Ag44(EBT)26(TPP)4 Nanoclusters With Tailored Molecular and Electronic Structure
Dr. Megalamane S. Bootharaju
Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826 Republic of Korea
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorSanghwa Lee
Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826 Republic of Korea
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorGuocheng Deng
State Key Laboratory for Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials, Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Sami Malola
Departments of Physics and Chemistry, Nanoscience Center, University of Jyväskylä, 40014 Jyväskylä, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorWoonhyuk Baek
Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hannu Häkkinen
Departments of Physics and Chemistry, Nanoscience Center, University of Jyväskylä, 40014 Jyväskylä, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Nanfeng Zheng
State Key Laboratory for Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials, Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Taeghwan Hyeon
Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Megalamane S. Bootharaju
Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826 Republic of Korea
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorSanghwa Lee
Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826 Republic of Korea
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorGuocheng Deng
State Key Laboratory for Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials, Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Sami Malola
Departments of Physics and Chemistry, Nanoscience Center, University of Jyväskylä, 40014 Jyväskylä, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorWoonhyuk Baek
Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hannu Häkkinen
Departments of Physics and Chemistry, Nanoscience Center, University of Jyväskylä, 40014 Jyväskylä, Finland
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Nanfeng Zheng
State Key Laboratory for Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials, Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Taeghwan Hyeon
Center for Nanoparticle Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), School of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Institute of Chemical Processes, Seoul National University, Seoul, 08826 Republic of Korea
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
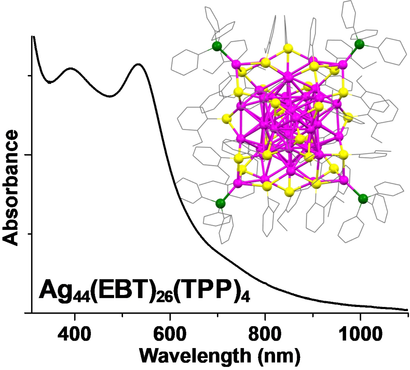
In this work, the synthesis and total structure determination of a novel Ag44(EBT)26(TPP)4 nanocluster, the first analogue of [Ag44(SR)30]4−, are reported. The identical size as well as similar core- and different surface-structures of these two nanoclusters enable the study of the structural effect on the optical and photophysical properties. The novel surface structure plays a crucial role in the enhancement of NIR-II photoluminescence.
Abstract
Although atomically precise metalloid nanoclusters (NCs) of identical size with distinctly different molecular structures are highly desirable to understand the structural effects on the optical and photophysical properties, their synthesis remains highly challenging. Herein, we employed phosphine and thiol capping ligands featuring appropriate steric effects and synthesized a charge-neutral Ag NC with the formula Ag44(EBT)26(TPP)4 (EBT: 2-ethylbenzenethiolate; TPP: triphenylphosphine). The single-crystal X-ray structure reveals that this NC has a hollow metal core of Ag12@Ag20 and a metal–ligand shell of Ag12(EBT)26(TPP)4. The presence of mixed ligands and long V-shaped metal–ligand motifs on this NC has resulted in an enhancement of the NIR-II photoluminescence quantum yield by >25-fold compared to an all-thiolate-stabilized anionic [Ag44(SR)30]4− NC (SR: thiolate). Time-dependent density-functional calculations show that our Ag44 NC is an 18-electron superatom with a modulated electronic structure as compared to the [Ag44(SR)30]4− anion, significantly influencing its optical properties.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202015907-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.4 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aM. Zhou, T. Higaki, G. Hu, M. Y. Sfeir, Y. Chen, D.-e. Jiang, R. Jin, Science 2019, 364, 279–282;
- 1bO. M. Bakr, V. Amendola, C. M. Aikens, W. Wenseleers, R. Li, L. Dal Negro, G. C. Schatz, F. Stellacci, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5921–5926; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 6035–6040.
- 2
- 2aL. He, Z. Gan, N. Xia, L. Liao, Z. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9897–9901; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 10002–10006;
- 2bI. Chakraborty, T. Pradeep, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8208–8271;
- 2cE. Khatun, P. Chakraborty, B. R. Jacob, G. Paramasivam, M. Bodiuzzaman, W. A. Dar, T. Pradeep, Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 611–619.
- 3
- 3aK. L. D. M. Weerawardene, P. Pandeya, M. Zhou, Y. Chen, R. Jin, C. M. Aikens, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 18715–18726;
- 3bX. Ma, Y. Bai, Y. Song, Q. Li, Y. Lv, H. Zhang, H. Yu, M. Zhu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17234–17238; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 17387–17391.
- 4
- 4aX. Kang, Y. Li, M. Zhu, R. Jin, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6443–6514;
- 4bX. Liu, J. Chen, J. Yuan, Y. Li, J. Li, S. Zhou, C. Yao, L. Liao, S. Zhuang, Y. Zhao, H. Deng, J. Yang, Z. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11273–11277; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 11443–11447;
- 4cQ. Tang, G. Hu, V. Fung, D.-e. Jiang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2793–2802.
- 5
- 5aT. Higaki, Y. Li, S. Zhao, Q. Li, S. Li, X.-S. Du, S. Yang, J. Chai, R. Jin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8291–8302; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 8377–8388;
- 5bS. Lee, M. S. Bootharaju, G. Deng, S. Malola, W. Baek, H. Häkkinen, N. Zheng, T. Hyeon, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 13974–13981.
- 6P. Chakraborty, A. Nag, K. S. Sugi, T. Ahuja, B. Varghese, T. Pradeep, ACS Mater. Lett. 2019, 1, 534–540.
- 7Y. Wang, X.-H. Liu, Q. Wang, M. Quick, S. A. Kovalenko, Q.-Y. Chen, N. Koch, N. Pinna, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7748–7754; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 7822–7828.
- 8S. Shahsavari, S. Hadian-Ghazvini, F. Hooriabad Saboor, I. Menbari Oskouie, M. Hasany, A. Simchi, A. L. Rogach, Mater. Chem. Front. 2019, 3, 2326–2356.
- 9
- 9aJ.-Y. Liu, F. Alkan, Z. Wang, Z.-Y. Zhang, M. Kurmoo, Z. Yan, Q.-Q. Zhao, C. M. Aikens, C.-H. Tung, D. Sun, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 195–199; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 201–205;
- 9bR.-W. Huang, J. Yin, C. Dong, A. Ghosh, M. J. Alhilaly, X. Dong, M. N. Hedhili, E. Abou-Hamad, B. Alamer, S. Nematulloev, Y. Han, O. F. Mohammed, O. M. Bakr, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 8696–8705;
- 9cX. Kang, M. Zhu, ACS Mater. Lett. 2020, 2, 1303–1314;
- 9dM. J. Alhilaly, R.-W. Huang, R. Naphade, B. Alamer, M. N. Hedhili, A.-H. Emwas, P. Maity, J. Yin, A. Shkurenko, O. F. Mohammed, M. Eddaoudi, O. M. Bakr, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9585–9592.
- 10
- 10aA. Schnepf, H. Schnöckel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 711–715; Angew. Chem. 2001, 113, 733–737;
- 10bA. Ecker, E. Weckert, H. Schnöckel, Nature 1997, 387, 379–381;
- 10cM. Binder, C. Schrenk, A. Schnepf, Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 12148–12151.
- 11
- 11aT. I. Levchenko, C. Kübel, B. Khalili Najafabadi, P. D. Boyle, C. Cadogan, L. V. Goncharova, A. Garreau, F. Lagugné-Labarthet, Y. Huang, J. F. Corrigan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1129–1144;
- 11bD. R. Kauffman, D. Alfonso, D. N. Tafen, J. Lekse, C. Wang, X. Deng, J. Lee, H. Jang, J.-s. Lee, S. Kumar, C. Matranga, ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 1225–1234.
- 12
- 12aL. He, J. Yuan, N. Xia, L. Liao, X. Liu, Z. Gan, C. Wang, J. Yang, Z. Wu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3487–3490;
- 12bT. Kawawaki, Y. Mori, K. Wakamatsu, S. Ozaki, M. Kawachi, S. Hossain, Y. Negishi, J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16081–16113;
- 12cI. Chakraborty, W. Kurashige, K. Kanehira, L. Gell, H. Häkkinen, Y. Negishi, T. Pradeep, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 3351–3355.
- 13Y. Chen, C. Zeng, D. R. Kauffman, R. Jin, Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3603–3609.
- 14
- 14aM. Bodiuzzaman, A. Ghosh, K. S. Sugi, A. Nag, E. Khatun, B. Varghese, G. Paramasivam, S. Antharjanam, G. Natarajan, T. Pradeep, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 189–194; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 195–200;
- 14bS. K. Barik, T.-H. Chiu, Y.-C. Liu, M.-H. Chiang, F. Gam, I. Chantrenne, S. Kahlal, J.-Y. Saillard, C. W. Liu, Nanoscale 2019, 11, 14581–14586.
- 15X. Yuan, C. Sun, X. Li, S. Malola, B. K. Teo, H. Häkkinen, L.-S. Zheng, N. Zheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11905–11911.
- 16R. S. Dhayal, W. E. van Zyl, C. W. Liu, Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 86–95.
- 17M. Qu, H. Li, L.-H. Xie, S.-T. Yan, J.-R. Li, J.-H. Wang, C.-Y. Wei, Y.-W. Wu, X.-M. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12346–12349.
- 18X. Kang, M. Zhu, Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 9939–9969.
- 19
- 19aF. Tian, R. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7107–7114;
- 19bX. Lin, C. Liu, X. Fu, J. Huang, Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 972–976.
- 20M. S. Bootharaju, H. Chang, G. Deng, S. Malola, W. Baek, H. Häkkinen, N. Zheng, T. Hyeon, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8422–8425.
- 21
- 21aY. Chen, M. Zhou, Q. Li, H. Gronlund, R. Jin, Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 8176–8183;
- 21bB. Kumar, T. Kawawaki, N. Shimizu, Y. Imai, D. Suzuki, S. Hossain, L. V. Nair, Y. Negishi, Nanoscale 2020, 12, 9969–9979;
- 21cT. Omoda, S. Takano, T. Tsukuda, Small 2021, 17, 2001439;
- 21dK. Kim, K. Hirata, K. Nakamura, H. Kitazawa, S. Hayashi, K. Koyasu, T. Tsukuda, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 11637–11641; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 11763–11767;
- 21eW. Choi, G. Hu, K. Kwak, M. Kim, D.-e. Jiang, J.-P. Choi, D. Lee, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44645–44653.
- 22
- 22aC. P. Joshi, M. S. Bootharaju, M. J. Alhilaly, O. M. Bakr, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11578–11581;
- 22bM. S. Bootharaju, S. M. Kozlov, Z. Cao, A. Shkurenko, A. M. El-Zohry, O. F. Mohammed, M. Eddaoudi, O. M. Bakr, L. Cavallo, J.-M. Basset, Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 2719–2725;
- 22cA. Schnepf, E. Weckert, G. Linti, H. Schnöckel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3381–3383;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19991115)38:22<3381::AID-ANIE3381>3.0.CO;2-P CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 1999, 111, 3578–3581;10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(19991115)111:22<3578::AID-ANGE3578>3.0.CO;2-2 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 22dA. Schnepf, G. Stößer, H. Schnöckel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1882–1884;
10.1002/1521-3773(20020603)41:11<1882::AID-ANIE1882>3.0.CO;2-N CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2002, 114, 1959–1962;
- 22eA. Schnepf, R. Köppe, E. Weckert, H. Schnöckel, Chem. Eur. J. 2004, 10, 1977–1981.
- 23
- 23aA. Desireddy, B. E. Conn, J. Guo, B. Yoon, R. N. Barnett, B. M. Monahan, K. Kirschbaum, W. P. Griffith, R. L. Whetten, U. Landman, T. P. Bigioni, Nature 2013, 501, 399–402;
- 23bH. Yang, Y. Wang, H. Huang, L. Gell, L. Lehtovaara, S. Malola, H. Häkkinen, N. Zheng, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2422.
- 24
- 24aA. Schnepf, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2624–2625; Angew. Chem. 2003, 115, 2728–2729;
- 24bG. N. Reddy, R. Parida, S. Giri, Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 13229–13232;
- 24cC. Schrenk, F. Winter, R. Pöttgen, A. Schnepf, Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 2992–2997.
- 25Deposition Number 2032634 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures.
- 26M. J. Alhilaly, M. S. Bootharaju, C. P. Joshi, T. M. Besong, A.-H. Emwas, R. Juarez-Mosqueda, S. Kaappa, S. Malola, K. Adil, A. Shkurenko, H. Häkkinen, M. Eddaoudi, O. M. Bakr, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 14727–14732.
- 27M. Walter, J. Akola, O. Lopez-Acevedo, P. D. Jadzinsky, G. Calero, C. J. Ackerson, R. L. Whetten, H. Grönbeck, H. Häkkinen, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9157–9162.
- 28
- 28aX.-K. Wan, W. W. Xu, S.-F. Yuan, Y. Gao, X.-C. Zeng, Q.-M. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9683–9686; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 9819–9822;
- 28bK. L. D. M. Weerawardene, C. M. Aikens, J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 2440–2447.
- 29
- 29aS. Zhu, R. Tian, A. L. Antaris, X. Chen, H. Dai, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900321;
- 29bX. Song, W. Zhu, X. Ge, R. Li, S. Li, X. Chen, J. Song, J. Xie, X. Chen, H. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1306–1312; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 1326–1332.
- 30X. Kang, S. Wang, M. Zhu, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 3062–3068.
- 31M.-B. Li, S.-K. Tian, Z. Wu, R. Jin, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4433–4436.
- 32
- 32aX. Kang, H. Abroshan, S. Wang, M. Zhu, Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 11000–11009;
- 32bJ. Yan, H. Su, H. Yang, C. Hu, S. Malola, S. Lin, B. K. Teo, H. Häkkinen, N. Zheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12751–12754.