Host–Guest Chemistry Within Cellulose Nanocrystal Gel Receptors
Dongjie Zhang
Department of Chemistry, University of British Columbia, 2036 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z1 Canada
MIIT Key Laboratory of Critical Materials Technology for New Energy Conversion and Storage, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMiguel A. Soto
Department of Chemistry, University of British Columbia, 2036 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z1 Canada
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLev Lewis
Department of Chemistry, University of British Columbia, 2036 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z1 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorWadood Y. Hamad
Transformation and Interfaces Group, Bioproducts Innovation Centre of Excellence, FPInnovations, 2665 East Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z4 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Mark J. MacLachlan
Department of Chemistry, University of British Columbia, 2036 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z1 Canada
Quantum Matter Institute, University of British Columbia, 2355 East Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z4 Canada
WPI Nano Life Science Institute, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, 920-1192 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorDongjie Zhang
Department of Chemistry, University of British Columbia, 2036 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z1 Canada
MIIT Key Laboratory of Critical Materials Technology for New Energy Conversion and Storage, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, 150001 P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMiguel A. Soto
Department of Chemistry, University of British Columbia, 2036 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z1 Canada
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLev Lewis
Department of Chemistry, University of British Columbia, 2036 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z1 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorWadood Y. Hamad
Transformation and Interfaces Group, Bioproducts Innovation Centre of Excellence, FPInnovations, 2665 East Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z4 Canada
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Mark J. MacLachlan
Department of Chemistry, University of British Columbia, 2036 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z1 Canada
Quantum Matter Institute, University of British Columbia, 2355 East Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, V6T 1Z4 Canada
WPI Nano Life Science Institute, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, 920-1192 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
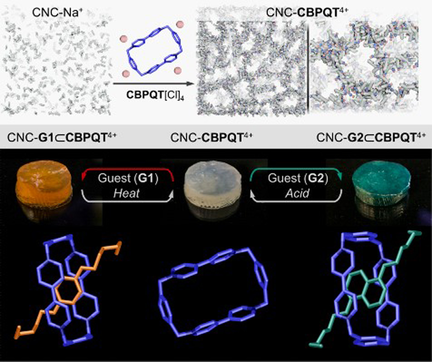
Mixing cellulose nanocrystal suspensions (CNC-Na+) with the polyionic macrocycle cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene) (CBPQT4+) yields gels with embedded active hosts. These materials reversibly absorb and recognize guests from solution to produce colorful host–guest complexes. This behavior has enabled CNC-CBPQT4+ gels to function as substrates for chromatography and encryption.
Abstract
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) spontaneously assemble into gels when mixed with a polyionic organic or inorganic salt. Here, we have used this ion-induced gelation strategy to create functional CNC gels with a rigid tetracationic macrocycle, cyclobis(paraquat-p-phenylene) (CBPQT4+). Addition of [CBPQT]Cl4 to CNCs causes gelation and embeds an active host inside the material. The fabricated CNC gels can reversibly absorb guest molecules from solution then undergo molecular recognition processes that create colorful host–guest complexes. These materials have been implemented in gel chromatography (for guest exchange and separation), and as elements to encode 2- and 3-dimensional patterns. We anticipate that this concept might be extended to design a set of responsive and selective gel-like materials functioning as, for instance, water-pollutant scavengers, substrates for chiral separations, or molecular flasks.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201913030-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.2 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1A. Nazir, A. Asghar, A. Aslam Maan, Food Gels: Gelling Process and New Applicastions in Advances in Food Rheology and Its Applications, Elsevier, Boston, 2017, pp. 335–353.
- 2B. Jeong, Y. H. Bae, D. S. Lee, S. W. Kim, Nature 1997, 388, 860–862.
- 3Y. Qiu, K. Park, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2001, 53, 321–339.
- 4C. Karavasili, D. G. Fatouros, Drug Discovery Today 2016, 21, 157–166.
- 5Z. Wei, J. H. Yang, J. Zhou, F. Xu, M. Zrínyi, P. H. Dussault, Y. Osada, Y. M. Chen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8114–8131.
- 6Z. Qi, C. A. Schalley, Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 2222–2233.
- 7L. Hines, K. Petersen, G. Z. Lum, M. Sitti, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603483.
- 8J. Zhang, Y. Hu, Y. Li, Gel Chemistry: Interactions, Structures and Properties, Springer Singapore, Singapore, 2018.
10.1007/978-981-10-6881-2 Google Scholar
- 9J.-R. Li, R. J. Kuppler, H.-C. Zhou, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1477–1504.
- 10N. Giri, M. G. Del Pópolo, G. Melaugh, R. L. Greenaway, K. Rätzke, T. Koschine, L. Pison, M. F. C. Gomes, A. I. Cooper, S. L. James, Nature 2015, 527, 216–220.
- 11K. Jie, Y. Zhou, E. Li, Z. Li, R. Zhao, F. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15320–15323.
- 12T. Wu, M. Chen, L. Zhang, X. Xu, Y. Liu, J. Yan, W. Wang, J. Gao, J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7612–7621.
- 13F. Jiang, Y.-L. Hsieh, J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6337–6342.
- 14D. M. Alzate-Sánchez, B. J. Smith, A. Alsbaiee, J. P. Hinestroza, W. R. Dichtel, Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8340–8346.
- 15D. Li, Q. Li, N. Bai, H. Dong, D. Mao, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5598–5607.
- 16J. Wang, X. Wang, X. Zhang, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4308–4313.
- 17S. Zhao, W. J. Malfait, N. Guerrero-Alburquerque, M. M. Koebel, G. Nyström, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7580–7608; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 7704–7733.
- 18D. Zhao, Y. Tian, X. Jing, Y. Lu, G. Zhu, J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 157–164.
- 19T. N. Plank, L. P. Skala, J. T. Davis, Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6235–6238.
- 20G.-F. Gong, Y.-Y. Chen, Y.-M. Zhang, Y.-Q. Fan, Q. Zhou, H.-L. Yang, Q.-P. Zhang, H. Yao, T.-B. Wei, Q. Lin, Soft Matter 2019, 15, 6348–6352.
- 21B. Li, B. Wang, X. Huang, L. Dai, L. Cui, J. Li, X. Jia, C. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 3885–3889; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 3925–3929.
- 22M. Kieffer, A. M. Garcia, C. J. E. Haynes, S. Kralj, D. Iglesias, J. R. Nitschke, S. Marchesan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7982–7986; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 8066–8070.
- 23Y. Habibi, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 1519–1542.
- 24S. Shafeiei-Sabet, W. Y. Hamad, S. G. Hatzikiriakos, Rheol. Acta 2013, 52, 741–751.
- 25X. M. Dong, J.- F. Revol, D. G. Gray, Cellulose 1998, 5, 19–32.
- 26S. Lombardo, A. Gençer, C. Schütz, J. Van Rie, S. Eyley, W. Thielemans, Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3181–3190.
- 27H. Dong, J. F. Snyder, K. S. Williams, J. W. Andzelm, Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3338–3345.
- 28S. Shafiei-Sabet, W. Y. Hamad, S. G. Hatzikiriakos, Cellulose 2014, 21, 3347–3359.
- 29M. Chau, S. E. Sriskandha, D. Pichugin, H. Thérien-Aubin, D. Nykypanchuk, G. Chauve, M. Méthot, J. Bouchard, O. Gang, E. Kumacheva, Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2455–2462.
- 30P. Bertsch, S. Isabettini, P. Fischer, Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 4060–4066.
- 31A.-L. Oechsle, L. Lewis, W. Y. Hamad, S. G. Hatzikiriakos, M. J. MacLachlan, Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 376–385.
- 32F. Zhang, H. Ren, J. Dou, G. Tong, Y. Deng, Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40096.
- 33N. Lin, A. Gèze, D. Wouessidjewe, J. Huang, A. Dufresne, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6880–6889.
- 34J. T. Korhonen, P. Hiekkataipale, J. Malm, M. Karppinen, O. Ikkala, R. H. A. Ras, ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1967–1974.
- 35A. E. Way, L. Hsu, K. Shanmuganathan, C. Weder, S. J. Rowan, ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 1001–1006.
- 36Y. Kobayashi, T. Saito, A. Isogai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10394–10397; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 10562–10565.
- 37K. J. De France, K. J. W. Chan, E. D. Cranston, T. Hoare, Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 649–660.
- 38S. Sultan, A. P. Mathew, Nanoscale 2018, 10, 4421–4431.
- 39B. Odell, M. V. Reddington, A. M. Z. Slawin, N. Spencer, J. F. Stoddart, D. J. Williams, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1988, 27, 1547–1550; Angew. Chem. 1988, 100, 1605–1608.
- 40E. Córdova, R. A. Bissell, N. Spencer, P. R. Ashton, J. F. Stoddart, A. E. Kaifer, J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 6550–6552.
- 41R. Castro, K. R. Nixon, J. D. Evanseck, A. E. Kaifer, J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 7298–7303.
- 42S. Nygaard, K. C.-F. Leung, I. Aprahamian, T. Ikeda, S. Saha, B. W. Laursen, S.-Y. Kim, S. W. Hansen, P. C. Stein, A. H. Flood, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 960–970.
- 43A. R. Bernardo, J. F. Stoddart, A. E. Kaifer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10624–10631.
- 44C.-H. Sue, S. Basu, A. C. Fahrenbach, A. K. Shveyd, S. K. Dey, Y. Y. Botros, J. F. Stoddart, Chem. Sci. 2010, 1, 119–125.
- 45M. Bria, G. Cooke, A. Cooper, J. F. Garety, S. G. Hewage, M. Nutley, G. Rabani, P. Woisel, Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 301–304.
- 46Complex G1⊂CBPQT4+ was prepared at [host]=[guest]=5×10−3 m. CNC-G1⊂CBPQT4+ gel (2 mL) was obtained and solvent-exchanged inside a UV-vis cuvette (10 mm pathlength); [host]≈1.9×10−3 m. The shown UV-vis spectrum of CNC-G1⊂CBPQT4+ was collected at t=31 h after the addition of G1. Full data set is shown in Figure S9a.
- 47This molar ratio was chosen to facilitate the spectroscopic detection of both guests by 1H NMR spectroscopy.