Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Covers
Cover Picture: Crystal Structure and NMR of an α,δ-Peptide Foldamer Helix Shows Side-Chains are Well Placed for Bifunctional Catalysis: Application as a Minimalist Aldolase Mimic (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36/2023)
- First Published: 19 July 2023

A helical catalyst that is constructed from α- and δ-amino acids: In their Research Article (e202305326), Alexander J. A. Cobb et al. present a foldamer helix whereby the catalytic functionalities are positioned in such a way that they can be exploited for bifunctional catalysis. The stability of the helix and the modularity of the system (represented by the jigsaw pieces) means that different α-amino acids can be used whilst maintaining the same helix type. The foldamer catalyst described acts as an aldolase (where a molecule is essentially split into two as depicted by the graphic).
Inside Cover: Thiol-Aldehyde Polycondensation for Bio-based Adaptable and Degradable Phenolic Polymers (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36/2023)
- First Published: 20 June 2023

A thiol–aldehyde polycondensation was developed for the polymerization of phenolic compounds. In their Research Article (e202305677), Shichao Xu, Liang Yuan et al. found several catalysts for making linear and network-structured phenolic polymers from plant-derived monomers. Since the repeating units are connected via dynamic dithioacetal groups, the cross-linked networks can be reprocessed and oxidatively degraded by DMSO to recover the monomers for reuse.
Inside Back Cover: Fast and Tunable Phosphorescence from Organic Ionic Crystals (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36/2023)
- First Published: 19 July 2023

Harvesting organic phosphorescence is essential for many fields in energy and materials sciences related to light generation. In their Research Article (e202305108), Andreas Steffen, Andrey Belyaev, Pi-Tai Chou, Igor O. Koshevoy et al. show that the anion–π interactions in crystalline diphosphonium iodides induce unusually fast room temperature triplet emission, which is associated with the external heavy atom effect and anion–π charge-transfer character of the excited states. This makes ionic luminophores a new design strategy beyond transition metals and organic delayed fluorophores.
Back Cover: Bilayer-Coating Strategy for Hydrophobic Nanoparticles Providing Colloidal Stability, Functionality, and Surface Protection in Biological Media (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 36/2023)
- First Published: 19 July 2023

A bilayer consisting of oleate and dodecylamine provides excellent colloidal stability and versatility to nanoparticles with upconversion luminescence. This surface modification strategy can be achieved in a fast and easy one-step reaction, as demonstrated by María J. Marín, Thomas Hirsch et al. in their Research Article (e202305165).
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Sandwich-Kernelled AgCu Nanoclusters with Golden Ratio Geometry and Promising Photothermal Efficiency
- First Published: 30 August 2023

Nanoclusters. A silver-copper nanocluster with a golden ratio pentangle structure was prepared by Nan Yan, Zhikun Wu et al. in their Research Article (e202305604). The cluster shows promising photothermal conversion efficiency.
Guest Editorial
Rethinking Chemistry
Rethinking Chemistry
- First Published: 30 August 2023
Climate change, loss of natural resources, and geopolitical conflicts are some of the global challenges humanity faces. As chemists, we have the unique possibility and the duty to contribute to a livable future for all. “Rethinking Chemistry” is the motto of the German Chemical Society Science Forum Chemistry (WiFo) 2023 to address these challenges as the guiding principle of all our endeavors and actions.
Graphical Abstract
Corrigenda
Corrigendum: Highly Reactive Hydrocarbon Soluble Alkylsodium Reagents for Benzylic Aroylation of Toluenes using Weinreb Amides
- First Published: 27 July 2023
Corrigendum: Exploiting Ru-Induced Lattice Strain in CoRu Nanoalloys for Robust Bifunctional Hydrogen Production
- First Published: 30 August 2023
Introducing …
Christos Pliotas
- First Published: 06 July 2023

“A turning point in my career was solving the structure of a mechanosensitive ion channel in the open state … If I could be granted a superpower, it would be the ability to travel in time because I could meet my science heroes and have the opportunity to learn from the best.” Find out more about Christos Pliotas in his Introducing … Profile.
Liang Yuan
- First Published: 10 July 2023

“My favorite material is rosin. It is sustainably available from the extrusion of pine trees and from papermill waste and has so many successful commercial applications … My favorite thing about my lab group is when a student excitedly tells me something unexpected and describes puzzling experimental observations.” Find out more about Liang Yuan in his Introducing … Profile.
Minireviews
Carbenes
1,3-Imidazole-Based Mesoionic Carbenes and Anionic Dicarbenes: Pushing the Limit of Classical N-Heterocyclic Carbenes
- First Published: 03 May 2023
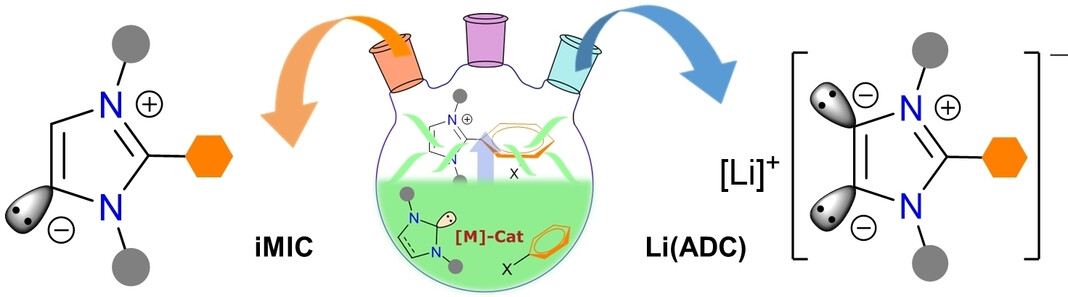
Mesoionic carbenes (iMICs) and anionic dicarbenes (ADCs) are readily accessible by the deprotonation of C2-arylated 1,3-imidazolium salts, which are prepared by the direct C2-arylation of classical N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs). The implications of iMICs as potent σ-donor ligands in organometallic catalysis and ADCs as unique building-blocks in accessing conceptually new main-group heterocycles with an annulated C4E2 ring are showcased.
Nanostructures
Stabilizing Liquids Using Interfacial Supramolecular Assemblies
- First Published: 17 May 2023
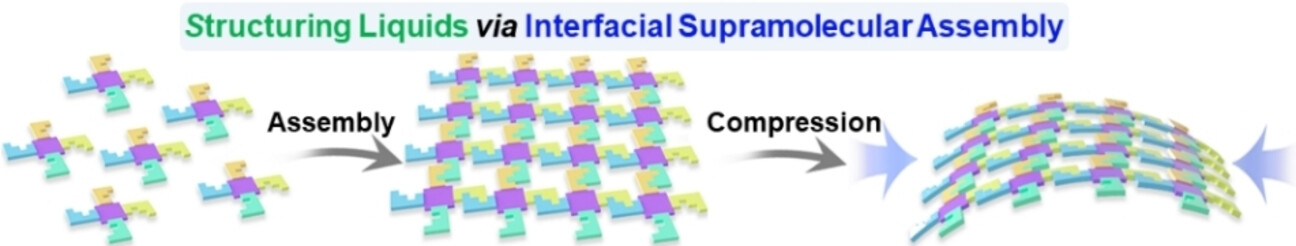
Stabilizing liquids based on supramolecular assembly (non-covalent intermolecular interactions) has attracted significant interest, due to the increasing demand for soft, liquid-based devices. Recent advances in structuring liquids based on non-covalent intermolecular interactions are highlighted and a perspective is provided on future directions to inspire further studies on structured liquids based on supramolecular assembly.
Reviews
Biomass Valorization
Radical-Mediated Photocatalysis for Lignocellulosic Biomass Conversion into Value-Added Chemicals and Hydrogen: Facts, Opportunities and Challenges
- First Published: 10 May 2023
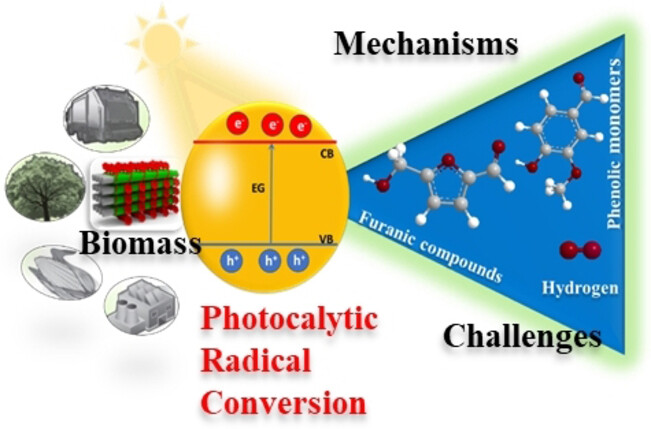
This review discusses recent developments in the chemistry of photocatalytic biomass conversion into chemicals and fuels, emphasizing the role of experimental factors and materials design. A critical technological analysis to facilitate the scaling up of this technology is provided based on the reported research studies and industrial need.
Isotopic Labeling
Modern Strategies for Carbon Isotope Exchange
- First Published: 19 April 2023
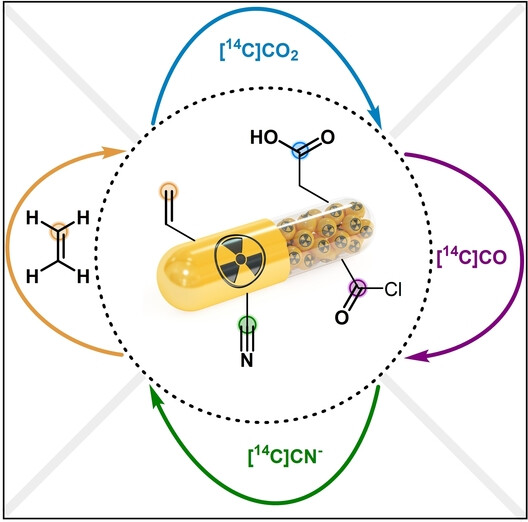
The field of carbon isotope labeling has recently explored new alternative avenues for better dealing with the hurdles of radiochemistry. This review focuses on the emerging opportunities provided by carbon isotope exchange (CIE) technologies. By dramatically reducing the number of steps and radioactive waste generated in preparation of tracers, CIE has great potential for accelerating clinical development of pharmaceuticals.
Research Articles
Nanoclusters
Sandwich-Kernelled AgCu Nanoclusters with Golden Ratio Geometry and Promising Photothermal Efficiency
- First Published: 19 May 2023
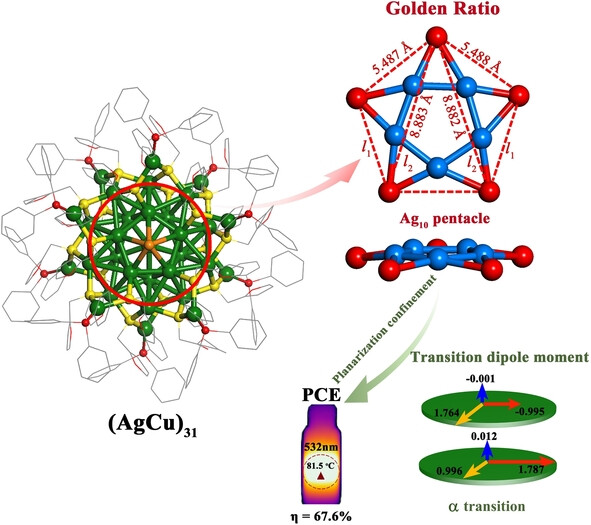
A silver copper nanocluster with a golden ratio pentangle structure is prepared. It shows promising photothermal conversion. It is a novel alloy nanocluster with a sandwich-like kernel (diameter≈0.9 nm and length≈0.25 nm), and gives insight into the relationship between structure and photothermal properties.
Glycoproteomics
Click-iG: Simultaneous Enrichment and Profiling of Intact N-linked, O-GalNAc, and O-GlcNAcylated Glycopeptides
- First Published: 10 July 2023
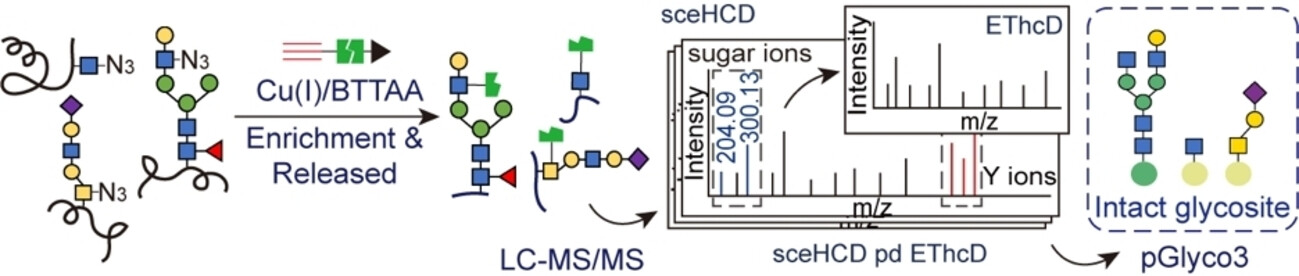
A glycoproteomics platform, Click-iG, is reported that integrates metabolic labeling of glycans with clickable unnatural sugars, an optimized MS method, and a tailored version of pGlyco3 software to enable simultaneous enrichment and profiling of three types of intact glycopeptides: N-linked, mucin-type O-linked, and O-GlcNAcylated glycopeptides.
Photocatalysis
Cl2⋅− Mediates Direct and Selective Conversion of Inert C(sp3)−H Bonds into Aldehydes/Ketones
- First Published: 06 July 2023
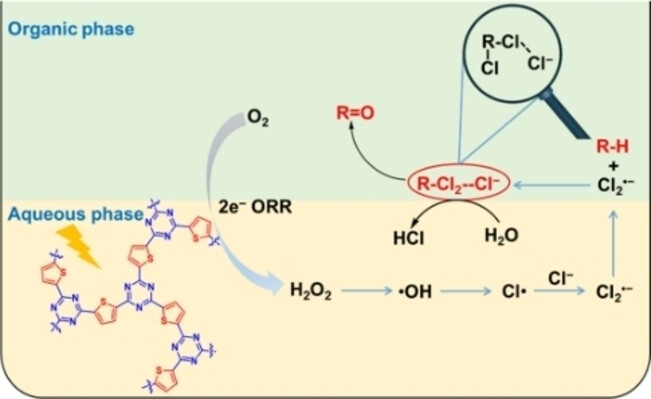
A thiophene-based covalent triazine polymer facilitates effective conversion of O2→H2O2→⋅OH→Cl⋅→Cl2.− in the aqueous phase. Cl2.−, with a longer lifetime, transfers into organic phase and activates C(sp3)−H bonds to generate unstable dichlorinated intermediates by successive hydrogen abstraction and chlorination. These unstable intermediates hydrolyze into either aldehydes or ketones with higher selectivity than that of benzyl dichloride.
Organic Crystals | Hot Paper
Fast and Tunable Phosphorescence from Organic Ionic Crystals
- First Published: 25 May 2023
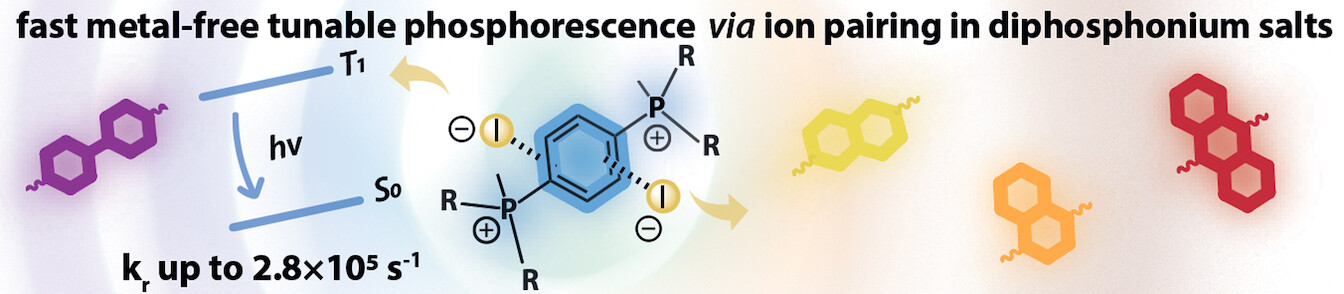
The photoluminescence mechanism of crystalline diphosphonium iodide salts strongly depends on anion-π interactions. In the case of iodide–π charge transfer combined with electrostatically controlled packing effects, high quantum yields (Φem up to 0.75) and fast radiative rate constants (kr of up to 2.77×105 s−1) of phosphorescence have been realized at room temperature, which are exceptionally rare for metal-free systems.
Foldamers
Crystal Structure and NMR of an α,δ-Peptide Foldamer Helix Shows Side-Chains are Well Placed for Bifunctional Catalysis: Application as a Minimalist Aldolase Mimic
- First Published: 23 May 2023
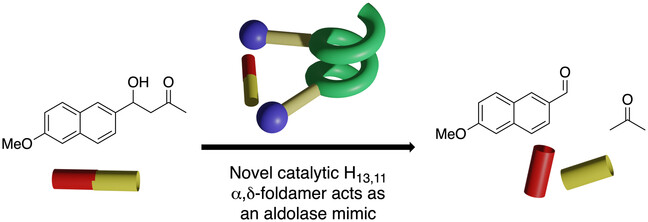
A new catalytic foldamer constructed of α- and bespoke δ-residues forms a helix which is not only stabilized by intramolecular H-bonds, but also by apolar interactions not observed in foldamer secondary structures until now. The resulting scaffold gives a useful juxtaposition of functionality and leads to bifunctional catalysis as demonstrated through an aldolase-like process.
Polymerization | Very Important Paper
Thiol-Aldehyde Polycondensation for Bio-based Adaptable and Degradable Phenolic Polymers
- First Published: 19 May 2023
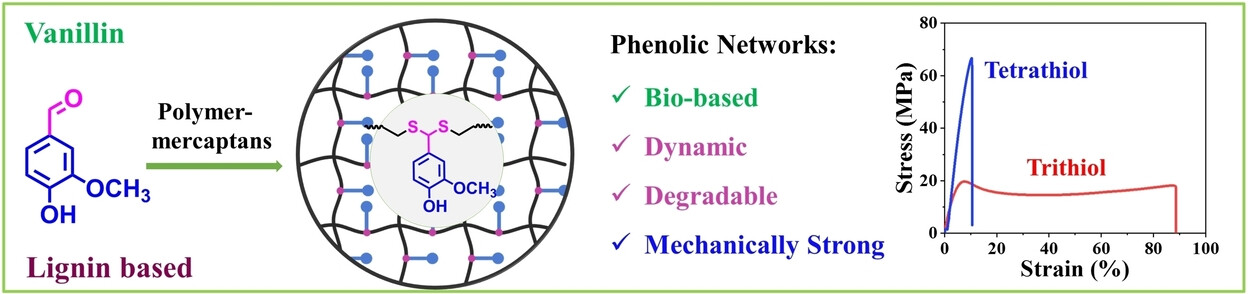
Lignin and synthetic phenolic polymers are difficult to degrade and reprocess. Through thiol-aldehyde polycondensation, degradable and reprocessable phenolic polymers with tensile strength up to 64 MPa were prepared from bioderived phenolic compounds. The developed method is promising for facile preparation of macromolecular antioxidants and dynamic networks.
Mass Spectrometry
Infrared Multiphoton Dissociation Enables Top-Down Characterization of Membrane Protein Complexes and G Protein-Coupled Receptors
- First Published: 17 June 2023
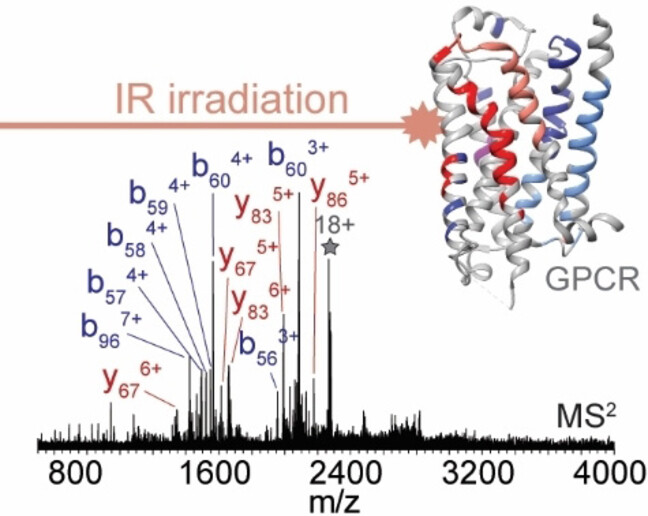
Top-down mass spectrometry using infrared multiphoton dissociation (IRMPD) of native membrane proteins such as G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) provides good sequence coverage from native protein ions. We observe successive cleavage of adjacent amino acids, specifically within transmembrane helices, enabling unambiguous identification of membrane proteins and their complexes.
CO2 Adsorption | Hot Paper
Highly Cooperative CO2 Adsorption via a Cation Crowding Mechanism on a Cesium-Exchanged Phillipsite Zeolite
- First Published: 12 June 2023
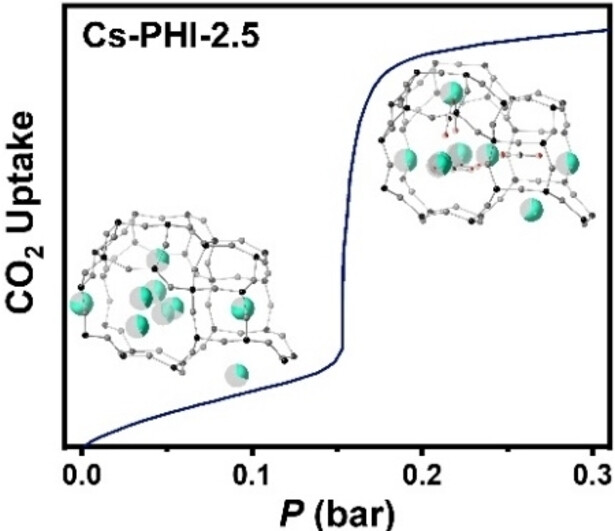
Highly cooperative CO2 adsorption on a flexible cesium-exchanged phillipsite, a channel-based small-pore zeolite, is operated by an unprecedented adsorption phenomenon: structural breathing (the narrow-to-wide pore) is associated with the crowding and dispersal of large Cs+ ions, depending on the CO2 pressure, termed the ‘cation crowding’ mechanism.
Organic Chemistry
Copper-Phosphido Catalysis: Enantioselective Addition of Phosphines to Cyclopropenes
- First Published: 18 June 2023
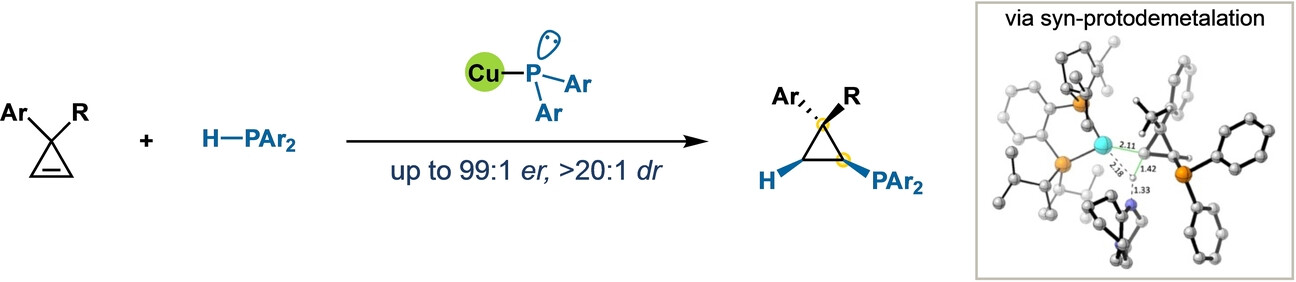
An enantioselective hydrophosphination of cyclopropenes that occurs at ambient temperature is reported. It proceeds through a copper-phosphido intermediate while various cyclopropylphosphines can now be accessed in high yields and enantioselectivities. Enrichment of phosphorus stereocenters is also demonstrated via a dynamic kinetic asymmetric transformation (DyKAT) process. Experimental studies and DFT calculations provide mechanistic insight.
Renewable Polymers | Very Important Paper
A Generic Platform for Upcycling Polystyrene to Aryl Ketones and Organosulfur Compounds
- First Published: 13 July 2023
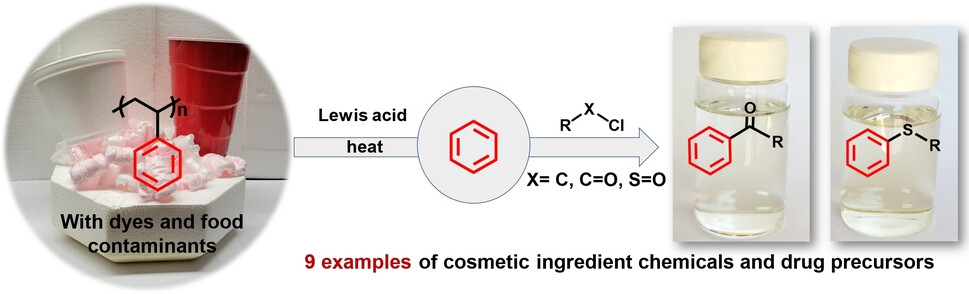
Thermochemical degradation utilizing AlCl3 recovers benzene from polystyrene in quantitative yields. The subsequent addition of acyl/alkyl and sulfinyl chlorides to the same reactor produces aryl ketones and sulfides in moderate to high yields. The one-pot cascade degradation–upcycling reactions present an effective strategy for converting polystyrene to valuable chemicals, including benzophenone, acetophenone, and diphenyl sulfide.
Synthetic Methods
[2+2+1+1] Cycloaddition for de novo Synthesis of Densely Functionalized Phenols
- First Published: 10 July 2023
![[2+2+1+1] Cycloaddition for de novo Synthesis of Densely Functionalized Phenols](/cms/asset/ac3a33ff-3932-4fe0-8d9b-a5a753fbe266/anie202307251-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Densely functionalized phenols can be easily obtained through formal [2+2+1+1] cycloaddition of two different alkynes and two molecules of CO. The new benzannulation strategy allows efficient regioselective installation of up to five different substituents on a phenol ring. The resulting phenols have a substitution pattern different from and complementary to those obtained from Dötz and Danheiser benzannulations.
Synthetic Methods | Hot Paper
Redox Reorganization: Aluminium Promoted 1,5-Hydride Shifts Allow the Controlled Synthesis of Multisubstituted Cyclohexenes
- First Published: 26 June 2023
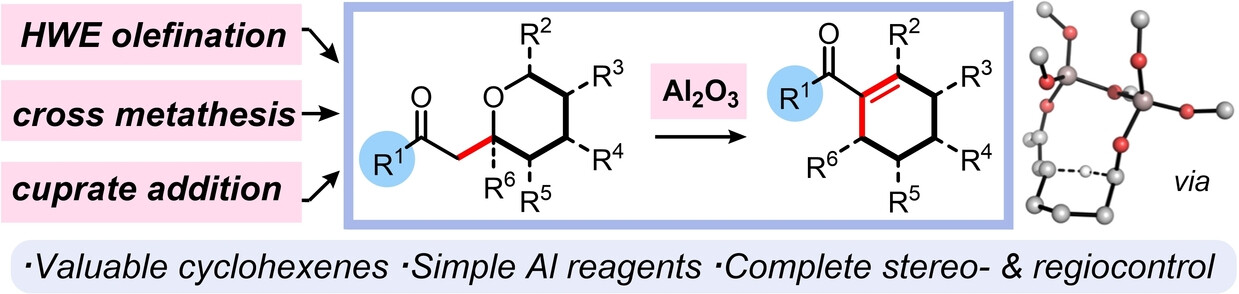
An efficient synthesis of multisubstituted cyclohexenes has been achieved from tetrahydropyrans (easily accessible via many synthetic approaches). The process operates via a tandem 1,5-hydride shift–aldol condensation mediated by simple aluminium reagents (e.g. Al2O3), enabling the synthesis of cyclohexenes (>40 examples) bearing substituents at each position around the cyclohexene ring with high levels of chemo-, stereo- and regioselectivity.
Antibodies
Trimming Crystallizable Fragment (Fc) Glycans Enables the Direct Enzymatic Transfer of Biomacromolecules to Antibodies as Therapeutics
- First Published: 12 July 2023
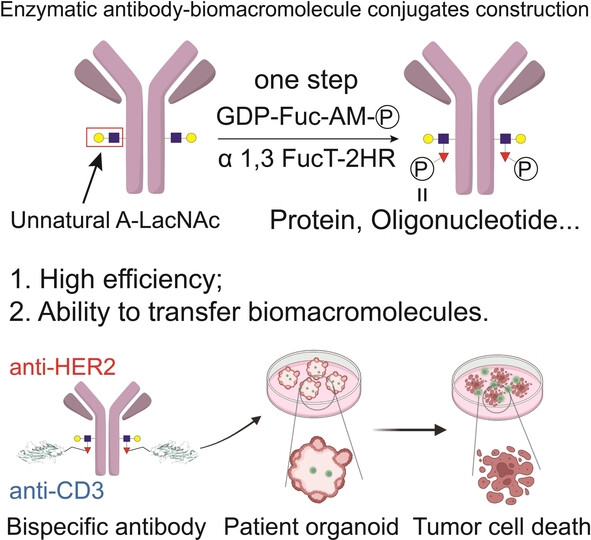
Reducing the complexity of crystallizable fragment glycans dramatically increased the efficiency of the conjugation of large payloads to antibodies via fucosyltransferase-mediated unnatural fucosylation. An anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and anti-cluster of differentiation 3 bispecific antibody was synthesized which enabled the recruitment and activation of endogenous cytolytic T lymphocyte cells for tumor killing within organoids.
Nitrogen Reduction Reaction | Very Important Paper
Eliminating Concentration Polarization with Cationic Covalent Organic Polymer to Promote Effective Overpotential of Nitrogen Fixation
- First Published: 13 July 2023
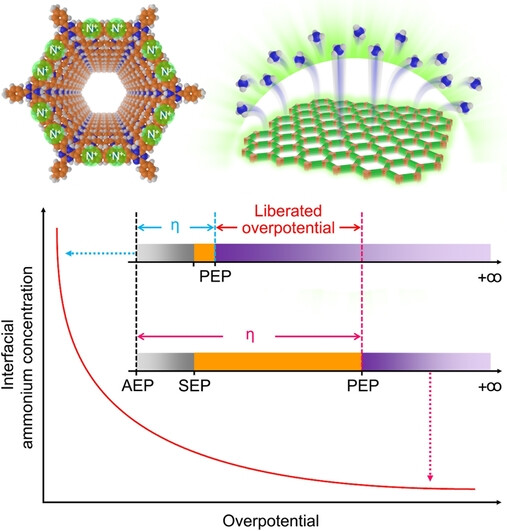
A novel covalent organic polymer with ordered periodic cationic sites is proposed to tackle the concentration polarization and drive the equilibrium of the nitrogen reduction reaction in the forward direction. With the given potential unchanged, the suppressed overpotential can be much liberated, ultimately leading to a 24-fold improvement generated in the Faradaic efficiency (73.74 %).
Reversible Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Deciphering Reversible Homogeneous Catalysis of the Electrochemical H2 Evolution and Oxidation: Role of Proton Relays and Local Concentration Effects
- First Published: 19 April 2023
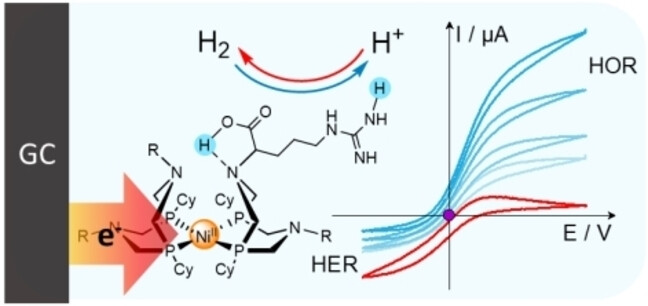
Analytical treatment allows determining all thermodynamic and kinetic parameters of reversible electrocatalytic oxidation and production of dihydrogen mediated by DuBois/Shaw nickel bisdiphosphine complexes bearing pendant bases. This analysis shed light on the key activity descriptors responsible for reversible vs. bidirectional catalysis and paves the way towards rational optimization of such molecular catalysts
Cooperative Photocatalysis
Coupling Benzylamine Oxidation with CO2 Photoconversion to Ethanol over a Black Phosphorus and Bismuth Tungstate S-Scheme Heterojunction
- First Published: 30 June 2023
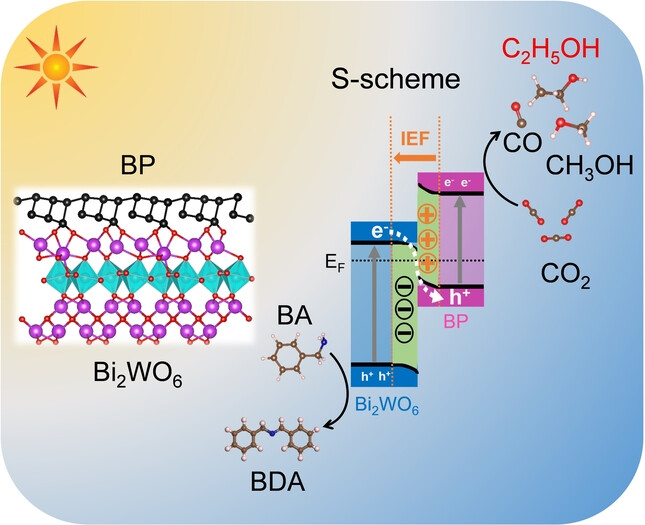
Photocatalytic CO2 reduction for efficient ethanol production is challenging. A 2D/2D S-Scheme heterojunction comprised of black phosphorus and bismuth tungstate (BP/BWO) was constructed for CO2 reduction, coupled with benzylamine (BA) oxidation to N-benzylidenebenzylamine (BDA). The catalyst generates ethanol with high yield and selectivity. This work provides insight into heterogeneous photocatalysts based on cooperative photoredox systems.
Peptide Self-Assembly
Dynamic Control of Cyclic Peptide Assembly to Form Higher-Order Assemblies
- First Published: 06 July 2023
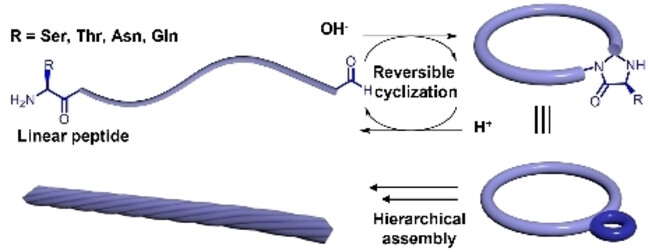
Asymmetrical cyclic peptides constructed by dynamic covalent chemistry provide a platform for the investigation of naturally occurring chirality inversion, ring-chain tautomerism, and hierarchical assembly. The insertion of a 4-imidazolidinone ring promotes the formation of intertwined nanostructures. The reversibility can be tuned by changing the pH value without producing other chemical waste except water.
Reaction Mechanisms
Mechanisms of Cysteine-Lysine Covalent Linkage—The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species and Competition with Disulfide Bonds
- First Published: 09 June 2023
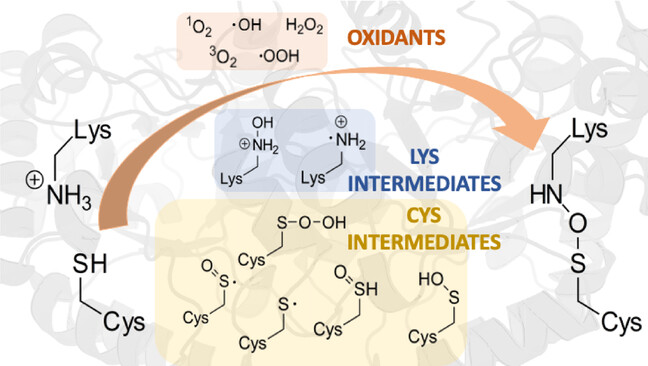
An unusual “NOS” bond with a bridging oxygen atom can form under oxidising conditions between a cysteine and a lysine residue. Now the reaction mechanisms for the formation of single and double NOS bonds in proteins have been computationally investigated. More than 30 reactions were considered for oxidation pathways involving different reactive oxygen species, providing a comprehensive overview of cysteine oxidation pathways.
Photoanode Materials
Enhanced Spatial Charge Separation in a Niobium and Tantalum Nitride Core-Shell Photoanode: In Situ Interface Bonding for Efficient Solar Water Splitting
- First Published: 18 July 2023
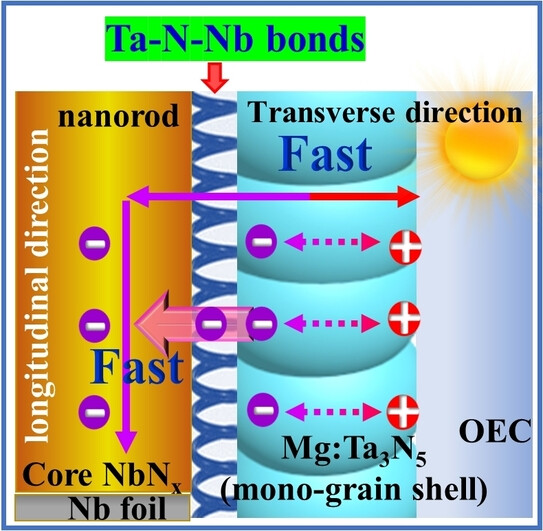
Highly efficient electron/hole separation and collection has been achieved by in situ interface bonding of an ultrathin high-crystallinity Ta3N5 mono-grain shell and conductive NbNx nanorod core. The photoanode attains a photocurrent density of 7 mA cm−2 at 1.23 V RHE with a Ta3N5 shell thickness of less than 30 nm.
G-Quadruplexes | Hot Paper
Organic-Platinum Hybrids for Covalent Binding of G-Quadruplexes: Structural Basis and Application to Cancer Immunotherapy
- First Published: 18 July 2023
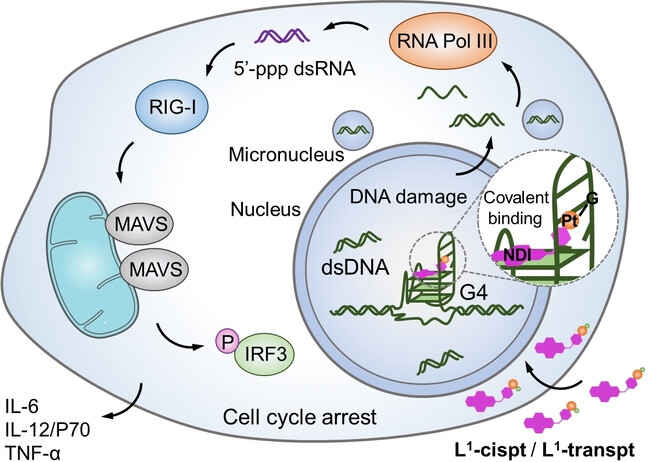
A novel class of G4-targeting organic-platinum hybrids, L1-cispt and L1-transpt, designed to covalently bind to the G4 binding site, could activate the retinoic acid-induced gene I (RIG-I) pathway, induce immunogenic cell death (ICD) and stimulate potent immunotherapy in vivo. This study highlights the importance of the rational combination of specific spatial recognition and covalent binding in G4-targeting drug design.
Supramolecular Chemistry | Hot Paper
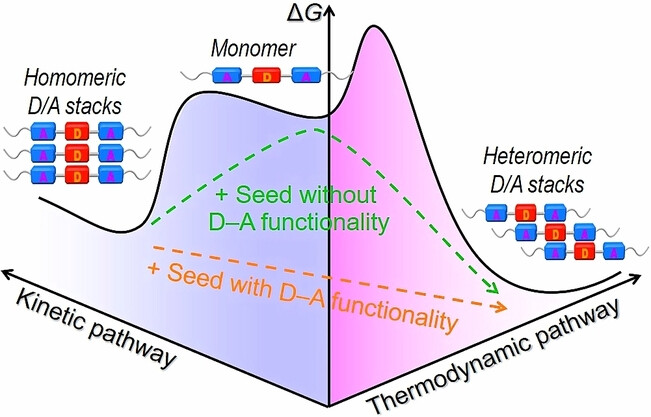
Pathway Control of π-Conjugated Supramolecular Polymers by Incorporating Donor-Acceptor Functionality
- First Published: 11 July 2023
Sustainable Polymers | Hot Paper
Closed-Loop Recycling of Vinylogous Urethane Vitrimers
- First Published: 13 July 2023
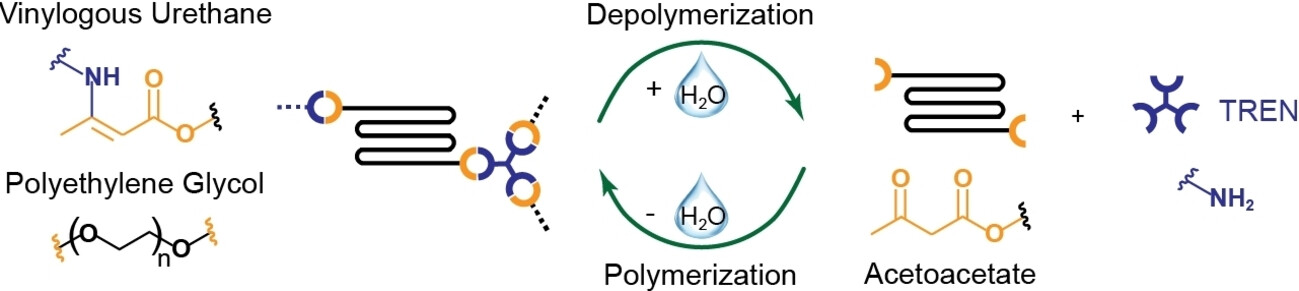
The closed-loop recycling of vinylogous urethane vitrimers made from acetoacetate-terminated polyethyleneglycol and tris(2-aminoethyl)amine is presented. Treatment with water allows the selective and quantitative recovery of the monomers, even from mixed waste streams. The modular synthetic approach allows the synthesis of materials that cover a broad range of mechanical properties and that are easy to reprocess.
Li–S Batteries
Polyoxometalate-Cyclodextrin-Based Cluster-Organic Supramolecular Framework for Polysulfide Conversion and Guest–Host Recognition in Lithium-sulfur Batteries
- First Published: 18 July 2023
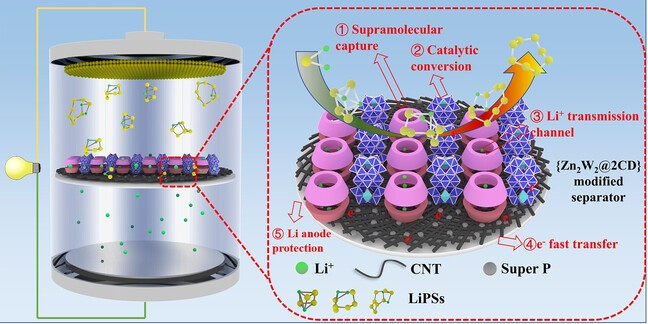
Polyoxometalate-cyclodextrin cluster-organic supramolecular framework (POM-CD-COSF)-based battery separator as an ideal lightweight barrier (ca. 0.3 mg cm−2) was first directly involved in the lithium-sulfur battery (Li−S) system to suppress the polysulfide shuttle effect through supramolecularly recognizing polysulfide guests and then catalyzing their conversion while simultaneously accelerating Li+ ions diffusion.
Drug Delivery | Very Important Paper
A Targeting Singlet Oxygen Battery for Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Deep-Tissue Infections
- First Published: 17 July 2023
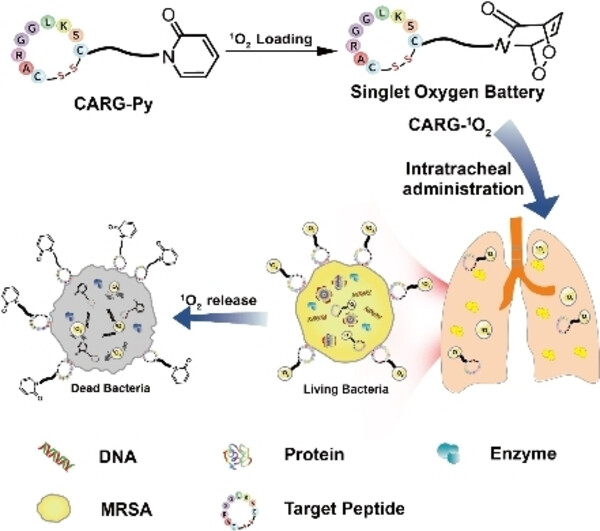
A targeting CARG-1O2 was designed as a “singlet oxygen battery” for the efficient treatment of MRSA deep-tissue infections. CARG-Py was able to store singlet oxygen by pre-irradiation and produce singlet oxygen over a time course of approximately 30min. CARG-1O2 potently combats biofilm-associated infections and disrupts MRSA biofilms, and it exerted a beneficial therapeutic impact in a MRSA-induced model of pneumonia.
CO2 Reduction Reaction | Hot Paper
Atomically Precise Copper Nanoclusters for Highly Efficient Electroreduction of CO2 towards Hydrocarbons via Breaking the Coordination Symmetry of Cu Site
- First Published: 19 July 2023
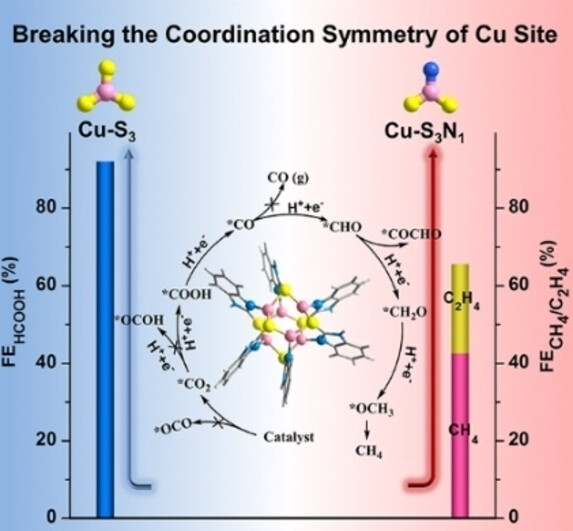
Breaking the coordination symmetry of Cu site in atomically precise Cu6 cluster forms Cu-S2N1 site, which rank the dx2-y2 orbital as the highest occupied d orbital to favor the specific coordination between C atom of CO2 and Cu−S2N1 site. This binding mode is conductive to the generation of *COOH instead of *OCHO, thereby switching the product of electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction to higher-valued hydrocarbons.
Bioimaging
Triazinium Ligation: Bioorthogonal Reaction of N1-Alkyl 1,2,4-Triazinium Salts
- First Published: 12 July 2023
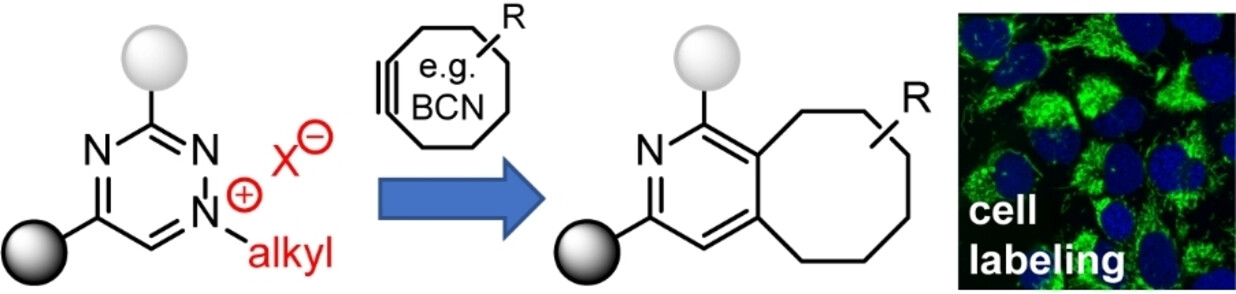
We describe N1-tert-butylated 1,2,4-triazinium salts as new bioorthogonal reagents. These heterodienes are stable under biological conditions and react selectively and at high rates with strained alkynes such as BCN, allowing efficient modification of biomolecules. The unique ionic character makes the compounds more water soluble and cell permeable. These features enable efficient labeling of intracellular targets in living cells.
Crystal Growth
Nonclassical Crystallization Causes Dendritic and Band-Like Microscale Patterns in Inorganic Precipitates
- First Published: 18 July 2023
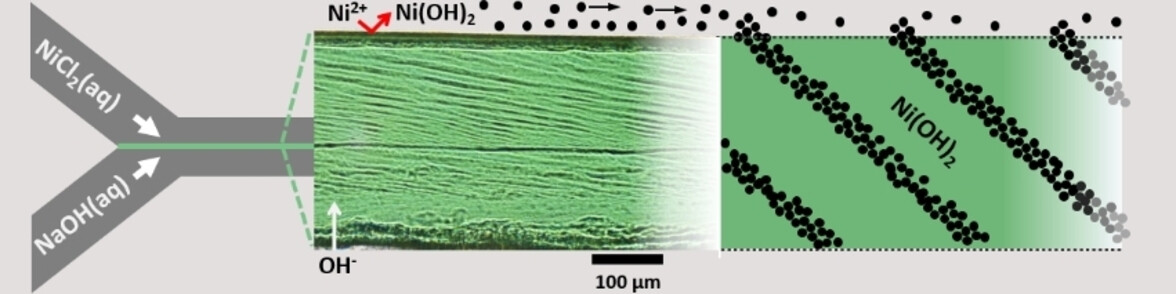
Microfluidic experiments yield compositionally pure Ni(OH)2 membranes that show internal microscale structures such as parallel bands, dendritic trees, and disorganized spots. These light-scattering patterns result from nonclassical crystallization and nanoparticle aggregation. The particles form in the flowing NiCl2 solution and self-organize aggregation zones—that for band patterns—move over the membrane surface in the upstream direction.
Rearrangement
Defluorinative Multi-Functionalization of Fluoroaryl Sulfoxides Enabled by Fluorine-Assisted Temporary Dearomatization
- First Published: 16 July 2023
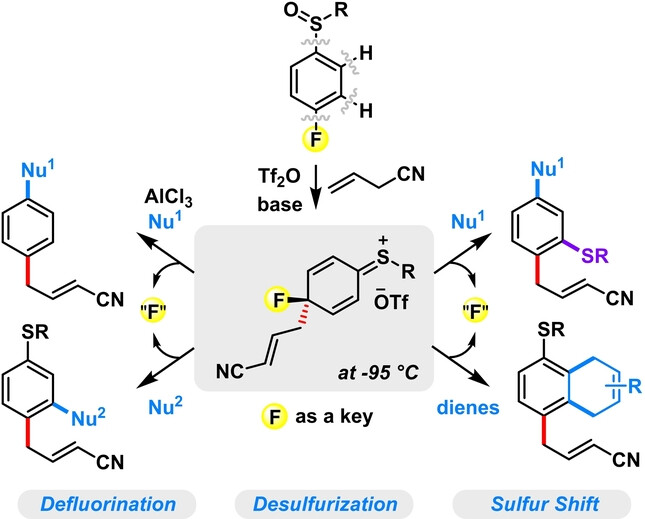
The potential reactivities of fluoroaryl sulfoxides have been unlocked by precisely constructing and elaborating their temporarily dearomatized intermediates via a robust [5,5]-sulfonium-rearrangement-triggered dearomatization/rearomatization process. Impressively, fluorine has shown its irreplaceable role for the success of the reaction.
Red Phosphorus | Hot Paper
Type-II Red Phosphorus: Wavy Packing of Twisted Pentagonal Tubes
- First Published: 19 July 2023
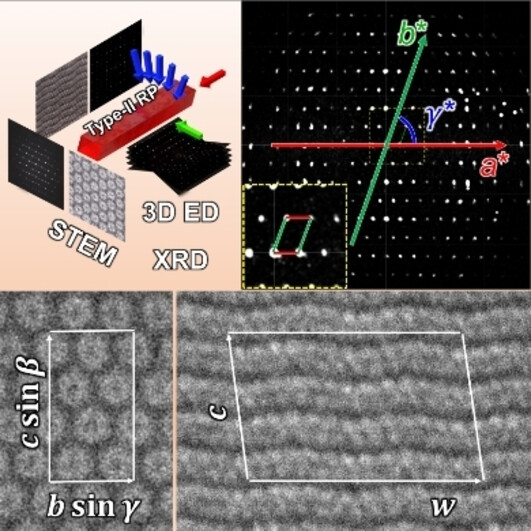
The crystal structure of type-II red phosphorus is investigated by various structural characterizations, including 3D electron diffraction, atomic-resolution STEM imaging, and powder X-ray diffraction. A triclinic unit cell with a large volume containing around 250 phosphorus atoms is identified via 3D electron diffraction. The twisted wavy tubular motif, a new variation of building blocks in phosphorus, is also revealed via STEM.
Protein Engineering
MET-Activating Ubiquitin Multimers
- First Published: 14 July 2023
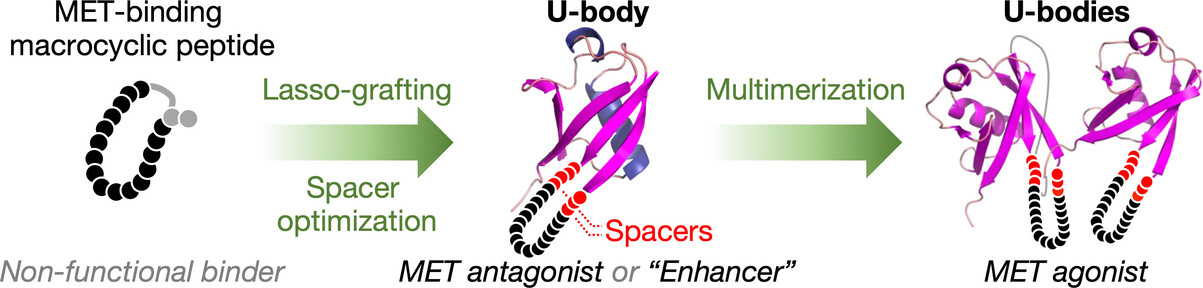
Monomeric small protein ligands, referred to as U-body constructs, were developed from ubiquitin and macrocyclic peptide pharmacophores via genetic implantation (lasso-grafting) and spacer optimization, showing antagonist or “enhancer” activity for a receptor tyrosine kinase MET. Subsequently, multimeric U-body-based proteins, U-bodies, were constructed, exhibiting potent agonist activity for MET.
CO2 Electroreduction | Hot Paper
High-Rate CO2 Electrolysis to Formic Acid over a Wide Potential Window: An Electrocatalyst Comprised of Indium Nanoparticles on Chitosan-Derived Graphene
- First Published: 19 July 2023
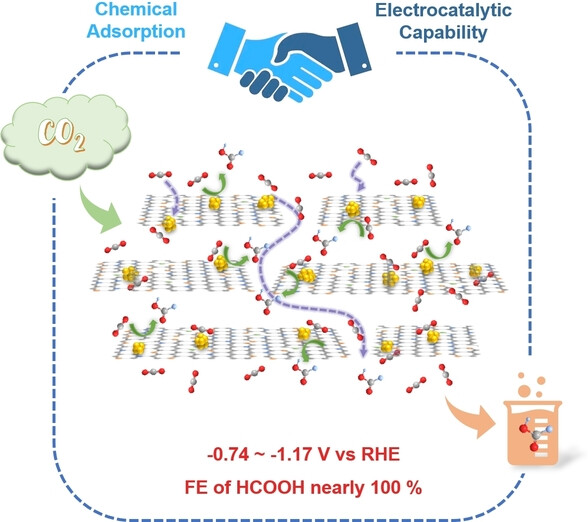
Indium nanoparticles on chitosan-derived N-doped defective graphene (In/N-dG) create bifunctional active centers that integrate chemical adsorption and electrocatalytic capabilities for CO2 electrolysis. The electrocatalyst demonstrated outstanding performance for the CO2 reduction reaction with a nearly 100 % Faradaic efficiency toward HCOOH across a wide potential window and with high current density.
Soft Matter
Single-Atom Catalysis
Atomic Insights into Synergistic Nitroarene Hydrogenation over Nanodiamond-Supported Pt1−Fe1 Dual-Single-Atom Catalyst
- First Published: 04 July 2023
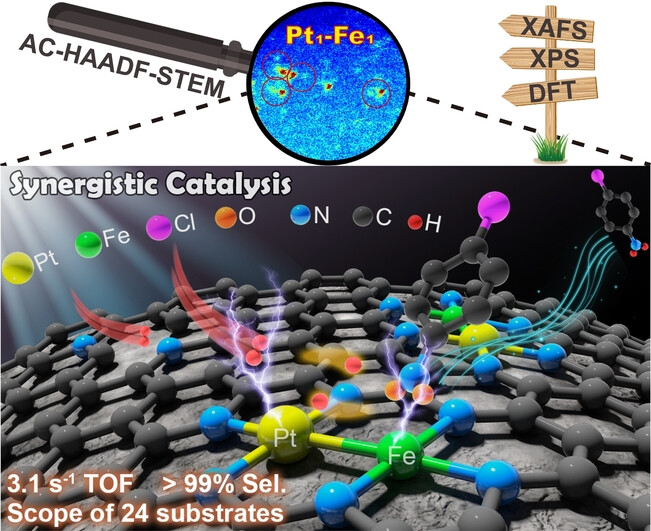
A simple method was developed for Pt1−Fe1/nanodiamond dual-single-atom catalyst construction. Synergistic chemoselective hydrogenation of nitroarenes was achieved, whereby hydrogen is activated on the Pt1−Fe1 dual site and nitro group is preferentially adsorbed at the Fe1 site. The activation energy is decreased, resulting in an appreciable catalytic performance (3.1 s−1 turnover frequency, ca. 100 % selectivity, and a scope of 24 substrates).
Chiral Hybrid Sb Halides
Multiple Stimuli-Responsive Luminescent Chiral Hybrid Antimony Chlorides for Anti-Counterfeiting and Encryption Applications
- First Published: 17 July 2023
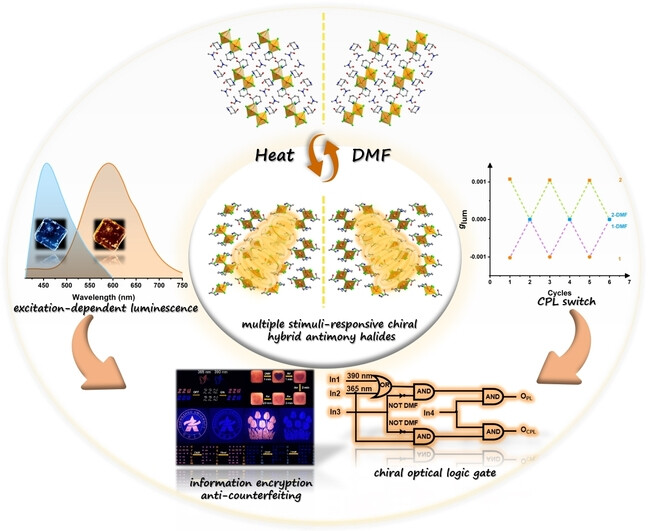
The chiral hybrid antimony halides R-/S-(C5H12NO)2SbCl5 have excitation-dependent emission originating from the synergistic effects of ligand and self-trapped excitons, and exhibit reversible structural transformation between non-emissive R-/S-(C5H12NO)2SbCl5 ⋅ DMF upon exposure to DMF and heat. CPL switch, chiral optical logic gate and anti-counterfeiting applications have been investigated based on the multiple stimuli-responsive properties.
CO2 Photoreduction
Cobalt-Porphyrin-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks with Donor-Acceptor Units as Photocatalysts for Carbon Dioxide Reduction
- First Published: 13 July 2023
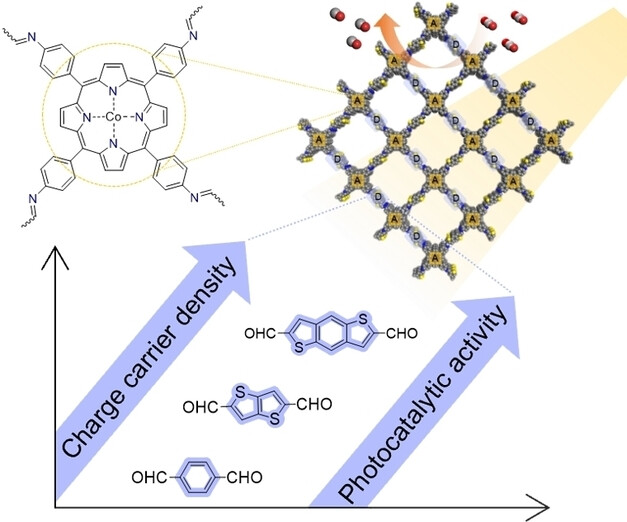
Cobalt-porphyrin-based covalent organic frameworks (Co-Por-COFs) were prepared with different donor building units. Their photophysical studies indicated that the Co-Por-COFs with higher charge-carrier density and longer conjugation length led to a more efficient charge separation with a reduced exciton binding energy, resulting in an enhanced photocatalytic activity of CO2 reduction into CO.
Cage Compounds
Construction of Covalent Organic Cages with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics from Metallacages for Mimicking Light-Harvesting Antenna
- First Published: 14 July 2023
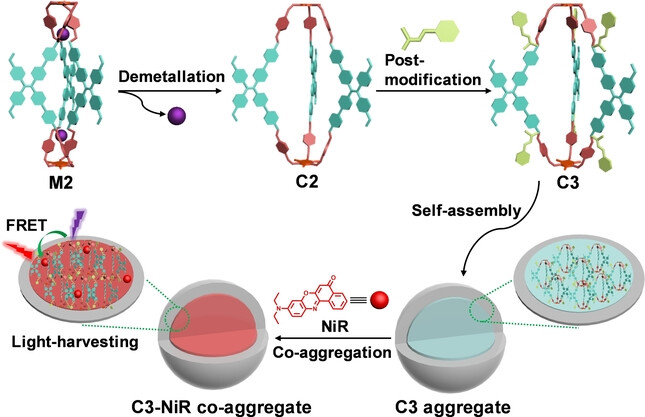
A series of covalent organic cages with aggregation-induced emission characteristics were elegantly prepared through the reduction of preorganized metallacages. These covalent cages performed well as energy donors for the construction of artificial light-harvesting systems for the photocatalytic dehalogenation reaction.
Solar Cells
Unidirectional Sidechain Engineering to Construct Dual-Asymmetric Acceptors for 19.23 % Efficiency Organic Solar Cells with Low Energy Loss and Efficient Charge Transfer
- First Published: 18 July 2023
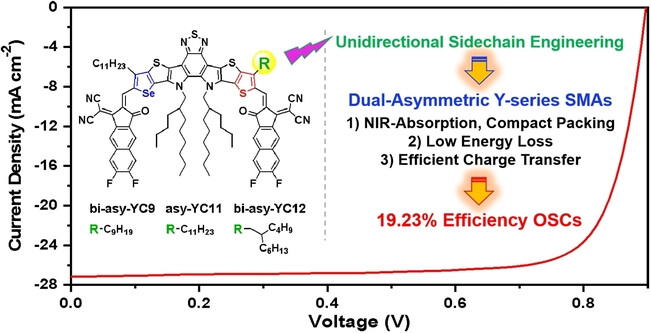
A dual-asymmetric Y-series acceptor is developed using unidirectional sidechain engineering. Thanks to the low energy loss and efficient charge transfer properties, the corresponding organic solar cells achieved an efficiency of 19.23 %, which is one of the highest values among annealing-free devices.
Oxygen Reduction
Epoxy-rich Fe Single Atom Sites Boost Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysis
- First Published: 15 July 2023
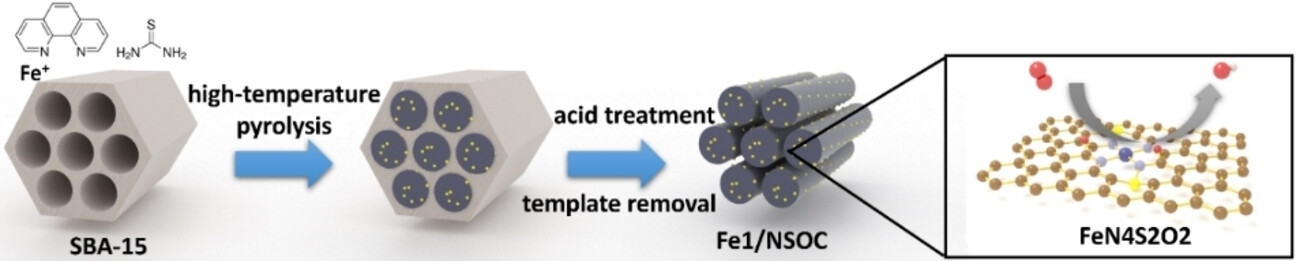
Fe single atom catalysts with sulfur and epoxy groups near the atomically dispersed metal centers (Fe1/NSOC) are designed for highly efficient oxygen reduction reactions. The presence of sulfur and epoxy groups modulates the electronic structure of Fe centers, while the epoxy groups also participate in the reduction reaction through reversible cleavage, lowering the energy barrier by functioning as an anchor site for OH* intermediates.
Li-Ion Batteries
Discovery of Two-dimensional Hexagonal MBene HfBO and Exploration on its Potential for Lithium-Ion Storage
- First Published: 14 July 2023
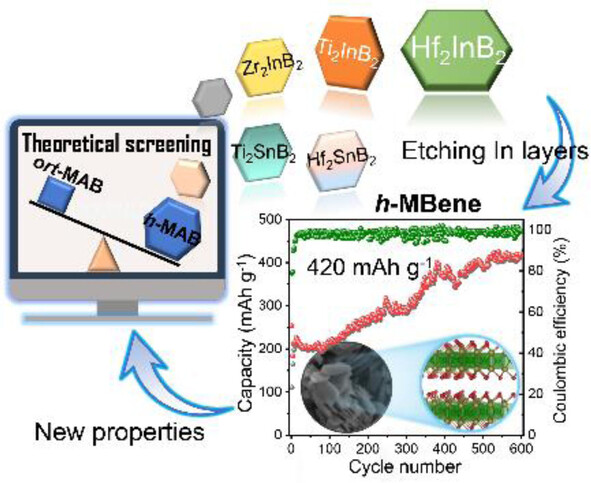
A combination of DFT calculations and experiments were used to discover a large class of exfoliable h-MAB phases and their derivative h-MBenes. A representative 2D h-MBene, HfBO, was successfully synthesized by selectively etching the In layers from Hf2InB2. The synthesized 2D HfBO was demonstrated to show lithium-ion storage performance for the first time.
Ferroptosis
Gallium Triggers Ferroptosis through a Synergistic Mechanism
- First Published: 15 July 2023
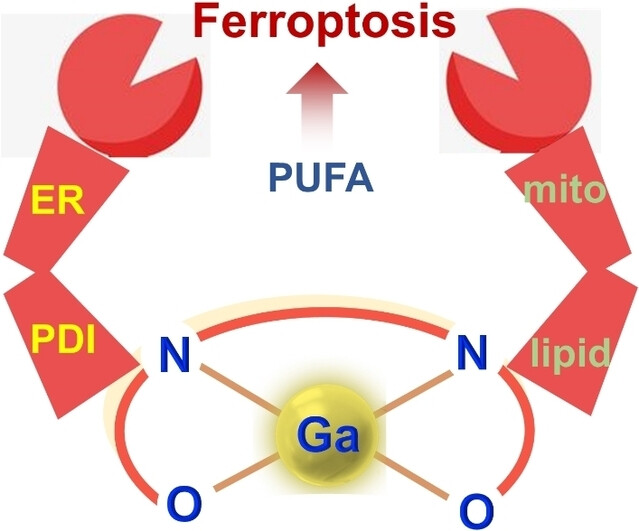
Ga-1 anchors to mitochondria by binding to the membrane phospholipids and results in the dysfunction of the electron transfer chain as well as iron release, eventually triggering ferroptosis. In addition, Ga-1 inhibits protein disulfide isomerase in the endoplasmic reticulum, breaking the antioxidant glutathione system. Both actions synergistically induce ferroptosis. In addition, exogenous polyunsaturated fatty acid enhances ferroptosis.
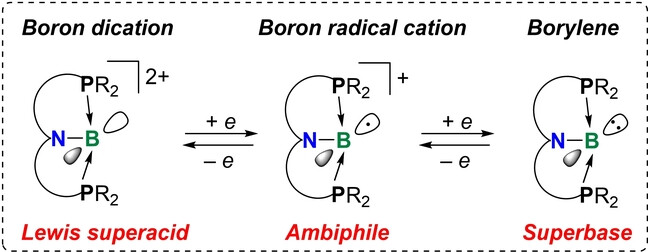
Lewis Superacids | Hot Paper
Geometrically Constrained Organoboron Species as Lewis Superacids and Organic Superbases
- First Published: 03 July 2023
H2O2 Production | Hot Paper
Synergistic Metal-Nonmetal Active Sites in a Metal-Organic Cage for Efficient Photocatalytic Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide in Pure Water
- First Published: 12 July 2023
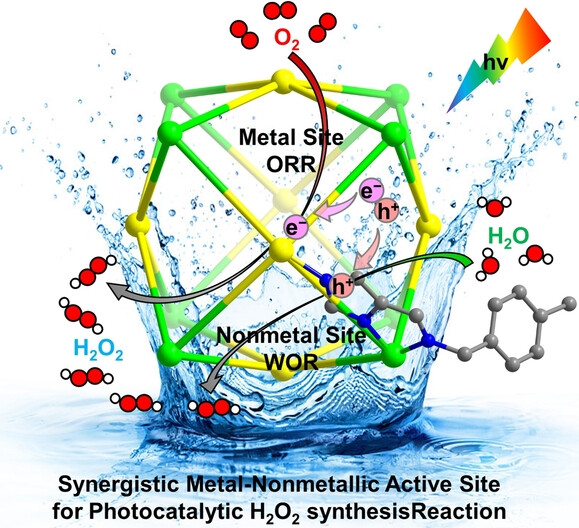
Two stable CoII-based metal-organic cages are efficient catalysts for photocatalytic synthesis of H2O2 in pure water and O2 or air atmospheres. The metal-nonmetal active site operates synergistically during photocatalytic H2O2 synthesis and the reaction substrate can more fully contact the catalytically active site through host–guest chemistry of cages, ultimately achieving a high H2O2 production rate.
Covalent Organic Frameworks
A Fully Conjugated Covalent Organic Framework with Oxidative and Reductive Sites for Photocatalytic Carbon Dioxide Reduction with Water
- First Published: 27 June 2023
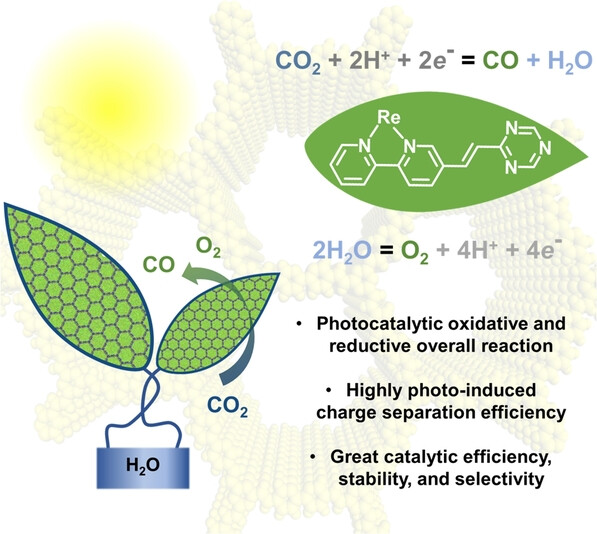
A crystalline network is constructed by incorporating rhenium complexes and triazine ring structures as catalytic sites via robust −C=C− bonding. Appreciable charge-separation and transfer efficiency drive both the photocatalytic oxidative and reductive reactions in the conversion of CO2 to CO with H2O, and without any additional sacrificial agents or photosensitizers.
Photocatalysis | Hot Paper
Controlled Partial Linker Thermolysis in Metal-Organic Framework UiO-66-NH2 to Give a Single-Site Copper Photocatalyst for the Functionalization of Terminal Alkynes
- First Published: 19 July 2023
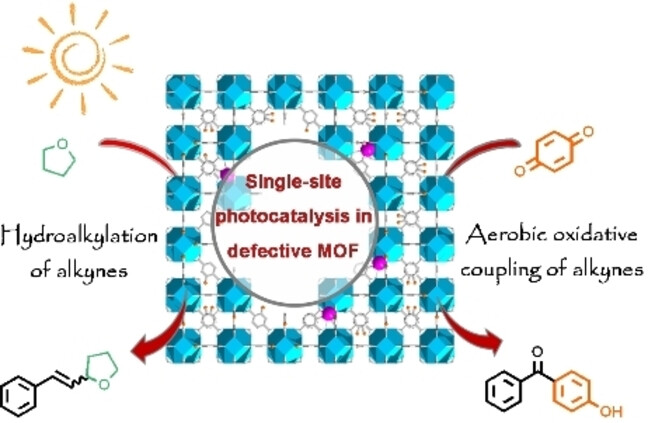
A straightforward method of controlled partial linker thermolysis allows the microporous metal–organic framework (MOF) photocatalyst UiO-66-NH2 to expand its porosity with a tailored pore environment. The resulting material accommodates single-site Cu species, shows significant mesoporosity and enhanced charge photogeneration. It has excellent performance in photocatalytic reactions for the functionalization of terminal alkynes.
CO2 Reduction | Hot Paper
Acidic Media Impedes Tandem Catalysis Reaction Pathways in Electrochemical CO2 Reduction
- First Published: 19 July 2023
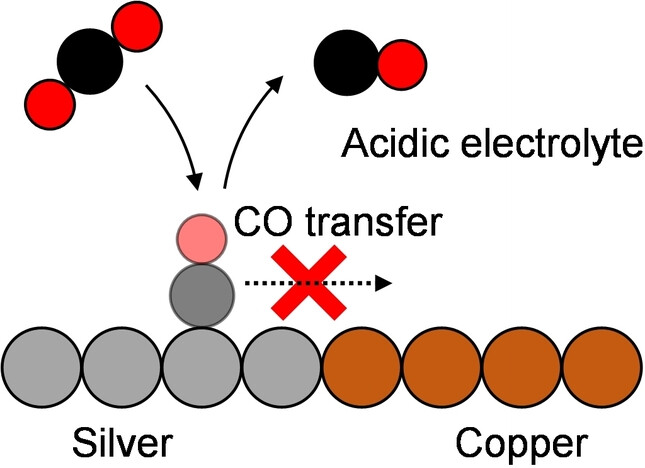
Tandem catalysis effects in electrochemical CO2 reduction were investigated through an isotopic labelling strategy involving the co-reduction of 13CO2/12CO mixtures. The results provide evidence that tandem catalysis does indeed occur in neutral electrolyte but is curtailed under acidic conditions. This is due to Cu becoming less effective at utilizing tandem-supplied CO in the presence of hydronium ions.
Li-S Batteries | Hot Paper
Fast Polysulfide Conversion Catalysis and Reversible Anode Operation by A Single Cathode Modifier in Li-Metal Anode-Free Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
- First Published: 21 July 2023
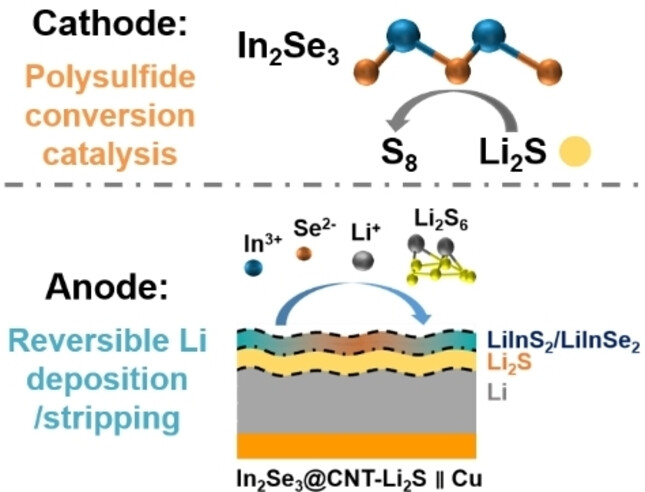
Multiple functionalities were enabled by a single cathode modifier: i) for the cathode, it can work as an effective catalyst to promote cathode reaction kinetics; ii) for the anode, trace amounts of dissolved In and Se ions are incorporated as LiInS2 and LiInSe2 in the anode solid electrolyte interface to facilitate reversible Li deposition/stripping.
Covalent Organic Frameworks | Hot Paper
The Keto-Switched Photocatalysis of Reconstructed Covalent Organic Frameworks for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 17 July 2023

Local reconstruction of imine-linked covalent organic frameworks (COFs) unlocks visible-light-promoted photocatalytic H2 evolution. The keto units in skeletal building blocks are active injectors, where hot π-electrons are emitted to Pt nanoparticles across a polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) insulting layer for reduction of protons to H2. A new benchmark H2 production rate of 53 mmol g−1 h−1 was achieved over β-ketoenamine-linked COFs.
Photocatalysis
Linkage Microenvironment of Azoles-Related Covalent Organic Frameworks Precisely Regulates Photocatalytic Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide
- First Published: 18 July 2023
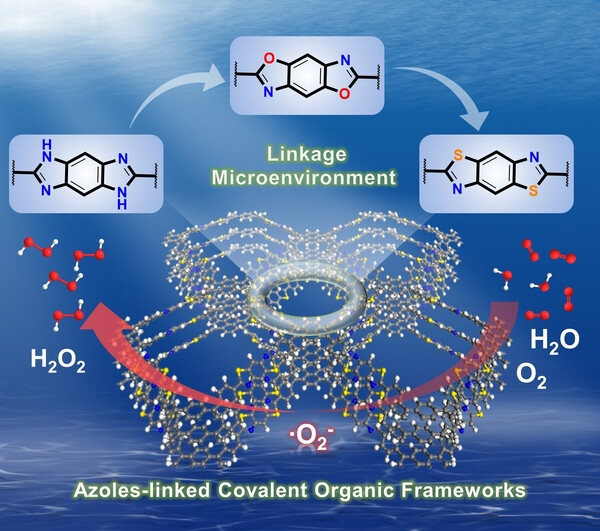
A tunable covalent organic framework (COF) platform with three azole-related linkages was prepared through linker exchange reactions. The linkage microenvironment changes the photoelectric properties and photocatalytic performance. The thiazole linkage was more favorable than the oxazole and imidazole linkages for the formation of *O2 intermediate in H2O2 production.
Upconverting Nanoparticles
Bilayer-Coating Strategy for Hydrophobic Nanoparticles Providing Colloidal Stability, Functionality, and Surface Protection in Biological Media
- First Published: 30 May 2023
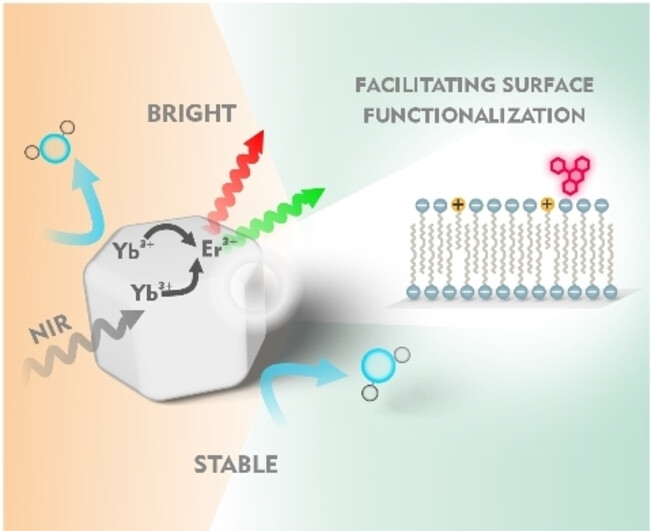
Modifying the surface of oleate-coated hydrophobic particles to render them stable in aqueous biological environments is often challenging. We present a one-step reaction, to form a bilayer consisting of oleate and dodecylamine moieties, which provides excellent stability and versatility as it allows further functionalization via carbodiimide chemistry.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
In Vivo Metabolic Imaging of [1-13C]Pyruvate-d3 Hyperpolarized By Reversible Exchange With Parahydrogen
- First Published: 13 July 2023
![In Vivo Metabolic Imaging of [1-13C]Pyruvate-d3 Hyperpolarized By Reversible Exchange With Parahydrogen**](/cms/asset/c6ed2faa-3707-4b5c-b1d5-400fa1c743a1/anie202306654-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Fast, low-cost parahydrogen-hyperpolarization via Signal Amplification By Reversible Exchange (SABRE) enables in vivo metabolic magnetic resonance imaging. We demonstrate the first in vivo application of SABRE-hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate-d3 in a purified, aqueous solution with ≈30 mM [1-13C]pyruvate-d3 polarized to ≈11 %, obtained by rapid solvent evaporation and metal filtering. This achievement paves the way for affordable and widespread metabolic imaging applications.
Nanostructures
Compartmentalized Polyampholyte Microgels by Depletion Flocculation and Coacervation of Nanogels in Emulsion Droplets
- First Published: 30 June 2023
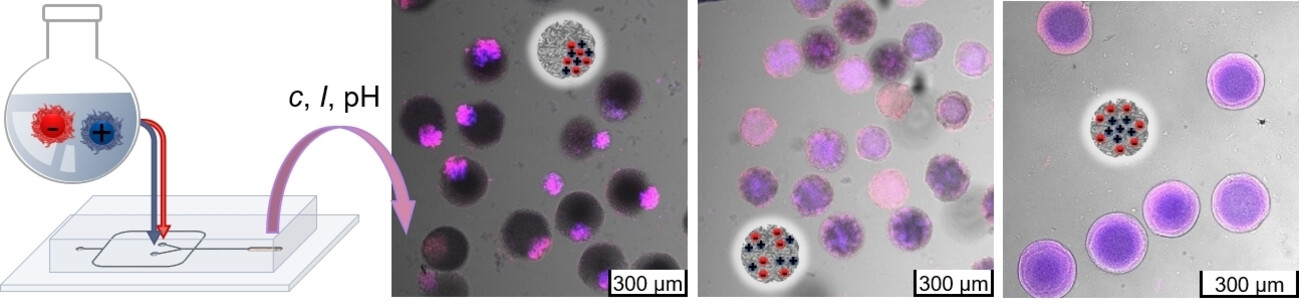
Novel step-by-step approach for the synthesis of polyampholyte nanogel-in-microgel colloids (NiM−C) was developed by incorporating nanogels into microgels via droplet-based microfluidics yielding different internal morphologies including phase-separated coacervates, statistically distributed coacervates and core–shell like arrangements by variation of synthesis parameters such as nanogel concentration, ionic strength and pH value.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Cooperative Lewis Acid-1,2,3-Triazolium-Aryloxide Catalysis: Pyrazolone Addition to Nitroolefins as Entry to Diaminoamides
- First Published: 26 June 2023
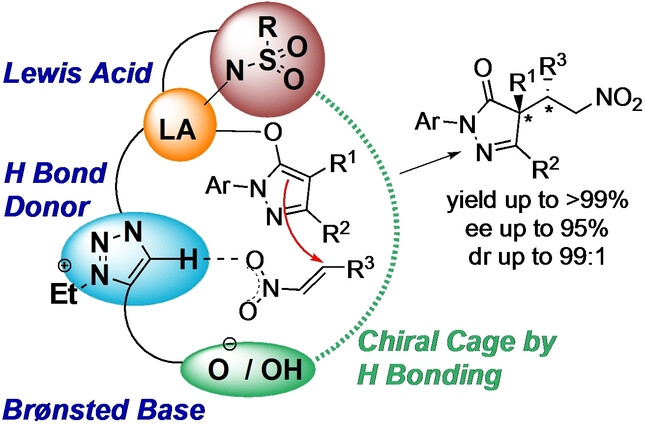
Pyrazolones represent an important structural motif in active pharmaceutical ingredients. A polyfunctional CuII-1,2,3-triazolium-aryloxide catalyst which enables their addition to nitroolefins with high enantio- and diastereocontrol is presented. DFT studies show that the catalyst adopts a rigid chiral cage structure by intramolecular hydrogen bonding. The products were used to form bioactive compounds, pyrazolidinones and β,γ’-diaminoamides.
Photopolymerization | Hot Paper
Cooperative Network Formation via Two-Colour Light-Activated λ-Orthogonal Chromophores
- First Published: 26 June 2023
Arsenic
Nucleophilic Attack at Pentaarsaferrocene [Cp*Fe(η5-As5)]—The Way to Larger Polyarsenide Ligands
- First Published: 05 July 2023
![Nucleophilic Attack at Pentaarsaferrocene [Cp*Fe(η5-As5)]—The Way to Larger Polyarsenide Ligands](/cms/asset/f41bae28-c778-410b-b560-b165b5f5d55a/anie202307696-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A selective way for the nucleophilic substitution of the cyclo-As5 ligand in [Cp*Fe(η5-As5)] (I) was found, resulting in first As5R entities. By the reduction of I, an access to the dianionic compound [(Cp*Fe)2{μ-η4:η4-As10}]2− (4), and by using As-based nucleophiles, the straightforward formation of tetramers representing the largest polyarsenide-containing (As20) molecular complexes could be achieved.
Semihydrogenation Catalysis
Catalytic Alkyne Semihydrogenation with Polyhydride Ni/Ga Clusters
- First Published: 05 July 2023
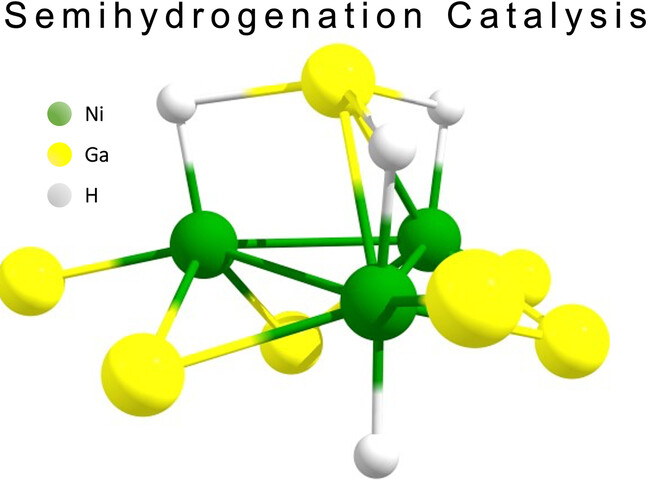
The bimetallic cluster [Ni3(GaTMP)7] reversibly forms di-, tetra- and hexahydride species under hydrogen pressure in solution, that were characterized by low temperature COSY and ROESY NMR experiments and DFT calculations. The work conceptually relates properties of molecular, atom-precise transition metal main-group bimetallic clusters to the respective solid-state phase in catalysis.
Communications
Organic Electronics | Very Important Paper
Unravelling the Superiority of Nonbenzenoid Acepleiadylene as a Building Block for Organic Semiconducting Materials
- First Published: 07 July 2023
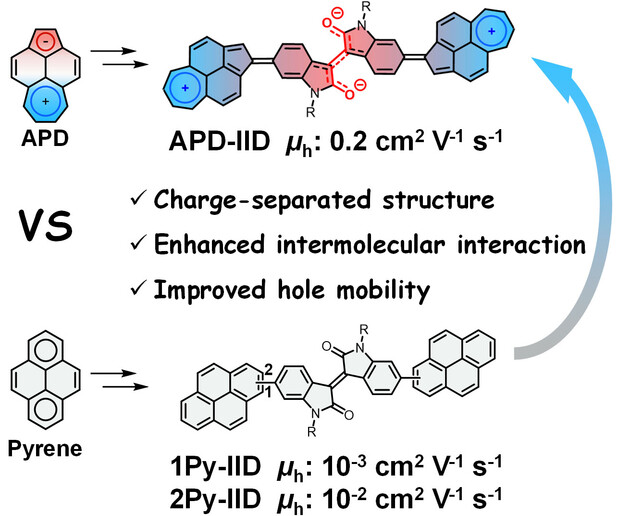
Nonbenzenoid acepleiadylene (APD) has been explored as a new building block to construct organic electronic material (APD-IID), which exhibits higher hole mobility than its pyrene-based isomers because of the stronger intermolecular interaction induced by the unique charge-separated character. These results demonstrate the superiority of nonbenzenoid arenes in the future development of organic semiconducting materials.
Covalent Organic Frameworks | Hot Paper
A Porous Crystalline Nitrone-Linked Covalent Organic Framework
- First Published: 13 July 2023
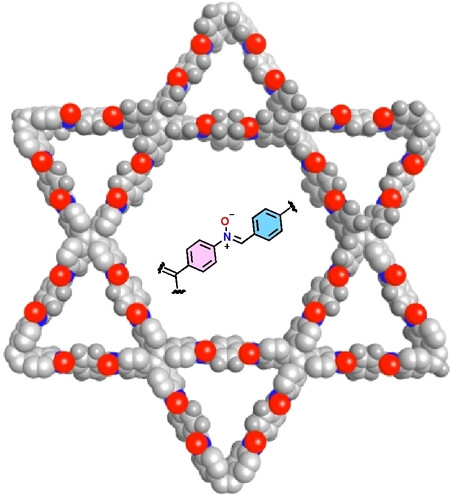
A nitrone-linked covalent organic framework, COF-115, has been synthesized for the first time via polycondensation reaction. The sorption analyses of COF-115 revealed a porosity of 1387 m2/g, and a superior potential for atmospheric water harvesting and CO2 capture applications compared to their imine-based analogs. Finally, COF-115 was found to undergo a photochemical rearrangement to the corresponding amide-linked material.
Water Oxidation Reaction
Tracking an FeV(O) Intermediate for Water Oxidation in Water
- First Published: 11 July 2023
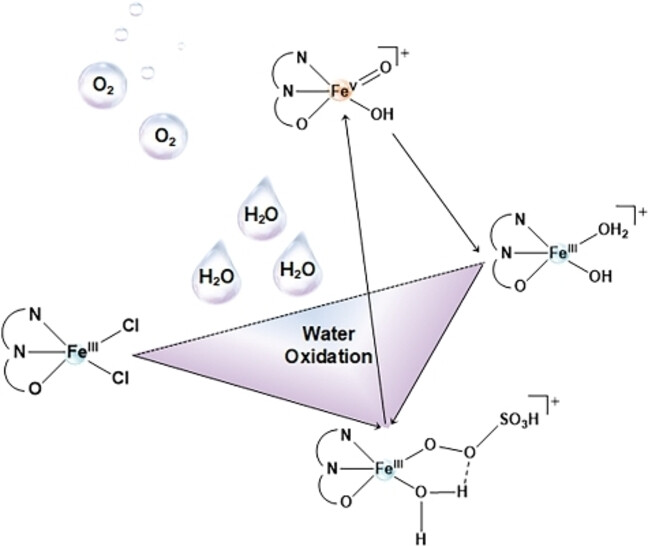
An electron-rich and oxidation-resistant ligand is effective at stabilizing high-valent iron-oxo intermediates involved in the water oxidation reaction. UV/Vis, XAS, EPR, electrochemical and kinetic measurements, allow a high-valent FeV(O) species that participates in O−O bond formation with higher reactivity and shorter lifetime to be tracked in a real catalytic water oxidation reaction.
Computational Chemistry
Tetra-tert-butyl-s-indacene is a Bond-Localized C2h Structure and a Challenge for Computational Chemistry
- First Published: 19 July 2023
Asymmetric Synthesis
Palladium-Catalyzed Arylation of Endocyclic 1-Azaallyl Anions: Concise Synthesis of Unprotected Enantioenriched cis-2,3-Diarylpiperidines
- First Published: 17 July 2023
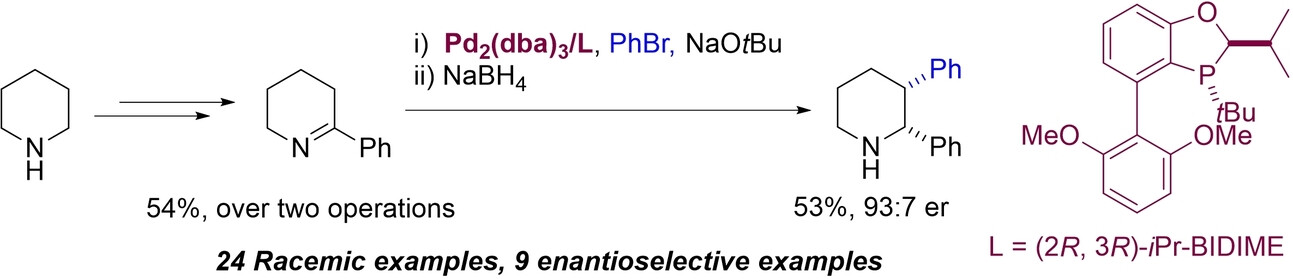
Unprotected cis-2,3-diarylpiperidines are synthesized from readily available piperidines in only three operations. The key step is a palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction between aryl halides and endocyclic 1-azallyl anions, elusive intermediates derived from the in situ deprotonation of 2-aryl-1-piperideines. This cross-coupling reaction can be achieved enantioselectively with a chiral mono-phosphine ligand.
Atropisomers
Chiral PSiSi-Ligand Enabled Iridium-Catalyzed Atroposelective Intermolecular C−H Silylation
- First Published: 18 July 2023
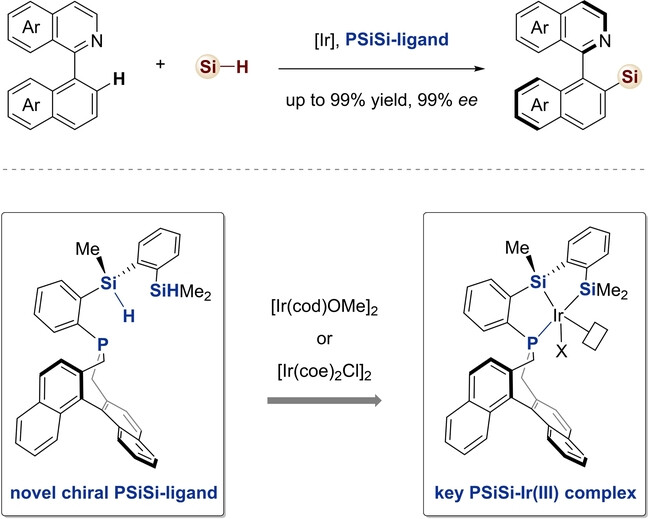
A new type of chiral pincer silyl ligand is developed, which enables an Iridium-catalyzed atroposelective intermolecular C−H silylation reaction. Key to the success of this transformation is the use of a novel chiral PSiSi-ligand, which facilitates the C−H silylation process with high chemical, regio- and stereo-control via a multi-coordinated silyl iridium complex.
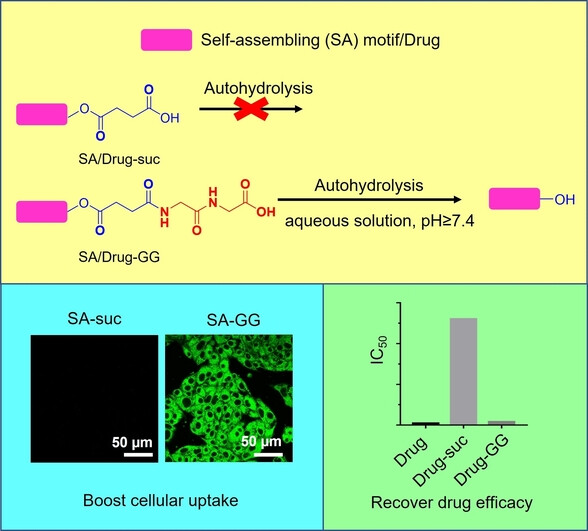
Self-Assembly | Very Important Paper
Autohydrolysis of Diglycine-Activated Succinic Esters Boosts Cellular Uptake
- First Published: 19 July 2023
Asymmetric Catalysis | Hot Paper
Synthesis of Enantioenriched 1,2-cis Disubstituted Cycloalkanes by Convergent NiH Catalysis
- First Published: 20 July 2023
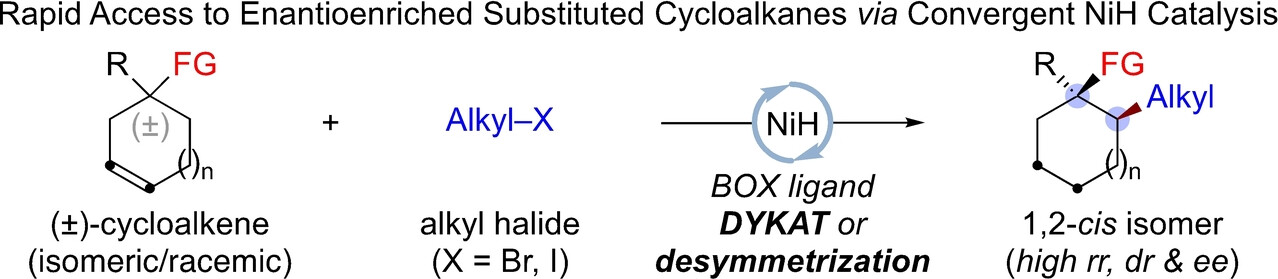
A NiH-catalyzed dynamic kinetic asymmetric transformation (DYKAT) of easily accessible racemic and isomeric mixture of cycloalkenes and a NiH-catalyzed desymmetrization transformation of prochiral cyclic alkenes are reported. This migratory hydroalkylation process produces enantioenriched thermodynamically disfavored 1,2-cis disubstituted cycloalkanes with excellent levels of regio-, diastereo- and enantioselectivities.
C-H Functionalization
Late-Stage Aryl C−H Bond Cyclopropenylation with Cyclopropenium Cations
- First Published: 17 July 2023
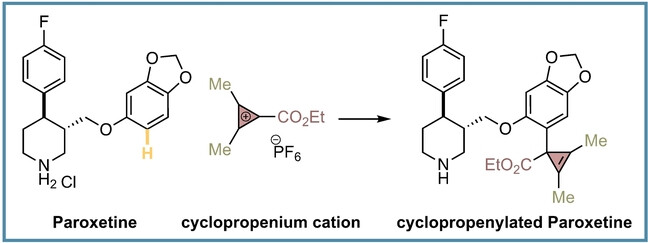
A new late-stage functionalization of complex molecules enables the installation of cyclopropene rings with excellent efficiency, thus reaching an uncharted cyclopropenylated chemical space. The cyclopropene ring generally improves the metabolic stability of the cyclopropenylated drug molecules and serves as a unique scaffold to access broad range of medically-relevant motifs.
Flow Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Efficient C(sp3)−H Carbonylation of Light and Heavy Hydrocarbons with Carbon Monoxide via Hydrogen Atom Transfer Photocatalysis in Flow
- First Published: 17 July 2023
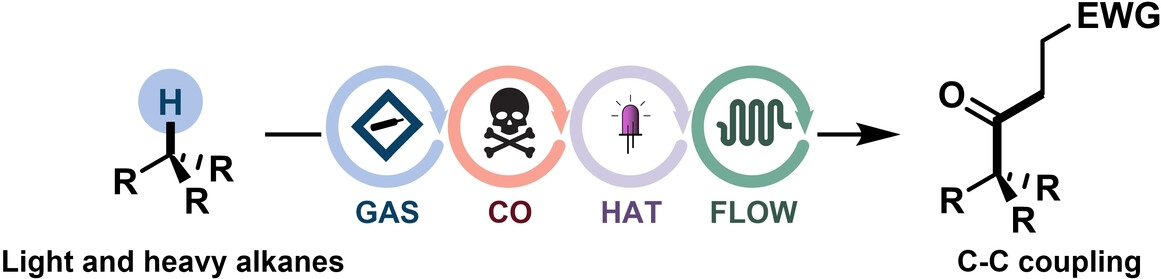
We report an efficient C−H functionalization process, enabling the regioselective installation of carbonyls in light and heavy hydrocarbons by using inexpensive carbon monoxide. Safe processing of hazardous CO and flammable alkanes is ensured in flow, with high gas-liquid mass transfer rates and fast reaction kinetics. Our method demonstrates the valorization of gaseous reagents, coupling light alkanes, CO, and an olefin as a terminal radical trap.
Hydrogen Isotope Exchange | Hot Paper
Environmental Chemistry
Overlooked Formation of Carbonate Radical Anions in the Oxidation of Iron(II) by Oxygen in the Presence of Bicarbonate
- First Published: 13 July 2023

The rapid generation of carbonate radical anions (CO3.−) in the oxidation of FeII by O2 in the presence of bicarbonate (HCO3−) is shown. The results highlight the importance of considering the formation of CO3.− in the geochemical cycling of iron and carbon and show that the presence of bicarbonate dramatically changes the mechanism and kinetics of the reaction of Fe(H2O)62++O2 under physiological and environmental conditions.