Controllable Synthesis of Graphdiyne Nanoribbons
Weixiang Zhou
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHan Shen
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYan Zeng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yuanping Yi
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zicheng Zuo
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yongjun Li
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yuliang Li
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWeixiang Zhou
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorHan Shen
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorYan Zeng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yuanping Yi
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zicheng Zuo
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yongjun Li
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yuliang Li
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences (BNLMS), CAS Research/Education Center for Excellence in Molecular Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Organic Solids, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 P. R. China
Department of Chemistry, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
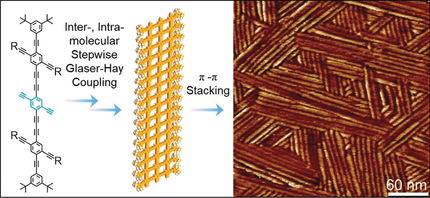
Graphdiyne nanoribbons with high chemical precision are of great significance for further understanding of the intrinsic properties of graphdiyne and the relationship between structure and properties. However, the reliable synthesis of graphdiyne nanoribbons with chemical precision remains a significant challenge. A facile method is now presented for fabrication of graphdiyne nanoribbons with uniform width through stepwise inter- and intramolecular Glaser–Hay coupling reaction of ethynyl groups. The synthetic ribbons were interwoven into nanotextiles by π–π stacking and were applied for protective coating of Li-electrode in Li-ion batteries, which efficiently suppressed the growth of the Li dendrites during cycling and prolonged the life span of Li-metal batteries.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201916518-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.1 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aG. X. Li, Y. L. Li, H. B. Liu, Y. B. Guo, Y. J. Li, D. B. Zhu, Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3256–3258;
- 1bY. J. Li, L. Xu, H. B. Liu, Y. L. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2572–2586;
- 1cZ. Y. Jia, Y. J. Li, Z. C. Zuo, H. B. Liu, C. S. Huang, Y. L. Li, Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 2470–2478;
- 1dC. S. Huang, Y. J. Li, N. Wang, Y. R. Xue, Z. C. Zuo, H. B. Liu, Y. L. Li, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 7744–7803;
- 1eX. Gao, H. Liu, D. Wang, J. Zhang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 908–936;
- 1fC. Huang, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904885.
- 2Y. Li, Y. Li, Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2018, 34, 992–1013.
- 3
- 3aH. T. Qi, P. Yu, Y. X. Wang, G. C. Han, H. B. Liu, Y. P. Yi, Y. L. Li, L. Q. Mao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5260–5263;
- 3bY. R. Xue, B. L. Huang, Y. P. Yi, Y. Guo, Z. C. Zuo, Y. J. Li, Z. Y. Jia, H. B. Liu, Y. L. Li, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1460;
- 3cX. Gao, J. Li, R. Du, J. Y. Zhou, M. Y. Huang, R. Liu, J. Li, Z. Q. Xie, L. Z. Wu, Z. F. Liu, J. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605308;
- 3dL. Hui, Y. Xue, H. Yu, Y. Liu, Y. Fang, C. Xing, B. Huang, Y. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 10677–10683;
- 3eY. Zhao, N. Yang, H. Yao, D. Liu, L. Song, J. Zhu, S. Li, L. Gu, K. Lin, D. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7240–7244;
- 3fY. Zhao, J. Wan, H. Yao, L. Zhang, K. Lin, L. Wang, N. Yang, D. Liu, L. Song, J. Zhu, L. Gu, L. Liu, H. Zhao, Y. Li, D. Wang, Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 924–931;
- 3gY. Zhao, H. Tang, N. Yang, D. Wang, Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800959.
- 4
- 4aJ. J. He, N. Wang, Z. L. Cui, H. P. Du, L. Fu, C. S. Huang, Z. Yang, X. Y. Shen, Y. P. Yi, Z. Y. Tu, Y. L. Li, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1172;
- 4bH. Shang, Z. C. Zuo, L. Li, F. Wang, H. B. A. Liu, Y. J. Li, Y. L. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 774–778; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 782–786;
- 4cN. Wang, J. J. He, Z. Y. Tu, Z. Yang, F. H. Zhao, X. D. Li, C. S. Huang, K. Wang, T. G. Jiu, Y. P. Yi, Y. L. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10740–10745; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 10880–10885;
- 4dF. Wang, Z. Zuo, L. Li, K. Li, F. He, Z. Jiang, Y. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15010–15015; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 15152–15157.
- 5
- 5aH. Ren, H. Shao, L. J. Zhang, D. Guo, Q. Jin, R. B. Yu, L. Wang, Y. L. Li, Y. Wang, H. J. Zhao, D. Wang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1500296;
- 5bJ. Li, T. Jiu, S. Chen, L. Liu, Q. Yao, F. Bi, C. Zhao, Z. Wang, M. Zhao, G. Zhang, Y. Xue, F. Lu, Y. Li, Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 6941–6947.
- 6C. Lu, Y. Yang, J. Wang, R. P. Fu, X. X. Zhao, L. Zhao, Y. Ming, Y. Hu, H. Z. Lin, X. M. Tao, Y. L. Li, W. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 752.
- 7
- 7aH. L. Yan, S. Y. Guo, F. Wu, P. Yu, H. B. Liu, Y. L. Li, L. Q. Mao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3922–3926; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 3986–3990;
- 7bZ. Jin, Q. Zhou, Y. Chen, P. Mao, H. Li, H. Liu, J. Wang, Y. Li, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3697–3702.
- 8
- 8aN. Parvin, Q. Jin, Y. Z. Wei, R. B. Yu, B. Zheng, L. Huang, Y. Zhang, L. H. Wang, H. Zhang, M. Y. Gao, H. J. Zhao, W. P. Hu, Y. L. Li, D. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606755;
- 8bJ. Liu, C. Chen, Y. Zhao, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1804386.
- 9S. C. Lin, M. J. Buehler, Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11801–11807.
- 10J. Zhou, J. Li, Z. Liu, J. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1803758.
- 11
- 11aW. Zhou, H. Shen, C. Wu, Z. Tu, F. He, Y. Gu, Y. Xue, Y. Zhao, Y. Yi, Y. Li, Y. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 48–52;
- 11bX. Gao, Y. Zhu, D. Yi, J. Zhou, S. Zhang, C. Yin, F. Ding, S. Zhang, X. Yi, J. Wang, L. Tong, Y. Han, Z. Liu, J. Zhang, Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat 6378;
- 11cC. Li, X. Lu, Y. Han, S. Tang, Y. Ding, R. Liu, H. Bao, Y. Li, J. Luo, T. Lu, Nano Res. 2018, 11, 1714–1721.
- 12
- 12aX. M. Qian, Z. Y. Ning, Y. L. Li, H. B. Liu, C. B. Ouyang, Q. Chen, Y. J. Li, Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 730–733;
- 12bT. Wang, J. M. Huang, H. F. Lv, Q. T. Fan, L. Feng, Z. J. Tao, H. X. Ju, X. J. Wu, S. L. Tait, J. F. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13421–13428.
- 13G. X. Li, Y. L. Li, X. M. Qian, H. B. Liu, H. W. Lin, N. Chen, Y. J. Li, J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 2611–2615.
- 14R. Matsuoka, R. Sakamoto, K. Hoshiko, S. Sasaki, H. Masunaga, K. Nagashio, H. Nishihara, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3145–3152.
- 15J. Y. Zhou, X. Gao, R. Liu, Z. Q. Xie, J. Yang, S. Q. Zhang, G. M. Zhang, H. B. Liu, Y. L. Li, J. Zhang, Z. F. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7596–7599.
- 16H. C. Bai, Y. Zhu, W. Y. Qiao, Y. H. Huang, RSC Adv. 2011, 1, 768–775.
- 17
- 17aY. Wan, S. Xiong, B. Ouyang, Z. Niu, Y. Ni, Y. Zhao, X. Zhang, ACS Omega 2019, 4, 4147–4152;
- 17bL. D. Pan, L. Z. Zhang, B. Q. Song, S. X. Du, H. J. Gao, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 173102.
- 18J. Kang, F. M. Wu, J. B. Li, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2012, 24, 165301.
- 19Y. Zhu, H. C. Bai, Y. H. Huang, ChemistryOpen 2016, 5, 78–87.
- 20M. Y. Han, B. Oezyilmaz, Y. Zhang, P. Kim, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 206805.
- 21X. Wang, H. Dai, Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 661–665.
- 22
- 22aD. V. Kosynkin, A. L. Higginbotham, A. Sinitskii, J. R. Lomeda, A. Dimiev, B. K. Price, J. M. Tour, Nature 2009, 458, 872–U875;
- 22bL. Jiao, L. Zhang, X. Wang, G. Diankov, H. Dai, Nature 2009, 458, 877–880.
- 23F. Negri, C. Castiglioni, M. Tommasini, G. Zerbi, J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 3306–3317.
- 24M. G. Schwab, A. Narita, Y. Hernandez, T. Balandina, K. S. Mali, S. De Feyter, X. Feng, K. Muellen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18169–18172.
- 25R. Dovesi, A. Erba, R. Orlando, C. M. Zicovich-Wilson, B. Civalleri, L. Maschio, M. Rerat, S. Casassa, J. Baima, S. Salustro, B. Kirtman, WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2018, 8, e1360.
- 26
- 26aM. Jain, J. R. Chelikowsky, S. G. Louie, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 216806;
- 26bM. Liu, M. Liu, L. She, Z. Zha, J. Pan, S. Li, T. Li, Y. He, Z. Cai, J. Wang, Y. Zheng, X. Qiu, D. Zhong, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14924.
- 27M. Q. Long, L. Tang, D. Wang, Y. L. Li, Z. G. Shuai, ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2593–2600.
- 28R. Gutzler, D. F. Perepichka, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16585–16594.
- 29
- 29aZ. Wang, A. Blaszczyk, O. Fuhr, S. Heissler, C. Woell, M. Mayor, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14442;
- 29bY. Liu, Y. Ma, Y. Zhao, X. Sun, F. Gandara, H. Furukawa, Z. Liu, H. Zhu, C. Zhu, K. Suenaga, P. Oleynikov, A. S. Alshammari, X. Zhang, O. Terasaki, O. M. Yaghi, Science 2016, 351, 365–369;
- 29cX. L. Wang, Q. Chao, E. B. Wang, X. Lin, Z. M. Su, C. W. Hu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5036–5040; Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 5146–5150.
- 30X. Yang, X. Dou, A. Rouhanipour, L. Zhi, H. J. Raeder, K. Muellen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4216–4217.
- 31P. Payamyar, B. T. King, H. C. Oettinger, A. D. Schlueter, Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 18–34.
- 32
- 32aH. Shang, Z. Zuo, Y. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 17678–17685;
- 32bF. Wang, Z. Zuo, L. Li, F. He, F. Lu, Y. Li, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806272.