Activation of Pyroptosis by Membrane-Anchoring AIE Photosensitizer Design: New Prospect for Photodynamic Cancer Cell Ablation
Min Wu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXingang Liu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHuan Chen
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYukun Duan
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorJingjing Liu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorYutong Pan
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Bin Liu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
Joint School of National University of Singapore and Tianjin University, International Campus of Tianjin University, Binhai New City, Fuzhou, 350207 China
Search for more papers by this authorMin Wu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXingang Liu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHuan Chen
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYukun Duan
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorJingjing Liu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorYutong Pan
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Bin Liu
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore, 4 Engineering Drive 4, Singapore, 117585 Singapore
Joint School of National University of Singapore and Tianjin University, International Campus of Tianjin University, Binhai New City, Fuzhou, 350207 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
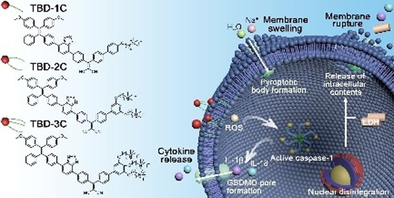
Pyroptosis as a lytic and inflammatory form of cell death is a powerful tool to fight against cancer. However, pyroptosis is usually activated by chemotherapeutic drugs, which limits its anti-tumor applications due to drug resistance and severe side effects. Herein, we demonstrate that membrane targeting photosensitizers can induce pyroptosis for cancer cell ablation with noninvasiveness and low side effects. A series of membrane anchoring photosensitizers (TBD-R PSs) with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) characteristics were prepared through conjugation of TBD and phenyl ring with cationic chains. Upon light irradiation, cytotoxic ROS were produced in situ, resulting in direct membrane damage and superior cancer cell ablation. Detailed study revealed that pyroptosis gradually became the dominant cell death pathway along with the increase of TBD-R PSs membrane anchoring capability. This study offers a photo-activated pyroptosis-based intervention strategy for cancer cell ablation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202016399-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.9 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1D. Hanahan, R. A. Weinberg, Cell 2000, 100, 57–70.
- 2
- 2aC. Y. Taabazuing, M. C. Okondo, D. A. Bachovchin, Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 507–514, e504;
- 2bI. Böhm, H. Schild, Mol. Imaging Biol. 2003, 5, 2–14.
- 3
- 3aM. C. Luna, C. J. Gomer, Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 4243–4249;
- 3bJ. Kralova, M. Kolar, M. Kahle, J. Truksa, S. Lettlova, K. Balusikova, P. Bartunek, Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44497.
- 4
- 4aJ. Shi, Y. Zhao, K. Wang, X. Shi, Y. Wang, H. Huang, Y. Zhuang, T. Cai, F. Wang, F. Shao, Nature 2015, 526, 660–665;
- 4bN. Kayagaki, I. B. Stowe, B. L. Lee, K. O'Rourke, K. Anderson, S. Warming, T. Cuellar, B. Haley, M. Roose-Girma, Q. T. Phung, Nature 2015, 526, 666–671.
- 5
- 5aP. Broz, V. M. Dixit, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 407–420;
- 5bI. Jorgensen, M. Rayamajhi, E. A. Miao, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 151.
- 6
- 6aJ. Shi, W. Gao, F. Shao, Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 245–254;
- 6bY. Wang, W. Gao, X. Shi, J. Ding, W. Liu, H. He, K. Wang, F. Shao, Nature 2017, 547, 99–103.
- 7B. C. Baguley, Mol. Biotechnol. 2010, 46, 308–316.
- 8
- 8aL. Cheng, C. Wang, L. Feng, K. Yang, Z. Liu, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10869–10939;
- 8bJ. M. Kim, S. H. Sohn, N. S. Han, S. M. Park, J. Kim, J. K. Song, ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 2917–2921;
- 8cJ. P. Celli, B. Q. Spring, I. Rizvi, C. L. Evans, K. S. Samkoe, S. Verma, B. W. Pogue, T. Hasan, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2795–2838;
- 8dY. Cheng, H. Cheng, C. Jiang, X. Qiu, K. Wang, W. Huan, A. Yuan, J. Wu, Y. Hu, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8785.
- 9
- 9aRef [2a];
- 9bB. Zhou, J.-y. Zhang, X.-s. Liu, H.-z. Chen, Y.-l. Ai, K. Cheng, R.-y. Sun, D. Zhou, J. Han, Q. Wu, Cell Res. 2018, 28, 1171–1185;
- 9cX. Zhang, J. Luan, W. Chen, J. Fan, Y. Nan, Y. Wang, Y. Liang, G. Meng, D. Ju, Nanoscale 2018, 10, 9141–9152;
- 9dD. Wu, S. Wang, G. Yu, X. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202010281; Angew. Chem. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202010281.
- 10
- 10aA. Garcia-Sampedro, A. Tabero, I. Mahamed, P. Acedo, J. Porphyrins Phthalocyanines 2019, 23, 11–27;
- 10bM. Wainwright, K. B. Crossley, J. Chemother. 2002, 14, 431–443.
- 11
- 11aW. H. Chen, G. F. Luo, X. Z. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1802725;
- 11bJ. W. Snyder, E. Skovsen, J. D. Lambert, P. R. Ogilby, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 14558–14559.
- 12
- 12aJ. Liang, B. Z. Tang, B. Liu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2798–2811;
- 12bD. Ding, K. Li, B. Liu, B. Z. Tang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2441–2453;
- 12cY. Yuan, S. Xu, X. Cheng, X. Cai, B. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6457–6461; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 6567–6571.
- 13
- 13aS. Singh, A. Aggarwal, N. D. K. Bhupathiraju, G. Arianna, K. Tiwari, C. M. Drain, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10261–10306;
- 13bRef. [11a].
- 14
- 14aL. Tong, Y. Zhao, T. B. Huff, M. N. Hansen, A. Wei, J. X. Cheng, Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3136–3141;
- 14bW. Ma, S.-N. Sha, P.-L. Chen, M. Yu, J.-J. Chen, C.-B. Huang, B. Yu, Y. Liu, L.-H. Liu, Z.-Q. Yu, Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 1901100;
- 14cW.-X. Qiu, M.-K. Zhang, L.-H. Liu, F. Gao, L. Zhang, S.-Y. Li, B.-R. Xie, C. Zhang, J. Feng, X.-Z. Zhang, Biomaterials 2018, 161, 81–94;
- 14dG. F. Luo, W. H. Chen, S. Hong, Q. Cheng, W. X. Qiu, X. Z. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702122.
- 15
- 15aJ. Kim, O. A. Santos, J.-H. Park, J. Controlled Release 2014, 191, 98–104;
- 15bC.-S. Lee, W. Park, S.-j. Park, K. Na, Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9227–9236;
- 15cY. Zhang, X. Chen, C. Gueydan, J. Han, Cell Res. 2018, 28, 9–21.
- 16K. S. Beckwith, M. S. Beckwith, S. Ullmann, R. S. Sætra, H. Kim, A. Marstad, S. E. Åsberg, T. A. Strand, M. Haug, M. Niederweis, H. A. Stenmark, T. H. Flo, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2270.
- 17
- 17aH. Chen, S. Li, M. Wu, Z. Huang, C. S. Lee, B. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 632–636; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 642–646;
- 17bB. Wang, M. Wang, A. Mikhailovsky, S. Wang, G. C. Bazan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5031–5034; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 5113–5116;
- 17cA. W. Thomas, Z. B. Henson, J. Du, C. A. Vandenberg, G. C. Bazan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3736–3739;
- 17dH. Yan, C. Catania, G. C. Bazan, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2958–2973.
- 18J. Mu, F. Liu, M. S. Rajab, M. Shi, S. Li, C. Goh, L. Lu, Q. H. Xu, B. Liu, L. G. Ng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 14357–14362; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 14585–14590.
- 19J. Li, Y. Anraku, K. Kataoka, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13526–13530; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 13628–13632.
- 20R. A. Aglietti, A. Estevez, A. Gupta, M. G. Ramirez, P. S. Liu, N. Kayagaki, C. Ciferri, V. M. Dixit, E. C. Dueber, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7858–7863.
- 21J. F. Kerr, A. H. Wyllie, A. R. Currie, Br. J. Cancer 1972, 26, 239–257.
- 22
- 22aW.-t. He, H. Wan, L. Hu, P. Chen, X. Wang, Z. Huang, Z.-H. Yang, C.-Q. Zhong, J. Han, Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1285–1298;
- 22bK. Schroder, J. Tschopp, Cell 2010, 140, 821–832.
- 23T. Zhang, Y. Li, Z. Zheng, R. Ye, Y. Zhang, R. T. Kwok, J. W. Lam, B. Z. Tang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5612–5616.
- 24I. Dolka, M. Król, R. Sapierzyński, Res. Vet. Sci. 2016, 105, 124–133.
- 25M. Lamkanfi, V. M. Dixit, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 137–161.