Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Ultra-Low-Field NMR Relaxation and Diffusion Measurements Using an Optical Magnetometer (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37/2014)
- Page: 9677
- First Published: 30 July 2014

An optical magnetometer used for making ultra-low-field NMR measurements of relaxation and diffusion has the chemical sensitivity required to distinguish between hydrocarbons and water in Earth's magnetic field (0.5 G). P. J. Ganssle, A. Pines et al. describe in their Communication on page 9766 ff., this important proof-of-concept for the commercial applicability of these robust, portable NMR sensors, particularly in the context of oil-well logging.
Inside Cover: Functionalized Graphene as a Gatekeeper for Chiral Molecules: An Alternative Concept for Chiral Separation (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37/2014)
- Page: 9678
- First Published: 15 July 2014

The attachment of a suitable “bouncer” molecule to the rim of a graphene pore prevents the passage of the undesired enantiomer while letting its mirror image through. In their Communication on page 9957 ff., A. W. Hauser, P. Schwerdtfeger et al. report that a small difference in the geometry of the temporary dimer complex, which is formed by the “bouncer” and the penetrating molecule, is transformed into a significant difference for the transmission barrier.
Inside Back Cover: An Unusual Protein–Protein Interaction through Coupled Unfolding and Binding (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37/2014)
- Page: 9961
- First Published: 07 July 2014

Protein–protein interactions can involve the folding of a disordered region to form the binding interface. In their Communication on page 9784 ff., J. Y. Suh and co-workers report the opposite case, in which binding is accompanied by local unfolding. The structure of an engineered peptide bound to fibronectin extradomain B reveals coupled unfolding and binding through β-strand displacement. The unfolding exposes a hydrophobic surface that provides key interactions for the complex.
Back Cover: A High-Pressure NMR Probe for Aqueous Geochemistry (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37/2014)
- Page: 9962
- First Published: 22 July 2014

Geochemical models for aqueous solution equilibria extend to pressures and temperatures well beyond experimental spectroscopies that could test the predictions. W. H. Casey and co-workers describe in their Communication on page 9788 ff. a simple NMR probe that can allow spectroscopy on solutions at pressures near those of the Earth's continental crust. (Greg Pautler Graphic Design, Ontario, Canada, is thanked for designing and donating the artwork.)
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Selective Photoelectrochemical Reduction of Aqueous CO2 to CO by Solvated Electrons
- First Published: 02 September 2014
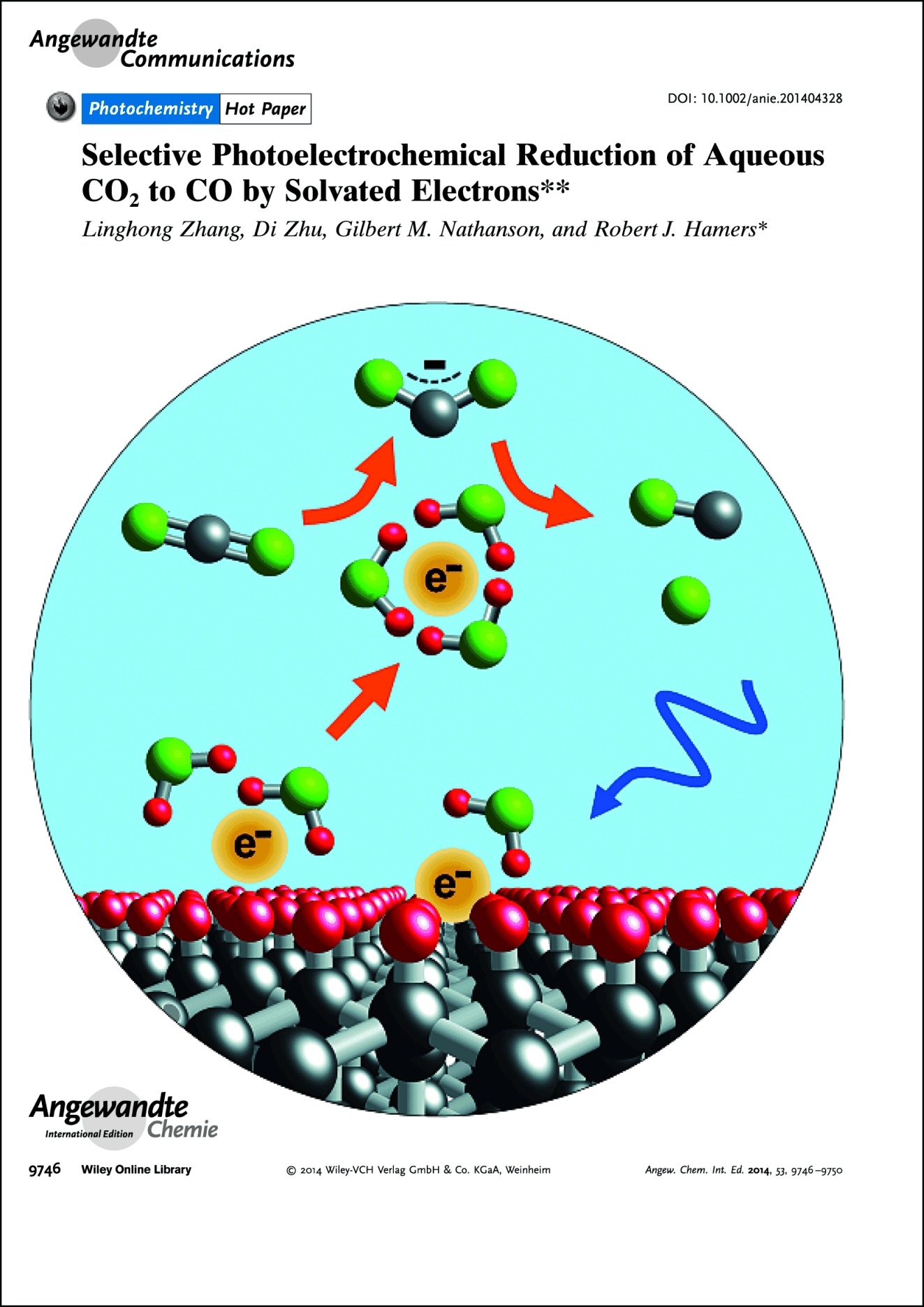
Photochemistry The efficient and selective reduction of CO2 to CO using solvated electrons, generated by illumination of inexpensive diamond substrates with UV light, is described by R. J. Hamers and co-workers in their Communication on page 9746 ff.
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37/2014
- Pages: 9681-9695
- First Published: 02 September 2014
Corrigenda
Corrigendum: Crowdsourcing Natural Products Discovery to Access Uncharted Dimensions of Fungal Metabolite Diversity
- Page: 9695
- First Published: 02 September 2014
Corrigendum: Metal-Free Annulation of Arenes with 2-Aminopyridine Derivatives: The Methyl Group as a Traceless Non-Chelating Directing Group
- Page: 9695
- First Published: 02 September 2014
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37/2014
- Pages: 9698-9701
- First Published: 02 September 2014
Author Profile
News
Obituary
Book Review
Highlight
Cycloadditions
Minireview
Bioinorganic Chemistry
Carbon-Monoxide-Releasing Molecules for the Delivery of Therapeutic CO In Vivo
- Pages: 9712-9721
- First Published: 28 July 2014
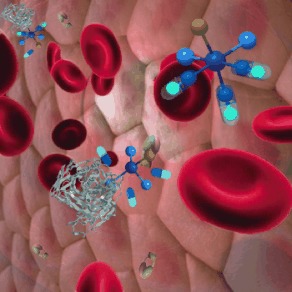
On target: Carbon-monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs) are promising agents for the treatment of several diseases. CORMs are particularly good for enabling CO delivery in a controlled manner without affecting oxygen transport by hemoglobin. Significant progress in the methods for CO detection in live cells and the understanding of the reactivity of CORMs in vivo provides insights into CO biology and the design of safer, and more selective and efficient CORMs for clinical use.
Review
Polyolefins
Post-Metallocenes in the Industrial Production of Polyolefins
- Pages: 9722-9744
- First Published: 21 August 2014
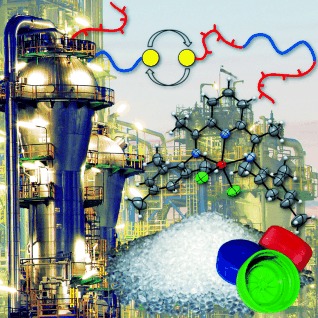
“Post-metallocene” polymerization catalysis research ranges from fundamental mechanistic studies by catalyst design to material properties of polyolefins. A common goal of these studies is the creation of practically useful new materials or processes. A comprehensive overview of post-metallocene polymerization catalysts that have been put into practice is provided. The decisive properties for this success of a given catalyst structure are delineated.
Communications
Photochemistry | Hot Paper
Selective Photoelectrochemical Reduction of Aqueous CO2 to CO by Solvated Electrons†
- Pages: 9746-9750
- First Published: 14 July 2014
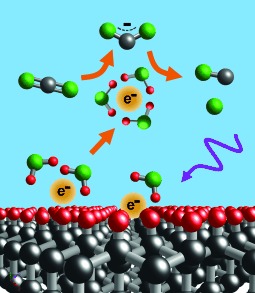
Diamond in the rough: Illumination of diamond substrates leads to emission of electrons into aqueous media. The solvated electrons are potent reducing agents and induce the direct one-electron reduction of CO2 to CO2.−, which then forms CO. This approach represents a new concept in catalysis by directly releasing electrons into reactant liquids.
Protein Dynamics | Hot Paper
Local Transient Unfolding of Native State PAI-1 Associated with Serpin Metastability†
- Pages: 9751-9754
- First Published: 22 July 2014
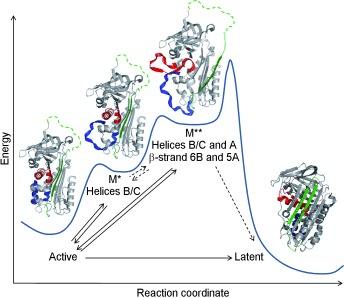
Serpin proteins are prone to pathological conformational change, for instance by conversion into an inactive, so-called latent form. By using advanced hydrogen/deuterium-exchange mass spectrometry, transient unfolding of a serpin is shown under native conditions. Based on these observations, a new mechanism (see picture) is proposed.
Biomass Conversion
Pd/NbOPO4 Multifunctional Catalyst for the Direct Production of Liquid Alkanes from Aldol Adducts of Furans†
- Pages: 9755-9760
- First Published: 18 July 2014
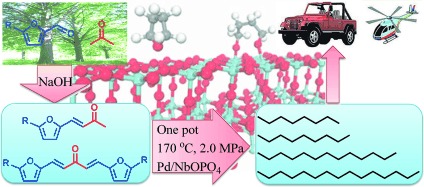
Fueling fuel production: Biomass conversion into liquid fuel depends on the design of multifunctional catalysts. In the direct conversion of furan-based aldol adducts into liquid alkanes over a Pd/NbOPO4 catalyst under mild conditions (see scheme), NbOx species played an important role in CO bond cleavage.
Lewis Acids
Highly Electron-Deficient and Air-Stable Conjugated Thienylboranes†
- Pages: 9761-9765
- First Published: 17 July 2014
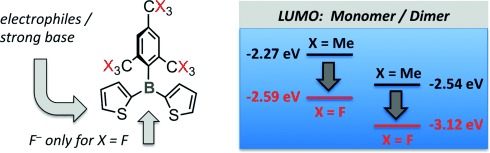
The bigger the better: Sterically demanding 2,4,6-tri-tert-butylphenyl (Mes*) or 2,4,6-tris(trifluoromethyl)phenyl (FMes) groups do not prevent but rather promote coplanarity and enhance electronic communication within conjugated thienylboranes. FMes exerts a strong electron-withdrawing effect which results in significant lowering of the LUMO energy level and high Lewis acidity toward fluoride anions, while ensuring stability in air and towards acid or base.
NMR Spectroscopy | Hot Paper
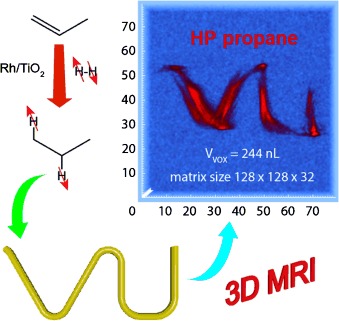
Ultra-Low-Field NMR Relaxation and Diffusion Measurements Using an Optical Magnetometer†
- Pages: 9766-9770
- First Published: 31 July 2014
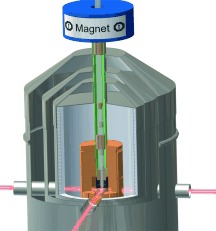
Portable NMR: NMR relaxometry and diffusometry can be highly effective in applications where high-resolution NMR spectroscopy is unnecessary or impractical, as is the case in the emerging field of portable chemical characterization. A proof-of-concept experiment is presented that demonstrates the use of high-sensitivity optical magnetometers as detectors for ultra-low-field NMR relaxation and diffusion measurements.
Molecular Electronics
Orientation-Controlled Single-Molecule Junctions†
- Pages: 9771-9774
- First Published: 15 July 2014
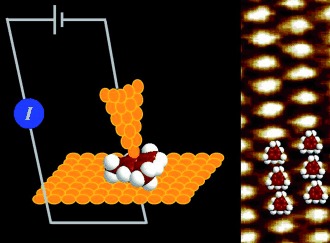
The conductivity of a single aromatic ring, perpendicular to its plane, is determined (see picture; I=current). The formation of highly ordered structures of mesitylene oriented parallel to an Au (111) plane enables direct contact between a scanning tunneling microscopy tip and the π-system of mesitylene to create highly conductive Au/aromatic/Au junctions under ambient conditions.
Membrane Preparation | Hot Paper
Coordination-Driven In Situ Self-Assembly Strategy for the Preparation of Metal–Organic Framework Hybrid Membranes†
- Pages: 9775-9779
- First Published: 22 July 2014
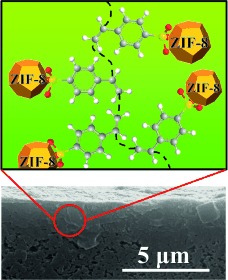
Mopping up the mess: A hybrid membrane composed of the metal–organic framework (MOF) ZIF-8 and poly(sodium 4-styrenesulfonate) was prepared by a coordination-driven in situ self-assembly method. The MOF particles were well-dispersed in the polymer in the resulting stable membrane (see picture), which showed excellent performance in the nanofiltration and separation of dyes from water.
Solid Electrolytes
Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-Supported Ionogels with a High Ionic Liquid Loading†
- Pages: 9780-9783
- First Published: 15 July 2014
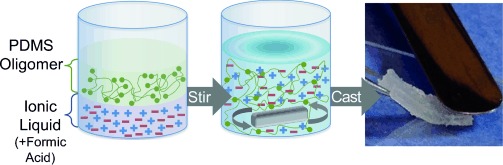
Supportive, despite their differences: The immiscibility of poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) and ionic liquids (ILs) has been overcome by a simple sol–gel reaction (see picture) to create PDMS-supported ILs (ionogels) with IL loadings of up to 80 % by mass. The ionogels exhibited high ionic conductivity and excellent mechanical behavior, with an elastic modulus of approximately 60 kPa without fatigue over 5000 cycles, even at elevated temperatures.
Protein–Protein Interactions | Hot Paper
An Unusual Protein–Protein Interaction through Coupled Unfolding and Binding†
- Pages: 9784-9787
- First Published: 01 July 2014
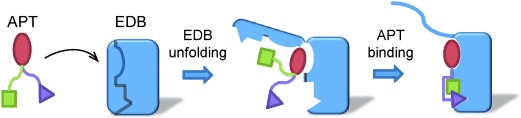
Unfold and hold: It is known that protein–protein interactions can involve coupled folding and binding, but coupled unfolding and binding is not well characterized. An unusual protein–protein interaction is described in which the binding of an aptide (APT) to fibronectin extradomain B (EDB) involves partial unfolding to expose the binding surface. The structural and energetic details were determined by NMR spectroscopy and thermodynamic analysis.
High-Pressure NMR Spectroscopy | Very Important Paper
A High-Pressure NMR Probe for Aqueous Geochemistry†
- Pages: 9788-9791
- First Published: 02 July 2014
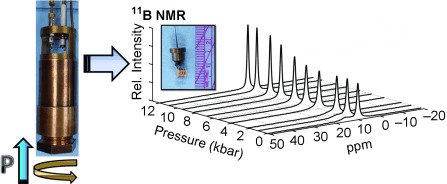
A non-magnetic piston-cylinder pressure cell has been developed for solution-state NMR spectroscopy up to 20 kbar for aqueous geochemical applications. 11B NMR spectroscopic investigations into the H3BO3–catechol equilibrium demonstrates a large pressure-driven exchange rate. The success of these experiments suggests that this probe design can be applied to a wide variety of NMR-active nuclei.
Polymer Sensors
Fluorescence Sensing of Amine Vapors Using a Cationic Conjugated Polymer Combined with Various Anions†
- Pages: 9792-9796
- First Published: 18 July 2014
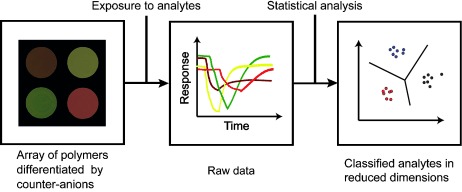
A sensor array comprising a conjugated cationic polymer combined with various counteranions has been developed. This simple approach allows the creation of polymer formulations able to detect vapors of industrially relevant amines in low ppm concentrations by fluorescence quenching measurements. Furthermore the array's response is useful to identify the nature of the analyte through pattern-based recognition algorithms.
Photophysics
UV Excited-State Photoresponse of Biochromophore Negative Ions†
- Pages: 9797-9801
- First Published: 15 July 2014
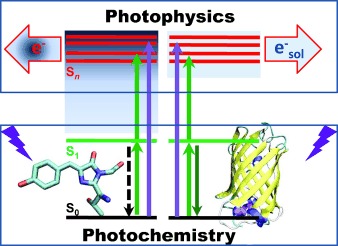
Higher electronically excited states of the green fluorescent protein chromophore anion have been probed directly by action absorption spectroscopy. The high density of these UV molecular resonances in the UV makes electron detachment in the gas phase efficient. Quantum calculations show this electronic band inside the protein to be resonant with the quasicontinuum of a solvated electron, thus suggesting its major role in the photophysics in the UV region.
Nitrogen Photofixation | Hot Paper
Plasmon-Induced Ammonia Synthesis through Nitrogen Photofixation with Visible Light Irradiation†
- Pages: 9802-9805
- First Published: 17 July 2014
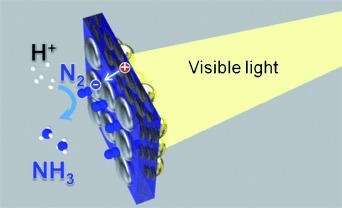
See the light of day: A plasmon-induced ammonia synthesis technique that responds to visible light and is based on a strontium titanate (SrTiO3) photoelectrode loaded with gold nanoparticles has been developed. It is deduced that plasmon-induced charge separation at the Au/SrTiO3 interface promotes oxidation in the anodic chamber and subsequent nitrogen reduction on the cathodic side.
Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Unprecedented Role of Hydronaphthoquinone Tautomers in Biosynthesis†
- Pages: 9806-9811
- First Published: 22 July 2014
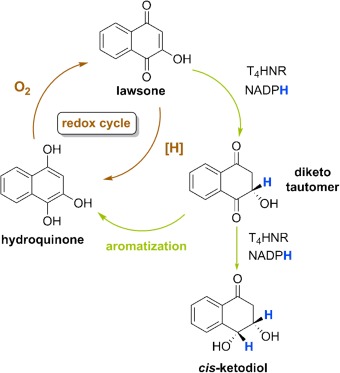
Breaking the cycle: In studies on the reduction of 2-hydroxynaphthoquinones to the stable 1,4-diketo tautomeric form of hydronaphthoquinones and their further reduction by fungal tetrahydroxynaphthalene reductase, diketo tautomers emerge as true intermediates in biosynthesis. Their formation breaks the (redox) cycle, thus protecting the cell from stress-related redox events.
Glycopeptides
Synthesis of the Highly Glycosylated Hydrophilic Motif of Extensins†
- Pages: 9812-9816
- First Published: 15 July 2014
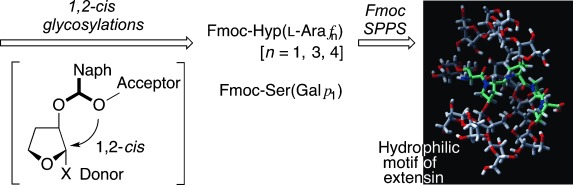
Just a phase: Stereoselective synthesis of one of the highly glycosylated hydrophilic motifs of extensins has been completed. Key steps were a 2-naphthylmethyl ether-mediated intramolecular aglycon delivery to the stereoselective construction of the Ser(Galp1) and Hyp(Arafn) (n=1, 3, 4) fragments and Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) for the highly glycosylated pentapeptide motif.
Gold–Carbenoids
Chemoselective Carbophilic Addition of α-Diazoesters through Ligand-Controlled Gold Catalysis†
- Pages: 9817-9821
- First Published: 23 July 2014
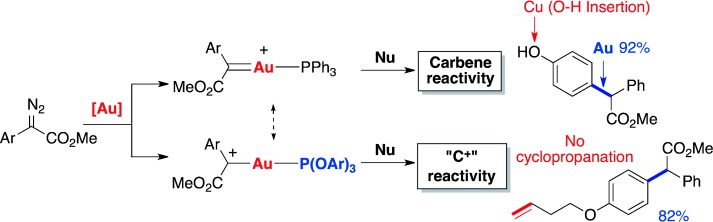
Carbocation or carbene? The chemoselective addition of arenes and 1,3-diketones to α-aryldiazoesters was achieved through ligand-controlled gold catalysis. The gold catalyst with electron-deficient phosphite as the ancillary ligand exclusively gave the carbophilic addition products, thus representing a new and efficient approach to form “carbophilic carbocations”, which selectively react with carbon nucleophiles.
Luminescence Imaging
Image-Contrast Technology Based on the Electrochemiluminescence of Porous Silicon and Its Application in Fingerprint Visualization†
- Pages: 9822-9826
- First Published: 17 July 2014
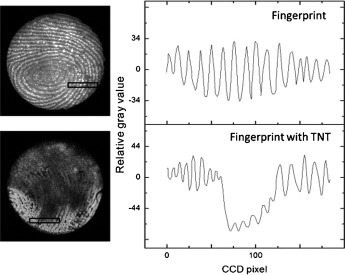
Fit for a modern Sherlock: Electrochemiluminescence by porous silicon (pSi) has a regular dynamic process involving activation, strong emission, and fading. This process can be perturbed by chemicals adsorbed on the pSi surface. The contrast in luminescence intensity between adjacent areas with different surface chemistry enabled the visualization of latent fingerprints and a trinitrotoluene (TNT) residue in a fingerprint with high resolution (see picture).
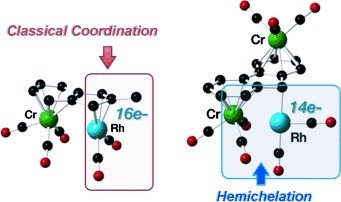
Metal–Metal Interactions
First Stabilization of 14-Electron Rhodium(I) Complexes by Hemichelation†
- Pages: 9827-9831
- First Published: 17 July 2014
Self-Assembly
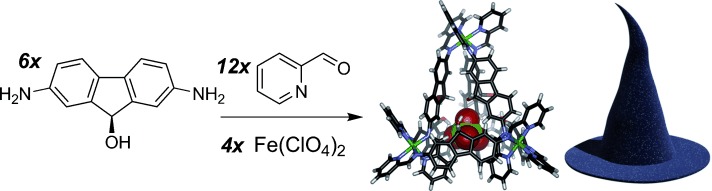
A Supramolecular Sorting Hat: Stereocontrol in Metal–Ligand Self-Assembly by Complementary Hydrogen Bonding†
- Pages: 9832-9836
- First Published: 17 July 2014
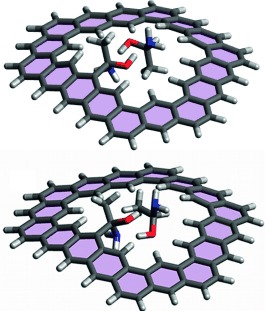
Noncovalent Interactions
Understanding a Host–Guest Model System through 129Xe NMR Spectroscopic Experiments and Theoretical Studies†
- Pages: 9837-9840
- First Published: 22 July 2014
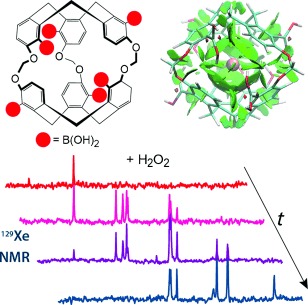
How hosts handle a noble guest: A combination of NMR spectroscopy and quantum chemistry enabled thorough analysis of the noncovalent interactions inside a xenon–host complex. The validation of this approach with a family of cryptophane hosts derived by treatment of the structure shown with H2O2 paves the way for the design of potent smart hyperpolarized 129Xe NMR sensors.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Targeting Human C-Type Lectin-like Molecule-1 (CLL1) with a Bispecific Antibody for Immunotherapy of Acute Myeloid Leukemia†
- Pages: 9841-9845
- First Published: 23 July 2014
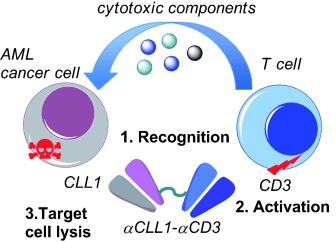
A bispecific antibody, αCLL1-αCD3, was synthesized using a genetically encoded unnatural amino acid, and shown to recruit cytotoxic T cells to CLL1-positive cells. The reported results validate the clinical potential of CLL1 as an AML-specific antigen for the generation of bispecific antibodies for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
Homologation | Very Important Paper
Stereocontrolled Synthesis of 1,5-Stereogenic Centers through Three-Carbon Homologation of Boronic Esters†
- Pages: 9846-9850
- First Published: 15 July 2014
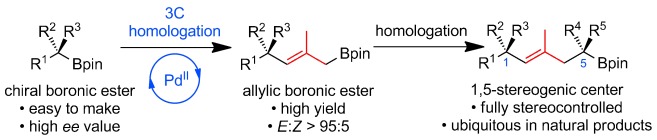
Three more: The 3C homologation of chiral pinacol boronic esters gives di- or trisubstituted allylic boronic esters with high yield and E selectivities. The combination of this method with lithiation–borylation enables the synthesis of alkyl chains that bear 1,5-stereogenic centers. The utility of the process was demonstrated in a formal synthesis of (+)-jasplakinolide.
CH Functionalization
Simple Sulfinate Synthesis Enables CH Trifluoromethylcyclopropanation†
- Pages: 9851-9855
- First Published: 03 August 2014
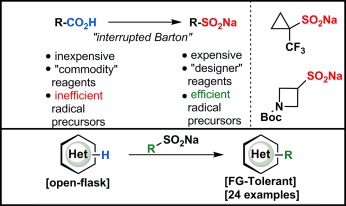
An interrupted Barton decarboxylation reaction has been used to convert readily available carboxylic acids into sulfinate salts (see scheme). Ten new sulfinate reagents were created and the reactivity of six of them towards CH functionalization was tested on a range of heterocycles. The simplicity of this approach (a cheap industrial oxidant, simple solvent, and no metals) is a clear advantage over other radical donors.
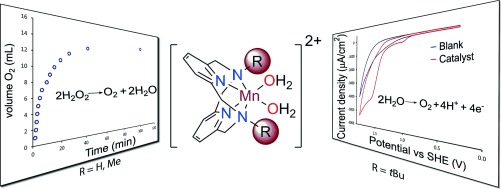
Water Oxidation
Ligand Modification Transforms a Catalase Mimic into a Water Oxidation Catalyst†
- Pages: 9856-9859
- First Published: 15 July 2014
Asymmetric Synthesis
Asymmetric Hydroxylative Phenol Dearomatization Promoted by Chiral Binaphthylic and Biphenylic Iodanes†
- Pages: 9860-9864
- First Published: 22 July 2014
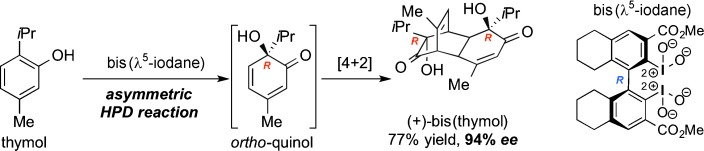
The selective oxygenation of iodobinaphthyls and iodobiphenyls afforded either λ3- or λ5-iodanes, which were evaluated for their capacity to promote asymmetric intermolecular hydroxylative phenol dearomatizations (HPDs). Most remarkably, a C2-symmetrical biphenylic λ5-iodane induced the HPD reaction/[4+2] cyclodimerization cascade of thymol into bis(thymol) with enantiomeric excesses of up to 94 %.
Cycloaddition
[HCo(CO)4]-Catalyzed Three-component Cycloaddition of Epoxides, Imines, and Carbon Monoxide: Facile Construction of 1,3-Oxazinan-4-ones†
- Pages: 9865-9869
- First Published: 18 July 2014
![[HCo(CO)4]-Catalyzed Three-component Cycloaddition of Epoxides, Imines, and Carbon Monoxide: Facile Construction of 1,3-Oxazinan-4-ones](/cms/asset/3b1de877-0d35-497d-a949-63c6171e60f9/mcontent.jpg)
Cobalt and CO: The title reaction is described to proceed in the presence of [HCo(CO)4] as the catalyst. The reaction occurs for a wide variety of imines and various substituted epoxides, thus providing an efficient and atom-economic route to 1,3-oxazinan-4-ones, with various substitution patterns, from simple and readily available starting materials.
Flavin Fluorescence
A Conical Intersection Controls the Deactivation of the Bacterial Luciferase Fluorophore†
- Pages: 9870-9875
- First Published: 14 July 2014
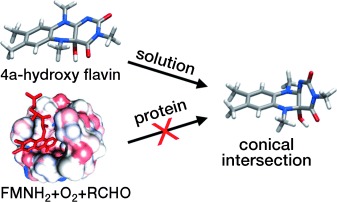
How nature lights up flavins: 4a-hydroxy flavins display weak fluorescence and ultrafast excited-state decay in solution, but exhibit strong fluorescence when produced in a protein cavity. A joint experimental and theoretical study explains the fluorescence properties of these flavin adducts in terms of a deactivation pathway mediated by a conical intersection that becomes inaccessible in sterically constrained environments.
Carbohydrates
Synthesis of the Heparin-Based Anticoagulant Drug Fondaparinux†
- Pages: 9876-9879
- First Published: 15 July 2014
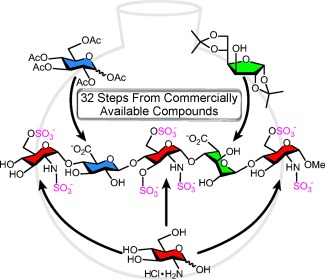
Working against the clot: The synthetic anticoagulant fondaparinux, a pentasaccharide based on the antithrombin-binding domain of heparin, was prepared in a concise and efficient manner in the shortest route reported to date. The application of one-pot strategies, the use of common intermediates, and the efficient preparation of monosaccharide building blocks from commercial sources are key features of this approach.
Strained Polycycles
Synthesis of Bridged Oxafenestranes from Pleuromutilin†
- Pages: 9880-9883
- First Published: 17 July 2014
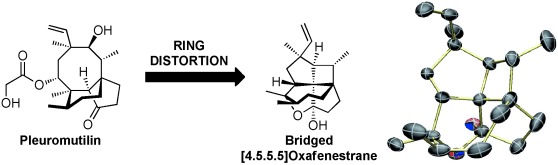
Fenestranes are highly strained molecules possessing a quaternary carbon atom with bonds that deviate from the canonical tetrahedral geometry. The natural product pleuromutilin can be used as a starting material for the synthesis of bridged [4.5.5.5]- and [4.5.7.5]oxafenestranes through a carbocation rearrangement cascade. X-ray crystallography shows that these compounds exhibit significant planarization of the central tetracoordinate carbon center.
CH Activation
Easily Accessible Auxiliary for Palladium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Amination of C(sp2)H and C(sp3)H Bonds at δ- and ε-Positions†
- Pages: 9884-9888
- First Published: 22 July 2014
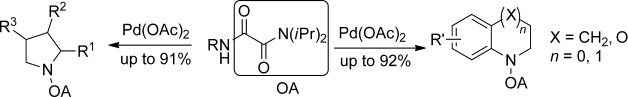
Remote access: The first application of an oxalyl amide to direct CH functionalizations at remote positions is reported. The results show both C(sp2)H and C(sp3)H bonds at δ- and ε-positions are effectively activated, thus giving tetrahydroquinolines, benzomorpholines, pyrrolidines, and indolines in moderate to excellent yields by palladium-catalyzed intramolecular CH amination.
Multiple CH Activation | Hot Paper
One-Pot Synthesis of Highly Substituted Polyheteroaromatic Compounds by Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Multiple CH Activation and Annulation†
- Pages: 9889-9892
- First Published: 17 July 2014
Modified Nucleosides
Synthesis and Duplex-Stabilizing Properties of Fluorinated N-Methanocarbathymidine Analogues Locked in the C3′-endo Conformation†
- Pages: 9893-9897
- First Published: 15 July 2014
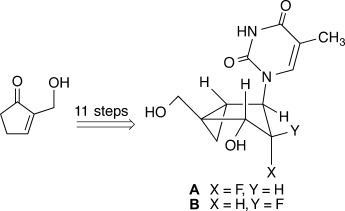
The power of conviction: The efficient synthesis, antiviral activity, and duplex-stabilizing properties of both isomers, A and B, of the 2′-fluoro analogue of N-methanocarbathymidine (N-MCT) are reported. Incorporation of the fluorine substituent at the 2′-position of the N-MCT scaffold was found to have a strong positive effect on duplex thermal stability.
Perovskite Solar Cells | Hot Paper
A Fast Deposition-Crystallization Procedure for Highly Efficient Lead Iodide Perovskite Thin-Film Solar Cells†
- Pages: 9898-9903
- First Published: 22 July 2014
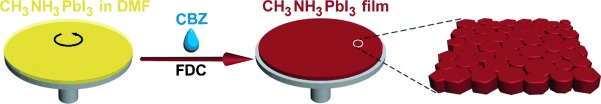
Fast and thin: Flat, uniform thin films of CH3NH3PbI3 perovskites have been produced by a fast, one-step procedure involving spin-coating of a DMF solution of CH3NH3PbI3 and immediate exposure to chlorobenzene to induce crystallization. Planar heterojunction solar cells made with these films gave a maximum power conversion efficiency of 16.2 %.
Heterocycles
Expedient Synthesis of Fused Azepine Derivatives Using a Sequential Rhodium(II)-Catalyzed Cyclopropanation/1-Aza-Cope Rearrangement of Dienyltriazoles†
- Pages: 9904-9908
- First Published: 15 July 2014
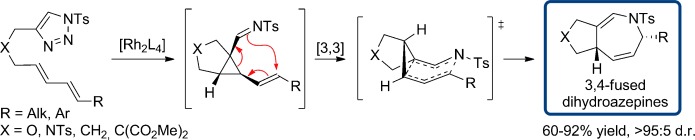
A general method for the formation of fused dihydroazepines from 1-sulfonyl-1,2,3-triazoles bearing a tethered diene is reported. The process involves an intramolecular cyclopropanation of an α-imino rhodium(II) carbenoid, leading to a transient 1-imino-2-vinylcyclopropane intermediate which rapidly undergoes a 1-aza-Cope rearrangement to generate the products in moderate to excellent yields. Ts=4-toluenesulfonyl.
Synthetic Methods
Nickel-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Functionalized Difluoromethyl Bromides and Chlorides with Aryl Boronic Acids: A General Method for Difluoroalkylated Arenes†
- Pages: 9909-9913
- First Published: 17 July 2014
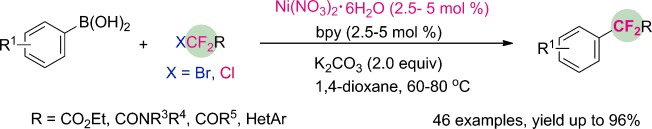
Simple and easy: The first example of a nickel-catalyzed difluoroalkylation of aryl boronic acids with functionalized difluoromethyl bromides and chlorides has been developed. This cross-coupling process features a broad substrate scope, a cheap catalyst, and excellent functional-group compatibility.
Sustainable Chemistry
An “All-Green” Catalytic Cycle of Aqueous Photoionization
- Pages: 9914-9916
- First Published: 22 July 2014
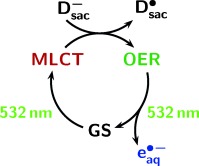
Green light and a cheap, even bioavailable, sacrificial donor produce hydrated electrons in the displayed catalytic cycle. The catalyst is a popular metal complex functioning as a “container” for a radical anion. The cycle could open a pathway toward the solar-driven reductive detoxification of halogenated organic waste.  =MeOPhO−;
=MeOPhO−;  =MeOPhO.; MLCT=*[RuIII(bpy)2(bpy.−)]2+; OER=[RuII(bpy)2(bpy.−)]+; GS=[RuII(bpy)3]2+; bpy=2,2′-bipyridine.
=MeOPhO.; MLCT=*[RuIII(bpy)2(bpy.−)]2+; OER=[RuII(bpy)2(bpy.−)]+; GS=[RuII(bpy)3]2+; bpy=2,2′-bipyridine.
Self-Assembly | Hot Paper
Reversible Supramolecular Assembly at Specific DNA Sites: Nickel-Promoted Bivalent DNA Binding with Designed Peptide and Bipyridyl–Bis(benzamidine) Components†
- Pages: 9917-9921
- First Published: 15 July 2014
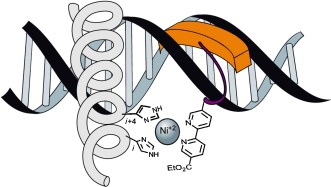
Nickel(II) salts promote the assembly of a bis(histidine)-modified peptide that is derived from a bZIP transcription factor and a bipyridine-substituted bis(benzamidine) unit at specific DNA sites. This supramolecular system features some key properties of naturally occurring DNA-binding proteins, such as bivalence, selectivity, responsiveness to external agents, and reversibility.
Electrocatalysis
Metal-Free Dihydrogen Oxidation by a Borenium Cation: A Combined Electrochemical/Frustrated Lewis Pair Approach†
- Pages: 9922-9925
- First Published: 18 July 2014
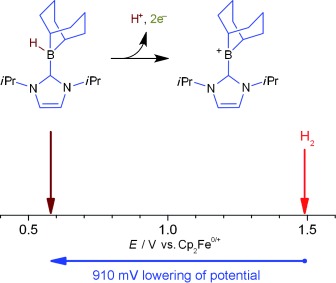
The potential that is required for non-aqueous H2 oxidation at a carbon electrode can be significantly reduced by using a borenium cation in a combined electrochemical/frustrated Lewis pair approach. This system exhibits faster electrode kinetics, increased stability to electrogenerated protons, and improved catalyst recycling over a previously reported system that is based on the borane Lewis acid B(C6F5)3.
Organocatalysis
Phosphoric Acid Catalyzed Desymmetrization of Bicyclic Bislactones Bearing an All-Carbon Stereogenic Center: Total Syntheses of (−)-Rhazinilam and (−)-Leucomidine B†
- Pages: 9926-9930
- First Published: 22 July 2014
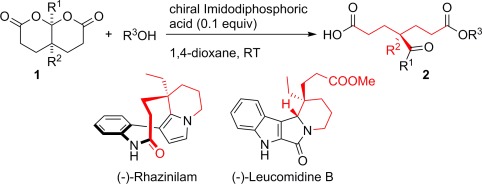
Breaking symmetry: Achiral bislactones (1) undergo desymmetrization by reaction with alcohol in the presence of chiral imidodiphosphoric acids. The monoacids 2, having an all-carbon stereogenic center, were obtained in good to excellent yields and enantioselectivities. Concise total syntheses of (−)-rhazinilam and (−)-leucomidine B were subsequently developed using 2 as a common starting material.
CH Functionalization
Catalytic 1,4-Rhodium(III) Migration Enables 1,3-Enynes to Function as One-Carbon Oxidative Annulation Partners in CH Functionalizations†
- Pages: 9931-9935
- First Published: 22 July 2014
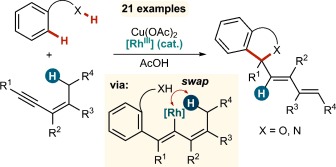
When two become one: 1,3-Enynes containing allylic hydrogen atoms cis to the alkyne are shown to act as one-carbon partners, rather than two-carbon partners, in various rhodium-catalyzed oxidative annulations. The mechanism of these unexpected transformations is proposed to occur through double CH activation, involving a hitherto rare example of the 1,4-migration of a RhIII species.
Asymmetric Catalysis
High Performance of a Palladium Phosphinooxazoline Catalyst in the Asymmetric Arylation of Cyclic N-Sulfonyl Ketimines†
- Pages: 9936-9939
- First Published: 18 July 2014
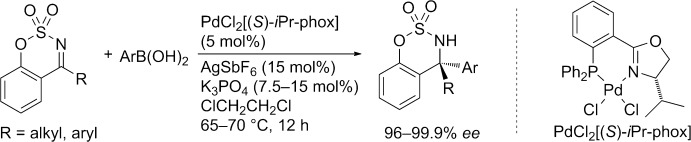
Chiral cyclic sulfamidates are obtained by the asymmetric addition of arylboronic acids to six-membered cyclic N-sulfonyl ketimines. A cationic palladium complex with a chiral phosphine-oxazoline ligand (iPr-phox) shows high catalytic activity and enantioselectivity to give the products in high yields with 96–99.9 % ee. The cyclic sulfamidates exhibit a tetrasubstituted stereogenic center with an amino group and a triaryl or alkyldiaryl group as substituents.
Dihydrogen Bonding
Evidence of Dihydrogen Bonding of a Chiral Amine–Borane Complex in Solution by VCD Spectroscopy†
- Pages: 9940-9943
- First Published: 15 July 2014
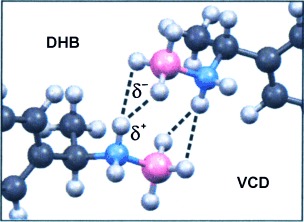
A chiral amine–borane is investigated by vibrational circular dichroism (VCD) spectroscopy. By comparison of experimental and calculated spectra, a unique VCD pattern associated with the formation of dihydrogen-bonded dimers in solution is identified. Different dihydrogen binding arrangements in solution and in the solid state are characterized.
Single-Electron-Transfer Catalysis
Oxidative Catalysis Using the Stoichiometric Oxidant as a Reagent: An Efficient Strategy for Single-Electron-Transfer-Induced Tandem Anion–Radical Reactions†
- Pages: 9944-9948
- First Published: 28 July 2014
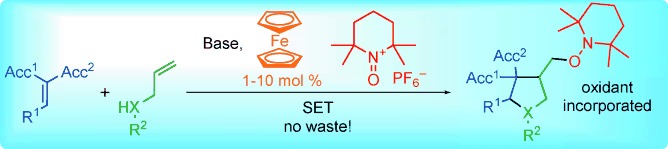
Making waste a functionality: Oxidative electron-transfer-mediated anion–radical transformations are rendered catalytic by employing a 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-N-oxopiperidinium salt and ferrocene. The method provides an asymmetric approach to highly functionalized cyclopentane and pyrrolidine derivatives. At the same time the co-generated reduced species TEMPO serves as a useful oxygenating functionality.
Iodine Adsorption
Adsorption of I2 by Macrocyclic Polyazadithiophenolato Complexes Mediated by Charge-Transfer Interactions†
- Pages: 9949-9952
- First Published: 30 July 2014
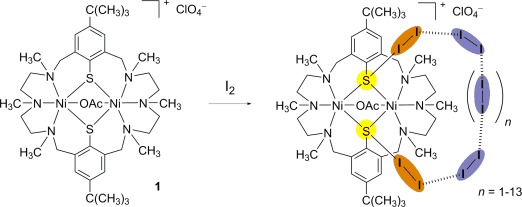
Seeing I to I: The macrocyclic complex [Ni2(L)(OAc)]ClO4 (1) adsorbs up to 17 molar equivalents (>270 wt %) of iodine, although it does not exhibit permanent porosity. IR and crystallographic studies reveal that two I2 molecules are captured by means of thiophenolate→I2 charge-transfer interactions, which enable the diffusion and sorption of further I2 molecules in a polyiodide-like network.
Group 14 Chemistry
N-Heterocyclic Carbene Coordinated Neutral and Cationic Heavier Cyclopropylidenes†
- Pages: 9953-9956
- First Published: 24 July 2014
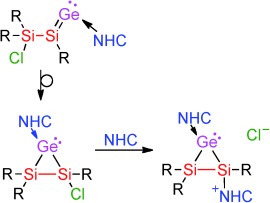
He is heavy and he′s my brother: NHC-coordinated cyclopropenylidene analogues with molecular scaffolds exclusively formed by heavier Group 14 elements are accessible from the corresponding vinylidene isomers by exchange of the NHC ligand for a smaller NHC. The residual chloride in one of these heavier cyclic carbenes can be expelled by a second equivalent of NHC to generate cationic derivatives of the imidazolium type.
Chiral Separation
Functionalized Graphene as a Gatekeeper for Chiral Molecules: An Alternative Concept for Chiral Separation†
- Pages: 9957-9960
- First Published: 13 July 2014