Synthesis of Ketones by C−H Functionalization of Aldehydes with Boronic Acids under Transition-Metal-Free Conditions
Dr. Silvia Roscales
Instituto Pluridisciplinar, Universidad Complutense, Campus de Excelencia Internacional Moncloa, Paseo de Juan XXIII, 1, 28040 Madrid, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Aurelio G. Csáky
Instituto Pluridisciplinar, Universidad Complutense, Campus de Excelencia Internacional Moncloa, Paseo de Juan XXIII, 1, 28040 Madrid, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Silvia Roscales
Instituto Pluridisciplinar, Universidad Complutense, Campus de Excelencia Internacional Moncloa, Paseo de Juan XXIII, 1, 28040 Madrid, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Aurelio G. Csáky
Instituto Pluridisciplinar, Universidad Complutense, Campus de Excelencia Internacional Moncloa, Paseo de Juan XXIII, 1, 28040 Madrid, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
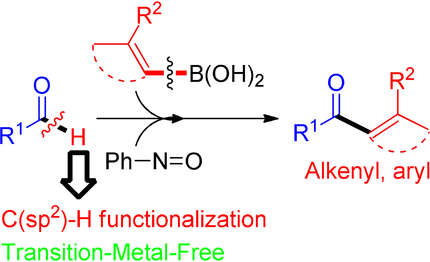
Nitrosobenzene can simultaneously activate the C−H bonds of aldehydes and the C−B bonds of boronic acids triggering a C−C bond-forming process that leads to the synthesis of ketones via an intramolecular migration from boron to carbon. These findings constitute a transition-metal-free practical, scalable, and operationally easy method for the synthesis of ketones.
Abstract
A method for the synthesis of ketones from aldehydes and boronic acids via a transition-metal-free C−H functionalization reaction is reported. The method employs nitrosobenzene as a reagent to drive the simultaneous activation of the boronic acid as a boronate and the activation of the C−H bond of the aldehyde as an iminium species that triggers the key C−C bond-forming step via an intramolecular migration from boron to carbon. These findings constitute a practical, scalable, and operationally straightforward method for the synthesis of ketones.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202015835-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.5 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aM. C. Cuquerella, V. Lhiaubet-Vallet, J. Cadet, M. A. Miranda, Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1558–1570;
- 1bY. Tan, K. J. Siebert, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3057–3064;
- 1cR. McDaniel, A. Thamchaipenet, C. Gustafsson, H. Fu, M. Betlach, M. Betlach, G. Ashley, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1846–1851;
- 1dP. V. Kamat, Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 267–300.
- 2
- 2a Modern Carbonyl Chemistry (Ed.: J. Otera), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2000;
10.1002/9783527613267 Google Scholar
- 2bN. J. Lawrence, J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1998, 1739–1749;
- 2cM. Blangetti, H. Rosso, C. Prandi, A. Deagostino, P. Venturello, Molecules 2013, 18, 1188–1213.
- 3See reference [2], and in addition:
- 3aS. Nahm, S. M. Weinreb, Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 3815–3818;
- 3bG. Sartori, R. Maggi, Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1077–1104;
- 3cW. S. Bechara, G. Pelletier, A. B. Charette, Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 228–234;
- 3dN. Miyaura, A. Suzuki, Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 2457–2483;
- 3eM. C. Willis, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 725–748;
- 3fX.-F. Wu, H. Neumann, M. Beller, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4986–5009;
- 3gT. Moragas, A. Correa, R. Martin, Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 8242–8258;
- 3hR. K. Dieter, Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 4177–4236;
- 3iM. Iinuma, K. Moriyama, H. Togo, Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 2961–2970;
- 3jY. Huang, R. Zhu, K. Zhao, Z. Gu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12669–12672; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 12860–12863;
- 3kM. Giannerini, C. Vila, V. Hornillos, B. L. Feringa, Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 1206–1209;
- 3lA. T. Wolters, V. Hornillos, D. Heijnen, M. Giannerini, B. L. Feringa, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2622–2625;
- 3mL.-J. Cheng, N. P. Mankad, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10200–10203.
- 4For some additional recent methods, see:
- 4aJ. Wang, B. P. Cary, P. D. Beyer, S. H. Gellman, D. J. Weix, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 12081–12085; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 12209–12213;
- 4bF. Q. Zhao, C. L. Li, X. F. Wu, Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 9182–9185;
- 4cJ. Wang, M. E. Hoerrner, M. P. Watson, D. J. Weix, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13484–13489; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 13586–13591;
- 4dR. Ruzi, K. Liu, C. Zhu, J. Xie, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3312;
- 4eN. Chalotra, S. Sultan, B. A. Shah, Asian J. Org. Chem. 2020, 9, 863–881;
- 4fH. Cao, Y. Kuang, X. Shi, K. L. Wong, B. B. Tan, J. M. C. Kwan, X. Liu, J. Wu, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1956, and references therein.
- 5P. Kumar, S. Dutta, S. Kumar, V. Bahadur, E. V. Van der Eycken, K. S. Vimaleswaran, V. S. Parmar, B. K. Singh, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 7987–8033.
- 6J. E. Steves, S. S. Stahl, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15742–15745.
- 7For the Corey-Seebach reaction, see:
- 7aE. J. Corey, D. Seebach, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1965, 4, 1077–1078; Angew. Chem. 1965, 77, 1136–1137;
- 7bA. B. Smith, C. M. Adams, Acc. Chem. Res. 2004, 37, 365–377;
- 7cB. Yucel, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 3659–3667;
- 7dS. A. Baker Dockrey, A. K. Makepeace, J. R. Schmink, Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 4730–4733;
- 7eK. Yao, D. Liu, Q. Yuan, T. Imamoto, Y. Liu, W. Zhang, Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 6296–6299;
- 7fN. Trongsiriwat, M. Li, A. Pascual-Escudero, B. Yucel, P. J. Walsh, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 502–509.
- 8For N-heterocyclic carbene-catalyzed reactions, see:
- 8aD. A. DiRocco, T. Rovis, Asymmetric Benzoin and Stetter Reactions Vol. 2, Georg Thieme, Stuttgart, 2011, pp. 835–862;
- 8bA. A. Rajkiewicz, M. Kalek, Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 1906–1909;
- 8cA. A. Rajkiewicz, N. Wojciechowska, M. Kalek, ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 831–841.
- 9
- 9aL. Wang, T. Wang, G.-J. Cheng, X. Li, J.-J. Wei, B. Guo, C. Zheng, G. Chen, C. Ran, C. Zheng, ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 7543–7551;
- 9bA. Banerjee, Z. Lei, M.-Y. Ngai, Synthesis 2019, 51, 303–333;
- 9cL. Revathi, L. Ravindar, W.-Y. Fang, K. P. Rakesh, H.-L. Qin, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 4652–4698;
- 9dX. Zhang, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 11353–11356;
- 9eH. Yi, G. Zhang, H. Wang, Z. Huang, J. Wang, A. K. Singh, A. Lei, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9016–9085;
- 9fS. Tripathi, S. N. Singh, L. D. S. Yadav, Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 4211–4214;
- 9gX.-H. Ouyang, R.-J. Song, C.-Y. Wang, Y. Yang, J.-H. Li, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14497–14500;
- 9hJ. Wang, C. Liu, J. Yuan, A. Lei, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2256–2259; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 2312–2315;
- 9iC. Chatgilialoglu, D. Crich, M. Komatsu, I. Ryu, Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 1991–2069.
- 10
- 10aJ. Ruan, O. Saidi, J. A. Iggo, J. Xiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10510–10511;
- 10bJ. K. Vandavasi, S. G. Newman, Synlett 2018, 29, 2081–2086;
- 10cZ. Shi, N. Schroeder, F. Glorius, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8092–8096; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 8216–8220;
- 10dT. Wakaki, T. Togo, D. Yoshidome, Y. Kuninobu, M. Kanai, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3123–3128.
- 11
- 11aM. Pucheault, S. Darses, J.-P. Genet, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15356–15357;
- 11bG. Mora, S. Darses, J.-P. Genet, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1180–1184;
- 11cC. Qin, J. Chen, H. Wu, J. Cheng, Q. Zhang, B. Zuo, W. Su, J. Ding, Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 1884–1888;
- 11dP. Álvarez-Bercedo, A. Flores-Gaspar, A. Correa, R. Martin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 466–467;
- 11eM. Kuriyama, N. Hamaguchi, K. Sakata, O. Onomura, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 3378–3385;
- 11fB. Suchand, G. Satyanarayana, J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 6409–6423;
- 11gY.-X. Liao, Q.-S. Hu, J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 6986–6989;
- 11hH. Li, Y. Xu, E. Shi, W. Wei, X. Suo, X. Wan, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7880–7882;
- 11iH. Zheng, J. Ding, J. Chen, M. Liu, W. Gao, H. Wu, Synlett 2011, 1626–1630;
- 11jC. Lei, D. Zhu, V. I. I. I. T. Tangcueco, J. S. Zhou, Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 5817–5822;
- 11kR. A. Swyka, W. G. Shuler, B. J. Spinello, W. Zhang, C. Lan, M. J. Krische, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6864–6868.
- 12
- 12aP. Gandeepan, L. Ackermann, Chem 2018, 4, 199–222;
- 12bA. Ghosh, K. F. Johnson, K. L. Vickerman, J. A. Walker, L. M. Stanley, Org. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 639–644;
- 12cM. C. Willis, Hydroacylation of Alkenes, Alkynes, and Allenes Vol. 4, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2014, pp. 961–994;
- 12dM. A. Garralda, Dalton Trans. 2009, 3635–3645.
- 13
- 13aO. Kronja, J. Matijević-Sosa, S. Uršić, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1987, 463–464;
- 13bM. Strah, S. Uršić, B. Zorc, Croat. Chem. Acta 1989, 62, 529–535;
- 13cS. Uršić, Helv. Chim. Acta 1993, 76, 131–138;
- 13dS. Uršić, V. Pilepic, V. Vrcek, M. Gabricevic, B. Zorc, J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1993, 509–514.
- 14
- 14aS. Roscales, A. G. Csaky, Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 1667–1671;
- 14bS. Roscales, A. G. Csákÿ, J. Chem. Educ. 2019, 96, 1738–1744;
- 14cS. Roscales, A. G. Csaky, ACS Omega 2019, 4, 13943–13953.
- 15 Boronic Acids: Preparation and Applications in Organic Synthesis Medicine and Materials (Ed.: D. G. Hall), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2011.
- 16G. Berionni, B. Maji, P. Knochel, H. Mayr, Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 878–882.
- 17
- 17aS. Roscales, A. G. Csaky, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8215–8225;
- 17bF. Sanchez-Sancho, A. G. Csaky, Synthesis 2016, 48, 2165–2177.
- 18
- 18aH. Wang, C. Jing, A. Noble, V. K. Aggarwal, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 16859–16872; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 17005–17018;
- 18bM. Kischkewitz, F. W. Friese, A. Studer, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 2077–2087;
- 18cK. K. Das, S. Panda, Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 14270–14282;
- 18dS. Paul, K. K. Das, S. Manna, S. Panda, Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 1922–1927;
- 18eS. Namirembe, J. P. Morken, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3464–3474;
- 18fS. Roscales, A. G. Csáky, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5159–5177.
- 19
- 19aN. A. Petasis, I. Akritopoulou, Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 583–586;
- 19bN. R. Candeias, F. Montalbano, P. M. S. D. Cal, P. M. P. Gois, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6169–6193;
- 19cP. Wu, M. Givskov, T. E. Nielsen, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 11245–11290.
- 20L. Bering, A. P. Antonchick, Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 3134–3137.
- 21K. Yang, F. Zhang, T. C. Fang, G. Zhang, Q. L. Song, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13421–13426; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 13555–13560.
- 22For the coordination of boronic acid derivatives to N-nucleophiles followed by C-migration, see:
- 22aK. Livingstone, J. Mowat, C. Jamieson, S. Bertrand, Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 10412–10416;
- 22bK. Livingstone, S. Bertrand, A. R. Kennedy, C. Jamieson, Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 10591–10597.
- 23P. K. Prasad, R. N. Reddi, S. Arumugam, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 9334–9348.
- 24J. M. Concellon, H. Rodriguez-Solla, Curr. Org. Chem. 2008, 12, 524–543.
- 25Y.-F. Chen, J. Chen, L.-J. Lin, G. J. Chuang, J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 11626–11630.
- 26J. Takagi, K. Takahashi, T. Ishiyama, N. Miyaura, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8001–8006.
- 27
- 27aR. A. Batey, A. N. Thadani, D. V. Smil, A. J. Lough, Synthesis 2000, 990–998; See also:
- 27bV. Ortega, A. G. Csaky, J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 3917–3923.
- 28Similarly to the transformation reported herein, electron-rich boronic acids are more reactive in Petasis-Mannich reactions. See for example:
- 28aM. Follmann, F. Graul, T. Schaefer, S. Kopec, P. Hamley, Synlett 2005, 1009–1011;
- 28bM. V. Shevchuk, A. E. Sorochinsky, V. P. Khilya, V. D. Romanenko, V. P. Kukhar, Synlett 2010, 73–76.