Selectively Upgrading Lignin Derivatives to Carboxylates through Electrochemical Oxidative C(OH)−C Bond Cleavage by a Mn-Doped Cobalt Oxyhydroxide Catalyst
Dr. Hua Zhou
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhenhua Li
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Si-Min Xu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lilin Lu
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430081 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Ming Xu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorKaiyue Ji
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ruixiang Ge
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorYifan Yan
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lina Ma
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xianggui Kong
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lirong Zheng
Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Haohong Duan
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hua Zhou
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhenhua Li
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Si-Min Xu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lilin Lu
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430081 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Ming Xu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorKaiyue Ji
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ruixiang Ge
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorYifan Yan
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lina Ma
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xianggui Kong
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering, College of Chemistry, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, 100029 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lirong Zheng
Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Haohong Duan
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
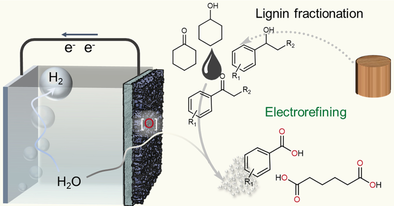
An electrochemical strategy has been developed for the oxidative cleavage of C(OH)−C bonds using a manganese-doped cobalt oxyhydroxide catalyst under mild conditions. Preliminary studies demonstrate its application in upgrading lignin-derived products with C(OH)-C or C(O)-C motifs, electrorefining them into valuable oxygenates, such as benzoate and adipate.
Abstract
Oxidative cleavage of C(OH)−C bonds to afford carboxylates is of significant importance for the petrochemical industry and biomass valorization. Here we report an efficient electrochemical strategy for the selective upgrading of lignin derivatives to carboxylates by a manganese-doped cobalt oxyhydroxide (MnCoOOH) catalyst. A wide range of lignin-derived substrates with C(OH)-C or C(O)-C units undergo efficient cleavage to corresponding carboxylates in excellent yields (80–99 %) and operational stability (200 h). Detailed investigations reveal a tandem oxidation mechanism that base from the electrolyte converts secondary alcohols and their derived ketones to reactive nucleophiles, which are oxidized by electrophilic oxygen species on MnCoOOH from water. As proof of concept, this approach was applied to upgrade lignin derivatives with C(OH)-C or C(O)-C motifs, achieving convergent transformation of lignin-derived mixtures to benzoate and KA oil to adipate with 91.5 % and 64.2 % yields, respectively.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202015431-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.2 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aR. Sang, P. Kucmierczyk, R. Duhren, R. Razzaq, K. Dong, J. Liu, R. Franke, R. Jackstell, M. Beller, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14365–14373; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 14503–14511;
- 1bZ. Zhang, G. W. Huber, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1351–1390.
- 2
- 2aS. Song, J. Zhang, G. Gozaydin, N. Yan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4934–4937; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 4988–4991;
- 2bH. Luo, L. Wang, S. Shang, G. Li, Y. Lv, S. Gao, W. Dai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 19268–19274; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 19430–19436;
- 2cM. Liu, Z. Zhang, J. Song, S. Liu, H. Liu, B. Han, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17393–17398; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 17554–17559;
- 2dM. Liu, Z. Zhang, J. Yan, S. Liu, H. Liu, Z. Liu, W. Wang, Z. He, B. Han, Chem 2020, 6, 3288–3296;
- 2eZ. Cai, J. Long, Y. Li, L. Ye, B. Yin, L. J. France, J. Dong, L. Zheng, H. He, S. Liu, S. C. E. Tsang, X. Li, Chem 2019, 5, 2365–2377.
- 3
- 3aX. Wu, X. Fan, S. Xie, J. Lin, J. Cheng, Q. Zhang, L. Chen, Y. Wang, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 772–780;
- 3bA. Rahimi, A. Ulbrich, J. J. Coon, S. S. Stahl, Nature 2014, 515, 249–252;
- 3cW. Lan, J. Behaghel de Bueren, J. Luterbacher, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2649–2654; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 2675–2680.
- 4
- 4aL. Zhang, X. Bi, X. Guan, X. Li, Q. Liu, B. D. Barry, P. Liao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11303–11307; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 11513–11517;
- 4bH. Liu, C. Dong, Z. Zhang, P. Wu, X. Jiang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12570–12574; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 12738–12742;
- 4cM. Wang, J. Lu, L. Li, H. Li, H. Liu, F. Wang, J. Catal. 2017, 348, 160–167;
- 4dH. Liu, M. Wang, H. Li, N. Luo, S. Xu, F. Wang, J. Catal. 2017, 346, 170–179;
- 4eS. K. Hanson, R. T. Baker, J. C. Gordon, B. L. Scott, D. L. Thorn, Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 5611–5618;
- 4fH.-R. Tian, Y.-W. Liu, Z. Zhang, S.-M. Liu, T.-Y. Dang, X.-H. Li, X.-W. Sun, Y. Lu, S.-X. Liu, Green Chem. 2020, 22, 248–255.
- 5
- 5aP. De Luna, C. Hahn, D. Higgins, S. A. Jaffer, T. F. Jaramillo, E. H. Sargent, Science 2019, 364, eaav3506;
- 5bY. X. Chen, A. Lavacchi, H. A. Miller, M. Bevilacqua, J. Filippi, M. Innocenti, A. Marchionni, W. Oberhauser, L. Wang, F. Vizza, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4036;
- 5cS. Verma, S. Lu, P. J. A. Kenis, Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 466–474;
- 5dX. Wei, Y. Li, L. Chen, J. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3148–3155; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 3185–3192.
- 6
- 6aM. Bajada, S. Roy, J. Warnan, K. Abdiaziz, A. Wagner, M. Roessler, E. Reisner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15633–15641; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 15763–15771;
- 6bY. Li, X. Wei, L. Chen, J. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202009854; Angew. Chem. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202009854;
- 6cY. Li, X. Wei, L. Chen, J. Shi, M. He, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5335;
- 6dW. J. Liu, Z. Xu, D. Zhao, X. Q. Pan, H. C. Li, X. Hu, Z. Y. Fan, W. K. Wang, G. H. Zhao, S. Jin, G. W. Huber, H. Q. Yu, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 265;
- 6eD. Wang, P. Wang, S. Wang, Y. H. Chen, H. Zhang, A. Lei, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2796;
- 6fY. Lum, J. E. Huang, Z. Wang, M. Luo, D.-H. Nam, W. R. Leow, B. Chen, J. Wicks, Y. C. Li, Y. Wang, C.-T. Dinh, J. Li, T.-T. Zhuang, F. Li, T.-K. Sham, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 14–22.
- 7
- 7aH. Huang, C. Yu, X. Han, H. Huang, Q. Wei, W. Guo, Z. Wang, J. Qiu, Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 4990–4999;
- 7bB. You, X. Liu, N. Jiang, Y. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 13639–13646;
- 7cH. G. Cha, K. S. Choi, Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 328–333;
- 7dS. Wang, N. Zhang, L. I. Tao, W. E. I. Chen, L. Zhou, Z. Liu, B. O. Zhou, G. E. N. Huang, Y. Zou, H. Lin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15895–15903; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 16042–16050;
- 7eP. Zhang, X. Sheng, X. Chen, Z. Fang, J. Jiang, M. Wang, F. Li, L. Fan, Y. Ren, B. Zhang, B. J. J. Timmer, M. S. G. Ahlquist, L. Sun, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9155–9159; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 9253–9257;
- 7fM. Rafiee, M. Alherech, S. D. Karlen, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 15266–15276;
- 7gL. Zhang, R. Chen, J. Luo, J. Miao, J. Gao, B. Liu, Nano Res. 2016, 9, 3388–3393.
- 8M. Wang, F. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901866.
- 9
- 9aR. Subbaraman, D. Tripkovic, K. C. Chang, D. Strmcnik, A. P. Paulikas, P. Hirunsit, M. Chan, J. Greeley, V. Stamenkovic, N. M. Markovic, Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 550–557;
- 9bA. Bergmann, T. E. Jones, E. Martinez Moreno, D. Teschner, P. Chernev, M. Gliech, T. Reier, H. Dau, P. Strasser, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 711–719;
- 9cJ. Huang, J. Chen, T. Yao, J. He, S. Jiang, Z. Sun, Q. Liu, W. Cheng, F. Hu, Y. Jiang, Z. Pan, S. Wei, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8722–8727; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 8846–8851.
- 10
- 10aE. Fabbri, M. Nachtegaal, T. Binninger, X. Cheng, B. J. Kim, J. Durst, F. Bozza, T. Graule, R. Schaublin, L. Wiles, M. Pertoso, N. Danilovic, K. E. Ayers, T. J. Schmidt, Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 925–931;
- 10bS. Song, J. Zhou, X. Su, Y. Wang, J. Li, L. Zhang, G. Xiao, C. Guan, R. Liu, S. Chen, H.-J. Lin, S. Zhang, J.-Q. Wang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2945–2953;
- 10cF. Dionigi, Z. Zeng, I. Sinev, T. Merzdorf, S. Deshpande, M. B. Lopez, S. Kunze, I. Zegkinoglou, H. Sarodnik, D. Fan, A. Bergmann, J. Drnec, J. F. Araujo, M. Gliech, D. Teschner, J. Zhu, W. X. Li, J. Greeley, B. R. Cuenya, P. Strasser, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2522.
- 11L. Ma, H. Zhou, M. Xu, P. Hao, X. Kong, H. Duan, Chem. Sci. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1039/D1030SC05499B.
- 12Y. Huang, X. Zhao, F. Tang, X. Zheng, W. Cheng, W. Che, F. Hu, Y. Jiang, Q. Liu, S. Wei, J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3202–3210.
- 13D. W. Wakerley, M. F. Kuehnel, K. L. Orchard, K. H. Ly, T. E. Rosser, E. Reisner, Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17021.
- 14A. J. Bard, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7559–7567.
- 15
- 15aY. Kwon, S. C. Lai, P. Rodriguez, M. T. Koper, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6914–6917;
- 15bY. Chiang, A. J. Kresge, J. Wirz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 6392–6395.
- 16H. B. Tao, Y. Xu, X. Huang, J. Chen, L. Pei, J. Zhang, J. G. Chen, B. Liu, Joule 2019, 3, 1498–1509.
- 17
- 17aH. N. Nong, L. J. Falling, A. Bergmann, M. Klingenhof, H. P. Tran, C. Spori, R. Mom, J. Timoshenko, G. Zichittella, A. Knop-Gericke, S. Piccinin, J. Perez-Ramirez, B. R. Cuenya, R. Schlogl, P. Strasser, D. Teschner, T. E. Jones, Nature 2020, 587, 408–413;
- 17bW. Chen, C. Xie, Y. Wang, Y. Zou, C.-L. Dong, Y.-C. Huang, Z. Xiao, Z. Wei, S. Du, C. Chen, B. Zhou, J. Ma, S. Wang, Chem 2020, 6, 2974–2993.
- 18N. Zhang, X. Feng, D. Rao, X. Deng, L. Cai, B. Qiu, R. Long, Y. Xiong, Y. Lu, Y. Chai, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4066.
- 19I. C. Man, H. Y. Su, F. Calle-Vallejo, H. A. Hansen, J. I. Martínez, N. G. Inoglu, J. Kitchin, T. F. Jaramillo, J. K. Nørskov, J. Rossmeisl, ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 1159–1165.
- 20X. Han, H. Sheng, C. Yu, T. W. Walker, G. W. Huber, J. Qiu, S. Jin, ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 6741–6752.
- 21H. Zhou, H. Xu, Y. Liu, Appl. Catal. B 2019, 244, 965–973.
- 22S. S. Wong, R. Shu, J. Zhang, H. Liu, N. Yan, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5510–5560.
- 23
- 23aY. Liao, S.-F. Koelewijn, G. Van den Bossche, J. Van Aelst, S. Van den Bosch, T. Renders, K. Navare, T. Nicolaï, K. Van Aelst, M. Maesen, H. Matsushima, J. Thevelein, K. Van Acker, B. Lagrain, D. Verboekend, B. F. Sels, Science 2020, 367, 1385–1390;
- 23bH. Liu, T. Jiang, B. Han, S. Liang, Y. Zhou, Science 2009, 326, 1250–1252;
- 23cH. Duan, N. Yan, R. Yu, C. R. Chang, G. Zhou, H. S. Hu, H. Rong, Z. Niu, J. Mao, H. Asakura, T. Tanaka, P. J. Dyson, J. Li, Y. Li, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3093;
- 23dQ. Meng, M. Hou, H. Liu, J. Song, B. Han, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14190;
- 23eY. L. Zhou, Y. J. Gao, X. Zhong, W. B. Jiang, Y. L. Liang, P. F. Niu, M. C. Li, G. L. Zhuang, X. N. Li, J. G. Wang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807651.