NIR-Actuated Remote Activation of Ferroptosis in Target Tumor Cells through a Photothermally Responsive Iron-Chelated Biopolymer Nanoplatform
Chencheng Xue
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMenghuan Li
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorChanghuang Liu
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYanan Li
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorYang Fei
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorYan Hu
Key Laboratory of Biorheological Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, College of Bioengineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorKaiyong Cai
Key Laboratory of Biorheological Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, College of Bioengineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorYanli Zhao
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, 21 Nanyang Link, 637371 Singapore, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhong Luo
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorChencheng Xue
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMenghuan Li
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorChanghuang Liu
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYanan Li
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorYang Fei
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorYan Hu
Key Laboratory of Biorheological Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, College of Bioengineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorKaiyong Cai
Key Laboratory of Biorheological Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, College of Bioengineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorYanli Zhao
Division of Chemistry and Biological Chemistry, School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Nanyang Technological University, 21 Nanyang Link, 637371 Singapore, Singapore
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhong Luo
School of Life Sciences, Chongqing University, Huxi, G75 Lanhai, Chongqing, 400044 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
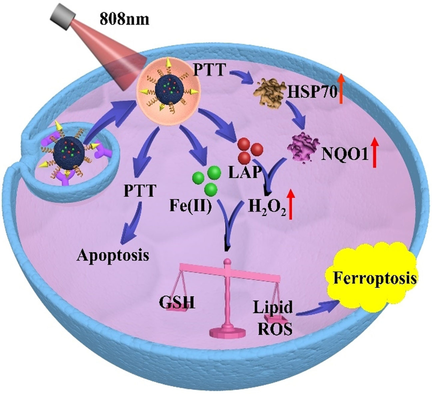
Ferroptosis is a new form of regulated cell death and holds promise for tumor inhibition. However, it is difficult to remotely control the initiation and execution of ferroptosis in specific sites. This study reports a biocompatible and biodegradable biopolymeric nanoplatform for tumor-targeted ferroptosis therapy, of which the pro-ferroptotic activities could be activated in an on-demand manner using near-infrared light as the triggering signal.
Abstract
Ferroptosis is a new form of regulated cell death that shows promise for tumor treatment. Most current ferroptosis tumor therapies are based on the intrinsic pathological features of the malignancies, and it would be of clinical significance to develop ferroptosis-inducing strategies with improved tumor specificity and modulability. Here we report a polydopamine-based nanoplatform (FeIIPDA@LAP-PEG-cRGD) for the efficient loading of Fe2+ and β-lapachone (LAP), which could readily initiate ferroptosis in tumor cells upon treatment with near-infrared light. PDA nanostructures could generate mild hyperthermia under NIR irritation and trigger the release of the ferroptosis-inducing Fe2+ ions. The NIR-actuated photothermal effect would also activate cellular heat shock response and upregulate the downstream NQO1 via HSP70/NQO1 axis to facilitate bioreduction of the concurrently released β-lapachone and enhance intracellular H2O2 formation to promote the Fe2+-mediated lipid peroxidation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202016872-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf4 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aS. Doll, F. P. Freitas, R. Shah, M. Aldrovandi, M. C. da Silva, I. Ingold, A. G. Grocin, T. N. X. da Silva, E. Panzilius, C. H. Scheel, A. Mourao, K. Buday, M. Sato, J. Wanninger, T. Vignane, V. Mohana, M. Rehberg, A. Flatley, A. Schepers, A. Kurz, D. White, M. Sauer, M. Sattler, E. W. Tate, W. Schmitz, A. Schulze, V. O'Donnell, B. Proneth, G. M. Popowicz, D. A. Pratt, J. P. F. Angeli, M. Conrad, Nature 2019, 575, 693–698;
- 1bS. Doll, B. Proneth, Y. Y. Tyurina, E. Panzilius, S. Kobayashi, I. IngoId, M. Irmler, J. Beckers, M. Aichler, A. Walch, H. Prokisch, D. Trumbach, G. W. Mao, F. Qu, H. Bayir, J. Fullekrug, C. H. Scheel, W. Wurst, J. A. Schick, V. E. Kagan, J. P. F. Angeli, M. Conrad, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 91–98.
- 2
- 2aW. M. Wang, M. Green, J. E. Choi, M. Gijon, P. D. Kennedy, J. K. Johnson, P. Liao, X. T. Lang, I. Kryczek, A. Sell, H. J. Xia, J. J. Zhou, G. P. Li, J. Li, W. Li, S. Wei, L. Vatan, H. J. Zhang, W. Szeliga, W. Gu, R. Liu, T. S. Lawrence, C. Lamb, Y. Tanno, M. Cieslik, E. Stone, G. Georgiou, T. A. Chan, A. Chinnaiyan, W. P. Zou, Nature 2019, 569, 270–274;
- 2bB. Hassannia, P. Vandenabeele, T. Vanden Berghe, Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 830–849;
- 2cJ. P. Friedmann Angeli, D. V. Krysko, M. Conrad, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 405–414.
- 3C. Liang, X. Zhang, M. Yang, X. Dong, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904197.
- 4Y. Zhang, H. Tan, J. D. Daniels, F. Zandkarimi, H. R. Liu, L. M. Brown, K. Uchida, O. A. O'Connor, B. R. Stockwell, Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 623–633.
- 5
- 5aP. Zhang, Y. Hou, J. Zeng, Y. Li, Z. Wang, R. Zhu, T. Ma, M. Gao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 11088–11096; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 11205–11213;
- 5bB. B. Ding, P. Zheng, P. A. Ma, J. Lin, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905823;
- 5cG. Q. Chen, F. A. Benthani, J. Wu, D. G. Liang, Z. X. Bian, X. J. Jiang, Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 242–254.
- 6
- 6aM. d'Ischia, A. Napolitano, V. Ball, C. T. Chen, M. J. Buehler, Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3541–3550;
- 6bM. A. Rahim, S. L. Kristufek, S. J. Pan, J. J. Richardson, F. Caruso, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1904–1927; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 1920–1945;
- 6cH. A. Lee, Y. F. Ma, F. Zhou, S. Hong, H. Lee, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 704–713;
- 6dK. Yamagishi, I. Kirino, I. Takahashi, H. Amano, S. Takeoka, Y. Morimoto, T. Fujie, Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 27–36.
- 7
- 7aW. Cheng, X. W. Zeng, H. Z. Chen, Z. M. Li, W. F. Zeng, L. Mei, Y. L. Zhao, ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8537–8565;
- 7bM. H. Li, X. T. Sun, N. Zhang, W. Wang, Y. Yang, H. Z. Jia, W. G. Liu, Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800155.
- 8
- 8aZ. Shen, J. Song, B. C. Yung, Z. Zhou, A. Wu, X. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704007;
- 8bM. Liu, B. Liu, Q. Liu, K. Du, Z. Wang, N. He, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 382, 160–180;
- 8cT. M. Seibt, B. Proneth, M. Conrad, Free Radical Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 144–152;
- 8dJ. Wu, A. M. Minikes, M. H. Gao, H. J. Bian, Y. Li, B. R. Stockwell, Z. N. Chen, X. J. Jiang, Nature 2019, 572, 402–406.
- 9
- 9aY. X. Wang, S. L. Li, P. B. Zhang, H. T. Bai, L. H. Feng, F. T. Lv, L. B. Liu, S. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705418;
- 9bY. J. Liu, G. M. Shu, X. Li, H. B. Chen, B. Zhang, H. Z. Pan, T. Li, X. Q. Gong, H. J. Wang, X. L. Wu, Y. Dou, J. Chang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802026;
- 9cT. D. Cong, Z. M. Wang, M. Hu, Q. Y. Han, B. G. Xing, ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5836–5844.
- 10
- 10aG. Z. Dong, H. Youn, M. T. Park, E. T. Oh, K. H. Park, C. W. Song, E. K. Choi, H. J. Park, Int. J. Hyperthermia 2009, 25, 477–487;
- 10bM. Pajares, A. I. Rojo, E. Arias, A. Diaz-Carretero, A. M. Cuervo, A. Cuadrado, Autophagy 2018, 14, 1310–1322.
- 11
- 11aW. Yin, W. D. Ke, W. J. Chen, L. C. Xi, Q. H. Zhou, J. F. Mukerabigwi, Z. S. Ge, Biomaterials 2019, 195, 63–74;
- 11bS. Son, M. Won, O. Green, N. Hananya, A. Sharma, Y. Jeon, J. H. Kwak, J. L. Sessler, D. Shabat, J. S. Kim, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1739–1743; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 1753–1757;
- 11cC. Z. Yao, Y. M. Li, Z. X. Wang, C. Z. Song, X. L. Hu, S. Y. Liu, ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1919–1935.
- 12T. G. Barclay, H. M. Hegab, S. R. Clarke, M. Ginic-Markovic, Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1601192.
- 13
- 13aD. T. Sun, L. Peng, W. S. Reeder, S. M. Moosavi, D. Tiana, D. K. Britt, E. Oveisi, W. L. Queen, ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 349–356;
- 13bW. F. Chen, Y. Wang, M. Qin, X. D. Zhang, Z. R. Zhang, X. Sun, Z. Gu, ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5995–6005.
- 14
- 14aM. Z. Ye, Y. X. Han, J. B. Tang, Y. Piao, X. R. Liu, Z. X. Zhou, J. Q. Gao, J. H. Rao, Y. Q. Shen, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702342;
- 14bL. L. Dai, X. Li, X. L. Duan, M. H. Li, P. Y. Niu, H. Y. Xu, K. Y. Cai, H. Yang, Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801807.
- 15
- 15aH. Shi, Y. D. Sun, R. Q. Yan, S. L. Liu, L. Zhu, S. Liu, Y. Z. Feng, P. Wang, J. He, Z. Y. Zhou, D. J. Ye, Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 937–947;
- 15bY. X. Lin, Y. Wang, H. W. An, B. W. Qi, J. Q. Wang, L. Wang, J. J. Shi, L. Mei, H. Wang, Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2968–2978;
- 15cQ. W. Zhu, X. Z. Ling, Y. L. Yang, J. T. Zhang, Q. Li, X. Niu, G. W. Hu, B. Chen, H. Y. Li, Y. Wang, Z. F. Deng, Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801899.
- 16B. Hassannia, B. Wiernicki, I. Ingold, F. Qu, S. Van Herck, Y. Y. Tyurina, H. Bayir, B. A. Abhari, J. P. F. Angeli, S. M. Choi, E. Meul, K. Heyninck, K. Declerck, C. S. Chirumamilla, M. Lahtela-Kakkonen, G. Van Camp, D. V. Krysko, P. G. Ekert, S. Fulda, B. G. De Geest, M. Conrad, V. E. Kagan, W. Vanden Berghe, P. Vandenabeele, T. Vanden Berghe, J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128, 3341–3355.
- 17
- 17aJ. Nam, S. Son, L. J. Ochyl, R. Kuai, A. Schwendeman, J. J. Moon, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1074;
- 17bL. S. Lin, Z. X. Cong, J. B. Cao, K. M. Ke, Q. L. Peng, J. H. Gao, H. H. Yang, G. Liu, X. Y. Chen, ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3876–3883.
- 18T. T. Mai, A. Hamaï, A. Hienzsch, T. Cañeque, S. Müller, J. Wicinski, O. Cabaud, C. Leroy, A. David, V. Acevedo, A. Ryo, C. Ginestier, D. Birnbaum, E. Charafe-Jauffret, P. Codogno, M. Mehrpour, R. Rodriguez, Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 1025–1033.
- 19
- 19aL. Lin, S. Wang, H. Deng, W. Yang, L. Rao, R. Tian, Y. Liu, G. Yu, Z. Zhou, J. Song, H.-H. Yang, Z.-Y. Chen, X. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15320–15330;
- 19bM. Hernández-Morales, T. Shang, J. Chen, V. Han, C. Liu, Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3250–3260, e3257;
- 19cR. L. Gonciarz, E. A. Collisson, A. R. Renslo, Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 7–18.
- 20M. J. Hangauer, V. S. Viswanathan, M. J. Ryan, D. Bole, J. K. Eaton, A. Matov, J. Galeas, H. D. Dhruv, M. E. Berens, S. L. Schreiber, F. McCormick, M. T. McManus, Nature 2017, 551, 247–250.
- 21P. L. Collins, C. Purman, S. I. Porter, V. Nganga, A. Saini, K. E. Hayer, G. L. Gurewitz, B. P. Sleckman, J. J. Bednarski, C. H. Bassing, E. M. Oltz, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3158.
- 22
- 22aJ. Zheng, M. Conrad, Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 920–937;
- 22bM. Gao, J. Yi, J. Zhu, A. M. Minikes, P. Monian, C. B. Thompson, X. Jiang, Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 354–363, e353.
- 23M. Pannuzzo, S. Esposito, L.-P. Wu, J. Key, S. Aryal, C. Celia, L. di Marzio, S. M. Moghimi, P. Decuzzi, Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4312–4321.
- 24
- 24aY. Liu, Z. Wang, Y. Liu, G. Zhu, O. Jacobson, X. Fu, R. Bai, X. Lin, N. Lu, X. Yang, W. Fan, J. Song, Z. Wang, G. Yu, F. Zhang, H. Kalish, G. Niu, Z. Nie, X. Chen, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10539–10548;
- 24bP. Korangath, J. D. Barnett, A. Sharma, E. T. Henderson, J. Stewart, S.-H. Yu, S. K. Kandala, C.-T. Yang, J. S. Caserto, M. Hedayati, T. D. Armstrong, E. Jaffee, C. Gruettner, X. C. Zhou, W. Fu, C. Hu, S. Sukumar, B. W. Simons, R. Ivkov, Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay1601;
- 24cM. P. Nikitin, I. V. Zelepukin, V. O. Shipunova, I. L. Sokolov, S. M. Deyev, P. I. Nikitin, Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 717–731.
- 25X. Huang, E. A. Motea, Z. R. Moore, J. Yao, Y. Dong, G. Chakrabarti, J. A. Kilgore, M. A. Silvers, P. L. Patidar, A. Cholka, F. Fattah, Y. Cha, G. G. Anderson, R. Kusko, M. Peyton, J. Yan, X. J. Xie, V. Sarode, N. S. Williams, J. D. Minna, M. Beg, D. E. Gerber, E. A. Bey, D. A. Boothman, Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 940–952.
- 26T. M. O'Shea, A. L. Wollenberg, J. H. Kim, Y. Ao, T. J. Deming, M. V. Sofroniew, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6203.
- 27
- 27aL. Zhang, Z. Wang, Y. Zhang, F. Cao, K. Dong, J. Ren, X. Qu, ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10201–10211;
- 27bH. Lin, Y. Wang, S. Gao, Y. Chen, J. Shi, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703284.