Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Li[LiCs2Cl][Ga3S6]: A Nanoporous Framework of GaS4 Tetrahedra with Excellent Nonlinear Optical Performance (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2020)
- Page: 4593
- First Published: 26 February 2020
![Cover Picture: Li[LiCs2Cl][Ga3S6]: A Nanoporous Framework of GaS4 Tetrahedra with Excellent Nonlinear Optical Performance (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2020) Volume 59 Issue 12, 2020](/cms/asset/aea76328-cfab-46b1-ac37-18c5e1806b83/anie202002283-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A new salt-inclusion chalcogenide that features an unprecedented 3D [Ga3S6] framework with nanosized tunnels is presented by X.-M. Jiang, G.-C. Guo, and co-workers in their Communication on page 4856. The covalent host and ionic guests synergistically contribute to a large nonlinear optical (NLO) coefficient and ultrawide bandgap, which indicates potential for application in infrared NLO materials.
Inside Cover: Photoacoustic Imaging Quantifies Drug Release from Nanocarriers via Redox Chemistry of Dye-Labeled Cargo (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2020)
- Page: 4594
- First Published: 27 January 2020

Photoacoustic imaging enables a new strategy to monitor drug delivery, as reported by J. V. Jokerst and co-workers in their Communication on page 4678. Here, the paclitaxel drug is tagged with redox-active methylene blue. This drug–dye conjugate was sealed inside a poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanocarrier in the reduced state where it does not absorb light. When the drug–dye conjugate is released, the dye is oxidized to report the location and quantity of the cargo.
Inside Back Cover: A Coordinative Dendrimer Achieves Excellent Efficiency in Cytosolic Protein and Peptide Delivery (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2020)
- Page: 4970
- First Published: 26 February 2020

A coordinative dendrimer delivers 30 types of cargo proteins and peptides into the cytosol of living cells, while maintaining their bioactivity after intracellular release. In their Research Article on page 4711, Y. Cheng et al. report that dendrimers modified with a dipicolylamine/zinc(II) complex are capable of binding proteins through a combination of ionic and coordination interactions. This provides a new strategy to develop robust and efficient polymers for cytosolic protein delivery.
Back Cover: Biomimetic Strain-Stiffening Self-Assembled Hydrogels (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2020)
- Page: 4971
- First Published: 26 February 2020

Biomimetic strain-stiffening supramolecular hydrogels were prepared through the self-assembly of molecular gelators, as shown by J. H. van Esch and co-workers in their Communication on page 4830. Orthogonal self-assembly of the molecular gelators and lipids led to hydrogel networks embedded with liposomes being formed that also showed strain-stiffening behavior, thus resembling both the structures and mechanical responsiveness of biological tissue.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Deconstructive Reorganization: De Novo Synthesis of Hydroxylated Benzofuran
- First Published: 09 March 2020

Cycloisomerization The de novo synthesis of hydroxylated benzofuran and the realization of a collective total synthesis of hydroxylated benzofuran-containing natural products are described by S. Zhu et al. in their Research Article on page 4670.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 12/2020
- Pages: 4597-4611
- First Published: 09 March 2020
Author Profile
News
American Chemical Society National Awards 2020
- Pages: 4616-4618
- First Published: 28 February 2020
Highlights
Carbon Nanomaterials
Bottom-Up Synthesis of Discrete Conical Nanocarbons
- Pages: 4620-4622
- First Published: 29 January 2020
Leaving graphitic flatland: The atomically precise synthesis of graphitic nanocones was achieved by bottom-up synthetic methods. This advancement provides access to a new class of discrete nanocarbons and, with that, unlocks opportunities in the field of three-dimensional graphitic architectures amenable to molecular design.
Minireviews
Graphene
Emerging Bottom-Up Strategies for the Synthesis of Graphene Nanoribbons and Related Structures
- Pages: 4624-4633
- First Published: 02 July 2019
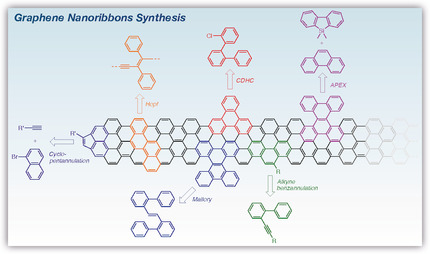
To prepare high-quality, defect-free graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), cycloaromatization reactions need to be very efficient, proceed without side reaction and mild enough to accommodate various functional groups. In this Minireview, the latest approaches for the synthesis of GNRs and related structures, including alkyne benzannulation, photochemical cyclodehydrohalogenation, Mallory and Pd- and Ni-catalyzed reactions are presented.
MOF-Based Electrocatalysis
Metal–Organic Frameworks Based Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction
- Pages: 4634-4650
- First Published: 17 September 2019
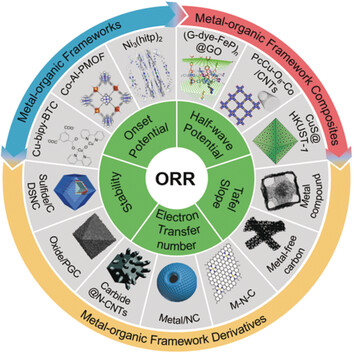
Despite the rapid developments in the past decade, many great challenges remain for the practical use of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) based electrocatalysts. This Minireview summaries some major recent research efforts and advances on MOF-based electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Some promising directions and strategies are also discussed.
Reviews
Switchable MOFs
Switching in Metal–Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 4652-4669
- First Published: 27 May 2019
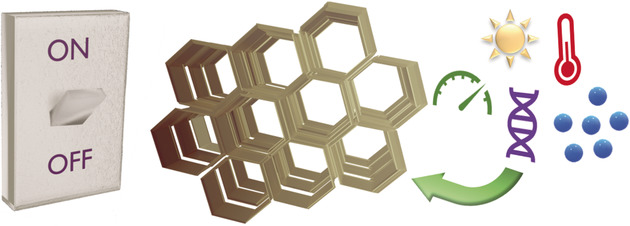
A switch in time: Although dynamic and flexible metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have been closely assessed in recent literature, analysis into the subcategory of switchable MOFs has been comparably lacking. By virtue of their steady rise in popularity, MOFs with intriguing, switchable responses to light, temperature, pressure, redox species and guests are surveyed.
Research Articles
Cycloisomerization
Deconstructive Reorganization: De Novo Synthesis of Hydroxylated Benzofuran
- Pages: 4670-4677
- First Published: 21 January 2020
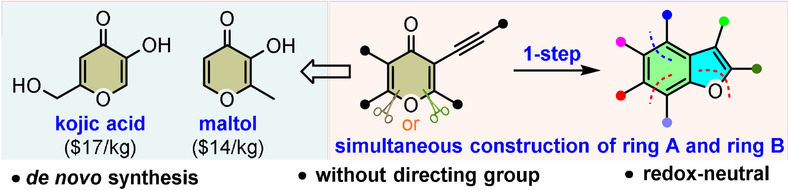
Deconstructive arene cycloisomerization is reported as unprecedented strategy for the de novo synthesis of hydroxylated benzofuran, using kojic acid- or maltol-derived alkynes as precursors. Several types of free hydroxyl groups are introduced into the benezofurans with different substitution patterns. A collective total synthesis of hydroxylated benzofuran-containing natural products (11 examples) is realized.
Drug Delivery
Photoacoustic Imaging Quantifies Drug Release from Nanocarriers via Redox Chemistry of Dye-Labeled Cargo
- Pages: 4678-4683
- First Published: 15 December 2019
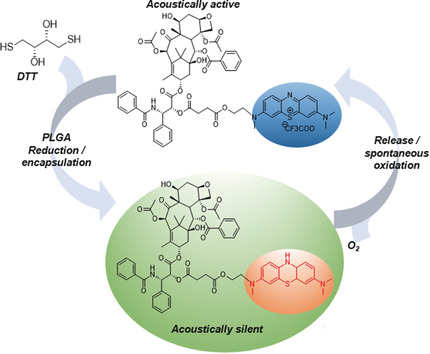
A covalently linked paclitaxel–methylene blue conjugate (PTX-MB) is used for real-time monitoring of drug release from nanocarriers via photoacoustic imaging. The PTX-MB remained in acoustically silent form when encapsulated in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles. After release, PTX-MB instantly oxidized to the photoacoustically active form to report quantity and biodistribution.
Perovskites
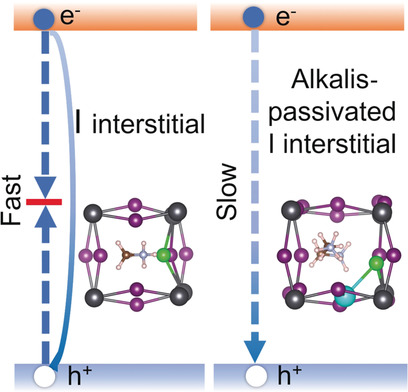
Extending Carrier Lifetimes in Lead Halide Perovskites with Alkali Metals by Passivating and Eliminating Halide Interstitial Defects
- Pages: 4684-4690
- First Published: 24 December 2019
Perovskites | Hot Paper
Guanine-Stabilized Formamidinium Lead Iodide Perovskites
- Pages: 4691-4697
- First Published: 17 December 2019
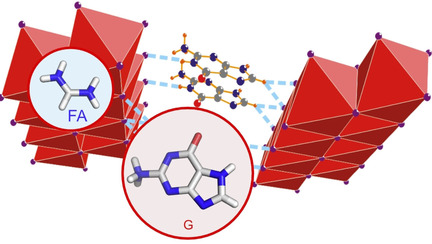
Guanine perovskites: Stabilization of the α-FAPbI3 phase (FA=formamidinium) is realized by using guaninium (G) based G2PbI4 low-dimensional perovskites, forming heterostructures that lead to improved performances and stabilities of the corresponding solar cells. The structural properties are investigated to unravel the mode of action and set the path for using this approach in perovskite solar cell research.
Doping Metals
Affecting an Ultra-High Work Function of Silver
- Pages: 4698-4704
- First Published: 10 January 2020
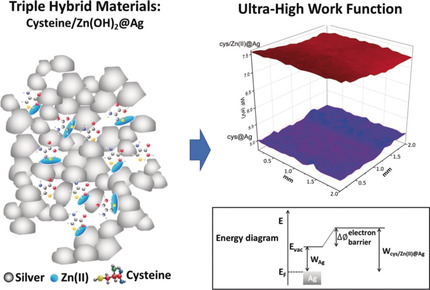
An ultra-high increase in the work function (WF) of silver, from 4.26 to 7.42 eV, by 3D dual-entrapment of the WF modifying components l-cysteine and Zn(OH)2 within the metal is reported. The WF enhancement mechanism is based on directly affecting the charge transfer ability of the metal, separately by cysteine and hydrolyzed zinc(II), and synergistically by the combination of the two, through the known Zn-cysteine finger redox trap effect.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Host–Guest Chemistry Within Cellulose Nanocrystal Gel Receptors
- Pages: 4705-4710
- First Published: 13 January 2020
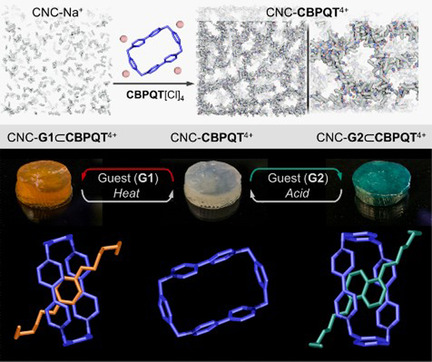
Mixing cellulose nanocrystal suspensions (CNC-Na+) with the polyionic macrocycle cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene) (CBPQT4+) yields gels with embedded active hosts. These materials reversibly absorb and recognize guests from solution to produce colorful host–guest complexes. This behavior has enabled CNC-CBPQT4+ gels to function as substrates for chromatography and encryption.
Protein Delivery | Hot Paper
A Coordinative Dendrimer Achieves Excellent Efficiency in Cytosolic Protein and Peptide Delivery
- Pages: 4711-4719
- First Published: 21 December 2019
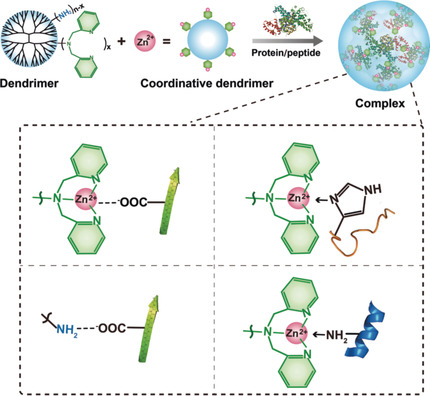
Stand and deliver: A coordinative dendrimer was rationally designed for cytosolic protein delivery. The synthesized polymer shows unprecedented efficiency in the cytosolic delivery of proteins and peptides with different isoelectric points. The bioactivities of the proteins are maintained after intracellular release.
Nanoparticles | Hot Paper
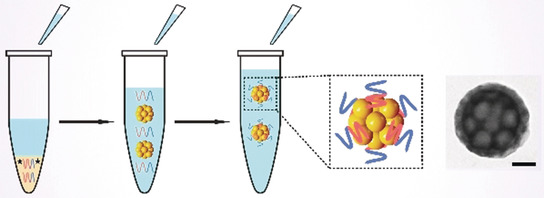
Stable Polymer Nanoparticles with Exceptionally High Drug Loading by Sequential Nanoprecipitation
- Pages: 4720-4728
- First Published: 16 January 2020
Bioconjugation | Very Important Paper
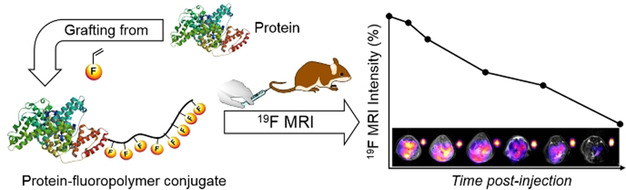
Low-Fouling Fluoropolymers for Bioconjugation and In Vivo Tracking
- Pages: 4729-4735
- First Published: 17 January 2020
Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Optimal Geometrical Configuration of Cobalt Cations in Spinel Oxides to Promote Oxygen Evolution Reaction
- Pages: 4736-4742
- First Published: 27 December 2019
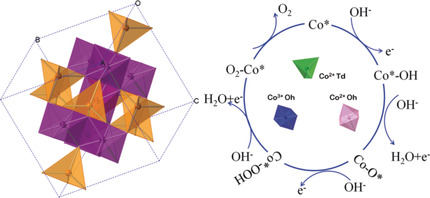
MgCo2O4, CoCr2O4, and Co2TiO4 were selected, where only Co3+ in the center of octahedron (Oh), Co2+ in the center of tetrahedron (Td), and Co2+ in the center of Oh can be active sites as model electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Co3+(Oh) sites are the best geometrical configuration; Co2+(Oh) sites exhibit better electrochemical activity than Co2+(Td).
Olefin Polymerization | Hot Paper
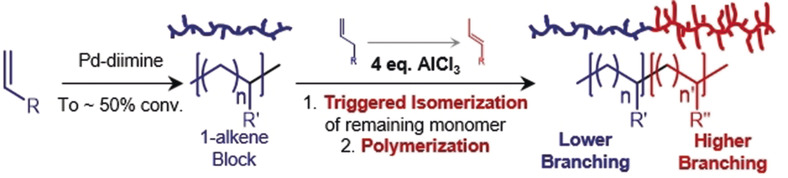
Branching Regulation in Olefin Polymerization via Lewis Acid Triggered Isomerization of Monomers
- Pages: 4743-4749
- First Published: 27 December 2019
Polymers
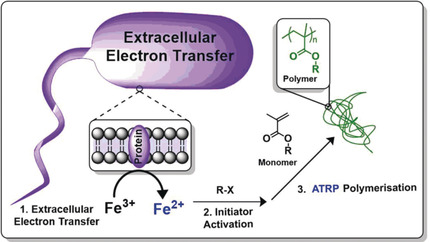
Iron-Catalysed Radical Polymerisation by Living Bacteria
- Pages: 4750-4755
- First Published: 02 January 2020
Phosphorescence
Stimuli-Responsive Circularly Polarized Organic Ultralong Room Temperature Phosphorescence
- Pages: 4756-4762
- First Published: 04 January 2020
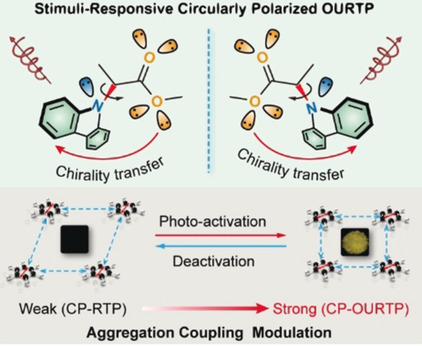
Circularly polarized organic ultralong room temperature phosphorescence (CP-OURTP) of small molecules is realized by direct bonding of achiral carbazole to a chiral ester chain for efficient chirality transfer and molecular packing arrangement upon photo-activation. The photo-activated CP-OURTP can be facilely deactivated by thermal treatment for stimuli-responsive reversible CP-OURTP with high photo/thermal stabilities.
Nanotechnology
Metal–Organic Frameworks as Metal Ion Precursors for the Synthesis of Nanocomposites for Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Pages: 4763-4769
- First Published: 27 December 2019
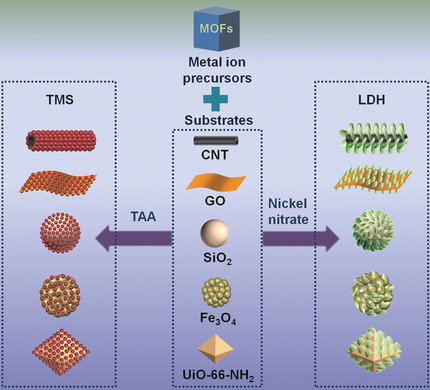
Benefits of instability: MOFs are used as metal ion precursors for the synthesis of nanocomposites by exploiting the instability of MOFs. The reaction occurs simply by mixing the MOFs, substrates, and other reactants (such as TAA and nickel nitrate). Through a heterogeneous growth process, nanomaterials with uniform structures can be formed on different substrates.
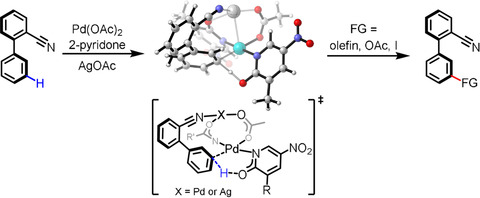
C−H Activation | Hot Paper
Rational Development of Remote C−H Functionalization of Biphenyl: Experimental and Computational Studies
- Pages: 4770-4777
- First Published: 14 January 2020
Elastomers
Liquid-Crystalline Soft Actuators with Switchable Thermal Reprogrammability
- Pages: 4778-4784
- First Published: 05 January 2020
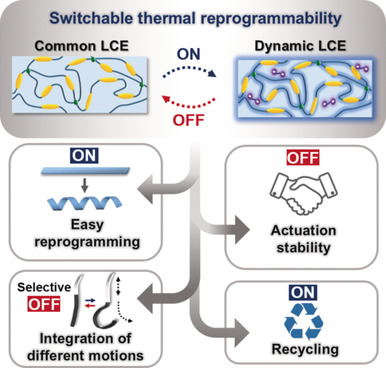
The old switcheroo: Soft actuators with switchable thermal reprogrammability have been developed. By flexibly switching on/off network dynamics, easy reprogramming and excellent actuation stability can be achieved, as well as efficient recycling and seamless integration of different motions in a very common siloxane liquid crystalline elastomer.
Fluorescence | Hot Paper
A General Strategy to Enhance Donor-Acceptor Molecules Using Solvent-Excluding Substituents
- Pages: 4785-4792
- First Published: 10 January 2020
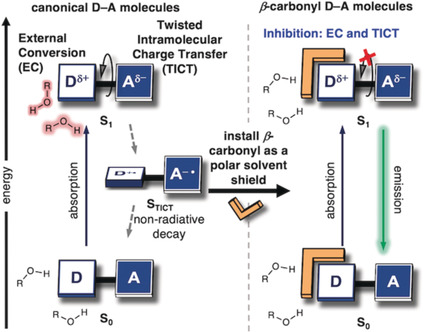
On the bright side: The photophysical behavior of donor-acceptor (D-A) molecules can be improved through installation of a polar, solvent-shielding auxiliary to an amino-donating group. This β-carbonyl substituent generally enhances the fluorescence quantum yield of D-A fluorophores, enabling brighter labeling probes for live-cell imaging.
Zinc–Air Batteries | Very Important Paper
A Flexible Rechargeable Zinc–Air Battery with Excellent Low-Temperature Adaptability
- Pages: 4793-4799
- First Published: 09 January 2020
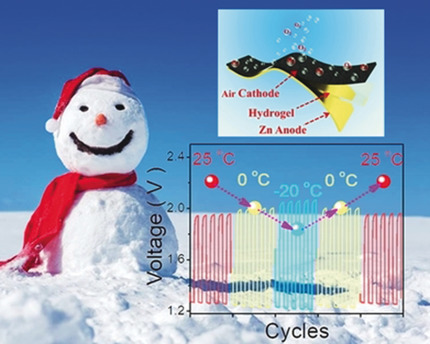
Powering the frozen world: The first flexible zinc–air battery with excellent low-temperature adaptability was achieved through the development of an innovative air-cathodic electrocatalyst and hydrogel electrolyte. The battery delivers a capacity of 691 mAh g−1 and an energy density of 798 Wh kg−1 at −20 °C, along with excellent flexibility and state-of-the-art low-temperature performance.
Immunotherapy
Homogeneous, Low-volume, Efficient, and Sensitive Quantitation of Circulating Exosomal PD-L1 for Cancer Diagnosis and Immunotherapy Response Prediction
- Pages: 4800-4805
- First Published: 08 January 2020
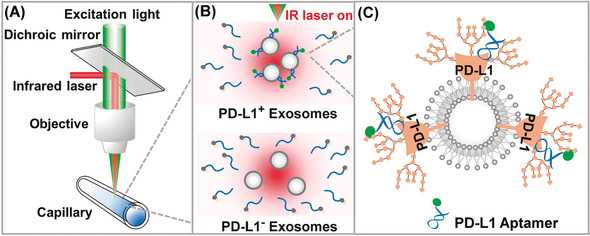
An aptamer-induced thermophoresis quantitation of exosomal programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1, a transmembrane protein) was developed, which integrates effective recognition of aptamer and homogeneous thermophoresis. The facile technique is more sensitive and efficient than the current enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)-based methods. Translation of the method into standard clinical practice for immunotherapy prediction and monitoring is anticipated.
Ion Channels
Polyhydrazide-Based Organic Nanotubes as Efficient and Selective Artificial Iodide Channels
- Pages: 4806-4813
- First Published: 16 January 2020
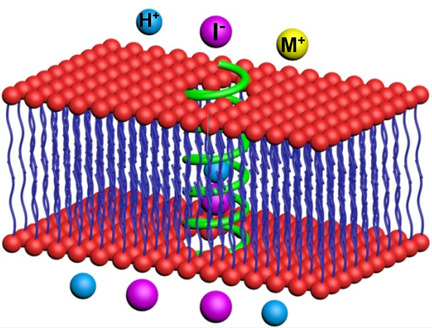
The right channels: A novel class of foldamer-based pore-forming helically folded polyhydrazides, having hydrophobic cavities of about a 6.5 Å diameter, promote transport of anions, rather than cations, across membranes, with iodide as the preferred transport species. The best channel, having a helical height of 3.6 nm, exhibits the highest recorded iodide transport activity (EC50=0.042 μm or 0.028 mol % relative to lipid) and high I−/Cl− selectivity of 11, in terms of EC50 values, or 42 based on initial rate constants.
Electrochemistry | Very Important Paper
In Situ Reconstruction of a Hierarchical Sn-Cu/SnOx Core/Shell Catalyst for High-Performance CO2 Electroreduction
- Pages: 4814-4821
- First Published: 16 January 2020
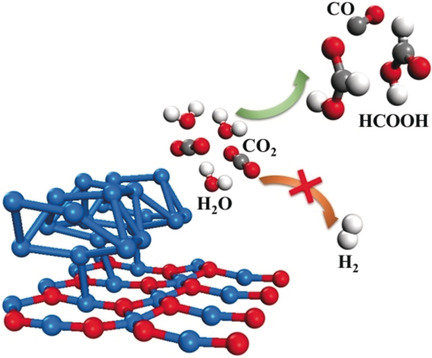
A Sn/SnOx interface reconstructed in situ facilitates formic acid production by optimizing the binding of the reaction intermediate HCOO* while promotes Faradaic efficiency of C1 products by suppressing the competitive hydrogen evolution reaction. This results in high Faradaic efficiency, current density, and stability of electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction at low overpotentials.
Quantum Materials | Very Important Paper
Intrinsically Low Thermal Conductivity and High Carrier Mobility in Dual Topological Quantum Material, n-Type BiTe
- Pages: 4822-4829
- First Published: 22 January 2020
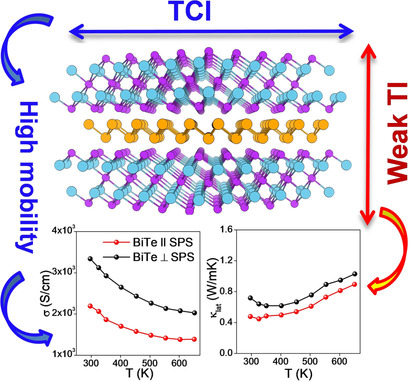
Highs and lows: Intrinsically low lattice thermal conductivity (κlat) and high carrier mobility (μ) occurs in BiTe, which is facilitated by its unique dual topological quantum phases. It is a weak topological insulator (WTI) as a result of its layered hetero-structure, and thus it exhibits low thermal conductivity; but simultaneously BiTe is also a topological crystalline insulator (TCI) and thus it has high carrier mobility.
Communications
Supramolecular Chemistry
Biomimetic Strain-Stiffening Self-Assembled Hydrogels
- Pages: 4830-4834
- First Published: 07 January 2020
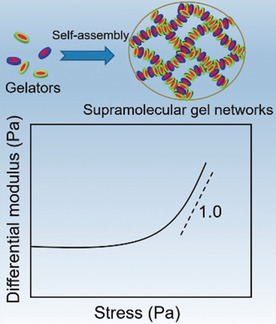
Biomimetic strain-stiffening hydrogels have been prepared through the self-assembly of molecular gelators. On the basis of orthogonal self-assembly of the molecular gelators and lipids, hydrogel networks embedded with liposomes are formed and show strain-stiffening behavior as well, resembling both the structures and mechanical responsiveness of biological tissue.
Biaryls
Synthesis of Biaryl-Bridged Cyclic Peptides via Catalytic Oxidative Cross-Coupling Reactions
- Pages: 4835-4839
- First Published: 04 December 2019
Supramolecular Polymers
Precise Size-Selective Sieving of Nanoparticles Using a Highly Oriented Two-Dimensional Supramolecular Polymer
- Pages: 4840-4845
- First Published: 21 December 2019
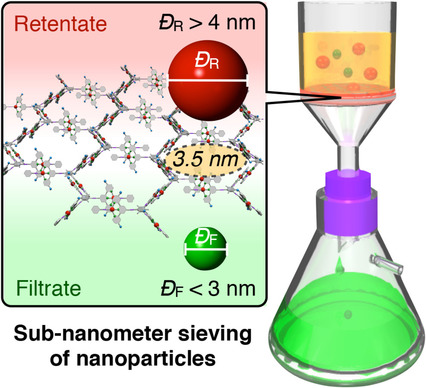
Sub-nm sieving: A flexible supramolecular membrane for the sub-nanometer sieving of nanoparticles is developed. This membrane comprises a highly oriented, honeycomb-like, two-dimensional supramolecular polymer with uniform nanocavities. Owing to this unique structural feature, a precise cutoff size of about 4 nm has been realized.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Enantioselective Radical-Polar Crossover Reactions of Indanonecarboxamides with Alkenes
- Pages: 4846-4850
- First Published: 12 January 2020
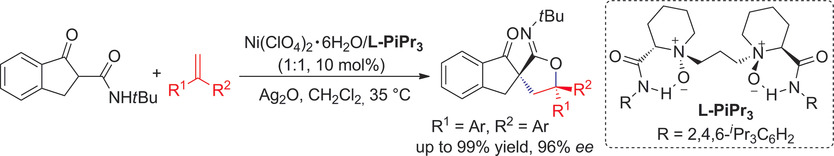
Crossing over: A highly efficient asymmetric radical-polar crossover reaction of indanonecarboxamides/esters and various electron-rich alkenes was realized by combining a chiral N,N′-dioxide/NiII complex catalyst with Ag2O. Five types of products could be obtained with good to excellent yields and ee values.
Catalysis
Pd-Catalyzed Selective Bifunctionalization of 3-Iodo-o-Carborane by Pd Migration
- Pages: 4851-4855
- First Published: 24 December 2019
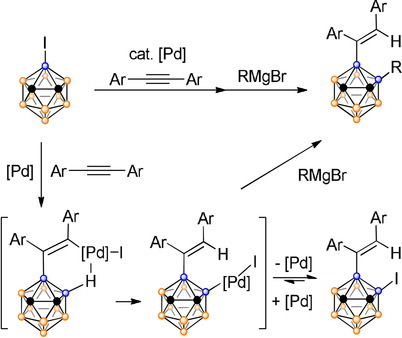
A highly regioselective sequential activation of cage B−I and B−H bonds in o-carborane has been achieved in a one-pot manner. The thermodynamically favorable migration of Pd from exo-alkenyl sp2 carbon to cage B(4) serves as a key step in this new process, which represents a new route for regioselective bifunctionalization of o-carborane with different substituents.
Nonlinear Optical Materials
Li[LiCs2Cl][Ga3S6]: A Nanoporous Framework of GaS4 Tetrahedra with Excellent Nonlinear Optical Performance
- Pages: 4856-4859
- First Published: 25 October 2019
![Li[LiCs2Cl][Ga3S6]: A Nanoporous Framework of GaS4 Tetrahedra with Excellent Nonlinear Optical Performance](/cms/asset/f4592d26-fb46-48ea-b12f-8f8a81c5c9e0/anie201912416-toc-0001-m.jpg)
The salt-inclusion chalcogenide Li[LiCs2Cl][Ga3S6] is presented, which features a 3D framework composed of [Ga3S6] nanosized tunnels. Introduction of an ionic guest to the covalent chalcogenide host produces a material with a moderate nonlinear optical (NLO) coefficient and an ultrawide band gap (Eg). These characteristics are promising for the development of infrared (IR) NLO materials.
Peptide Synthesis
Ribosomal Incorporation of Aromatic Oligoamides as Peptide Sidechain Appendages
- Pages: 4860-4864
- First Published: 02 January 2020
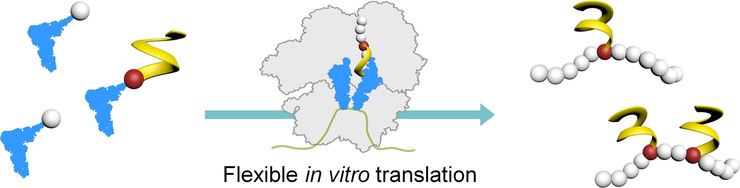
The ribosome tolerates aromatic oligoamide foldamer–peptide hybrids not only when the foldamer belongs to the initiation unit, but also when it is appended as a sidechain within the peptide or at the C-terminus of the peptide. This expands the range of substrates known to be accepted by the ribosome to include significantly larger and more structurally defined substrates.
Capacitors
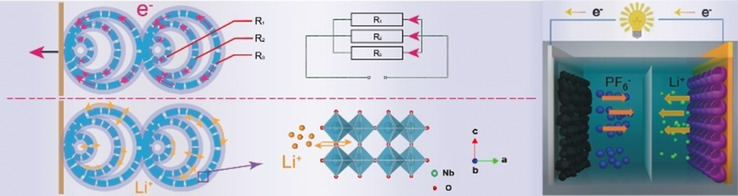
A Hollow Multi-Shelled Structure for Charge Transport and Active Sites in Lithium-Ion Capacitors
- Pages: 4865-4868
- First Published: 16 January 2020
Biocatalysis
Production of Hydroxy Acids: Selective Double Oxidation of Diols by Flavoprotein Alcohol Oxidase
- Pages: 4869-4872
- First Published: 08 January 2020
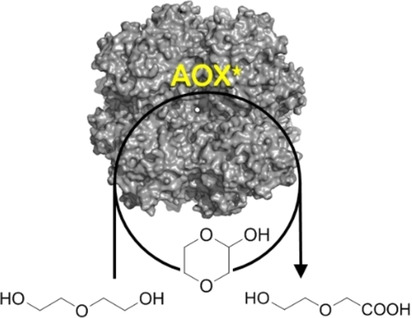
Triple action: The flavoprotein alcohol oxidase (AOX*) facilitates the double and triple oxidations of diols. Interestingly, depending on the diol substrate, these reactions result in formation of either lactones or hydroxy acids. Such biocatalytic route towards hydroxy acids has potential for the preparation of polyester building blocks.
Reaction Mechanisms
Formation and Fate of Formaldehyde in Methanol-to-Hydrocarbon Reaction: In Situ Synchrotron Radiation Photoionization Mass Spectrometry Study
- Pages: 4873-4878
- First Published: 14 January 2020
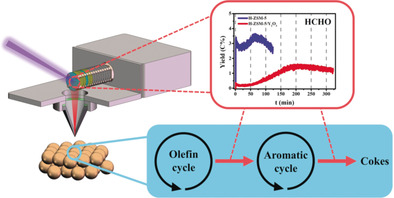
Formaldehyde (HCHO) was unambiguously detected and quantified for the first time during methanol-to-hydrocarbon catalysis over HSAPO-34 and HZSM-5 by in situ synchrotron radiation photoionization mass spectrometry. The time-resolved profiles of products show that HCHO is mainly derived from the disproportionation of methanol at acidic sites, HCHO affects the hydrogen-transfer processes of olefins into aromatics and aromatics into coke, and HCHO controls the contribution of the aromatic-based cycle.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Enantio- and Diastereoselective Synthesis of Homopropargyl Amines by Copper-Catalyzed Coupling of Imines, 1,3-Enynes, and Diborons
- Pages: 4879-4882
- First Published: 09 January 2020
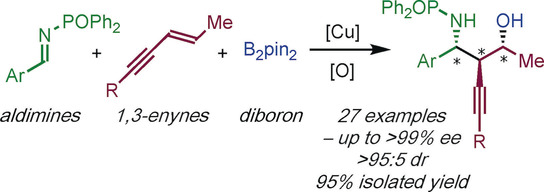
The enantio- and diastereoselective, copper-catalyzed three-component coupling of imines, 1,3-enynes, and diborons delivers complex, chiral homopropargyl amines; useful building blocks on the way to biologically- and medicinally-relevant compounds. In particular, functionalized homopropargyl amines bearing up to three contiguous stereocenters can be prepared in a single step.
Mechanochemistry
Mechanical Force Induces Ylide-Free Cycloaddition of Nonscissible Aziridines
- Pages: 4883-4887
- First Published: 16 January 2020
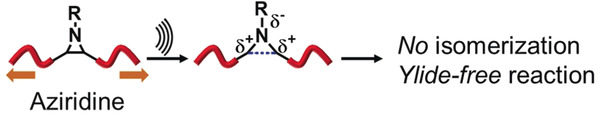
The force awakens: Mechanical-force-induced cycloaddition of intact aziridine groups in a macromolecule with dipolarophiles does not follow the reaction pathways that occur under traditional thermal and photochemical conditions. The aziridines do not undergo cis–trans isomerization, thus suggesting retention of the ring structure under force. This demonstrates that nonvulnerable chemical structures can be attractive mechanophores.
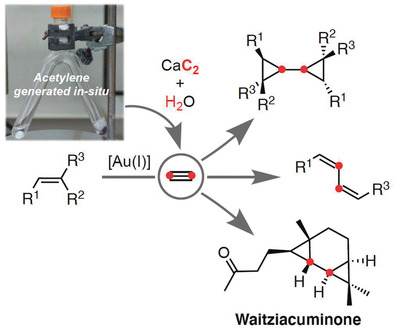
Gold Catalysis
Acetylene as a Dicarbene Equivalent for Gold(I) Catalysis: Total Synthesis of Waitziacuminone in One Step
- Pages: 4888-4891
- First Published: 08 January 2020
Carbon Nanotubes | Very Important Paper
Nanoparticle-Assisted Alignment of Carbon Nanotubes on DNA Origami
- Pages: 4892-4896
- First Published: 13 January 2020
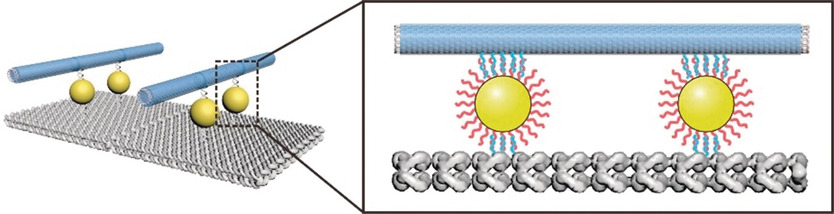
Spherical nucleic acids (SNAs) are used to precisely position carbon nanotubes (CNTs) on DNA origami. The DNA hybridization occurring at the interface of the SNA and DNA-coated CNTs leads to an approximately five-fold improvement in the positioning efficiency in comparison to the positioning of DNA-coated CNTs directly on the DNA origami.
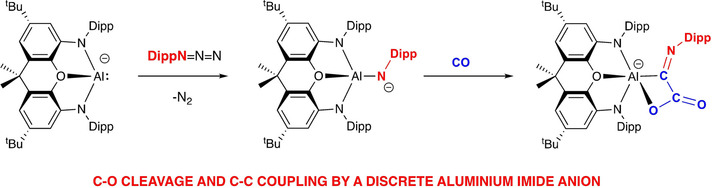
Bond Activation | Very Important Paper
Carbon Monoxide Activation by a Molecular Aluminium Imide: C−O Bond Cleavage and C−C Bond Formation
- Pages: 4897-4901
- First Published: 30 January 2020
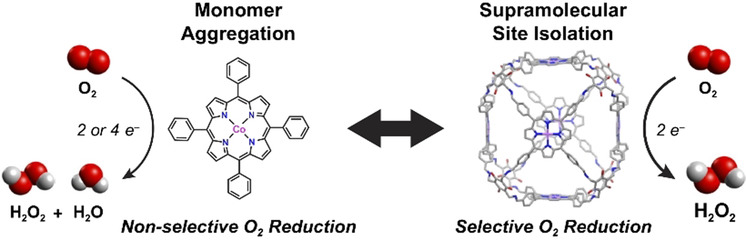
Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Supramolecular Tuning Enables Selective Oxygen Reduction Catalyzed by Cobalt Porphyrins for Direct Electrosynthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide
- Pages: 4902-4907
- First Published: 07 January 2020
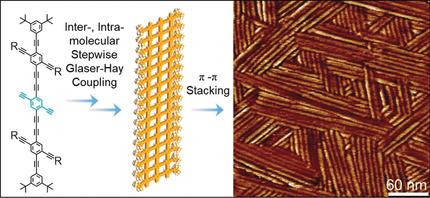
Interfacial Assembly | Very Important Paper
Controllable Synthesis of Graphdiyne Nanoribbons
- Pages: 4908-4913
- First Published: 20 January 2020
CO2 reduction reaction | Very Important Paper
Molecular Evidence for Metallic Cobalt Boosting CO2 Electroreduction on Pyridinic Nitrogen
- Pages: 4914-4919
- First Published: 14 January 2020
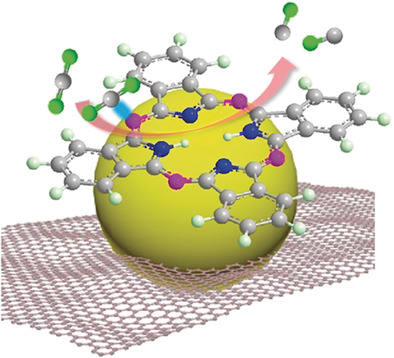
Nitrogen-doped carbon catalysts are presented for application in the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR). Molecular probes were designed to clarify the genuine catalytically active sites. CO2RR takes place preferentially on pyridinic rather than pyrrolic nitrogen, and metallic cobalt nanoparticles enhance the CO2RR on pyridinic nitrogen significantly.
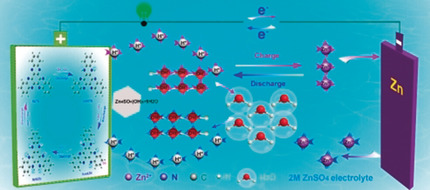
Batteries | Very Important Paper
Proton Insertion Chemistry of a Zinc–Organic Battery
- Pages: 4920-4924
- First Published: 14 January 2020
Polymer Actuators | Very Important Paper
“Self-Lockable” Liquid Crystalline Diels–Alder Dynamic Network Actuators with Room Temperature Programmability and Solution Reprocessability
- Pages: 4925-4931
- First Published: 20 January 2020
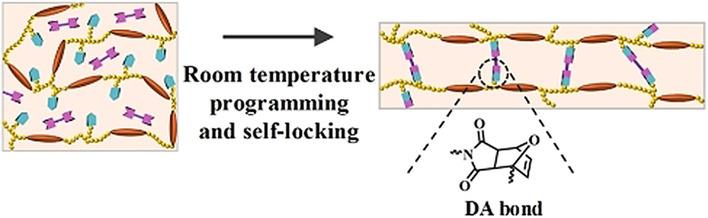
Liquid crystalline dynamic networks can be shaped into 3D objects at room temperature while being stabilized by slowly formed Diels–Alder-bonded (DA) cross-links. The actuators demonstrate thermally or optically induced reversible shape change for the purpose of performing mechanical work or locomotion.
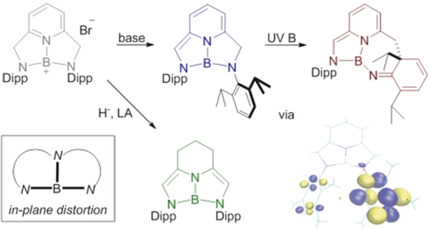
BN Heterocycles
Synthesis and Reactivity of Cationic Boron Complexes Distorted by Pyridine-based Pincer Ligands: Isolation of a Photochemical Hofmann–Martius-type Intermediate
- Pages: 4932-4936
- First Published: 22 January 2020
Asymmetric Catalysis
Rhodium-Catalyzed Enantioselective [4+2] Cycloadditions of Vinylcarbenes with Dienes
- Pages: 4937-4941
- First Published: 07 January 2020
![Rhodium-Catalyzed Enantioselective [4+2] Cycloadditions of Vinylcarbenes with Dienes](/cms/asset/f4dcc18d-a694-46e0-b7b6-c6bb9d79054a/anie201914354-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Selective [4+2] cycloaddition: A mechanistically unusual approach for a highly enantioselective [4+2] cycloaddition between rhodium-stabilized vinylcarbenes and siloxydienes was developed. The reaction is initiated by attack of the diene at the vinylogous position of the vinylcarbene and the outcome is dependent of the reacting conformation of the vinylcarbene intermediate.
Biomimetic Chemistry
Biomimetic Hydrogenation Catalyzed by a Manganese Model of [Fe]-Hydrogenase
- Pages: 4942-4946
- First Published: 10 December 2019
![Biomimetic Hydrogenation Catalyzed by a Manganese Model of [Fe]-Hydrogenase](/cms/asset/90559bf7-4025-45b7-aab8-c7cb19e13307/anie201914377-toc-0001-m.jpg)
The design and development of a manganese(I) mimic of [Fe]-hydrogenase is reported. This complex exhibits the highest activity and broadest scope in catalytic hydrogenation among known mimics. Thanks to its biomimetic nature, the complex exhibits unique activity in the hydrogenation of compounds analogous to methenyl-H4MPT+, the natural substrate of [Fe]-hydrogenase.
Polymers
Access to Hydroxy-Functionalized Polypropylene through Coordination Polymerization
- Pages: 4947-4952
- First Published: 29 December 2019
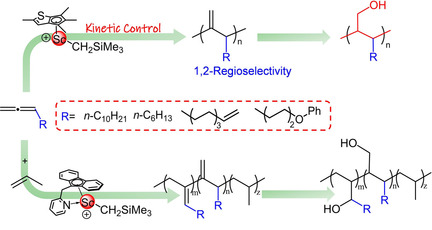
1,2-Selective coordination polymerization of allenes was achieved using rare-earth-metal precursors. The resultant polyallenes can be easily transformed into the poly(allyl alcohol) derivatives through hydroboration/oxidation. The copolymerization of propylene and allene monomers also proceeds to afford unprecedented hydroxy-functionalized polypropylene after post-functionalization. DFT simulations suggests kinetic rather than thermodynamic control.
Luminescence
Emerging Cubic Chirality in γCD-MOF for Fabricating Circularly Polarized Luminescent Crystalline Materials and the Size Effect
- Pages: 4953-4958
- First Published: 20 January 2020
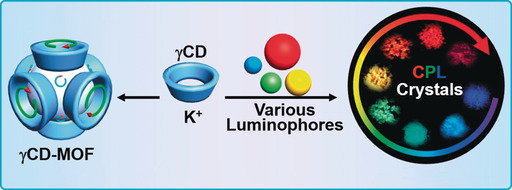
The host–guest interaction between the chiral void of γCD-MOF and achiral luminophores with different charges and sizes are presented. Numerous achiral luminophores could be integrated into γCD-MOF and emitted significantly boosted positive or negative circularly polarized luminescence (CPL). When the size of the guest luminophores was close to the cube size, strong negative CPL was observed.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Enantioselective Construction of Axially Chiral Amino Sulfide Vinyl Arenes by Chiral Sulfide-Catalyzed Electrophilic Carbothiolation of Alkynes
- Pages: 4959-4964
- First Published: 22 January 2020
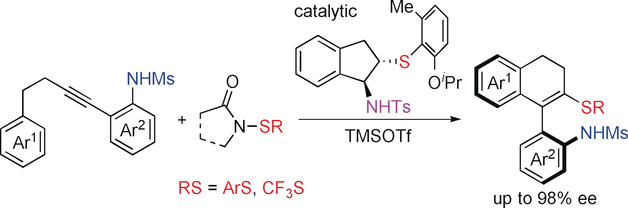
Enantioselective construction of axially chiral compounds by the electrophilic carbothiolation of alkynes is disclosed. This transformation is enabled by the use of a tosyl-protected bifunctional sulfide catalyst and mesyl-protected ortho-alkynylaryl amines. The obtained products can easily be converted into biaryl amino sulfides, biaryl amino sulfoxides, biaryl amines, vinyl–aryl amines, and other valuable difunctionalized compounds.
C−H Activation
Direct Regio- and Diastereoselective Synthesis of δ-Lactams from Acrylamides and Unactivated Alkenes Initiated by RhIII-Catalyzed C−H Activation
- Pages: 4965-4969
- First Published: 11 February 2020
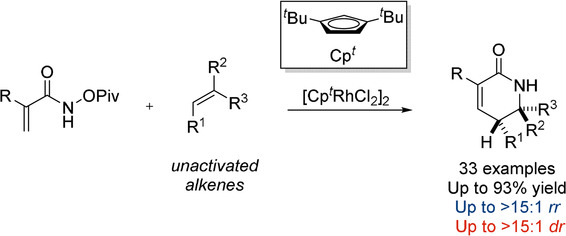
Regio- and diastereoselective synthesis of unprotected δ-lactams has been realized starting from readily accessible acrylamides and unactivated alkenes. The reaction provides an efficient means of synthesizing a diverse set of δ-lactams in good yield and stereoselectivity, which serve as useful building blocks for substituted piperidines.