Low-Fouling Fluoropolymers for Bioconjugation and In Vivo Tracking
Dr. Changkui Fu
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Baris Demir
School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorSheilajen Alcantara
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, 3010 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Vinod Kumar
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Felicity Han
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorHannah G. Kelly
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, 3010 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorXiao Tan
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorYe Yu
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorWeizhi Xu
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jiacheng Zhao
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cheng Zhang
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hui Peng
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Cyrille Boyer
Centre for Advanced Macromolecular Design (CAMD) and Australian Centre for NanoMedicine (ACN), School of Chemical Engineering, UNSW Australia, Sydney, NSW, 2052 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Trent M. Woodruff
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Stephen J. Kent
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, 3010 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Debra J. Searles
School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Andrew K. Whittaker
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Changkui Fu
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Baris Demir
School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorSheilajen Alcantara
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, 3010 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Vinod Kumar
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Felicity Han
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorHannah G. Kelly
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, 3010 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorXiao Tan
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorYe Yu
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorWeizhi Xu
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jiacheng Zhao
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cheng Zhang
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hui Peng
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Cyrille Boyer
Centre for Advanced Macromolecular Design (CAMD) and Australian Centre for NanoMedicine (ACN), School of Chemical Engineering, UNSW Australia, Sydney, NSW, 2052 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Trent M. Woodruff
School of Biomedical Sciences, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Stephen J. Kent
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, 3010 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Debra J. Searles
School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Andrew K. Whittaker
ARC Centre of Excellence in Convergent Bio-Nano Science and Technology and Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, St Lucia, Queensland, 4072 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
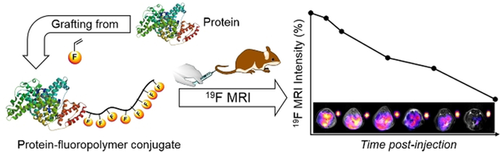
The conjugation of hydrophilic low-fouling polymers to therapeutic molecules and particles is an effective approach to improving their aqueous stability, solubility, and pharmacokinetics. Recent concerns over the immunogenicity of poly(ethylene glycol) has highlighted the importance of identifying alternative low fouling polymers. Now, a new class of synthetic water-soluble homo-fluoropolymers are reported with a sulfoxide side-chain structure. The incorporation of fluorine enables direct imaging of the homopolymer by 19F MRI, negating the need for additional synthetic steps to attach an imaging moiety. These self-reporting fluoropolymers show outstanding imaging sensitivity and remarkable hydrophilicity, and as such are a new class of low-fouling polymer for bioconjugation and in vivo tracking.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201914119-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.4 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aJ. S. Suk, Q. Xu, N. Kim, J. Hanes, L. M. Ensign, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51;
- 1bS. C. Larnaudie, J. Sanchis, T.-H. Nguyen, R. Peltier, S. Catrouillet, J. C. Brendel, C. J. Porter, K. A. Jolliffe, S. Perrier, Biomaterials 2018, 178, 570–582;
- 1cY. Hou, J. Yuan, Y. Zhou, J. Yu, H. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10995–11000;
- 1dX. Liu, M. Sun, J. Sun, J. Hu, Z. Wang, J. Guo, W. Gao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10435–10438;
- 1eR. J. Mancini, J. Lee, H. D. Maynard, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8474–8479;
- 1fN. Adams, U. S. Schubert, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2007, 59, 1504–1520;
- 1gA. J. Keefe, S. Jiang, Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 59;
- 1hF. Wurm, C. Dingels, H. Frey, H.-A. Klok, Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1161–1171;
- 1iL. Tao, G. Mantovani, F. Lecolley, D. M. Haddleton, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13220–13221.
- 2J. Nicolas, V. San Miguel, G. Mantovani, D. M. Haddleton, Chem. Commun. 2006, 4697–4699.
- 3L. S. Karfeld-Sulzer, E. A. Waters, N. E. Davis, T. J. Meade, A. E. Barron, Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1429–1436.
- 4Q. Li, J. B. White, N. C. Peterson, K. W. Rickert, C. O. Lloyd, K. L. Allen, K. Rosenthal, X. Gao, H. Wu, W. F. Dall'Acqua, J. Controlled Release 2018, 279, 126–135.
- 5
- 5aT.-L. Cheng, K.-H. Chuang, B.-M. Chen, S. R. Roffler, Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 881–899;
- 5bP. Debie, J. Van Quathem, I. Hansen, G. Bala, S. Massa, N. Devoogdt, C. Xavier, S. Hernot, Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1145–1153;
- 5cC. Cilliers, I. Nessler, N. Christodolu, G. M. Thurber, Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1623–1633.
- 6
- 6aM. A. Sowers, J. R. McCombs, Y. Wang, J. T. Paletta, S. W. Morton, E. C. Dreaden, M. D. Boska, M. F. Ottaviani, P. T. Hammond, A. Rajca, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5460;
- 6bH. Yamada, Y. Hasegawa, H. Imai, Y. Takayama, F. Sugihara, T. Matsuda, H. Tochio, M. Shirakawa, S. Sando, Y. Kimura, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 799–806.
- 7I. Tirotta, V. Dichiarante, C. Pigliacelli, G. Cavallo, G. Terraneo, F. B. Bombelli, P. Metrangolo, G. Resnati, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1106–1129.
- 8
- 8aZ. X. Jiang, X. Liu, E. K. Jeong, Y. B. Yu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4755–4758; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4849–4852;
- 8bI. Tirotta, A. Mastropietro, C. Cordiglieri, L. Gazzera, F. Baggi, G. Baselli, M. G. Bruzzone, I. Zucca, G. Cavallo, G. Terraneo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8524–8527;
- 8cO. Munkhbat, M. Canakci, S. Zheng, W. Hu, B. Osborne, A. A. Bogdanov, S. Thayumanavan, Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 790–800;
- 8dA. A. Kislukhin, H. Xu, S. R. Adams, K. H. Narsinh, R. Y. Tsien, E. T. Ahrens, Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 662;
- 8eA. T. Preslar, F. Tantakitti, K. Park, S. Zhang, S. I. Stupp, T. J. Meade, ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7376–7384.
- 9
- 9aK. J. Thurecht, I. Blakey, H. Peng, O. Squires, S. Hsu, C. Alexander, A. K. Whittaker, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5336–5337;
- 9bC. Zhang, S. S. Moonshi, W. Wang, H. T. Ta, Y. Han, F. Y. Han, H. Peng, P. Král, B. E. Rolfe, J. J. Gooding, ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9162–9176.
- 10
- 10aH. Peng, I. Blakey, B. Dargaville, F. Rasoul, S. Rose, A. K. Whittaker, Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 374–381;
- 10bC. Fu, C. Zhang, H. Peng, F. Han, C. Baker, Y. Wu, H. Ta, A. K. Whittaker, Macromolecules 2018, 51, 5875–5882;
- 10cY. Koda, T. Terashima, M. Sawamoto, H. D. Maynard, Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 240–247.
- 11R. Bhat, H. Patel, P.-C. Tsai, X.-L. Sun, D. Daoud, R. Lalancette, B. Michniak-Kohn, A. Pietrangelo, Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 5993–6000.
- 12
- 12aJ. J. Glass, L. Chen, S. Alcantara, E. J. Crampin, K. J. Thurecht, R. De Rose, S. J. Kent, ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 586–592;
- 12bJ. J. Glass, Y. Li, R. De Rose, A. P. Johnston, E. I. Czuba, S. Y. Khor, J. F. Quinn, M. R. Whittaker, T. P. Davis, S. J. Kent, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12182–12194.
- 13
- 13aJ. Huang, L. Bu, J. Xie, K. Chen, Z. Cheng, X. Li, X. Chen, ACS Nano 2010, 4, 7151–7160;
- 13bC. He, Y. Hu, L. Yin, C. Tang, C. Yin, Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3657–3666.
- 14J. Xu, K. Jung, N. A. Corrigan, C. Boyer, Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 3568–3575.
- 15B. S. Tucker, M. L. Coughlin, C. A. Figg, B. S. Sumerlin, ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 452–457.