High Performance of a Palladium Phosphinooxazoline Catalyst in the Asymmetric Arylation of Cyclic N-Sulfonyl Ketimines†
Chunhui Jiang
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Yixin Lu
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Tamio Hayashi
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)
Institute of Materials Research and Engineering, A*STAR, 3 Research Link, Singapore 117602 (Singapore)
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorChunhui Jiang
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Yixin Lu
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Tamio Hayashi
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)
Institute of Materials Research and Engineering, A*STAR, 3 Research Link, Singapore 117602 (Singapore)
Department of Chemistry, National University of Singapore, 3 Science Drive 3, Singapore 117543 (Singapore)Search for more papers by this authorWe thank the National University of Singapore and the Ministry of Education (MOE) of Singapore (R-143-000-362-112 and R-143-000-539-133) for financial support.
Graphical Abstract
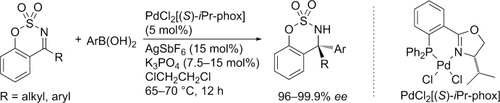
Chiral cyclic sulfamidates are obtained by the asymmetric addition of arylboronic acids to six-membered cyclic N-sulfonyl ketimines. A cationic palladium complex with a chiral phosphine-oxazoline ligand (iPr-phox) shows high catalytic activity and enantioselectivity to give the products in high yields with 96–99.9 % ee. The cyclic sulfamidates exhibit a tetrasubstituted stereogenic center with an amino group and a triaryl or alkyldiaryl group as substituents.
Abstract
A cationic palladium complex with a chiral phosphine-oxazoline ligand (iPr-phox) showed high catalytic activity and enantioselectivity in the asymmetric addition of arylboronic acids to six-membered cyclic N-sulfonyl ketimines to give high yields of the corresponding chiral cyclic sulfamidates with 96–99.9 % ee. The products have tetrasubstituted stereogenic centers with an amino group and a triaryl or alkyldiaryl group as substituents.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201406147_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf10.6 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1For reviews on the transition-metal-catalyzed asymmetric addition of organometallic reagents to imines, see:
- 1aS. Kobayashi, Y. Mori, J. S. Fossey, M. M. Salter, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2626;
- 1bC. S. Marques, A. J. Burke, ChemCatChem 2011, 3, 635;
- 1cK. Yamada, K. Tomioka, Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2874;
- 1dG. K. Friestad, A. K. Mathies, Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 2541.
- 2For recent examples of the transition-metal-catalyzed asymmetric addition of organometallic reagents to imines, see:
- 2aS. Hirner, A. Kolb, J. Westmeier, S. Gebhardt, S. Middel, K. Harms, P. von Zezschwitz, Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3162;
- 2bZ. Cui, Y.-J. Chen, W.-Y. Gao, C.-G. Feng, G.-Q. Lin, Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 1016;
- 2cB. Gopula, C.-W. Chiang, W.-Z. Lee, T.-S. Kuo, P.-Y. Wu, J. P. Henschke, H.-L. Wu, Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 632.
- 3
- 3aT. Nishimura, A. Noishiki, G. C. Tsui, T. Hayashi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5056; See, also:
- 3bT. Nishimura, A. Noishiki, Y. Ebe, T. Hayashi, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 1821;
10.1002/ange.201208593 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1777;
- 3cT. Nishimura, A. Y. Ebe, H. Fujimoto, T. Hayashi, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5504.
- 4
- 4aY. Luo, A. J. Carnell, H. W. Lam, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 6866; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6762;
- 4bY. Luo, H. B. Hepburn, N. Chotsaeng, H. W. Lam, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 8434; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8309.
- 5
- 5aH. Wang, T. Jiang, M.-H. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 971;
- 5bH. Wang, M.-H. Xu, Synthesis 2013, 45, 2125.
- 6G. Yang, W. Zhang, Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 7688; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7540.
- 7Ring opening of benzosulfamidate with nickel-catalyzed Grignard cross-coupling, see:
- 7aP. M. Wehn, J. Du Bois, Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 4685; Ring opening with LiAlH4 reduction, see:
- 7bY.-Q. Wang, C.-B. Yu, D.-W. Wang, X.-B. Wang, Y.-G. Zhou, Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2071.
- 8For reviews on the rhodium-catalyzed asymmetric addition of arylboron reagents, see:
- 8aT. Hayashi, K. Yamasaki, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2829;
- 8bS. Darses, J.-P. Genet, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 4313;
- 8cJ. Christoffers, G. Koripelly, A. Rosiak, M. Rössle, Synthesis 2007, 1279;
- 8dN. Miyaura, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 81, 1535;
- 8eJ. D. Hargrave, J. C. Allen, C. G. Frost, Chem. Asian J. 2010, 5, 386;
- 8fH. J. Edwards, J. D. Hargrave, S. D. Penrose, C. G. Frost, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2093;
- 8gP. Tian, H.-Q. Dong, G.-Q. Lin, ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 95.
- 9For a review on the palladium-catalyzed asymmetric addition of arylboron reagents, see: Y.-W. Sun, P.-L. Zhu, Q. Xu, M. Shi, RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 3153.
- 10A chiral phosphinooxazoline-palladium complex has been used as a catalyst for the asymmetric addition of arylboronic acids to isatins: Q. Li, P. Wan, S. Wang, Y. Zhuang, L. Lia, Y. Zhou, Y. He, R. Cao, L. Qiu, Z. Zhou, Appl. Catal. A 2013, 458, 201.
- 11
- 11aP. von Matt, A. Pfaltz, Angew. Chem. 1993, 105, 614; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1993, 32, 566;
- 11bJ. Sprinz, G. Helmchen, Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 1769;
- 11cG. J. Dawson, C. G. Frost, J. M. J. Williams, S. J. Coote, Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 3149.
- 12
- 12aY. Uozumi, K. Kato, T. Hayashi, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 1998, 9, 1065;
- 12bA. J. Blacker, M. L. Clarke, M. S. Loft, M. F. Mahon, M. E. Humphries, J. M. J. Williams, Chem. Eur. J. 2000, 6, 353.
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3765(20000117)6:2<353::AID-CHEM353>3.0.CO;2-U CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 13Cationic bisphosphine-palladium catalysts have been used for the conjugate addition of boron reagents to α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds; for reviews, see:
- 13aA. Gutnov, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 4547;
- 13bY. Yamamoto, T. Nishikata, N. Miyaura, J. Synth. Org. Chem. Jpn. 2006, 64, 1112;
- 13cG. Berthon-Gelloz, T. Hayashi, Boronic Acids, Vol. 1, 2nd ed. (Ed.: ), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2011, Chap. 5, pp. 263–313.
- 14Zhang reported (Ref. [6]) that the addition of PhB(OH)2 to 1 b (R=Me) catalyzed by a chiral pyridyloxazoline-palladium complex in a sealed tube charged with oxygen at 80 °C for 48 h gave 58 % yield of the corresponding benzosulfamidate (95 % ee).
- 15A palladium complex coordinated with chiral pyridinooxazoline ligand was reported to be an efficient catalyst for asymmetric conjugate addition reactions to cyclic enones:
- 15aK. Kikushima, J. C. Holder, M. Gatti, B. M. Stoltz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6902;
- 15bJ. C. Holder, A. N. Marziale, M. Gatti, B. Mao, B. M. Stoltz, Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 74.
- 16The racemization of arylation product 3 ep under the reaction conditions was confirmed experimentally by exposing enantiomerically enriched 3 ep (99.2 % ee) to the reaction conditions of entry 3 in Table 3, which resulted in the complete racemization of 3 ep.