Electrochemical Radical Silyl-Oxygenation of Activated Alkenes
Dr. Jie Ke
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wentan Liu
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXujiang Zhu
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorXingfa Tan
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Chuan He
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jie Ke
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wentan Liu
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXujiang Zhu
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorXingfa Tan
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Chuan He
Shenzhen Grubbs Institute and Department of Chemistry, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the 10th anniversary of Department of Chemistry, SUSTech
Graphical Abstract
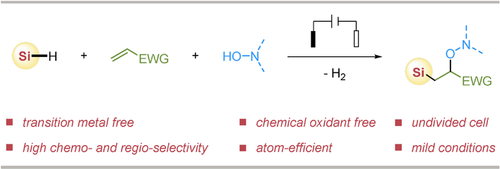
An efficient electrochemical radical silyl-oxygenation of electron-deficient alkenes is demonstrated, which gives access to a variety of highly functionalized silicon-containing molecules, including β-silyl-cyanohydrin derivatives in good yields with excellent chemo- and regio-selectivity under mild conditions without the use of transition-metal catalyst or chemical oxidant.
Abstract
An efficient electrochemical radical silyl-oxygenation of electron-deficient alkenes is demonstrated, which gives access to a variety of new highly functionalized silicon-containing molecules, including β-silyl-cyanohydrin derivatives in good yields with excellent chemo- and regio-selectivity. This electrochemical radical silylation process conducts under mild conditions without the use of transition metal catalyst or chemical oxidant and exhibits a wide scope of substrate silanes with high functional-group tolerance. The ability to access silyl radicals using electrochemical Si−H activation offers new perspectives for the synthesis of valuable organosilicon compounds in a sustainable and green manner.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202016620-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.6 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1For selected books and reviews, see:
- 1aM. Brook, Silicon in Organic, Organometallic and Polymer Chemistry, Wiley, New York, 2000;
- 1b The Chemistry of Organic Silicon Compounds (Eds.: Z. Rappoport, Y. Apeloig), Wiley, Chichester, 2003;
- 1c Organosilicon Chemistry: Novel Approaches and Reactions (Eds.: T. Hiyama, M. Oestreich), Wiley, Weinheim, 2019;
10.1002/9783527814787 Google Scholar
- 1dE. Langkopf, D. Schinzer, Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1375–1408;
- 1eW. Bains, R. Tacke, Curr. Opin. Drug Discovery Dev. 2003, 6, 526–543;
- 1fS. Yamaguchi, K. Tamao, Chem. Lett. 2005, 34, 2–7;
- 1gJ. Chen, Y. Cao, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 1714–1742;
- 1hM. Shimizu, T. Hiyama, Synlett 2012, 973–989;
- 1iA. K. Franz, S. O. Wilson, J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 388–405;
- 1jS. Fujii, Y. Hashimoto, Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 485–505;
- 1kR. Ramesh, D. S. Reddy, J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3779–3798.
- 2For selected books and reviews, see:
- 2aB. Marciniec, J. Gulinski, W. Urbaniac, Z. W. Kornetka, Comprehensive Handbook on Hydrosilylation, Pergamon, Oxford, 1992;
- 2bB. Marciniec, Hydrosilylation: A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances, Springer, Berlin, 2009;
10.1007/978-1-4020-8172-9 Google Scholar
- 2cB. Marciniec, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 2374–2390;
- 2dD. Troegel, J. Stohrer, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1440–1459;
- 2eJ. Sun, L. Deng, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 290–300;
- 2fX. Du, Z. Huang, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1227–1243;
- 2gJ. V. Obligacion, P. J. Chirik, Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 15–34;
- 2hY. Naganawa, K. Inomata, K. Sato, Y. Nakajima, Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151513;
- 2iL. D. de Almeida, H. Wang, K. Junge, X. Cui, M. Beller, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 550–565; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 558–573.
- 3
- 3aM. Murakami, P. G. Andersson, M. Suginome, Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 3987–3988;
- 3bM. Tanaka, Y. Uchimaru, H. J. Lautenschlager, J. Organomet. Chem. 1992, 428, 1–12;
- 3cM. Murakami, M. Suginome, K. Fujimoto, H. Nakamura, P. G. Andersson, Y. Ito, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 6487–6498;
- 3dS. Nii, J. Terao, N. Kambe, J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 5291–5297;
- 3eV. Liepins, J.-E. Backvall, Chem. Commun. 2001, 265–266;
- 3fS. Nakamura, M. Uchiyama, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 28–29;
- 3gZ. Liu, J. Chen, H.-X. Lu, X. Li, Y. Gao, J. R. Coombs, M. J. Goldfogel, K. M. Engle, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17068–17073; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 17224–17229.
- 4For selected reviews, see:
- 4aC. Chatgilialoglu, Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1229–1251;
- 4bC. Chatgilialoglu, C. Ferreri, Y. Landais, V. I. Timokhin, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6516–6572;
- 4cX. Shang, Z.-Q. Liu, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 7829–7831;
- 4dJ.-S. Li, J. Wu, ChemPhotoChem 2018, 2, 839–846;
- 4eX. Zhang, J. Fang, C. Cai, G. Lu, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.09.058; for selected papers about the formation of silyl radicals from hydrosilanes, see:
- 4fD. Leifert, A. Studer, Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 386–389;
- 4gL. Xu, S. Zhang, P. Li, Org. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 459–463;
- 4hL. Zhang, Z. Hang, Z.-Q. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 236–239; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 244–247;
- 4iR. Sakamoto, B.-N. Nguyen, K. Maruoka, Asian J. Org. Chem. 2018, 7, 1085–1088;
- 4jL.-J. Wu, Y. Yang, R.-J. Song, J.-X. Yu, J.-H. Li, D.-L. He, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 1367–1370;
- 4kY. Yang, R.-J. Song, Y. Li, X.-H. Ouyang, J.-H. Li, D.-L. He, Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 1441–1444;
- 4lH. Zhang, X. Wu, Q. Zhao, C. Zhu, Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 2453–2457;
- 4mY. Zeng, X.-D. Liu, X.-Q. Guo, Q.-S. Gu, Z.-L. Li, X.-Y. Chang, X.-Y. Liu, Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 1529–1536;
- 4nY. Li, K. Shu, P. Liu, P. Sun, Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 6304–6307; for selected papers about the formation of silyl radicals from disilanes, see:
- 4oX. Yu, M. Luebbesmeyer, A. Studer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 675–679; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 685–689;
- 4pP. Trefonas, R. West, R. D. Miller, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 2737–2742;
- 4qA. R. Wolff, R. West, Appl. Organomet. Chem. 1987, 1, 7–14;
- 4rT. Kusukawa, W. Ando, J. Organomet. Chem. 1998, 559, 11–22.
- 5
- 5aO. Tayama, T. Iwahama, S. Sakaguchi, Y. Ishii, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 2286–2289;
- 5bY. Lan, X.-H. Chang, P. Fan, C.-C. Shan, Z.-B. Liu, T.-P. Loh, Y.-H. Xu, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 7120–7125;
- 5cY. Yang, R.-J. Song, X.-H. Ouyang, C.-Y. Wang, J.-H. Li, S. Luo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 7916–7919; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 8024–8027.
- 6
- 6aJ. Hou, A. Ee, H. Cao, H.-W. Ong, J.-H. Xu, J. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 17220–17224; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 17466–17470;
- 6bZ. Zhang, X. Hu, ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 777–782.
- 7For selected books and reviews, see:
- 7a Fundamentals and Applications of Organic Electrochemistry: Synthesis Materials, Devices (Eds.: T. Fuchigami, M. Atobe, S. Inagi), Wiley, Hoboken, 2014;
10.1002/9781118670750 Google Scholar
- 7b Organic Electrochemistry: Revised and Expanded, 5th ed. (Eds.: O. Hammerich, B. Speiser), CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2016;
- 7cR. Francke, R. D. Little, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2492–2521;
- 7dM. Yan, Y. Kawamata, P. S. Baran, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13230–13319;
- 7eY. Jiang, K. Xu, C. Zeng, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4485–4540;
- 7fM. D. Kärkäs, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5786–5865;
- 7gY. Okada, K. Chiba, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4592–4630;
- 7hS. Tang, Y. Liu, A. Lei, Chem 2018, 4, 27–45;
- 7iS. R. Waldvogel, S. Lips, M. Selt, B. Riehl, C. J. Kampf, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6706–6765;
- 7jA. Wiebe, T. Gieshoff, S. Moehle, E. Rodrigo, M. Zirbes, S. R. Waldvogel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5594–5619; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5694–5721;
- 7kJ.-i. Yoshida, A. Shimizu, R. Hayashi, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4702–4730;
- 7lQ.-L. Yang, P. Fang, T.-S. Mei, Chin. J. Chem. 2018, 36, 338–352;
- 7mK.-J. Jiao, Y.-K. Xing, Q.-L. Yang, H. Qiu, T.-S. Mei, Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 300–310;
- 7nP. Xiong, H.-C. Xu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 3339–3350.
- 8For selected reviews and papers, see:
- 8aG. S. Sauer, S. Lin, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 5175–5187;
- 8bJ. B. Parry, N. Fu, S. Lin, Synlett 2018, 29, 257–265;
- 8cL. Zhang, G. Zhang, P. Wang, Y. Li, A. Lei, Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 7396–7399;
- 8dY. Yuan, Y. Chen, S. Tang, Z. Huang, A. Lei, Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat5312;
- 8eY. Yuan, Y. Cao, Y. Lin, Y. Li, Z. Huang, A. Lei, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 10871–10875;
- 8fY. Wang, L. Deng, H. Mei, B. Du, J. Han, Y. Pan, Green Chem. 2018, 20, 3444–3449;
- 8gN. Fu, G. S. Sauer, A. Saha, A. Loo, S. Lin, Science 2017, 357, 575–579;
- 8hN. Fu, G. S. Sauer, S. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15548–15553;
- 8iN. Fu, L. Song, J. Liu, Y. Shen, J. C. Siu, S. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14480–14485;
- 8jP. Xiong, H. Long, J. Song, Y. Wang, J.-F. Li, H.-C. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16387–16391;
- 8kC.-Y. Cai, H.-C. Xu, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3551;
- 8lC.-Y. Cai, X.-M. Shu, H.-C. Xu, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4953;
- 8mX. Zhang, T. Cui, X. Zhao, P. Liu, P. Sun, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3465–3469; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 3493–3497;
- 8nJ.-H. Qin, M.-J. Luo, D.-L. An, J.-H. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1861–1868; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 1889–1896.
- 9
- 9aV. Jouikov, ECS Trans. 2008, 13, 11–16;
- 9bJ. Zeitouny, V. Jouikov, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 7161–7170.
- 10L. Lu, J. C. Siu, Y. Lai, S. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21272–21278.
- 11
- 11aD. Mu, W. Yuan, S. Chen, N. Wang, B. Yang, L. You, B. Zu, P. Yu, C. He, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 13459–13468;
- 11bB. Yang, W. Yang, Y. Guo, L. You, C. He, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22217–22222; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 22401–22406.
- 12B. Zu, J. Ke, Y. Guo, C. He, Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 627–632.
- 13While our manuscript was under preparation, the Zhang group reported an electrochemical hydrolysis of hydrosilane to silanol via anodically generated silyl cation, in which silyl radical is proposed as an intermediate before the formation of silyl cation: H. Liang, L.-J. Wang, Y.-X. Ji, H. Wang, B. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1839–1844; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 1867–1872.
- 14
- 14aJ. E. Nutting, M. Rafiee, S. S. Stahl, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 4834–4885;
- 14bF. Wang, S. S. Stahl, Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 561–574;
- 14cF. Recupero, C. Punta, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3800–3842.
- 15R. J. H. Gregory, Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 3649–3682.
- 16Deposition Number 2049036 (for 4t) contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures.
- 17W. Adam, C. M. Mitchell, C. R. Saha-Moeller, O. Weichold, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 2097–2103.
- 18
- 18aS. J. Wittenberger, B. G. Donner, J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 4139–4141;
- 18bH. Yoneyama, N. Oka, Y. Usami, S. Harusawa, Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151517.
- 19X. Li, Y.-D. Wu, D. Yang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1428–1438.