Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Outside Front Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 04 November 2024

Outside Front Cover: The cover image is based on the article Water wisteria genome reveals environmental adaptation and heterophylly regulation in amphibious plants by Gaojie Li et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.15050.
Inside Front Cover Image
- Page: ii
- First Published: 04 November 2024
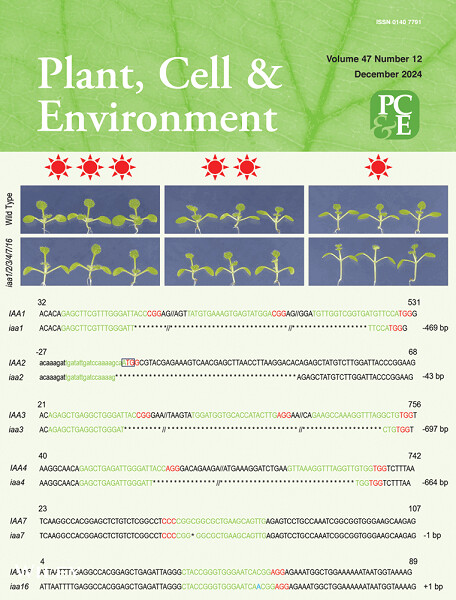
Inside Front Cover: The cover image is based on the article Sextuple knockouts of a highly conserved and coexpressed AUXIN/INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID gene set confer shade avoidance-like responses in Arabidopsis by Xinxing Yang et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.15039.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Sextuple knockouts of a highly conserved and coexpressed AUXIN/INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID gene set confer shade avoidance-like responses in Arabidopsis
- Pages: 4483-4497
- First Published: 16 July 2024
A highly conserved and coexpressed gene set of Arabidopsis thaliana Aux/IAAs was inactivated by genomic editing. The shade-avoidance-like phenotypes of these iaa1/2/3/4/7/16 sextuple mutants revealed their essential roles for the optimal integration between light and auxin signalling pathways.
Rice CRYPTOCHROME-INTERACTING BASIC HELIX-LOOP-HELIX 1-LIKE interacts with OsCRY2 and promotes flowering by upregulating Early heading date 1
- Pages: 4498-4515
- First Published: 16 July 2024
Rice transcription factor CRYPTOCHROME-INTERACTING BASIC HELIX-LOOP-HELIX 1-LIKE (OsCIB1L) promotes flowering time by interacting with OsCRY2 to mediate blue light-induced upregulation of Early heading date 1. Natural alleles in OsCIB1L and OsCRY2 contribute to the adaptive expansion of rice cultivation areas.
Biochemical versus stomatal acclimation of dynamic photosynthetic gas exchange to elevated CO2 in three horticultural species with contrasting stomatal morphology
- Pages: 4516-4529
- First Published: 16 July 2024
Three important horticultural crops with contrasting stomatal density (cucumber > tomato > chrysanthemum) acclimated to elevated CO2 with very different strategies: Cucumber mostly acclimated via stomatal conductance responses, whereas chrysanthemum mostly acclimated via photosynthetic biochemistry.
Heat waves induce milkweed resistance to a specialist herbivore via increased toxicity and reduced nutrient content
- Pages: 4530-4542
- First Published: 16 July 2024
By disentangling the direct and indirect effects of climate change on species interactions, here we demonstrate that indirect effects—rather than direct—on the plant and insect herbivore physiology are key to understand how plant-herbivore interactions may proceed in a changing world.
The P2 protein of wheat yellow mosaic virus acts as a viral suppressor of RNA silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana to facilitate virus infection
- Pages: 4543-4556
- First Published: 17 July 2024
Wheat yellow mosaic virus P2 protein exerts VSR activity in Nicotiana benthamiana by interfering with the CaM–CAMTA3 interaction to facilitate virus efficient systemic infection.
Metagenomic insights into nitrogen cycling functional gene responses to nitrogen fixation and transfer in maize–peanut intercropping
- Pages: 4557-4571
- First Published: 19 July 2024
The metagenomic analyses and structural equation modelling indicated that Bradyrhizobium significantly affected the nitrogen fixation, whereas the nrfC and nirA influenced the nitrogen transfer. Overall, our study identified key bacterial genus and genes associated with nitrogen fixation and transfer, thus advancing our understanding of interspecific interactions and highlighting the pivotal role of soil microorganisms and functional genes in maintaining soil ecosystem stability from a molecular ecological perspective.
Discrimination of relatedness drives rice flowering and reproduction in cultivar mixtures
- Pages: 4572-4585
- First Published: 22 July 2024
This study identified the role and mechanisms of relatedness-mediated neighbour discrimination in the improvement of performance and yield in rice cultivar mixtures, and found root-secreted (–)-loliolide's role as a key component of rice response to neighbour genetic relatedness interactions.
Stomatal dynamics in Alloteropsis semialata arise from the evolving interplay between photosynthetic physiology, stomatal size and biochemistry
- Pages: 4586-4598
- First Published: 22 July 2024
Stomatal dynamics in a wild grass arise from the evolving interplay between photosynthetic physiology and the size and biochemical function of stomatal complexes.
3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase 19 contributes to the biosynthesis of seed lipids and cuticular wax in Arabidopsis and abiotic stress tolerance
- Pages: 4599-4614
- First Published: 23 July 2024
KCS19, encoding a fatty acid elongase 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase, plays a crucial role in synthesizing very-long-chain fatty acids for cuticular wax and seed storage lipids in Arabidopsis. Its function significantly impacts plant responses to drought and salt stress.
Ignited competition: Impact of bioactive extracellular compounds on organelle functions and photosynthetic systems in harmful algal blooms
- Pages: 4615-4629
- First Published: 24 July 2024
The bioactive extracellular compounds of Alexandrium minutum can induce interspecies interaction by affecting the cell physiology of related harmful algae, mainly showing damage to photosynthetic organelles and redistribution of intracellular biomacromolecules.
FveDREB1B improves cold tolerance of woodland strawberry by positively regulating FveSCL23 and FveCHS
- Pages: 4630-4650
- First Published: 25 July 2024
FveDREB1B activates FveSCL23, and both interact with FveDELLA to inhibit the initiation of reproductive growth, respectively. FveDREB1B activates FveCHS and promotes anthocyanin accumulation in leaves. Both pathways contribute to the cold tolerance of woodland strawberry.
The invertase gene PWIN1 confers chilling tolerance of rice at the booting stage via mediating pollen development
- Pages: 4651-4663
- First Published: 25 July 2024
The rice pollen-preferential invertase gene PWIN1 was required for pollen chilling tolerance. PWIN1 deficiency reduced pollen viability and seed-setting rate, while overexpression increased pollen viability and seed-setting rate as compared with the wild-type under chilling conditions. This study provides a new module to improve chilling-tolerance of rice at the booting stage.
A viroid-derived small interfering RNA targets bHLH transcription factor MdPIF1 to regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in Malus domestica
- Pages: 4664-4682
- First Published: 25 July 2024
Our work identifies an apple dimple fruit viroid-derived small RNA that mediating the cleavage of mRNA of a bHLH transcription factor MdPIF1, a positive regulator in anthocyanin biosynthesis, resulting in decreased synthesis and accumulation of anthocyanin in apple (Malus domestica) fruits.
Growing in phosphorus-impoverished habitats in south-western Australia: How general are phosphorus-acquisition and -allocation strategies among Proteaceae, Fabaceae and Myrtaceae species?
- Pages: 4683-4701
- First Published: 29 July 2024
Rather than depending solely on mycorrhizal symbioses, Myrtaceae and Fabaceae showed multiple P-acquisition strategies growing in severely P-impoverished environments as did Proteaceae. High investment of metabolite P and low investment of nucleic acid P was associated with high P-use efficiency.
An AP2/ERF member LlERF012 confers thermotolerance via activation of HSF pathway in lily
- Pages: 4702-4719
- First Published: 29 July 2024
An unreported regulatory mechanism of heat stress response mediated by the module LlERF012-LlHSFA1 was proposed, which confers thermotolerance by activating both the class A and the class B HSF pathway. The results provide new evidence on ERF-mediated coordination of different HSFs in plant thermotolerance.
Water wisteria genome reveals environmental adaptation and heterophylly regulation in amphibious plants
- Pages: 4720-4740
- First Published: 30 July 2024
We investigated the genome and transcriptome of Hygrophila difformis, establishing a model for heterophylly and functions of environmental factors on phenotype.
Hydraulic plasticity and water use regulation act to maintain the hydraulic safety margins of Mediterranean trees in rainfall exclusion experiments
- Pages: 4741-4753
- First Published: 30 July 2024
Mediterranean species submitted to aggravated water stress have maintained their hydraulic safety margin (HSM). For Pinus halepensis and Quercus pubescens, HSM maintenance resulted from their capacity to escape water stress, while it results from the plasticity of Ψtlp and P50 for Quercus ilex.
The bryophyte rhizoid-sphere microbiome responds to water deficit
- Pages: 4754-4767
- First Published: 30 July 2024
Here, we explore the microbiome around the rhizoids of bryophyte plants, termed rhizoid-sphere. These microbiome changes under drought are similar to the rhizosphere of angiosperms. Microbes that could promote plant growth and fix nitrogen seem to be recruited by specific bryophyte species.
Insights into response of seagrass (Zostera marina) to sulfide exposure at morphological, physiochemical and molecular levels in context of coastal eutrophication and warming
- Pages: 4768-4785
- First Published: 30 July 2024
Little is known about the molecular response and resistance mechanisms of seagrass to sulfide stress. This study indicates that photosynthesis-related pathways in eelgrass are significantly inhibited under sulfide stress, while carbohydrate and sulfur metabolism-related pathways are markedly activated, which may represent potential resistance mechanisms.
CIPK11 phosphorylates GSTU23 to promote cold tolerance in Camellia sinensis
- Pages: 4786-4799
- First Published: 01 August 2024
CsCIPK11 decodes cold signals and modulates antioxidant capacity by phosphorylating CsGSTU23, leading to improved cold tolerance in tea plants. CsCIPK11- CsGSTU23 module regulates cold tolerance in tea plant and supplies gene resources for cold-resistant tea cultivar breeding.
A novel Pik allele confers extended resistance to rice blast
- Pages: 4800-4814
- First Published: 01 August 2024
We employed BSA-seq to identify a novel Pik allele, Pik-W25, from the wild rice WR25. Pik-W25 can recognise AvrPik-C, -D, or -E alleles and trigger resistance. Notably, the Pik-W25 NIL showed enhanced field resistance to leaf and panicle blast without significant morphological or developmental differences. These findings advance our knowledge of rice blast resistance mechanisms and offer valuable resources for effective and sustainable rice blast control strategies.
Reduced mesophyll conductance under chronic O3 exposure in poplar reflects thicker cell walls and increased subcellular diffusion pathway lengths according to the anatomical model
- Pages: 4815-4832
- First Published: 05 August 2024
O3-caused decrease of gm in two Populus × canadensis Moench clones is mainly driven by altered subcellular traits, notably cell wall and cytoplasm thickening, inter-chloroplast spacing and the ratio of exposed chloroplasts to mesophyll surface area (Sc/Sm). However, the observed gm-anatomy relationship is clone-dependent.
Molecular mechanisms underlying natural deficient and ultraviolet-induced accumulation of anthocyanin in the peel of ‘Jinxiu’ peach
- Pages: 4833-4848
- First Published: 05 August 2024
To explore the mechanisms for natural deficient and UV-induced anthocyanin accumulation in ‘Jinxiu’ peach peel, the study was conducted and it was revealed that anthocyanin accumulation is regulated by a transcriptional cascade involving activators PpMYB10.1/10.3 and repressor PpMYB80.
Optimising height-growth predicts trait responses to water availability and other environmental drivers
- Pages: 4849-4869
- First Published: 05 August 2024
Eco-evolutionary theory (EEO) can yield insight into how plant traits are likely to adapt to future climatic conditions. However, current implementations typically focus on maximising plant carbon gain while omitting important processes related to tissue construction and relative allocation which are important for understanding plant growth rates, and consequently, fitness. Using a height-growth based trait optimisation framework incorporating plant hydraulics, we predict how four key traits: leaf mass per area, sapwood area to leaf area ratio (Huber value), wood density and sapwood-specific conductivity, respond to soil moisture, atmospheric aridity, and light availability and consider these predictions in light of empirical observations. Finally, we use this framework to explore how simultaneous optimisation of multiple traits can yield species turnover across a soil moisture gradient. The model shows that, when plants maximise height-growth rate, the optimal value of leaf-mass-per-area, Huber value, wood density and sapwood-specific conductivity shifts with the environment and through plant ontogeny in line with empirical results.
Plant traits mediate foliar uptake of deposited nitrogen by mature woody plants
- Pages: 4870-4885
- First Published: 05 August 2024
We conducted a 15N-labelling experiment on canopy leaves of 19 woody species with diverse traits. We found that species with acquisitive traits had higher foliar nitrogen (N) uptake than conservative species, providing insights into the necessity of accounting foliar uptake into ecosystem N budget.
Photosynthetic capacity in middle-aged larch and spruce acclimates independently to experimental warming and elevated CO2
- Pages: 4886-4902
- First Published: 05 August 2024
Our study demonstrates that there is no interactive effect of warming and elevated CO2 on the photosynthetic capacity (Vcmax and Jmax) of mature trees (~45 years old) of black spruce and tamarack, when grown under realistic field conditions.
OPINION
Manipulating hormones to mitigate trade-offs in crops
- Pages: 4903-4907
- First Published: 05 August 2024
Addressing trait coupling due to gene pleiotropy presents challenges in conventional breeding system. However, targeted hormonal manipulation and precise genetic engineering designs hold promise to alleviate trade-offs and unlock the potential of crops for multiple desirable traits.
Function of plastid translation in plant temperature acclimation: Retrograde signalling or extraribosomal ‘moonlighting’ functions?
- Pages: 4908-4916
- First Published: 05 August 2024
Specific components of the plastid ribosome could act as pivotal limiting factors in plant temperature acclimation. We endeavour to elucidate the molecular nexus between plastid translation and temperature acclimation by incorporating the concept of extraribosomal ‘moonlighting’ functions of plastid ribosome proteins.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Effects of water stress on apoplastic barrier formation in soil grown roots differ from hydroponically grown roots: Histochemical, biochemical and molecular evidence
- Pages: 4917-4931
- First Published: 07 August 2024
In soil-grown roots of barley, the endodermal cell suberization was initiated far much closer towards the root tip, suberin amounts were almost doubled, and roots were more than twofold longer compared with hydroponics. There is a very different plastic response to water stress in soil-grown roots compared with hydroponically cultivated roots.
Soybean transcription factor GmNF-YB20 confers resistance to stripe rust in transgenic wheat by regulating nonspecific lipid transfer protein genes
- Pages: 4932-4944
- First Published: 08 August 2024
The soybean transcription factor GmNF-YB20 confers resistance to stripe rust in transgenic wheat by regulating nonspecific lipid transfer protein genes. Our findings provide perspective regarding the molecular mechanism of GmNF-YB20 in wheat and highlight the potential use for wheat breeding.
OPINION
Lignin lite: Boosting plant power through selective downregulation
- Pages: 4945-4962
- First Published: 08 August 2024
This article explores the dual benefits of reducing lignin content in plants, which streamlines biofuel production while maintaining robust defence mechanisms. It discusses how plants compensate for lower lignin levels through alternative defence strategies, recent biotechnological advances in lignin modification, and the implications for agriculture and industry.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The effector PHYL1JWB from Candidatus Phytoplasma ziziphi induces abnormal floral development by destabilising flower development proteins
- Pages: 4963-4976
- First Published: 09 August 2024
How Candidatus Phytoplasma ziziphi induces abnormal floral development in their hosts is largely unknown. Here we reported a novel effector, PHYL1JWB, mediates the degradation of flower morphogenetic regulators by relying on the 26S proteasome and acting independently of lysine ubiquitination.
The potential link between gas diffusion and embolism spread in angiosperm xylem: Evidence from flow-centrifuge experiments and modelling
- Pages: 4977-4991
- First Published: 09 August 2024
Based on flow-centrifuge experiments and modelling, we found that embolism formation is not only driven by pressure, but also involves gas movement, which is affected by time, temperature, and vessel anatomy. These findings contribute to a better understanding of plant water transport.
Predicting key water stress indicators of Eucalyptus viminalis and Callitris rhomboidea using high-resolution visible to short-wave infrared spectroscopy
- Pages: 4992-5006
- First Published: 09 August 2024
This study explored the use of proximal spectroscopy in predicting plant water stress indicators of two native Australian tree species. We derived new spectral indices that enabled very high prediction of leaf water potential, equivalent water thickness, and fuel moisture content.
Tomato NADPH oxidase SlWfi1 interacts with the effector protein RipBJ of Ralstonia solanacearum to mediate host defence
- Pages: 5007-5020
- First Published: 12 August 2024
This study demonstrates that a tomato plasma membrane-bound NADPH oxidase is a direct interactor of a bacterial effector protein to mediate plant defence, providing important new information on the interplay between this devastating pathogen and its host plant.
Identification and expression analysis of Phosphate Transporter 1 (PHT1) genes in the highly phosphorus-use-efficient Hakea prostrata (Proteaceae)
- Pages: 5021-5038
- First Published: 13 August 2024
Gβγ dimers mediate low K+ stress-inhibited root growth via modulating auxin redistribution in Arabidopsis
- Pages: 5039-5052
- First Published: 13 August 2024
We demonstrate that Gβγ dimers modulate auxin distribution at the root tip via the auxin efflux transporters PIN1/PIN2, consequently enhancing the adaptive response of plant roots to low K+ conditions. This underscores the critical role of G protein β and γ subunits in the morphogenetic processes of root architecture under low K+ stress.
OPINION
Variations in ectomycorrhizal exploration types parallel seedling fine root traits of two temperate tree species under extreme drought and contrasting solar radiation treatments
- Pages: 5053-5066
- First Published: 14 August 2024
High solar radiation exacerbated the negative effects of extreme drought on plant growth and fine root traits. Ectomycorrhizae did not compensate for fine roots under drought stress. Fine roots biomass determined the role of ectomycorrhizal fungi, supporting the energy limitation hypothesis.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Abscisic acid increase correlates with the soil water threshold of transpiration decline during drought
- Pages: 5067-5075
- First Published: 14 August 2024
The mechanism that initiates stomatal closure during drought is not fully understood. We find that an increase in abscisic acid levels in leaves triggers the onset of stomatal closure during drought.
Analysis of root-environment interactions reveals mechanical advantages of growth-driven penetration of roots
- Pages: 5076-5088
- First Published: 14 August 2024
Inspired by the exceptional penetration abilities of plant roots, here we perform an experimental and computational analysis of root-soil mechanical interactions. We find that, compared to pushing, a grow-driven strategy reduces frictional forces and mechanical work, with lower propagation of displacements in the surrounding medium.
Characterisation of a major QTL for sodium accumulation in tomato grown in high salinity
- Pages: 5089-5103
- First Published: 15 August 2024
The genetic diversity of sodium accumulation in tomato shoot under salt stress is associated with an expression QTL of SlHKT1.2. This gene, already identified as involved in tomato salinity tolerance, has been differentially selected during domestication and is of interest for the development of salinity-tolerant varieties.
SlWRKY51 regulates proline content to enhance chilling tolerance in tomato
- Pages: 5104-5114
- First Published: 15 August 2024
The transcription factor WRKY51 enhances proline production in tomato by regulating the expression of the D-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase gene SlP5CS1 under chilling stress.
Distinct profiles of plant immune resilience revealed by natural variation in warm temperature-modulated disease resistance among Arabidopsis accessions
- Pages: 5115-5125
- First Published: 20 August 2024
Arabidopsis immune variation at warm temperature is independent of the thermosensitive salicylic acid regulator BASIC HELIX LOOP HELIX 059 but shows accession-specific dependence on sustained expression of CALMODULIN BINDING PROTEIN 60-LIKE G and SYSTEMIC ACQUIRED RESISTANCE DEFICIENT1, which encode master transcription factors of plant immunity.
Unique root hydraulic and mechanical properties support the resilience of grapevines adapted to the Atacama Desert
- Pages: 5126-5139
- First Published: 20 August 2024
MAPKKK28 functions upstream of the MKK1-MPK1 cascade to regulate abscisic acid responses in rice
- Pages: 5140-5157
- First Published: 21 August 2024
This manuscript demonstrated that MAPKKK28, a previously uncharacterized mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase in rice, functions upstream of the MKK1-MPK1 cascade to positively regulate abscisic acid responses and the tolerance to oxidative stress and osmotic stress.
Nonlinear models based on leaf architecture traits explain the variability of mesophyll conductance across plant species
- Pages: 5158-5171
- First Published: 21 August 2024
We demonstrated that systematic training and testing of random forest regression models using a comprehensive data set, covering different plant functional types, can pinpoint leaf structural and anatomical traits that determine mesophyll conductance.
Liana attachment to supports leads to profound changes in xylem anatomy and transcriptional profile of cambium and differentiating xylem
- Pages: 5172-5188
- First Published: 22 August 2024
The drastic change in wood anatomy in woody vines offers an excellent model for studying wood differentiation and the adaptation of vines to climbing. In Bignonia magnifica (Bignoniaceae), attachment to supports triggers increased vessel size, broader vessel distribution, reduced fibre content, and higher water conductivity. These changes coincide with the downregulation of genes for cell division and cell wall biosynthesis, and the upregulation of transcription factors, defense/cell death, and hormone-responsive genes.
REVIEW
Nucleolar actions in plant development and stress responses
- Pages: 5189-5204
- First Published: 22 August 2024
The nucleolus, a dynamic membrane-less structure within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, serves as a prominent site of ribosome biogenesis. Recent research has demonstrated that it plays a multifaceted role in plant growth and development, as well as in responses to environmental stresses. This review explores the latest advances in the impact of nucleolar actions on plant development and stress responses. Understanding these processes may facilitate the development of promising strategies to enhance crop resilience and mitigate the impact of biotic and abiotic stresses in agricultural systems.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
DkDTX1/MATE1 mediates the accumulation of proanthocyanidin and affects astringency in persimmon
- Pages: 5205-5219
- First Published: 22 August 2024
The differential expression and preferential transport activity of DkDTX1/MATE1 promote the accumulation of more epigallocatechin gallate in the early stage of fruit development, which leads to the high astringency of fruit in persimmon.
Caught between two states: The compromise in acclimation of photosynthesis, transpiration and mesophyll conductance to different amplitudes of fluctuating irradiance
- Pages: 5220-5236
- First Published: 22 August 2024
We investigated photosynthesis acclimation and dynamics of leaf transpiration under specific light fluctuations in A. thaliana. The response was stronger for more intense fluctuations and showed a divergent response whereby photosynthesis is reduced but transpiration rose compared to steady light.
CDK8 of the mediator kinase module connects leaf development to the establishment of correct stomata patterning by regulating the levels of the transcription factor SPEECHLESS (SPCH)
- Pages: 5237-5251
- First Published: 23 August 2024
The components of the mediator kinase module are highly conserved across eukaryotic lines and cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8) is essential for correct cell proliferation and development. We show here that control of leaf development is closely linked to the establishment of correct stomata patterning through the impact of CDK8. Comprehending the plasticity of plant morphology and the mechanisms behind it is essential for our understanding of plant environmental responses and the consequences of climate change.
Introduction of broadleaf tree species can promote the resource use efficiency and gross primary productivity of pure forests
- Pages: 5252-5264
- First Published: 23 August 2024
- 1)
The effects of introduced broadleaf tree species on benefits of pure forest (PF) was evaluated.
- 2)
Both species probably have competition for water at low levels in the mixed forests (MF).
- 3)
Although the co-existing tree limited the Basal area increment of MF, the water use efficiency and gross primary productivity increased.
- 4)
The introduction of MFs enhances the water and nutrient acquisition resources.
Hydrogen sulphide alleviates root growth inhibition induced by phosphate starvation
- Pages: 5265-5279
- First Published: 23 August 2024
We unveil a novel function of DES1-mediated H2S in alleviating the inhibition of primary root growth induced by phosphate starvation. By promoting the expression of SQD1 in Arabidopsis thaliana, H2S effectively counteracts the adverse effects of phosphate deficiency on root growth.
Balancing the nutrient needs: Optimising growth in Malus sieversii seedlings through tailored nitrogen and phosphorus effects
- Pages: 5280-5296
- First Published: 26 August 2024
N10 and N20 are the most suitable fertilisation modes for seedlings of Malus sieversii in the study area. In contrast, phosphorus-containing fertilisation (including adding P and N20Px) has proven to be less suitable for these seedlings in this specific region. Additionally, we have proposed for the first time the hypothesis that plant resource allocation determines trait relationships, aiming to explain the differences in plant trait networks under varying environmental conditions.
AtCIPK20 regulates microtubule stability to mediate stomatal closure under drought stress in Arabidopsis
- Pages: 5297-5314
- First Published: 27 August 2024
AtCIPK20 localises to the cortical microtubules, a subcellular distribution feature disrupted by its interactions with CBL partners. It regulates microtubule depolymerization mediated by ABA, thereby promoting stomatal closure and positively modulating Arabidopsis drought resistance.
Carboxylation capacity is the main limitation of carbon assimilation in High Arctic shrubs
- Pages: 5315-5329
- First Published: 27 August 2024
The photosynthetic capacity and limitations in Arctic shrubs revealing contrasting adaptations among Salix species that may influence their ability to provide negative carbon feedback to the atmosphere in high-Arctic tundra, despite their similar photosynthetic rate compared to a global data set.
DATA INSIGHT
In-silico identification of putatively functional intergenic small open reading frames in the cucumber genome and their predicted response to biotic and abiotic stresses
- Pages: 5330-5342
- First Published: 27 August 2024
We identified small open reading frames× (sORF) in the intergenic regions of the cucumber genome. Analysing genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics data revealed the possible expression of sORF. Five predicted proteins in cucumber interact with proteins in Meloidogyne incognita and Powdery mildew.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Plant growth-promoting abilities of Methylobacterium sp. 2A involve auxin-mediated regulation of the root architecture
- Pages: 5343-5357
- First Published: 27 August 2024
Arabidopsis thaliana–Methylobacterium sp. 2A interaction and communication involve the modulation of plant hormones, root colonisation, and the production of volatile organic compounds. Methylobacterium sp. 2A promotes plant growth via auxin-mediated regulation of the root architecture.
The B-box protein BBX13/COL15 suppresses photoperiodic flowering by attenuating the action of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis
- Pages: 5358-5371
- First Published: 27 August 2024
BBX13, a previously uncharacterized protein in the B-Box family of transcription factors, negatively regulates flowering time in Arabidopsis thaliana. BBX13 physically and genetically interacts with CO and inhibits the CO-mediated transcriptional activation of FT.
Participation of the stress-responsive CDSP32 thioredoxin in the modulation of chloroplast ATP-synthase activity in Solanum tuberosum
- Pages: 5372-5390
- First Published: 27 August 2024
The atypical CDSP32 thioredoxin participates in the response to saline-alkaline stress and in the activation of photosynthesis in Solanum tuberosum, likely by affecting the redox regulation of the γ subunit of ATP-synthase complex.
A chloroplast sulphate transporter modulates glutathione-mediated redox cycling to regulate cell division
- Pages: 5391-5410
- First Published: 27 August 2024
The cell cycle is associated with periodic oscillation of the cellular redox environment. Our investigation of subcellular glutathione and thiol-containing molecules in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has provided new insights into their role in regulating the cell cycle.
DATA INSIGHT
Resin acid δ13C and δ18O as indicators of intra-seasonal physiological and environmental variability
- Pages: 5411-5423
- First Published: 27 August 2024
We studied the poorly understood intra-seasonal dynamics of resin δ13C and δ18O. We found that resin δ13C was c. 2‰ lower than sucrose δ13C, while resin δ18O was c. 20‰ higher than xylem water δ18O in mature Pinus sylvestris. Both resin δ13C and δ18O recorded a signal of soil water potential.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The B-box transcription factor BnBBX22.A07 enhances salt stress tolerance by indirectly activating BnWRKY33.C03
- Pages: 5424-5442
- First Published: 27 August 2024
BnBBX22.A07 functions positively in salt responses not only by activating ROS scavenging-related genes, but also by indirectly activating BnWRKY33.C03 in Brassica napus.
miR1432 negatively regulates cold tolerance by targeting OsACAs
- Pages: 5443-5456
- First Published: 27 August 2024
The Ca2+ATPase family gene OsACAs were identified as new targets of miR1432. The effect of the miR1432-OsACA module on abiotic stress response was first identified in rice.
Rewatering after drought: Unravelling the drought thresholds and function recovery-limiting factors in maize leaves
- Pages: 5457-5469
- First Published: 29 August 2024
Hydraulic failure alone is insufficient to induce maize leaf death, extended dehydration led to leaf death at −2.7 to −2.9 MPa or 55−58% relative water content. With leaf development, this lethal threshold remains relatively constant, while the recoverable safety margin (stomatal closure to recovery capacity loss) significantly decreased.
Genomic insights into the modifications of spike morphology traits during wheat breeding
- Pages: 5470-5482
- First Published: 29 August 2024
In this study, we investigated the genetic basis of changes in spike morphology during wheat breeding. We identified candidate regions responsible for consistent alterations in spike morphology traits that led to increased yield. Furthermore, we constructed a genetic network of related genomic regions. Our findings unveil the genetic underpinnings of breeding selection and the interplay of spike morphology traits, offering valuable resources for the regulation of spike morphology in wheat.
Exposure of Arabidopsis thaliana Mutants to Genotoxic Stress Provides New Insights for the Involvement of TDP1α and TDP1β genes in DNA-Damage Response
- Pages: 5483-5497
- First Published: 02 September 2024
The function of the plant TDP1 genes and their roles in DDR are far from being elucidated. By using Arabidopsis thaliana single and double mutants, our study indicates that TDP1β may play relevant functions related to the presence of double-strand breaks and replication stress, thus providing novel data regarding its role in DNA repair.
Genome-Wide Identification of Pentatricopeptide Repeat (PPR) Gene Family and Multi-Omics Analysis Provide New Insights Into the Albinism Mechanism of Kandelia obovata Propagule Leaves
- Pages: 5498-5510
- First Published: 02 September 2024
We obtained 16 candidate PPR genes associated with albino phenotype of Kandelia obovata propagule leaves. We successfully predicted target genes of Maker00002998 protein including rps14, rpoC1, and rpoC2, in which RNA editing sites were experimentally verified. In vitro RNA pull-down assay confirmed that Maker00002998 protein could bind to rps14 transcript. In this study, we proposed a working model to describe the involvement of Maker00002998-medidated RNA editing in plastid development.
Nitrogen nutrition effects on δ13C of plant respired CO2 are mostly caused by concurrent changes in organic acid utilisation and remobilisation
- Pages: 5511-5526
- First Published: 02 September 2024
Phaseolus vulgaris and Spinacia oleracea grown under varying NH4+:NO3− ratio show 13C-depletion in leaf-respired CO2 as NH4+ proportion increases. Supervised multivariate analysis shows that δ13C of respired CO2 is mostly determined by malate-citrate metabolism in leaves and roots of both species.









