Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Bio-adhesive Nanoporous Module: Toward Autonomous Gating (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2021)
- Page: 8557
- First Published: 01 March 2021

A bio-adhesive covalent organic framework with calmodulin as a proteinous gate is reported by Takuzo Aida, Kou Okuro et al. in their Research Article on page 8932. The gate functionality is used for calcium-ion-triggered guest release from the nanopores.
Inside Cover: Fe/Fe3C Boosts H2O2 Utilization for Methane Conversion Overwhelming O2 Generation (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2021)
- Page: 8558
- First Published: 08 March 2021

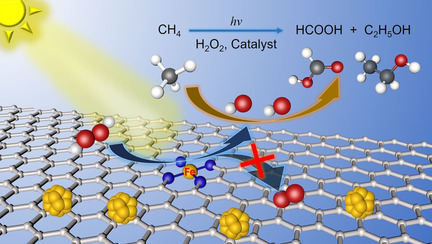
Fe-Nx in the low-spin state is the active site in the homolytic cleavage of H2O2 to .OH, as reported by Wenting Wu, Mingbo Wu, and co-workers in their Research Article on page 8889. Fe/Fe3C promotes the formation of Fe-Nx sites for this homolytic cleavage process, enabling the highly selective oxidation of CH4 to HCOOH under light irradiation.
Inside Back Cover: One Polyketide Synthase, Two Distinct Products: Trans-Acting Enzyme-Controlled Product Divergence in Calbistrin Biosynthesis (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2021)
- Page: 9143
- First Published: 01 March 2021

Calbistrin biosynthesis involves an unusual dual-functional polyketide synthase CalA, which synthesizes both of the two structurally distinct moieties of calbistrins. The product divergence is intriguingly controlled by two trans-acting enzymes, a trans-acting enoylreductase CalK and a trans-acting C-methyltransferanse CalH, to yield the decalin and polyene portions, respectively. The esterification of the two polyketide parts is catalyzed by the acyltransferase CalD, as reported by Yudai Matsuda, Ikuro Abe, and co-workers in their Research Article on page 8851.
Back Cover: Tautomeric Molecule Acts as a “Sunscreen” for Metal Halide Perovskite Solar Cells (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2021)
- Page: 9144
- First Published: 01 March 2021

UV light and surface defects accelerate the degradation process of perovskite solar cells (PSCs). In their Communication on page 8673, Mingzhu Li, Yanlin Song, and co-workers utilize the tautomerism of “sunscreen” molecules under UV light illumination to protect the PSC from degradation and enable molecular defect passivation, achieving high efficiency and long-term UV stability of PSCs.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Traceless Removal of Two Kernel Atoms in a Gold Nanocluster and Its Impact on Photoluminescence
- First Published: 01 April 2021

Nanoclusters The synthesis and characterization of two novel gold nanoclusters is reported by Nan Xia, Zhikun Wu et al. in their Communication on page 8668. The traceless removal of two kernel atoms has been achieved for the first time.
Frontispiece: Rapid High-Resolution 3D Printing and Surface Functionalization via Type I Photoinitiated RAFT Polymerization
- First Published: 01 April 2021

3D Printing In their Research Article on page 8839, Kenny Lee, Nathaniel Corrigan, and Cyrille Boyer make use of a type I photoinitiated RAFT polymerization for rapid high-resolution 3D printing and surface functionalization.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 16/2021
- Pages: 8561-8580
- First Published: 01 April 2021
Minireviews
Carbon Dots
The Rapid and Large-Scale Production of Carbon Quantum Dots and their Integration with Polymers
- Pages: 8585-8595
- First Published: 15 May 2020
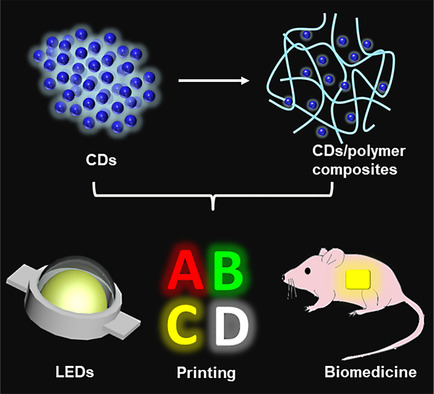
The latest developments in the large-scale production of carbon quantum dots by using microwave, ultrasonic, plasma, magnetic hyperthermia, and microfluidic techniques are outlined. The synthetic methods for generating carbon dot/polymer composites are summarized, whereby the carbon quantum dots can serve as fillers, monomers, or initiators. Promising applications, current challenges, and future perspectives are also highlighted and discussed.
Genome Editing
Spatiotemporal Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing Machinery Using Stimuli-Responsive Vehicles
- Pages: 8596-8606
- First Published: 09 May 2020
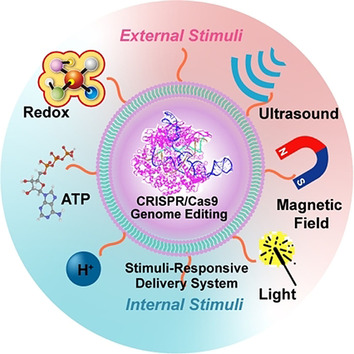
Spatiotemporal delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing machinery is of great importance for developing chemical biology tools for manipulating cellular DNA sequences to treat genetic disorders. This Minireview provides an overview of synthetic approaches and specific chemistries that have been used to develop stimuli-responsive vehicles for CRISPR/Cas9 delivery and genome editing in a controlled manner.
Reviews
Multicolor Fluorescence
Multicolor Fluorescent Polymeric Hydrogels
- Pages: 8608-8624
- First Published: 30 August 2020
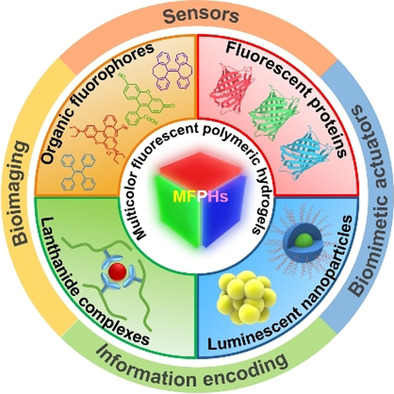
Multicolor fluorescent polymeric hydrogels (MFPHs), rising stars of luminescent materials, are the marriage of multicolor fluorescent materials and polymeric hydrogels. They have many extraordinary properties, such as a tissue-like modulus, an intrinsic soft and wet nature, and fluorescence color change. In this Review, recent progress in MFPHs is summarized, with a particular focus on the construction methods and important applications.
Main Group Multiple Bonds
Acid–Base Free Main Group Carbonyl Analogues
- Pages: 8626-8648
- First Published: 13 July 2020
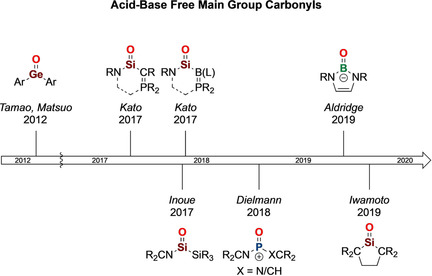
Recently, hitherto elusive acid- and base-free main group carbonyl analogues (R2E=O) derived from group 13 to 15 elements have been isolated in crystalline form. Their unperturbed nature elicits exciting new chemistry, spanning the vista from classical organic carbonyl-type reactions to transition metal-like oxide ion transfer chemistry.
Circadian Clocks
Circadian Rhythms and the Transcriptional Feedback Loop (Nobel Lecture)
- Pages: 8650-8666
- First Published: 26 February 2021
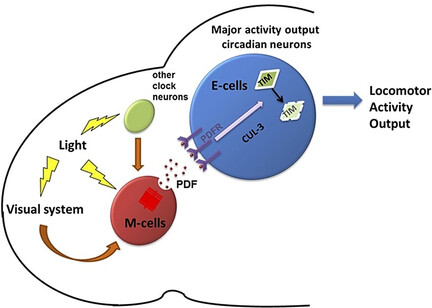
Circadian rhythms are present in most if not all animals, plants, and even photosynthetic cyanobacteria. These cyanobacterial clocks as well as plant clocks are very different from those of animals, with no credible homology between the different clock proteins. Therefore circadian rhythms probably emerged multiple times in evolution, which underscores their importance.
Communications
Gold Nanoclusters | Hot Paper
Traceless Removal of Two Kernel Atoms in a Gold Nanocluster and Its Impact on Photoluminescence
- Pages: 8668-8672
- First Published: 29 January 2021
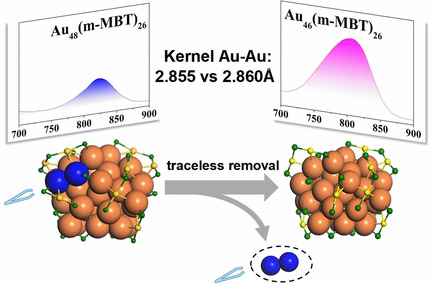
Two novel nanoclusters Au48(m-MB)26 and Au46(m-MBT)26 have been synthesized and fully characterized, and the traceless removal of two kernel atoms in metal nanoclusters has been achieved for the first time. The two kernel atoms reduction leads to the photoluminescence quantum yield (QY) increase by almost four times. In addition, kernel bond length dependent photoluminescence and kernel charge state were first revealed.
Perovskite Solar Cells | Very Important Paper
Tautomeric Molecule Acts as a “Sunscreen” for Metal Halide Perovskite Solar Cells
- Pages: 8673-8677
- First Published: 04 February 2021
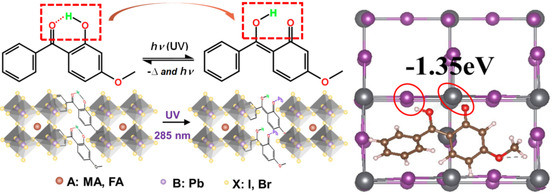
Harmful UV light and surface defects accelerate the degradation of perovskite solar cells (PSCs). A tautomeric “sunscreen” molecule can be used to protect the PSC from UV degradation and enable molecular defect passivation (defect formation energy: −1.35 eV) through interactions between functional groups and defects. This strategy provides high-efficiency PSCs with long-term UV stability.
Photoswitches
Cryo-EM Resolves Molecular Recognition Of An Optojasp Photoswitch Bound To Actin Filaments In Both Switch States
- Pages: 8678-8682
- First Published: 15 January 2021
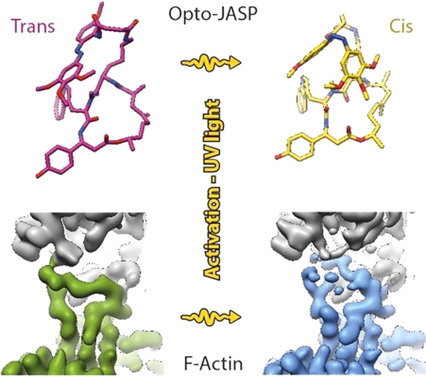
Targeting actin requires spatiotemporal control of drug activity. Optojasps are photo-switchable small molecules, providing direct optical spatiotemporal control of the actin cytoskeleton. We present high-resolution cryo-EM structures of both isomeric states of an optojasp bound to F-actin and describe in detail the binding pocket and conformational changes associated with switching of the azobenzene.
Quantum Bits | Hot Paper
Blatter-Radical-Grafted Mesoporous Silica as Prospective Nanoplatform for Spin Manipulation at Ambient Conditions
- Pages: 8683-8688
- First Published: 24 January 2021
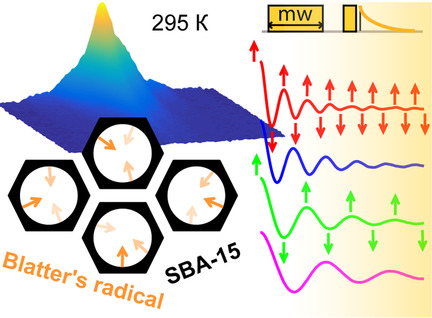
Extremely stable Blatter's type organic radicals grafted into the mesoporous silica show advanced relaxation properties at room temperature. Electron spin decoherence time exceeds that in many other qubit candidates, allowing efficient spin manipulation at ambient conditions. The tuneable multifunctional nature of such composite materials promotes them as promising nanoplatforms for developing new spin-based quantum bits.
MXenes
Ambient-Stable Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide (MXene) Enabled by Iodine Etching
- Pages: 8689-8693
- First Published: 22 January 2021
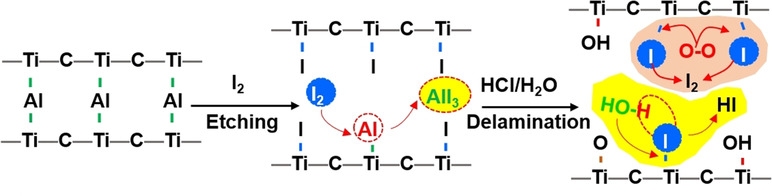
An iodine-assisted method has been developed for etching bulk Ti3AlC2 in anhydrous acetonitrile (CH3CN), resulting in 2D MXene sheets (Ti3C2Tx, T=O, OH) with intact lattice, high yield (71 %), large size (1.8 μm) and ultimate thickness (<5 nm). 2D MXene sheets present great ambient stability in water for at least 2 weeks and high gravimetric capacitances of 293 F g−1 at 1 mV s−1 when serving as electrode materials for supercapacitors.
Interfacial Assemblies | Hot Paper
Visualizing Interfacial Jamming Using an Aggregation-Induced-Emission Molecular Reporter
- Pages: 8694-8699
- First Published: 24 January 2021
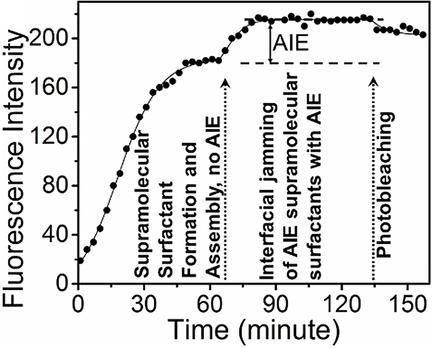
With the interfacial jamming of nanoparticles (NPs), a load-bearing network of NPs forms as the areal density of NPs increases, converting a liquid-like assembly into a solid-like assembly. Real-time fluorescence imaging has been used to probe the evolution of the interfacial dynamics of nanoparticle surfactants at the water/oil interface by using aggregation-induced emission as a reporter for the transition of the assemblies into the jammed state (see graph).
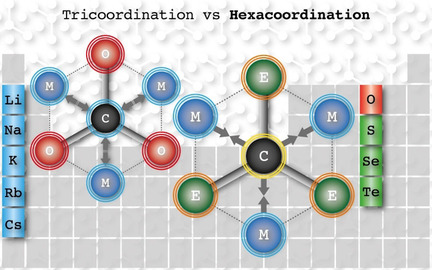
Computational Chemistry | Hot Paper
Planar Hexacoordinate Carbons: Half Covalent, Half Ionic
- Pages: 8700-8704
- First Published: 01 February 2021
Photocatalysis | Hot Paper
Efficient Infrared-Light-Driven CO2 Reduction Over Ultrathin Metallic Ni-doped CoS2 Nanosheets
- Pages: 8705-8709
- First Published: 20 January 2021
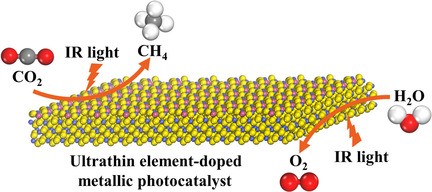
It is a tough task to achieve IR-light-driven CO2 reduction. Herein, an element-doped ultrathin metallic photocatalyst is designed to achieve IR-light-driven CO2 reduction. Among the reported single-component photocatalysts, the most efficient IR-light-driven CO2 reduction is realized by Ni-doped CoS2 nanosheets.
Self-Assembly | Hot Paper
Stable Thermotropic 3D and 2D Double Gyroid Nanostructures with Sub-2-nm Feature Size from Scalable Sugar–Polyolefin Conjugates
- Pages: 8710-8716
- First Published: 10 February 2021
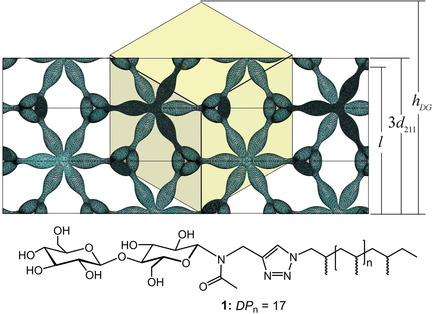
Ultra-low molecular weight disaccharide–polyolefin conjugates with cellobiose, lactose and maltose head groups and atactic polypropene tails, such as 1, provide highly ordered and exceptionally stable thermotropic hexagonal perforated lamellar (HPL) and double gyroid (DG) nanostructured phases. The unique stability of this DG phase extends further down to the two-dimensional limit of 15 nm in which film thickness, l, is now less than the surface-oriented unit cell height, hDG.
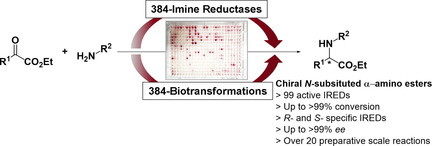
Biocatalysis
Asymmetric Synthesis of N-Substituted α-Amino Esters from α-Ketoesters via Imine Reductase-Catalyzed Reductive Amination
- Pages: 8717-8721
- First Published: 08 February 2021
DNA Nanotechnology
A Long and Reversibly Self-Assembling 1D DNA Nanostructure Built from Triplex and Quadruplex Hybrid Tiles
- Pages: 8722-8727
- First Published: 12 February 2021
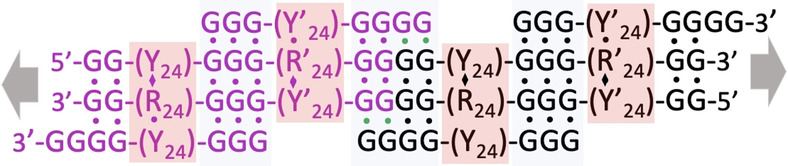
A new and reversible 1-dimensional DNA nanostructure, assembled from DNA triplexes and G-quadruplexes, is reported. These “TQ Hybrid” nanostructures require potassium ions and acidic pH to form and are easily disassembled by removal of either requirement. We anticipate that they will find unique and varied application as communication modules, sensors, logic gates, and in diverse other uses of DNA nanotechnology.
Synthetic Methods
Synthesis of Ketones by C−H Functionalization of Aldehydes with Boronic Acids under Transition-Metal-Free Conditions
- Pages: 8728-8732
- First Published: 21 January 2021

Nitrosobenzene can simultaneously activate the C−H bonds of aldehydes and the C−B bonds of boronic acids triggering a C−C bond-forming process that leads to the synthesis of ketones via an intramolecular migration from boron to carbon. These findings constitute a transition-metal-free practical, scalable, and operationally easy method for the synthesis of ketones.
Helicenes
Chiral Near-Infrared Fluorophores by Self-Promoted Oxidative Coupling of Cationic Helicenes with Amines/Enamines
- Pages: 8733-8738
- First Published: 22 January 2021
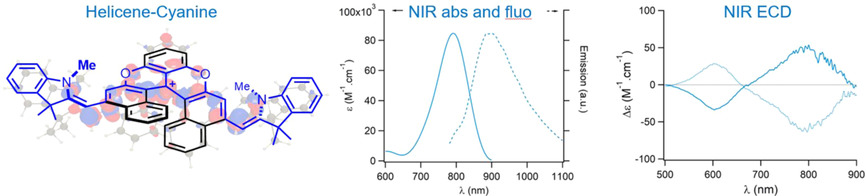
Cationic dioxa[6]helicene oxidizes alkyl amines to enamines and further reacts in situ as an electrophile to form, in one-pot multi-step cascades, fully delocalized mono or bis donor-π-acceptor coupling products. This original approach provides chiral cyanine-like chromophores that absorb up to the NIR and fluoresce alike, with intense NIR ECD (Δϵ up to 60 M−1 cm−1). DFT showcases the importance of conformers in the strong chiroptical response.
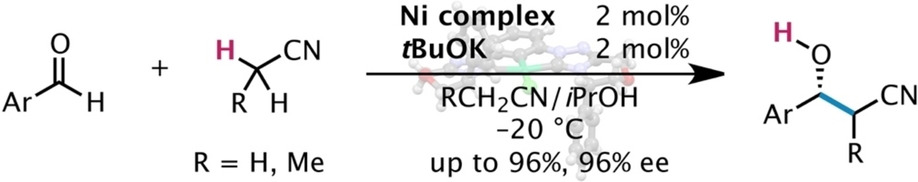
Homogeneous Catalysis
Direct Catalytic Asymmetric Addition of Alkylnitriles to Aldehydes with Designed Nickel–Carbene Complexes
- Pages: 8739-8743
- First Published: 02 February 2021
Electrosynthesis
Electrochemical Radical Silyl-Oxygenation of Activated Alkenes
- Pages: 8744-8749
- First Published: 03 February 2021
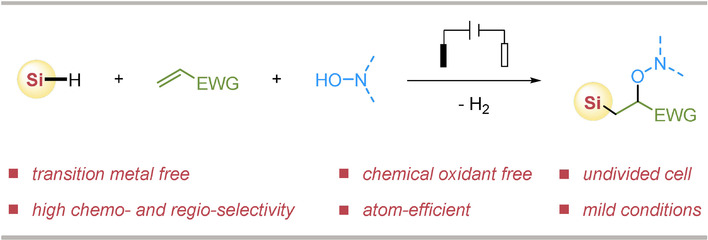
An efficient electrochemical radical silyl-oxygenation of electron-deficient alkenes is demonstrated, which gives access to a variety of highly functionalized silicon-containing molecules, including β-silyl-cyanohydrin derivatives in good yields with excellent chemo- and regio-selectivity under mild conditions without the use of transition-metal catalyst or chemical oxidant.
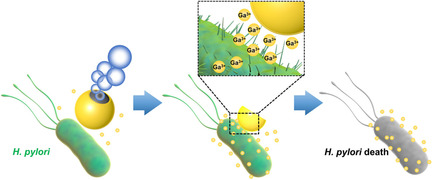
Micromotors | Hot Paper
Bubble-Propelled Janus Gallium/Zinc Micromotors for the Active Treatment of Bacterial Infections
- Pages: 8750-8754
- First Published: 22 January 2021
Polycations | Hot Paper
Formation of Nanoscale [Ge4O16Al48(OH)108(H2O)24]20+ from Condensation of ϵ-GeAl128+ Keggin Polycations
- Pages: 8755-8759
- First Published: 22 January 2021
Epigenetics | Hot Paper
Structure-Guided Discovery of a Potent and Selective Cell-Active Inhibitor of SETDB1 Tudor Domain
- Pages: 8760-8765
- First Published: 28 January 2021
Fluorescent Probes | Hot Paper
GlycoBODIPYs: Sugars Serving as a Natural Stock for Water-soluble Fluorescent Probes of Complex Chiral Morphology
- Pages: 8766-8771
- First Published: 25 January 2021
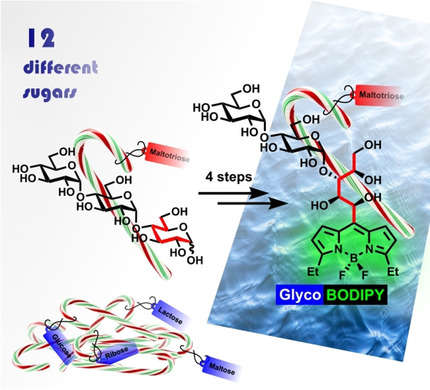
Twelve sugars, differing in size and stereochemistry, were used as building blocks in a modular, efficient four-step synthetic route to multifunctional BODIPY glycoconjugates with high fluorescence and hydrophilicity. The chiral information was transferred unchanged, thereby providing complex and distinct probes for target-oriented binding studies and specific in vivo imaging.
Iron Catalysis | Hot Paper
Iron-Catalyzed Radical Activation Mechanism for Denitrogenative Rearrangement Over C(sp3)–H Amination
- Pages: 8772-8780
- First Published: 19 January 2021
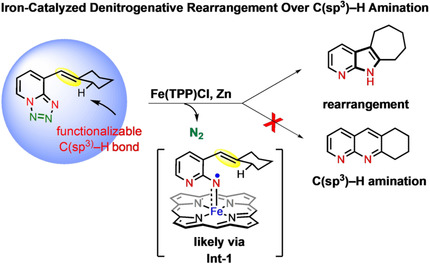
An iron-catalyzed rearrangement of 1,2,3,4-tetrazole is developed over the competitive C(sp3)–H amination. This catalytic rearrangement follows an unprecedented metalloradical activation mechanism. Employing the developed method, a wide number of complex-N-heterocyclic product classes have been accessed.
Biosynthesis
A Desaturase-Like Enzyme Catalyzes Oxazole Formation in Pseudomonas Indolyloxazole Alkaloids
- Pages: 8781-8785
- First Published: 18 January 2021
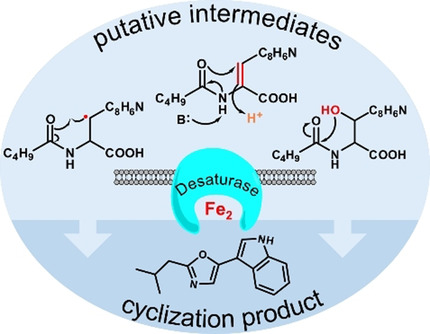
Indolyloxazole alkaloids are widespread natural products with diverse bioactivities but previously unknown biosynthesis. Transposon mutagenesis, heterologous pathway expression, and labeling experiments provide evidence for a Pseudomonas pathway involving oxazole formation by cyclization as a new reaction type catalyzed by a desaturase-like enzyme.
Organocatalysis
Hydrogen-Bonding Assisted Catalytic Kinetic Resolution of Acyclic β-Hydroxy Amides
- Pages: 8786-8791
- First Published: 24 December 2020
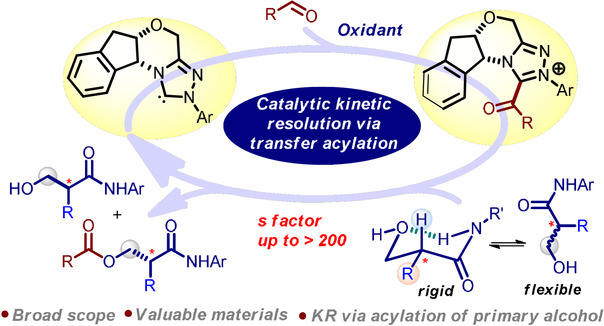
A method for catalytic kinetic resolution (KR) of acyclic α-substituted β-hydroxy amides was developed via enantioselective acylation of primary alcohol with an N-heterocyclic carbene. Enhanced selectivity was realized for the catalytic KR process using cyclic tertiary amine as a base additive. Diastereomeric transition state models are proposed to rationalize the origin of enantioselectivity.
Natural Products
Structural Revision of Natural Cyclic Depsipeptide MA026 Established by Total Synthesis and Biosynthetic Gene Cluster Analysis
- Pages: 8792-8797
- First Published: 02 February 2021
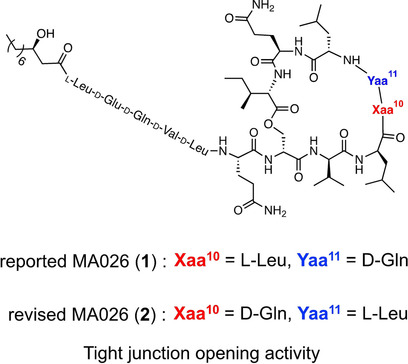
A revised structure of natural cyclic depsipeptide MA026 with tight junction opening activity was established by physicochemical analysis and confirmed by its total solid-phase synthesis. Bioinformatic analysis of the putative MA026 biosynthetic gene cluster demonstrated that the stereochemistry of amino acid residue in the revised structure can be reasonably explained.
CO2 Reduction
Boosting Production of HCOOH from CO2 Electroreduction via Bi/CeOx
- Pages: 8798-8802
- First Published: 29 January 2021

The limited current density, production rate as well as selectivity hinder the improvement of HCOOH production from CO2 electroreduction. Here, bismuth/cerium oxide (Bi/CeOx) displays outstanding performances for CO2 electroreduction to HCOOH, which not only shows excellent selectivity, but also achieves a high current density (149 mA cm−2) and especially the maximum HCOOH production rate (2600 μmol h−1 cm−2) ever reported.
Molecular Switches
The Atypical Hysteresis of [Fe(C6F5Tp)2]: Overlay of Spin-Crossovers and Symmetry-Breaking Phase Transition
- Pages: 8803-8807
- First Published: 26 January 2021
![The Atypical Hysteresis of [Fe(C6F5Tp)2]: Overlay of Spin-Crossovers and Symmetry-Breaking Phase Transition](/cms/asset/ae988d98-29a1-4d46-ac67-85eec7462db7/anie202015994-toc-0001-m.jpg)
The [FeII(C6F5Tp)2] complex is converted through melting from a crystal phase showing a very gradual spin-crossover to another one showing a broad hysteretic spin-transition. The uncommon “rounded” hysteresis occurs in a non-cooperative SCO system. It is due to a symmetry-breaking phase transition that is triggered when roughly ca. 50 % of the SCO complexes are switched.
Indoles
Unprecedented Reactivity of γ-Amino Cyclopentenone Enables Diversity-Oriented Access to Functionalized Indoles and Indole-Annulated Ring Structures
- Pages: 8808-8812
- First Published: 01 February 2021
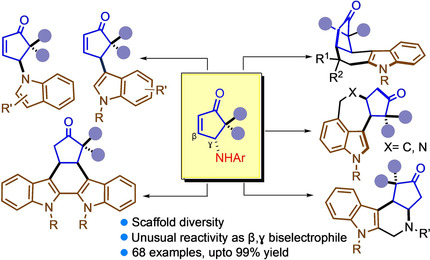
This work highlights diversity-oriented access to cyclopentenoid indoles and indole-alkaloid like structures which is pillared on an unprecedented latent reactivity of γ-aminoenones. The transformation highlights γ- or β,γ-functionalization of enones to generate new structural space. A reverse-aza-Piancatelli rearrangement seemed to be operating, which should invoke new attributes to its mechanism.
Organic Solar Cells
A Facile Synthesized Polymer Featuring B-N Covalent Bond and Small Singlet-Triplet Gap for High-Performance Organic Solar Cells
- Pages: 8813-8817
- First Published: 08 March 2021
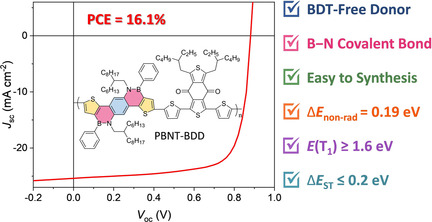
An easily synthesized building block BNT and a relevant polymer PBNT-BDD featuring B-N covalent bond were synthesized for application in solar cells. The polymer offered a power conversion efficiency of 16.1 %, a nonradiative recombination energy loss of 0.19 eV, and a singlet-triplet gap as low as 0.15 eV, demonstrating the promising prospect of B-N-containing materials in organic photovoltaics.
Synthetic Methods | Hot Paper
Pd/Cu-Catalyzed Defluorinative Carbonylative Coupling of Aryl Iodides and gem-Difluoroalkenes: Efficient Synthesis of α-Fluorochalcones
- Pages: 8818-8822
- First Published: 04 February 2021
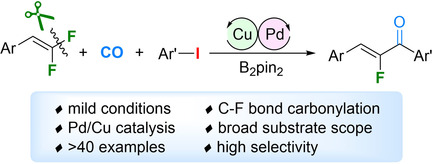
Enabled by a Pd/Cu cooperative catalyst system, the first example of defluorinative carbonylative coupling has been established. With gem-difluoroalkenes and aryl iodides as the substrates, this methodology offers flexible and facile access to privileged α-fluorochalcones under mild reaction conditions in moderate-to-excellent yields.
NMR Spectroscopy | Hot Paper
Dynamic Nuclear Polarization Enhanced Nuclear Spin Optical Rotation
- Pages: 8823-8826
- First Published: 18 January 2021
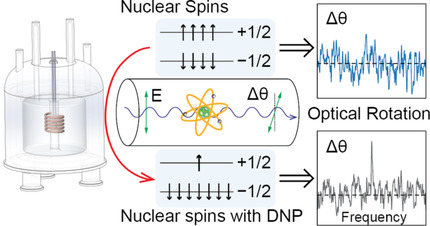
Nuclear spin optical rotation (NSOR) signals are enhanced by hyperpolarization of nuclear spins using dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization. The signal enhancement leads to the measurement of the NSOR constant of dimethyl sulfoxide. A spectroscopy based on hyperpolarized NSOR offers the possibility to provide information on ground and excited electronic states in molecules, localized to an NMR-addressable site.
Synthetic Methods
Enantioselective Reductive Cyanation and Phosphonylation of Secondary Amides by Iridium and Chiral Thiourea Sequential Catalysis
- Pages: 8827-8831
- First Published: 22 January 2021
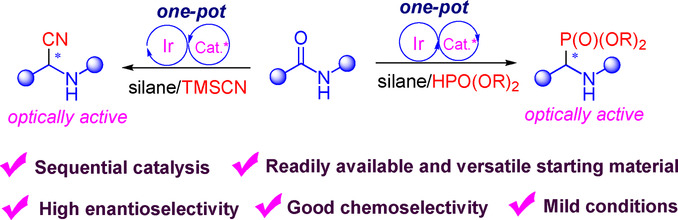
The first enantioselective reductive cyanation and phosphonylation of secondary amides have been achieved by the combination of iridium with chiral thiourea catalysis. The protocol is highly efficient and enantioselective, providing a novel route for the synthesis of optically active α-aminonitriles and α-aminophosphonates from bench-stable feedstocks.
Spin–Electric Effect | Hot Paper
Spin–Electric Coupling in a Cobalt(II)-Based Spin Triangle Revealed by Electric-Field-Modulated Electron Spin Resonance Spectroscopy
- Pages: 8832-8838
- First Published: 28 January 2021

This contribution describes the observation of spin–electric coupling utilizing electric-field-modulated ESR (EFM-ESR) spectroscopy for single-crystals of a spin triangle which is characterized by the strong magnetic anisotropy of the individual cobalt(II) centers and a pronounced sensitivity of the molecular energy levels on the relative orientation of their magnetic axes as well as the exchange coupling between them.
Research Articles
3D Printing | Hot Paper
Rapid High-Resolution 3D Printing and Surface Functionalization via Type I Photoinitiated RAFT Polymerization
- Pages: 8839-8850
- First Published: 15 January 2021

Rapid RAFT 3D Printing: Photoinduced RAFT polymerization is applied to 3D printing, resulting in rapid prints with a broad window of operation. High resolution surface patterning from the 3D printed objects is readily achieved by reactivation of dormant RAFT functionalities in the polymeric material.
Biosynthesis | Very Important Paper
One Polyketide Synthase, Two Distinct Products: Trans-Acting Enzyme-Controlled Product Divergence in Calbistrin Biosynthesis
- Pages: 8851-8858
- First Published: 22 January 2021
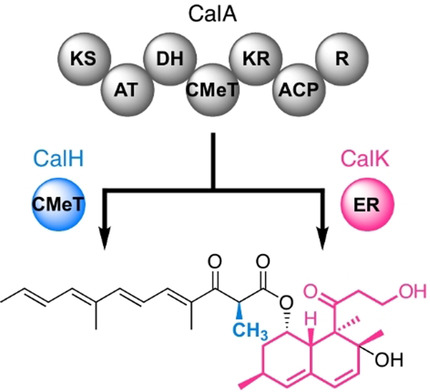
Calbistrin biosynthesis involves an unusual dual-functional polyketide synthase CalA, which synthesizes both of the two structurally distinct moieties of calbistrins. The product divergence is intriguingly controlled by two trans-acting enzymes, a trans-acting enoylreductase CalK and a trans-acting C-methyltransferase CalH, to yield the decalin and polyene portions, respectively.
Peptide Design | Hot Paper
Dynamic Stereoselection of Peptide Helicates and Their Selective Labeling of DNA Replication Foci in Cells
- Pages: 8859-8866
- First Published: 08 December 2020
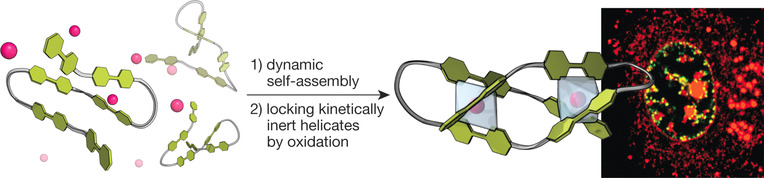
Artificial bipyridine-containing peptide ligands encode in their sequence the stereoselective folding into chiral three-stranded FeII or CoII peptide helicates and as kinetically inert dinuclear CoIII complexes by in-situ oxidation. These peptide helicates selectively label DNA replication foci in functional cells.
Structural Proteomics | Hot Paper
Free-Radical Membrane Protein Footprinting by Photolysis of Perfluoroisopropyl Iodide Partitioned to Detergent Micelle by Sonication
- Pages: 8867-8873
- First Published: 10 March 2021

Laser-mediated free-radical footprinting of an integral membrane protein (IMP) is described. Compared to canonical footprinting, the approach exploits tip sonication to ensure efficient transport of a highly hydrophobic perfluoroalkyl iodide to footprint transmembrane domains. This approach, which is amenable to native IMP structures, yields 100 % coverage for tyrosine, and it is compatible with standard proteomic mass spectrometric analysis.
Homogeneous Catalysis
Unified Approach to Furan Natural Products via Phosphine-Palladium Catalysis
- Pages: 8874-8881
- First Published: 02 February 2021
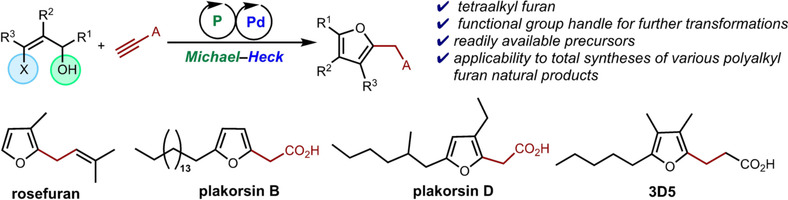
Highly substituted polyalkyl furans can be synthesized using sequential Michael–Heck reactions between functionalized (Z)-β-halo allylic alcohols and activated alkynes. This method provides facile access to tetraalkyl furans containing a C2-carboxyalkyl chain, which is readily functionalized to enable the total syntheses of several classes of bioactive furans, including furanoterpenes, polyketides, and furan fatty acids.
Fuel Cells | Very Important Paper
Platinum Dissolution in Realistic Fuel Cell Catalyst Layers
- Pages: 8882-8888
- First Published: 06 January 2021
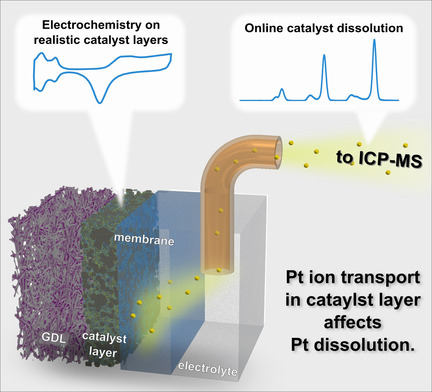
An in situ technique is presented that closes the gap between catalyst degradation studies in real devices and fundamental electrochemical analyses. The method involves direct measurement of platinum dissolution in realistic catalyst layers and through Nafion membranes. The impact of catalyst loading and electrode–electrolyte interface on platinum dissolution, as well as transport behavior of dissolved Pt species through Nafion membranes, are investigated.
Methane Oxygenation | Hot Paper
Fe/Fe3C Boosts H2O2 Utilization for Methane Conversion Overwhelming O2 Generation
- Pages: 8889-8895
- First Published: 04 February 2021
Porous Materials | Very Important Paper
Chiral Self-sorting of Giant Cubic [8+12] Salicylimine Cage Compounds
- Pages: 8896-8904
- First Published: 21 January 2021
![Chiral Self-sorting of Giant Cubic [8+12] Salicylimine Cage Compounds](/cms/asset/38882fc4-dd18-47e9-a0ab-dd086559490b/anie202016592-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Highly selective chiral self-sorting. The chiral self-sorting behavior of large cubic [8+12] salicylimine cage compounds was investigated, revealing a high selectivity for the most symmetric cage compounds, for which an explanation is presented. The properties of the isolated enantiopure and meso cage compounds were investigated by single crystal X-ray diffraction and gas sorption measurements showing high porosities and selectivities.
Nanomaterials | Very Important Paper
Constructing Electron Levers in Perovskite Nanocrystals to Regulate the Local Electron Density for Intensive Chemodynamic Therapy
- Pages: 8905-8912
- First Published: 02 February 2021
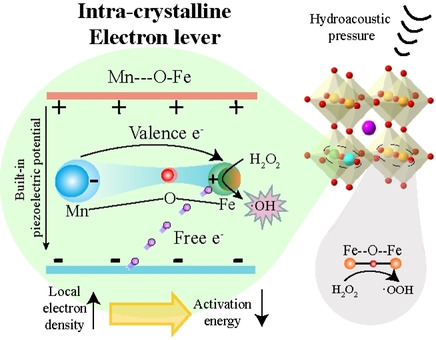
An intra-crystalline electron lever strategy is proposed by constructing Mn-doped BiFeO3 nanocrystals with a Mn4+−O−Fe3+ bond lever, which can specifically increase the local electron density of the Fe reaction centre to improve the kinetics of chemodynamic therapy. This method is promising in future research on the quantitative regulation of electron density and on-demand chemical reactivity adjustment.
Operando Modeling | Hot Paper
Quantifying the Likelihood of Structural Models through a Dynamically Enhanced Powder X-Ray Diffraction Protocol
- Pages: 8913-8922
- First Published: 25 January 2021
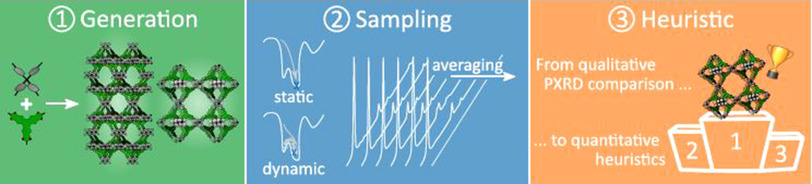
Structurally characterizing new and poorly crystalline materials such as covalent organic frameworks is highly challenging. The dynamic protocol of this work overcomes this challenge through a systematic likelihood ordering based on intuitive heuristics and X-ray diffraction patterns. It succeeds in unambiguously identifying a material's atomic-level structure, accounting for the operando conditions and inherent temporal character of experiments.
Fluorescence Imaging | Hot Paper
Organelle-Specific Photoactivation of DNA Nanosensors for Precise Profiling of Subcellular Enzymatic Activity
- Pages: 8923-8931
- First Published: 22 January 2021
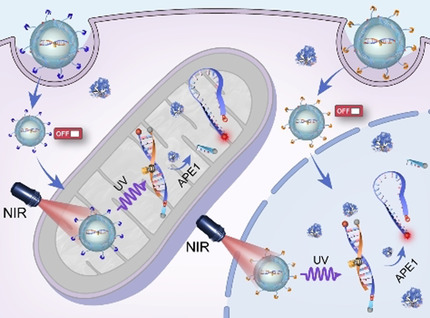
By integrating organelle-specific targeting and NIR-light-mediated photoactivation with DNA sensor technology, precise imaging of a specific enzyme in a chosen organelle (e.g., mitochondria or nucleus) was possible (see picture). The spatiotemporal control enabled imaging of enzyme translocation at subcellular resolution in response to oxidative stress in vitro and in vivo.
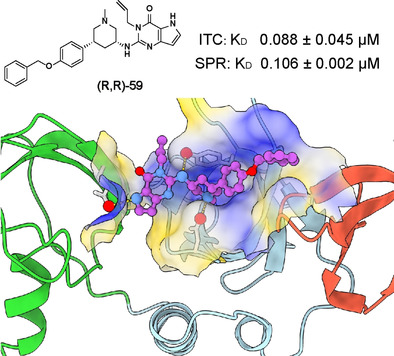
Covalent Organic Frameworks | Hot Paper
Bio-adhesive Nanoporous Module: Toward Autonomous Gating
- Pages: 8932-8937
- First Published: 02 February 2021
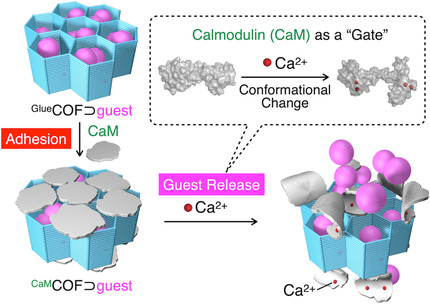
A porous covalent organic framework (GlueCOF) carrying guanidinium ion pendants has been developed that can accommodate guests and bind to biopolymers. The strong bio-adhesive nature of GlueCOF was used to noncovalently bind to calmodulin (CaM), which acted as a gating component for the guest-loaded 1D nanopores (CaMCOF⊃guest). The conformational change of the CaM gate upon selective binding with Ca2+ enabled the release of guest molecules.
Ferroptosis | Hot Paper
NIR-Actuated Remote Activation of Ferroptosis in Target Tumor Cells through a Photothermally Responsive Iron-Chelated Biopolymer Nanoplatform
- Pages: 8938-8947
- First Published: 04 February 2021
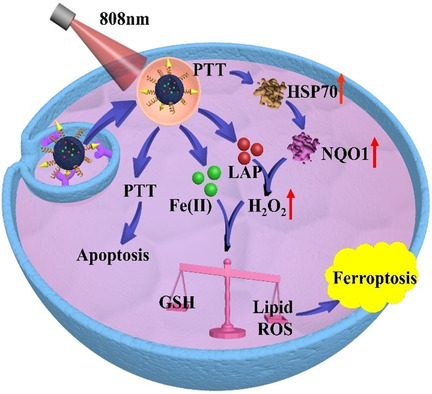
Ferroptosis is a new form of regulated cell death and holds promise for tumor inhibition. However, it is difficult to remotely control the initiation and execution of ferroptosis in specific sites. This study reports a biocompatible and biodegradable biopolymeric nanoplatform for tumor-targeted ferroptosis therapy, of which the pro-ferroptotic activities could be activated in an on-demand manner using near-infrared light as the triggering signal.
Ionic Crystals | Hot Paper
A Superstrong and Reversible Ionic Crystal-Based Adhesive Inspired by Ice Adhesion
- Pages: 8948-8959
- First Published: 02 February 2021
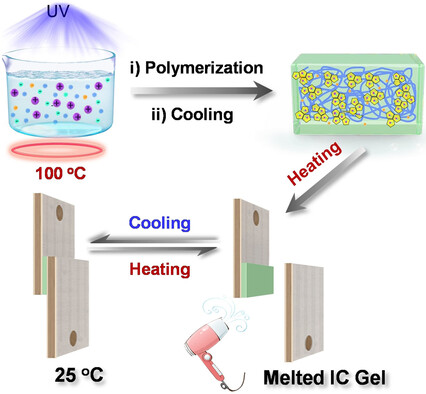
Inspired by reversible ice adhesion, a reversible ionic crystal (IC) based gel adhesive was prepared, which showed superstrong and reversible adhesion due to the phase transition of ICs. In addition, the reversible adhesion can be adjusted by heating and light, and be effectively monitored by resistance and capacitance.
Endohedral Fullerenes | Hot Paper
A Solid-State Intramolecular Wittig Reaction Enables Efficient Synthesis of Endofullerenes Including Ne@C60, 3He@C60, and HD@C60
- Pages: 8960-8966
- First Published: 07 February 2021
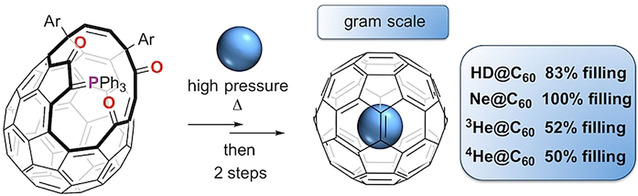
Solid-state filling of a stable phosphorus ylid open-cage fullerene is followed by heating, inducing an in situ intramolecular Wittig reaction to reduce the size of the cage opening and trapping a single gas atom or molecule inside. Expensive gases can be compressed to high pressure, leading to high incorporation of the endohedral species. Cage closure steps allow preparation of gram-scale endohedral fullerenes including 3He@C60, HD@C60, and Ne@C60.
Supramolecular Chemistry | Hot Paper
Macrocyclic Arenes-Based Conjugated Macrocycle Polymers for Highly Selective CO2 Capture and Iodine Adsorption
- Pages: 8967-8975
- First Published: 04 February 2021
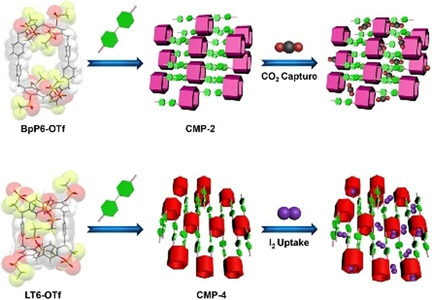
Four catcher-type conjugated macrocycle polymers (CMP-n, n=1–4) have been designed and synthesized successfully, exhibiting interesting application in CO2 and I2 uptake. The CMP-2 is able to capture CO2 with excellent selectivity and the CMP-4 is capable of adsorbing iodine with outstanding capacity.
Lignin Upgrading | Hot Paper
Selectively Upgrading Lignin Derivatives to Carboxylates through Electrochemical Oxidative C(OH)−C Bond Cleavage by a Mn-Doped Cobalt Oxyhydroxide Catalyst
- Pages: 8976-8982
- First Published: 08 February 2021
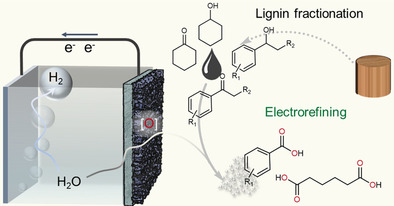
An electrochemical strategy has been developed for the oxidative cleavage of C(OH)−C bonds using a manganese-doped cobalt oxyhydroxide catalyst under mild conditions. Preliminary studies demonstrate its application in upgrading lignin-derived products with C(OH)-C or C(O)-C motifs, electrorefining them into valuable oxygenates, such as benzoate and adipate.
CO2 Reduction | Hot Paper
Robust Biological Hydrogen-Bonded Organic Framework with Post-Functionalized Rhenium(I) Sites for Efficient Heterogeneous Visible-Light-Driven CO2 Reduction
- Pages: 8983-8989
- First Published: 25 January 2021
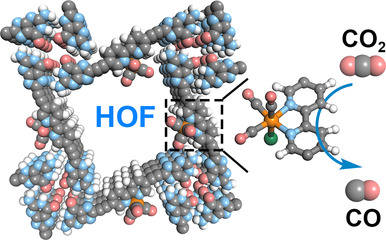
A robust porous biological HOF with bpy docking groups has been designed, prepared, and post-modified to precisely load Re(bpy)(CO)3Cl as molecular catalyst on the basis of the hydrogen-bonded and π-π stacking metal-free G-quadruplex moieties. With the help of the sensitizer, the post-functionalized HOF promotes efficient and selective CO2-to-CO conversion in a heterogeneous system under the visible-light irradation.
Biosynthesis | Hot Paper
Two Cryptic Self-Resistance Mechanisms in Streptomyces tenebrarius Reveal Insights into the Biosynthesis of Apramycin
- Pages: 8990-8996
- First Published: 04 February 2021
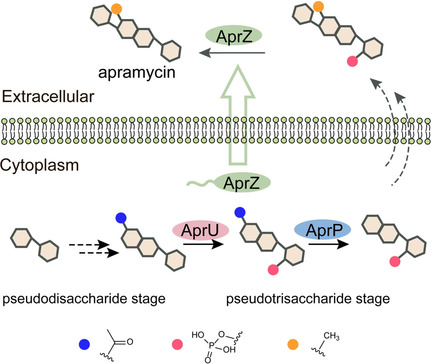
Two cryptic self-resistance mechanisms involving C-5 phosphorylation and N-7′ acetylation were discovered in Streptomyces tenebrarius to avoid auto-toxicity during apramycin biosynthesis. Characterization of the corresponding enzymes revealed the apramycin's assembly line at the pseudotrisaccharide stage.
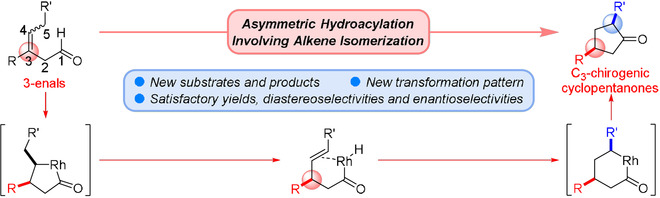
Asymmetric Synthesis | Very Important Paper
Asymmetric Hydroacylation Involving Alkene Isomerization for the Construction of C3-Chirogenic Center
- Pages: 8997-9002
- First Published: 28 January 2021
High Energy Density | Very Important Paper
Stabilization of Polynitrogen Anions in Tantalum–Nitrogen Compounds at High Pressure
- Pages: 9003-9008
- First Published: 08 February 2021

Direct reaction between nitrogen and tantalum at approximately 100 GPa results in the energetic nitrogen-rich compounds TaN4 and TaN5, which feature N4 chains and unprecedented branched single-bonded polymeric nitrogen chains in the crystal structures, respectively. TaN5 possesses an extraordinary volumetric energy density of 18 kJ cm−3, exceeding well-known high-energy-density materials.
Materials Synthesis
An Unexpected Cubic Symmetry in Group IV Alloys Prepared Using Pressure and Temperature
- Pages: 9009-9014
- First Published: 02 February 2021
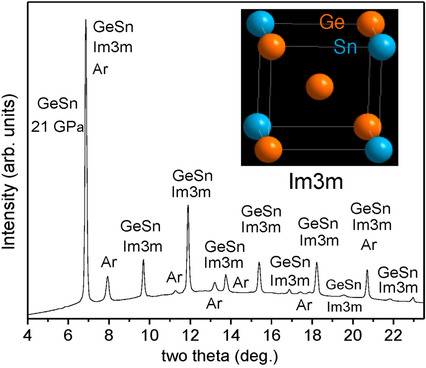
New materials can be created without the need to follow conventional criteria and routes to synthesis. We demonstrate this for Ge–Sn, a system actively investigated for optoelectronic applications to overcome conventional cubic Si's deficiencies. Ge and Sn are however unreactive in the bulk, but we remove reactivity barriers and form a different structure, a simple new cubic solid solution.
Enzyme Catalysis
“NAD-display”: Ultrahigh-Throughput in Vitro Screening of NAD(H) Dehydrogenases Using Bead Display and Flow Cytometry
- Pages: 9015-9021
- First Published: 19 January 2021
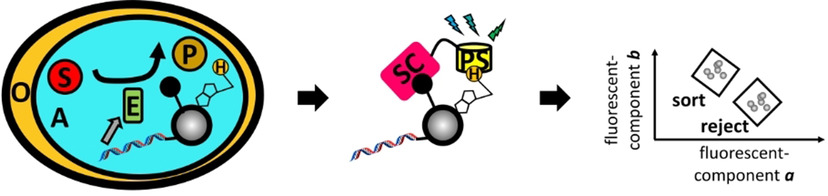
A detection system was devised to screen dehydrogenase enzymes (DH) at ultrahigh-throughput in in vitro droplet compartments. An NAD(H) analogue and a DH DNA library were co-immobilised on beads. Water-in-oil emulsion droplets containing cell-free expression mix and substrate allow compartmentalised protein production and catalysis. A fluorescent sensor of NAD(H) redox state was loaded onto beads, allowing bulk sorting of 2×104 DH variants in a day by flow cytometry.
Peptide Functionalization
Cys–Cys and Cys–Lys Stapling of Unprotected Peptides Enabled by Hypervalent Iodine Reagents
- Pages: 9022-9031
- First Published: 15 January 2021
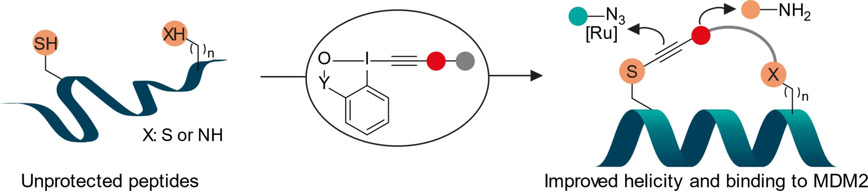
Bifunctional hypervalent iodine reagents for two-component cysteine-cysteine and cysteine-lysine stapling are reported. Efficient and selective stapling on non-protected peptides was observed, and post-stapling modification could be easily achieved using reactive esters or cycloaddition on the thioalkynes formed on the cysteine residue. One stapled peptide displayed both enhanced helicity and binding to the MDM2 protein.
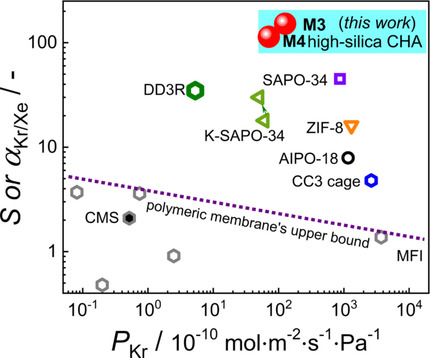
Gas Separation
High-Silica CHA Zeolite Membrane with Ultra-High Selectivity and Irradiation Stability for Krypton/Xenon Separation
- Pages: 9032-9037
- First Published: 02 February 2021
Nanoclusters
Ag44(EBT)26(TPP)4 Nanoclusters With Tailored Molecular and Electronic Structure
- Pages: 9038-9044
- First Published: 28 December 2020
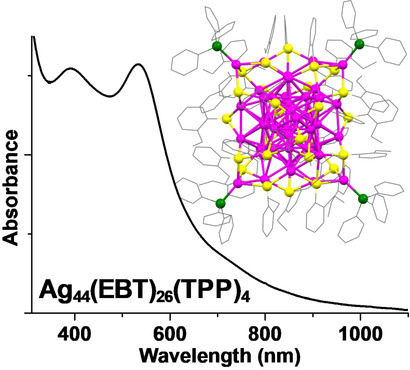
In this work, the synthesis and total structure determination of a novel Ag44(EBT)26(TPP)4 nanocluster, the first analogue of [Ag44(SR)30]4−, are reported. The identical size as well as similar core- and different surface-structures of these two nanoclusters enable the study of the structural effect on the optical and photophysical properties. The novel surface structure plays a crucial role in the enhancement of NIR-II photoluminescence.
Photoreduction
Efficient and Selective Interplay Revealed: CO2 Reduction to CO over ZrO2 by Light with Further Reduction to Methane over Ni0 by Heat Converted from Light
- Pages: 9045-9054
- First Published: 20 January 2021
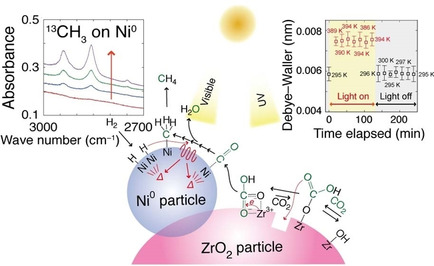
CO2 photoreduction with Ni-ZrO2 as a catalyst under UV/Vis light was monitored by 13C-labeled mass chromatography, FTIR spectroscopy, and EXAFS. The interplay of bicarbonate reduction to CO over ZrO2 owing to charge separation by light with subsequent hydrogenation of CO over Ni heated from light enabled CO2 reduction to methane.
Photocatalysis
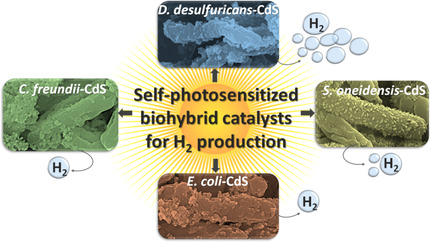
Enhanced Light-Driven Hydrogen Production by Self-Photosensitized Biohybrid Systems
- Pages: 9055-9062
- First Published: 15 January 2021
Acenes
(Aza)Acenes Share the C2 Bridge with (Anti)Aromatic Macrocycles: Local vs. Global Delocalization Paths
- Pages: 9063-9070
- First Published: 06 January 2021
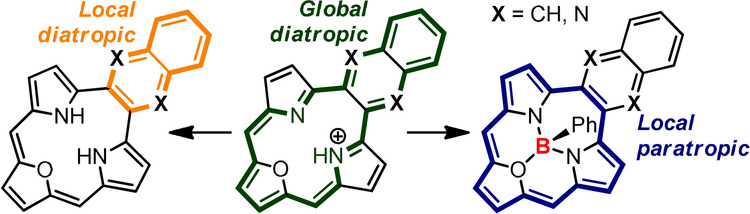
Global switch for local effect: The linear fusion of (aza)acene and a redox switchable macrocycle (i.e. triphyrin(2.1.1)) gives a set of fused systems merging two π-conjugated clouds. A competition between local and global effects can be distinguished as documented in spectroscopic properties with a domination of (aza)acene diatropic current obtained after a redox switching within the macrocyclic flank.
Analytical Methods
Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Bio-oligomer Polydispersity in Plant Tissues by Laser Desorption Ionization from Silicon Nanopost Arrays
- Pages: 9071-9077
- First Published: 02 February 2021
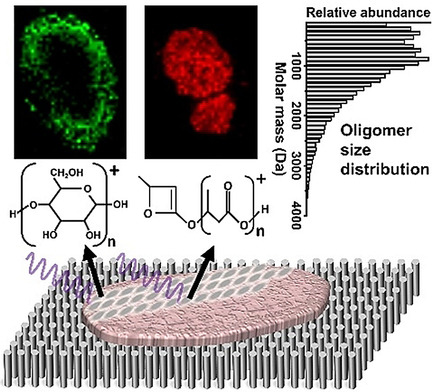
Simultaneous chemical analysis and spatial mapping of homopolymers used for energy storage and molecular feedstock in biological tissues are challenging using conventional MS imaging. Here, the spatial and size distributions for oligomers from polyhydroxybutyrate, polysaccharide, and polyglutamic acid are profiled in rhizobia-infected soybean root nodules by MS imaging using nanophotonic ionization from silicon nanopost arrays and MALDI.
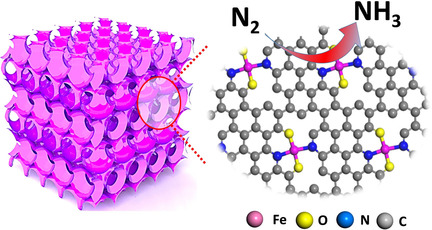
Nitrogen Reduction | Very Important Paper
Boosting Electroreduction Kinetics of Nitrogen to Ammonia via Tuning Electron Distribution of Single-Atomic Iron Sites
- Pages: 9078-9085
- First Published: 14 February 2021
Enantioselective Synthesis | Very Important Paper
Catalytic Enantioselective Desymmetrizing Fischer Indolization through Dynamic Kinetic Resolution
- Pages: 9086-9092
- First Published: 08 February 2021
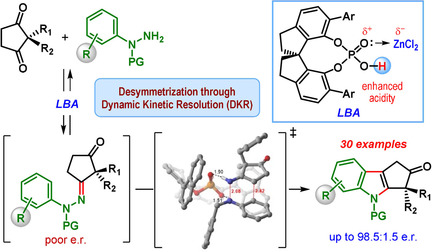
The first catalytic enantioselective desymmetrizing Fischer indolization of prochiral diketones, containing enantiotopic carbonyl groups, is developed and shown to proceed through dynamic kinetic resolution. Catalyzed by a combination of a spirocyclic chiral phosphoric acid and ZnCl2, this reaction delivers cyclopenta[b]indolones, containing an all-carbon quaternary stereocenter, with up to 98.5:1.5 e.r.
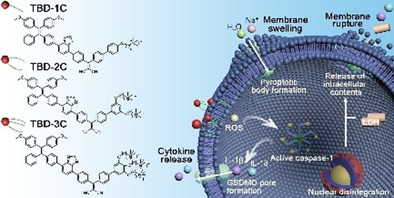
Photodynamic Therapy | Hot Paper
Activation of Pyroptosis by Membrane-Anchoring AIE Photosensitizer Design: New Prospect for Photodynamic Cancer Cell Ablation
- Pages: 9093-9098
- First Published: 04 February 2021
Metal-Organic Cages | Hot Paper
Metal-Organic Cages with Missing Linker Defects
- Pages: 9099-9105
- First Published: 28 January 2021
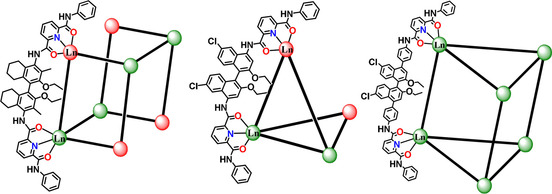
Tetrahedral and hexahedral coordination cages with one or two missing linkers, as well as regular trigonal prismatic cages, are synthesized by employing steric hindrance of organic linkers to manipulate coordination modes of lanthanide(III) ions. The defective cages, especially the hexahedral cage, are conformationally flexible and adapt its structure to accommodate various guest molecules with sizes comparable or much larger than the cavity portals that are not accessible to the non-defective cage.
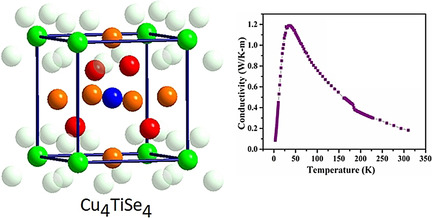
Solid-State Materials
Ultralow Lattice Thermal Conductivity at Room Temperature in Cu4TiSe4
- Pages: 9106-9113
- First Published: 04 November 2020
Organic Lasers
Cascaded Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer Towards Near-Infrared Organic Lasers Beyond 850 nm
- Pages: 9114-9119
- First Published: 03 February 2021
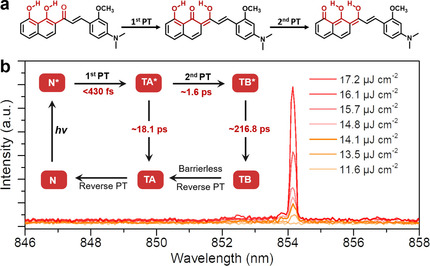
Six-level energy systems are constructed through the cascaded occurrence of excited-state intramolecular proton transfer consisting of a first ultrafast proton transfer of <430 fs and a following dominant and irreversible proton transfer of ca. 1.6 ps, which support the NIR single-mode lasing at 854 nm for exploiting energy-level systems of OSSLs, especially at the NIR region from 780 to 2500 nm.
Photophysics
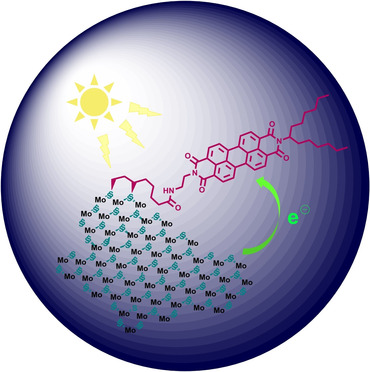
Unveiling the Photoinduced Electron-Donating Character of MoS2 in Covalently Linked Hybrids Featuring Perylenediimide
- Pages: 9120-9126
- First Published: 09 February 2021
Black Phosphorus
Surface Functionalization of Black Phosphorus with Nitrenes: Identification of P=N Bonds by Using Isotopic Labeling
- Pages: 9127-9134
- First Published: 18 December 2020
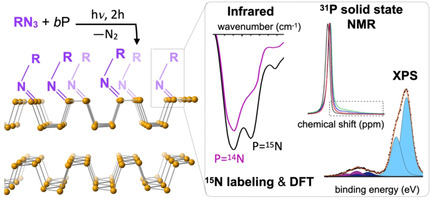
A mild, surface-specific method for the surface functionalization of few-layer black phosphorus nanosheets is developed using a family of photolytically generated nitrenes (RN) from the corresponding azides. By embedding spectroscopic tags in the organic backbone, a multitude of techniques can be used to investigate the chemical structure of the modified nanosheets.
CO2 Electroreduction | Hot Paper
B-Cu-Zn Gas Diffusion Electrodes for CO2 Electroreduction to C2+ Products at High Current Densities
- Pages: 9135-9141
- First Published: 09 February 2021
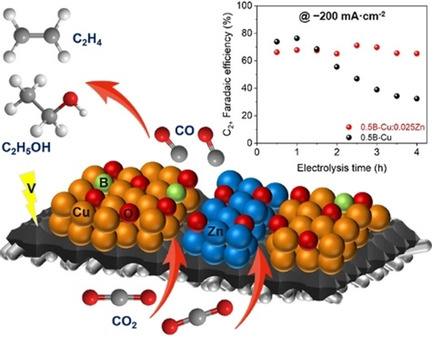
A B-Cu gas diffusion electrode (GDE) system was developed for highly selective CO2 conversion to C2+ products at high relevant current densities by mitigating the flooding problem and tuning the three-phase boundary. Anodic protection by sacrificial Zn nanosheets remarkably improved the long-term stability for CO2 electroreduction at high current densities.





![Formation of Nanoscale [Ge4O16Al48(OH)108(H2O)24]20+ from Condensation of ϵ-GeAl128+ Keggin Polycations**](/cms/asset/29cc8406-1cce-4c31-86e6-ccb833ddaecb/anie202017321-toc-0001-m.jpg)