Traceless Removal of Two Kernel Atoms in a Gold Nanocluster and Its Impact on Photoluminescence
Yue Zhou
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lingwen Liao
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shengli Zhuang
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYan Zhao
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zibao Gan
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWanmiao Gu
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Jin Li
Tsinghua University-Peking University Joint Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Haiteng Deng
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinformatics, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Nan Xia
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zhikun Wu
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYue Zhou
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lingwen Liao
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shengli Zhuang
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYan Zhao
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Zibao Gan
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWanmiao Gu
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Jin Li
Tsinghua University-Peking University Joint Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Haiteng Deng
MOE Key Laboratory of Bioinformatics, School of Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Nan Xia
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Zhikun Wu
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics, Anhui Key Laboratory of Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, Institute of Solid State Physics, HFIPS, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, Anhui, 230031 P. R. China
Institute of Physical Science and Information Technology, Anhui University, Hefei, 230601 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
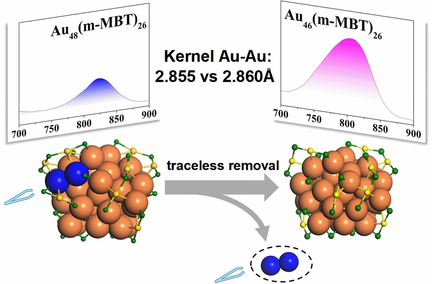
Two novel nanoclusters Au48(m-MB)26 and Au46(m-MBT)26 have been synthesized and fully characterized, and the traceless removal of two kernel atoms in metal nanoclusters has been achieved for the first time. The two kernel atoms reduction leads to the photoluminescence quantum yield (QY) increase by almost four times. In addition, kernel bond length dependent photoluminescence and kernel charge state were first revealed.
Abstract
Removing or adding kernel atoms of metal nanoclusters (NCs) without leaving a trace is a substantial challenge because the kernel atoms are inside and covered by the outer staples. However, such kernel tuning is very important for improving the properties and acquiring an in-depth understanding of the kernel-property correlation. Photoluminescence (PL) is one of the most intriguing characteristics of metal NCs but has not been well understood until now. Inspired by these challenges/questions, we conducted this study and, for the first time, achieved the traceless removal of two kernel atoms in a gold nanocluster by applying a simple thermal treatment and revealed its impact on PL. Further, we demonstrated that the kernel Au-Au bond length can be an indicator for a comparison of the PL or kernel charge state between nanoclusters with similar kernel structures and sizes.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202016692-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.8 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aR. Jin, C. Zeng, M. Zhou, Y. Chen, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10346–10413;
- 1bI. Chakraborty, T. Pradeep, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8208–8271;
- 1cQ. Yao, X. Yuan, T. Chen, D. T. Leong, J. Xie, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802751;
- 1dZ. B. Gan, N. Xia, Z. K. Woo, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2774–2783;
- 1eA. Ghosh, O. F. Mohammed, O. M. Bakr, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 3094–3103;
- 1fS. Hossain, Y. Niihori, L. V. Nair, B. Kumar, W. Kurashige, Y. Negishi, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 3114–3124;
- 1gZ. Wang, R. K. Gupta, G.-G. Luo, D. Sun, Chem. Rec. 2020, 20, 389–402;
- 1hY. Du, H. Sheng, D. Astruc, M. Zhu, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 526–622;
- 1iJ. Yan, B. K. Teo, N. Zheng, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 3084–3093;
- 1jS. Knoppe, T. Bürgi, Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1318–1326;
- 1kH. Häkkinen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1847–1859;
- 1lP. D. Jadzinsky, G. Calero, C. J. Ackerson, D. A. Bushnell, R. D. Kornberg, Science 2007, 318, 430–433;
- 1mY. Negishi, K. Nobusada, T. Tsukuda, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5261–5270;
- 1nD. M. Chevrier, L. Raich, C. Rovira, A. Das, Z. Luo, Q. Yao, A. Chatt, J. Xie, R. Jin, J. Akola, P. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15430–15436;
- 1oQ. Tang, G. Hu, V. Fung, D.-e. Jiang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2793–2802.
- 2
- 2aY. Negishi, T. Iwai, M. Ide, Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4713–4715;
- 2bH. Qian, D.-e. Jiang, G. Li, C. Gayathri, A. Das, R. R. Gil, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16159–16162;
- 2cM. Zhou, C. Zeng, Y. Chen, S. Zhao, M. Y. Sfeir, M. Zhu, R. Jin, Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13240–13246;
- 2dJ. Chai, S. Yang, Y. Lv, T. Chen, S. Wang, H. Yu, M. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15582–15585;
- 2eJ.-S. Yang, Z. Han, X.-Y. Dong, P. Luo, H.-L. Mo, S.-Q. Zang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11898–11902; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 11996–12000.
- 3
- 3aX.-K. Wan, J.-Q. Wang, Z.-A. Nan, Q.-M. Wang, Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701823;
- 3bY. Chen, C. Liu, Q. Tang, C. Zeng, T. Higaki, A. Das, D.-e. Jiang, N. L. Rosi, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1482–1485;
- 3cN. Xia, J. Yuan, L. Liao, W. Zhang, J. Li, H. Deng, J. Yang, Z. Wu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 12140–12145;
- 3dK. L. D. M. Weerawardene, C. M. Aikens, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11202–11210.
- 4
- 4aQ. Li, T.-Y. Luo, M. G. Taylor, S. Wang, X. Zhu, Y. Song, G. Mpourmpakis, N. L. Rosi, R. Jin, Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1603193;
- 4bZ. Wu, Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2017, 33, 1930–1931.
- 5L. He, J. Yuan, N. Xia, L. Liao, X. Liu, Z. Gan, C. Wang, J. Yang, Z. Wu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3487–3490.
- 6Z. Wu, R. Jin, Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2568–2573.
- 7
- 7aK. Pyo, V. D. Thanthirige, K. Kwak, P. Pandurangan, G. Ramakrishna, D. Lee, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8244–8250;
- 7bZ. B. Gan, Y. J. Lin, L. Luo, G. M. Han, W. Liu, Z. J. Liu, C. H. Yao, L. H. Weng, L. W. Liao, J. S. Chen, X. Liu, Y. Luo, C. M. Wang, S. Q. Wei, Z. K. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11567–11571; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 11739–11743;
- 7cA. Nag, P. Chakraborty, M. Bodiuzzaman, T. Ahuja, S. Antharjanam, T. Pradeep, Nanoscale 2018, 10, 9851–9855;
- 7dZ. Wu, Y. Du, J. Liu, Q. Yao, T. Chen, Y. Cao, H. Zhang, J. Xie, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8139–8144; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 8223–8228.
- 8S. L. Zhuang, L. W. Liao, J. Y. Yuan, N. Xia, Y. Zhao, C. M. Wang, Z. B. Gan, N. Yan, L. Z. He, J. Li, H. T. Deng, Z. Y. Guan, J. L. Yang, Z. K. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4510–4514; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 4558–4562.
- 9
- 9aR. Jin, H. Qian, Z. Wu, Y. Zhu, M. Zhu, A. Mohanty, N. Garg, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 2903–2910;
- 9bS. Zhuang, L. Liao, J. Yuan, C. Wang, Y. Zhao, N. Xia, Z. Gan, W. Gu, J. Li, H. Deng, J. Yang, Z. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15450–15454; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 15676–15680.
- 10L. Liao, C. Yao, C. Wang, S. Tian, J. Chen, M.-B. Li, N. Xia, N. Yan, Z. Wu, Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11297–11301.
- 11
- 11aH. Qian, W. T. Eckenhoff, Y. Zhu, T. Pintauer, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8280–8281;
- 11bJ. Chen, Q.-F. Zhang, T. A. Bonaccorso, P. G. Williard, L.-S. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 92–95;
- 11cX.-K. Wan, S.-F. Yuan, Q. Tang, D.-e. Jiang, Q.-M. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5977–5980; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 6075–6078;
- 11dC. P. Joshi, M. S. Bootharaju, M. J. Alhilaly, O. M. Bakr, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11578–11581;
- 11eC. Zeng, Y. Chen, K. Kirschbaum, K. J. Lambright, R. Jin, Science 2016, 354, 1580–1584;
- 11fN. Yan, N. Xia, L. Liao, M. Zhu, F. Jin, R. Jin, Z. Wu, Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat7259;
- 11gC. A. Hosier, C. J. Ackerson, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 309–314;
- 11hM. W. Heaven, A. Dass, P. S. White, K. M. Holt, R. W. Murray, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 3754–3755;
- 11iM. Zhu, C. M. Aikens, F. J. Hollander, G. C. Schatz, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5883–5885.
- 12
- 12aC. Zeng, Y. Chen, K. Iida, K. Nobusada, K. Kirschbaum, K. J. Lambright, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3950–3953;
- 12bZ. Ma, P. Wang, Y. Pei, Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17044–17054;
- 12cC. Zeng, C. Liu, Y. Chen, N. L. Rosi, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8710–8713;
- 12dN. A. Sakthivel, S. Theivendran, V. Ganeshraj, A. G. Oliver, A. Dass, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15450–15459.
- 13
- 13aM. Walter, J. Akola, O. Lopez-Acevedo, P. D. Jadzinsky, G. Calero, C. J. Ackerson, R. L. Whetten, H. Gronbeck, H. Hakkinen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9157–9162;
- 13bZ. Wu, R. Jin, Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 13966–13970;
- 13cH. Häkkinen, Adv. Phys. X 2016, 1, 467–491.
- 14S. L. Zhuang, L. W. Liao, Y. Zhao, J. Y. Yuan, C. H. Yao, X. Liu, J. Li, H. T. Deng, J. L. Yang, Z. K. Wu, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2437–2442.
- 15M. Zhu, W. T. Eckenhoff, T. Pintauer, R. Jin, J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 14221–14224.
- 16
- 16aZ. Gan, J. Chen, L. Liao, H. Zhang, Z. Wu, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 204–208;
- 16bZ. Gan, J. Chen, J. Wang, C. Wang, M.-B. Li, C. Yao, S. Zhuang, A. Xu, L. Li, Z. Wu, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14739–14744.
- 17Deposition Numbers 2055463 and 2055972 (for Au48(m-MBT)26and Au46(m-MBT)26) contain the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures.