker's pneumoconiosis
- Pages: 5953-5963
- First Published: 23 November 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
IL-6/YAP1/β-catenin signaling is involved in intervertebral disc degeneration
- Pages: 5964-5971
- First Published: 03 December 2018
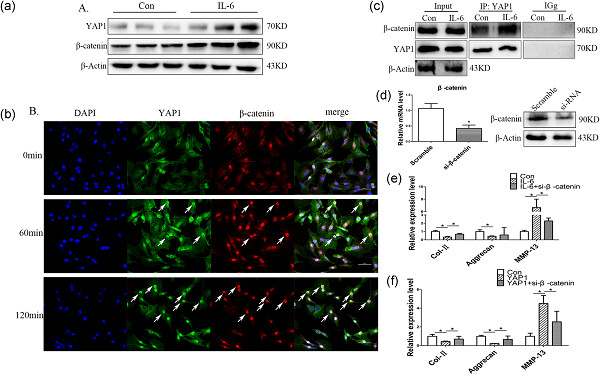
Overexpression yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) decreased Sox-9, Col-II, aggrecan expression, whereas increased matrix metalloproteinases 13 level in NP cells. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) enhanced YAP1 and β-catenin interaction and nuclear accumulation, β-catenin was essential for IL-6/YAP1 signaling induced intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). Moreover, we found that verteporfin, an FDA approved drug, effectively alleviated IDD development.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: Long noncoding RNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 impacts cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of glioma through regulating miR-139-5p/ CDK6
- Pages: 5972-5987
- First Published: 04 December 2018
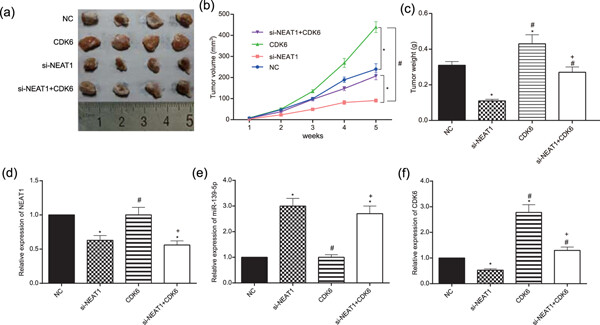
Graphical abstract
We aimed to explore the impact of long noncoding RNA (LncRNA) nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) on cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of glioma. The results of our study showed that LncRNA NEAT1 promotes cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of glioma through regulating miR-139-5p/CDK6 pathway.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Effects of inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system on reducing blood pressure and expression of inflammatory factors in CHD patients: A network meta-analysis
- Pages: 5988-5997
- First Published: 07 December 2018
MiR302c, Sp1, and NFATc2 regulate interleukin-21 expression in human CD4+CD45RO+ T lymphocytes
- Pages: 5998-6011
- First Published: 21 October 2018
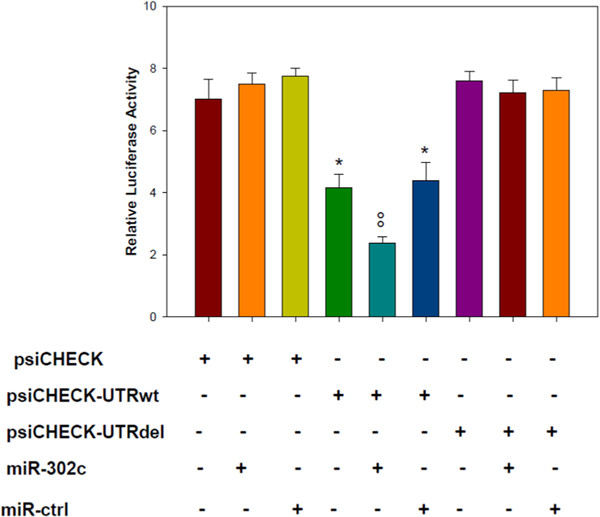
We defined the promoter region of human interleukin-21 (IL-21) gene and identified different mechanisms, including Sp1 and NFATc2 transcription factors. Acetylation status of histones and miR-302c is be involved in regulating the IL-21 expression. These molecular mechanisms could, therefore, be targeted to manipulate IL-21 expression in the context of disease treatment.
Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome attenuates spinal cord injury-induced lung injury in mice
- Pages: 6012-6022
- First Published: 27 December 2018
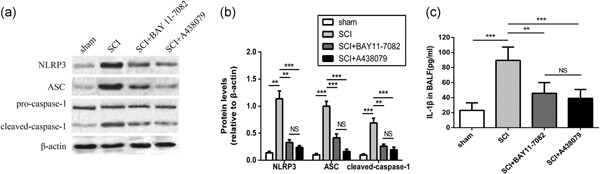
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is one kind of severe traumatic injury, resulting in systemic inflammatory response syndrome and secondary lung injury, which is an important pathological basis of respiratory complications. Our data reveal that nucleotide-binding domain-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome inhibitor BAY 11-7082 or A438079 attenuates the inflammatory response, reverses mitochondrial dysfunction, and subsequently alleviates secondary lung injury following SCI.
Downregulated microRNA-27b attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via activation of NF-E2-related factor 2 and inhibition of nuclear factor κB signaling pathway
- Pages: 6023-6032
- First Published: 24 December 2018
Downregulation of microRNA-592 protects mice from hypoplastic heart and congenital heart disease by inhibition of the Notch signaling pathway through upregulating KCTD10
- Pages: 6033-6041
- First Published: 27 November 2018
microRNA-186 inhibition of PI3K–AKT pathway via SPP1 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis in mice with osteoarthritis
- Pages: 6042-6053
- First Published: 30 November 2018
Glucagon attenuates lipid accumulation in cow hepatocytes through AMPK signaling pathway activation
- Pages: 6054-6066
- First Published: 27 November 2018
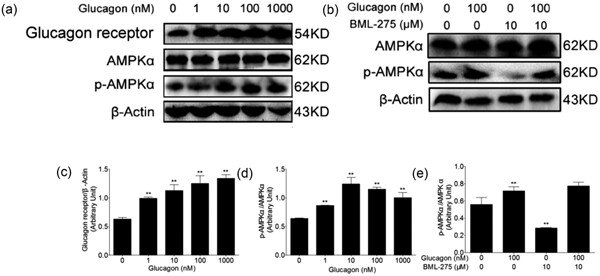
The ketotic cows displayed hepatic lipid metabolic disorder and high blood concentration of glucagon. The present study indicates that glucagon activates the AMPK signalling pathway to increase lipid oxidation and VLDL assembly and decrease lipid synthesis in cow hepatocytes, thereby reducing liver fat accumulation.
HDAC8 regulates canonical Wnt pathway to promote differentiation in skeletal muscles
- Pages: 6067-6076
- First Published: 24 September 2018
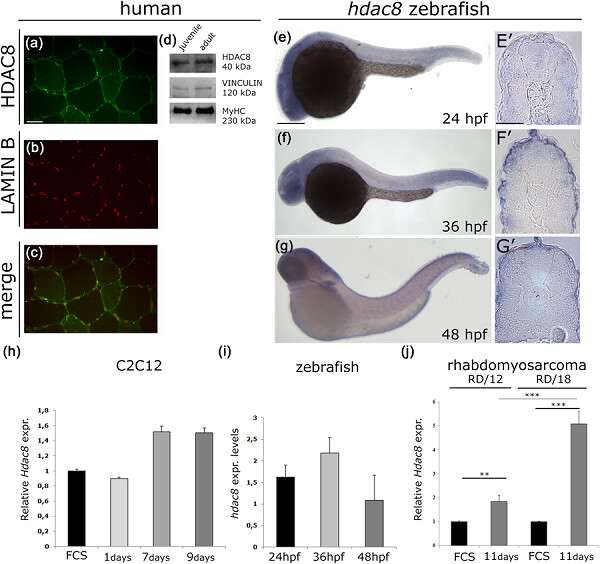
In this study, we have shown for the first time that histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) is expressed in human and zebrafish skeletal muscles specifically in an advanced stage of muscle differentiation. The HDAC8 inhibition through a specific PCI-34051 inhibitor in murine C2C12 myoblasts and zebrafish embryos led to skeletal muscle differentiation impairment. We also found a positive regulation of the canonical Wnt signaling by HDAC8 that might explain muscle differentiation defects.
The phosphorylation of Tudor-SN mediated by JNK is involved in the regulation of milk protein synthesis induced by prolactin in BMECs
- Pages: 6077-6090
- First Published: 06 September 2018
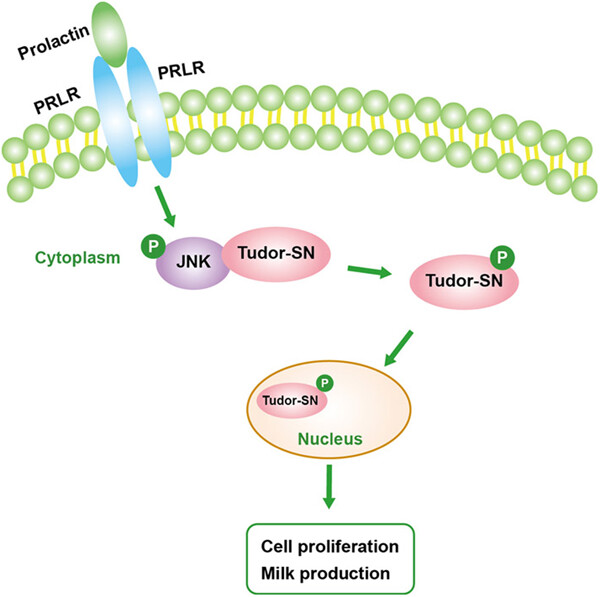
Prolactin (PRL) binding with PRL receptor stimulates the activation of JNK, which facilitates the formation of the complex of JNK-Tudor staphylococcal nuclease (Tudor-SN). JNK further activates the phosphorylation of Tudor-SN, which promotes the nuclear transport of Tudor-SN. Then, activated Tudor-SN positively regulates the proliferation of bovine mammary epithelial cells and milk production.
Pre-eclampsia onset and SPARC: A possible involvement in placenta development
- Pages: 6091-6098
- First Published: 13 November 2018
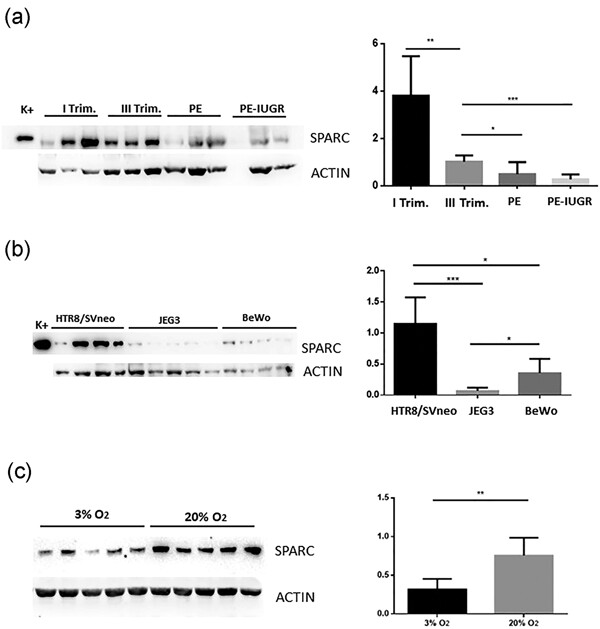
SPARC was mainly expressed in the villous and extravillous cytotrophoblastic cells in first trimester, whereas in PE, PE–IUGR and at term placentas, SPARC immunostaining was visible in both cytotrophoblastic cells and syncytiotrophoblast. SPARC expression significantly decreased in normal placenta from first to third trimester and a further significant reduction was demonstrated in PE and PE–IUGR. The latter downregulation of SPARC depends on hypoxic condition as shown by in vitro models.
Formulation and evaluation of anticancer and antiangiogenesis efficiency of PLA–PEG nanoparticles loaded with galbanic acid in C26 colon carcinoma, in vitro and in vivo
- Pages: 6099-6107
- First Published: 30 October 2018
In vivo microscopic and optical coherence tomography classification of neurotrophic keratopathy
- Pages: 6108-6115
- First Published: 21 September 2018
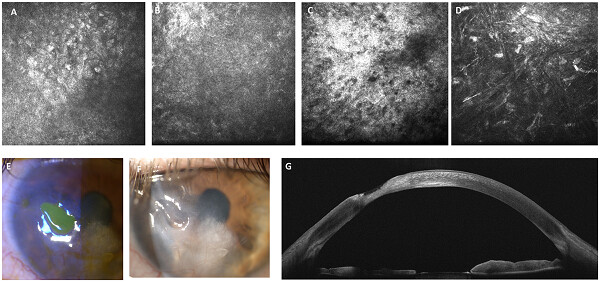
In vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM) and anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) are diagnostic devices useful to analyze neurotrophic keratopathy (NK). Based on the IVCM and AS-OCT results, a new classification of NK can be proposed. According to this classification, important information about prognosis, follow-up, and therapeutic approach can be achieved
LINC01433 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via modulating the miR-1301/STAT3 axis
- Pages: 6116-6124
- First Published: 14 October 2018
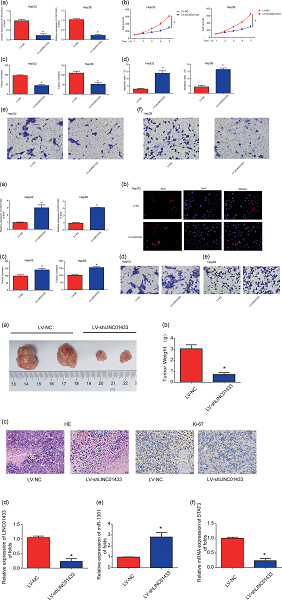
In our study, we found that silencing of LINC01433 repressed hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) progression by sponging miR-1301. In addition, STAT3 could act as a direct target of miR-1301, and miR-1301 mimics inhibited STAT3 expression significantly in HCC cells. Our data suggested that the LINC01433/miR-1301/STAT3 axis was involved in HCC progression and LINC01433 might serve as a biomarker for HCC.
Autophagy participates in cyst breakdown and primordial folliculogenesis by reducing reactive oxygen species levels in perinatal mouse ovaries
- Pages: 6125-6135
- First Published: 24 September 2018
Stromal vascular fraction cells plus sustained release VEGF/Ang-1-PLGA microspheres improve fat graft survival in mice
- Pages: 6136-6146
- First Published: 21 September 2018
Our study demonstrates that stromal vascular fraction cells combined with dual sustained release VEGF/ANG-1-PLGA microspheres can improve angiogenesis and graft survival. Nude mice treated with stromal vascular fraction cells and the microspheres developed in this study exhibited reduced fibrosis and increased microvascular density. These findings provide a practical method for improving graft survival after autologous fat transplantation.
Snake venoms promote stress-induced senescence in human fibroblasts
- Pages: 6147-6160
- First Published: 14 October 2018
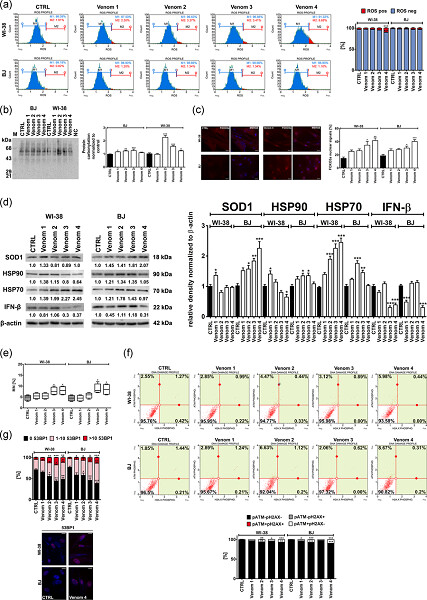
In the current study, we show that subtoxic concentrations of selected snake venoms promote FOXO3a-mediated oxidative stress response and to a lesser extent DNA damage response that results in changes in the levels of cell cycle regulators leading to cell cycle arrest and stress-induced premature senescence (SIPS) in human fibroblasts in vitro.
Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 modulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating miR-23a-3p/SMC1A in acute myeloid leukemia
- Pages: 6161-6172
- First Published: 24 September 2018
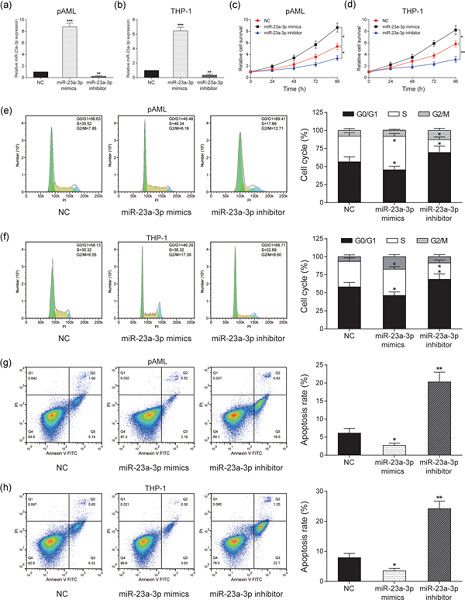
- 1.
This study illustrates the molecular interaction between nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 (NEAT1), miR-23a, and structural maintenance of chromosome 1 alpha (SMC1A) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
- 2.
Reduced expression of NEAT1 induced the tumorigenesis and progression of AML through the miR-23a-3p/SMC1A axis.
- 3.
These results suggest that this axis can be used as a promising therapeutic target to mitigate the progression of AML.
HOTAIR promotes osteosarcoma development by sponging miR-217 and targeting ZEB1
- Pages: 6173-6181
- First Published: 26 October 2018
microRNA-874 inhibition targeting STAT3 protects the heart from ischemia–reperfusion injury by attenuating cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a mouse model
- Pages: 6182-6193
- First Published: 28 October 2018
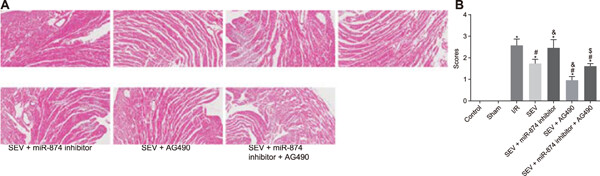
The findings indicate microRNA (miR)-874 as a contributory role in cardiac ischemia–reperfusion injury (I/R) injury, with miR-874 inhibition alleviating cardiac I/R injury in mice following sevoflurane pretreatment by targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) through the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/STAT3 signaling pathway.
Cinnamaldehyde regulates H2O 2-induced skeletal muscle atrophy by ameliorating the proteolytic and antioxidant defense systems
- Pages: 6194-6208
- First Published: 14 October 2018
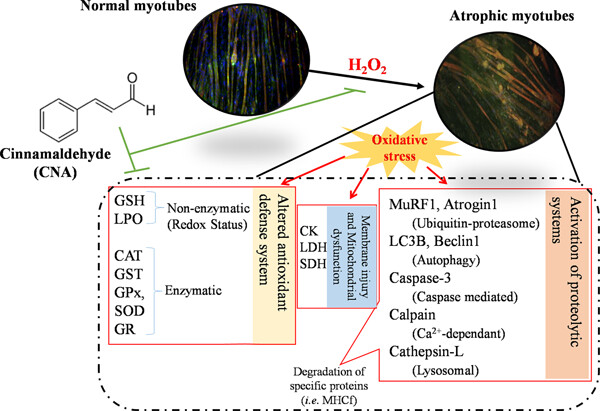
H2O 2 alters MuRF1/LC3b/cathepsin/calpain/caspase-3-dependent proteolytic systems. Cinnamaldehyde (CNA) ameliorates the altered proteolytic systems. CNA normalizes the antioxidant enzymes level in H 2O 2-treated cells. CNA shows its protective effect against H 2O 2-induced myotube atrophy by suppressing multiple dysregulated pathways
Distinct Tie2 tyrosine phosphorylation sites dictate phenotypic switching in endothelial progenitor cells
- Pages: 6209-6219
- First Published: 24 September 2018
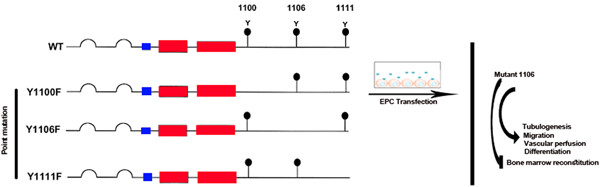
Tie2 C-terminal tyrosine 1106 is indispensable for the maintenance of the stemness features of bone marrow endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). Missense mutation in the codon encoding tyrosine 1106 of Tie2 prompts a phenotypic switching in bone marrow EPCs. Tie2 C-terminal tyrosine 1106 restores the potency of bone marrow–derived EPCs for bone marrow reconstitution after myelosuppression.
Melatonin defends mouse oocyte quality from benzo[ghi]perylene-induced deterioration
- Pages: 6220-6229
- First Published: 14 October 2018
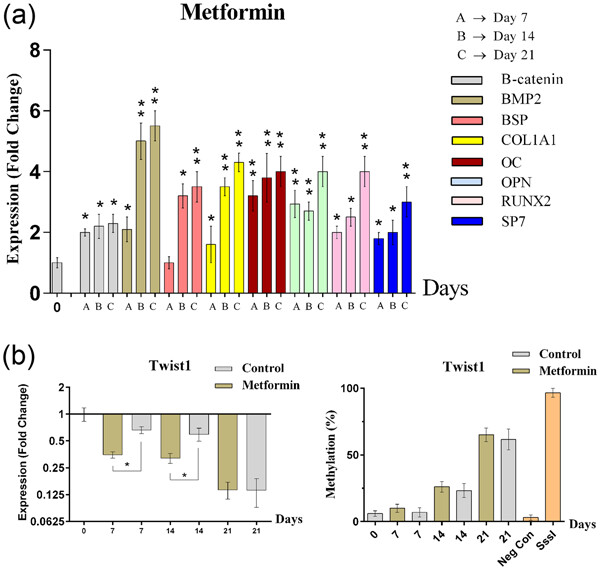
Gene expression of TWIST1 and ZBTB16 is regulated by methylation modifications during the osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
- Pages: 6230-6243
- First Published: 24 September 2018
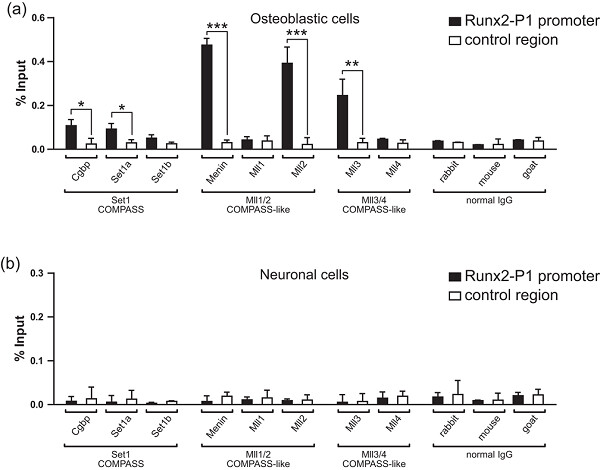
Mll-COMPASS complexes mediate H3K4me3 enrichment and transcription of the osteoblast master gene Runx2/p57 in osteoblasts
- Pages: 6244-6253
- First Published: 07 September 2018
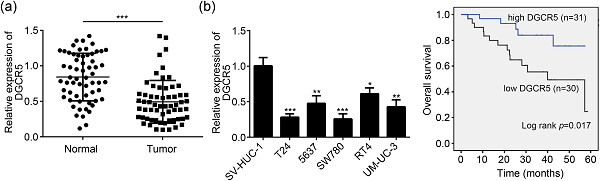
Upregulation of lncRNA DGCR5 correlates with better prognosis and inhibits bladder cancer progression via transcriptionally facilitating P21 expression
- Pages: 6254-6262
- First Published: 21 September 2018
TGF-β1-PML SUMOylation-peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 (Pin1) form a positive feedback loop to regulate cardiac fibrosis
- Pages: 6263-6273
- First Published: 24 September 2018
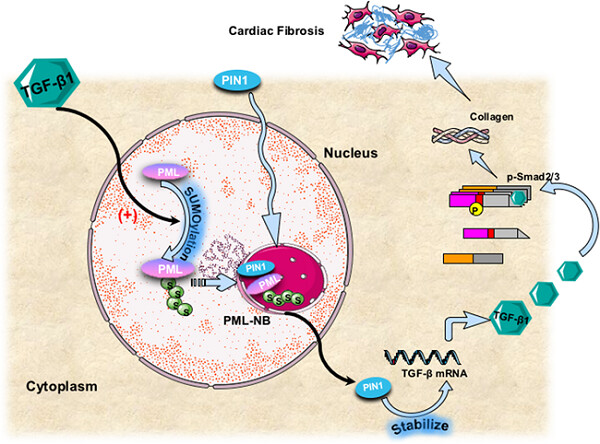
Exogenous transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β1) is added into neonatal mouse cardiac fibroblasts, triggering promyelocytic leukemia (PML) SUMOylation and PML nuclear bodies (NBs) formation. Meanwhile, Pin1 is recruited into the PML-NBs and colocated in the nuclear body. Then, the messenger RNA level and protein level of TGF-β1 are both increased, activating the TGF-β/Smad-2/3 signaling pathway, increasing collagen formation, and ultimately leading to cardiac fibrosis.
Lysophosphatidic acid induces the crosstalk between the endovascular human trophoblast and endothelial cells in vitro
- Pages: 6274-6285
- First Published: 26 October 2018
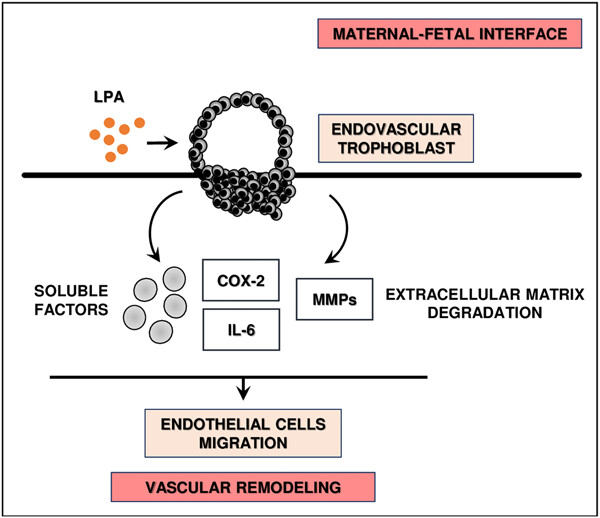
The current study demonstrates that lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) promotes the interaction between the endovascular human first trimester trophoblast and endothelial cells at the maternal–fetal interface. This crosstalk depends on the secretion of LPA-induced trophoblast soluble factors belonging to cyclooxygenase-2 and IL-6 pathways. Our findings shed new light on the significance of LPA signaling in the vascular events that lead to a successful pregnancy.
Tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 1 promotes hypoxic gene induction and cell migration in colon cancer
- Pages: 6286-6297
- First Published: 26 October 2018
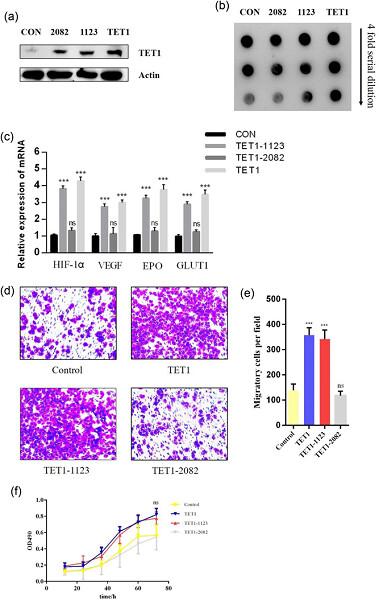
In this paper, we revealed a mechanism that ten-eleven translocation 1 (TET1) regulated hypoxia-inducible factor-1-alpha (HIF-1α) and targeted hypoxia-responsive genes through interfering the binding of HIF-1α to their hypoxia-responsive elements by enhancing promoter methylation. We also identified two novel TET1 gene mutations in 120 paired tumor/normal tissue specimens and found that TET1 E2082K mutant blocked the TET1-enhanced migration. Because hypoxia prevails on solid tumors, by demonstrating the mechanism that TET1 regulated HIF-1α-responsive genes, we showed that epigenetic mechanism and tumor microenvironment-driven models coexisted and mutually affected.
Curcumin attenuates proangiogenic and proinflammatory factors in human eutopic endometrial stromal cells through the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Pages: 6298-6312
- First Published: 27 September 2018
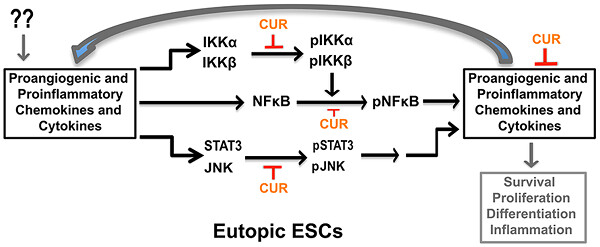
Endometriosis is a chronic gynecological inflammatory disorder in which immune system dysregulation is thought to play a role in its initiation and progression. In the current study, we examined the effects of curcumin (CUR, diferuloylmethane ), an anti-inflammatory folk medicine in Asian countries, on eutopic endometrial stromal cells derived from woman with or without endometriosis. The basal level of proinflammatory and proangiogenic chemokines and cytokines expression were higher in primary cultures of stromal cells derived from eutopic endometrium of endometriosis (EESC) subjects compared with normal endometrial stromal cells (NESC). The treatment of EESC and NESC with CUR significantly and dose-dependently reduced chemokine and cytokine secretion over the time course. Notably, CUR treatment significantly decreased phosphorylation of the IKKα/β, NF-κB, STAT3, and JNK signaling pathways under these experimental conditions. Taken together, our findings suggest that CUR has therapeutic potential to reduce inflammation associated with endometriosis.
Protein malnutrition mitigates the effects of a high-fat diet on glucose homeostasis in mice
- Pages: 6313-6323
- First Published: 14 October 2018
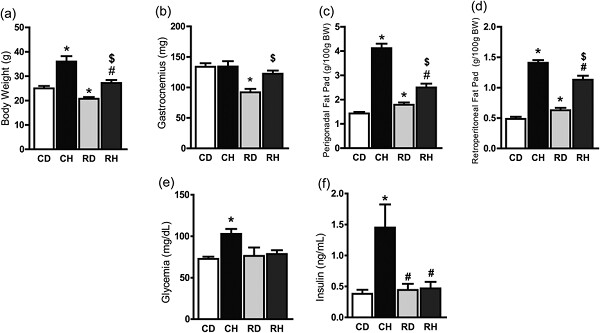
Evidence suggests that overfeeding after nutrient deprivation may favor the disruption of metabolism and, therefore, favor the development of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and comorbidities. In animal models, the effects of fat-enriched diets in protein-restricted mice are still controversial. Protein restriction programmed skeletal muscle metabolism increased mitochondrial function and prevented fat accumulation and increment on fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentration.
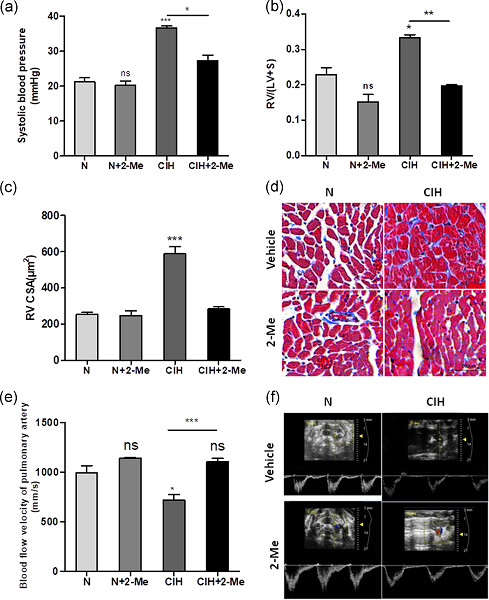
2-Methoxyestradiol attenuates chronic-intermittent-hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension through regulating microRNA-223
- Pages: 6324-6335
- First Published: 24 September 2018
1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4-heptadien-3-one induces lung cancer cell apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways
- Pages: 6336-6349
- First Published: 24 September 2018
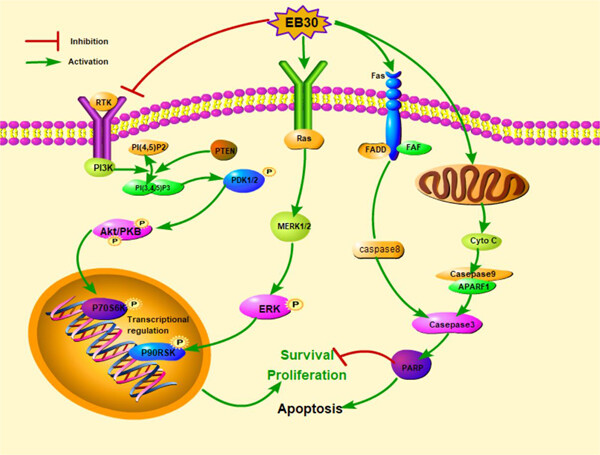
The results of this study indicated that EB30 could decrease cell viability, induce apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest. The induction of apoptosis was found to be mediated through the mitochondrial intrinsic pathway and extrinsic pathway. The apoptotic effects of EB30 were mediated by suppressing the PI3K/Akt pathway, whereas activating the ERK1/2 signaling.
Identification of a novel cell cycle-related gene signature predicting survival in patients with gastric cancer
- Pages: 6350-6360
- First Published: 21 September 2018
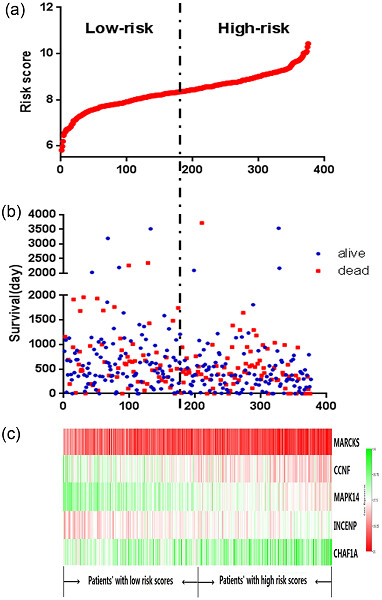
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most fatal cancers in the world. Thousands of biomarkers have been explored that might be related to survival and prognosis via database mining. We aimed to develop a novel gene signature to improve the prognosis prediction of GC. In conclusion, we developed a five-gene signature related to the cell cycle that can predict survival for GC.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 contributes to cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer through EGFR activation
- Pages: 6361-6370
- First Published: 19 September 2018
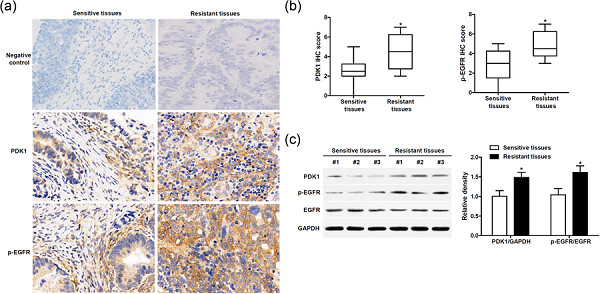
Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1) was upregulated in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer. PDK1 knockdown in resistant ovarian cancer cells led to increased sensitivity to cisplatin-induced cell death and apoptosis, and reversed the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cell motility. There was a feed-forward PDK1/EGFR crosstalk in ovarian cancer cells that drives cisplatin resistance in terms of both cellular growth and EMT.
Curcumin induces concentration-dependent alterations in mitochondrial function through ROS in C2C12 mouse myoblasts
- Pages: 6371-6381
- First Published: 24 September 2018
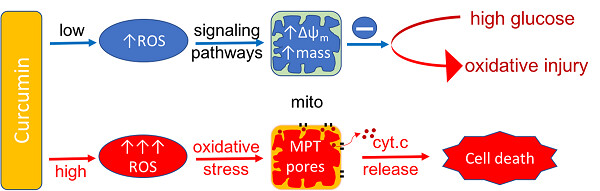
Curcumin regulates cellular redox status depending on cell sensitivity and/or curcumin concentration in normal cells. Mitochondria respond differentially depending on curcumin concentration-dependent induction of ROS. Curcumin may be an effective therapeutic target for diabetes and other mitochondrial diseases when used in low concentrations.
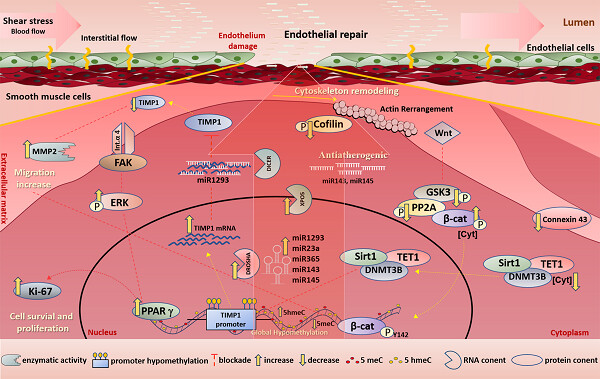
Laminar shear stress-provoked cytoskeletal changes are mediated by epigenetic reprogramming of TIMP1 in human primary smooth muscle cells
- Pages: 6382-6396
- First Published: 21 September 2018
Understanding molecular biology of codon usage in mitochondrial complex IV genes of electron transport system: Relevance to mitochondrial diseases
- Pages: 6397-6413
- First Published: 11 November 2018
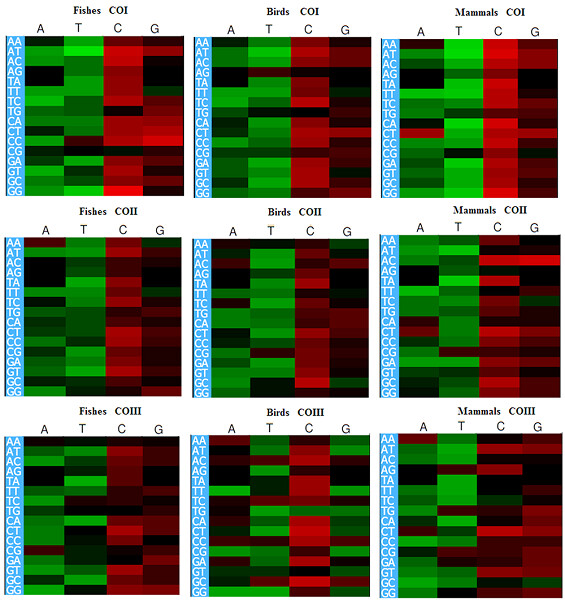
The mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase (CO) genes are involved in complex IV of the electron transport system (ETS), and dysfunction of CO genes leads to several diseases. nHowever, no work has been reported on the codon usage pattern of these genes. We used bioinformatic methods to analyze the compositional properties and the codon usage pattern of the COI, COII, and COIII genes in fishes, birds, and mammals to understand the similarities and dissimilarities of codon usage in these genes, which gave an insight into the molecular biology of these genes.
Iturin A-like lipopeptides from Bacillus subtilis trigger apoptosis, paraptosis, and autophagy in Caco-2 cells
- Pages: 6414-6427
- First Published: 21 September 2018
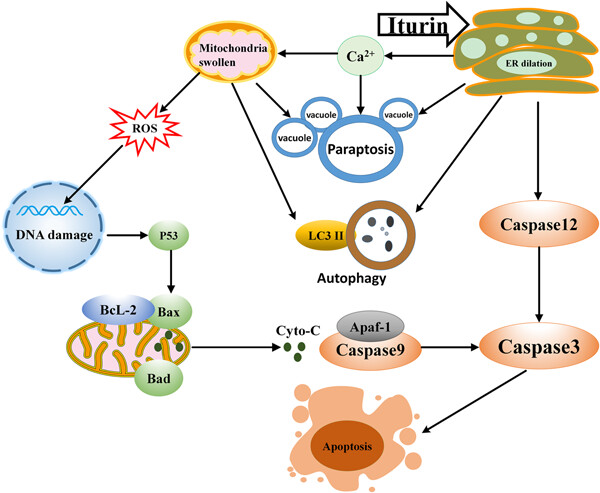
Endoplasmic reticulum stress caused by Iturin A-like lipopeptides human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells the appeared reaction, resulting in the increase of intracellular calcium and swelling and dysfunction of mitochondria. A large number of vacuoles appeared in the cell, and the parabed apoptosis occurred. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) was released in mitochondria, DNA was damaged and mitochondria permeability increased. Then the endogenous apoptosis pathway is triggered. A large number of damaged organelles and proteins in the cell lead to the activation of autophagy pathway.
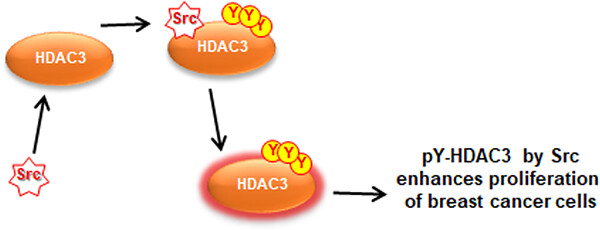
Tyrosine phosphorylation of HDAC3 by Src kinase mediates proliferation of HER2-positive breast cancer cells
- Pages: 6428-6436
- First Published: 14 October 2018
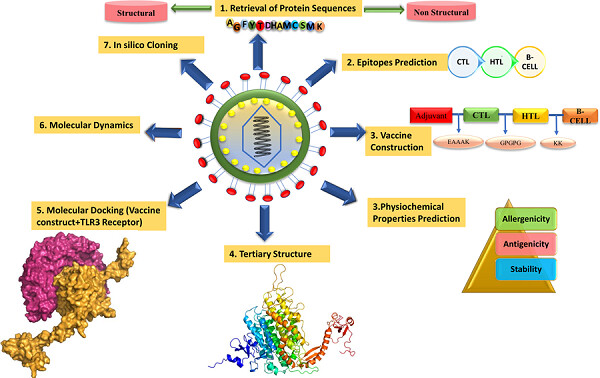
Contriving multiepitope subunit vaccine by exploiting structural and nonstructural viral proteins to prevent Epstein–Barr virus-associated malignancy
- Pages: 6437-6448
- First Published: 26 October 2018
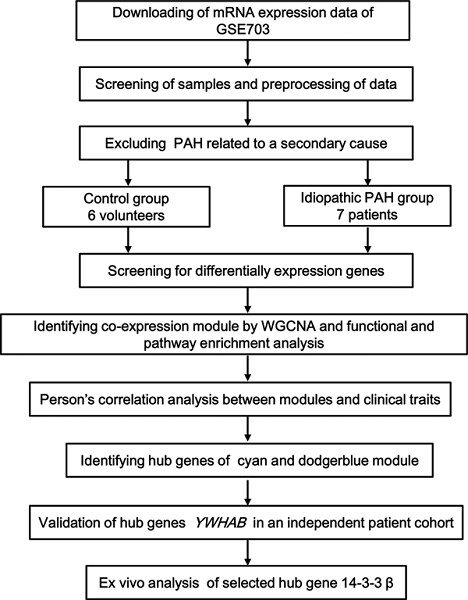
Integrated bioinformatic analysis reveals YWHAB as a novel diagnostic biomarker for idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Pages: 6449-6462
- First Published: 14 October 2018
Tannic acid protects against experimental acute lung injury through downregulation of TLR4 and MAPK
- Pages: 6463-6476
- First Published: 24 September 2018
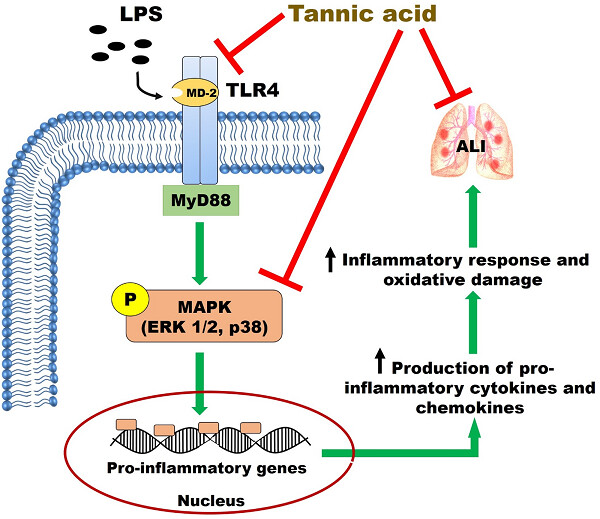
Acute lung injury and its severe form acute respiratory distress syndrome remain a major cause of morbidity and mortality in critically ill patients, and no specific therapies are still available to control the mortality rate. In this study, our results demonstrated that tannic acid, a natural polyphenol treatment attenuated lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response and oxidative stress by blocking toll-like receptor 4 expression and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation
Helvolic acid attenuates osteoclast formation and function via suppressing RANKL-induced NFATc1 activation
- Pages: 6477-6488
- First Published: 20 October 2018
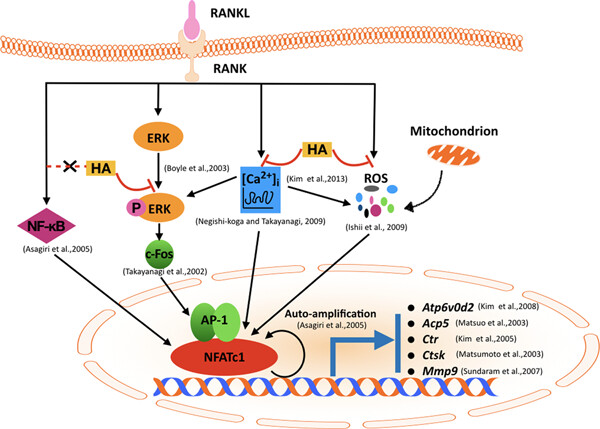
Helvolic acid (HA), a mycotoxin originally isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus, is demonstrated to be capable of significantly inhibiting receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vitro by suppressing nuclear factor of activated T cells 1 (NFATc1) activation without affecting nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation. Mechanistically, HA greatly attenuated multiple upstream pathways of NFATc1, including extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation, c-Fos signaling, and intracellular Ca2+oscillation. Taken together, HA can be potentially used in the development of a novel drug for osteoclast-related bone diseases.
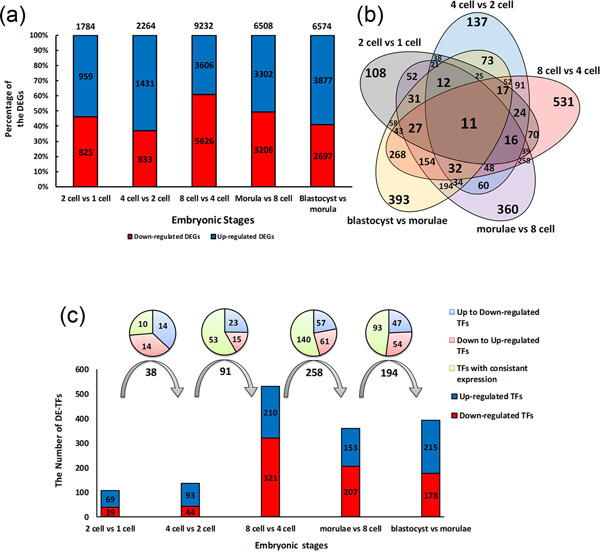
Dynamics changes in the transcription factors during early human embryonic development
- Pages: 6489-6502
- First Published: 24 September 2018
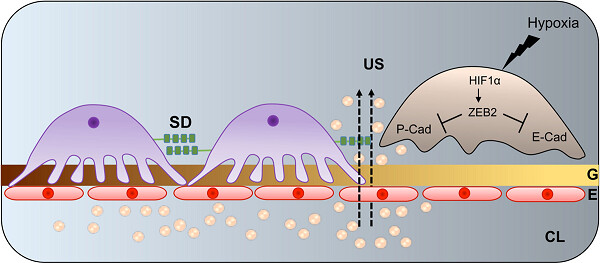
Hypoxia induces ZEB2 in podocytes: Implications in the pathogenesis of proteinuria
- Pages: 6503-6518
- First Published: 21 September 2018
Prognostic value of aberrantly expressed methylation gene profiles in lung squamous cell carcinoma: A study based on The Cancer Genome Atlas
- Pages: 6519-6528
- First Published: 24 September 2018
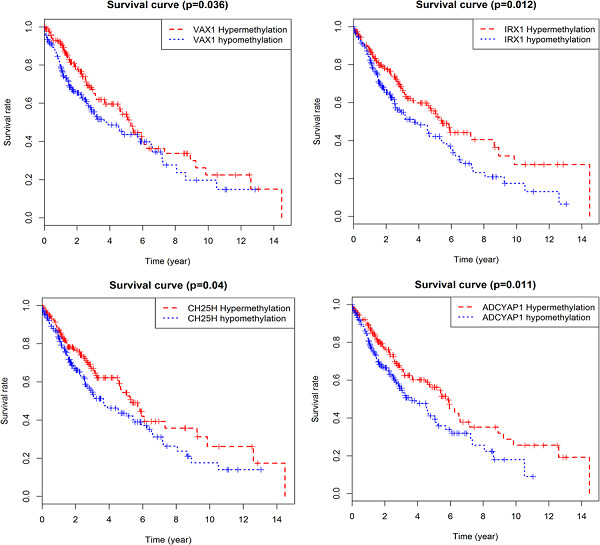
In this study, we performed whole-genome methylation analysis of LUSC patients based on the TCGA database. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that the prognostic risk model constructed by four abnormally methylated genes (VAX1, CH25H, ADCYAP1, and IRX1) proved to be an independent prognostic factor for LUSC. Also, the expression and methylation levels of the key gene IRX1 are significantly correlated with prognosis and are negatively correlated with the methylation of the site cg09232937 and cg10530883. This study is based on high-throughput data mining and provides an effective bioinformatics basis for further understanding the pathogenesis and prognosis of LUSC, which has important theoretical significance for follow-up studies on LUSC.
USP49 inhibits ischemia–reperfusion-induced cell viability suppression and apoptosis in human AC16 cardiomyocytes through DUSP1–JNK1/2 signaling
- Pages: 6529-6538
- First Published: 24 September 2018
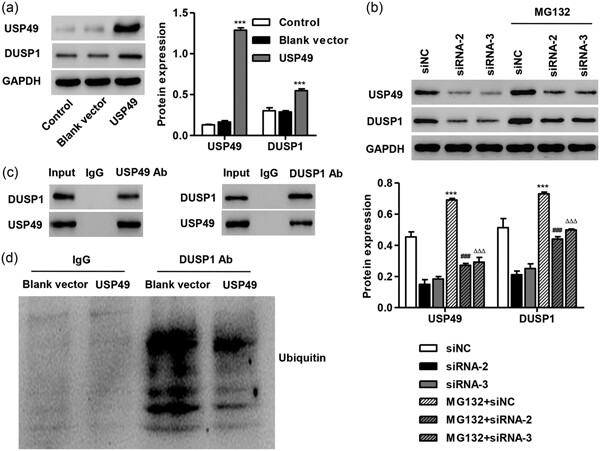
Inhibiting c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1)/2 activation significantly inhibited ubiquitin-specific peptidase 49 (USP49) knockdown-induced the cell viability inhibition, apoptosis, and the JNK1/2 activation in AC16 cardiomyocytes. USP49 positively regulated dual-specificity protein phosphatases 1 (DUSP1) expression through deubiquitinating DUSP1. USP49 as a novel regulator of DUSP1–JNK1/2 signaling pathway with a protective role in cardiac I/R injury.
Efficient penetration of Scp01-b and its DNA transfer abilities into cells
- Pages: 6539-6547
- First Published: 19 September 2018
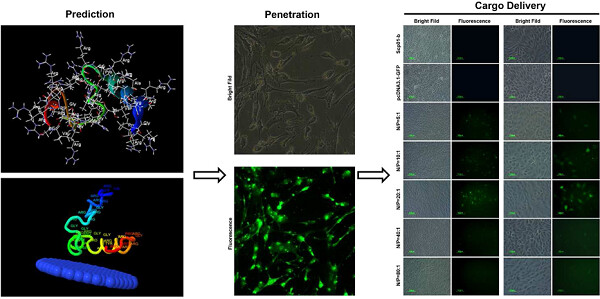
New peptide Scp01-b with more residues compared to conventional cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), and this cell-permeable peptide can efficiently mediate nucleic acid intracellular delivery, acting as a powerful DNA carrier for non-viral-based reprogramming in regenerative medicine and the field of gene editing research
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: LncRNA CRNDE promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through regulating miR-203/ BCAT1 axis
- Pages: 6548-6560
- First Published: 19 December 2018
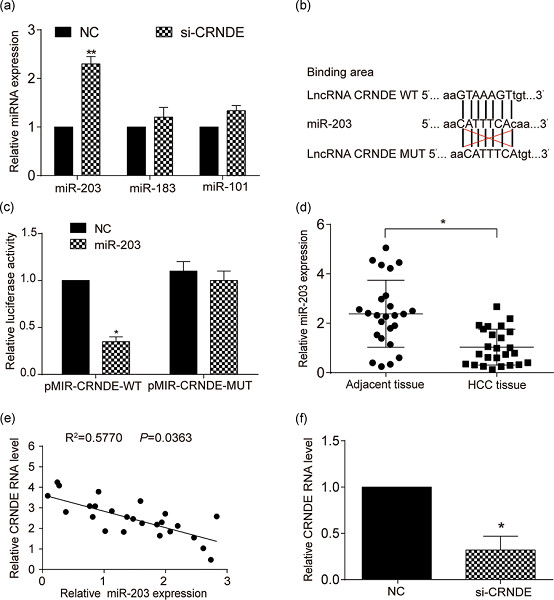
Long noncodingRNA colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed (CRNDE) could facilitate hepatocellular cancer (HCC) cell propagation, invasiveness, and migration through regulating miR-203/ BCAT1 axis. This finding not only disclosed the regulatory mechanism of CRNDE/miR-203/BCAT1 network in HCC, but also provided novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
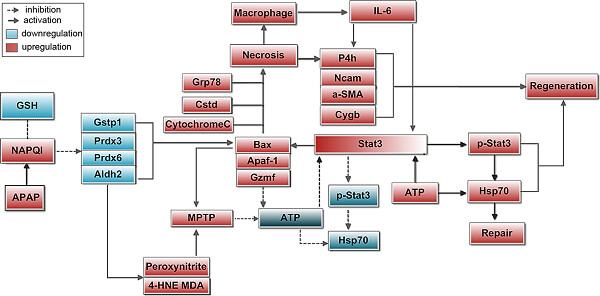
Integrative proteomics and immunochemistry analysis of the factors in the necrosis and repair in acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice
- Pages: 6561-6581
- First Published: 11 November 2018
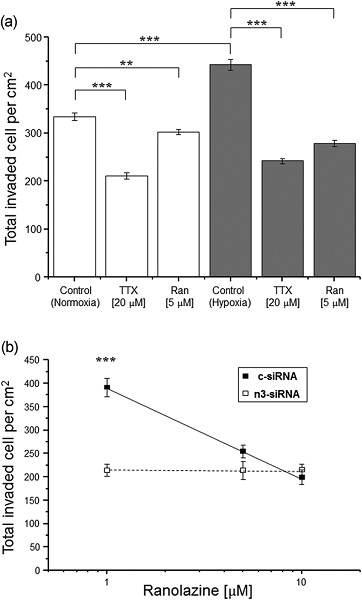
Colorectal cancer invasiveness in vitro: Predominant contribution of neonatal Nav1.5 under normoxia and hypoxia
- Pages: 6582-6593
- First Published: 20 October 2018
Upregulation of long noncoding RNA XIST is associated with poor prognosis in human cancers
- Pages: 6594-6600
- First Published: 20 October 2018
We found that highly expressed X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) is associated with poor overall survival in human cancers. Highly expressed XIST is associated with lymph node metastasis, tumor size, differentiation and clinical stage, but not with age or gender. XIST might serve as a potential novel biomarker for predicting the clinical outcomes in human cancers.
MicroRNA-382 silencing induces a mitonuclear protein imbalance and activates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response in muscle cells
- Pages: 6601-6610
- First Published: 11 November 2018
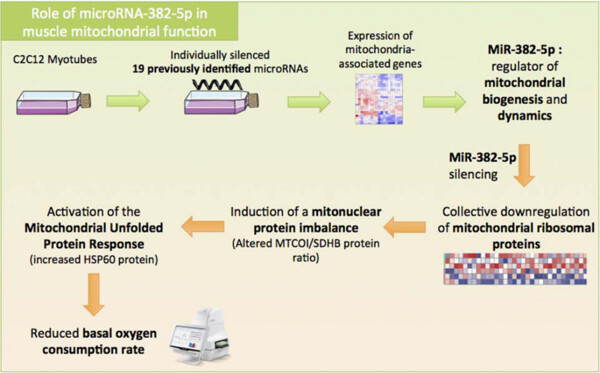
In the current study, microRNA-382-5p was identified as a regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis and dynamics at mRNA levels. Silencing of miRNA-382-5p in C2C12 myotubes revealed a collective downregulation of mitochondrial ribosomal proteins and respiratory chain proteins. MiR-382 silenced C2C12 showed a mitonuclear protein imbalance that led to the activation of the mitochondrial unfolded protein response and a reduced basal oxygen consumption rate without affecting mitochondrial content.
Chloride channel-3 mediates multidrug resistance of cancer by upregulating P-glycoprotein expression
- Pages: 6611-6623
- First Published: 19 September 2018
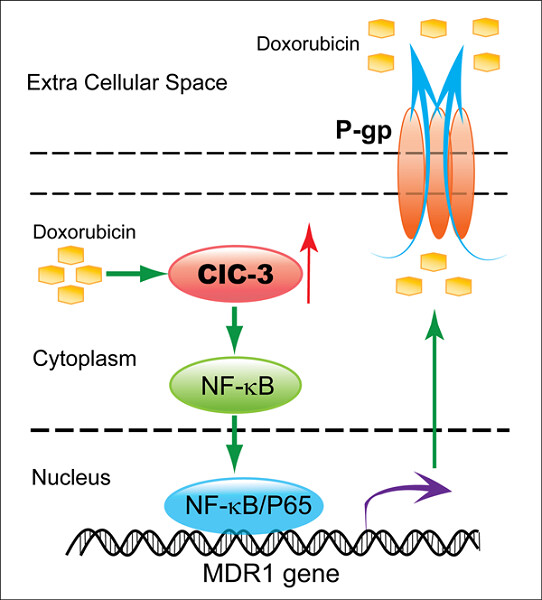
Upregulated chloride channel-3 induced by chemotherapeutic drugs activates the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-signaling pathway and leads to the nuclear translocation of NF-κB P65. This consequently enhances the transcriptional activity of multidrug resistance 1, ultimately increases P-glycoprotein expression, and promotes the efflux of chemotherapeutic drugs.
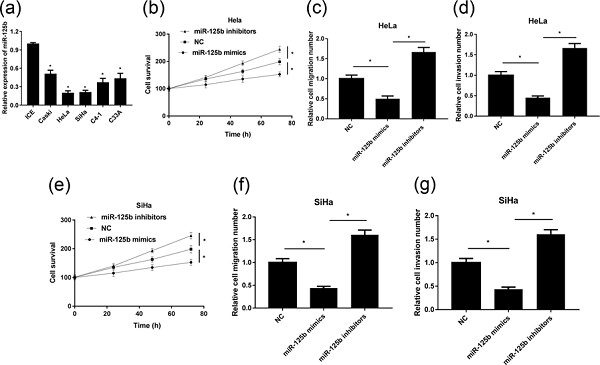
Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 promotes the progression of cervical cancer via modulating miR-125b/STAT3 axis
- Pages: 6624-6632
- First Published: 24 September 2018
Long noncoding RNA Gm6135 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate toll-like receptor 4 expression by sponging miR-203-3p in diabetic nephropathy
- Pages: 6633-6641
- First Published: 08 October 2018
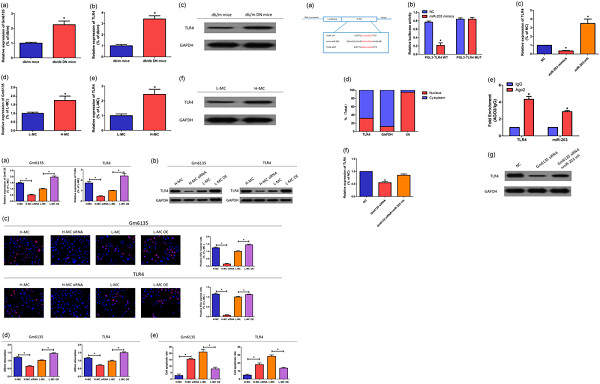
We found Gm6135 negatively regulated relative expression of miR-203, stimulated expression of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and promoted cell proliferation of SV40-MES-13 cells. Our study proved that the Gm6135/miR-203/TLR4 axis played an important role in diabetic nephropathy (DN) and provided a novel perspective for the pathogenesis of DN.
Preventative tracheal administration of interleukin-27 attenuates allergic asthma by improving the lung Th1 microenvironment
- Pages: 6642-6653
- First Published: 26 October 2018
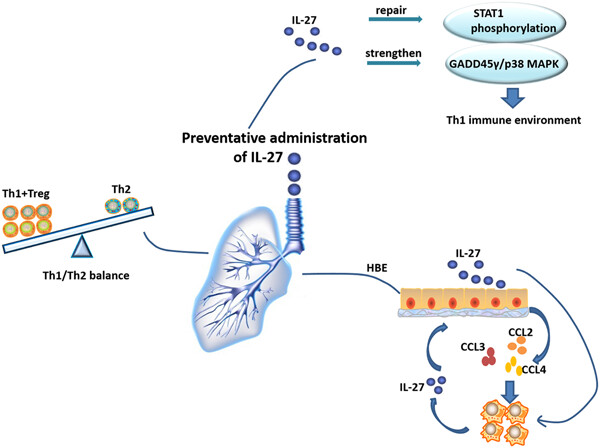
Preventative intranasal administration of interleukin-27 (IL-27) can recruit more IL-27-secreted monocytes to the airway and change the different T-cell classes in lung. The improved type 1 T helper (Th1) environment helps to alleviate type 2 T helper (Th2)-mediated allergic asthma by repairing the signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) pathway but not the STAT4 pathway.
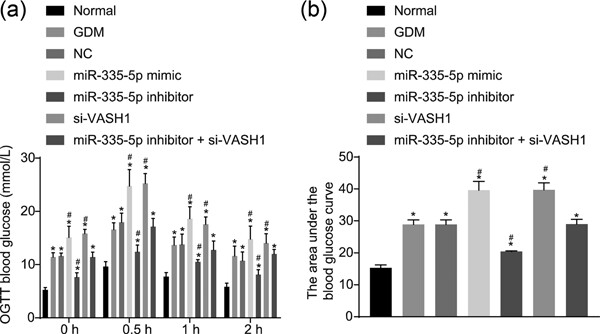
miR-335-5p induces insulin resistance and pancreatic islet β-cell secretion in gestational diabetes mellitus mice through VASH1-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway
- Pages: 6654-6666
- First Published: 20 October 2018
Chronic kidney disease after 5/6 nephrectomy disturbs the intestinal microbiota and alters intestinal motility
- Pages: 6667-6678
- First Published: 14 October 2018
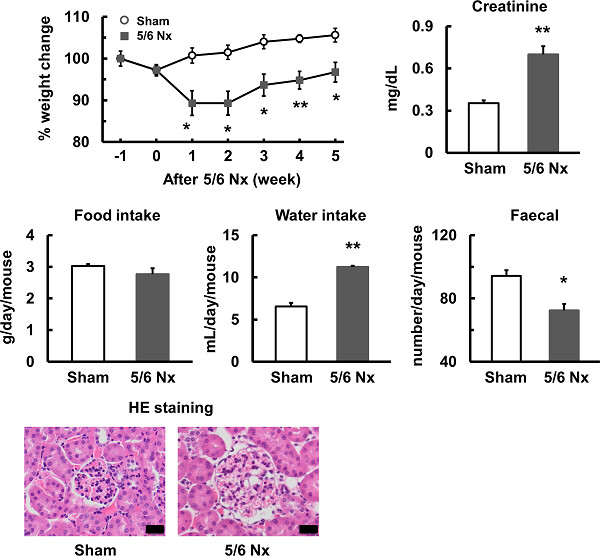
We focused the relation between the kidney and gastrointestinal tract among a number of organ–organ crosstalk is involved in homeostasis. In this study, using generated 5/6 nephrectomy mice, we show chronic kidney disease disturbed the balance of gut microbiota, altered gastrointestinal motilities, and caused constipation.
Runx2 is required for postnatal intervertebral disc tissue growth and development
- Pages: 6679-6687
- First Published: 20 October 2018
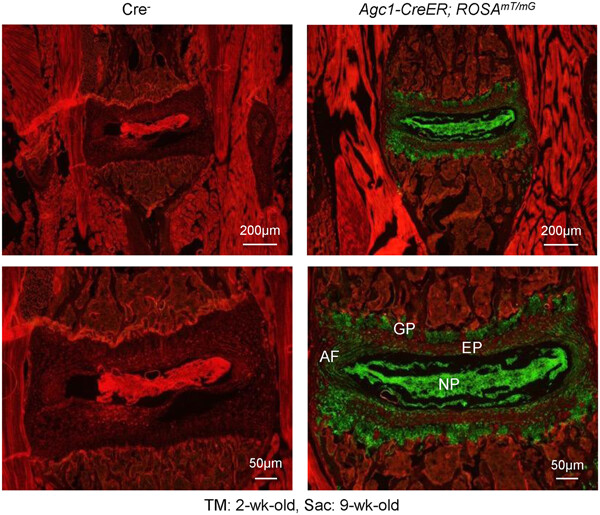
Agc1-CreER mice could efficiently target disc cells, including growth plate (GP) cartilage cells, annulus fibrosus (AF) and nucleus pulposus (NP) cells. We have used these mice to specifically delete runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2) in disc cells and analyzed disc tissue phenotype of Runx2 knockout (KO) mice.
SP1, MYC, CTNNB1, CREB1, JUN genes as potential therapy targets for neuropathic pain of brain
- Pages: 6688-6695
- First Published: 27 November 2018
Our results suggested a potential application of SP1, MYC, CTNNB1, CREB1, and JUN genes as prognostic biomarkers in the clinical management of neuropathic pain, and two most important signaling pathways, immune response and reception reactions, were found to be closely related to the occurrence and development of neuropathic pain. The more specific mechanism of these genes with the brain tissue related to neuropathic pain stimulation needs further research.
Homogentisic acid induces morphological and mechanical aberration of ochronotic cartilage in alkaptonuria
- Pages: 6696-6708
- First Published: 20 October 2018
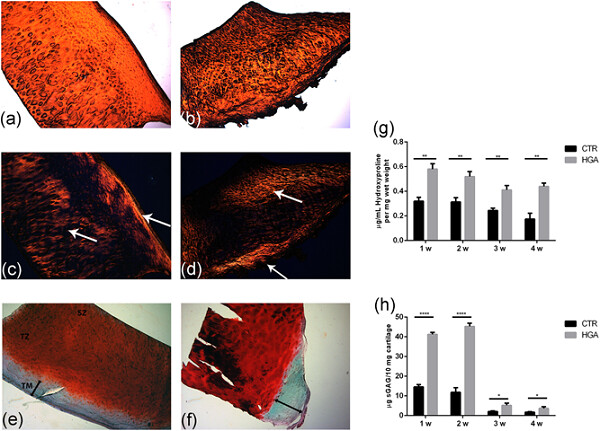
Although efforts were made, the exact biochemical mechanism of cartilage degradation in alkaptonuria (AKU) is not clarified in detail yet. Our multidisciplinary study provides novel insights on how homogentisic acid and the ochronotic pigment affect the physico–thermal and mechanical properties of AKU cartilage.
Extended proliferation of chicken- and Okinawa rail-derived fibroblasts by expression of cell cycle regulators
- Pages: 6709-6720
- First Published: 11 November 2018
Slug mediates myofibroblastic differentiation to promote fibrogenesis in buccal mucosa
- Pages: 6721-6730
- First Published: 19 September 2018
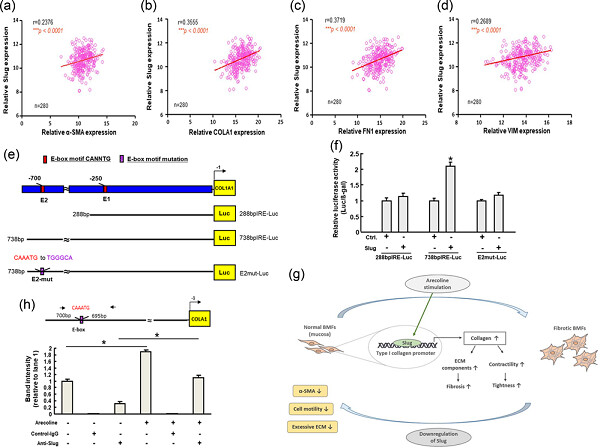
In normal BMFs, arecoline stimulation will elevate the expression of Slug, which directly binds to the promotor of type I collagen, leading to increased collagen deposition and myofibroblasts transdifferentiation. In fibrotic BMFs, inhibition of Slug will reduce the expression of the myofibroblast marker, α-SMA, and the myofibroblast activities as well as downregulate the ECM accumulation, which may relieve the fibrotic condition.
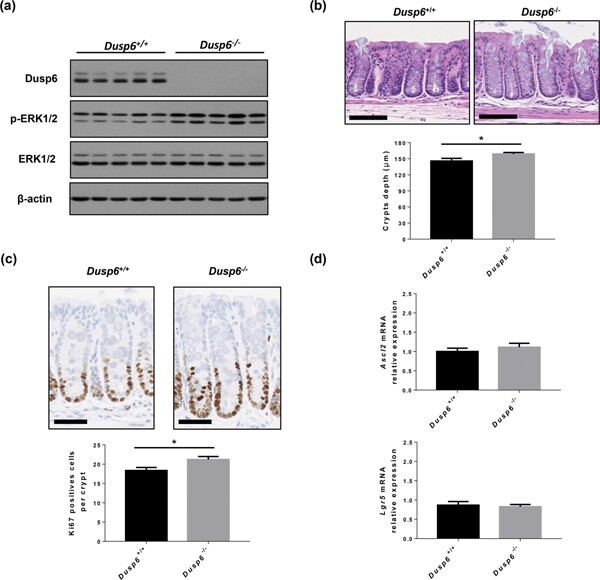
Dual-specificity phosphatase 6 deletion protects the colonic epithelium against inflammation and promotes both proliferation and tumorigenesis
- Pages: 6731-6745
- First Published: 01 October 2018
Long noncoding RNA DLEU1 aggravates pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma carcinogenesis via the miR-381/CXCR4 axis
- Pages: 6746-6757
- First Published: 01 November 2018
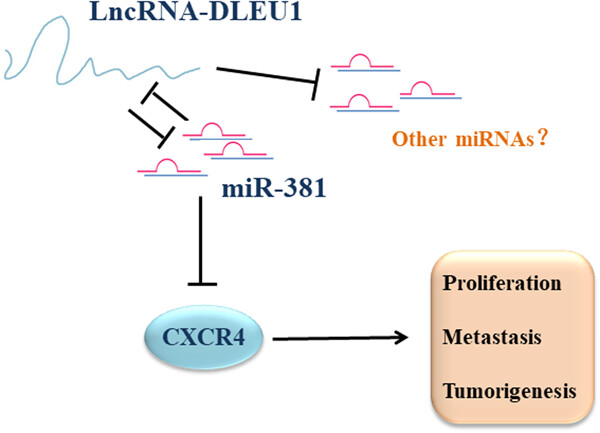
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA)-DLEU1 was significantly overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) tissues and cells and negatively associated with miR-381 expression. Furthermore, DLEU1 knockdown inhibited PDAC cell growth, metastasis, and invasion by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-381, illustrating the oncogenic role of DLEU1 in PDAC and its underlying mechanism.
OCT4&SOX2-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes plus programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor presented with synergistic effect on killing lung cancer stem-like cells in vitro and treating drug-resistant lung cancer mice in vivo
- Pages: 6758-6768
- First Published: 01 November 2018
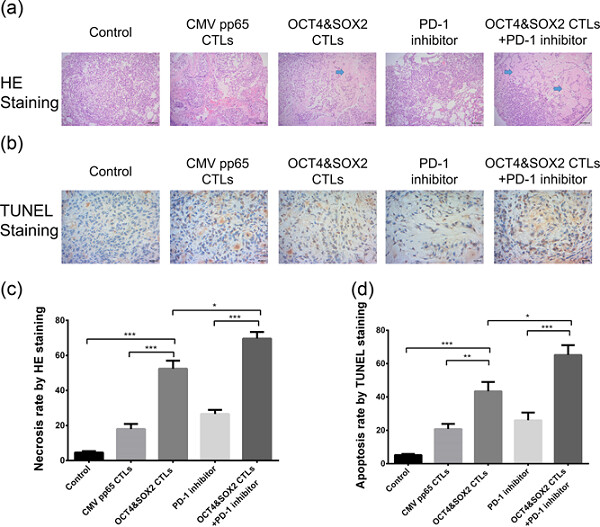
This study aimed to investigate the synergistic effect of octamer-binding transcription factor 4 and sex determining region Y-box 2 (OCT4&SOX2)-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) inhibitor on killing lung cancer stem-like cells (LCSCs) and their efficacy in treating drug-resistant lung cancer (DRLC) mice. OCT4&SOX2-specific CTLs and PD-1 inhibitor presented with the synergistic effect on killing LCSCs in vitro and treating DRLC mice in vivo.
Identification of LINC01234 and MIR210HG as novel prognostic signature for colorectal adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 6769-6777
- First Published: 26 October 2018
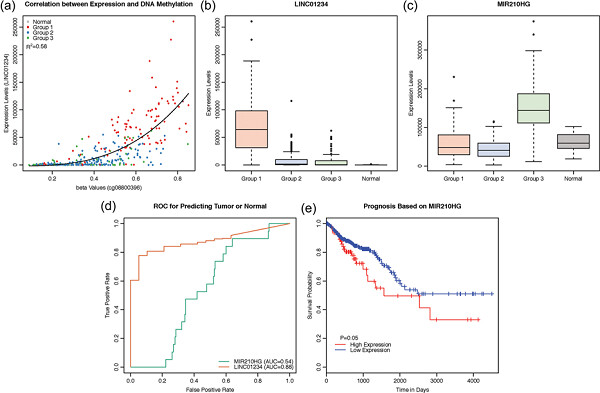
This study aimed to identify potential biomarkers and the therapeutic targets for colorectal adenocarcinoma by systematically evaluate a large scale of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) expression data from TCGA. The algorithm t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding and hierarchical clustering were utilized to group the samples into three clusters that showed a different prognosis. To identify the relationship between the clustered groups and different histoclinical features, different statistical methods were used. The functions of LINC01234 and MIR210HG were investigated with the help of the public database. The results showed that the expression levels of lncRNAs were able to distinguish the tumor samples from the normal tissues and in further they were able to predict the prognosis of the patients. We proposed two potential lncRNAs, which might serve as a biomarker or therapeutic targets. LINC01234 can be a good biomarker. In contrast, MIR210HG participated in the progression of colorectal adenocarcinoma by regulating hypoxia. It might function through an lncRNA–microRNA–messenger RNA regulatory network with MIR210 and RASSF7.
The antiproliferative effects of cold atmospheric plasma-activated media on different cancer cell lines, the implication of ozone as a possible underlying mechanism
- Pages: 6778-6782
- First Published: 01 November 2018
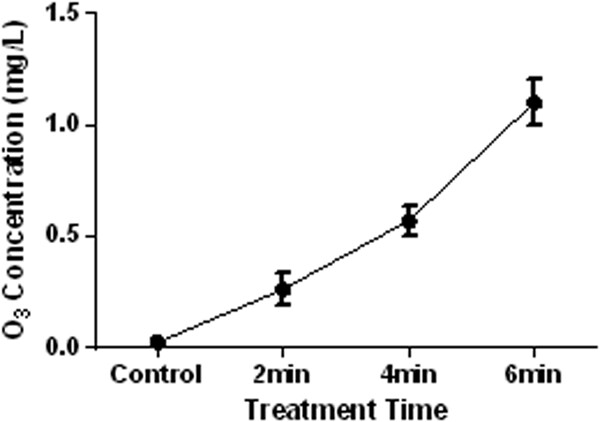
Recently, media treated with cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) have also found to effectively eradicate cancer cells similar to the CAP. Based on advantages, many researchers prefer to apply CAP-activated media (PAM) as an alternative to cap in treatment of cancer. However, less has been achieved regarding the anticancer effects and anticancer mechanisms of PAM. Investigating the selective anticancerous activities of PAM, the viability of SKBR3, MCF7, ASPC-1, A-549, G-292, and SW742 cancer cell liness, as well as normal human skin fibroblasts (FMGB-1) and MCF10A cells in relation to the media activation time, and the length of exposure was studied.
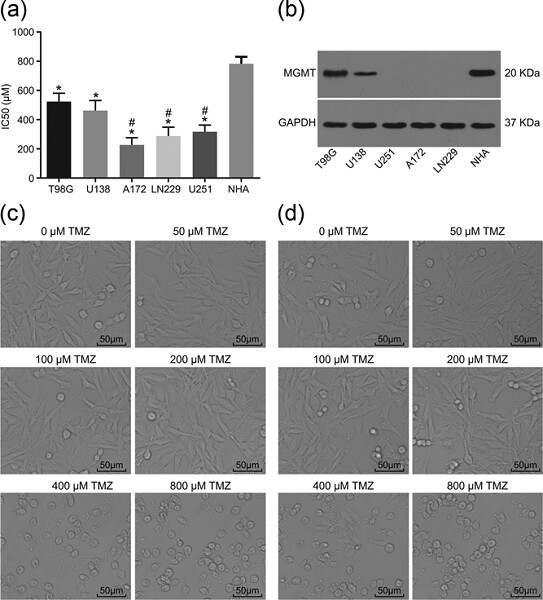
Resveratrol restores sensitivity of glioma cells to temozolamide through inhibiting the activation of Wnt signaling pathway
- Pages: 6783-6800
- First Published: 14 October 2018
Differentiation of microfluidic-encapsulated trabecular meshwork mesenchymal stem cells into insulin producing cells and their impact on diabetic rats
- Pages: 6801-6809
- First Published: 14 October 2018
A six-microRNA risk score model predicts prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 6810-6819
- First Published: 01 November 2018
Esophageal cancer ranks the eighth most common cancer and the sixth most common cause of cancer death worldwide. Here, we collected the data of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma from both Gene Expression Ominus and The Cancer Genome Atlas and constructed a six-microRNAs signature. Then we performed a series of function experiments to reveal the regulatory role of these miRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
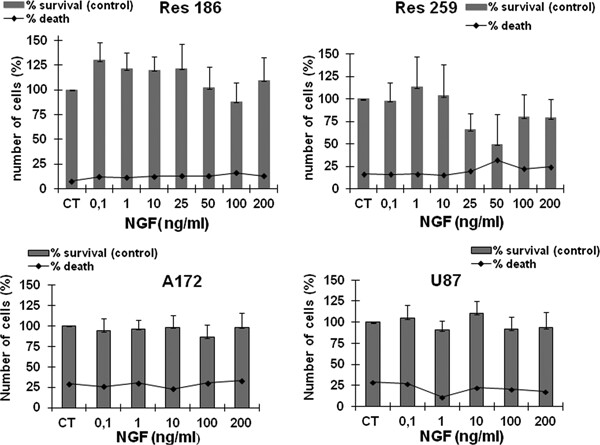
Ectopic nerve growth factor prevents proliferation in glioma cells by senescence induction
- Pages: 6820-6830
- First Published: 11 November 2018
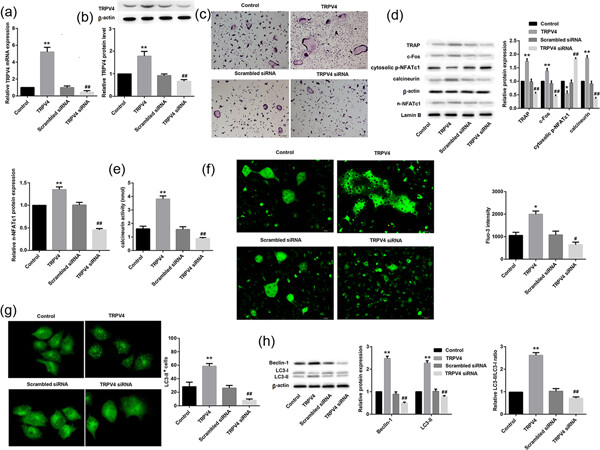
Knockdown of TRPV4 suppresses osteoclast differentiation and osteoporosis by inhibiting autophagy through Ca2+–calcineurin–NFATc1 pathway
- Pages: 6831-6841
- First Published: 01 November 2018
Altered plasma proteins released from platelets and endothelial cells are associated with human patent ductus arteriosus
- Pages: 6842-6853
- First Published: 27 November 2018
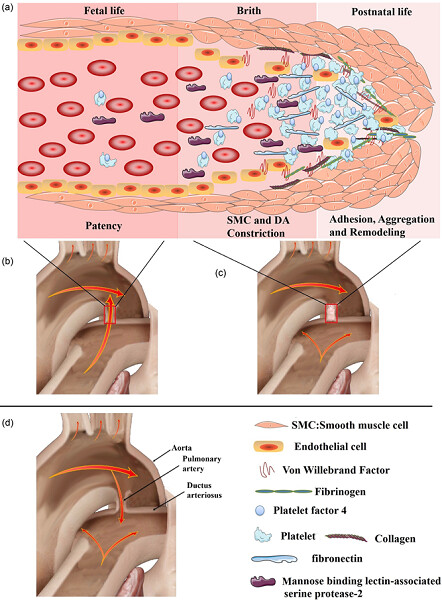
Ductus arteriosus closure involves functional and structural remodeling, controlled by many factors and we for the first time demonstrate six key differential plasma proteins in human patent ductus arteriosus patients using proteomic technology and present a model to illustrate the constriction and closure of ductus arteriosus. Those proteins are closely related to platelet activation and coagulation cascades, complement mannan-binding-lectin, and other systemic signaling pathways. Our findings for the first time indicate that the differential proteins involved in different pathways may play key roles in the nonclosure of the ductus arteriosus in humans and may be developed as biomarkers for diagnosis. All those findings may be served as the basis of understanding the etiology and pathogenesis of patent ductus arteriosus.
Laurus nobilis leaf extract controls inflammation by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- Pages: 6854-6864
- First Published: 01 November 2018
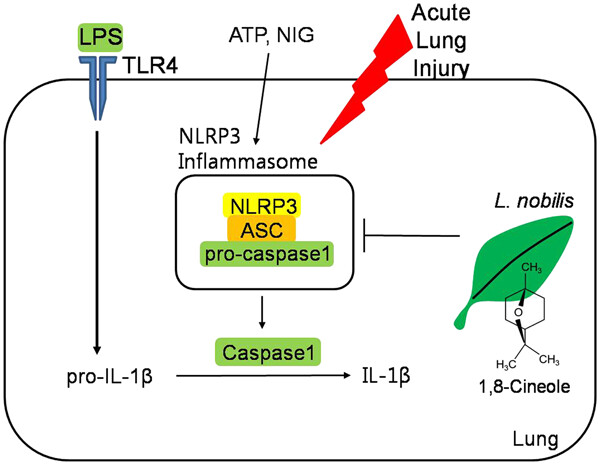
Laurus nobilis Linn. (Lauraceae) has been used as a traditional medicine in the Mediterranean and Europe to treat diverse immunological disorders. Our results provide the first evidence that L. nobilis leaf extract modulates inflammatory signaling by suppressing NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation.
Activation of Pyk2 by CaM kinase II in cultured hypothalamic neurons and gonadotroph cells
- Pages: 6865-6875
- First Published: 11 November 2018
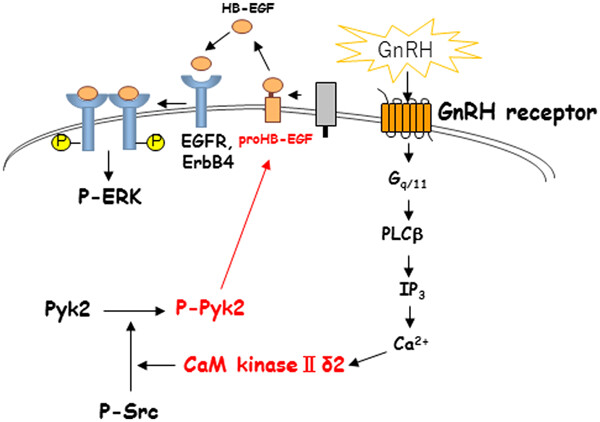
We found that Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaM kinase II) activated proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2) in cultured gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons and gonadotroph cells. In addition, our inhibitor studies indicated that Pyk2 and CaM kinase II were involved in the GnRH-induced shedding of proHB-EGF. Our results suggested that CaM kinase II activated the ERK pathway through Pyk2 activation and HB-EGF production in response to GnRH.
Transcriptional landscape of alternative splicing during peripheral nerve injury
- Pages: 6876-6885
- First Published: 26 October 2018
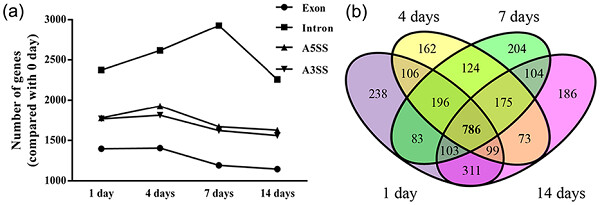
Our study elucidated alternative splicing events following peripheral nerve injury and bioinformatic analysis indicated that these alternatively spliced genes were mainly correlated to immune response, cellular growth, and cellular function maintenance. These study might help deepen our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying peripheral nerve regeneration.
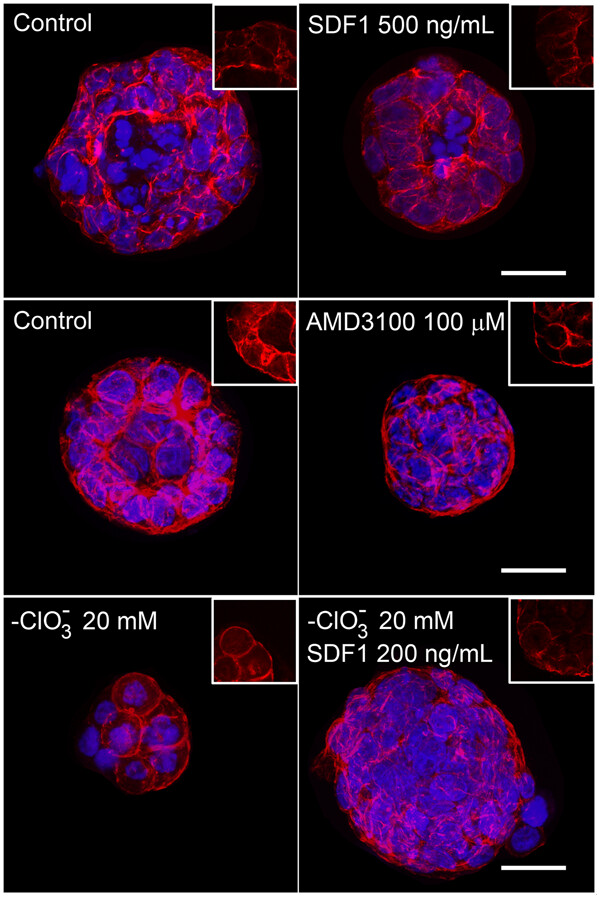
The role of SDF1 in prostate epithelial morphogenesis
- Pages: 6886-6897
- First Published: 26 October 2018
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: Effects of microRNA-370 on mesangial cell proliferation and extracellular matrix accumulation by binding to canopy 1 in a rat model of diabetic nephropathy
- Pages: 6898-6907
- First Published: 14 October 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
LINC00707 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through activating ERK/JNK/AKT pathway signaling pathway
- Pages: 6908-6916
- First Published: 14 October 2018
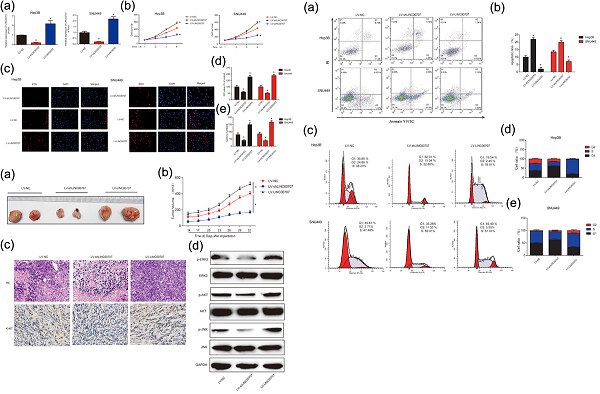
We indicated that LINC00707 exhibited an oncogenic role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. It was found that silencing of LINC00707 blocked HCC progression through inactivating the ERK/JNK/AKT signaling pathway. Taken together, our results implied that LINC00707 was involved in HCC progression and might act as a novel biomarker for HCC.
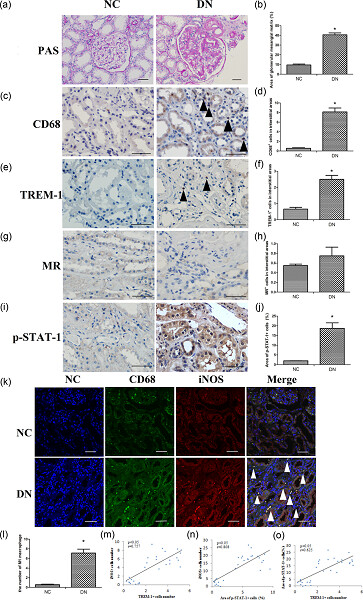
Active vitamin D regulates macrophage M1/M2 phenotypes via the STAT-1-TREM-1 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Pages: 6917-6926
- First Published: 27 November 2018
Fibronectin-1 modulated by the long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1/miR-200b-3p axis contributes to doxorubicin resistance of osteosarcoma cells
- Pages: 6927-6939
- First Published: 11 September 2018
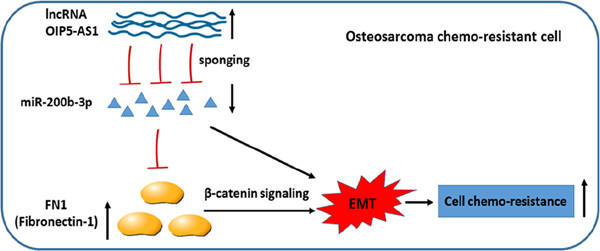
First report about expression, function and potential clinical significance of fibronectin-1 (FN1), miR-200b-3p, lncRNA OIP5-AS1 in osteosarcoma (OS) doxorubicin resistance; Regulatory mechanism of FN1 expression was identified and lncRNA OIP5-AS1/miR-200b-3p/FN1 regulatory pathway was first constructed in OS doxorubicin resistance.
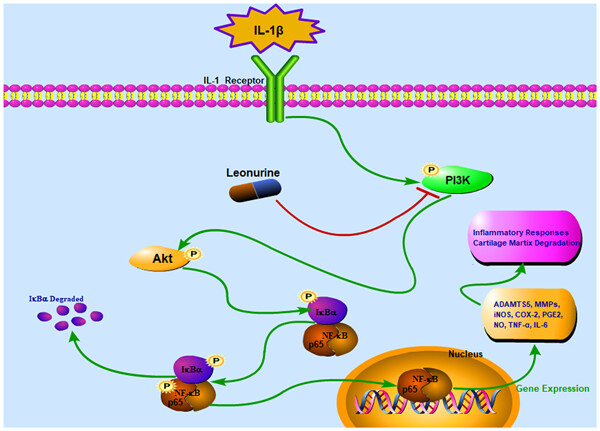
Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling with leonurine for ameliorating the progression of osteoarthritis: In vitro and in vivo studies
- Pages: 6940-6950
- First Published: 11 November 2018
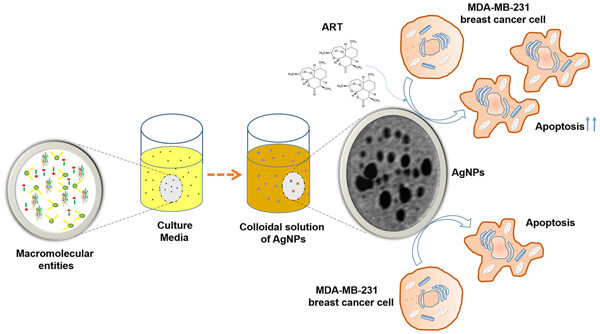
Potential of bacterial culture media in biofabrication of metal nanoparticles and the therapeutic potential of the as-synthesized nanoparticles in conjunction with artemisinin against MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells
- Pages: 6951-6964
- First Published: 15 November 2018
Inactivation of ADAMTS18 by aberrant promoter hypermethylation contribute to lung cancer progression
- Pages: 6965-6975
- First Published: 11 November 2018
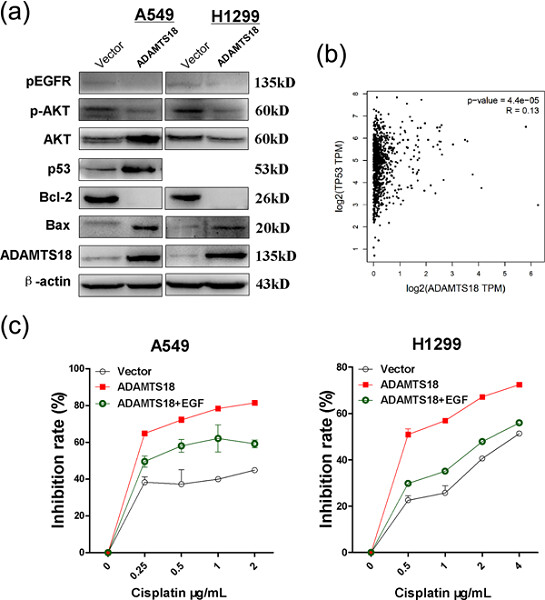
Our results demonstrated that the tumor suppressor gene ADAMTS18 was downregulated in lung cancer by promoter CpG methylation, and it promoted sensitivity to cisplatin via epidermal growth factor receptor/protein kinase B signaling. Our study suggests that ADAMTS18 promoter methylation is a potential epigenetic biomarker for early detection of lung cancer and warrants investigation as therapeutic target for early-stage lung cancer.
Chromatin-regulatory genes served as potential therapeutic targets for patients with urothelial bladder carcinoma
- Pages: 6976-6982
- First Published: 14 October 2018
Urothelial bladder carcinoma is the ninth most common cancer in the world, with an estimated 150,000 deaths per year. Two comprehensive analysis based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) urothelial bladder carcinoma reported that chromatin modifier gene mutations were common in bladder cancer. We aimed to find how the mutations and transcriptional profiles of the genes involving in chromatin modification affected the prognosis of patients.
Estrogen deprivation aggravates intracellular calcium dyshomeostasis in the heart of obese-insulin resistant rats
- Pages: 6983-6991
- First Published: 11 November 2018
PURB is a positive regulator of amino acid-induced milk synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells
- Pages: 6992-7003
- First Published: 26 October 2018

Amino acids (Met and Leu) trigger PURB expression in the nucleus via the PI3K signaling and binding to the promoters of mTOR and SREBP-1c, and PURB is required for amino acids to stimulate the gene expression of mTOR and SREBP-1c leading to milk protein and fat synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells.
Identification of CD28 and PTEN as novel prognostic markers for cervical cancer
- Pages: 7004-7011
- First Published: 26 October 2018
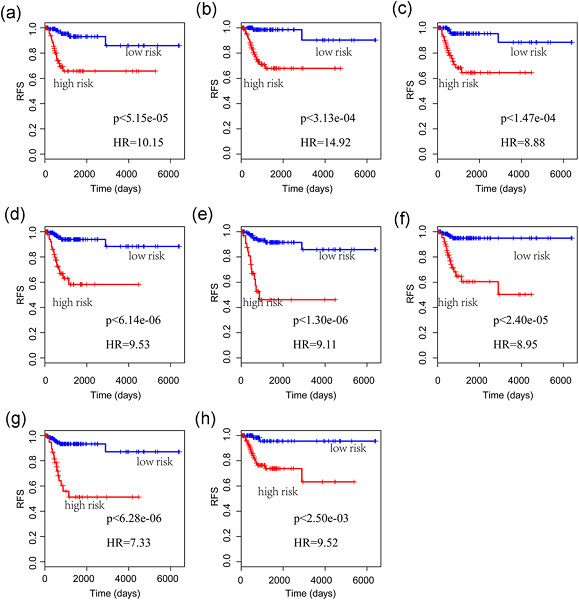
This study aimed to investigate the molecular mechanisms of Diabetic Kidney Disease (DKD) and to explore new potential therapeutic strategies and biomarkers for DKD. First we analyzed the differentially expressed changes between DKD patients and the control group using the chip data in Gene Expression Omnibus database. Then the gene chip was subjected to be annotated again, so as to screen long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and study expression differences of these lncRNAs in DKD and controlled samples. At last, the function of the differential lncRNAs was analyzed. A total of 252 lncRNAs were identified, and 14 were differentially expressed. In addition, there were 1629 differentially expressed. Messenger RNAs genes, and PEA15, MIR22, and LINC00472 were significantly differentially expressed in DKD samples. Through functional analysis of the encoding genes coexpressed by the three lncRNAs, we found these genes were mainly enriched in type 1 diabetes and autoimmune thyroid disease pathways, while in Gene Ontology function classification, they were also mainly enriched in the immune response, type I interferon-signaling pathways, interferon-γ mediated signaling pathways, and so forth. To summary, we identified EA15, MIR22, LINC00472 may serve as the potential diagnostic markers of DKD.
A genetic variant in LINGO2 contributes to the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in a Chinese population
- Pages: 7012-7018
- First Published: 13 November 2018
Glucose intolerance in monosodium glutamate obesity is linked to hyperglucagonemia and insulin resistance in α cells
- Pages: 7019-7031
- First Published: 14 October 2018
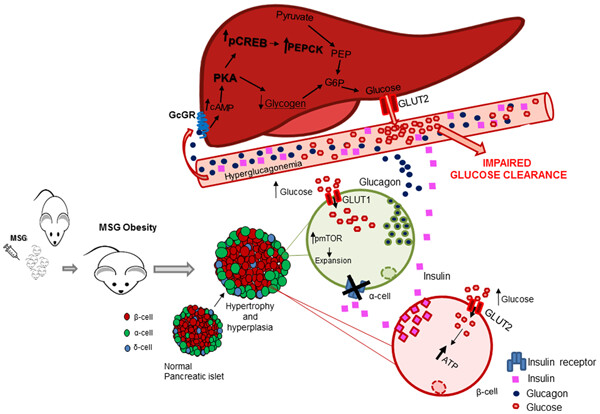
Neonatal treatment with monosodium glutamate (MSG) induces obesity and impaired body glucose control at adulthood in mice. We demonstrated that pancreatic α cells of MSG mice did not suppress glucagon release in response to increased glucose and insulin levels, leading to hyperglucagonemia and the loss of capacity to enhance insulin/glucagon ratio in the fed state. Hyperglucagonemia in turn exacerbates hepatic glucose production, impairing glucose clearance, and homeostasis in MSG mice. Since increased phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin (pmTOR) immunoreactivity was detected in MSG α cells, this protein may account for the α-cell dysfunction, hypertrophy and enlarged mass. Therefore, these data indicate that both β and α cells must be considered for understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms that lead to glucose control disruption in obesity.
Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNA SNHG15 correlates with liver metastasis and poor survival in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 7032-7039
- First Published: 14 October 2018
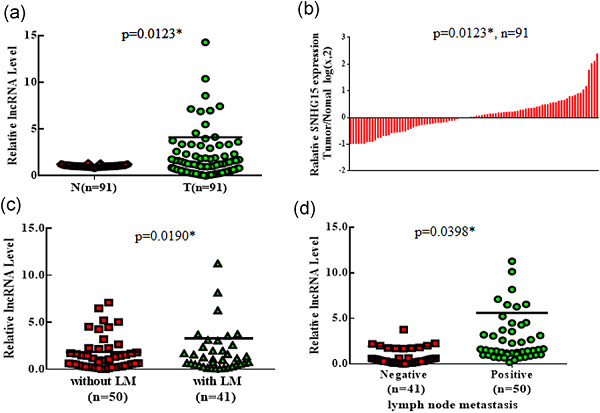
Long non coding RNAs-small-nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (lncRNAs-SNHG15) overexpression may serve as a poor prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer (CRC) patients (p = 0.049; Cox Regression: 2.731). Lnc-SNHG15 overexpression was significantly associated with colorectal liver metastasis and high expression of lnc-SNHG15 in CRC was an independent predictor of poor survival.
Molecular interaction of NFκB and NICD in monocyte–macrophage differentiation is a target for intervention in atherosclerosis
- Pages: 7040-7050
- First Published: 27 November 2018
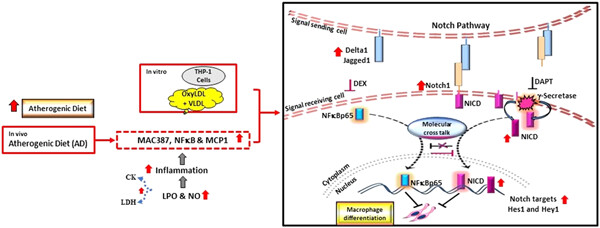
Inhibition of NFκB regulated notch intracellular domain (NICD), which, in turn, downturned macrophage differentiation. Inhibition of both NFκB–NICD is a potential target for intervention in early stage of atherosclerosis (monocyte to macrophage differentiation), to prevent the furtherance of disease.
Toll-like receptor 3 agonist poly I:C reinforces the potency of cytotoxic chemotherapy via the TLR3-UNC93B1-IFN-β signaling axis in paclitaxel-resistant colon cancer
- Pages: 7051-7061
- First Published: 01 November 2018
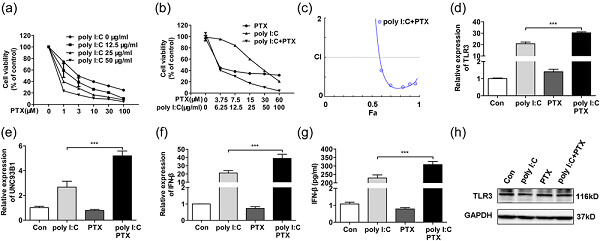
The toll-like receptor (TLR3) agonist polyinosinic: polycytidylic acid (poly I:C) specifically impairs the paclitaxel (PTX)-resistant cell viability of HCT-8/PTX by simultaneously promoting cell apoptosis and inhibiting cell proliferation. Poly I:C reinforces the potency of cytotoxic chemotherapeutics in HCT-8/PTX cells through the TLR3-UNC93B1-IFN-β signaling pathway, which supplies a novel mechanism of poly I:C for the chemotherapy sensitizing effect in the PTX-resistant tumor.
Central adiponectin induces trabecular bone mass partly through epigenetic downregulation of cannabinoid receptor CB1
- Pages: 7062-7069
- First Published: 27 November 2018
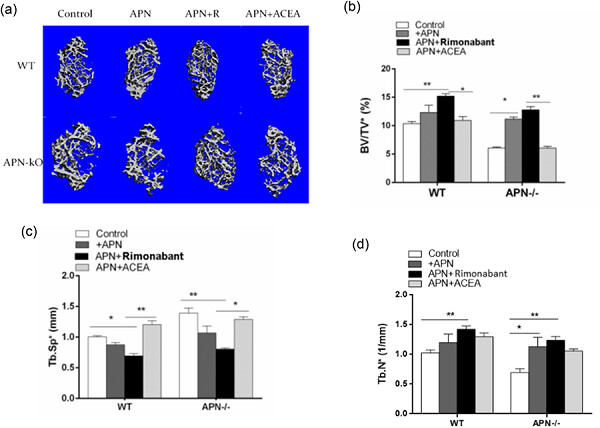
- 1. Globular adiponectin (gAPN) enhanced expression levels of various histone deacetylases (HDACs), especially HDAC5.
- 2. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays revealed HDAC5 bound to the transcriptional start site 2 (TSS2) region of the CB1 promoter.
- 3. Our study identified a possible novel central APN-HDAC5-CB1 signaling mechanism that promotes peripheral bone formation through epigenetic regulation of hypothalamic CB1 expression.
Gene expression profiling of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenic differentiation
- Pages: 7070-7077
- First Published: 30 October 2018
Apoptosis in HepaRG and HL-7702 cells inducted by polyphyllin II through caspases activation and cell-cycle arrest
- Pages: 7078-7089
- First Published: 26 October 2018
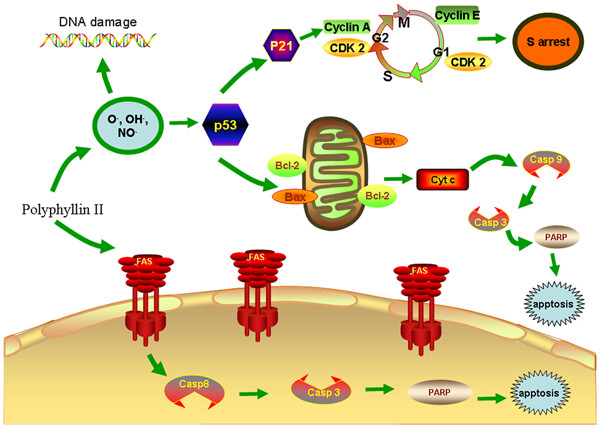
This study confirmed the hepatotoxicity of the polyphyllin II in vitro, which has never been discovered and gave a wake-up call for the clinical application of Rhizoma Paridis. Moreover, we identified two signaling pathways of apoptosis induced by polyphyllin II including death receptor pathway and the mitochondria pathway.
MicroRNA-212 promotes the recovery function and vascular regeneration of endothelial progenitor cells in mice with ischemic stroke through inactivation of the notch signaling pathway via downregulating MMP9 expression
- Pages: 7090-7103
- First Published: 15 December 2018
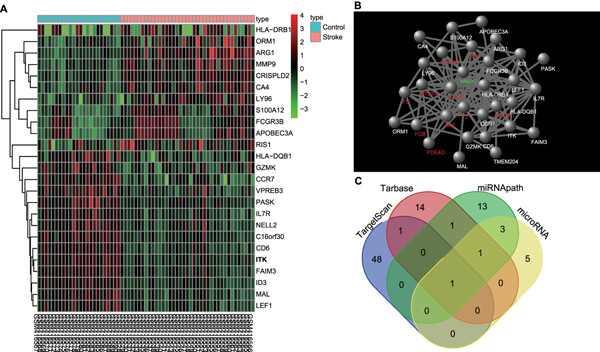
Our study suggests that miR-212 promotes recovery function and vascular regeneration of endothelial progenitor cells through negative regulation of the Notch signaling pathway via downregulating expression of matrix metallopeptidase 9, thus provides a clinical theoretical basis for ischemic stroke therapy.
Identification of intracellular peptides associated with thermogenesis in human brown adipocytes
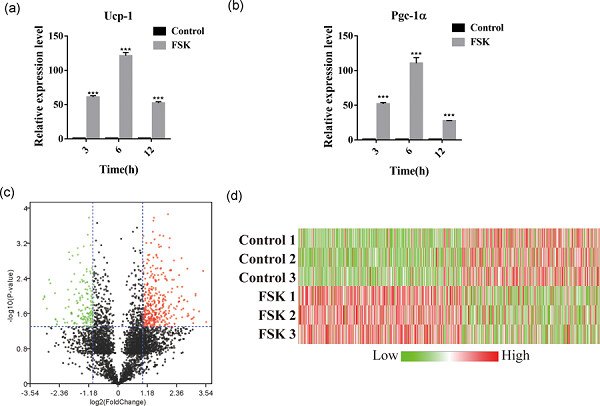
- Pages: 7104-7114
- First Published: 01 November 2018
LINC00641 regulates autophagy and intervertebral disc degeneration by acting as a competitive endogenous RNA of miR-153-3p under nutrition deprivation stress
- Pages: 7115-7127
- First Published: 30 October 2018
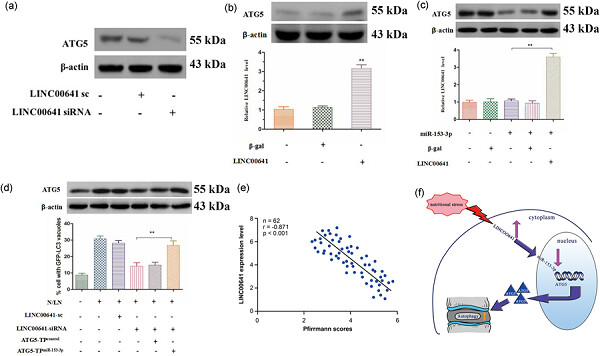
We demonstrated that long intergenic nonprotein coding RNA 641 (LINC00641) acts as endogenous sponge RNA and inhibits miR-153-3p expression and its biological function. Therefore, modulation of LINC00641 may represent a novel treatment paradigm in human IDD. These findings shed new light on the importance of the orchestrated interactions between lncRNAs, miRNAs, and autophagy in maintaining cellular homeostasis and suggest that a disturbance in these networks might lead to diseases.
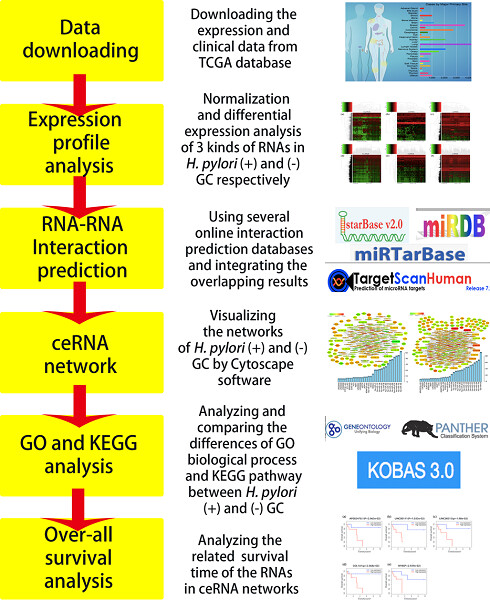
ceRNA network construction and comparison of gastric cancer with or without Helicobacter pylori infection
- Pages: 7128-7140
- First Published: 28 October 2018
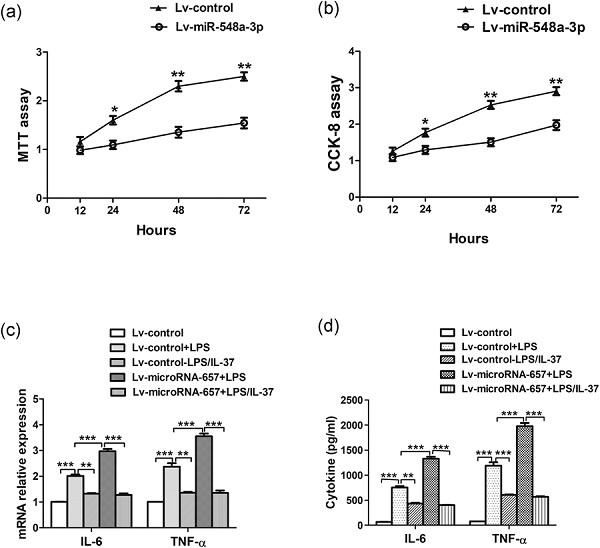
Dysregulation of microRNA-657 influences inflammatory response via targeting interleukin-37 in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 7141-7148
- First Published: 26 October 2018
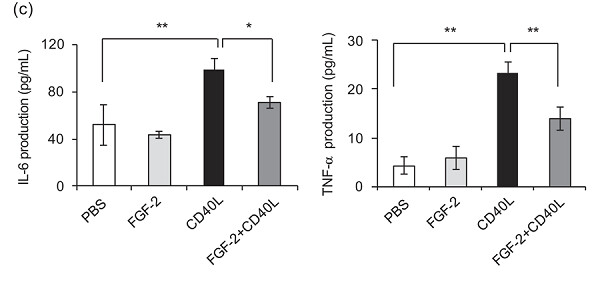
Fibroblast growth factor-2 inhibits CD40-mediated periodontal inflammation
- Pages: 7149-7160
- First Published: 28 October 2018
Tetrandrine, a novel inhibitor of ether-à-go-go-1 (Eag1), targeted to cervical cancer development
- Pages: 7161-7173
- First Published: 26 October 2018
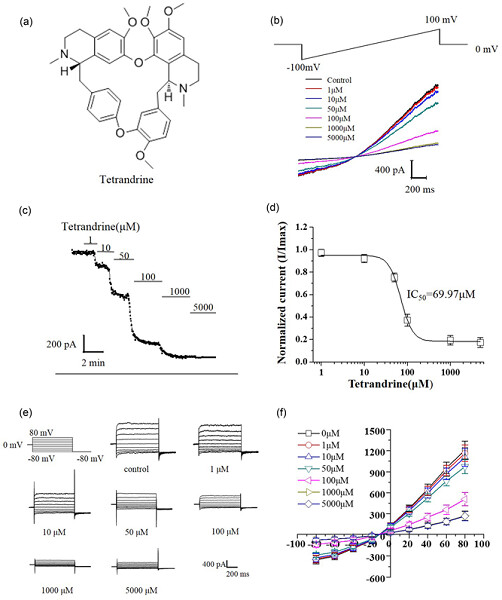
We identified the first natural inhibitor of ether-à-go-go-1 (Eag1), the traditional Chinese medicine agent tetrandrine, and explored the underlying mechanism. Tetrandrine is a potent and selective Eag1 channel inhibitor, and could act as a leading compound in the development of therapies for Eag1 ion channel dysfunction-induced diseases.
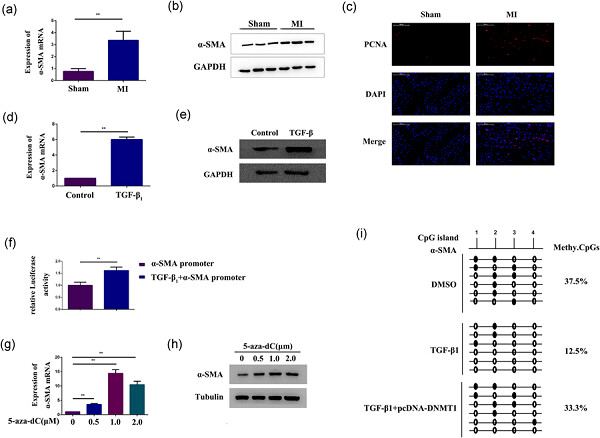
DNA methylation regulates α-smooth muscle actin expression during cardiac fibroblast differentiation
- Pages: 7174-7185
- First Published: 26 October 2018
Dental pulp stem cells senescence and regenerative potential relationship
- Pages: 7186-7197
- First Published: 26 October 2018
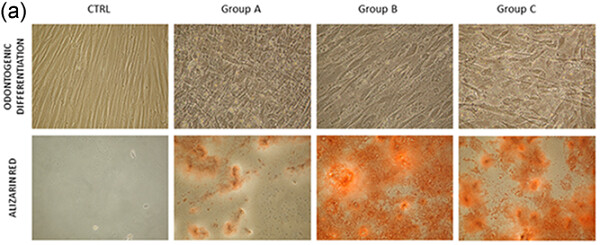
The purpose of our study was to deep our knowledge of age-related changes in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from dental pulp (DPSCs). Increased aging populations pose new challenges and emphasize the need for customized approaches to repair dental tissues lost through trauma or disease. DPSCs may be considered an attractive MSCs reservoir for dental and bone tissue engineering perspective.
Pre-cold acclimation improves the immune function of trachea and resistance to cold stress in broilers
- Pages: 7198-7212
- First Published: 26 October 2018
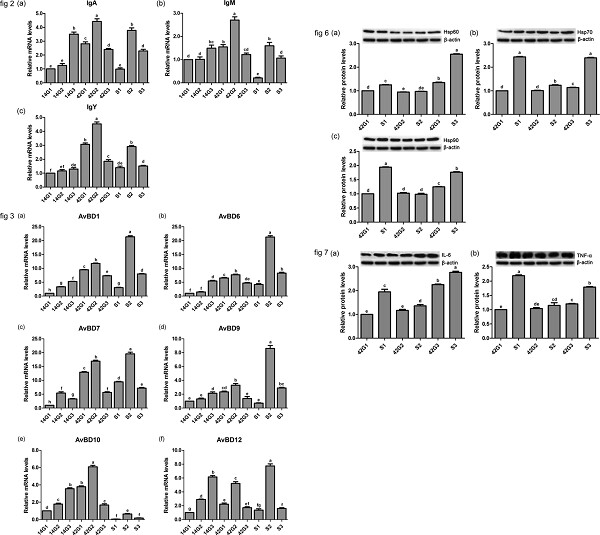
We found that cold stimulation environment of 3°C lower than normal from 8 to 42 days of age could make the chicken establish cold acclimation. Cold acclimation improved immune function of trachea and the resistance to cold stress of the birds to a certain extent Cold acclimation effectively alleviated oxidative stress induced by cold stress and reduced levels of heat shock proteins, which may be a protective mechanism of cold acclimation.
Cholesterol burden in the liver induces mitochondrial dynamic changes and resistance to apoptosis
- Pages: 7213-7223
- First Published: 21 September 2018
Albumin induces CD44 expression in glomerular parietal epithelial cells by activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway
- Pages: 7224-7235
- First Published: 26 October 2018
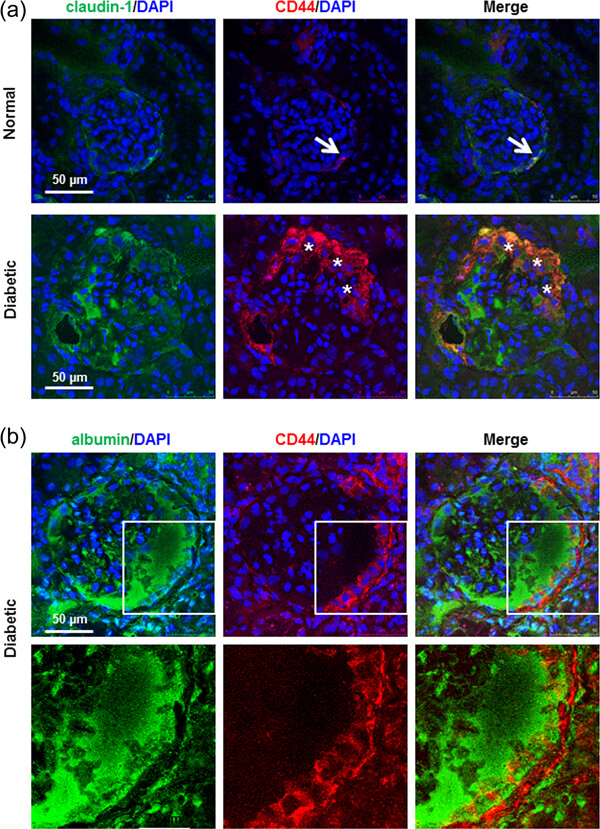
This study evaluated the localization and expression levels of CD44 in glomeruli of diabetic rat kidneys and primary cultured glomerular parietal epithelial cells upon albumin stimulation. Our results demonstrate that albumin induces CD44 expression by parietal epithelial cells via the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway, which is partially mediated by endocytic receptor megalin.
Expression of myostatin in human hematopoietic cells unveils novel autocrine/paracrine actions for the hormone
- Pages: 7236-7246
- First Published: 28 October 2018
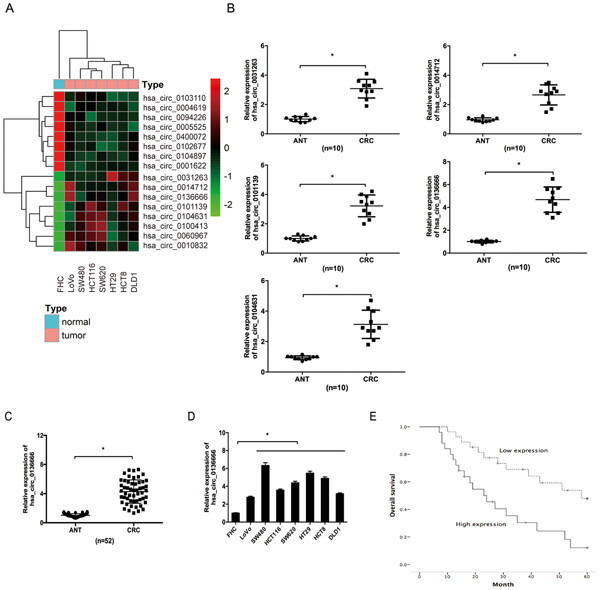
Hsa_circ_0136666 promotes the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer through miR-136/SH2B1 axis
- Pages: 7247-7256
- First Published: 28 October 2018
LINC00961 restrains cancer progression via modulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition in renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 7257-7265
- First Published: 26 October 2018
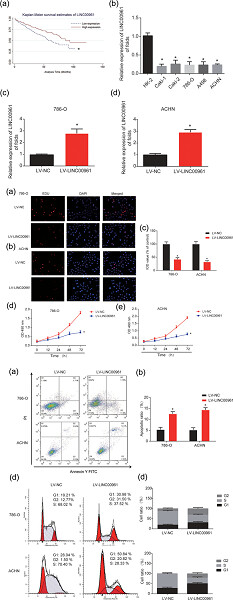
We indicated that LINC00961 exhibited a tumor suppressive role in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) development. We found that overexpression of LINC00961 depressed RCC progression through modulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) signaling pathway. Taken these together, it was implied that LINC00961 was involved in RCC progression and it could function as a novel biomarker for RCC.
LncRNA DANCR promotes cervical cancer progression by upregulating ROCK1 via sponging miR-335-5p
- Pages: 7266-7278
- First Published: 26 October 2018
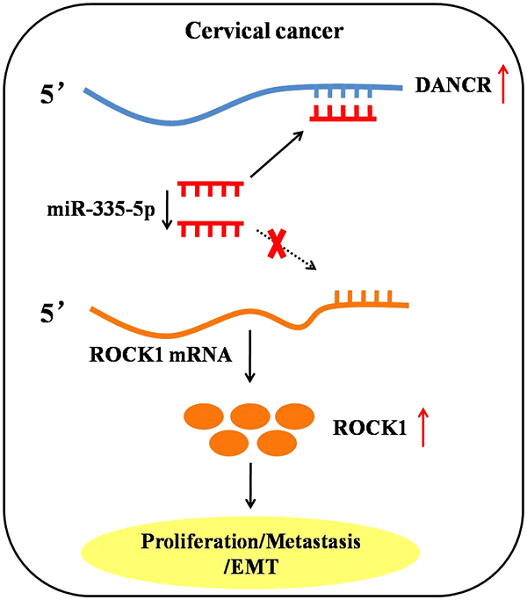
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA) differentiation antagonizing nonprotein coding RNA (DANCR) was significantly elevated in cervical cancer tissues and closely correlated with poor prognosis in cervical cancer patients. LncRNA DANCR promoted cervical cancer progression by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to regulate Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) expression via sponging miR-335-5p in vitro.
Rs217727 polymorphism in H19 promotes cell apoptosis by regulating the expressions of H19 and the activation of its downstream signaling pathway
- Pages: 7279-7291
- First Published: 26 October 2018
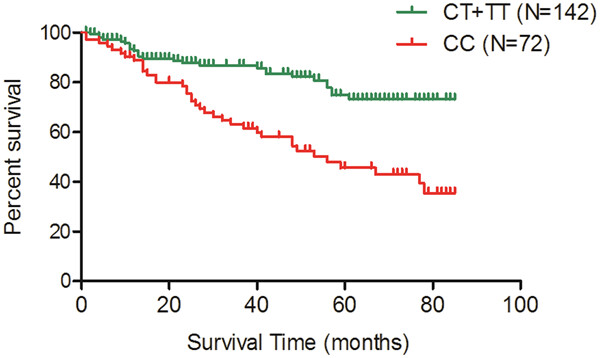
The objective of the current study was to explore the role of H19 rs217727 polymorphism in the control of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). And we came to the conclusion that the polymorphism of rs217727 in H19 was associated with HCC via the H19/miR-675/FADD/caspase-8/caspase-3/apoptosis signaling pathway.
DGCR5 attenuates neuropathic pain through sponging miR-330-3p and regulating PDCD4 in CCI rat models
- Pages: 7292-7300
- First Published: 14 October 2018
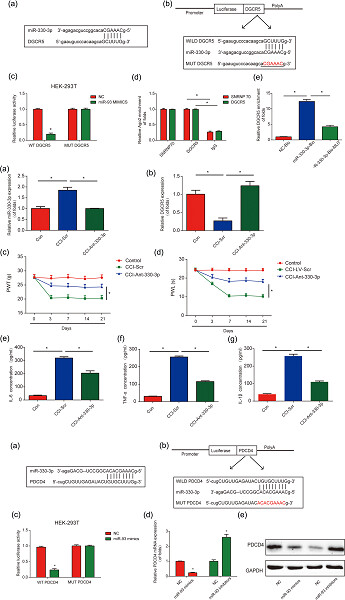
We observed that DGCR5 can inhibit neuroinflammation by reducing tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and IL-1β through targeting miR-330-3p. MiR-330-3p was validated as a target of DGCR5 and PDCD4 was predicted as a downstream target of miR-330-3p, respectively. Overexpression of DGCR5 elevated PDCD4 levels via sponging miR-330-3p in vivo.
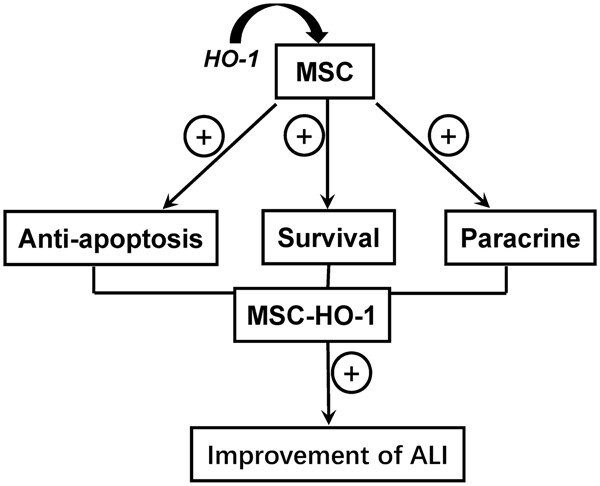
Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing heme oxygenase-1 ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats
- Pages: 7301-7319
- First Published: 26 October 2018
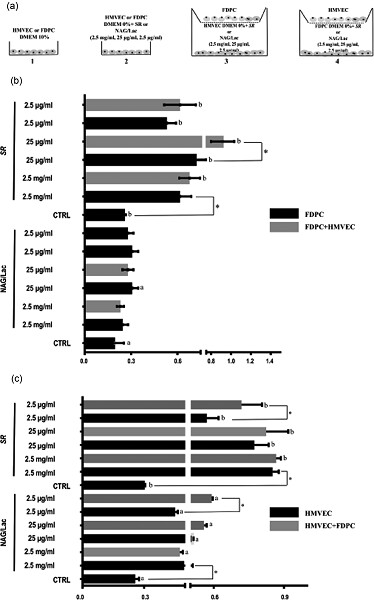
Serenoa repens and N-acetyl glucosamine/milk proteins complex differentially affect the paracrine communication between endothelial and follicle dermal papilla cells
- Pages: 7320-7329
- First Published: 12 November 2018
Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide inhibits UVB-induced melanogenesis by antagonizing cAMP/PKA and ROS/MAPK signaling pathways
- Pages: 7330-7340
- First Published: 26 October 2018
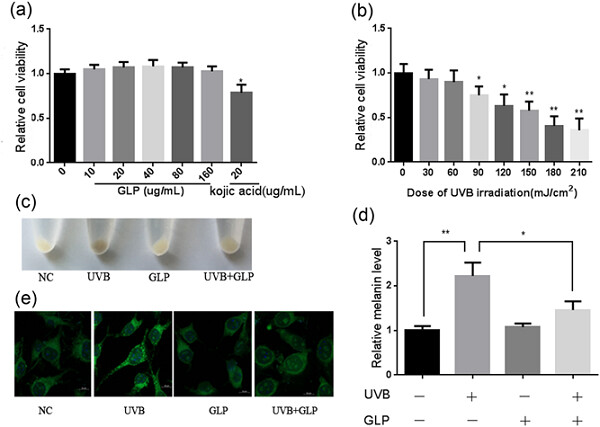
This study is the first to explore the role of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide (GLP) in inhibiting Ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced melanogenesis and its possible mechanism. we found that GLP could inhibit UVB-induced melanogenesis by antagonizing cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A (cAMP/PKA) and reactive oxygen species/mitogen-activated protein kinase (ROS/MAPK) signaling pathways and is a potential natural safe whitening sunscreen additive
CXCL8 gene silencing promotes neuroglial cells activation while inhibiting neuroinflammation through the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB-signaling pathway in mice with ischemic stroke
- Pages: 7341-7355
- First Published: 26 October 2018
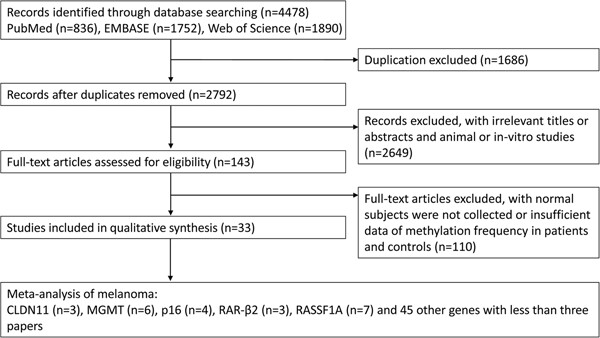
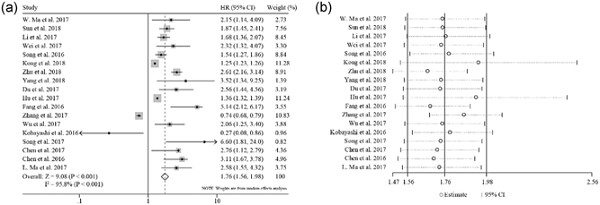
Promoter methylation as biomarkers for diagnosis of melanoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 7356-7367
- First Published: 28 October 2018
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: Molecular insights into development of Trichoderma interfusants for multistress tolerance enhancing antagonism against Sclerotium rolfsii Sacc
- Pages: 7368-7383
- First Published: 28 October 2018
The study addressed development of diverse Trichoderma fusants for fungicides, drought and salt tolerance, gene specific confirmation for heterozygous and homozygous mutants, and identified potent fusants for biocontrol activity against the pathogen Sclerotium rolfsii. The potent fusant (Fu21) derived from the current study could be utilized for in vivo inhibition of S. rolfsii causing stem rot in groundnut by formulating an effective bioformulation with a low dose of fungicides as part of integrated disease management under adverse conditions (abiotic stresses-drought and salt).
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Exogenous glutathione improves intracellular glutathione synthesis via the γ-glutamyl cycle in bovine zygotes and cleavage embryos
- Pages: 7384-7394
- First Published: 26 October 2018
- (1)
Dynamic changes in concentrations of reactive oxygen species (ROS), glutathione (GSH), and GSX were measured for 0–32-hr postinsemination in the embryos which is conductive to identify the periods of sensitivity to oxidative stress and redox potential in the first cell cycle of early embryos.
- (2)
Addition of GSH in culture medium could improve the GSH contents of zygote.
- (3)
The influence way was via γ-glutamyl cycle.
Characterizing the multiple roles of FGF-2 in SOD1G93A ALS mice in vivo and in vitro
- Pages: 7395-7410
- First Published: 28 October 2018

Characterization of fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) and other growth factors and signaling effectors in vivo and in vitro in the SOD1G93A mouse model. Tissue-specific opposing gene regulation of FGF-2 and overall dysregulation of other growth factors were observed, which in the gastrocnemius muscle was associated with reduced downstream-extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (ERK) and protein kinase B (AKT) activation.
Downregulation of miR-24-3p promotes osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells by targeting SMAD family member 5
- Pages: 7411-7419
- First Published: 30 October 2018
Knockdown of long noncoding RNA urothelial carcinoma associated 1 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis via modulating autophagy
- Pages: 7420-7434
- First Published: 26 October 2018
Dehydroepiandrosterone stimulates inflammation and impairs ovarian functions of polycystic ovary syndrome
- Pages: 7435-7447
- First Published: 23 December 2018
To explore the relationship between the inflammation cytokines and PCOS, alterations of serum proteins in dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)-induced PCOS rats were screened by protein array, and the concentration of IFN-γ was further measured by using the sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. DHEA-induced PCOS rats had a decreased level of IFN-γ compared with the control rats, which was restored partly in flutamide-treated rats. Using the KGN cell line, we demonstrated that the DHEA downregulated the expression and secretion of IFN-γ, which could be restored to some extent by treating with flutamide. As the results showed, DHEA inhibited the proliferation and promoted the apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells through downregulating the expression of IFN-γ which could be restored by flutamide, and IFN-γ may serve as a potential inflammation biomarker for PCOS detection.
RNA-binding protein, human antigen R regulates hypoxia-induced autophagy by targeting ATG7/ATG16L1 expressions and autophagosome formation
- Pages: 7448-7458
- First Published: 14 October 2018
Long-term evaluation of corneal sub-basal nerve recovery after photorefractive keratectomy and influence of pars plana vitrectomy
- Pages: 7459-7466
- First Published: 11 November 2018
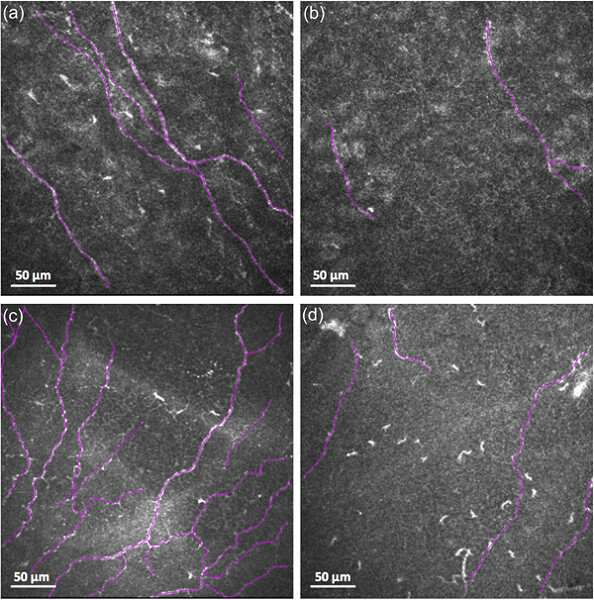
The aim of the study is to evaluate corneal sub-basal nerves (SBN) a mean of 15.6 years after photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) and the effects on them of pars plana vitrectomy (PPV), using in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM). PRK eyes showed reduced SBN plexus compared with non-PRK eyes. In addition, SBN density showed a slow but continuous recovery process up to the end of our follow-up (25 years) after PRK. Both PRK and non-PRK eyes showed a marked reduction in SBN density 6 months after PPV.
Exercise ameliorates insulin resistance via regulating TGFβ-activated kinase 1 (TAK1)-mediated insulin signaling in liver of high-fat diet-induced obese rats
- Pages: 7467-7474
- First Published: 26 October 2018
OxLDL induces vascular endothelial cell pyroptosis through miR-125a-5p/TET2 pathway
- Pages: 7475-7491
- First Published: 28 October 2018
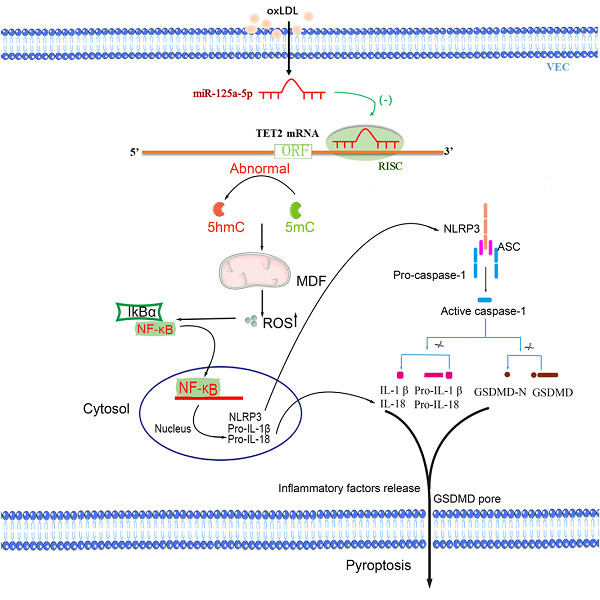
In this study, we revealed that miR-125a-5p mediates oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL)-induced pyroptosis in the vascular endothelial cell (VECs) by downregulating tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2 (TET2). TET2 suppression will increasing nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation, activating NLRP3 and caspase-1, and ultimately causing pyroptosis of VECs. After TET2 downregulation, abnormal DNA methylation will occur, and subsequently, mitochondrial dysfunction will induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, which activates NLRP3 inflammasome, leading to the activation of caspase-1. Activated caspase-1 triggers pore formation of the membrane, DNA fragmentation, and release of mature interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18 from cells, causing a sterile inflammation response and further contributing to pyroptotic cell death and subsequently promoting atherosclerosis.
Intersectin-Cdc42 interaction is required for orderly meiosis in porcine oocytes
- Pages: 7492-7497
- First Published: 27 November 2018
Garcinol suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and its underlying mechanism
- Pages: 7498-7509
- First Published: 23 November 2018
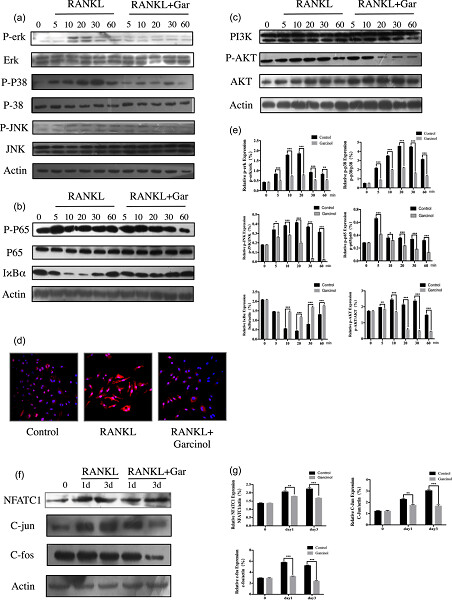
-
Garcinol suppresses osteoclast (OCs) formation and function in vitro.
-
Garcinol impairs the receptor activator for the nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced mitogen-associated protein kinases (MAPK), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), and AKT signaling pathway.
-
Garcinol suppresses osteolysis in vivo.
-
Garcinol may be a new therapeutic option for osteolytic bone diseases
Mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibition of myoblast differentiation in mice with high-fat-diet-induced pre-diabetes
- Pages: 7510-7523
- First Published: 26 October 2018
Repression of TXNIP–NLRP3 axis restores intestinal barrier function via inhibition of myeloperoxidase activity and oxidative stress in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- Pages: 7524-7538
- First Published: 01 November 2018

Taken together, our findings demonstrated that inhibited activation of the TXNIP–NLRP3 axis reduced myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and oxidative stress and thus restored the intestinal barrier function in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). TXNIP–NLRP3 axis may be a promising therapeutic strategy for the NASH treatment.
Crucial role of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP-1) in cellular proliferation of Dictyostelium discoideum
- Pages: 7539-7547
- First Published: 14 October 2018
PROSTAGLANDIN E2 stimulates cancer-related phenotypes in prostate cancer PC3 cells through cyclooxygenase-2
- Pages: 7548-7559
- First Published: 26 October 2018
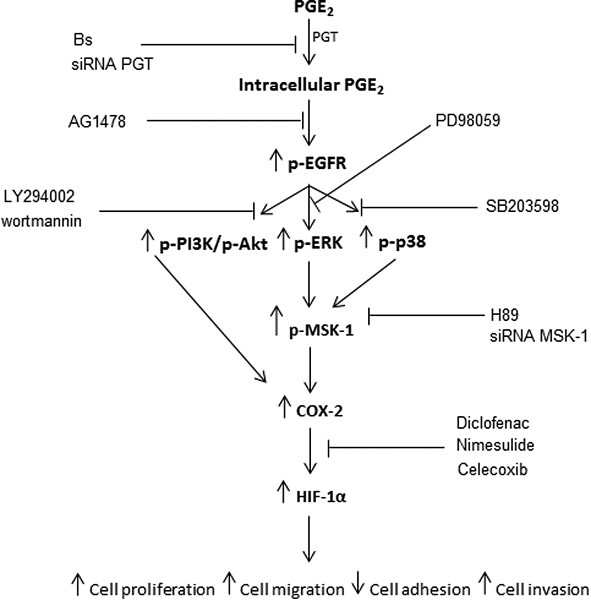
In this study, we have shown that cyclooxygenase (COX-2) activity is an absolute requirement for the protumorigenic intracrine effects of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in PC3 cells. Furthermore, our data show a novel positive feedback loop through which intracellular PGE 2 (iPGE 2) upregulates COX-2 and that might underlie the intracrine effects of PGE2 in PC3 cells.
Licochalcone A attenuates abdominal aortic aneurysm induced by angiotensin II via regulating the miR-181b/SIRT1/HO-1 signaling
- Pages: 7560-7568
- First Published: 11 November 2018
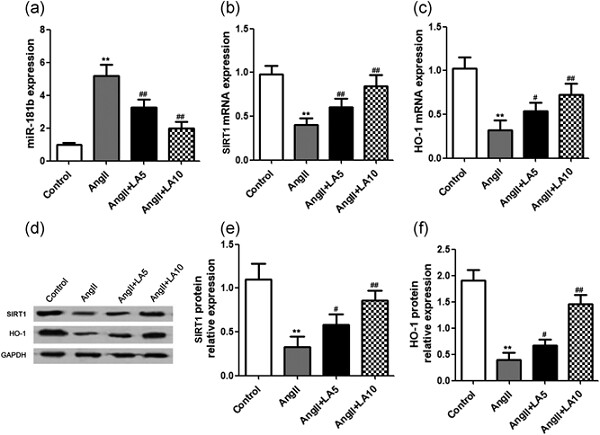
LA administration dose-dependently reduced the incidence of AngII-induced AAA, aneurysm diameter enlargement, elastin degradation, matrix metalloproteinase production, pro-inflammatory cytokines and miR-181b expression, and vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis. LA could attenuate AngII-induced AAA by modulating the miR-181b/SIRT1/HO-1 signaling.
Matrix stiffness modulates the differentiation of neural crest stem cells in vivo
- Pages: 7569-7578
- First Published: 26 October 2018
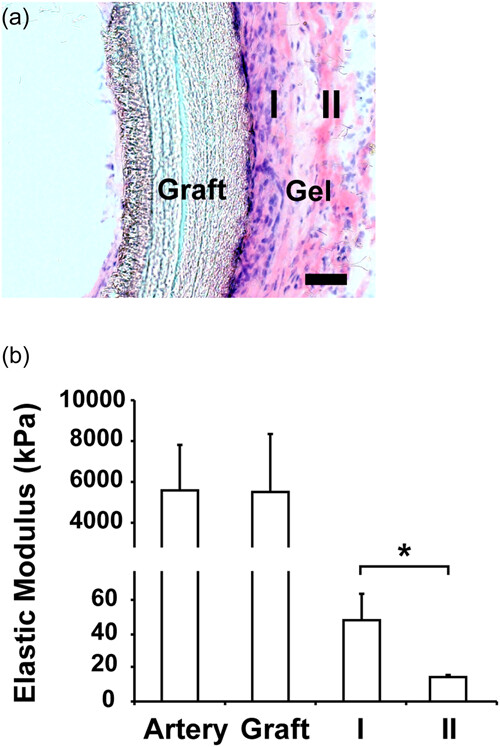
Stem cells are often transplanted for tissue regeneration, however, it is unclear how the transplanted stem cell fate is regulated in vivo. In this study, we found that matrix stiffness was a key factor in regulating the differentiation of transplanted neural crest stem cells, which differentiated into smooth muscle cells in the stiff matrix and into glial cells in the soft matrix. This finding has important implications in stem cell therapies and tissue engineering.
Multiomics analysis on DNA methylation and the expression of both messenger RNA and microRNA in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 7579-7586
- First Published: 28 October 2018
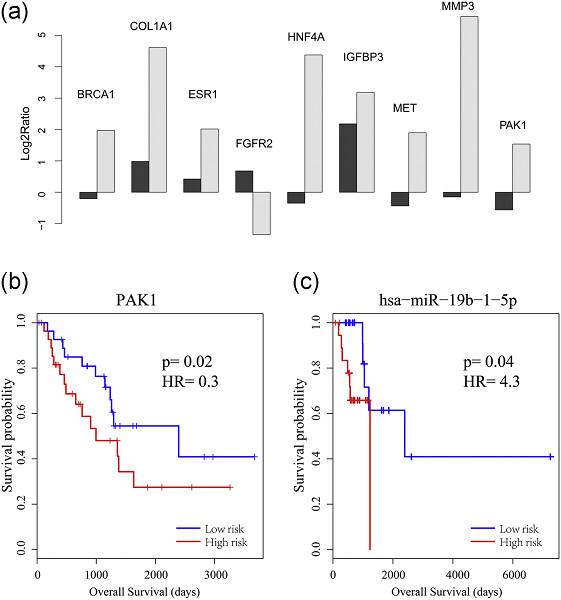
a total of nine genes that play important roles in the development of LUAD were identified, and PAK1 and FGFR2 can be served as prognostic biomarkers for LUAD patients. The genes found in this study played different roles in the tumor progression of LUAD, which indicating these genes may be considered as potential target genes for LUAD treatment.
MicroRNA-145 induces the senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells through the activation of p53 pathway by ZEB2
- Pages: 7587-7599
- First Published: 27 November 2018
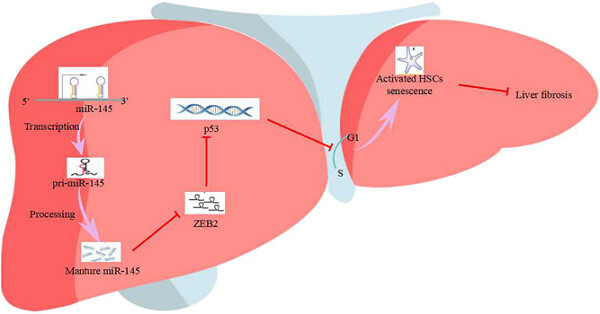
MicroRNA-145 (miR-145) exerts its functions by targeting zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 (ZEB2) depended on p53 manner. Schematic representation of the proposed mechanism. Transcription of miR-145 gene increases the expression of mature miR-145 which targets the 3′-untranslated regions of ZEB2 to suppress its translation. Reduced expression of ZEB2 can no longer effectively inhibit p53 transcription factors, thereby accelerating the expression of p53. Ultimately, the increased level of p53 inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes the senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells, thereby inhibiting liver fibrosis.
Hepcidin and iron regulatory proteins coordinately regulate ferroportin 1 expression in the brain of mice
- Pages: 7600-7607
- First Published: 28 October 2018
Iron regulatory proteins (IRPs) and hepcidin coordinately regulate ferroportin 1 (FPN1) expression. IRP2 knockout led to an increase in FPN1 expression in mouse brain, whereas IRP1/IRP2 dual knockdown caused a massive increase in FPN1 expression. Knockout of IRP2 severely affected the regulation effect of hepcidin on FPN1 in mice, and the compromised hepcidin–FPN1 regulation directly depended on the iron regulation element (IRE) in FPN1 messenger RNA.
Amino acids stimulate glycyl-tRNA synthetase nuclear localization for mammalian target of rapamycin expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells
- Pages: 7608-7621
- First Published: 23 November 2018
Glycyl-tRNA synthetase (GlyRS) has a bipartite type of nuclear localization signals in its WHEP domain, and amino acids (Met, Leu, and Lys) trigger GlyRS phosphorylation at Thr544 and Ser704 in the cytoplasm and subsequent nuclear translocation. Nuclear p-GlyRS physically interacts with and stimulates nuclear factor kappa B1 phosphorylation, thereby stimulating the expression of its downstream gene mammalian target of rapamycin and inhibiting autophagy.
Romina: A powerful strawberry with in vitro efficacy against uterine leiomyoma cells
- Pages: 7622-7633
- First Published: 14 October 2018
Strawberry of cultivars Alba, Romina, and Romina anthocyanin fraction induced apoptosis and increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels of leiomyoma cells, while increased cell viability and decreased ROS concentrations of myometrial cells. Leiomyoma cells showed also a decrease of glycolysis (extracellular acidification rate) and fibrotic gene (collagen 1A1, fibronectin, versican, and activin A) expression after strawberry (cultivars Alba, Romina, and Romina anthocyanin) treatment.
miR-145-5p affects the differentiation of gastric cancer by targeting KLF5 directly
- Pages: 7634-7644
- First Published: 26 October 2018
Interleukin-37 inhibits osteoclastogenesis and alleviates inflammatory bone destruction
- Pages: 7645-7658
- First Published: 10 November 2018





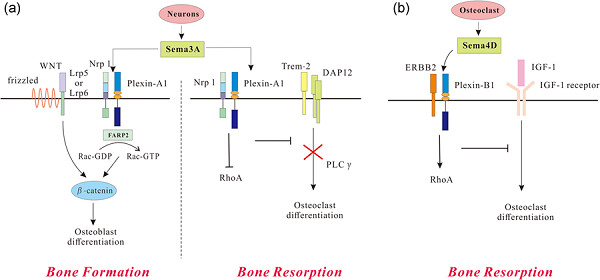
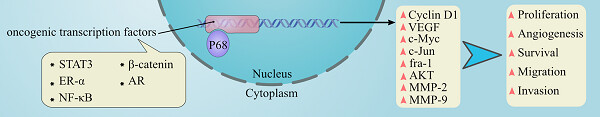
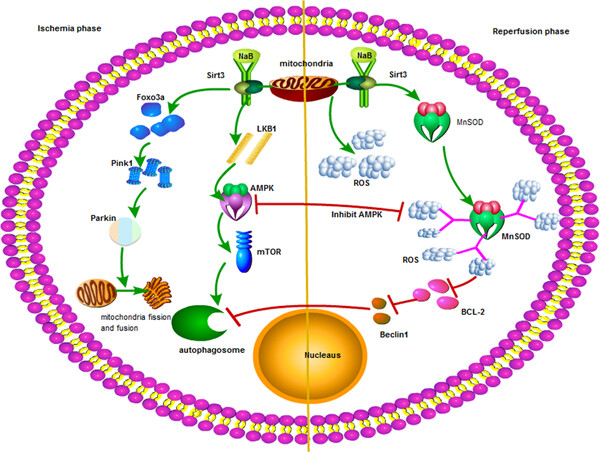


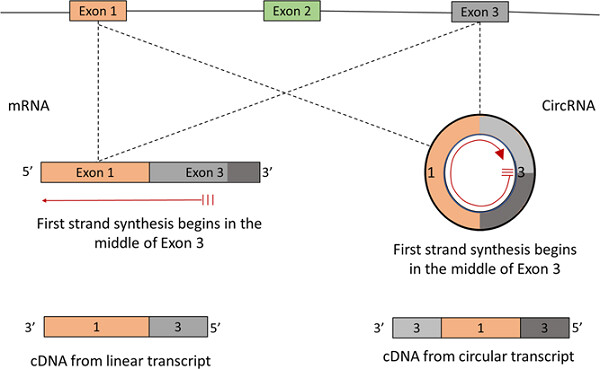
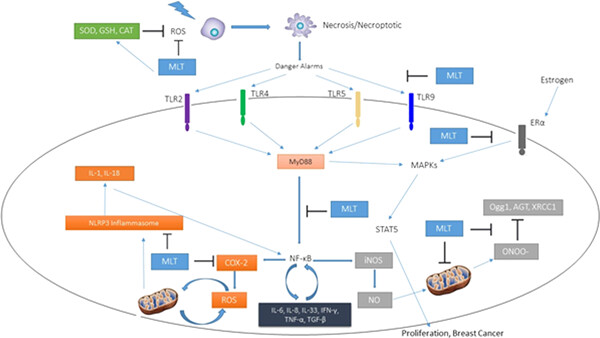
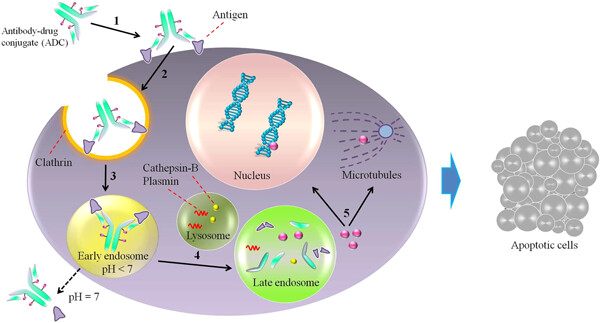
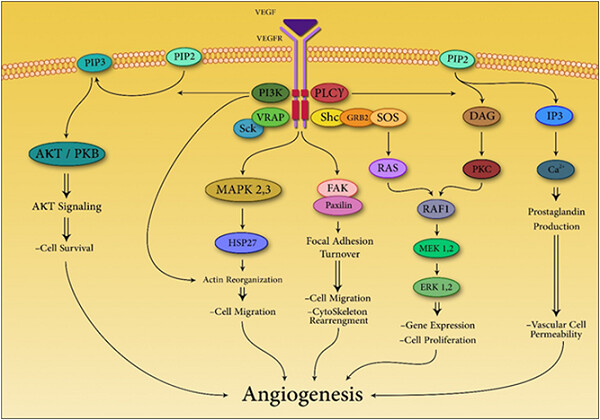
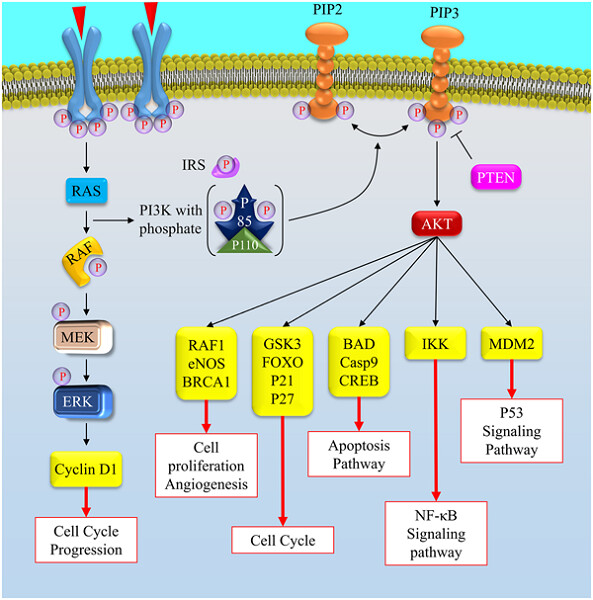
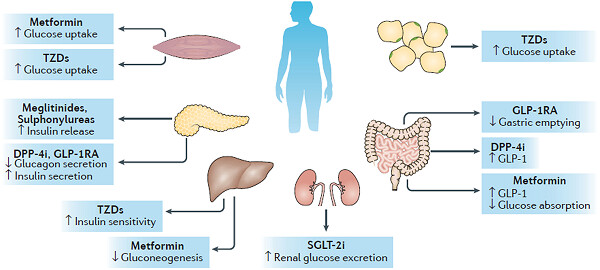
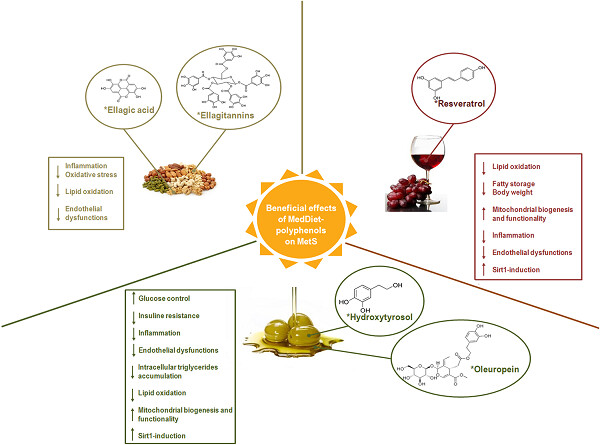
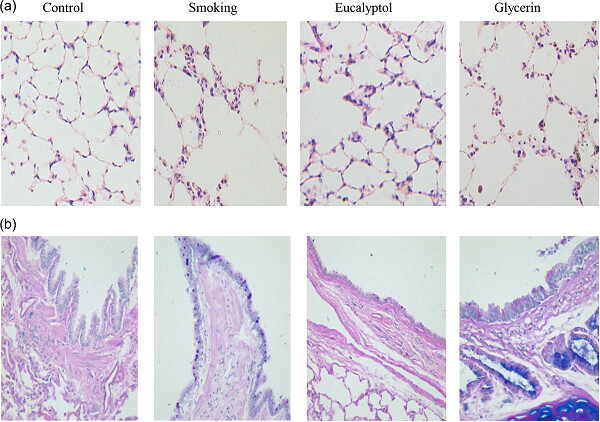
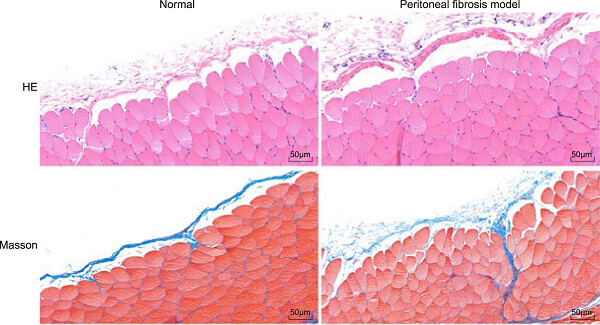
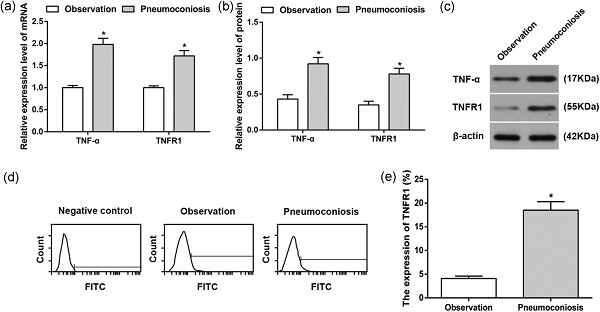
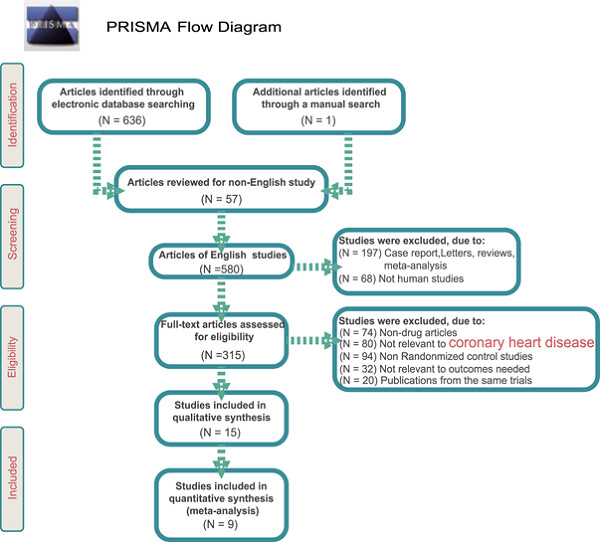
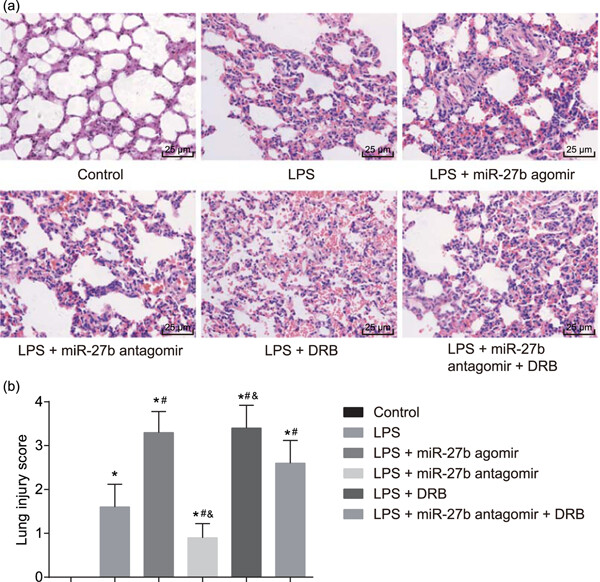
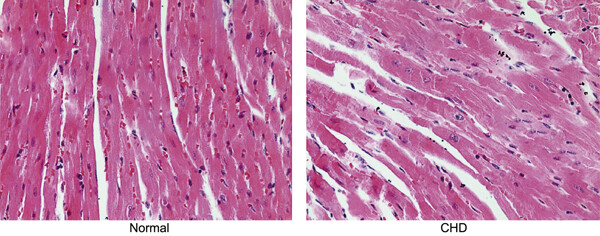
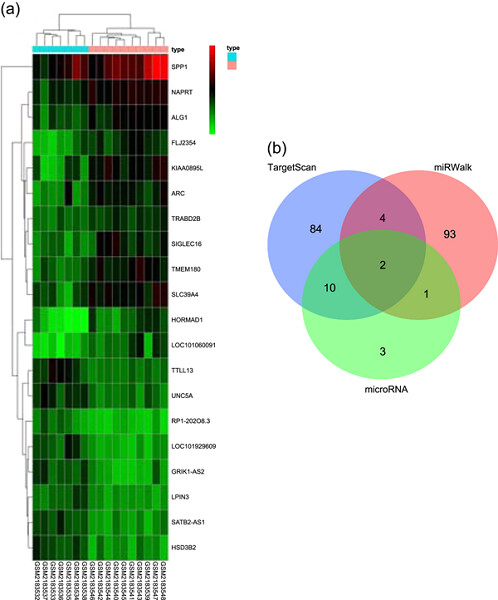
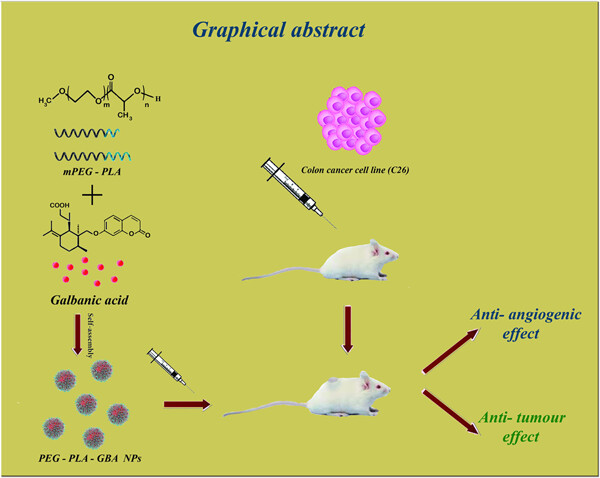
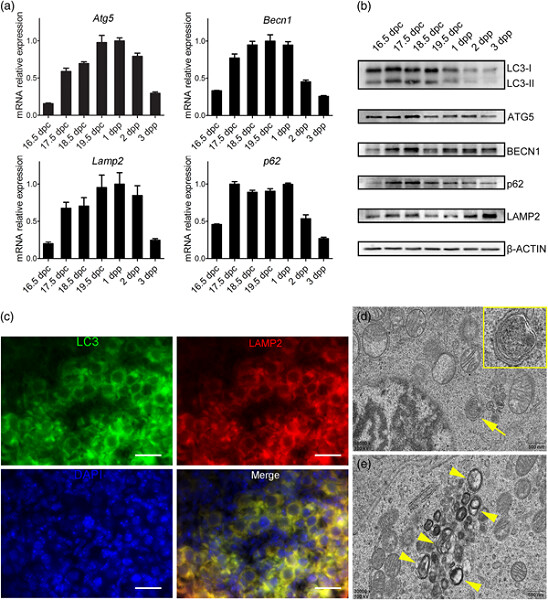
![Melatonin defends mouse oocyte quality from benzo[ghi]perylene-induced deterioration](/cms/asset/2dc47b27-d35b-4d2c-9acd-3c73c87b6105/jcp27351-gra-0001-m.jpg)