Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
MINI-REVIEWS
COVID-19 under spotlight: A close look at the origin, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of the 2019-nCoV disease
- Pages: 8873-8924
- First Published: 26 May 2020
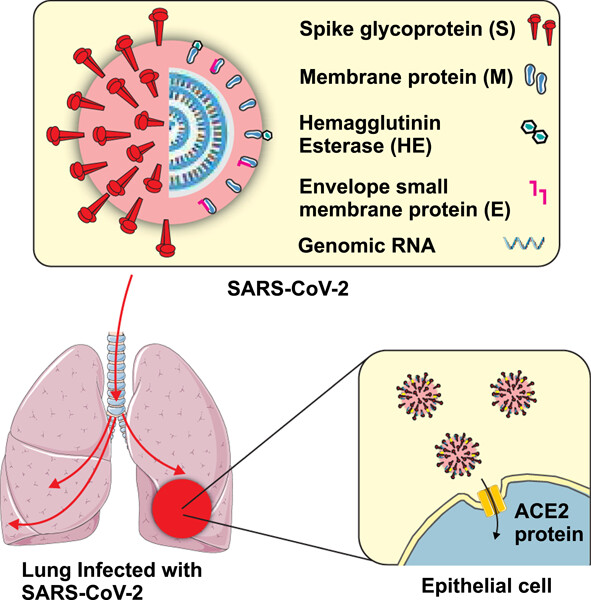
Since the causative agent, SARS-CoV-2, is a recently discovered species, there is no specific medicine for downright treatment of the infection. This has led to an unprecedented societal fear of the newly born disease, adding a psychological aspect to the physical manifestation of the virus. Herein, the COVID-19 structure, epidemiology, pathogenesis, etiology, diagnosis, and therapy have been reviewed.
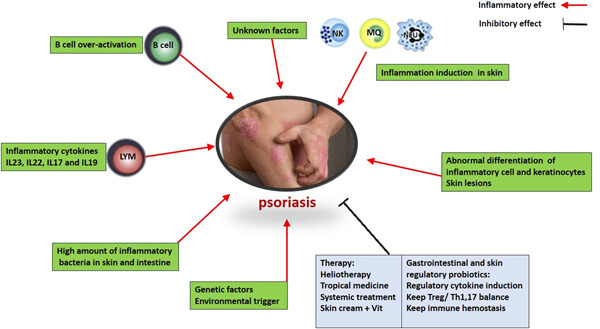
Probiotics with ameliorating effects on the severity of skin inflammation in psoriasis: Evidence from experimental and clinical studies
- Pages: 8925-8937
- First Published: 28 April 2020
The roles of GRP81 as a metabolic sensor and inflammatory mediator
- Pages: 8938-8950
- First Published: 28 April 2020

GPR81 (also named as HCA1) is a member of a subfamily of orphan G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), coupled to Gi-type G proteins. GPR81 was discovered in 2001 and identified as the only known endogenous receptor of lactate under physiological conditions in 2008, which opened a new field of research on how lactate may act as a signal molecule along with the GPR81 expression in roles of metabolic process and inflammatory response. Recent studies showed that the physiological functions of GPR81 include lipid metabolism in adipose tissue, metabolic excitability in the brain, cellular development, and inflammatory response modulation. These findings may reveal a novel therapeutic strategy to treat clinical, metabolic, and inflammatory diseases. This article summarizes past research on GPR81, including its characteristics of distribution and expression, functional residues, pharmacological, and physiological agonists, involvement in signal transduction, and pharmacological applications.
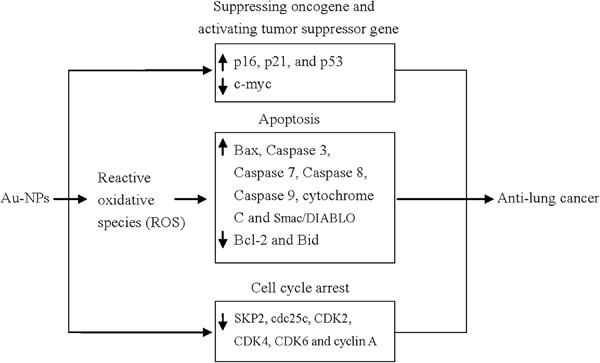
Recent advances in the antilung cancer activity of biosynthesized gold nanoparticles
- Pages: 8951-8957
- First Published: 13 May 2020
Mechanism underlying the regulation of sortilin expression and its trafficking function
- Pages: 8958-8971
- First Published: 31 May 2020
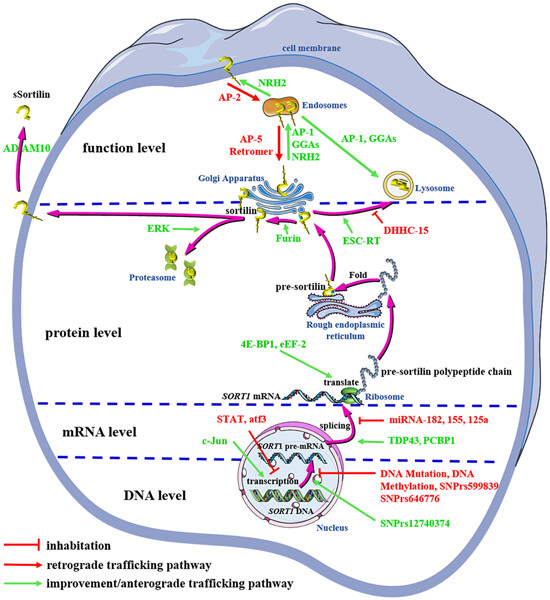
This review summarizes and analyzes the updated information on the regulation of sortilin expression and its trafficking function. Recent advances in the regulation of sortilin expression and function, and its related mechanisms will help the ongoing research related to sortilin and promote future clinical application via sortilin intervention.
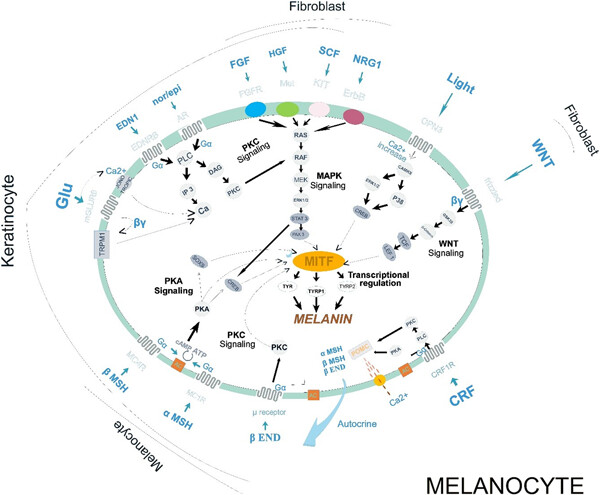
Molecular and biochemical mechanisms of human iris color: A comprehensive review
- Pages: 8972-8982
- First Published: 02 June 2020
What makes leader cells arise: Intrinsic properties and support from neighboring cells
- Pages: 8983-8995
- First Published: 22 June 2020
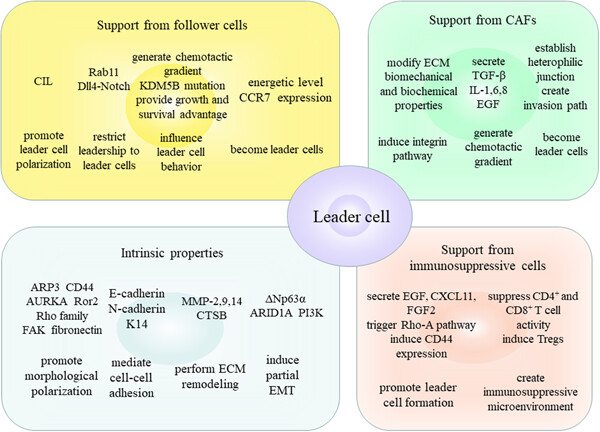
To become leader cells, cancer cells need intrinsic properties to confer them with the potential to acquire leader cell phenotype and the support from the neighboring cells can convert the potential into specific leader cell behavior. Intrinsic properties include the distinct genetic expression, protein synthesis, and signaling cascades to promote cytoskeletal rearrangements, structural reorganization, and morphological polarization. Meanwhile, follower and stromal cells in the microenvironment can steer the potential leader cells to initiate appropriate polarization, exert leader cell behavior, and consolidate leadership by cell–cell junctions, the stimulation of multiple chemokines, and growth factors and modification of the microenvironment.
REVIEW ARTICLES
The effector cells and cellular mediators of immune system involved in cardiac inflammation and fibrosis after myocardial infarction
- Pages: 8996-9004
- First Published: 30 April 2020

- 1.
Inflammatory effectors and mediators can exert protective or detrimental role post-cardiac infarction.
- 2.
Inflammatory response facilitated cardiac repair, but excessive inflammation lead to adverse left ventricular remodeling.
- 3.
Broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory agents, may produce a short-term effect on inflammatory response, but it would cause catastrophic consequence for myocardial repair.
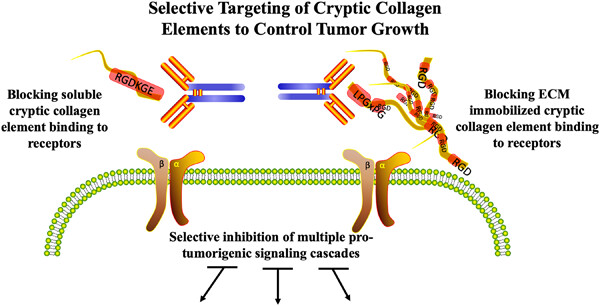
Cryptic collagen elements as signaling hubs in the regulation of tumor growth and metastasis
- Pages: 9005-9020
- First Published: 12 May 2020
Cellular effects and clinical implications of SLC2A3 copy number variation
- Pages: 9021-9036
- First Published: 05 May 2020
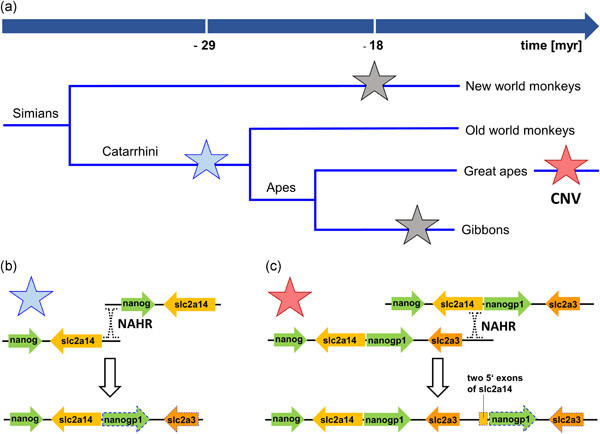
This review summarizes the cellular and clinical implications of deletion and duplication variants of the SLC2A3 gene which encodes the glucose transporter 3. Disease associations of these copy number variants with neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders, congenital heart defects, and autoimmune diseases are discussed, focussing on how metabolic alterations may influence cellular development and degeneration.
Emerging landscape of circular RNAs as biomarkers and pivotal regulators in osteosarcoma
- Pages: 9037-9058
- First Published: 26 May 2020
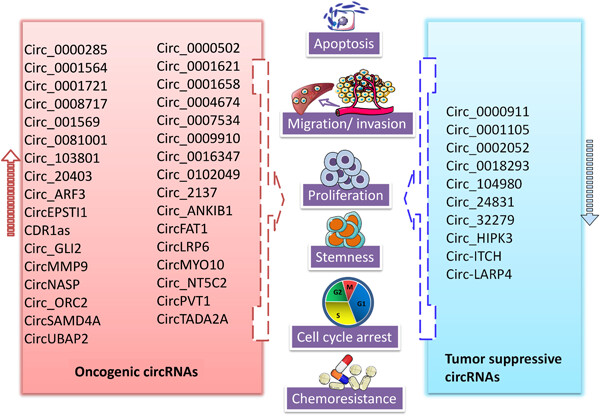
- 1.
circRNAs are capable of various biological functions including miRNA sponge, mediating alternatives, regulating genes at posttranscriptional levels, and interacting with proteins, indicating a pivotal role of circRNA in osteosarcoma initiation, progression, chemoresistance and immune response.
- 2.
circRNAs have been thrust into the spotlight as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in osteosarcoma.
Protective mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide in myocardial ischemia
- Pages: 9059-9070
- First Published: 15 June 2020
Highly upregulated in liver cancer (HULC): An update on its role in carcinogenesis
- Pages: 9071-9079
- First Published: 05 May 2020
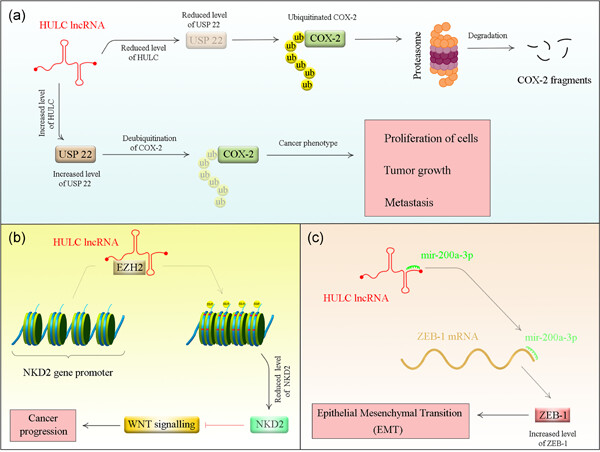
Summary of proposed mechanisms for participation of HULC in the pathogenesis of cancer. (a) HULC increases expression of ubiquitin-specific peptidase 22 (USP22), which reduces ubiquitin-induced degradation of COX-2 protein by eliminating the conjugated polyubiquitin chains from COX-2 and increasing stability of COX2 protein. (b) HULC interacts with EZH2 to inhibit expression of NKD2, a negative regulator of Wnt signaling. (c) HULC participates in ZEB1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) by acting as competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) to seize miR-200a-3p signaling.
Immune checkpoints in hematologic malignancies: What made the immune cells and clinicians exhausted!
- Pages: 9080-9097
- First Published: 07 May 2020
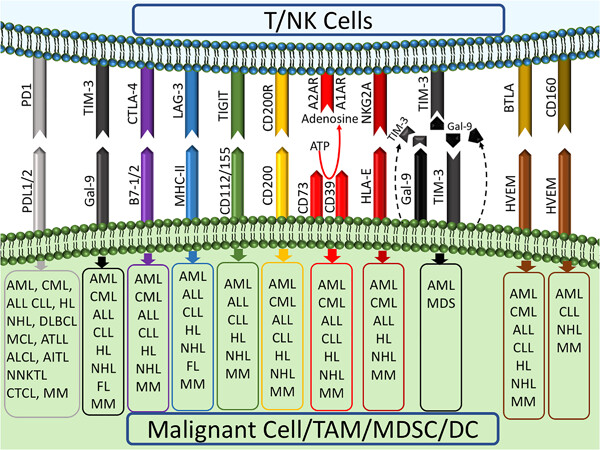
Despite the beneficial roles of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) in hematologic malignancies, relapse is still a nettlesome challenge. Hematologic cancer cells induce exhaustion in immune cells through several mechanisms, such as inhibitory immune checkpoints, which lead to immune escape and relapses after HSCT. We reviewed the clinical roles of immune checkpoints in hematologic malignancies and post-HSCT relapses.
Vaccine development and therapeutic design for 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2: Challenges and chances
- Pages: 9098-9109
- First Published: 18 June 2020
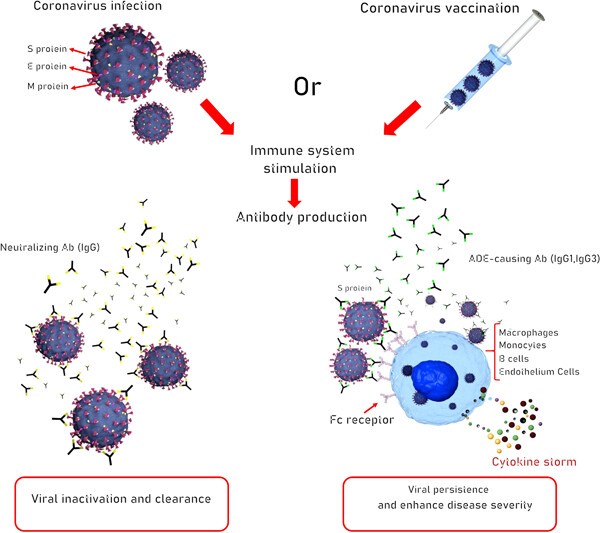
-
Multiepitope vaccines that are designed by immunoinformatics methods are favorable for outbreaks of great proportions.
-
The enhancing antibody problem appears to be a contributing factor in coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) vaccine design.
-
The broad global access for the pandemic COVID-19 vaccine, if available, should be ensured to avoid the potential of disease outbreak in the future.
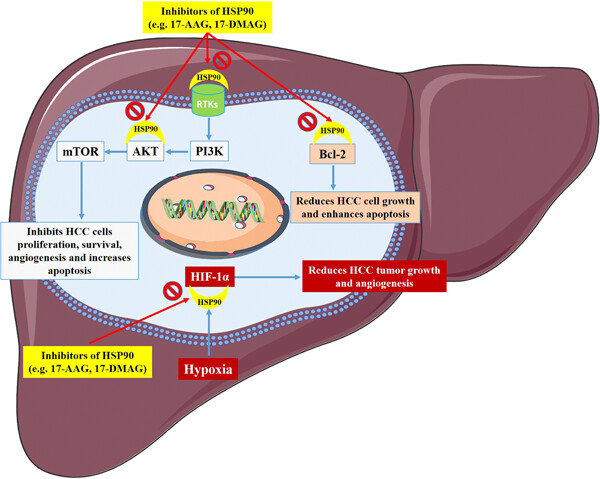
The role of HSP90 molecular chaperones in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 9110-9120
- First Published: 26 May 2020
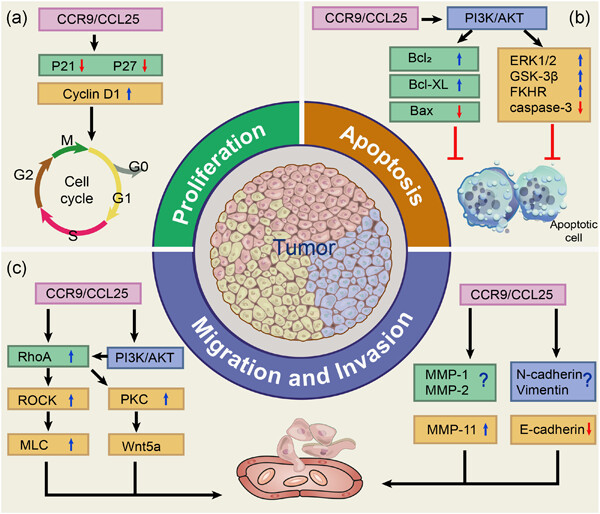
CCR9 and CCL25: A review of their roles in tumor promotion
- Pages: 9121-9132
- First Published: 13 May 2020
A global treatments for coronaviruses including COVID-19
- Pages: 9133-9142
- First Published: 11 May 2020
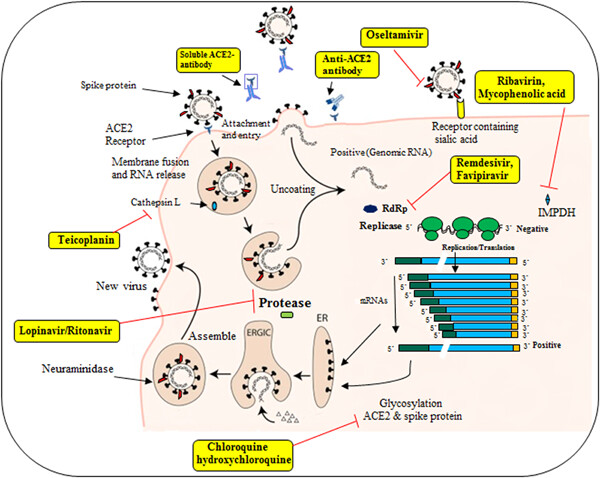
In late December 2019 in Wuhan, China, several patients with viral pneumonia were identified as 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). So far, there are no specific treatments for patients with coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19), and the treatments available today are based on previous experience with similar viruses such as severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and Influenza virus. In patients with COVID-19, hydroxychloroquine decreases the inflammatory response and cytokine storm, but overdose causes toxicity and mortality. Neuraminidase inhibitors such as oseltamivir, peramivir, and zanamivir are invalid for 2019-nCoV and are not recommended for treatment but protease inhibitors such as lopinavir/ritonavir (LPV/r) inhibit the progression of MERS-CoV disease and can be useful for patients of COVID-19 and, in combination with Arbidol, has a direct antiviral effect on early replication of SARS-CoV. Favipiravir increases clinical recovery and reduces respiratory problems and has a stronger antiviral effect than LPV/r. Currently, appropriate treatment for patients with COVID-19 is an angiotensin-converting-enzyme 2 inhibitor and a clinical problem reducing agent such as favipiravir in addition to hydroxychloroquine and corticosteroids.
Advances and challenges in the treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma
- Pages: 9143-9165
- First Published: 18 May 2020
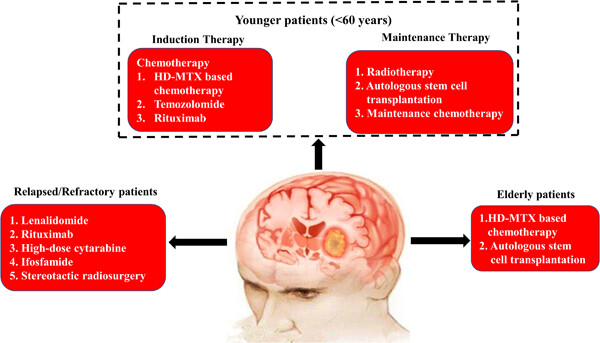
This review provides an overview of advances in surgical approaches, induction chemotherapy, radiotherapy, autologous stem-cell transplantation, salvage treatments, and novel therapeutic approaches in immunocompetent patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) in the past 5 years. Additionally, therapeutic progress in elderly patients and in those with relapsed/refractory PCNSL is also summarized based on the outcomes of recent clinical studies.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) as game-changing tools in the treatment of neurodegenerative disease: Mirage or reality?
- Pages: 9166-9184
- First Published: 21 May 2020
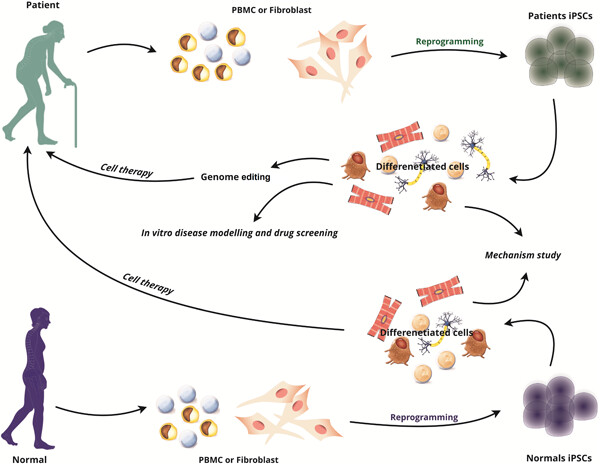
In this review, we summarize iPSC-based disease modeling in neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's disease (PD), and Huntington's disease (HD). Moreover, we discuss the efficacy of cell-replacement therapies for neurodegenerative disease.
Mesenchymal stromal cells; a new horizon in regenerative medicine
- Pages: 9185-9210
- First Published: 26 May 2020
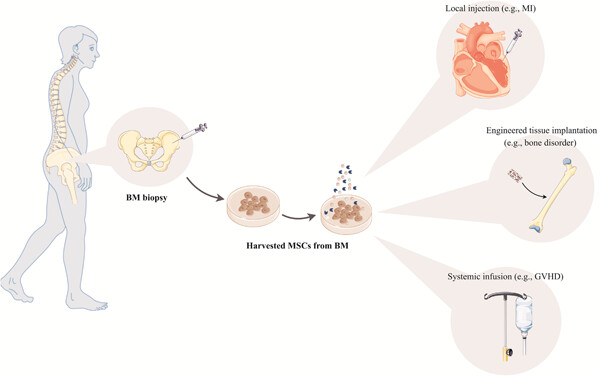
In the current review, we provide a brief overview of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) sources, isolation, and expansion as well as immunomodulatory activities. More important, we try to collect and discuss recent Preclinical and clinical research and evaluate current challenges in the context of the MSC-based cell therapy for regenerative medicine.
The outlook for diagnostic purposes of the 2019-novel coronavirus disease
- Pages: 9211-9229
- First Published: 26 May 2020
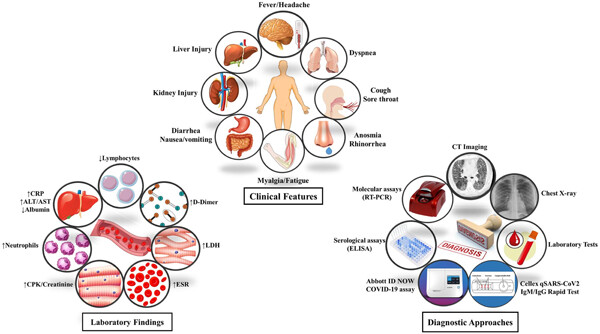
At the end of December 2019, a novel acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2) named COVID-19 emerged in Wuhan, China. Coronavirus becoming a critical challenge in global public health due to rapid development and extreme spread by active carriers in human-to-human transmission. Accordingly, there is a critical requirement for early diagnosis of COVID-19 infected or suspected cases for applying appropriate care and treatment. In this review, we comprehensively present the clinical and para-clinical diagnostic approaches to COVID-19 and their various applications, advantages, and disadvantages aspects, which would be useful for expanding perspectives and understanding more about diagnostic methods.
Regenerative potential of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A new horizon of stem cell therapy
- Pages: 9230-9240
- First Published: 18 June 2020
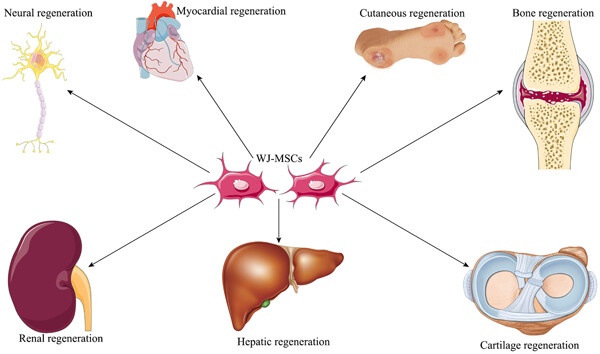
Wharton's jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells (WJ-MSCs) have rapidly advanced into clinical trials for the treatment of a wide range of disorders. Therefore, this paper summarized the current preclinical and clinical studies performed to investigate the regenerative potential of WJ-MSCs in neural, myocardial, skin, liver, kidney, cartilage, bone, muscle, and other tissue injuries.
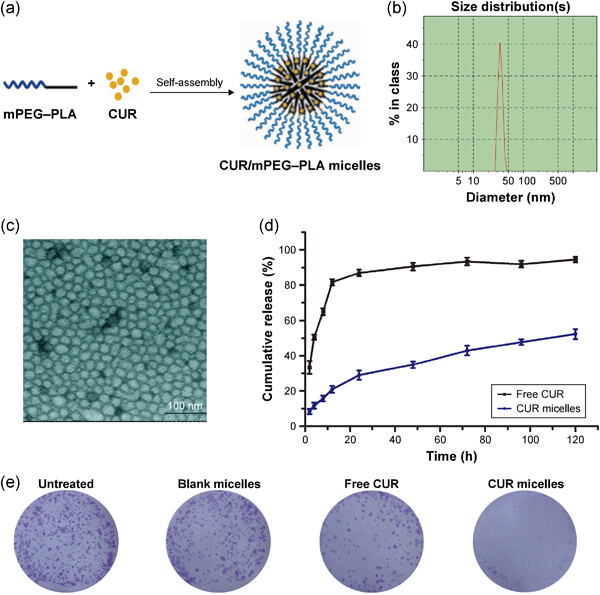
Versatile role of curcumin and its derivatives in lung cancer therapy
- Pages: 9241-9268
- First Published: 09 June 2020
Expression profile of lncRNAs and miRNAs in esophageal cancer: Implications in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic response
- Pages: 9269-9290
- First Published: 11 June 2020
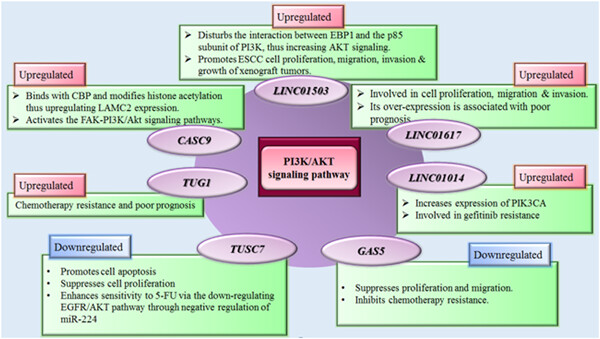
The expression of HOTAIR has been increased in esophageal cancer. HOTAIR sponges miR-148a to increase the expression of Snail2. Snail2 has a prominent role in the induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Moreover, HOTAIR enhances the trimethylation of H2K27 in the WIF-1 promoter through PRC2. WIF-1 is an inhibitor of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Thus, HOTAIR activates this pathway to further enhance EMT.
Ten-year update of the international registry on cytokine-induced killer cells in cancer immunotherapy
- Pages: 9291-9303
- First Published: 02 June 2020
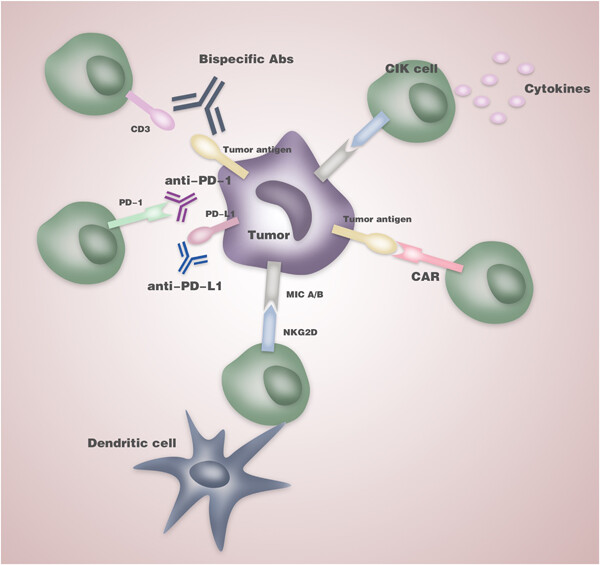
Cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells featuring non-MHC-restricted tumor-killing activity have provided encouraging results in clinical studies. Here, we update the clinical data including a total of 106 trials enrolled in the international registry on CIK cells (IRCC) established in 2010. The recent multiple improvements both on antitumoral efficacy and toxicity make CIK cells an important therapeutic approach in clinical practice of cancer immunotherapy.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Immune-related long noncoding RNA signature for predicting survival and immune checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 9304-9316
- First Published: 24 April 2020
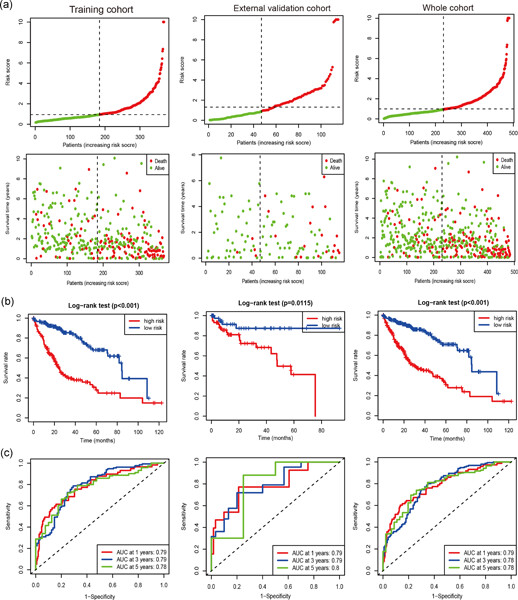
- (1)
Immune-related long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) signature had an important value for disease progression and survival prediction in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
- (2)
Immune-related lncRNA signature may have the potential to measure the response to immune checkpoint blockade immunotherapy.
- (3)
Our study showed immune-related lncRNA signature provided valuable clinical applications in antitumor immunotherapy in HCC.
The point mutation analysis of Cyp2C9*2 (Arg144Cys C>T), Cyp2C9*3 (Ile359Leu A>C) and VKORC1 (1639G>A) in women with cervical cancer related to HPV: A case-control study
- Pages: 9317-9322
- First Published: 12 May 2020
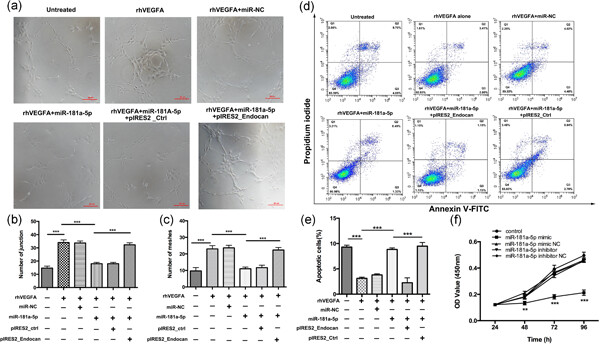
Overexpression of miR-181a-5p inhibits retinal neovascularization through endocan and the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- Pages: 9323-9335
- First Published: 28 April 2020
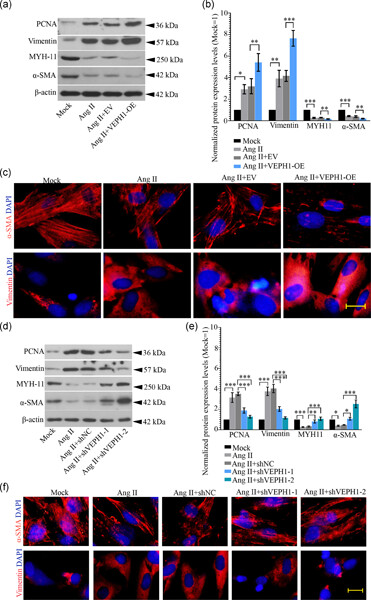
A novel role of VEPH1 in regulating AoSMC phenotypic switching
- Pages: 9336-9346
- First Published: 27 April 2020
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor alters lipid composition and protein distribution in MPP+-injured differentiated SH-SY5Y cells
- Pages: 9347-9360
- First Published: 30 April 2020
In this study, we explored the effect of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) on 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-injured differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. The results showed considerable protein and lipid alterations in response to GDNF, especially altered levels of dopamine-β-hydroxylase, heat shock 70 kDa protein, neural cell adhesion molecule, cytoskeletal proteins, and long-chain polysaturated/unsaturated fatty acids. We hope these findings could reveal a new avenue to explore the relationships between GDNF, lipid rafts, and Parkinson's disease (PD) and support the hypothesis that GDNF may be a useful treatment for PD.
Knockdown of NEAT1 exerts suppressive effects on diabetic retinopathy progression via inactivating TGF-β1 and VEGF signaling pathways
- Pages: 9361-9369
- First Published: 30 April 2020
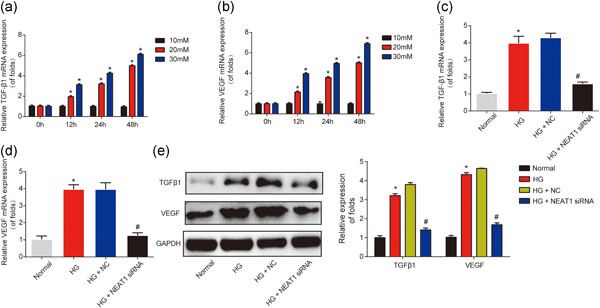
Long noncoding RNAs nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) were greatly increased in patients with diabetic retinopathy (DR), in the retina of diabetic rats and mice, and knockdown of NEAT1 enhanced proliferation, repressed high-glucose (HG)-induced apoptosis, and reduced HG-triggered oxidative stress injury in human retinal endothelial cells. Furthermore, the silence of NEAT1 could reduce the enhanced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) induced by HG. Hence, NEAT1 might contribute to the development of DR through activating TGF-β1 and VEGF.
The correlation between CT features and insulin resistance levels in patients with T2DM complicated with primary pulmonary tuberculosis
- Pages: 9370-9377
- First Published: 28 April 2020
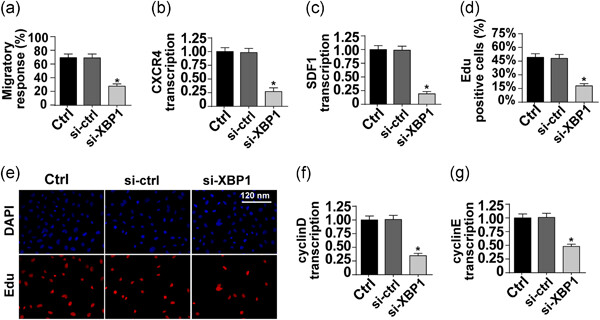
Spliced X-box binding protein 1 induces liver cancer cell death via activating the Mst1-JNK-mROS signalling pathway
- Pages: 9378-9387
- First Published: 26 April 2020
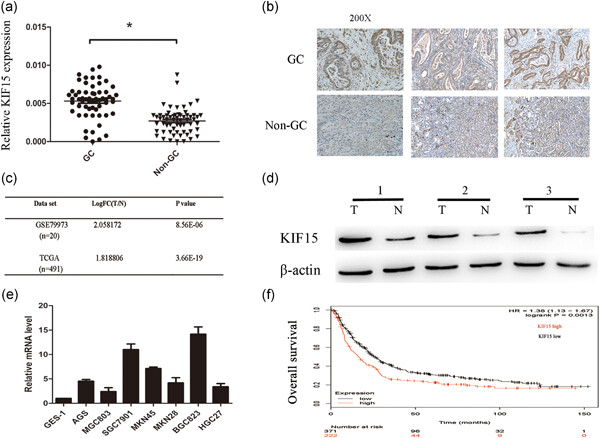
KIF15 promotes the evolution of gastric cancer cells through inhibition of reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis
- Pages: 9388-9398
- First Published: 27 April 2020
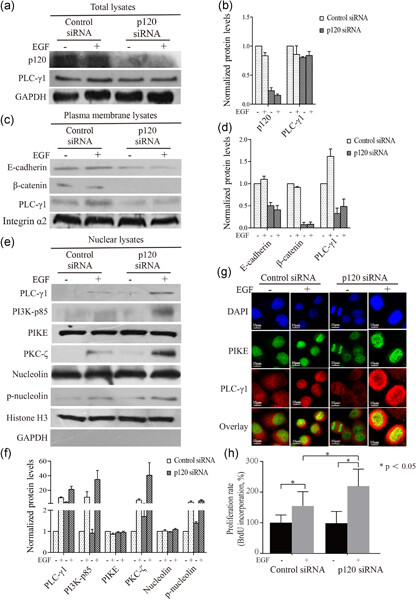
p120-catenin suppresses proliferation and tumor growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma via inhibiting nuclear phospholipase C-γ1 signaling
- Pages: 9399-9413
- First Published: 30 April 2020
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: MicroRNA-29a-3p regulates abdominal aortic aneurysm development and progression via direct interaction with PTEN
- Pages: 9414-9423
- First Published: 07 May 2020
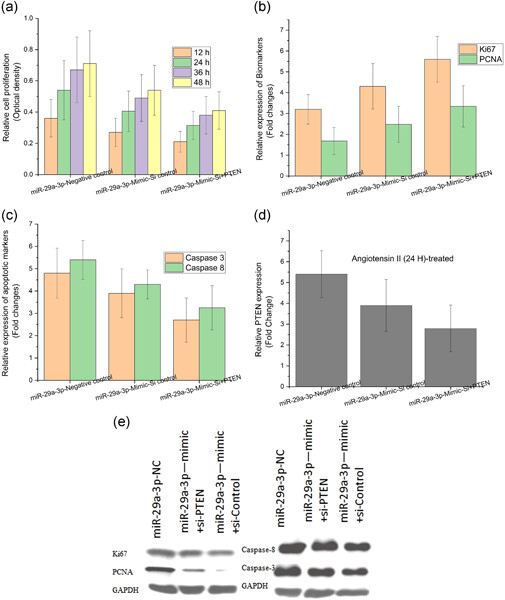
The current research article comprehensively discusses the molecular mechanism between microRNA-29a-3p and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) in the development and progression of AAA. It can be understood that the PTEN was directly targeted by microRNA-29a-3p so as to regulate the AAA progression. PTEN was found to strengthen the proliferation effect of microRNA-29a-3p in AAA cells.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Evaluating the mechanism underlying antitumor effect of interleukin 27 on B cells of chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients
- Pages: 9424-9431
- First Published: 07 May 2020
Interleukin-6 increases adrenal androgen release by regulating the expression of steroidogenic proteins in NCI-H295R cells
- Pages: 9432-9444
- First Published: 28 April 2020
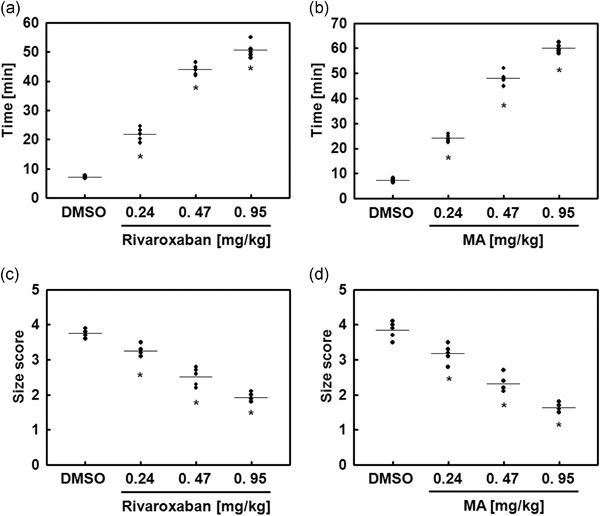
Novel factor Xa inhibitor, maslinic acid, with antiplatelet aggregation activity
- Pages: 9445-9456
- First Published: 30 April 2020
STAT3 inhibition reduced PD-L1 expression and enhanced antitumor immune responses
- Pages: 9457-9463
- First Published: 13 May 2020
Bifidobacterium breve M-16V alters the gut microbiota to alleviate OVA-induced food allergy through IL-33/ST2 signal pathway
- Pages: 9464-9473
- First Published: 11 May 2020
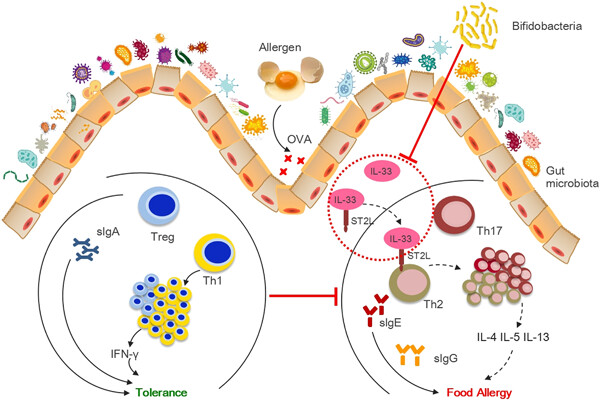
Food allergy (FA) has emerged as a life-threatening disease worldwide with gastrointestinal damage. The imbalance of intestinal flora and immune response are related to food sensitivities. It is found that the interleukin-33/suppression of tumorigenicity 2 pathway may involve the occurrence and development of allergic diseases. This study aimed to examine the relationships among gut microbiota, immune function, and FA, and evaluate the potential of an oral exposure to Bifidobacterium breve M-16V (Bb M-16V) to relieve allergy symptoms in a mouse model of FA. The results seek to provide a new basis for the application of Bb M-16V in FA and reveal the vital function of different intestinal microbiota composition after exposure to allergen in regulating T cell responses to intestinal allergic reactivity.
The N-terminal polypeptide derived from vMIP-II exerts its antitumor activity in human breast cancer through CXCR4/miR-7-5p/Skp2 pathway
- Pages: 9474-9486
- First Published: 05 May 2020
Effect of Rooibos (Aspalathus linearis) extract on atorvastatin-induced toxicity in C3A liver cells
- Pages: 9487-9496
- First Published: 27 May 2020
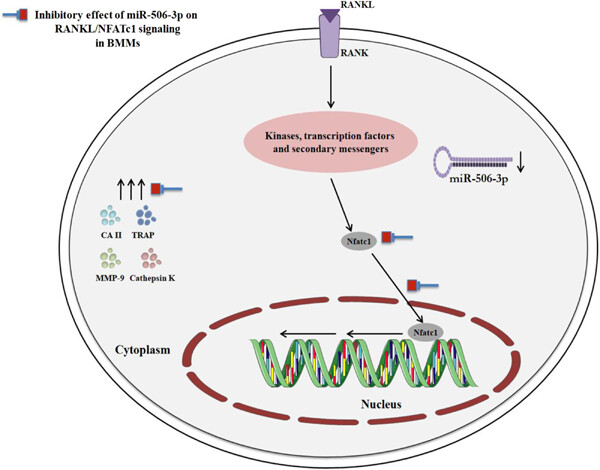
miR-506-3p alleviates uncontrolled osteoclastogenesis via repression of RANKL/NFATc1 signaling pathway
- Pages: 9497-9509
- First Published: 05 May 2020
PCTR1 improves pulmonary edema fluid clearance through activating the sodium channel and lymphatic drainage in lipopolysaccharide-induced ARDS
- Pages: 9510-9523
- First Published: 11 June 2020
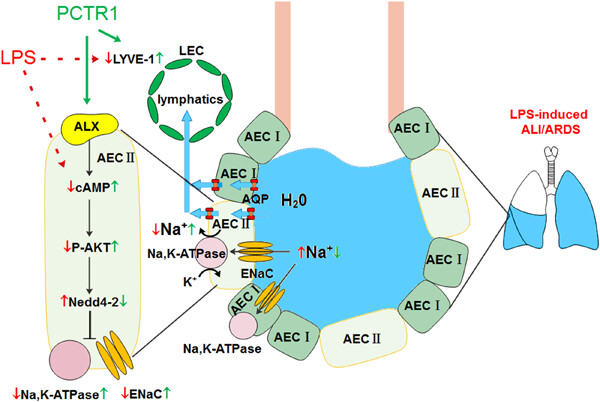
Protectin conjugates in tissue regeneration 1 (PCTR1) upregulates sodium channel expression via activating the ALX/cAMP/P-Akt/Nedd4-2 pathway and increases Na, K-ATPase expression and activity to promote alveolar fluid clearance. Moreover, PCTR1 also promotes the expression of LYVE-1 to recover the lymphatic drainage resulting in an increase of lung interstitial fluid clearance.
FoxA2 inhibits the proliferation of hepatic progenitor cells by reducing PI3K/Akt/HK2-mediated glycolysis
- Pages: 9524-9537
- First Published: 04 June 2020

FoxA2 is expressed by hepatic progenitor cells in cirrhotic human liver. FoxA2 suppresses the proliferation of hepatic progenitor cells via reducing glycolysis. FoxA2 inhibits gene transcription, protein expression, and enzyme activities of HK2. FoxA2 reduces PI3K expression and Akt phosphorylation, thus restricting HK2 activity, glycolysis, and proliferation.
IGFBP6 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and morphology via cyclin E–CDK2
- Pages: 9538-9556
- First Published: 11 June 2020
NLRC3 inhibits PDGF-induced PASMCs proliferation via PI3K-mTOR pathway
- Pages: 9557-9567
- First Published: 07 May 2020
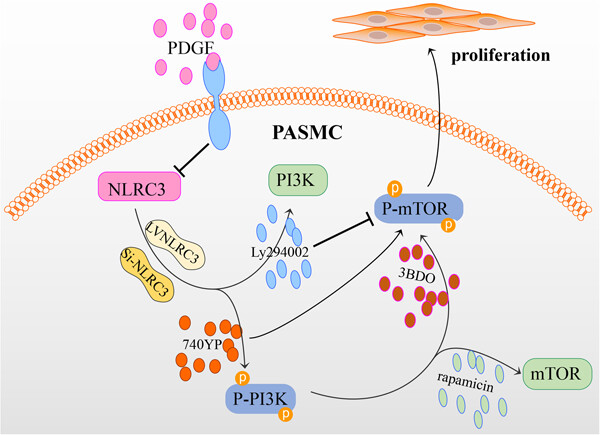
Platelet-derived growth factor can induce abnormal proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). Nucleotide-oligomerization domain-like receptor subfamily C3 (NLRC3) suppresses activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling thus inhibits PASMCs proliferation. These findings unveiled the effect of NLRC3 as an inhibitor of the PI3K-mTOR pathway mediating protection against PASMCs proliferation.
Blood and tissue levels of lncRNAs in periodontitis
- Pages: 9568-9576
- First Published: 05 May 2020
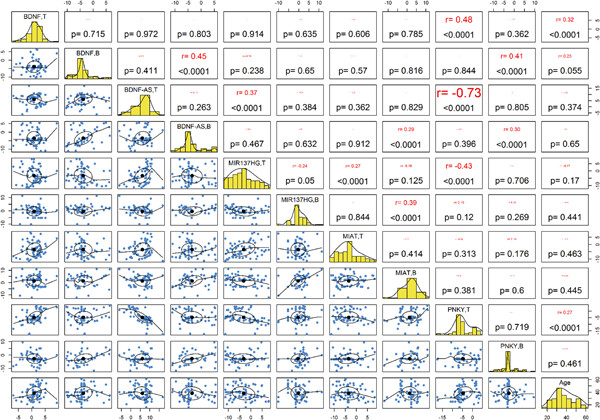
Tissue expression levels of BDNF and PNKY were correlated with age (p < .0001). Significant inverse correlations were detected between the tissue expression levels of PNKY and both BDNF-AS and MIR137HG (r = −.73, p < .0001 and r = −.43, p < .0001, respectively). Significant pairwise correlations were found between blood levels of BDNF and both BDNF-AS and PNKY, blood levels of MIR137HG, and MIAT as well as tissue levels of BDNF-AS and MIR137HG.
Elevated cell-free fetal DNA contributes to placental inflammation and antiangiogenesis via AIM2 and IFI16 during pre-eclampsia
- Pages: 9577-9588
- First Published: 07 May 2020
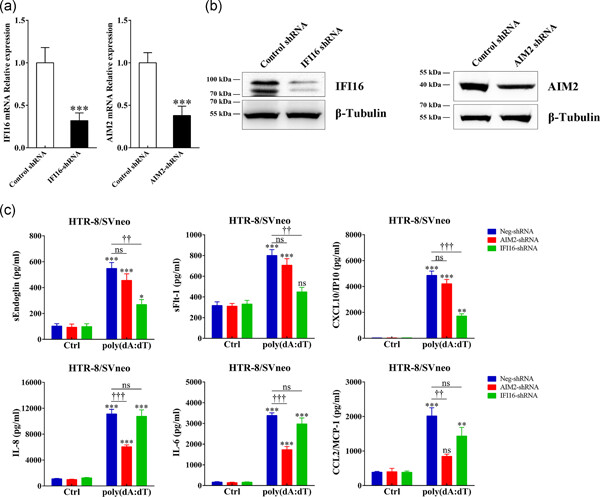
In this study, we found that trophoblast cells constitutively expressed the cytosolic DNA sensors, absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) and interferon-inducible protein 16 (IFI16). Elevated cell-free fetal DNA might increase the AIM2 and IFI16 activation in women with pre-eclampsia, and elicited increased production of AIM2-mediated IL-8, IL-6 and CCL2 and IFI16-mediated sEndoglin, sFlt-1 and CXCL10, which correlate with the severity of the disease.
Impaired actin filaments decrease cisplatin sensitivity via dysfunction of volume-sensitive Cl− channels in human epidermoid carcinoma cells
- Pages: 9589-9600
- First Published: 05 May 2020
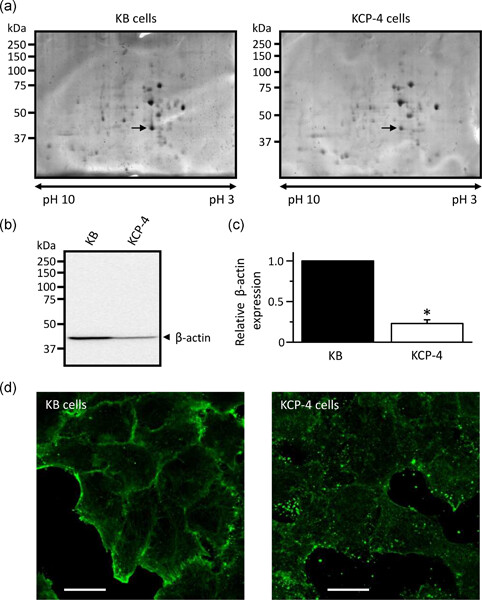
Our results indicated that cisplatin-resistant human epidermoid carcinoma KCP-4 cells showed lower β-actin expression and structural disruption of actin filaments, but not its parental KB cells. We here demonstrated that disruption of actin filaments caused dysfunction of volume-sensitive anion channels, which elicits cisplatin resistance in human epidermoid carcinoma cells.
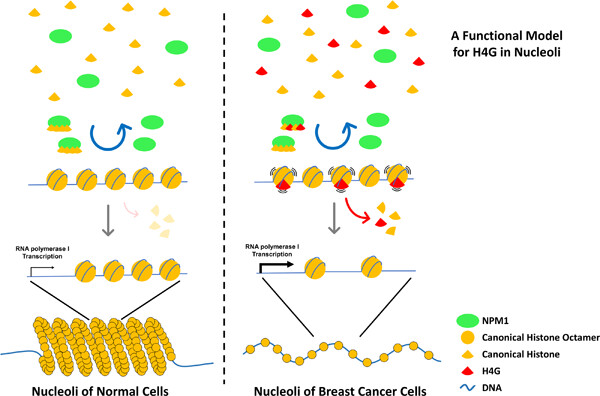
Histone H4 variant, H4G, drives ribosomal RNA transcription and breast cancer cell proliferation by loosening nucleolar chromatin structure
- Pages: 9601-9608
- First Published: 09 May 2020
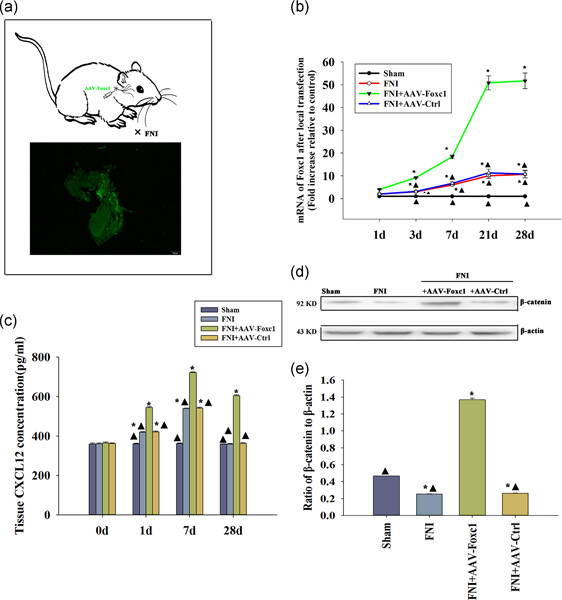
Overexpression of Foxc1 regenerates crushed rat facial nerves by promoting Schwann cells migration via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Pages: 9609-9622
- First Published: 11 May 2020
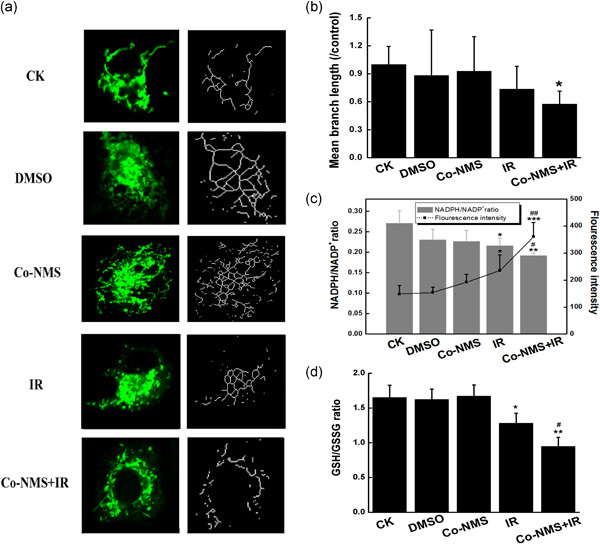
Radiosensitivity enhancement by Co-NMS-mediated mitochondrial impairment in glioblastoma
- Pages: 9623-9634
- First Published: 11 May 2020
Preliminary study on the mechanism of long noncoding RNA SENCR regulating the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells
- Pages: 9635-9643
- First Published: 13 May 2020
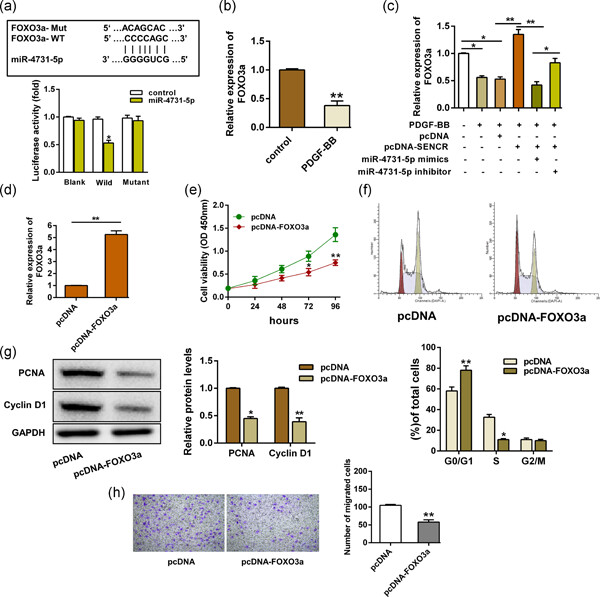
The proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells are one of the key regulatory links of atherosclerosis. Our research suggested that smooth muscle and endothelial cell-enriched migration/differentiation-associated lncRNA (SENCR) affects human aortic-VSMCs proliferation and migration via regulating the miR-4731-5p/FOXO3a pathway.
Temporal modulation of calcium sensing in hematopoietic stem cells is crucial for proper stem cell expansion and engraftment
- Pages: 9644-9666
- First Published: 11 May 2020
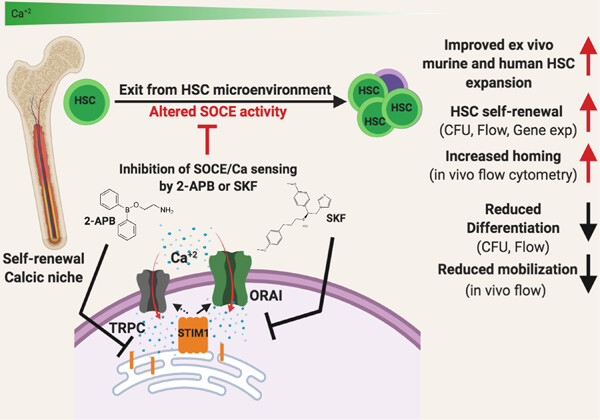
Temporal modulation of calcium sensing in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) by store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) inhibitors SKF and 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) could be used to expand HSCs ex vivo. Human bone marrow (BM)-HSC and mPB-HSC are highly responsive to modulation of calcium-sensing pathways in comparison with UBC HSCs. SKF and 2-APB significantly increases CFU-GEMM colonies.
BDNF Val66Met polymorphism alters food intake and hypothalamic BDNF expression in mice
- Pages: 9667-9675
- First Published: 19 May 2020
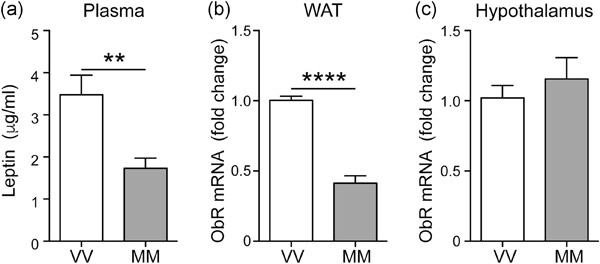
We described that homozygous knock-in BDNF Met/Met mice were overweight and hyperphagic compared to wildtype BDNF Val/Val mice. These alterations were associated with gene expression changes of BDNF, SIRT1, and ObR in the hypothalamus and white adipose tissue. Moreover, plasmatic leptin levels were decreased in BDNF Met/Met mice.
The P2Y6 receptor signals through Gαq/Ca2+/PKCα and Gα13/ROCK pathways to drive the formation of membrane protrusions and dictate cell migration
- Pages: 9676-9690
- First Published: 18 May 2020
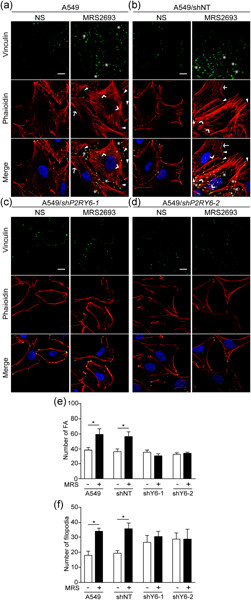
The expression of the G-protein-coupled P2Y6 receptor increases in response to inflammatory stressors. In this study, we have shown that this receptor activity stimulates the formation of key migratory structures to drive cell migration by a dialogue between the Gq/calcium/PKCα and G13/ROCK pathways.
Epigenetic modifier trichostatin A enhanced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting NF-κB (p65) DNA binding and promoted periodontal repair in rats
- Pages: 9691-9701
- First Published: 12 May 2020
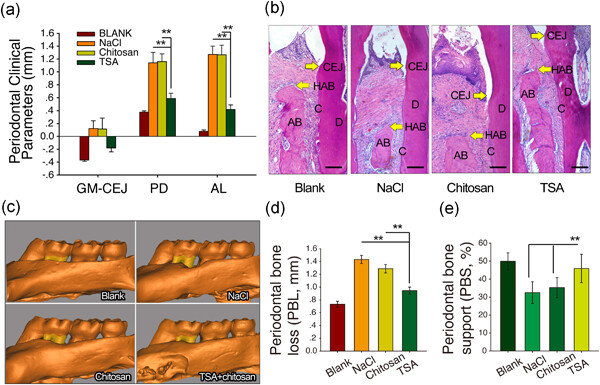
This study showed that trichostatin A (TSA) could rescue impaired osteogenic differentiation of gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cell (GMSCs) from inflammatory conditions, reduce inflammation, and promote periodontal tissue repair in vivo by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling. These results indicated that epigenetic modifiers might be a promising therapeutic approach in clinical treatments of periodontitis.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
RETRACTED: Coinhibition of S1PR1 and GP130 by siRNA-loaded alginate-conjugated trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles robustly blocks development of cancer cells
- Pages: 9702-9717
- First Published: 18 May 2020
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
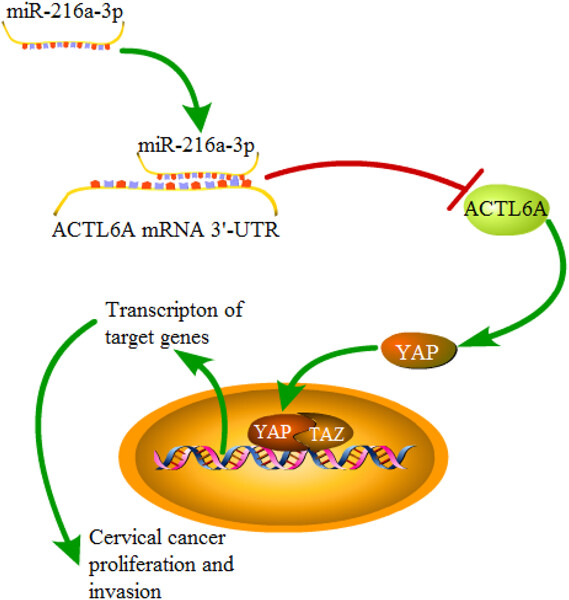
MiR-216a-3p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer through downregulation of ACTL6A-mediated YAP signaling
- Pages: 9718-9728
- First Published: 13 May 2020
Tumor-associated macrophages promote prostate cancer progression via exosome-mediated miR-95 transfer
- Pages: 9729-9742
- First Published: 14 May 2020
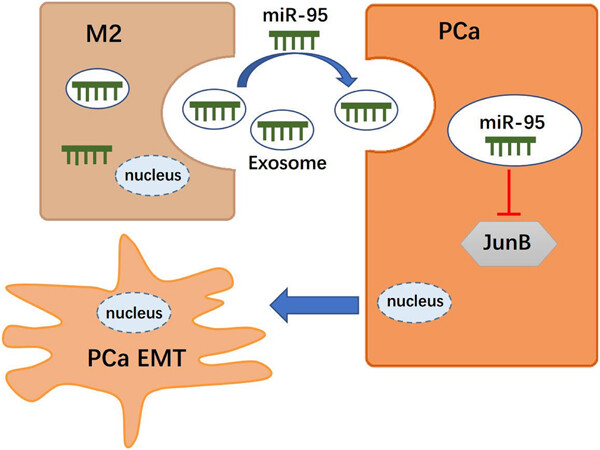
Our results demonstrated that TAM-mediated prostate cancer (PCa) progression is partially attributed to the aberrant expression of miR-95 in TAM-derived exosomes, and the miR-95/JunB axis provides the groundwork for research on tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) to further develop more-personalized therapeutic approaches for patients with PCa.
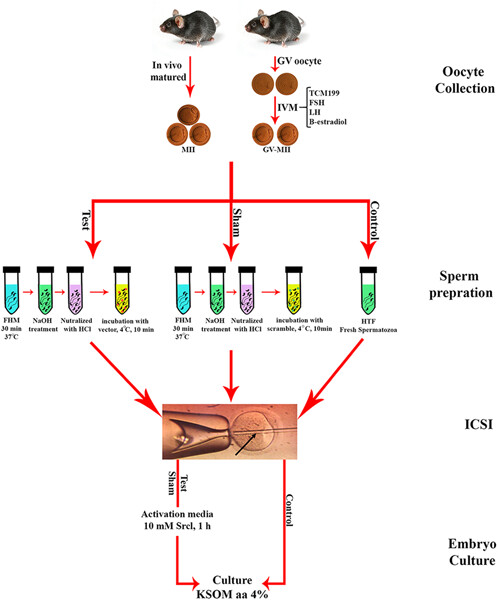
Mechanistic insights into the reduced developmental capacity of in vitro matured oocytes and importance of cumulus cells in oocyte quality determination
- Pages: 9743-9751
- First Published: 16 May 2020
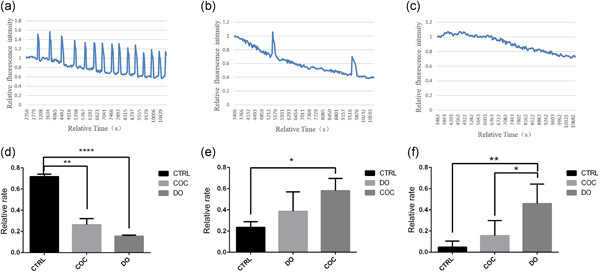
In this study, we focused on the effects of in vitro maturation (IVM) on mitochondrial function and Ca2+ oscillations in oocytes. We analyzed three groups: in vivo matured oocytes, oocytes matured in vitro with cumulus cells (cumulus oocyte complex [COC] group), and oocytes matured in vitro without cumulus cells (denuded oocyte [DO] group) in our experiments.
Upregulation of Toll-like receptor 4 through anti-miR-Let-7a enhances blastocyst attachment to endometrial cells in mice
- Pages: 9752-9762
- First Published: 16 May 2020
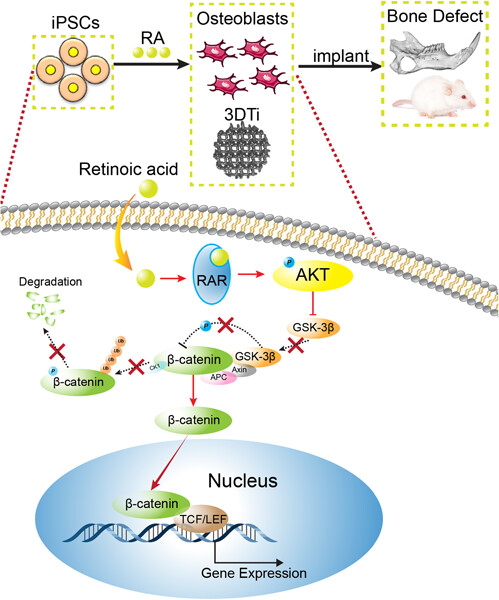
Rapid human-derived iPSC osteogenesis combined with three-dimensionally printed Ti6Al4V scaffolds for the repair of bone defects
- Pages: 9763-9772
- First Published: 18 May 2020
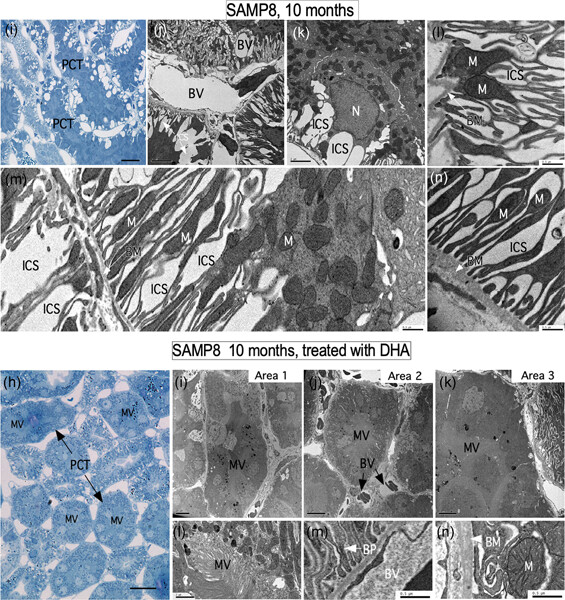
Dehydroascorbic acid, the oxidized form of vitamin C, improves renal histology and function in old mice
- Pages: 9773-9784
- First Published: 21 May 2020
Pten deletion in Dmp1-expressing cells does not rescue the osteopenic effects of Wnt/β-catenin suppression
- Pages: 9785-9794
- First Published: 11 June 2020
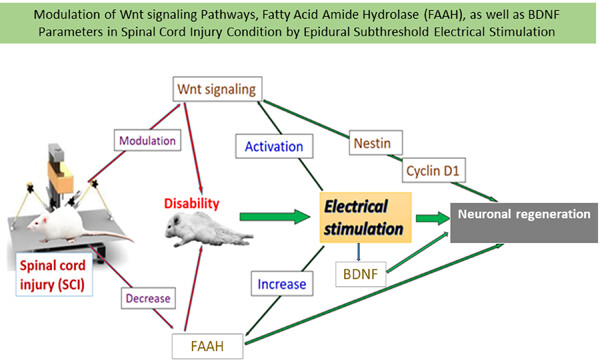
Impacts of epidural electrical stimulation on Wnt signaling, FAAH, and BDNF following thoracic spinal cord injury in rat
- Pages: 9795-9805
- First Published: 02 June 2020
Adjunctive mesenchymal stem/stromal cells augment microvascular function in poststenotic kidneys treated with low-energy shockwave therapy
- Pages: 9806-9818
- First Published: 19 May 2020
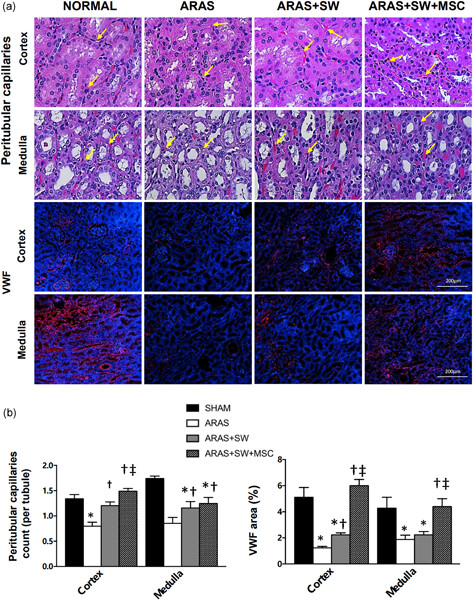
Effective therapeutic strategies are needed to preserve renal function in patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis (ARAS). The current study shows that addition of MSCs improves density of capillaries and microvascular endothelial function in vivo in SW-treated stenotic kidneys, possibly by increasing nitric oxide bioavailability, decreasing renal oxidative stress, and upregulating anti-inflammatory mediators.
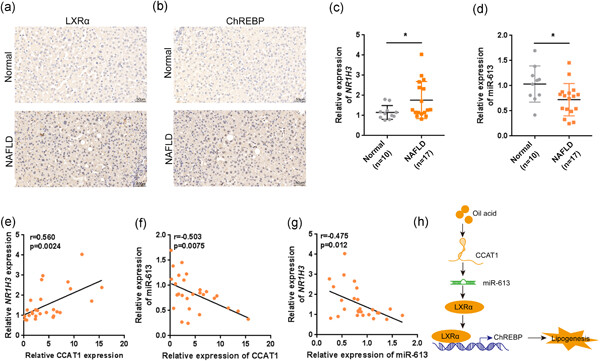
Long noncoding RNA CCAT1 inhibits miR-613 to promote nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via increasing LXRα transcription
- Pages: 9819-9833
- First Published: 15 May 2020
Identification of a four immune-related genes signature based on an immunogenomic landscape analysis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 9834-9850
- First Published: 26 May 2020
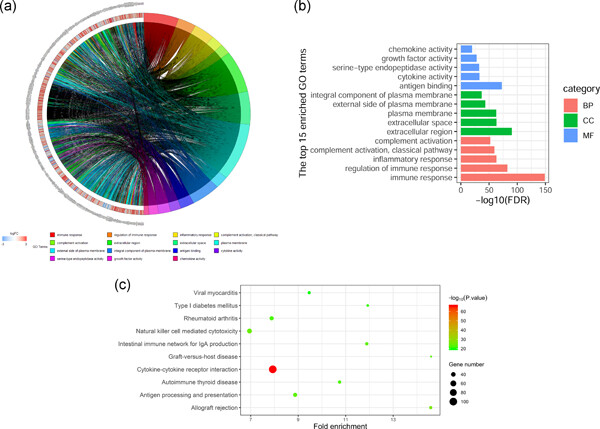
We identified a four immune-related genes (IRGs) signature consisting of four IRGs (CXCL2, SEMA3G, PDGFD, and UCN) through lasso regression and multivariate Cox regression analysis,and this four IRGs signature could effectively predict the prognosis of patients with renal clear cell carcinoma (ccRCC), and its predictive power is independent of other clinical factors. In addition, the correlation analysis of immune cell infiltration showed that this four IRGs signature could effectively reflect the level of immune cell infiltration of ccRCC.
MicroRNA-204-5p modulates mitochondrial biogenesis in C2C12 myotubes and associates with oxidative capacity in humans
- Pages: 9851-9863
- First Published: 26 May 2020

Silencing of microRNA-204-5p (miRNA-204-5p) in C2C12 myotubes enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis, via regulation of PGC-1α. In humans, low expression of miRNA-204-5p in skeletal muscle was associated high oxidative capacity. These findings identify miRNA-204-5p as an interesting modulator of mitochondrial function in human skeletal muscle.
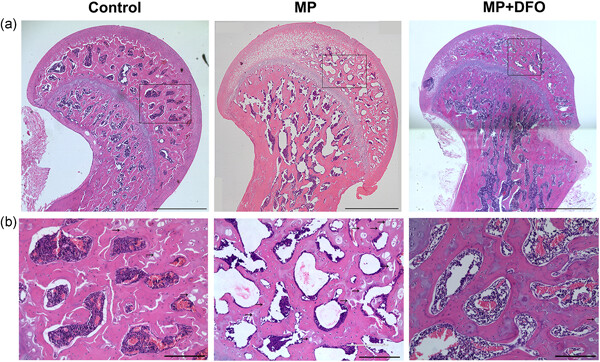
Desferoxamine protects against glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via activating HIF-1α expression
- Pages: 9864-9875
- First Published: 21 May 2020
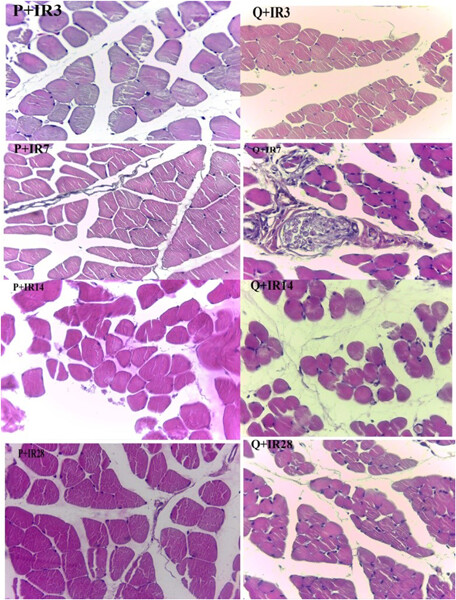
Quercetin postconditioning attenuates gastrocnemius muscle ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats
- Pages: 9876-9883
- First Published: 21 May 2020
Single-cell RNA analysis on ACE2 expression provides insights into SARS-CoV-2 potential entry into the bloodstream and heart injury
- Pages: 9884-9894
- First Published: 08 June 2020
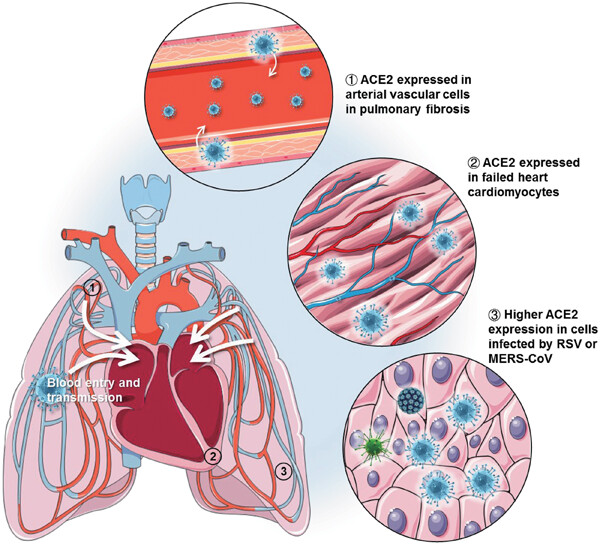
We found that angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2) expression in fibrotic lungs mainly locates in arterial vascular cells, and might provide a route for bloodstream spreading of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Failed human hearts have a higher percentage of ACE2-expressing cardiomyocytes, and SARS-CoV-2 might attack cardiomyocytes through the bloodstream in patients with heart failure. Moreover, ACE2 was highly expressed in cells infected by RSV or Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) and in mice treated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
P53 and H3K4me2 activate N6-methylated LncPGCAT-1 to regulate primordial germ cell formation via MAPK signaling
- Pages: 9895-9909
- First Published: 27 May 2020
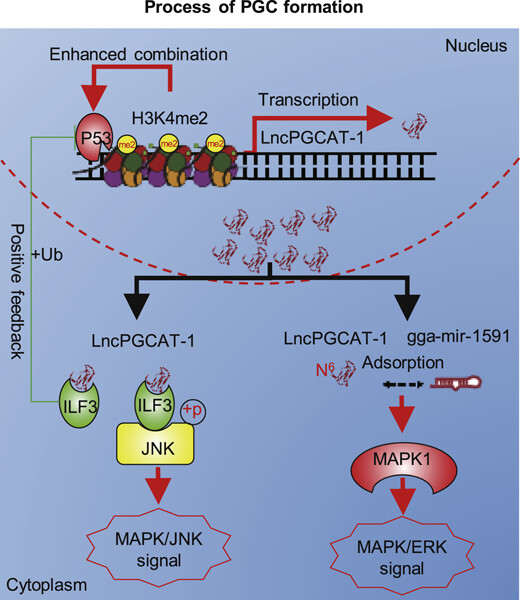
A high level of N6-methylation in LncPGCAT-1 can enhance the adsorption capacity of LncPGCAT-1 to gga-mir-1591 for activating the MAPA1/ERK signal to regulate the formation of PGC by relieving the inhibition of MAPK1 expression with gga-mir-1591. Meanwhile, LncPGCAT-1 can interact with ILF3 for regulating the ubiquitination of P53 and phosphorylation of JNK to achieve self-positive feedback regulation of LncPGCAT-1 and activation of the JNK signal, respectively, for promoting the formation of PGC.
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids inhibit the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in murine macrophages
- Pages: 9910-9921
- First Published: 26 May 2020
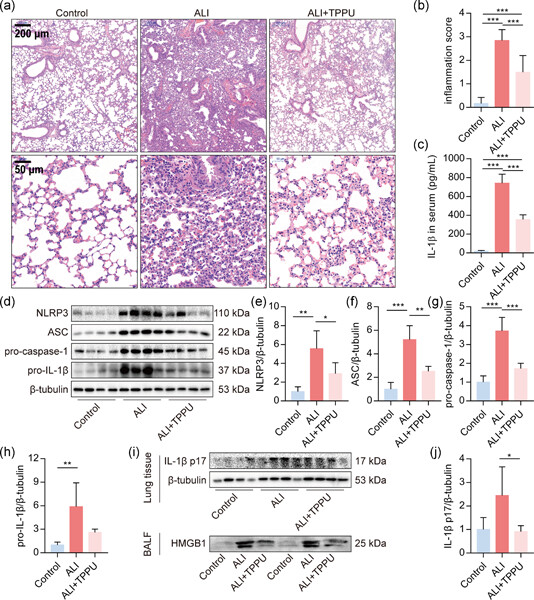
We have reported that blocking the degradation of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) derived from arachidonic acid could attenuate the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury (ALI) in mice. The underlying mechanisms remain important questions. Herein, we found that EETs inhibit the activation of nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat-containing receptor, pyrin domain-containing-3 inflammasome by suppressing calcium overload and reactive oxygen species production in macrophages, contributing to the therapeutic potency to ALI.
Human papillomavirus elevated genetic biomarker signature by statistical algorithm
- Pages: 9922-9932
- First Published: 14 June 2020
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: Paeoniflorin promotes angiogenesis and tissue regeneration in a full-thickness cutaneous wound model through the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Pages: 9933-9945
- First Published: 15 June 2020
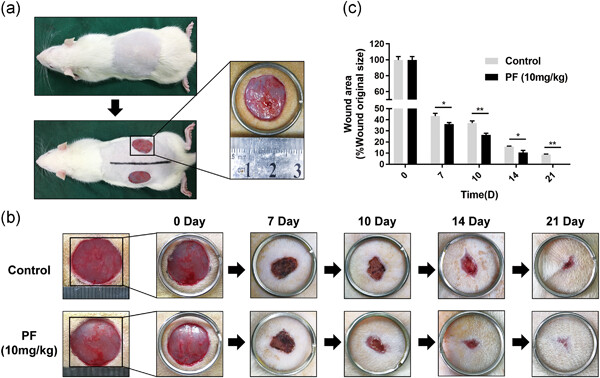
The capacity for angiogenesis in endothelial cells could be enhanced by paeoniflorin (PF) treatment via the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) pathway in vitro and could accelerate the wound healing process in vivo through collagen deposition and angiogenesis in regenerated tissue. This study provides evidence that application of PF represents a novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of cutaneous wounds.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Effects of methylation of deiodinase 3 gene on gene expression and severity of Kashin–Beck disease
- Pages: 9946-9957
- First Published: 27 May 2020
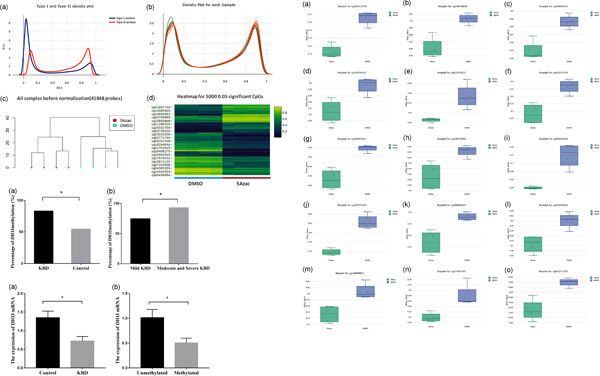
Kashin–Beck disease (KBD) is a complex endemic osteoarthropathy. We performed a bioinformatics analysis first to identify the biological mechanisms involved in selenoproteins. The methylation status of iodothyronine deiodinases 3 (DIO3) gene and DIO3 gene expression, as well as DIO3-related regulatory genes in patients with KBD, were analyzed. We found that 15 CpG sites of six selenoproteins were hypomethylated with 5-azacytidine treatment. DIO3 hypermethylation was associated with an increased risk of KBD and may lead to downregulation of DIO3 gene expression as well as be an indicator of the severity of KBD, which may provide a new insight for gene–environment correlations and interactions in etiology and pathogenesis of KBD.
Cre/loxP approach-mediated downregulation of Pik3c3 inhibits the hypertrophic growth of renal proximal tubule cells
- Pages: 9958-9973
- First Published: 31 May 2020
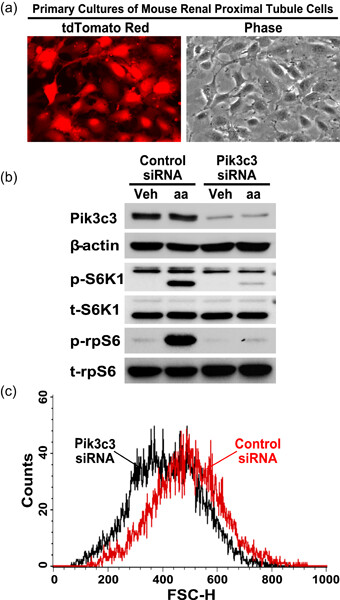
Using Cre-loxP-based approaches, we for the first time demonstrated that tamoxifen-induced Cre-recombinase-mediated downregulation of Pik3c3 expression in renal proximal tubule cells alone is sufficient to significantly inhibit UNX- or amino acid-stimulated mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling to phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6) and, consequently, prevent UNX- or amino acid-induced hypertrophic nephron growth in adult mice. Our additional cell culture experiments using RNAi confirmed that knocking down Pik3c3 expression inhibits amino acid-stimulated mTORC1–S6K1 signaling activity and blunts cellular growth in the primary cultures of renal proximal tubule cells. Together, both in vivo and in vitro experimental results in the present study indicate that Pik3c3 is a major mechanistic mediator responsible for sensing amino acid availability and initiating hypertrophic growth of renal proximal tubule cells by activation of the mTORC1–S6K1–rpS6 signaling pathway through a mechanism of recruiting mTOR to its activation site—the lysosomal membranes.
A possible role for inducible arginase isoform (AI) in the pathogenesis of chronic venous leg ulcer
- Pages: 9974-9991
- First Published: 27 May 2020
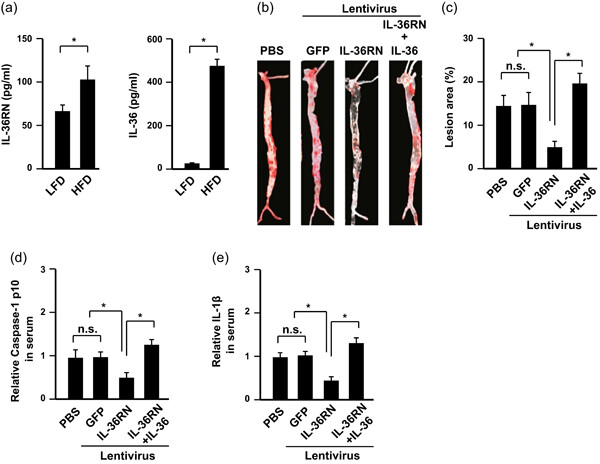
Interleukin-36 receptor antagonist attenuates atherosclerosis development by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome
- Pages: 9992-9996
- First Published: 02 June 2020
Arginase-II promotes melanoma migration and adhesion through enhancing hydrogen peroxide production and STAT3 signaling
- Pages: 9997-10011
- First Published: 29 May 2020
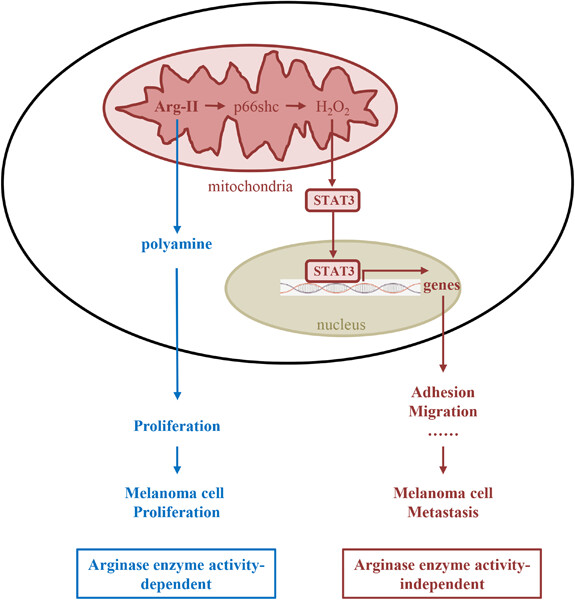
Arginase type II (Arg-II) promotes melanoma cell proliferation dependently of its enzymatic activity, while promotes metastasis-related migration and adhesion to endothelial cells through H2O2-STAT3 pathway independently of the enzymatic activity.
Suppressing Arg-II expression rather than inhibiting its enzymatic activity may represent a novel strategy for the treatment of melanoma.
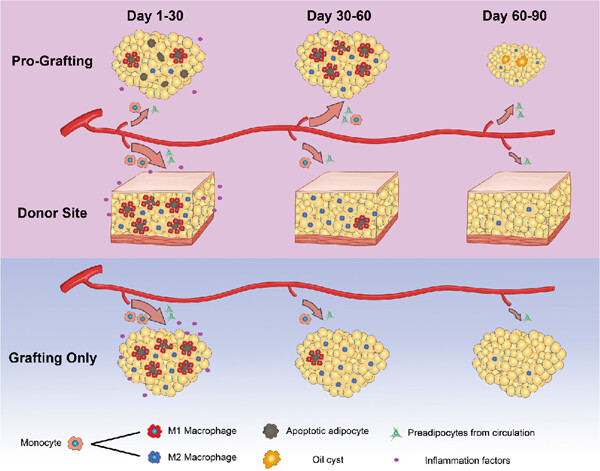
The effects of macrophage-mediated inflammatory response to the donor site on long-term retention of a fat graft in the recipient site in a mice model
- Pages: 10012-10023
- First Published: 17 June 2020
miR-448-3p alleviates diabetic vascular dysfunction by inhibiting endothelial–mesenchymal transition through DPP-4 dysregulation
- Pages: 10024-10036
- First Published: 15 June 2020
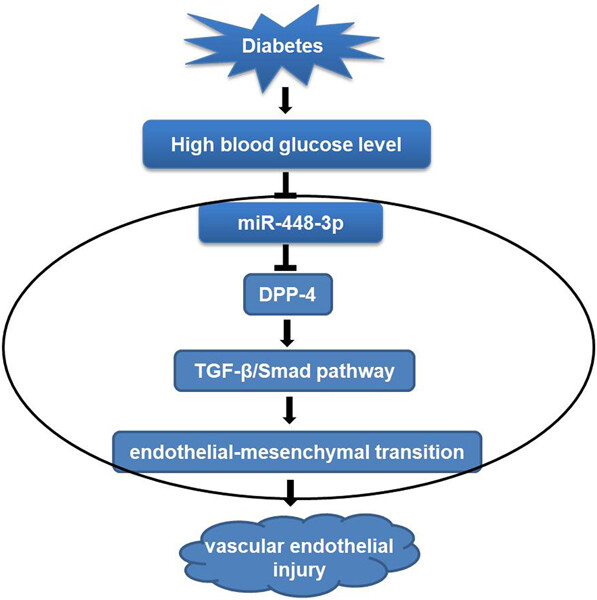
The dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) was identified as a direct and functional target of miR-448-3p in the development of diabetic vascular dysfunction. miR-448-3p alleviated the aortic endothelium damage via inhibited endothelial–mesenchymal transition (EndMT) by degrading DPP-4. Moreover, DPP-4 might regulate EndMT through the transforming growth factor-β/Smad pathway in diabetic endothelial dysfunction.
Suppression of TRPM7 enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells
- Pages: 10037-10050
- First Published: 29 May 2020
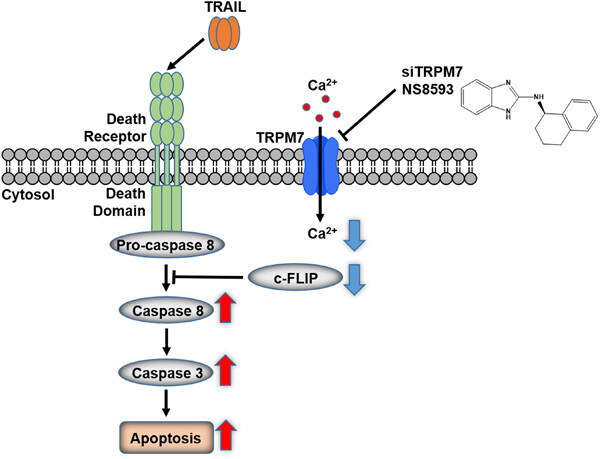
We demonstrate that suppression of transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 7 (TRPM7) via TRPM7 knockdown or pharmacological inhibition synergistically increases TRAIL-induced antiproliferative effects and apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. Furthermore, we show that the synergistic interaction might be associated with TRPM7 channel activities using combination treatments of TRAIL and TRPM7 inhibitors (NS8593 as a TRPM7 channel inhibitor and TG100-115 as a TRPM7 kinase inhibitor). We reveal that downregulation of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) via inhibition of Ca2+ influx might be involved in the synergistic interaction.
miR-34a/c induce caprine endometrial epithelial cell apoptosis by regulating circ-8073/CEP55 via the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways
- Pages: 10051-10067
- First Published: 31 May 2020
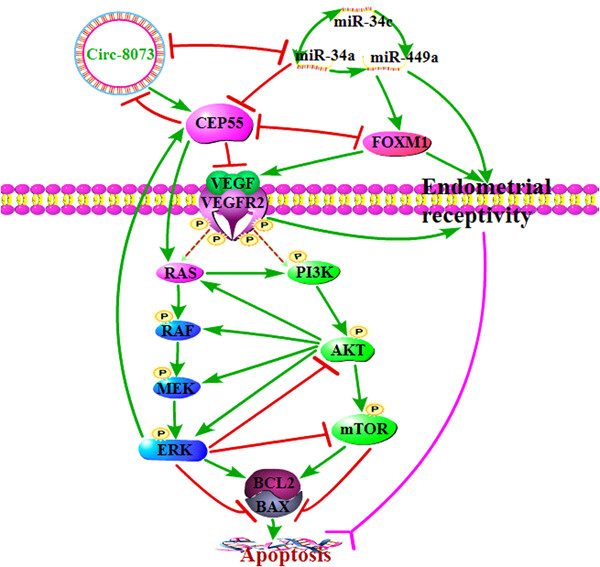
microRNAs (miRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs) are important for endometrial receptivity establishment and embryo implantation in mammals. These results suggest that miR-34a/c not only induce caprine endometrial epithelial cell (CEEC) apoptosis by binding to circ-8073 and CEP55 via the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways, but may also regulate RE establishment in dairy goats.
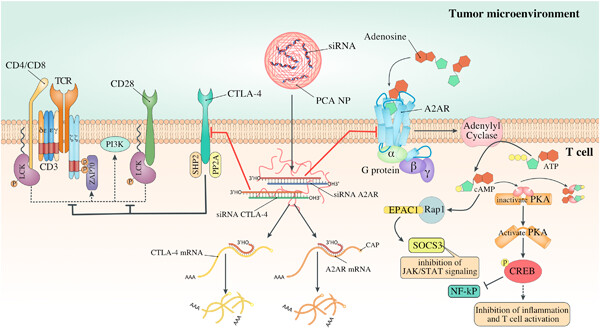
Concomitant blockade of A2AR and CTLA-4 by siRNA-loaded polyethylene glycol-chitosan-alginate nanoparticles synergistically enhances antitumor T-cell responses
- Pages: 10068-10080
- First Published: 02 June 2020
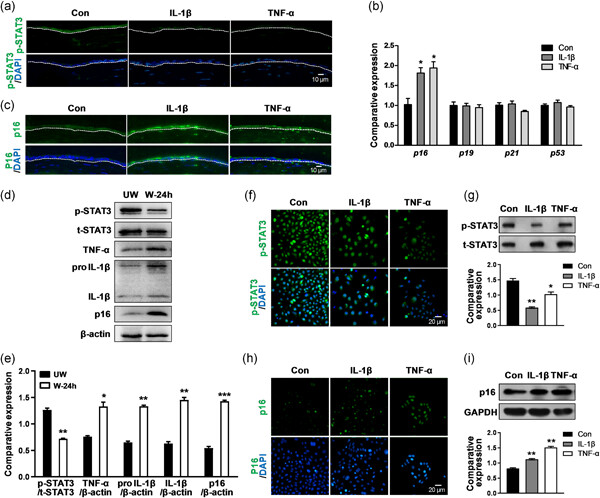
The proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α modulate corneal epithelial wound healing through p16Ink4a suppressing STAT3 activity
- Pages: 10081-10093
- First Published: 31 May 2020
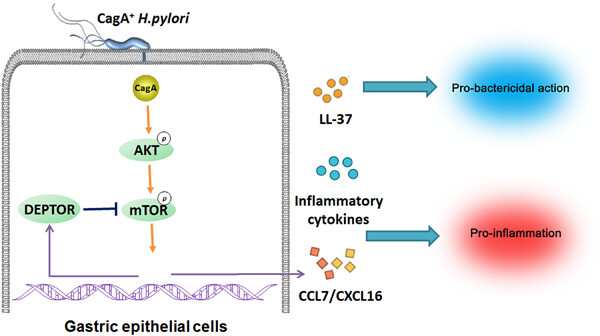
Helicobacter pylori promote inflammation and host defense through the cagA-dependent activation of mTORC1
- Pages: 10094-10108
- First Published: 28 July 2020
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Image duplication in E Galmozzi et al, J Cell Physiol, 200 (2004), pp. 82-88
- Page: 10109
- First Published: 14 May 2020
FROM THE BENCH
MORPHEUS: An automated tool for unbiased and reproducible cell morphometry
- Pages: 10110-10115
- First Published: 21 June 2020
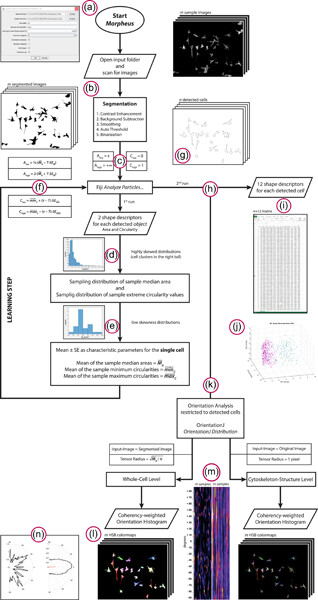
Here we present MORPHEUS, a new Fiji/ImageJ2 plugin for the automated evaluation of cell morphometry from images acquired by fluorescence microscopy. The whole algorithm is implemented as a one-click procedure, thus minimizing the user's intervention. By reducing biases and errors of human origin, MORPHEUS is intended to be a useful tool to enhance reproducibility in bioimage analysis