Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover
Titelbild: Interdependence of Support Wettability - Electrodeposition Rate- Sodium Metal Anode and SEI Microstructure (Angew. Chem. 8/2025)
- First Published: 16 January 2025

Electrodeposition of sodium metal in an anode-free battery can be dendritic. The tree at the center of the cover image represents a single crystalline dendrite, branched and complex in its morphology, originating at the support and growing towards the cathode. Its multicolor leaves are the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) that cover the metal surface. The SEI is a complex mosaic containing crystalline sodium fluoride, sodium hydride and sodium hydroxide, as well as organic constituents. Details of this study are reported by David Mitlin, Yu-chen Karen Chen-Wiegart et al. in their Research Article (e202412550).
Innentitelbild: Bienzymatic Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Secondary Alcohols by Esterification/Racemization in Water (Angew. Chem. 8/2025)
- First Published: 09 January 2025

A two-enzyme-catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) of racemic secondary alcohols in water was achieved by Wolfgang Kroutil, Paweł Borowiecki, and co-workers (e202420133). The cover image illustrates the cooperative action of an engineered alcohol dehydrogenase (bottom left), which mediates racemization via a hydrogen-borrowing mechanism (indicated by the swirl), and an acyltransferase (bottom right) that enables enantioselective acylation. This organic-solvent- and metal-free DKR offers a novel approach for the deracemization of sec-alcohols in an aqueous system using exclusively biocatalysts. The cover was designed by Verena Resch.
Innenrücktitelbild: Room-temperature Magnetocapacitance Spanning 97K Hysteresis in Molecular Material (Angew. Chem. 8/2025)
- First Published: 16 January 2025

Magnetocapacitance has been studied for the first time in molecular complexes. The weak interaction between cations and anions in organic-inorganic hybrid materials triggers their structural thermal phase transition. The distinguished Jahn–Teller distortions in high- and low-temperature phases lead to different magnetoelectric coupling, as reported by Zhao-Bo Hu, Yan Peng, Jing Ma, You Song et al. in their Research Article (e202416380).
Rücktitelbild: Air-Mediated Biomimetic Synthesis of Polyhydroxyalkanoate with C4 Diol (Angew. Chem. 8/2025)
- First Published: 14 February 2025
A strategy for the biomimetic synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) using C4 diol and air, catalyzed by a synergistic catalyst, was presented by Qiuquan Cai and co-workers in their Research Article (e202417660). The resulting PHA can reversibly convert back to a small-molecule monomer in the form of a five-membered ring, demonstrating excellent ecological sustainability. This study highlights the potential for large-scale synthesis of high-value PHAs from diverse non-grain-based diols.
Frontispiz
Frontispiz: Divergent Activity Shifts of Tin-Based Catalysts for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction: pH-Dependent Behavior of Single-Atom Versus Polyatomic Structures
- First Published: 17 February 2025
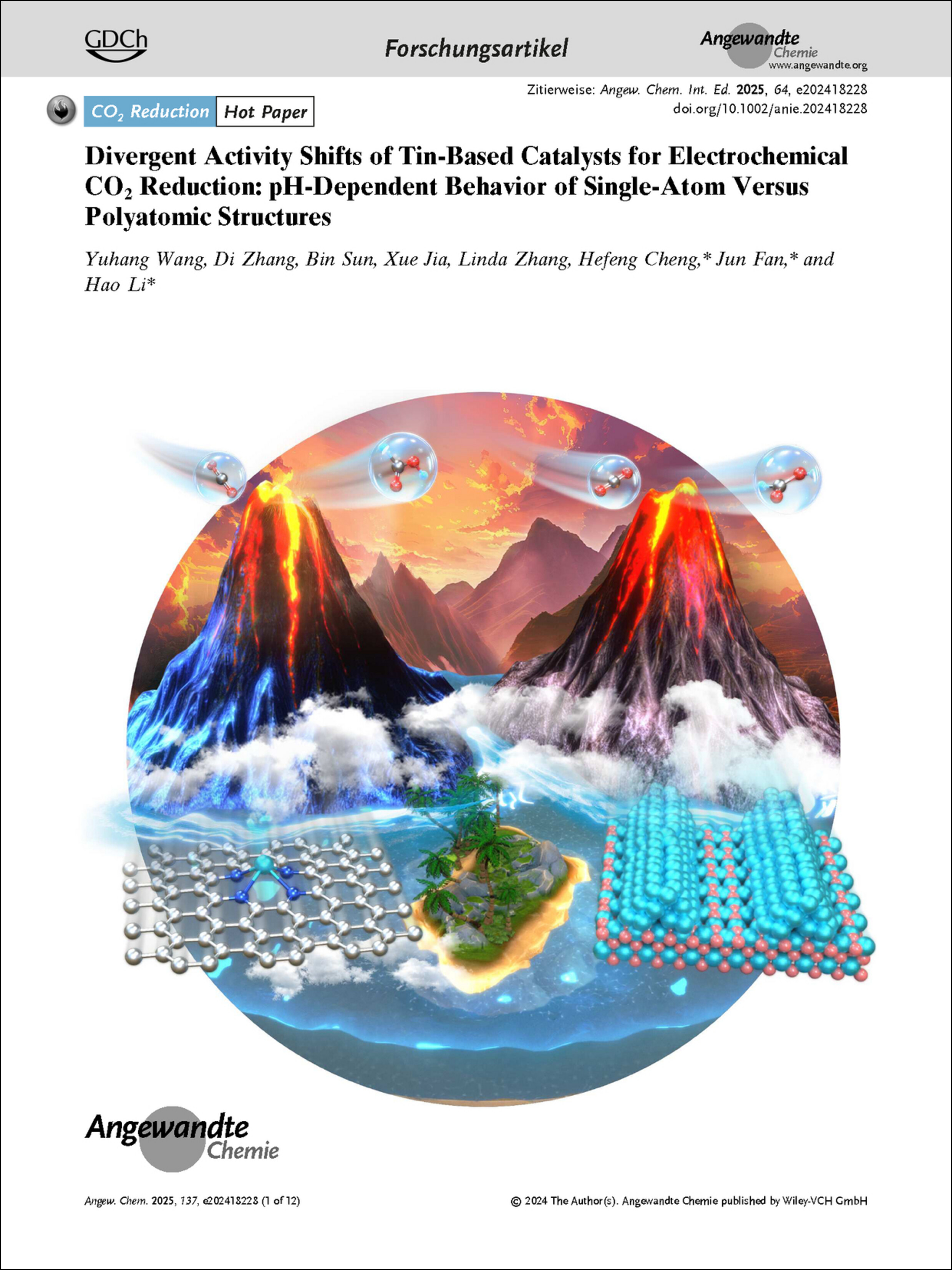
In their Communication (e202418228), Hao Li and co-workers reveal an exciting contrast: the electric field response of the binding strength of *OCHO on Sn-N4-C and polyatomic Sn displays opposite behaviors. This response results in a fascinating, opposite pH-dependent volcano evolution for Sn-N4-C and polyatomic Sn. Most importantly, we propose that distinct strategies are necessary for designing catalysts using single-atom versus polyatomic metal catalysts.
Frontispiz: Chemical Synthesis of ~1 nm Multilevel Capacitor-like Particles with Atomic Precision
- First Published: 17 February 2025
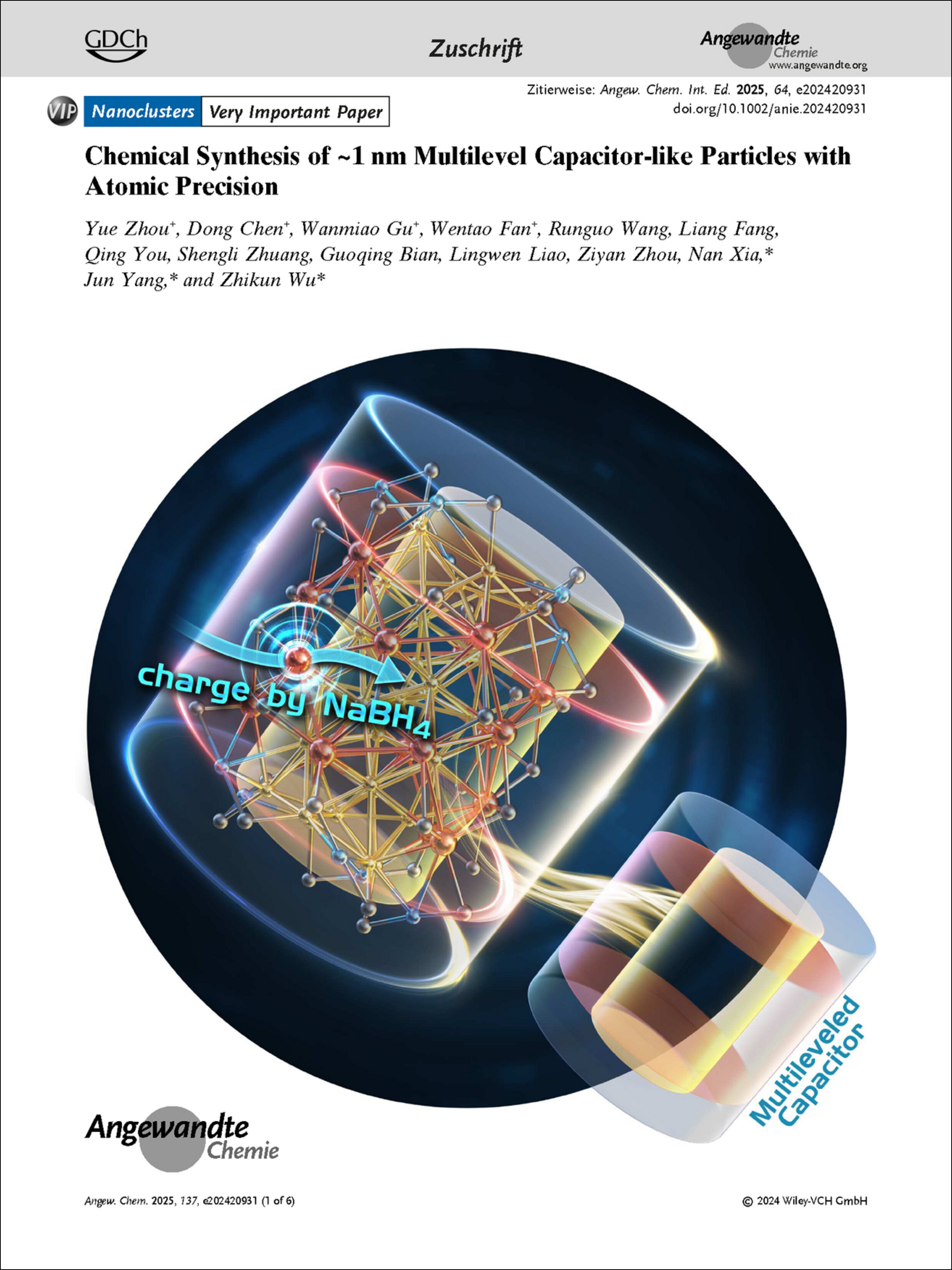
An increasing need for the miniaturization of optoelectronic devices or machines has become evident as we are entering the post-Moore era. One bold conceit is that chemically synthesized nanoparticles (NP) can function as nanodevices or nanomachines. In their Research Article (e202420931), Zhikun Wu, Jun Yang, Nan Xia et al. demonstrate the feasibility by reporting a novel nanocluster with multileveled capacitor-like character, which is identified by a Cd(II) transport from the outershell to the innermost position after charged with NaBH4, as well as some other ways such as NPA charge distribution, voltammetry and electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO. An intra-NP anti-galvanic reduction was found after the migrating of charge carrier.
Introducing …
Kurzaufsatz
Artificial Cells
Synthetic Biomolecular Condensates: Phase-Separation Control, Cytomimetic Modelling and Emerging Biomedical Potential
- First Published: 22 November 2024

Synthetic biomolecular condensates are appealing candidates to replicate key features and functions of intracellular membrane-less organelles. Their dynamic phase-separation control provides crucial insights into the regulation of fundamental cell processes. Via integration with ambitious cell-like features and behaviors, synthetic biomolecular condensates offer innovative solutions for engineering active materials with sophisticated functions.
Enzyme Immobilization
Integrating Enzymes with Reticular Frameworks To Govern Biocatalysis
- First Published: 13 January 2025
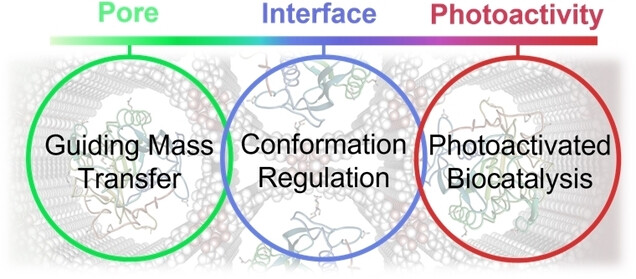
This Minireview summarizes recent advances in the development of hybrid biocatalysts by integrating enzymes with reticular frameworks, with specific emphasis on how framework architecture and host-guest interactions influence bioreactivity. Three key regulatory mechanisms are highlighted: 1) guiding mass transfer through pore structures, 2) regulating enzyme conformation via interfacial interactions, and 3) enabling photoactivated biocatalysis by leveraging photoactive reticular frameworks.
Aufsatz
Electrocatalytic O2 Evolution
Leveraging Iron in the Electrolyte to Improve Oxygen Evolution Reaction Performance: Fundamentals, Strategies, and Perspectives
- First Published: 14 January 2025
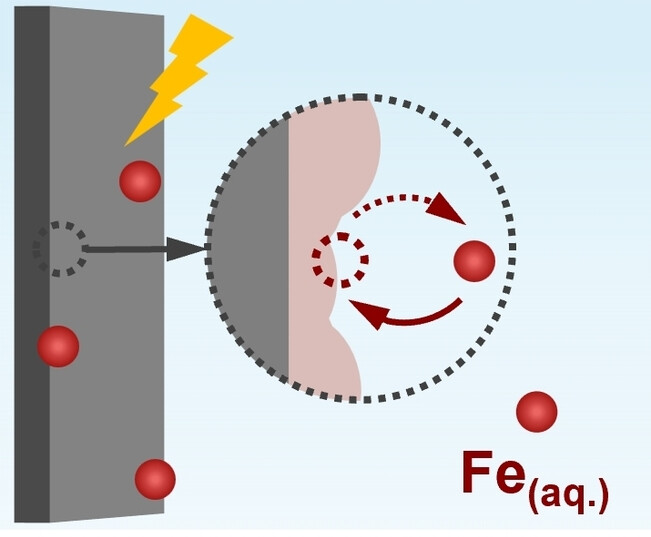
The controlled introduction of iron ions into the electrolyte, coupled with a suitable host material to facilitate in situ iron deposition, opens new strategies for creating highly efficient and dynamically stable electrochemical interfaces to continuously catalyze the oxygen evolution reaction at a steady rate, thereby breaking the trade-off between catalytic activity and material stability.
Forschungsartikel
CO2 Reduction | Hot Paper
Divergent Activity Shifts of Tin-Based Catalysts for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction: pH-Dependent Behavior of Single-Atom Versus Polyatomic Structures
- First Published: 28 November 2024
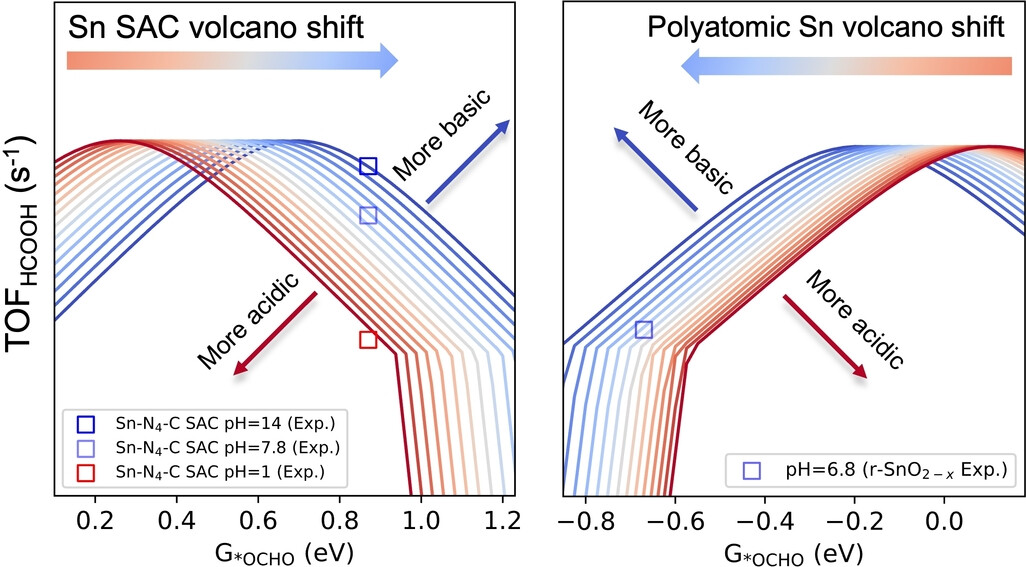
We reveal an exciting contrast: the electric field response of the binding strength of *OCHO on Sn−N4−C and polyatomic Sn displays opposite behaviors. This response results in a fascinating, opposite pH-dependent volcano evolution for Sn−N4−C and polyatomic Sn. Most importantly, we propose that distinct strategies are necessary for designing catalysts using single-atom versus polyatomic metal catalysts.
Batteries | Very Important Paper
Interdependence of Support Wettability - Electrodeposition Rate- Sodium Metal Anode and SEI Microstructure
- First Published: 15 September 2024
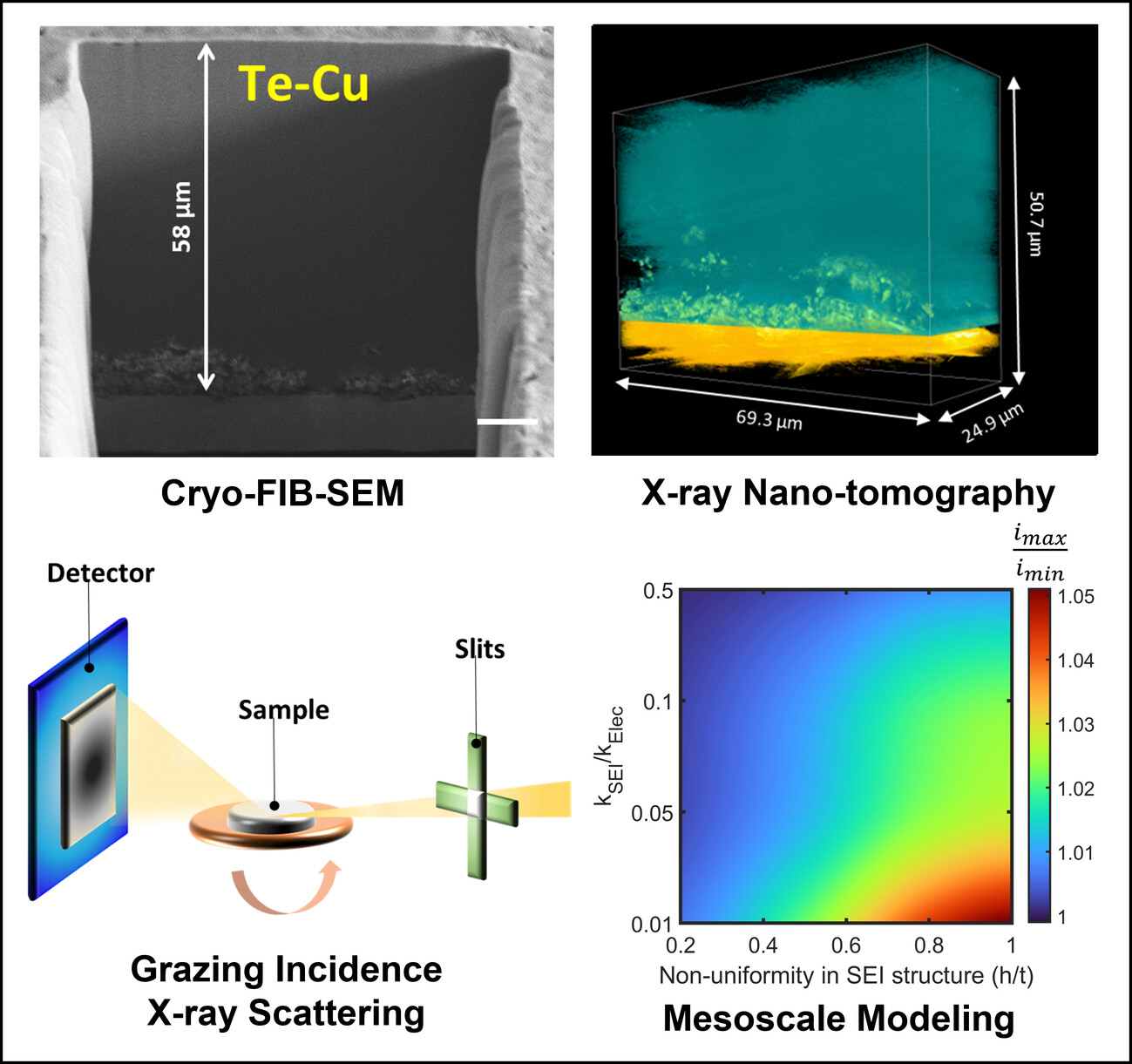
This study examines how current collector chemistry and electrodeposition rate affect microstructure of sodium metal and its solid electrolyte interphase. Synchrotron X-ray nanotomography, grazing-incidence wide-angle X-ray scattering, and cryogenic focused ion beam microscopy reveal differences in film morphology, internal porosity, and crystallographic preferred orientation. Mesoscale modeling delineates the role of SEI on electrodeposit growth and onset of electrochemical instability.
Biocatalysis
Bienzymatic Dynamic Kinetic Resolution of Secondary Alcohols by Esterification/Racemization in Water
- First Published: 22 November 2024
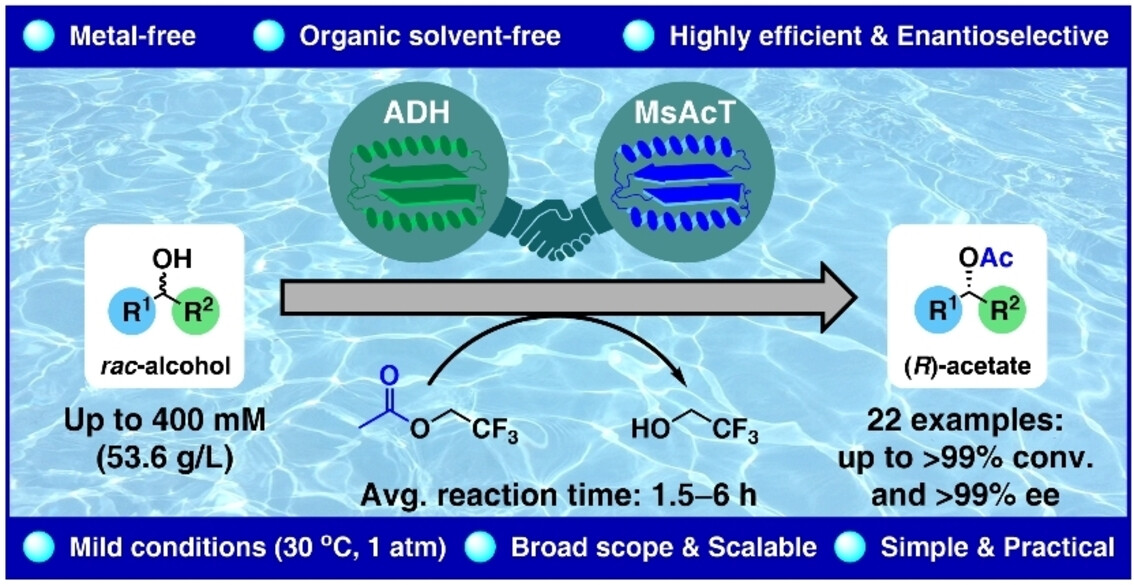
A two-enzyme-catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution (DKR) of racemic secondary alcohols in water—a ′Holy Grail of DKR′—was accomplished using an engineered alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) for racemization through a hydrogen-borrowing sequence and variants of the acyltransferase from Mycobacterium smegmatis (MsAcT) for enantioselective acylation.
Magnetic Properties
Room-temperature Magnetocapacitance Spanning 97K Hysteresis in Molecular Material
- First Published: 25 October 2024
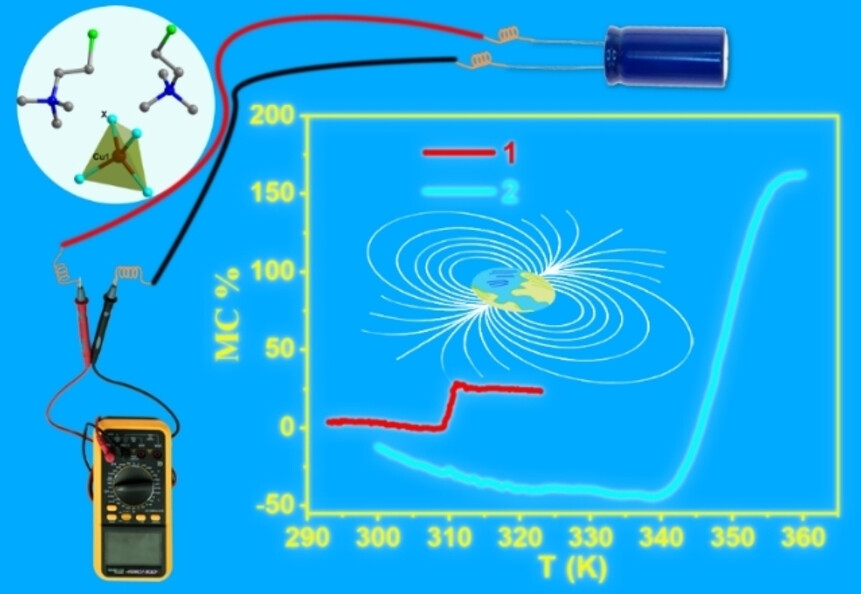
Two novel organic–inorganic hybrid materials (CETAB)2[CuCl4] (1) and (CETAB)2[CuBr4] (2) (CETAB=(2-chloroethyl)trimethylammonium) possess superior magnetocapacitance and a record thermal hysteresis width of 97 K. The magnetocapacitance comes from their intrinsic nature, rather than the composite results found in inorganic materials. Meanwhile, this is still the first time so far to study magnetocapacitance in molecule-based materials.
Polymer Chemistry
Air-Mediated Biomimetic Synthesis of Polyhydroxyalkanoate with C4 Diol
- First Published: 23 December 2024
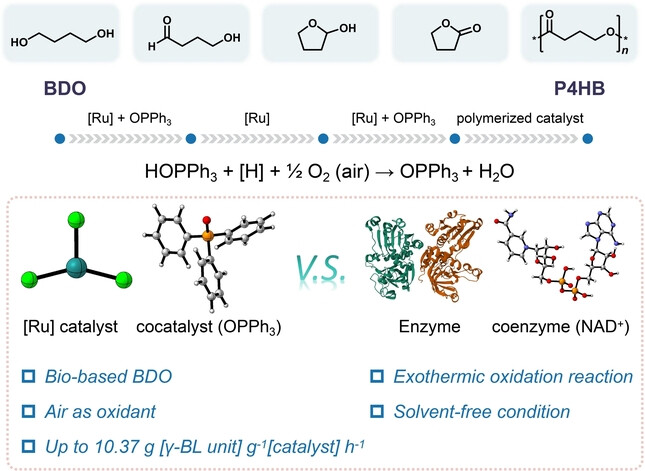
We reported a strategy that utilizes a ruthenium-phosphorus synergistic catalytic system, mimicking enzyme-coenzyme functionality, to efficiently catalyze the air-mediated oxidation of the C4 diol, 1,4-butanediol, to produce the intermediate monomer γ-butyrolactone. This monomer is then used in ring-opening polymerization to synthesize high molecular weight polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) products extracellularly.
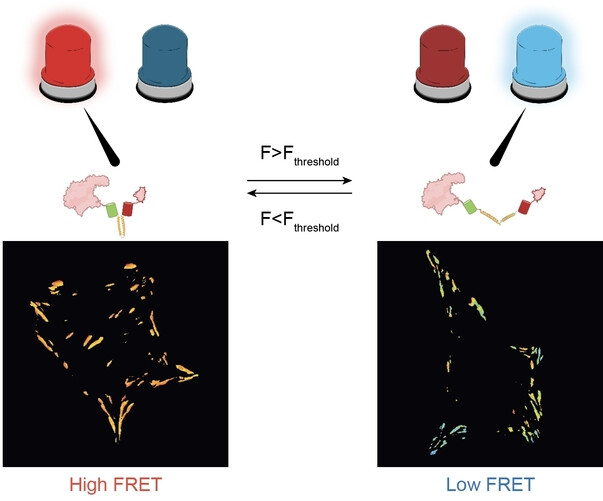
Biosensors
Digital and Tunable Genetically Encoded Tension Sensors Based on Engineered Coiled-Coils
- First Published: 13 January 2025
Peptide Inhibitors
Mirror-Image Random Nonstandard Peptides Integrated Discovery (MI-RaPID) Technology Yields Highly Stable and Selective Macrocyclic Peptide Inhibitors for Matrix Metallopeptidase 7
- First Published: 30 August 2024

Mirror-image RaPID (MI-RaPID) technology was developed for the discovery of innate protease-resistant macrocyclic peptides. Metalloproteinase 7 (MMP7) plays a crucial role in cancer, making it an attractive target for therapeutic development. Using MI-RaPID technology, we identified a highly selective and stable macrocyclic peptide, which consists of D-amino acids, one β-amino acid, and a thioether bond, and inhibited MMP7 with an IC50 of 90 nM.
Structural Phase Transition | Hot Paper
Supramolecular Spring-Like Fe(II) Spin-Crossover Complexes Experiencing Giant and Anisotropic Thermal Expansion Across Two Distinct Temperature Regimes
- First Published: 06 November 2024
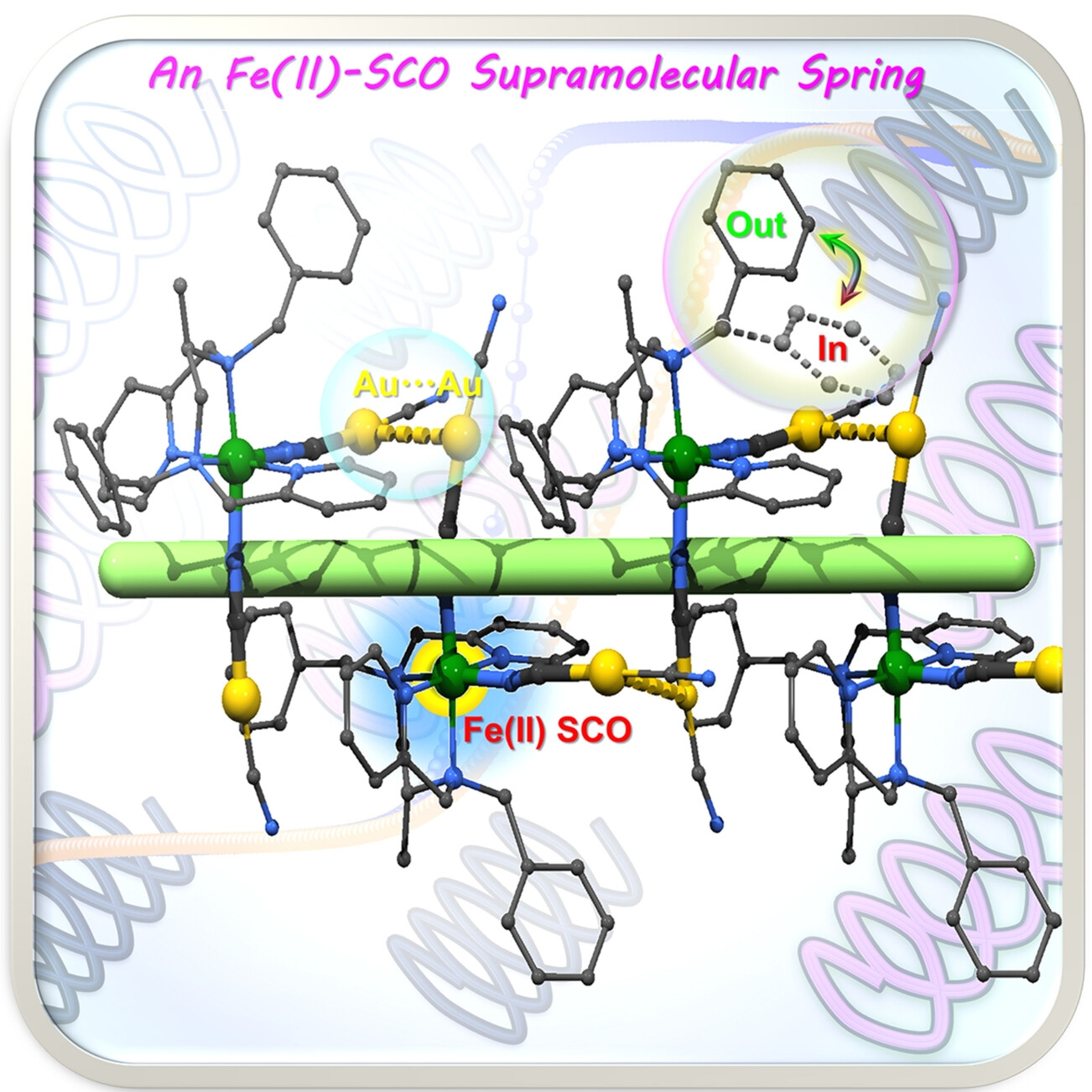
A unique supramolecular spring-like Fe(II)-SCO complex has been reported, showcasing multiple dynamic factors, including SCO events, ring rotation, and flexible Au⋅⋅⋅Au distances. This synergy results in various switchings in magnetism and structure, along with a remarkable “breathing” thermal expansion feature across two temperature regions, highlighting its potential as a multifunctional dynamic material for future devices.
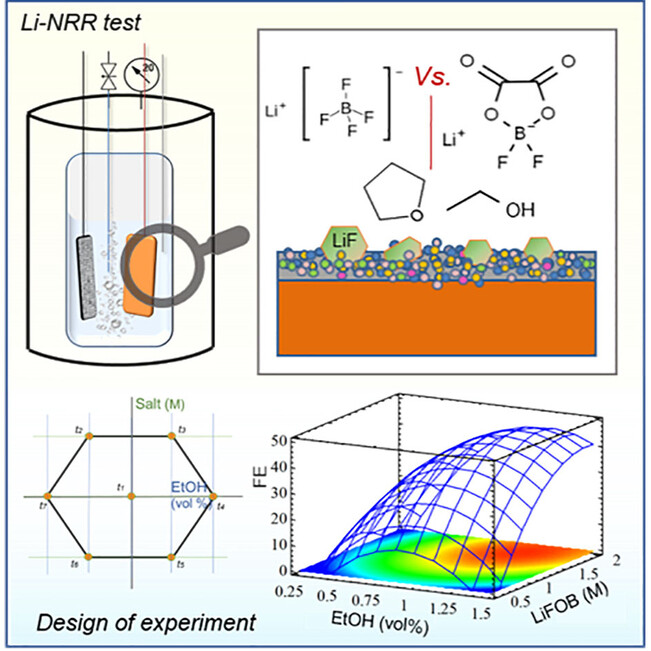
Ammonia Production
Multivariate Approaches Boosting Lithium-Mediated Ammonia Electrosynthesis in Different Electrolytes
- First Published: 17 January 2025
Supramolecular Materials | Hot Paper
From Natural Product Derivative to Hexagonal Prism Supermolecule: Potent Biofilm Disintegration, Enhanced Foliar Affinity, and Effective Management of Tomato Bacterial Canker
- First Published: 17 January 2025
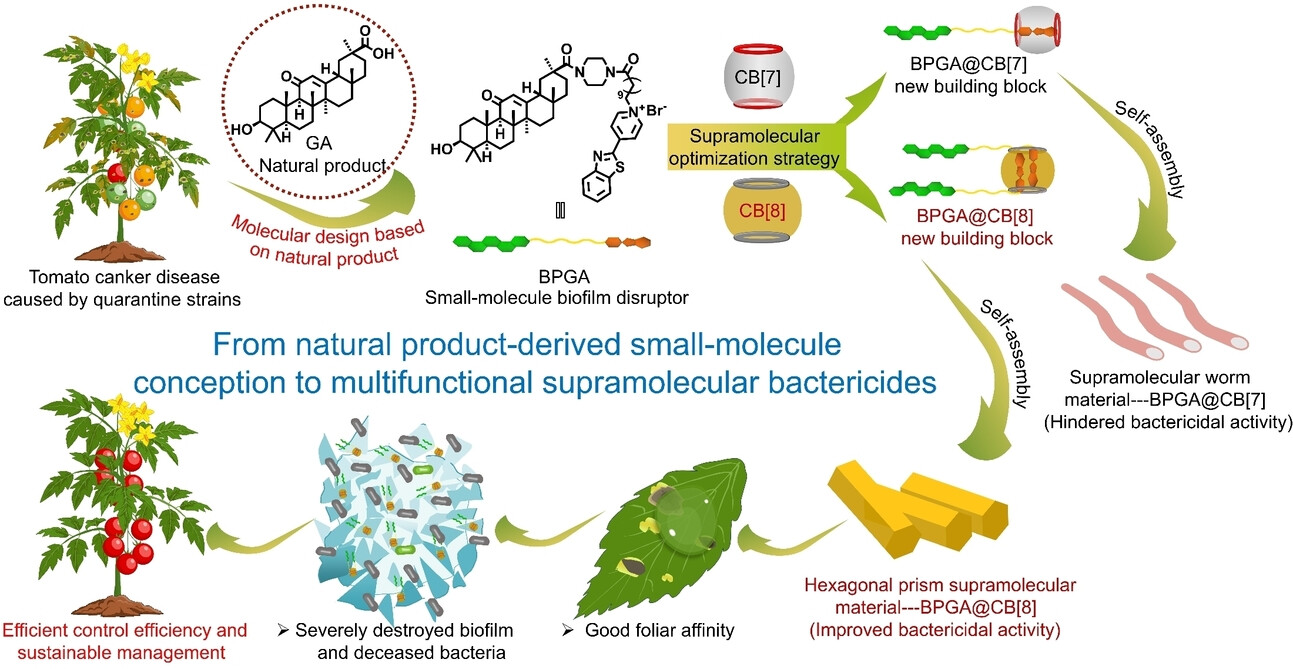
A bioactive benzothiazole-modified glycyrrhetinic acid (BPGA) and cucurbit[7,8]uril (CB[7,8]) undergo self-assembly, culminating in the fabrication of a multifunctional hexagonal prism supramolecular bactericidal material, BPGA@CB[8]. This smart supramolecular assembly effectively disorganizes Clavibacter michiganensis (Cmm) biofilms and enhances foliar affinity, thereby enabling a highly effective management strategy for tomato bacterial canker.
Sodium Metal Batteries
Deciphering and Enhancing Rate-Determining Step of Sodium Deposition towards Ultralow-Temperature Sodium Metal Batteries
- First Published: 17 January 2025
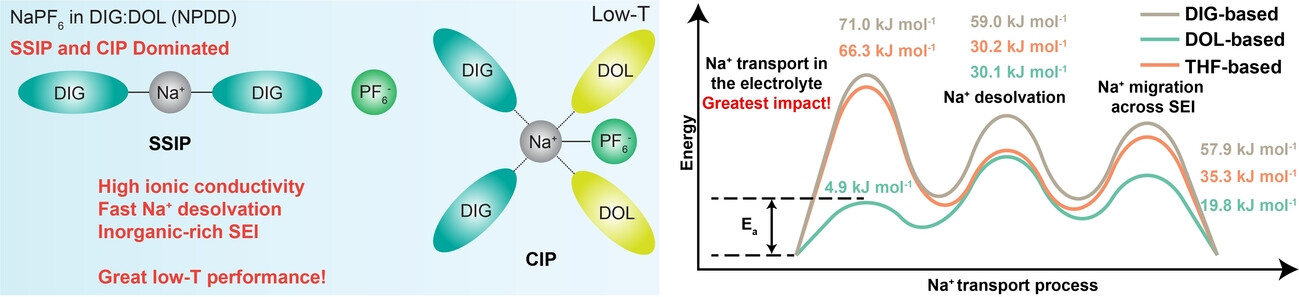
The DOL-based electrolyte, with dominant SSIP and CIP structures, achieves 1.78×10−3 S cm−1 Na+ conductivity and strong low-temperature kinetics. Kinetic analysis identifies cation transport as the key factor in battery operation. High-loading full cells cycled stably for 600 cycles at −40 °C and 50 cycles at −78 °C, showing promise for high-voltage sodium batteries in extreme conditions.
Electrochemical CO2 Reduction
Copper-Catalysed Electrochemical CO2 Methanation via the Alloying of Single Cobalt Atoms
- First Published: 13 January 2025
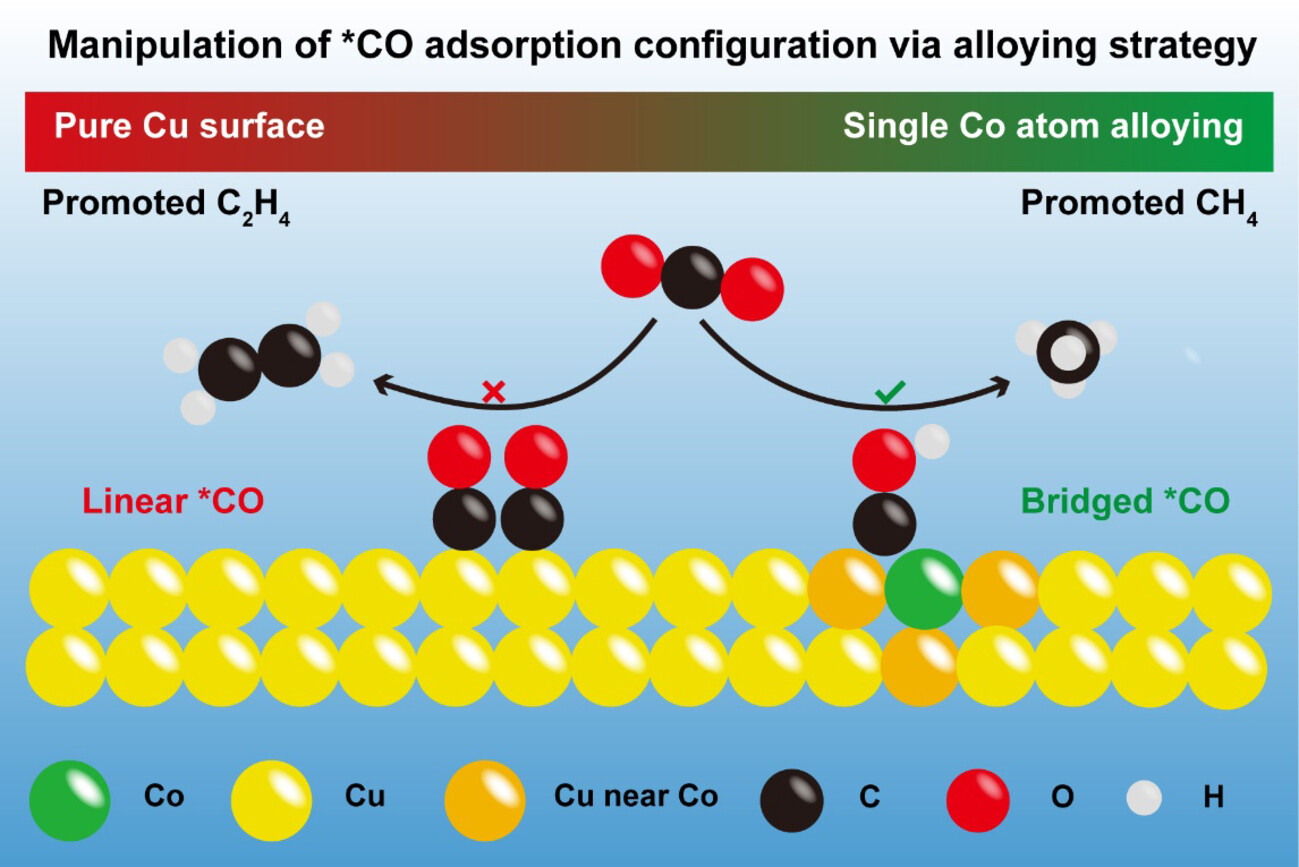
We developed a single-atom cobalt doped copper catalyst (Co1Cu) that achieved a methane (CH4) Faradaic efficiency exceeding 60 % with a partial current density of −482.7 mA cm−2. In situ spectroscopic experiments and density functional theory simulations demonstrated that the modulation of the *CO adsorption configuration, with stronger bridge-binding, favours deep reduction to CH4 over the C−C coupling or CO desorption pathways.
Photocatalysis
Orthorhombic Covalent Organic Frameworks with fmj Topology as Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 06 January 2025
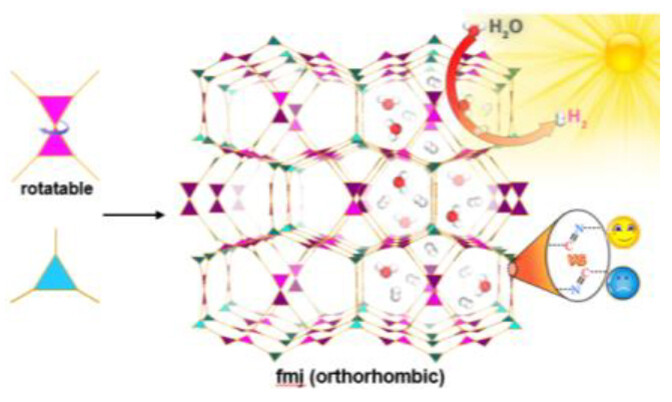
The first construction of orthorhombic three-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (3D COFs) with fmj topology has been realized on the basis of rotatable monomers. Significant isomeric effects on protonation, optoelectronic properties, and photocatalytic activity have been revealed for 3D COFs and a high photocatalytic hydrogen evolution rate has been achieved.
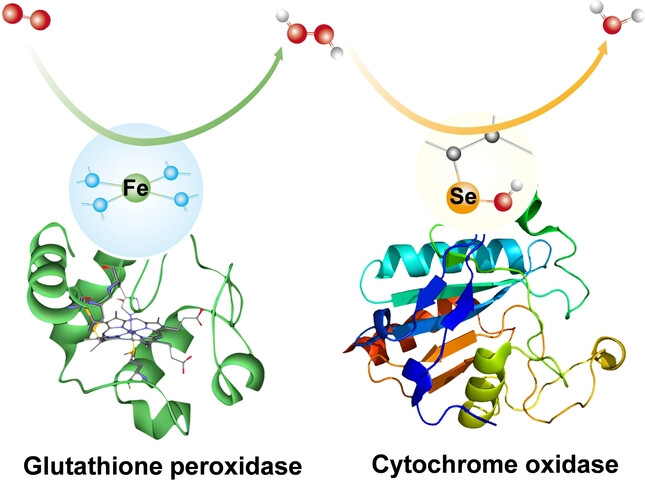
Oxygen Reduction | Very Important Paper
Enzyme-Inspired Single Selenium Site for Selective Oxygen Reduction
- First Published: 20 January 2025
Selective Alkyne Functionalisation
Zero-Valent Copper Catalysis Enables Regio- and Stereoselective Difunctionalization of Alkynes
- First Published: 13 January 2025
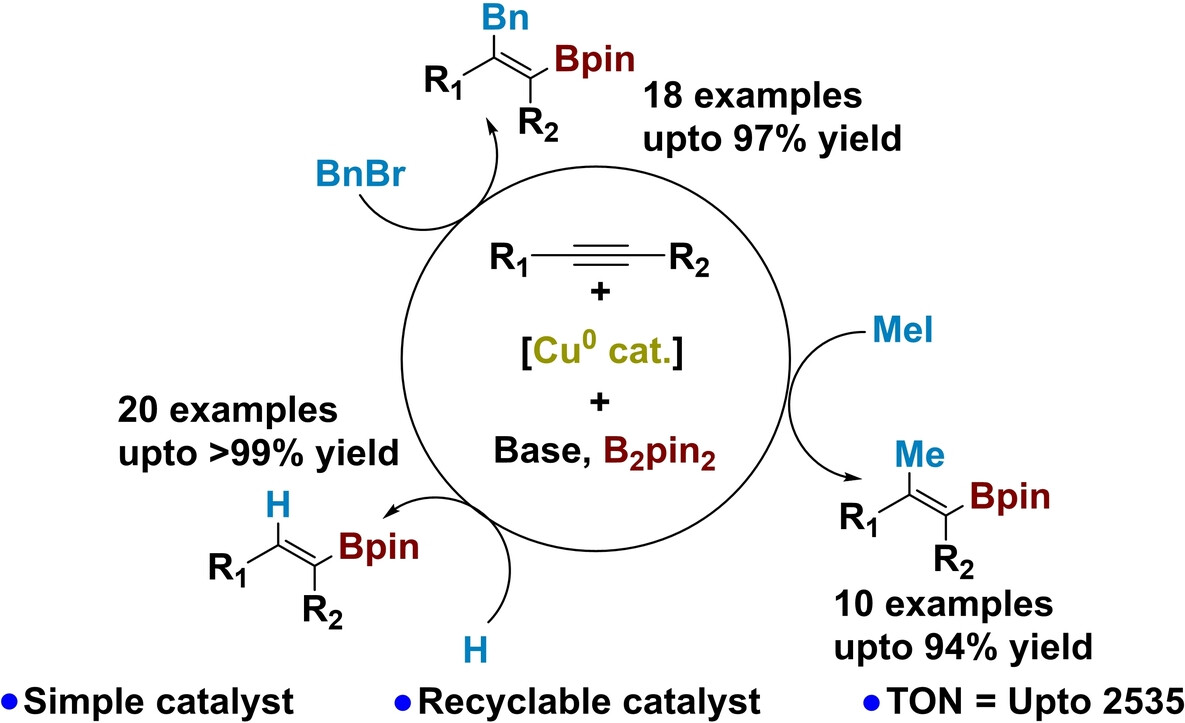
A highly efficient, stable, and reusable Cu(0) catalyst for the difunctionalization of alkynes using different electrophiles and bis(pinacolato)diboron (B2pin2) as chemical feedstocks to afford di- and trisubstituted vinylboronate ester derivatives under mild reaction conditions with excellent regio-, chemo-, and stereo-selectivity has been developed.
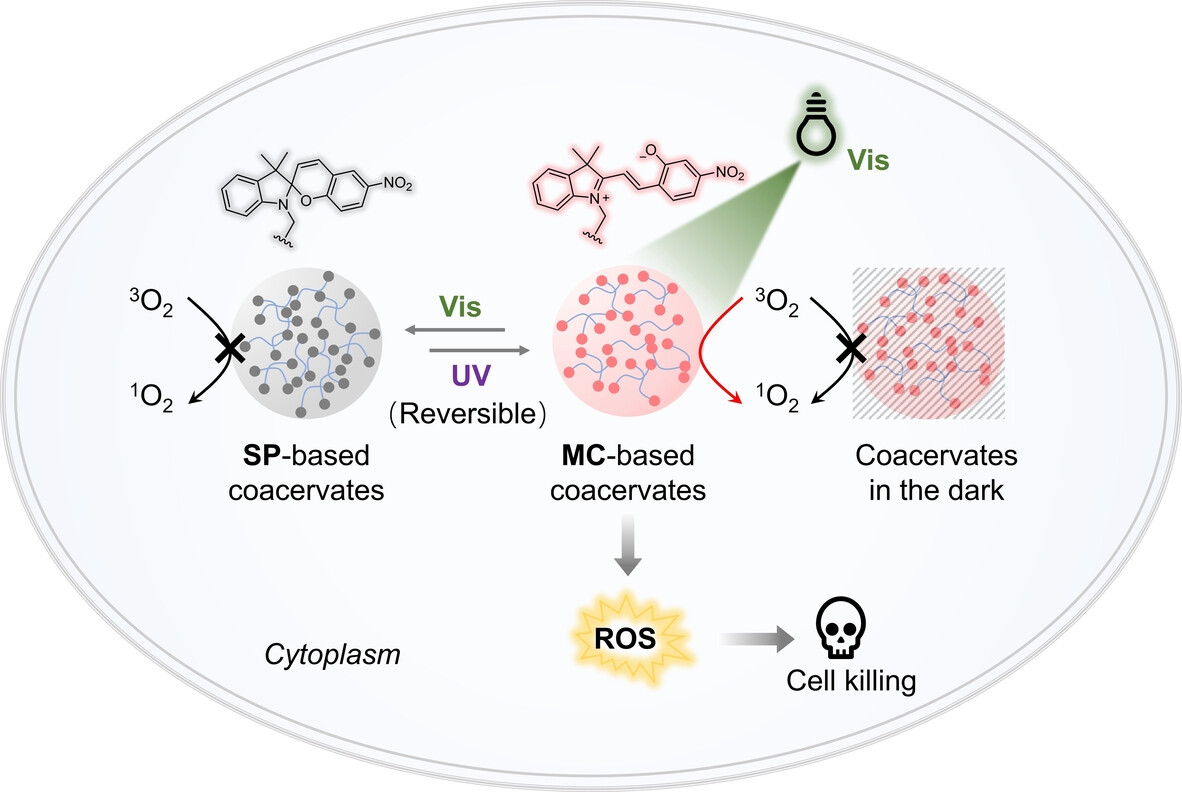
Coacervates
Phase-Separated Spiropyran Coacervates as Dual-Wavelength-Switchable Reactive Oxygen Generators
- First Published: 02 January 2025
C−O Coupling
Defluorinative C−O Coupling between Trifluoromethylarenes and Alcohols via Copper Photoredox Catalysis
- First Published: 01 January 2025
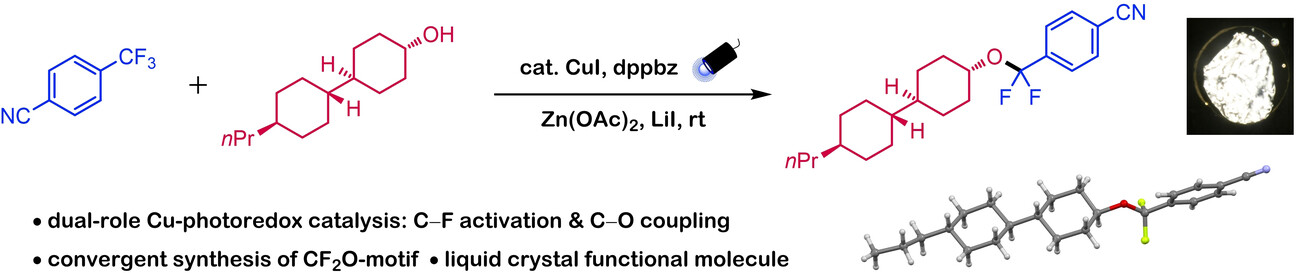
CF2O-compounds are prepared via photoinduced, Cu-catalyzed defluorinative coupling between readily available trifluoromethylarenes and alcohols. A molecule displaying liquid crystal property was synthesized through this convergent and step-economical method. Mechanistic studies suggested that a homoleptic Cu-bisphosphine complex serves as the photocatalyst, and the two salt additives are crucial in orchestrating this dual-cycle system.
Fragmentbasierte Arzneimittelforschung | Hot Paper
Untersuchung der Adressierbarkeit des Cysteinoms der Proteinkinasen durch Kovalente Fragmente
- First Published: 24 December 2024
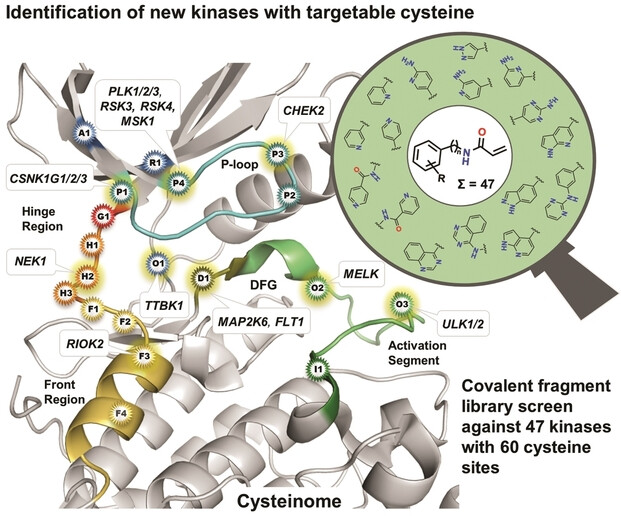
Trotz umfangreicher Forschungsarbeiten an kovalenten Kinaseinhibitoren bleibt ein Großteil des „Cysteinoms“ der Proteinkinasen unerforscht. Hier skizzieren wir einen verallgemeinerbaren Ansatz zur Adressierung von Cysteinen der ATP-Bindetasche mit fragmentartigen kovalenten Inhibitoren. Auf diese Weise erweitern wir das Repertoire der adressierbaren Cysteine im Kinom erheblich, geben Einblicke in einzigartige Bindungsmodi und präsentieren wertvolle Hits für die Entwicklung kovalenter chemischer Sonden und Medikamente.
Electrocatalysis | Hot Paper
Deciphering pH Mismatching at the Electrified Electrode–Electrolyte Interface towards Understanding Intrinsic Water Molecule Oxidation Kinetics
- First Published: 07 January 2025
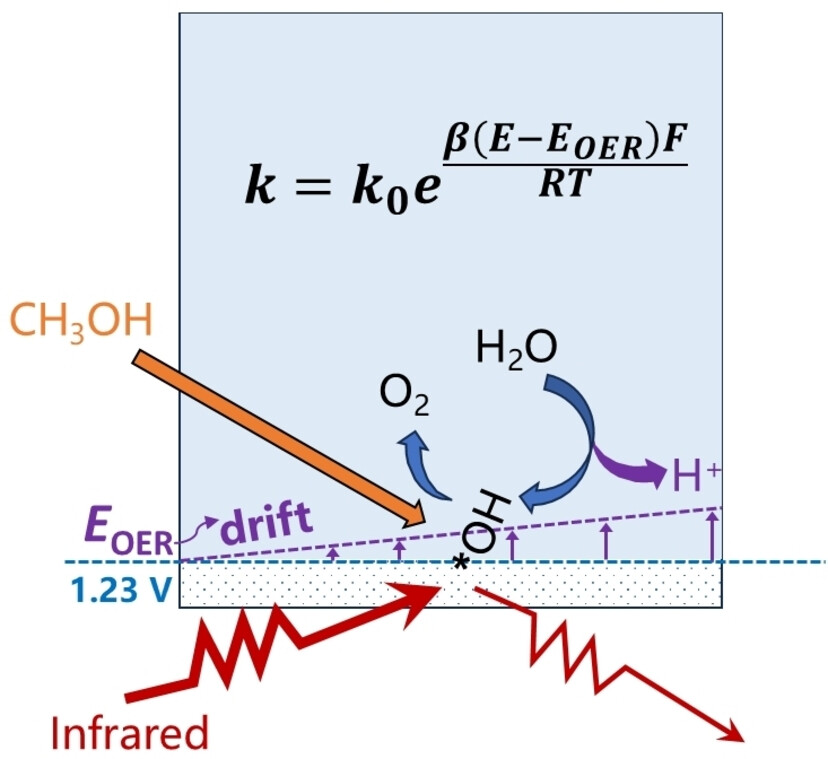
By integrating operando electrochemical methods with (micro)kinetic modelling, the dynamic local pH effect for the oxygen evolution reaction is clarified. An unconventional reversible hydrogen reference electrode is employed, enabling a clearer interpretation of intrinsic electrochemical kinetics. This approach offers deeper insights into the microscopic electrode processes in the electrified electrode-electrolyte interface with dynamic local pH.
Chiral Self-assemblies
Generating Strong Circularly Polarized Luminescence from Self-assembled Films of Chiral Selenium Nanoparticles and Upconversion Nanoparticles
- First Published: 26 December 2024
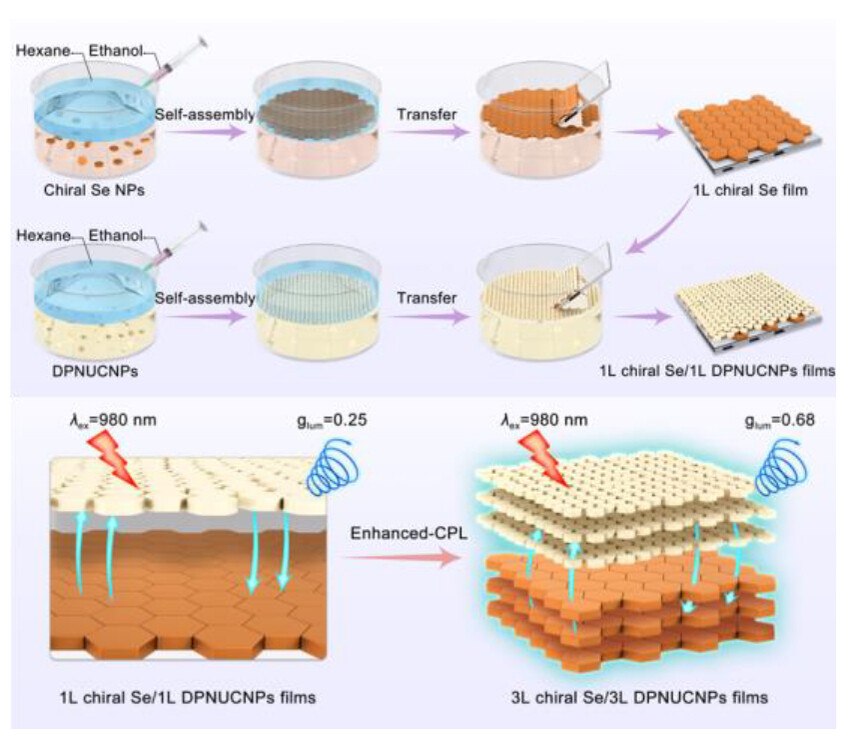
Chiral Se/DPNUCNPs films have been successfully developed with circularly polarized luminescence (CPL) activity under laser excitation at 980 nm. By controlling the assembly sequence and layer number, the chiral film exhibited strong circular dichroism (CD) signals and CPL activity, with a high luminescence dissymmetry factor (glum) of 0.68.
Carbonylkomplexe | Hot Paper
Formal nullwertige Bis(aren)Germylenkomplexe von Zirconium und Hafnium
- First Published: 19 November 2024
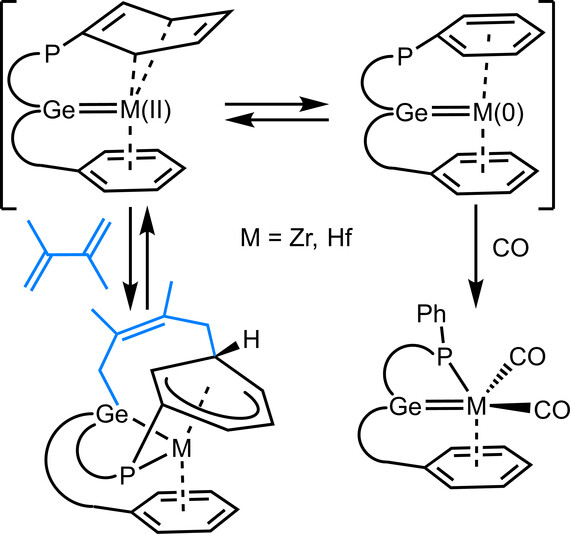
Bis(aren)koordinationsverbindungen von Zirconium und Hafnium wurden in großen Ausbeuten durch 4-Elektronenreduktion von Tetrachloridaddukten mit einem Germylen-Phosphor-Lewis-Paar synthetisiert. Ein gefalteter Koordinationsmodus einer Areneinheit wird im Hinblick auf strukturelle und spektroskopische Daten diskutiert. Carbonylkomplexe wurden hergestellt. Dimethylbutadien reagiert unter Bildung eines Cyclohexadienyl- und Triorganogermatliganden. Diese Addition ist im Falle des Zirconiums bei Raumtemperatur reversibel.
Metal-Organic Frameworks
2H NMR as a Practical Tool for Following MOF Formation: A Case Study of UiO-66
- First Published: 15 January 2025
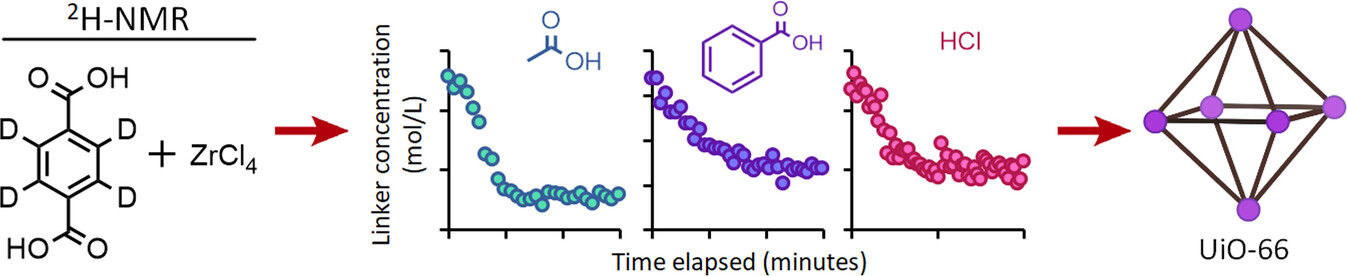
The article investigates UiO-66 synthesis over time using deuterium NMR, focusing on three modulators: acetic acid, benzoic acid, and hydrochloric acid. It reveals that slow linker incorporation results in the fastest and most defect-free MOF formation due to an acid-assisted dissociative mechanism. Deuterium NMR was crucial, enabling separate probing of components without altering the synthetic protocol.
Photomechanical Crystals | Hot Paper
Distinctive Photomechanical Shape Change of p-Phenylenediacrylic Acid Dimethyl Ester Single Crystals Induced by a Spatially Heterogeneous Photoreaction
- First Published: 19 November 2024

The photoreaction dynamics of p-phenylenediacrylic acid dimethyl ester in single crystals were examined, revealing a reaction front propagation from the edge to the center. As the photoreaction progresses, the crystal undergoes a distinctive shape transformation, changing from a parallelogram to a distorted “fluttering flag” shape and eventually becoming a rectangle. Density functional theory calculations predict the post-reaction crystal structure, explaining this unique shape change through the spatially heterogeneous nature of the photoreaction.
Electroluminescence
Spiro-Carbon-Locking and Sulfur-Embedding Strategy for Constructing Deep-Red Organic Electroluminescent Emitter with High Efficiency
- First Published: 04 November 2024
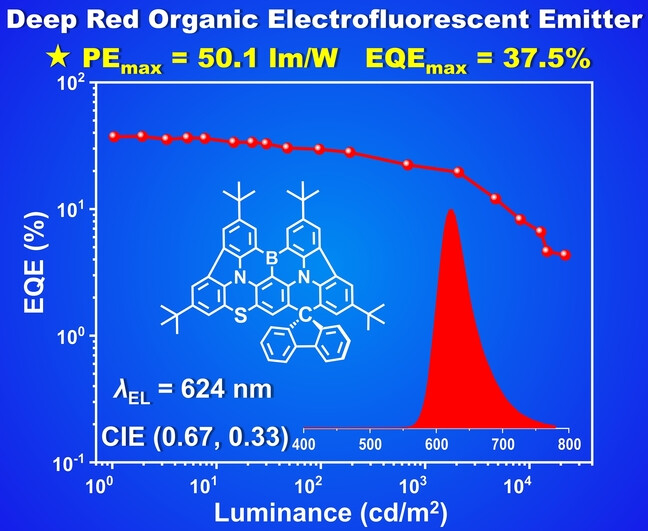
A strategy based on carbon locking and sulfur embedding has been used to construct a high-performance red multiple resonance (MR) emitter. The fabricated organic light-emitting diode (OLED) based on the target molecule exhibits Commission Internationale de l’Éclairage coordinates of (0.67,0.33) and a record-high power efficiency of 50.1 lm W−1.
Magic-sized Clusters | Hot Paper
Unexpected Magnetic Moments in Manganese-Doped (CdSe)13 Nanoclusters: Role of Ligands
- First Published: 06 December 2024
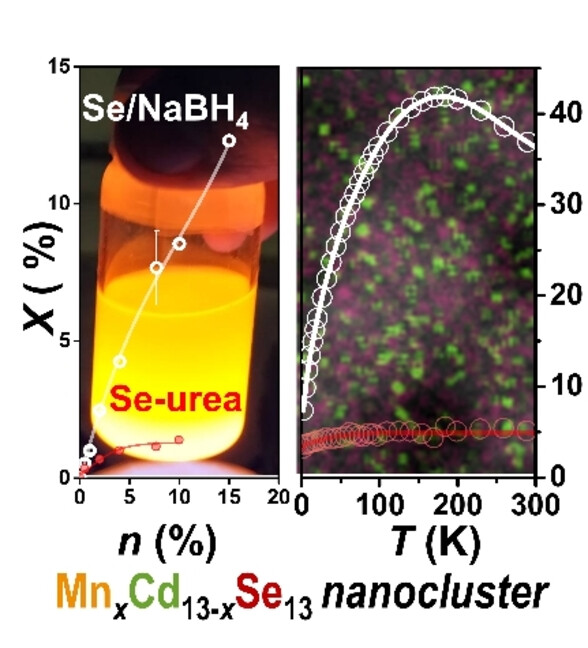
Mn2+-doped (CdSe)13 nanoclusters synthesized with Se-NaBH4 and Se-urea exhibit distinct magnetic and photoluminescent properties. Se-NaBH4-derived nanoclusters demonstrate superior Mn2+ doping efficiency (12.3 %) compared to Se-urea-derived clusters, leading to exceptional magnetic moments (40 μB at 180 K) and pronounced spin fluctuations.
Perovskite Solar Cells | Hot Paper
Bridged Carbolong Modulating Interfacial Charge Transfer Enhancement for High-Performance Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 29 November 2024
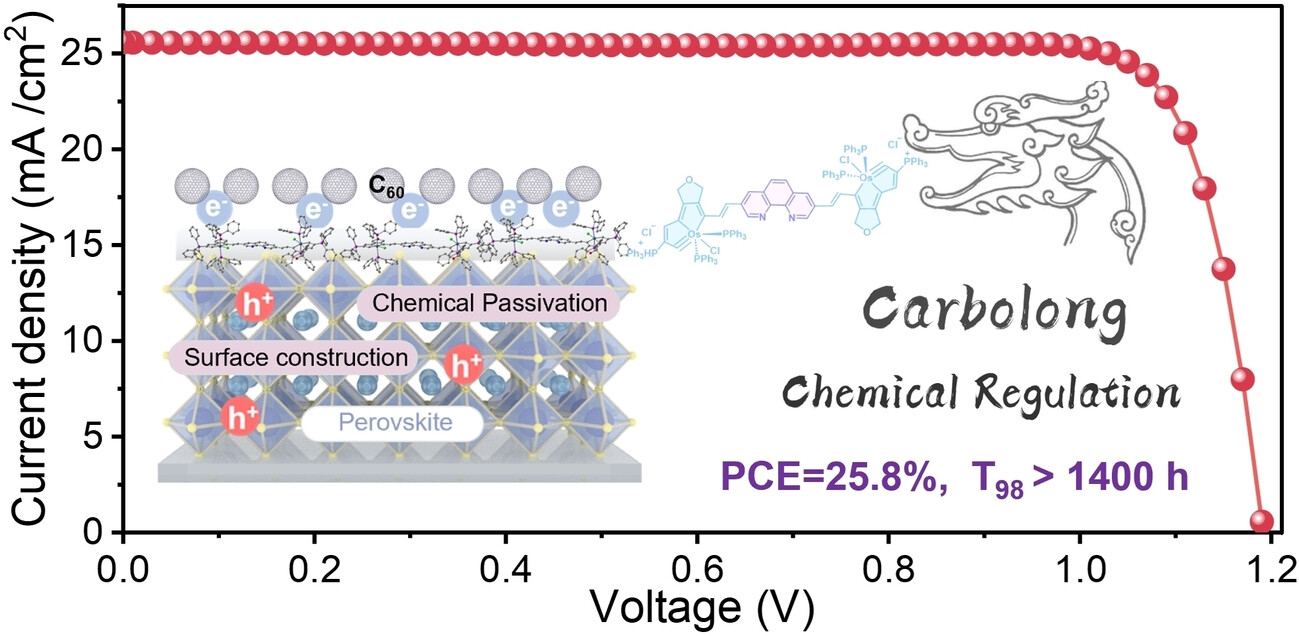
Bridged Carbolong Modulating for high-performance perovskite solar cells: A bridged carbolong modulating strategy to regulate the perovskite/C60 to accelerate interfacial electron transfer, reduce non-radiative recombination and suppress ion migration. The photo- and thermal-stable devices reached 25.80% of efficiency and maintained 98% of its initial efficiency over 1400 h of illumination, and the efficiency of modules achieved 20.72% (25.25 cm2 active area) with robust operational stability.
Covalent Organic Frameworks
Highly Efficient Chiral Separation Based on Alkali-proof Protein Immobilization by Covalent Organic Frameworks
- First Published: 22 November 2024
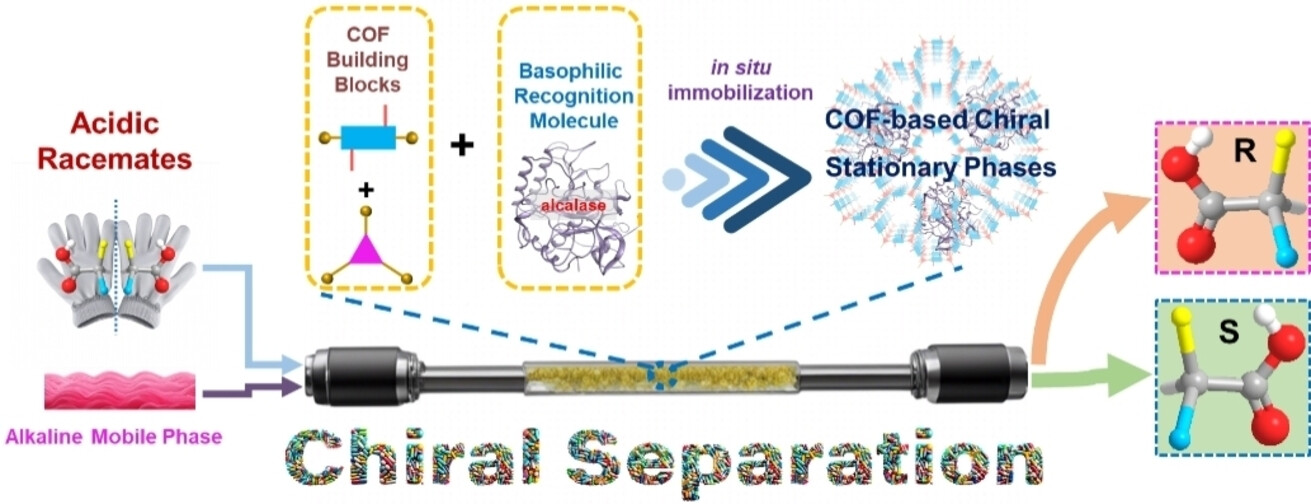
Basophilic alcalase is creatively developed to fabricate ultrastable protein-based chiral stationary phases that can efficiently work under alkaline conditions. Upon incorporating CSPs into chiral separation columns, we enable high-precision chiral chromatographic separation with exceptional stability.
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Heterogeneous Catalysis of Molecular-Like Au8M(PPh3)8n+ Clusters Cultivated in Mesoporous SBA-15
- First Published: 02 December 2024
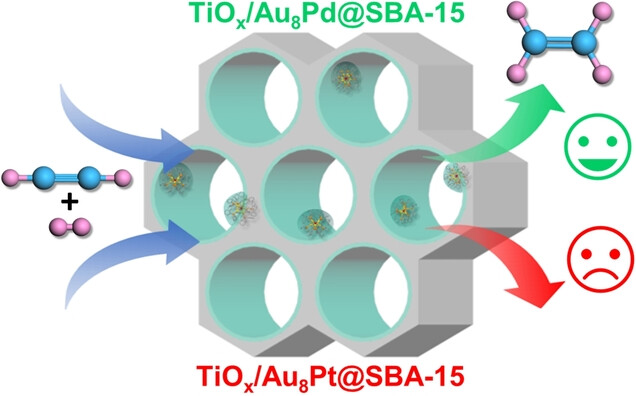
In this work, we report a push-and-pull synthesis strategy for designing the heterogeneous catalyst denoted as TiOx/cluster@SBA, where the three functional units of clusters, SBA-15 and TiOx are combined into one heterogeneous catalyst, and thereby we learn how the atom-by-atom tailoring of a heterogeneous catalyst can switch on elusive heterogeneous mechanisms with cluster catalysis.
Zinc-Ion Batteries | Hot Paper
Polyoxotungstate Featuring Zinc-Ion-Triggered Structural Transformation as An Efficient Electrolyte Additive for Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 27 November 2024
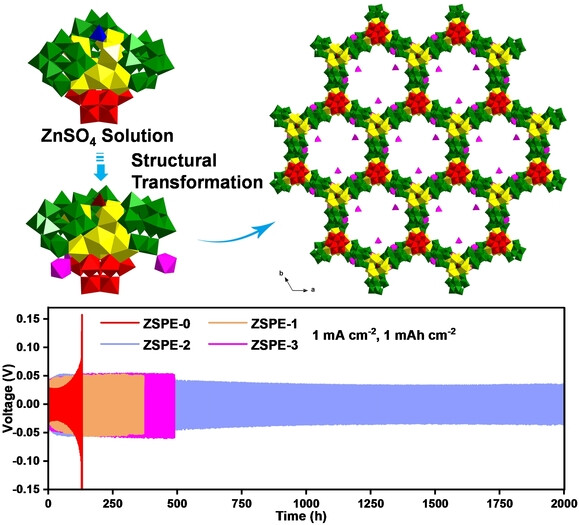
Here, we present a rare instance of a soluble high-nuclearity polyoxometalate exhibiting Zn2+-triggered structural transformation from 0D nanocluster to 2D layer in ZnSO4 solution. Further, we showcase that such a kind of polyoxometalate, possessing Zn2+-triggered structural transformation properties, represents a new-type and promising class of additives for aqueous zinc battery electrolytes with significant potential applications.
Molecular Electrocatalysts | Very Important Paper
Subtle Modifications in Interface Configurations of Iron/Cobalt Phthalocyanine-Based Electrocatalysts Determine Molecular CO2 Reduction Activities
- First Published: 25 November 2024
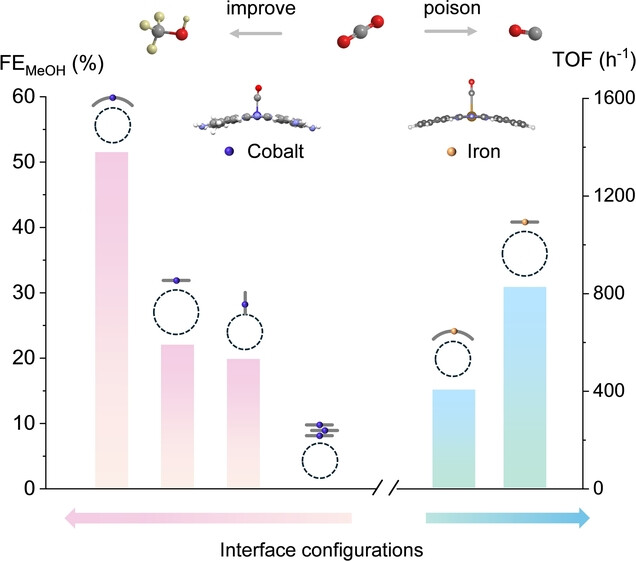
Molecular strain has an adverse or conducive effect on catalytic activity. Strained cobalt tetraaminophthalocyanine improves *CO binding for subsequent hydrogenation, attaining methanol Faradaic efficiency up to 52 %. However, strained iron phthalocyanine exacerbates *CO poisoning, leading to inferior CO production. We proposed *CO binding strength as an indicator for activity prediction.
MXene Synthesis | Hot Paper
General and Fast Gas–Solid Synthesis of Functional MXenes and Derivatives on the Scale of Tens of Grams
- First Published: 26 November 2024
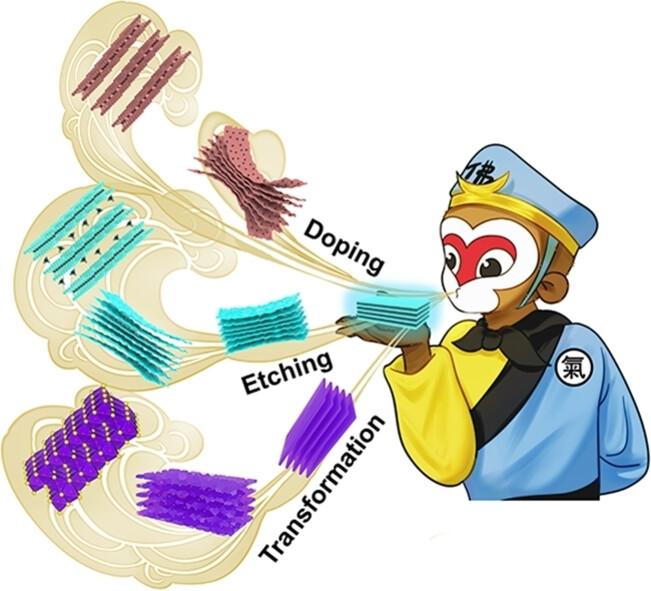
Gas-solid reaction system with high selectivity, controllability and compatibility enables fast etching, doping and transformation of MAX phases and the large-scale production of MXenes and their derivatives. The as-obtained samples exhibit excellent capability in effectively reducing the shutting effect of lithium polysulfides via chemical adsorption and catalytic conversion as evidenced by both of theoretical and experimental results.
Circularly Polarized Luminescence
Excitation-Dependent Circularly Polarized Luminescence Inversion Driven by Dichroic Competition of Achiral Dyes in Cholesteric Liquid Crystals
- First Published: 29 November 2024
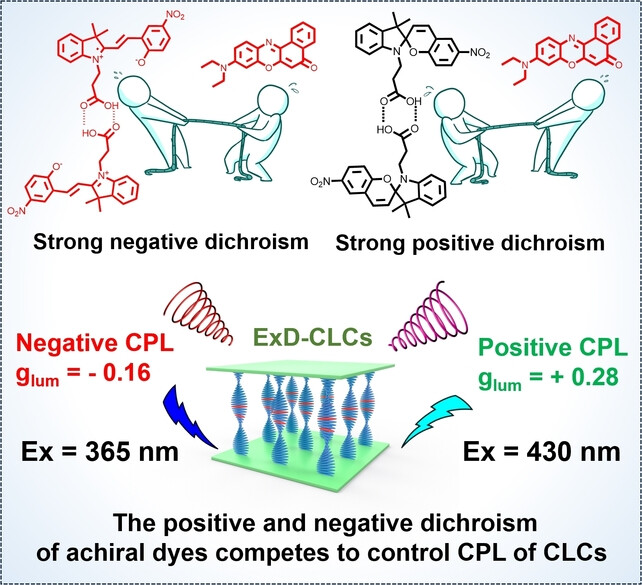
Establishing a dynamically photoresponsive dichroic competition between two achiral dyes within a chiral cholesteric liquid crystal has led to an excitation-dependent material. Excitation at 365 nm generates a negative CPL signal (glum=−0.16) at 650 nm, while excitation at 430 nm results in inversion of the CPL signal and an increase in the glum value to +0.26, with the helical superstructure and handedness of the materials remaining unchanged.
Ammonia-Fueled Engine | Hot Paper
A Scenario for a Carbon-Neutral Ammonia-Fueled Engine Mediated by Catalytic NH3 Cracking and CO2 Hydrogenation
- First Published: 21 November 2024
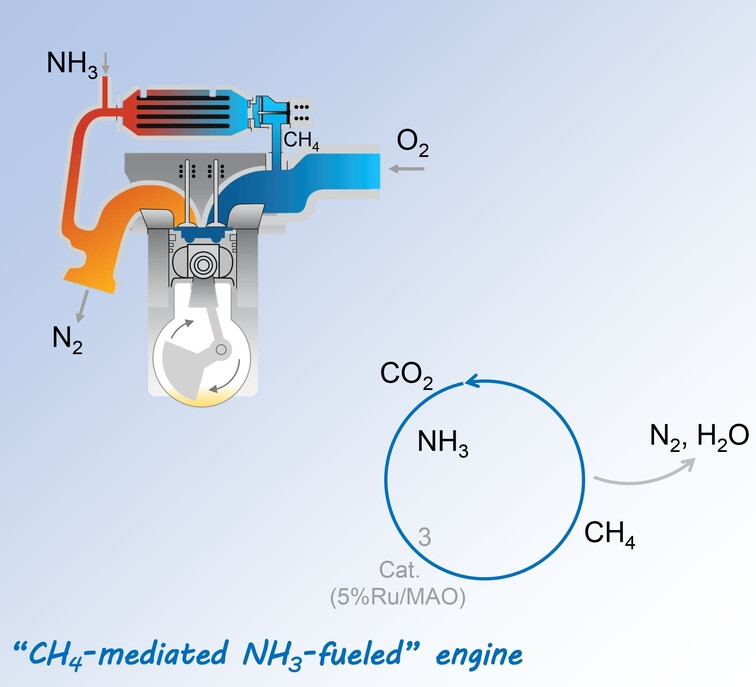
The direct use of ammonia as engine fuel faces challenges like low flame velocity and high NOx emissions. We propose a novel scenario for converting a conventional “CH4-fueled” engine to “NH3-fueled” engine. Specifically, CH4 is used to power the internal combustion engine and release CO2 as the exhaust which then reacts with NH3 to generate N2 and CH4 for enclosing the carbon cycle.
Capacitive Deionization | Hot Paper
Elaborate Designed Three-Dimensional Hierarchical Conductive MOF/LDH/CF Nanoarchitectures for Superior Capacitive Deionization
- First Published: 17 January 2025
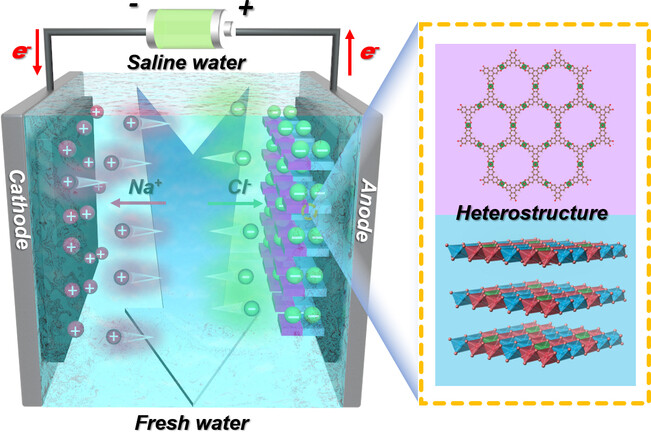
This work provides a facile method to fabricated hierarchical composite M-CAT/LDH/CF, the well-ordered NiCoCu-LDH acts as interior templates to create an interface by embedding c-MOFs and aligning two crystal lattice systems, facilitating the graft growth of c-MOFs/LDH heterostructures along the LDH. This improves ion accessibility, speeds up ion transfer, and enhances ion transport pathways for excellent desalination performance.
Zeolite-based Catalysts
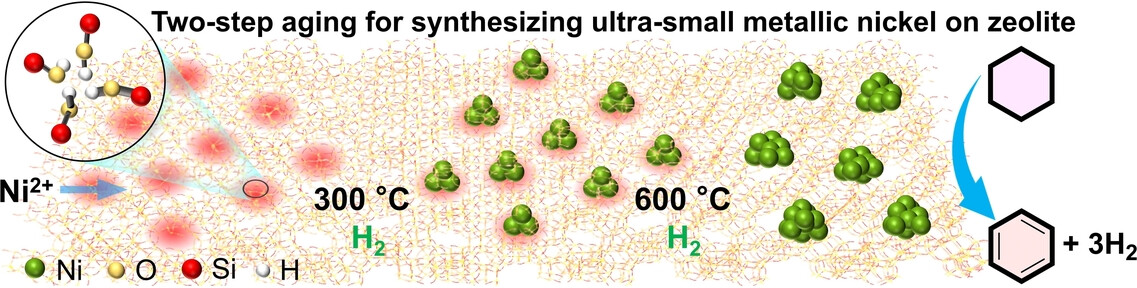
Ultra-small Metallic Nickel Nanoparticles on Dealuminated Zeolite for Active and Durable Catalytic Dehydrogenation
- First Published: 02 December 2024
Polymer Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Enantiomorphic Site-Assisted Chain End Control Stereospecific Alternating Copolymerization of Chiral Cyclic Diesters
- First Published: 28 October 2024
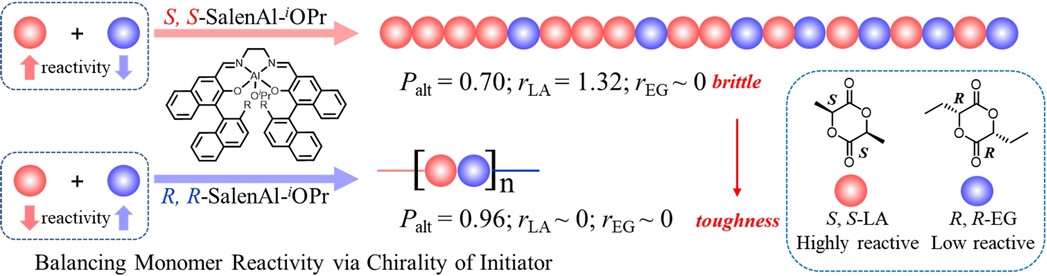
A perfectly alternating sequence-controlled polymerization of cyclic esters with remarkably different reactivities be a challenge, in this work, a remarkable enantiomorphic site effect on chain end control was successfully utilized to balance the reactivities of highly reactive S, S-lactide and low reactive R, R-ethylglycolide, and a perfectly alternating copolymer with a high alternating level was achieved and exhibited a high break strain.
Nitrogen Fixation | Hot Paper
Achieving Photocatalytic Overall Nitrogen Fixation via an Enzymatic Pathway on a Distorted CoP4 Configuration
- First Published: 23 December 2024
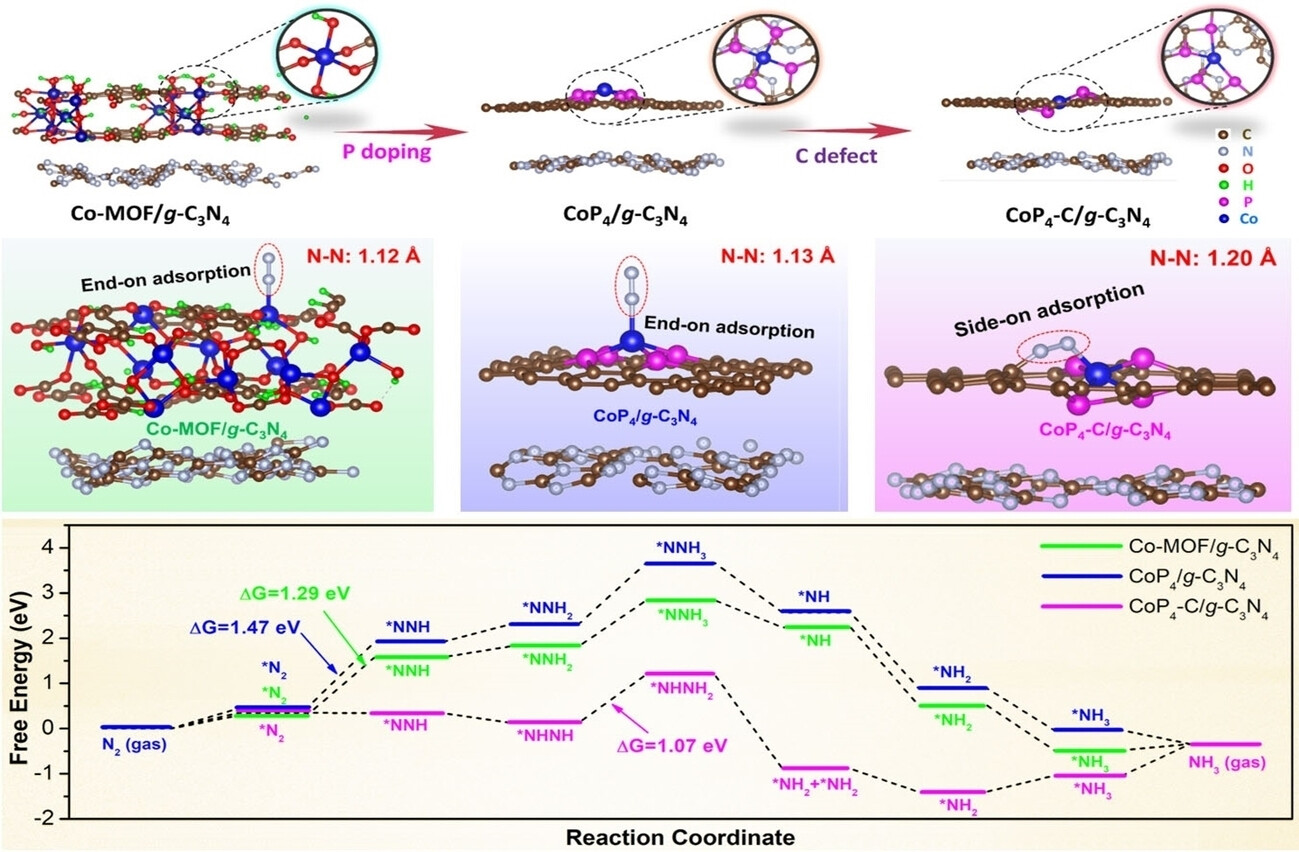
A Co single-atom catalyst (SAC) with a C-defect-evoked CoP4 distorted configuration was fabricated. The N2 adsorption pattern on the Co-SAC switched from an “end-on” to a “side-on” mode, notably decreasing the N2 adsorption/activation energy barrier. In the absence of sacrificial agents, the Co SAC achieved excellent photocatalytic overall N2 fixation performance via an enzymatic pathway.
CO Electroreduction | Hot Paper
Boosting C2+ Alcohols Selectivity and Activity in High-Current CO Electroreduction using Synergistic Cu/Zn Co-Catalysts
- First Published: 09 December 2024
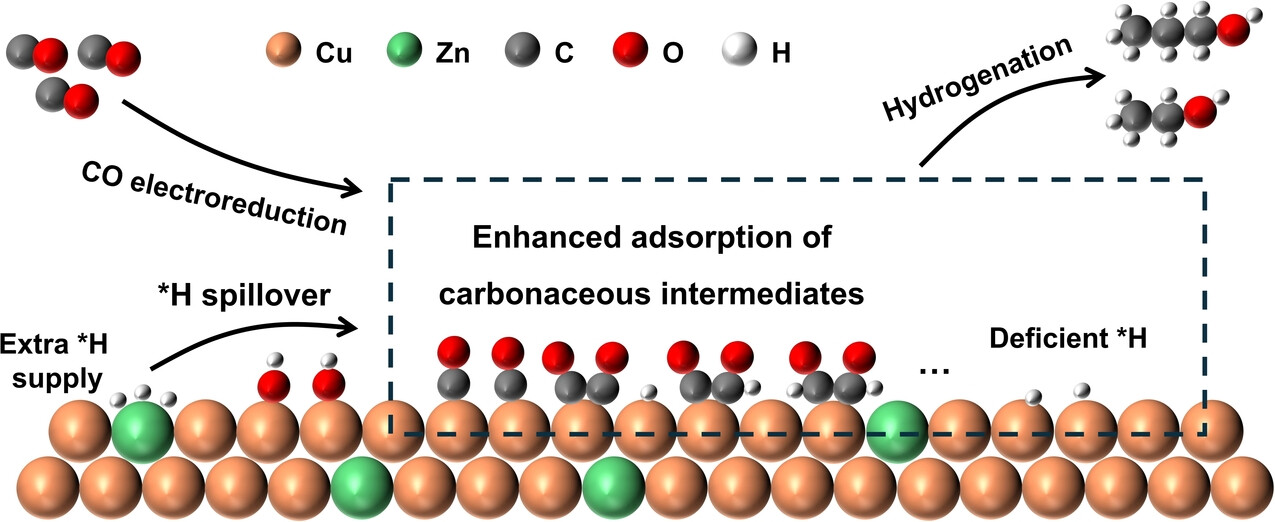
To unify the selectivity and activity of CO electroreduction for C2+ alcohols, a Cu/Zn alloy catalyst was developed to balance the competition between CO reduction and hydrogen evolution on Cu sites. Zn alloying increases CO coverage on Cu and facilitates hydrogen spillover from Zn to Cu, synergistically promoting alcohol formation, achieving a 50 % Faradaic efficiency for alcohol synthesis at a current density of 1.1 A cm−2.
Ammonia Production | Hot Paper
Enhancing Low-Concentration Electroreduction of NO to NH3 via Potential-Controlled Active Site-Intermediate Interactions
- First Published: 20 November 2024
Goldkatalyse
Goldkatalysierte Intramolekulare Reaktion von Alkinen mit Sulfoximinen als N- und O-Transferreagenzien
- First Published: 11 December 2024
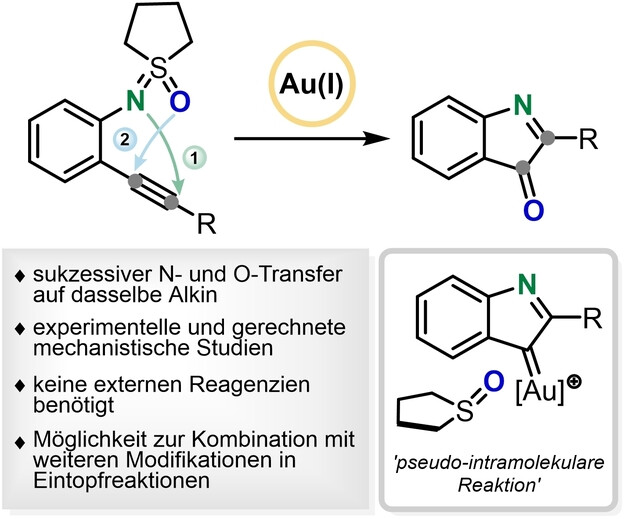
Sulfoximine werden als selektive N- und O-Transferreagenzien für Alkine bei der goldkatalysierten Umwandlung von N-(2-Alkinylphenyl)sulfoximinen zu 3H-Indol-3-onen eingesetzt. Die Art des Reaktionsmechanismus wird anhand experimenteller und theoretischer Studien diskutiert. Da externe Oxidationsmittel vermieden werden, weist die Methode eine ausgezeichnete Toleranz gegenüber funktionellen Gruppen auf und kann mit weiteren Transformationen in Eintopfverfahren kombiniert werden.
Perovskite Solar Cell | Hot Paper
Insights Into the Role of π-Electrons of Aromatic Aldehydes in Passivating Perovskite Defects
- First Published: 12 December 2024
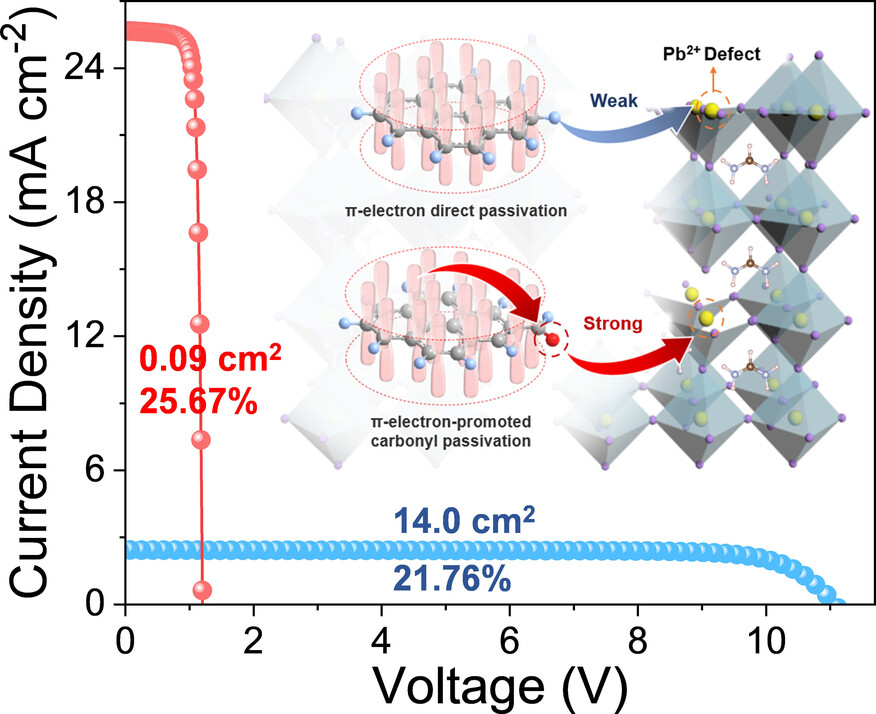
The impact of π-electrons in the carbonyl-containing aromatic materials on their passivation ability was thoroughly investigated. With the increase of aromatic conjugated system, the increased π-electrons mainly enhance the defect passivation of the carbonyl group, although they do not directly present strong passivation with the defects in the perovskite films. Finally, perovskite solar cells incorporating pyrene-1-carbaldehyde achieved power conversion efficiencies of 25.67 % (0.09 cm2) and 21.76 % (14.0 cm2) with excellent long-term stability.
Hydroboration | Hot Paper
Hydrogen Isotope Separation
High-Entropy Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks for Dynamic Hydrogen Isotope Separation
- First Published: 03 December 2024
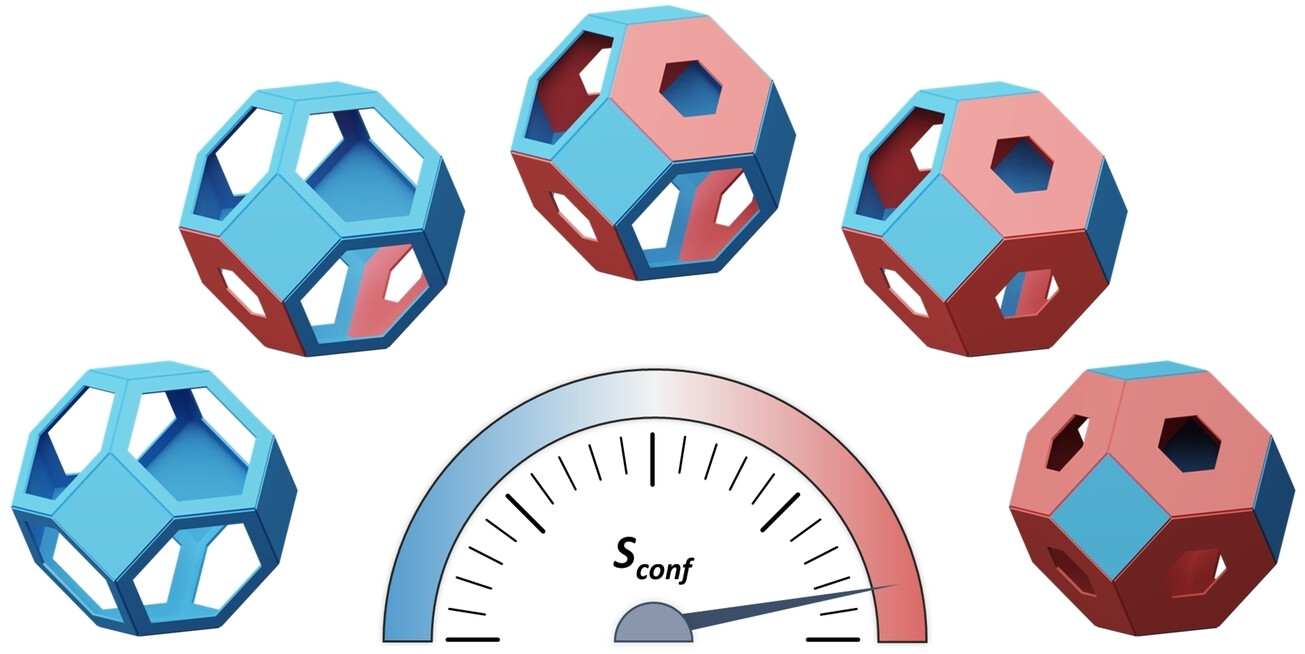
As configurational entropy increases, bulky functionalities progressively block the apertures in sod-ZIF-1 series, enabling programmable control over the pore structure. This controlled reduction in porosity enhances selective interactions with hydrogen isotopes. The gradual tightening of apertures directly impacts gas adsorption and separation performance, particularly in hydrogen isotope separation.
Organic Solar Cells | Hot Paper
“Double-Gene” Small Molecule as Guest Component Promotes the Efficiency of Organic Solar Cells Beyond 19.5 %
- First Published: 02 January 2025
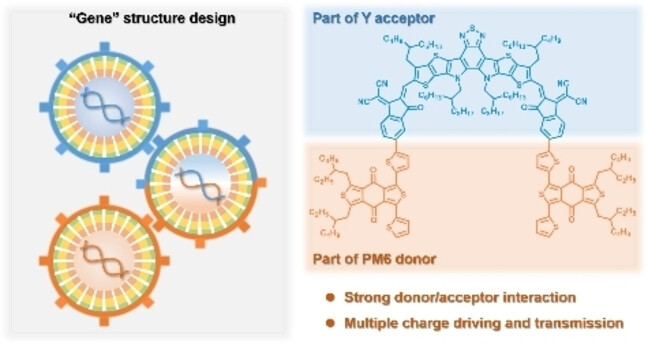
A new “double-gene” small molecule L-DBDD is synthesized based on the concept of “structural-gene“ engineering by combination of the parent structures of donor and acceptor. It is employed as a guest component and a bridge to enhance the donor-acceptor interaction and accelerate exciton dissociation and transmission, enabling efficiency of solar cell reaching 19.51 %.
Atropisomerism | Very Important Paper
Copper-Catalyzed Enantioselective Skeletal Editing through a Formal Nitrogen Insertion into Indoles to Synthesize Atropisomeric Aminoaryl Quinoxalines
- First Published: 17 December 2024
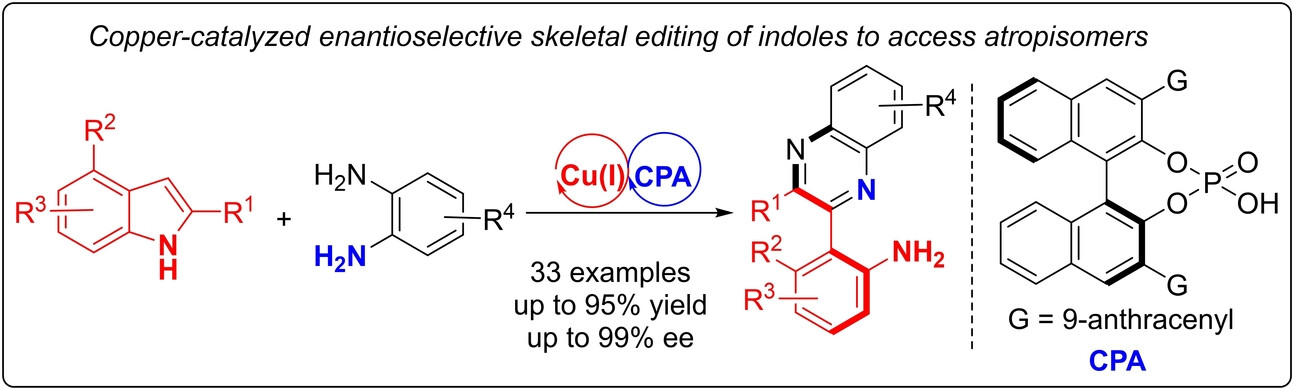
A copper(I) and chiral phosphoric acid (CPA) relay catalyzed enantioselective skeletal editing of indoles with 1,2-aminoarenes to quinoxaline ring has been developed to prepare various axially chiral aminoaryl quinoxalines in good yields and excellent enantioselectivity. Moreover, axially chiral aminoaryl quinoxalines could be converted into various axially chiral building blocks and aminoaryl quinoxaline derived ligand is demonstrated to be applicable to asymmetric catalysis.
Monovalent Nickel | Hot Paper
Unlocking CO2 Activation With a Novel Ni−Hg−Ni Trinuclear Complex
- First Published: 07 January 2025
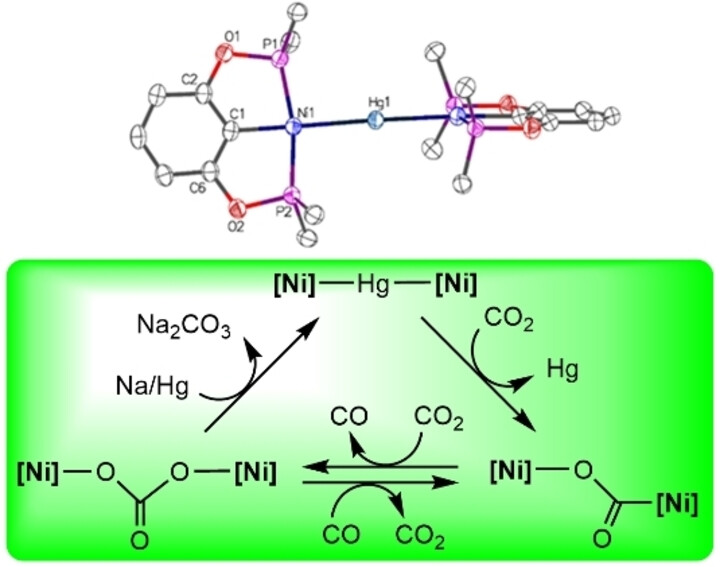
Reduction of the divalent precursor (κP,κC,κP'-2,6-(i-Pr2PO)2C6H3)NiBr has given the diamagnetic trinuclear complex [Ni2Hg] featuring two (formally) monovalent Ni centers bonded to a bridging mercury atom. The thermally stable but fairly labile Ni−Hg−Ni core in [Ni2Hg] facilitates a smooth disproportionation of CO2, according to the net equation “2 CO2+2 e−→CO32−+CO”. This process begins with an initial CO2 insertion that expels Hg to give the intermediate [Ni2CO2], whereas the latter can promote a second CO2 insertion followed by CO gas release to give [Ni2CO3]. This μ-carbonate species can be reduced with Na/Hg to regenerate the original complex [Ni2Hg].
Photocatalysis | Very Important Paper
Dual Regulation of Sensitizers and Cluster Catalysts in Metal–Organic Frameworks to Boost H2 Evolution
- First Published: 25 November 2024
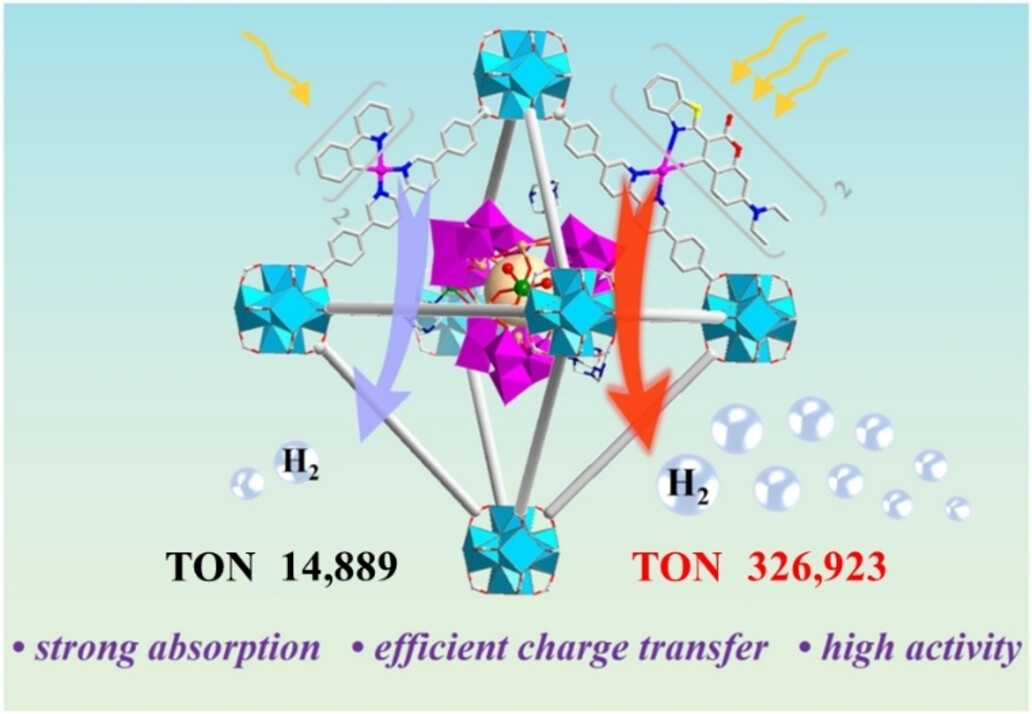
A photosensitizer/catalyst dual regulation strategy was proposed based on POM@MOF molecular platform to construct the highly efficient catalysts for photocatalytic H2 evolution. Impressively, the resulting Ni−Sb9@UiO−Ir−C6 can efficiently drive water splitting into H2 with a TON of 326923, representing a record value among all the POM@MOF composites.
Electrochemistry | Very Important Paper
High-Rate Lithium-Ion Capacitor Diode Towards Multifrequency Ion/Electron-Coupling Logic Operations
- First Published: 08 January 2025
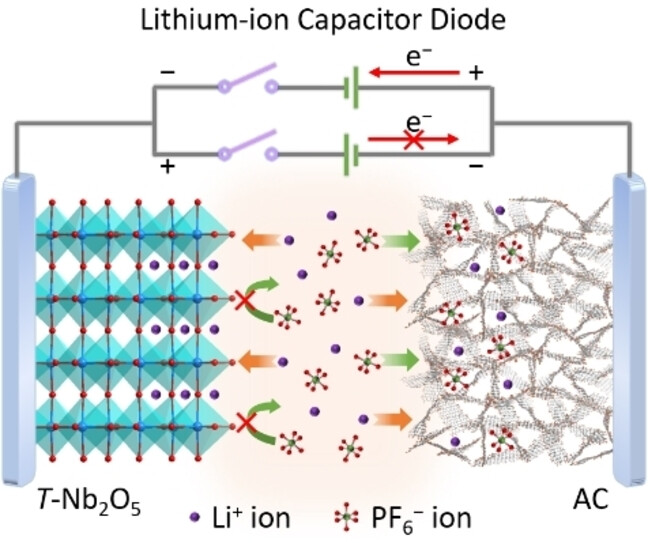
An orthorhombic niobium pentoxide (T-Nb2O5) based lithium-ion capacitor diode (CAPode) with thoroughly improved response frequency and rectification ratio has been successfully developed. It is demonstrated to be fully competent in typical AND and OR logic gates over a wide frequency range of 1–100 Hz, validating great potential in the burgeoning field of multifrequency ion/electron-coupling logic operations.
Electrolyte Design | Very Important Paper
Coulombic Condensation of Liquefied Gas Electrolytes for Li Metal Batteries at Ambient Pressure
- First Published: 09 December 2024

Dimethyl ether (Me2O) gas can be condensed through ion-dipole interactions with lithium bis(fluorosulfonyl)imide at sufficiently high concentrations, which elevates the boiling of point Me2O, imparting enhanced physical and electrochemical properties for battery applications. The approach of Coulombic condensation by facilitating ion-dipole interactions with weakly coordinating solvents offers a promising strategy for next-generation electrolyte design.
Batteries
Fluorination from Surface to Bulk Stabilizing High Nickel Cathode Materials with Outstanding Electrochemical Performance
- First Published: 19 December 2024
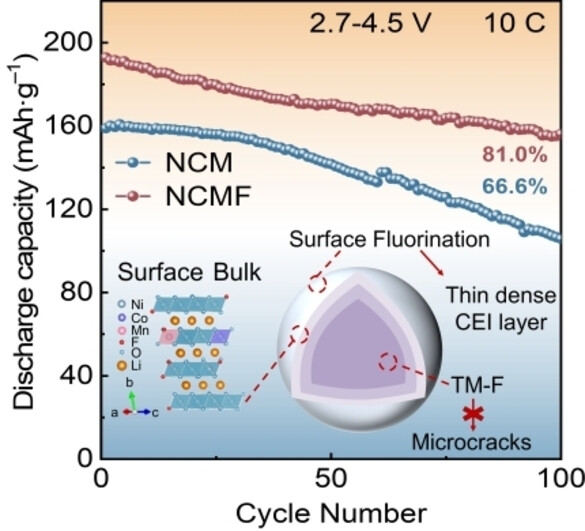
Through interfacial fluorination and introducing F ions to bulk phase as anchors, the high-voltage high-rate cycling performance of high nickel cathodes is boosted. The fluorinated surface induces the formation of a thin, dense CEI layer to facilitate Li+ migration and hinder electrolyte erosion. Additionally, the substitution of F for O in bulk phase forms strong TM−F bonds, thereby enhancing surface and internal structural stability, and hindering the formation of microcracks and gas evolution.
Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence | Hot Paper
Rational Molecular Design for Balanced Locally Excited and Charge- Transfer Nature for Two-Photon Absorption Phenomenon and Highly Efficient TADF-Based OLEDs
- First Published: 25 November 2024
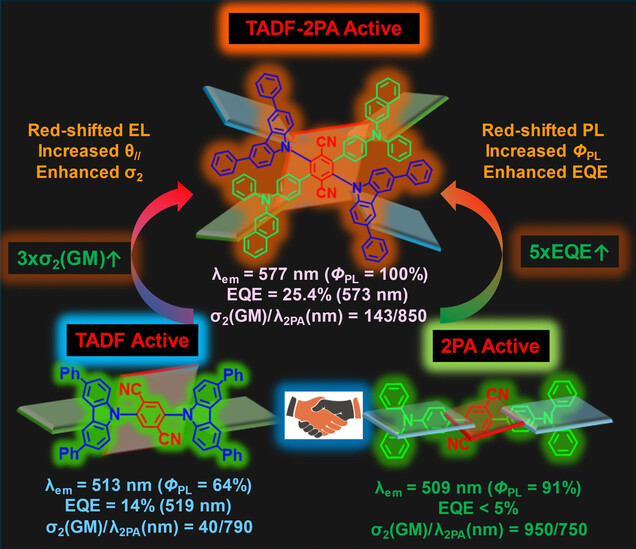
Synergistic modulation of π-conjugation and electron-donating strengths has been used to induce hybridized localized electronic and charge-transfer characters. This has led to donor-acceptor-donor (π-DAD) structures showing a maintained elevated two-photon absorption cross-section value and highly efficient thermally activated delayed fluorescence.
Chiral Nanosheets | Very Important Paper
Unveiling Chirality in MoS2 Nanosheets: A Breakthrough in Phase Engineering for Enhanced Chiroptical Properties
- First Published: 07 January 2025
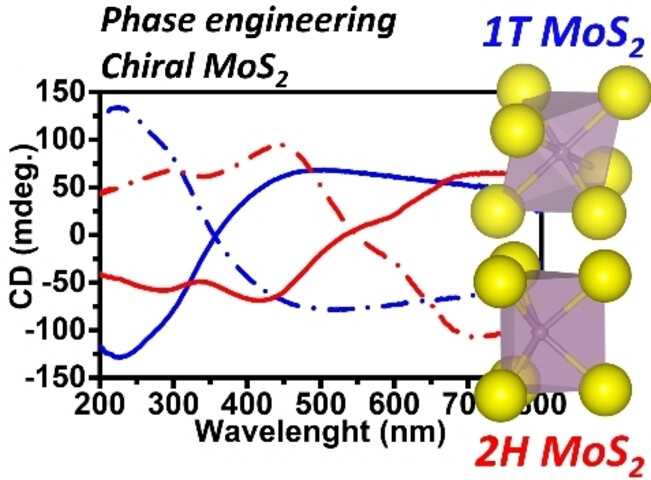
Semiconductor 2H Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets with high chiroptical activity have been produced using a novel synthetic strategy based on phase engineering. Our approach is based on the conversion of chiral metastable metallic 1T MoS2 nanosheets into the thermodynamically stable 2H phase via a thermal annealing step specifically designed to preserve the chiral morphology during the metallic-to-semiconductor phase transition.
CO2 Surface Chemistry
CO2-Driven Oxygen Vacancy Diffusion and Healing on TiO2(110) at Ambient Pressure
- First Published: 03 January 2025
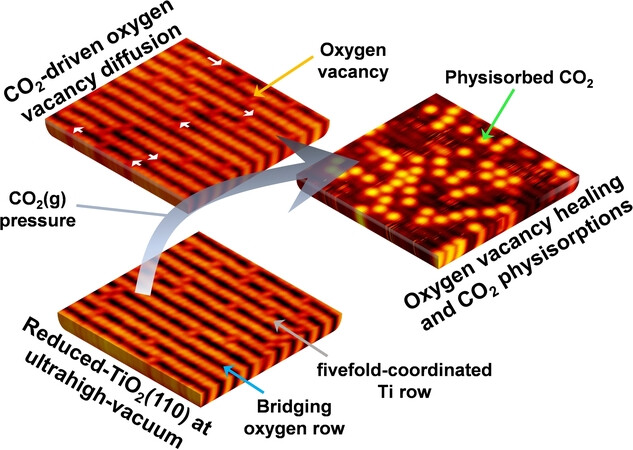
We explore the initial CO2 activation processes on the reduced TiO2(110) surface by using in situ ambient-pressure techniques. The interactions between oxygen vacancy, Ti3+ interstitial, and CO2 molecules are revealed depending on CO2(g) pressure and observation time. The oxygen vacancy diffusion mechanism and dynamics of physisorbed CO2 modes are unraveled.
Organic Solar Cells | Hot Paper
Construction of Linear Tetramer-Type Acceptors for High-Efficiency and High-Stability Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 02 January 2025
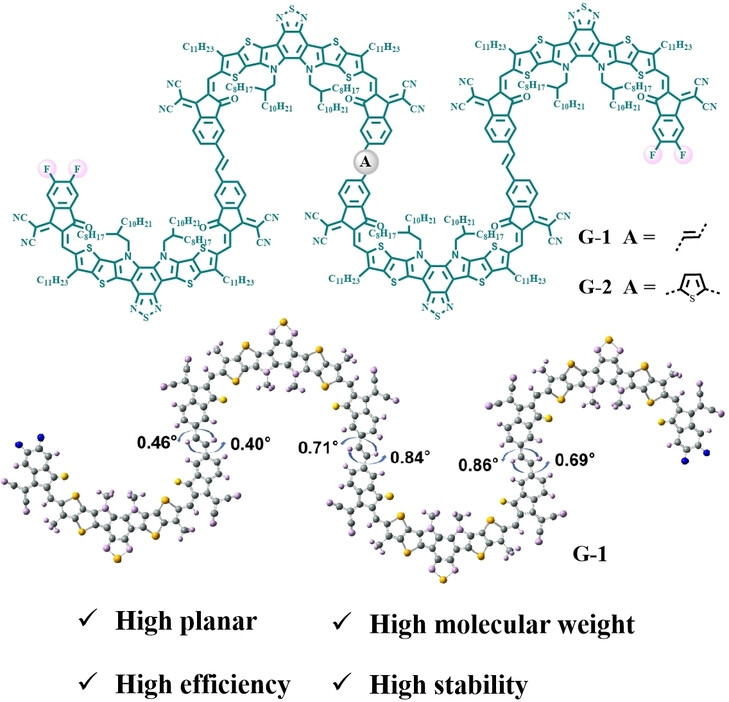
We have successfully constructed two linear tetramer-type acceptor materials, G-1 and G-2, terminating in the strongly electron-withdrawing INCN-2F. Both tetramers have molecular weights in excess of 7,000. DFT calculations and experimental results show that the fully alkene-bonded tetramer G-1 has an almost completely planar molecular structure and relatively strong crystallinity. In addition, G-1-based OSC achieved high PCE (19.6 %) and high stability (T80 lifetime over 10000 hours).
Photocatalysis
Photocatalyzed Azidofunctionalization of Alkenes via Radical-Polar Crossover
- First Published: 02 January 2025
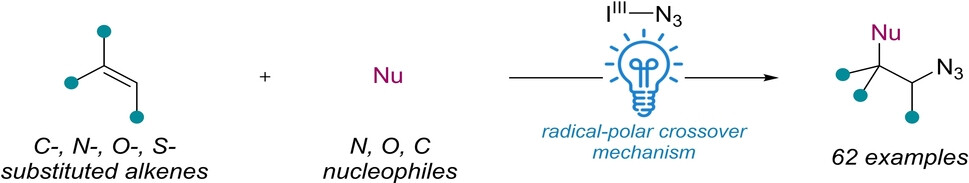
The azidofunctionalization of alkenes using a hypervalent iodine reagent and various nucleophiles (Nu) under photoredox conditions is described. This method enables the synthesis of 1,2-difunctionalized products from a wide range of alkenes and nucleophiles significantly improving the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates. The generality and limitations of the approach in the alkene and nucleophile dimensions were examined through a standardized, unbiased substrate selection.
Electrocatalysis | Hot Paper
Strong Heteroatomic Bond-Induced Confined Restructuring on Ir−Mn Intermetallics Enable Robust PEM Water Electrolyzers
- First Published: 27 December 2024
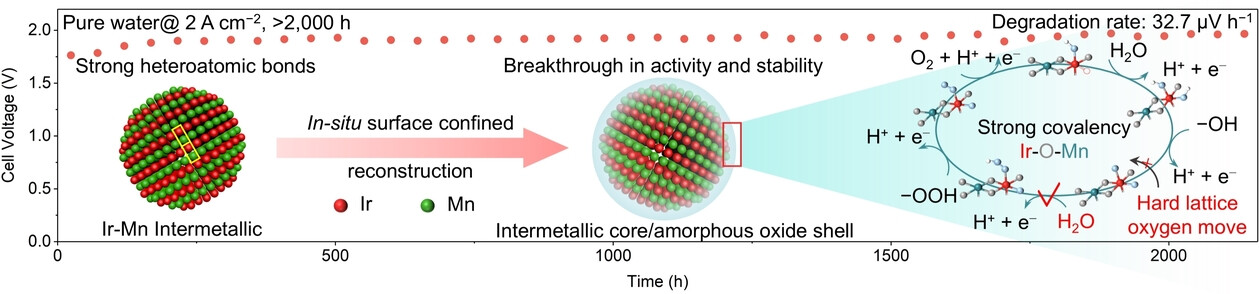
This work reveals the contribution of the atomic ordering strategy to the favorable reconstruction in acidic OER. The in situ confined reconstruction layer with strong covalent Ir−O−Mn units induced by the rich strong heteroatomic bonds of Ir−Mn intermetallics (IMC) optimizes the adsorption of oxygen intermediates and suppresses the participation of lattice oxygen, thus achieving a double breakthrough in activity and stability.
Organic Light-Emitting Diodes
Excited-State Engineering of Chalcogen-Bridged Chiral Molecules for Efficient OLEDs with Diverse Luminescence Mechanisms
- First Published: 23 December 2024
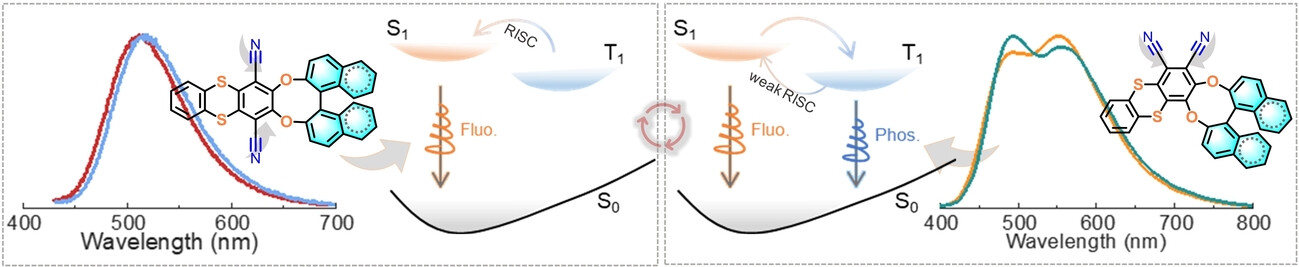
By utilizing isomeric molecular engineering to tune electronic and vibrational spin-orbital coupling effects, several chiral molecules have been developed to exploit both thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) and room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) mechanisms for efficient luminescence. The TADF-based OLEDs achieve a high external quantum efficiency of 30.1 %, and by modulating the TADF and RTP emissions, single-molecule white emission has been realized.
Zn-Air Batteries
Breaking the Stability-Activity Trade-off of Oxygen Electrocatalyst by Gallium Bilateral-Regulation for High-Performance Zinc-Air Batteries
- First Published: 23 December 2024
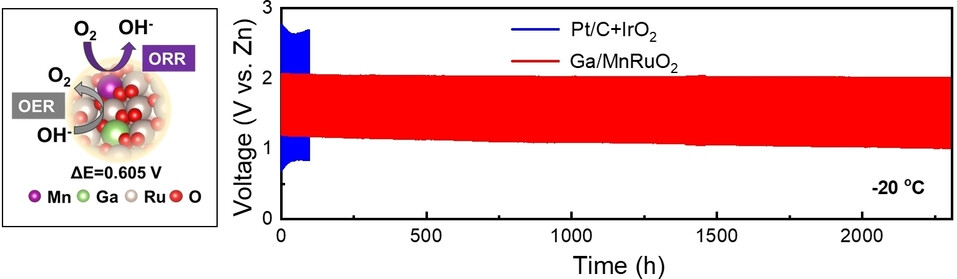
An atomic-level bilateral regulation strategy was developed to optimize the electronic environment of Mn−O and Ru−O in Ga/MnRuO2 by doping Ga to overcome the activity-stability restriction of bifunctional electrocatalysts and thus achieving the high bifunctional performance for ORR/OER and zinc-air battery.
Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
Anionic Doping in Layered Transition Metal Chalcogenides for Robust Lithium-Sulfur Batteries
- First Published: 17 December 2024
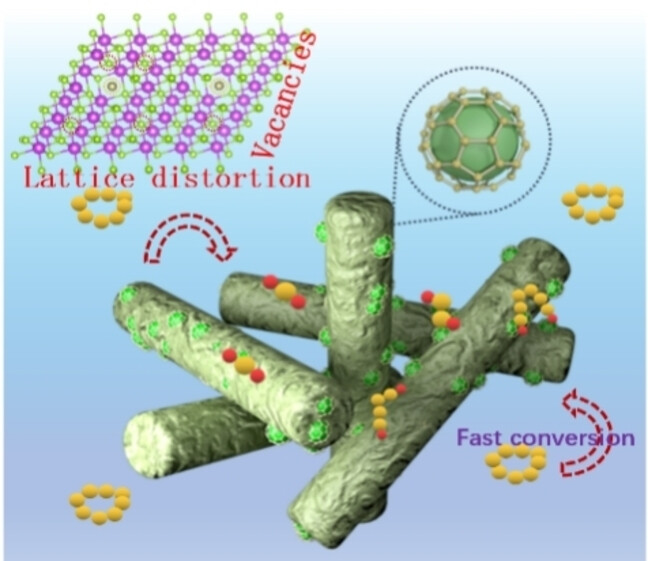
The role of vacancies and lattice distortion induced by ionic doping in layered transition metal chalcogenides is elucidated as a key factor in enhancing charge transfer during the Li−S reaction, providing valuable insights for designing advanced cathode materials for next-generation sulfur-based batteries.
Metal Cluster Photocatalysts
Photocatalytic Hydroxylation and Oxidative Coupling Reactions Mediated by Multinuclear Au(I) Supramolecular Clusters
- First Published: 23 December 2024
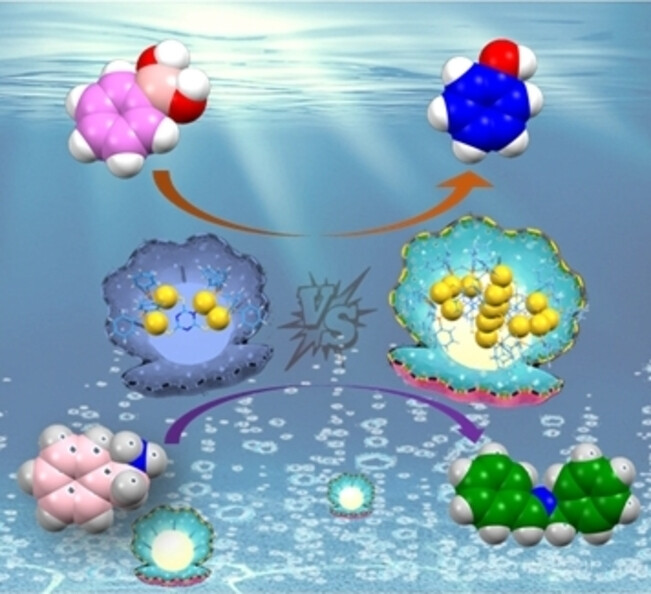
Two high-nuclearity Au(I) cluster photocatalysts (Au4 and Au16) were precisely synthesized using a multicomponent collaborative self-assembly strategy. Both supramolecular clusters demonstrated photocatalytic capabilities for the oxidative hydrolysis of phenylboronic acid and the oxidative coupling of benzylamines under mild conditions, achieving catalytic efficiencies exceeding 90 %. Notably, the photocatalytic efficiency for the oxidation of arylboric acid is currently the highest.
Organic Materials | Very Important Paper
Pressure-Engineered Through-Space Conjugation for Precise Control of Clusteroluminescence
- First Published: 25 November 2024
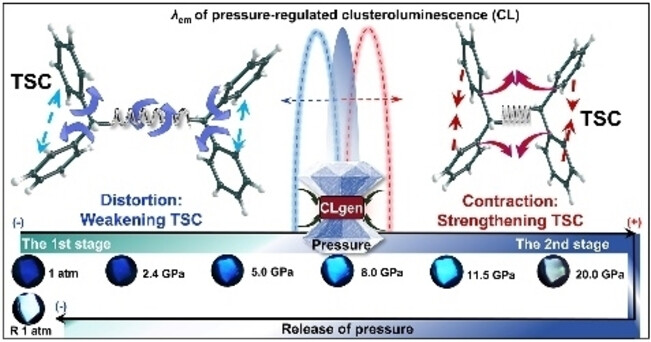
Through-space conjugation in a series of tetraphenylalkanes-based nonconjugated clusteroluminogens is engineered via high-pressure structural regulation. Abnormal blue shift and remarkable emission enhancement are realized, exhibiting distinct structural factors. Intense white-light emission is realized after high-pressure treatment, disrupting the typical excited-state even-odd effects in ambient study.
Sodium-Ion Batteries | Very Important Paper
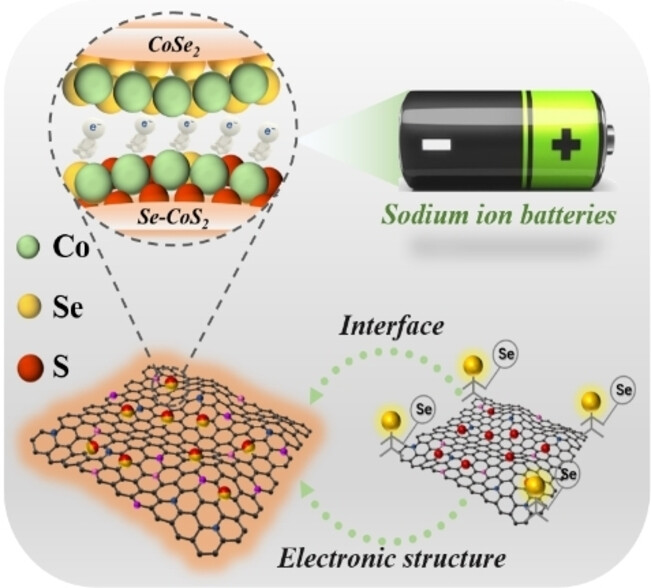
Cascade Selenization Regulated the Electronic Structure and Interface Effect of Transition Metal Sulfides for Enhanced Sodium Storage
- First Published: 30 December 2024
Hybrid Perovskites | Hot Paper
Unlocking Cage-Confined Cations Molecular Dynamics toward High-Tc Perovskite Ferroelectrics
- First Published: 03 December 2024
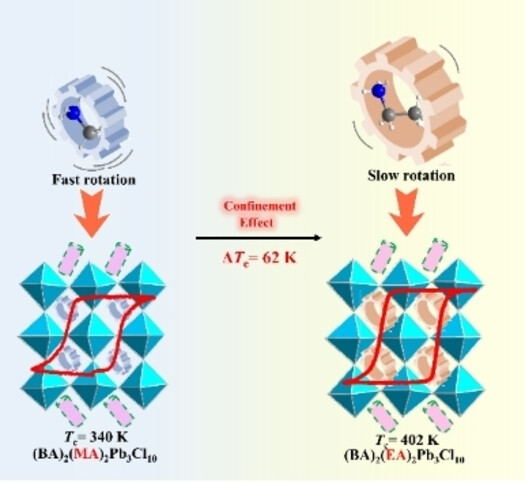
For the first time, the cage-confinement effect is established to exploit new high-Tc ferroelectrics, of which the Tc is dramatically promoted to 402 K (>BaTiO3, 393 K). Further, Deep understanding of cage-confinement effect and high-Tc ferroelectricity is well elaborated by combining in situ solid-state NMR spectroscopy and theoretical calculations on potential energies. This paves a new pathway and makes a breakthrough in the field of molecular ferroelectrics.
Batteries | Very Important Paper
Thiosulfate-Mediated Polysulfide Redox for Energetic Aqueous Battery
- First Published: 27 November 2024
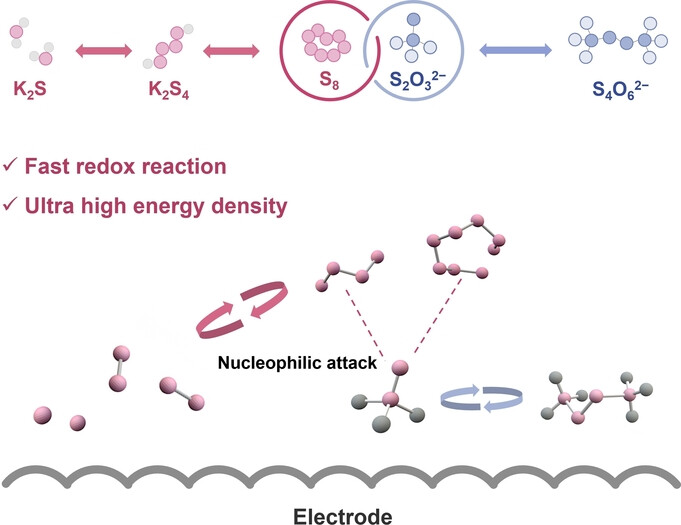
The sluggish redox kinetics of polysulfides significantly impeded the performance of sulfur-based aqueous batteries (SABs). We proposed an effective redox regulation strategy via a thiosulfate-mediated ligand-chain interaction within the K2S2O3 electrolyte, which accelerates the polysulfide redox process (S0/S2−) and provides an additional capacity contribution through the thiosulfate redox pair (S2O32−/S4O62−). The thiosulfate-mediated SAB exhibits an unprecedented K+ storage capacity of 2470 mAh g−1 and a high energy density of 616 Wh kgS+Zn−1, surpassing both organic K–S batteries and conventional aqueous battery systems.
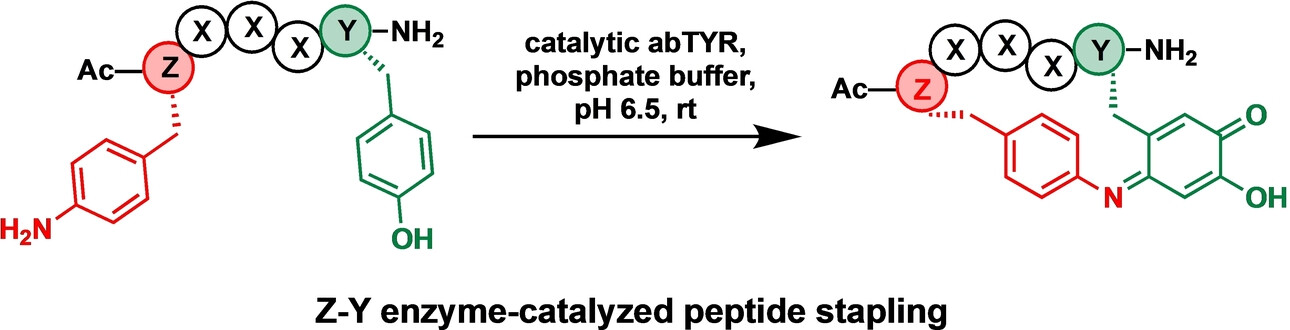
Peptide Stapling
Tyrosinase-Catalyzed Peptide Stapling Using Para-Amino Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Anchoring Residues
- First Published: 07 January 2025
Perovskite Solar Cells | Hot Paper
P-Dopant with Spherical Anion for Stable n-i-p Perovskite Solar Cells
- First Published: 03 January 2025
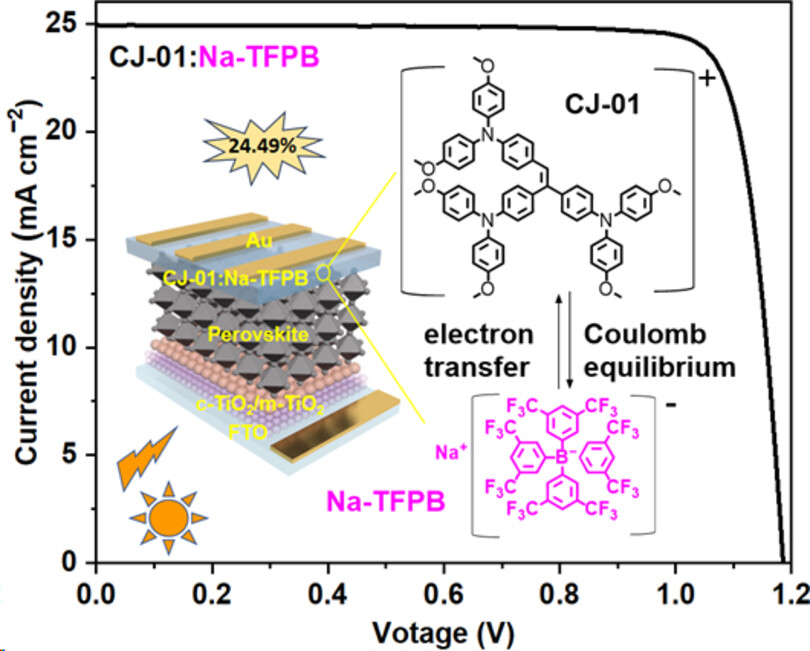
The spherical dopant (Na-TFPB) was developed to improve the stability and efficiency of perovskite solar cells via adjusting various factors such as defect passivation ability and doping effect. The doping uniformity of spherical Na-TFPB is better than that of linear Li-TFSI. The devices fabricated with the shape- and radius-regulated p-dopant achieve remarkable efficiencies of 24.49 % and 24.31 % for CJ-01 and spiro-OMeTAD, respectively, representing the highest efficiency values recorded for organic dopants to date.
Struktur-Reaktivitäts-Beziehungen | Hot Paper
Fluormethyltriflat und Fluormethylfluorsulfonat: Einfach zugängliche und leistungsstarke Fluormethylierungs-Reagenzien
- First Published: 17 December 2024
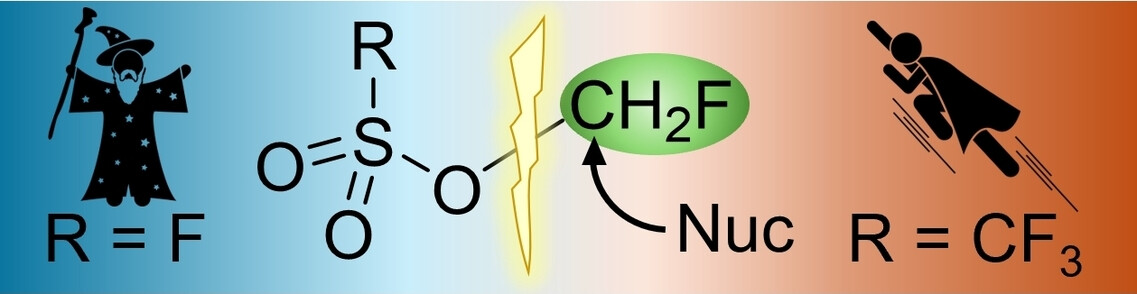
Die vielseitigen Fluormethylierungsreagenzien Fluormethyltriflat (Superfluormethyl, SFM, FH2COSO2CF3) und Fluormethylfluorsulfonat (Magisches Fluormethyl, MFM, FH2COSO2F) wurden einfach zugänglich gemacht. Beide enthalten lange O−CH2F-Bindungen, die für die elektrophile Monofluormethylierungsreaktivität charakteristisch sind, und sind in der Lage, verschiedene Nukleophile auf Chalkogenbasis in kurzen Reaktionszeiten, hohen Ausbeuten und mit einfacher Aufarbeitung zu fluormethylieren.
Lithium-Sulfur Batteries | Hot Paper
Cooperation of Multifunctional Redox Mediator and Separator Modification to Enhance Li-S Batteries Performance under Low Electrolyte/Sulfur Ratios
- First Published: 23 December 2024
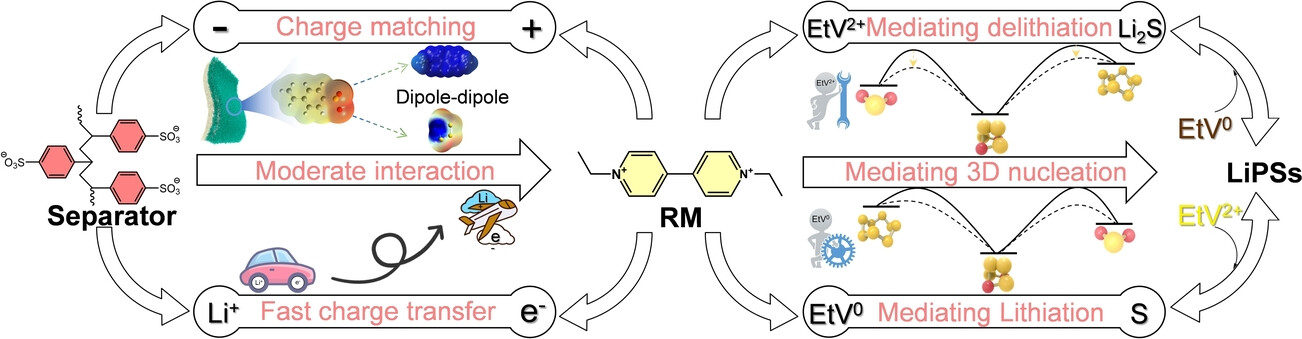
A unique redox mediator (RM) molecule ethyl viologen (EtV2+), owning two well matched redox couples (EtV2+/EtV+, EtV+/EtV0) towards redox chemistry of sulfur species, is demonstrated to function as multifunctional catalysts for reducing S, modulating Li2S nucleation and oxidizing Li2S simultaneously. Its electropositive nature in oxidation state allows the synergetic inhibition of shuttle effect of EtV2+/ EtV+ when coupling with separator modification with electronegative -SO3Li groups and the electrically-charged EtV2+ and LiPSs.
Nanozyme
A Self-Reinforced “Microglia Energy Modulator” for Synergistic Amyloid-β Clearance in Alzheimer's Disease Model
- First Published: 23 December 2024
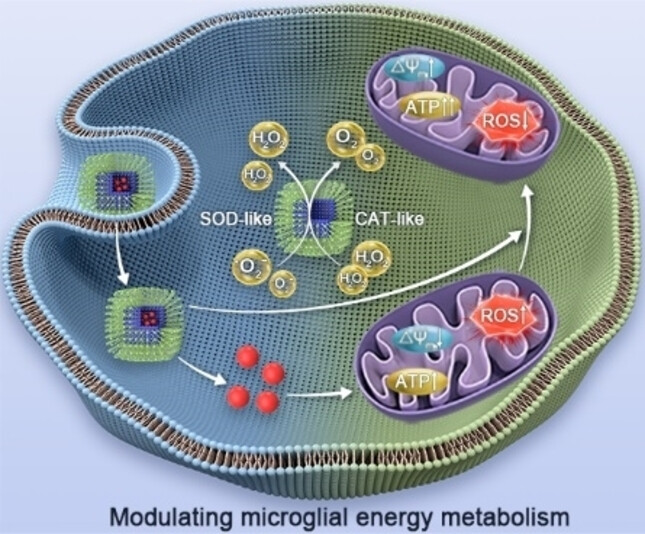
A mutually reinforcing microglia energy modulator is developed by repurposing lonidamine and hollow mesoporous Prussian blue for synergistic clearance of amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease. The modulator improves microglial phagocytic function, decreases amyloid-β deposits, mitigates neuroinflammation, and ameliorates cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease mouse model.
Zuschrift
Nanoclusters | Very Important Paper
Chemical Synthesis of ~1 nm Multilevel Capacitor-like Particles with Atomic Precision
- First Published: 02 December 2024
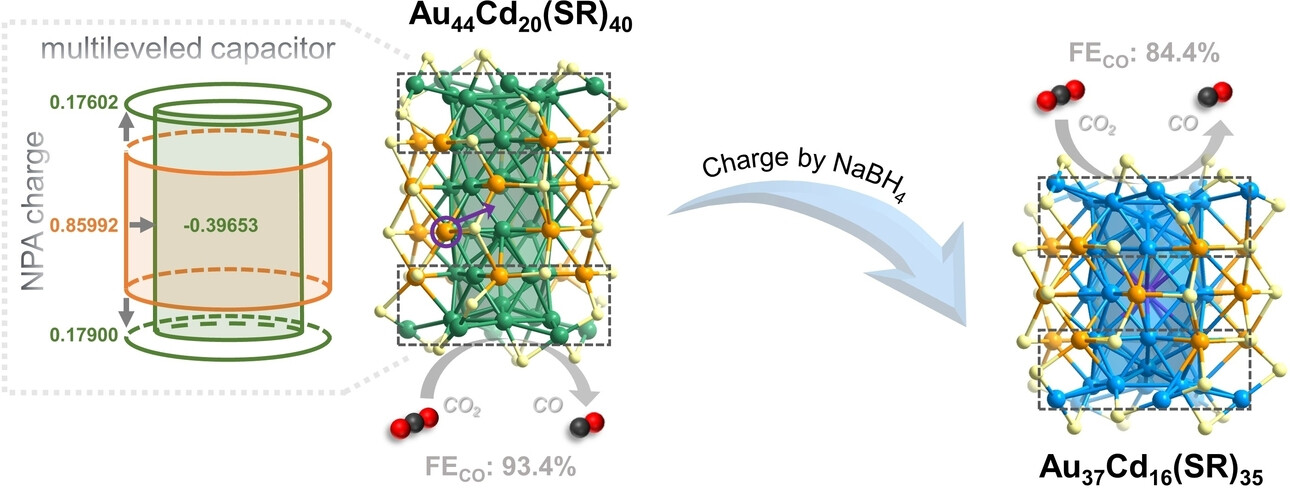
The multilevel capacitor-like character of a novel Au44Cd20 nanoparticle (NP) is identified by NPA charge calculations, charge carrier transport, voltammetry and electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO. Intra-NP anti-galvanic reduction leads to the unanticipated innermost Cd occupation in the cannula-like Au−Cd nanoclusters with Au−Cd segregation.
Photocatalysis
Tuning Co-Operative Energy Transfer in Copper(I) Complexes Using Two-Photon Absorbing Diimine-Based Ligand Sensitizers
- First Published: 18 September 2024
Photochemistry
B,N-Embedded Helical Nanographenes Showing an Ion-Triggered Chiroptical Switching Function
- First Published: 08 January 2025
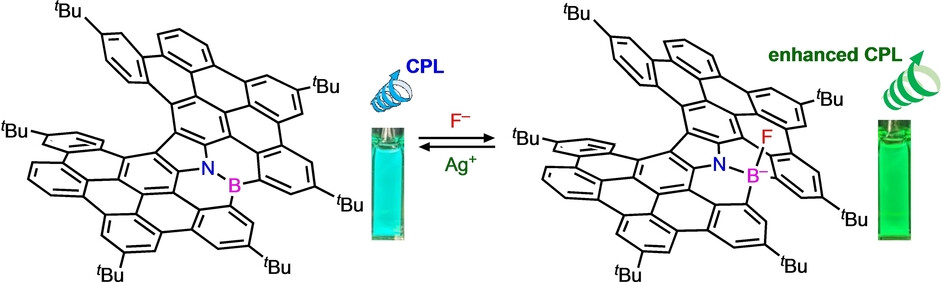
Eight phenyl groups were fused into carbazole to give a novel π-extended azahelicene. Boron incorporation furnished a B,N-embedded helical nanographene showing an ion-triggered chiroptical switch between the three-coordinate boron and four-coordinate boron species with the change in the color and glum values.
Main-Group Chemistry
Observation of the Smallest Three-Dimensional Neutral Boron Cluster
- First Published: 14 January 2025
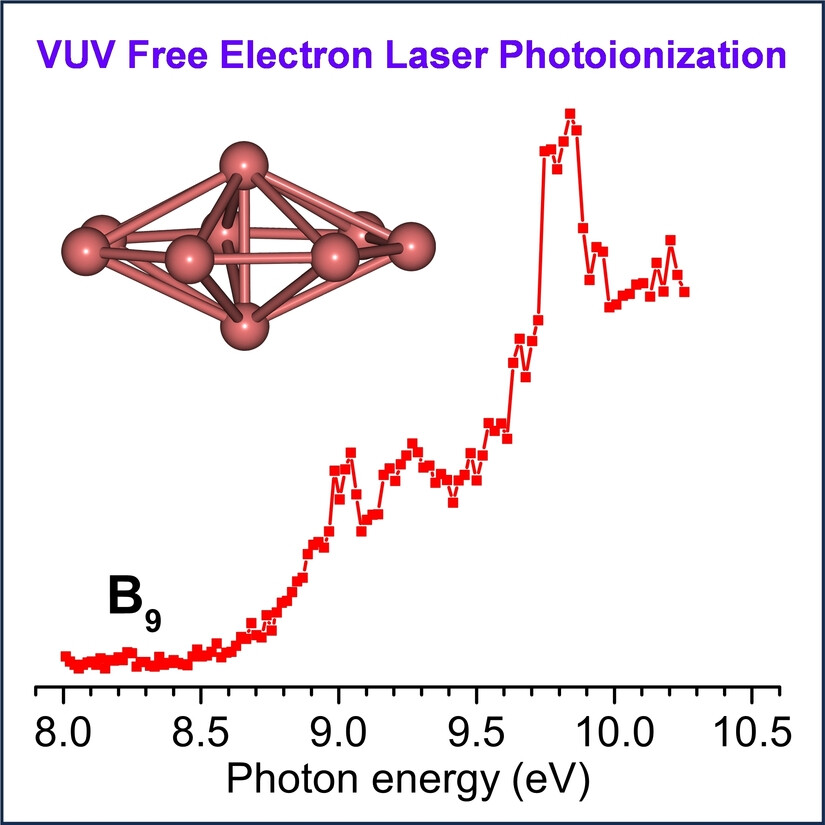
The photoionization efficiency spectrum of B9 was measured by using VUV free electron laser. B9 was characterized to be the smallest 3D neutral boron cluster with a heptagonal bipyramid D7h structure, quite different from the planar molecular wheel of B9-. A single-electron B-B bond between the capping atoms is found to be crucial in stabilizing the D7h structure of B9.
Iridium Catalysis
Remote Hydrogen Bonding between Ligand and Substrate Accelerates C–H Bond Activation and Enables Switchable Site Selectivity
- First Published: 20 January 2025
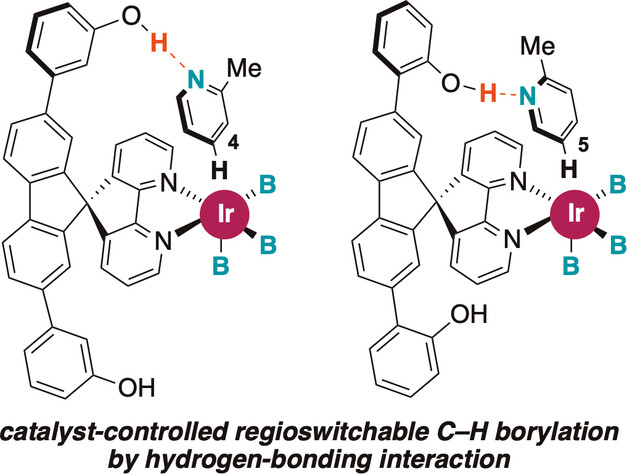
A spirobipyridine ligand bearing a hydroxy group recognizes pyridine and quinoline substrates through hydrogen bonding, and in combination with an iridium catalyst enables C−H borylation with site selectivity that can be switched by changing the position of the hydroxy group on the ligand. The catalyst also accelerates the reaction, overrides steric bias, and selectively recognizes the pyridine substrate in a manner reminiscent of enzyme catalysis.
Ring Expansion | Hot Paper
Accessing Azetidines through Magnesium-Mediated Nitrogen Group Transfer from Iminoiodinane to Donor-Acceptor Cyclopropanes
- First Published: 07 January 2025
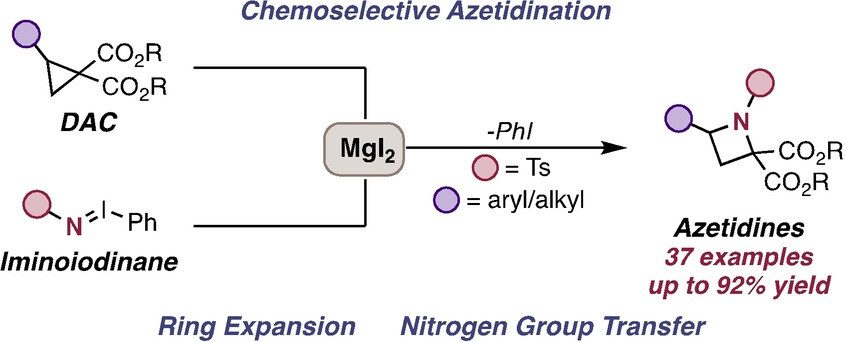
We report a magnesium-mediated ring expansion of donor-acceptor cyclopropanes (DACs) to substituted azetidines via nucleophilic nitrogen group transfer from readily accessible iminoiodinane. Mechanistically, the coordination of a magnesium-Lewis acid to the DAC promotes nucleophilic ring opening with a putative Mg-amide species generated from the iminoiodinane under the reaction conditions to furnish the azetidine products.
Microgels | Very Important Paper
Sprayed Aqueous Microdroplets for Spontaneous Synthesis of Functional Microgels
- First Published: 17 January 2025
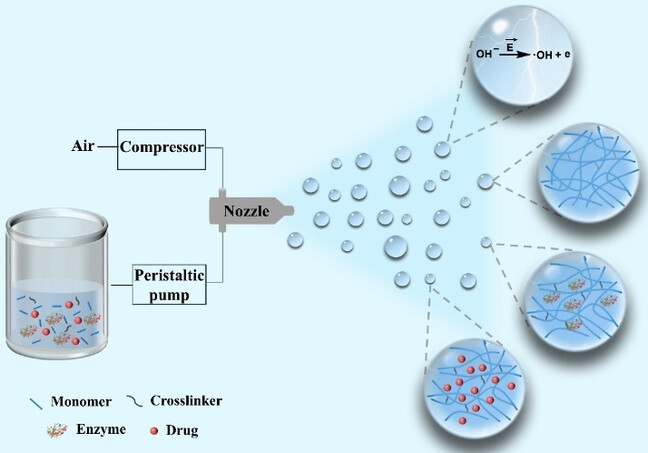
A facile solution spray method is developed for spontaneous synthesis of microgels without confined emulsion, additional initiators/catalysts and deoxygenation. The strategy is applicable to a variety of monomers and enables the synthesis of microgels with tunable chemical structures and variable sizes. Moreover, this strategy allows the in situ encapsulation of biologics into microgels, enabling enzyme catalysis and controlled drug release.
Hydrophosphorylation
Electrifying P(V): Access to Polar and Radical Reactivity
- First Published: 06 January 2025
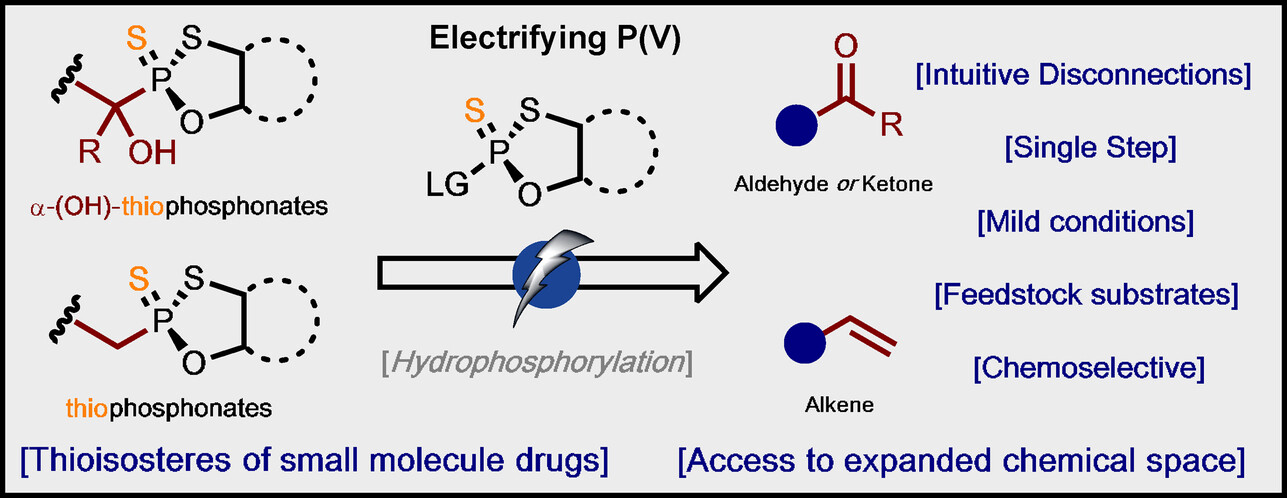
Electrochemical, fully stereoselective P(V)-hydrophosphorylation of olefins and carbonyl compounds using a P(V) reagent is disclosed. By strategically selecting the anode material. Radical reactivity is accessible for alkene hydrophosphorylation, whereas a polar pathway operates for ketone hydrophosphorylation. A comprehensive investigation into the mechanistic intricacies of the chemoselectivity was conducted, providing deeper insight into the underlying reaction pathways and selectivity factors.
Covalent Organic Framework | Very Important Paper
An sp2 Carbon-Conjugated Covalent Organic Framework for Fusing Lipid Droplets and Engineered Macrophage Therapy
- First Published: 15 January 2025
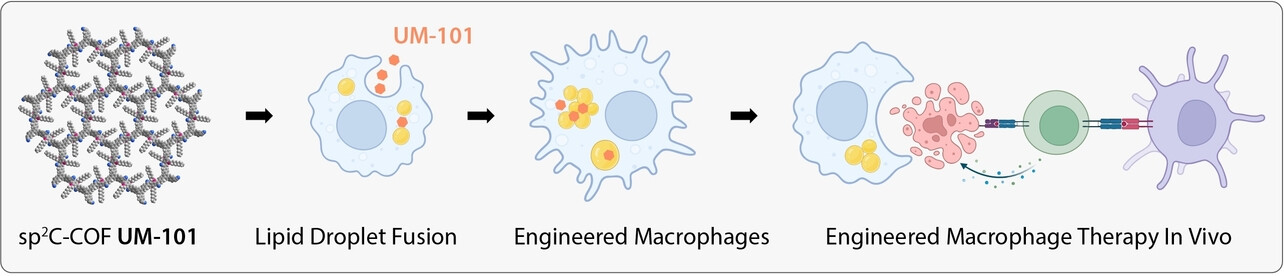
This study presents a “lipid droplet fusion” strategy for engineering macrophages, promoting their antitumor activation. The mildly synthesized sp2C-conjugated covalent organic framework (COF) UM-101 induces lipid droplet fusion and metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. The intravenous injection of UM-101–engineered macrophages effectively inhibited CT26 tumor progression.
Cancer Therapy | Hot Paper
Near-Infrared Light-Triggered Cascade Nanosystems for Spatiotemporally Controlled Gene-Silencing and Gas Synergistic Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 12 December 2024
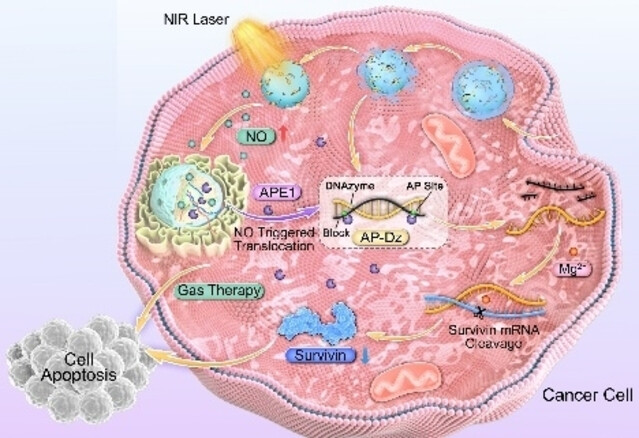
A NIR-triggered cascade effect system is developed to achieve precise spatiotemporal gene silencing and gas-synergistic cancer therapy. This strategy harnesses the power of NIR-induced NO release to orchestrate the relocation of APE1, thereby achieving enhanced efficiency and spatiotemporal controllability of gene silencing.
Organische Elektrosynthese | Hot Paper
Die Elektrochemische Iodierung von Elektronenarmen Aromaten
- First Published: 28 January 2025
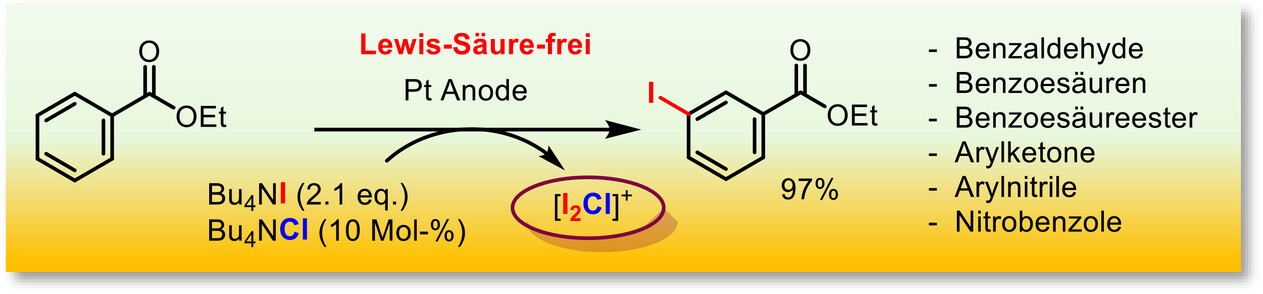
YES WE CAN – die elektrochemische Iodierung von elektronenarmen Aromaten unter Lewis-Säure-freien Bedingungen in einer geteilten Zelle wird durch die Oxidation der Iod-Quelle Bu4NI an der Anode erreicht in Anwesenheit von katalytischen Mengen Bu4NCl um das postulierte Iodierungsreagenz [I2Cl]+ zu erzeugen. Die Iodierung kann auf eine Reihe interessanter halogenierter Aromaten, aromatische Aldehyde, Benzoesäuren, Benzoesäureester, Arylnitrile, Arylketone und Nitrobenzolderivative angewendet werden, um die gewünschten iodierten Produkte zu erhalten.
Catenanes
Highly Selective Construction of Unique Cyclic [4]Catenanes Induced by Multiple Noncovalent Interactions
- First Published: 23 December 2024
![Highly Selective Construction of Unique Cyclic [4]Catenanes Induced by Multiple Noncovalent Interactions](/cms/asset/358fa7ad-45bb-410c-9a97-dba25464496a/ange202422444-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Two unprecedented cyclic [4]catenanes, 1 and 2, were prepared based on the selection of naphthalenediimide (NDI)-based Cp*Rh/Ir building blocks E1/E2 (Cp*=pentamethylcyclopentadienyl) and diimidazole ligand L1. 1, exhibiting a broad-band absorption in UV/Vis to NIR regions and a remarkable photothermal conversion was used to build new 1 membrane. The solar power-induced water steam generation performance of 1 membrane could reach a value of 2.37 kg ⋅ m−2 ⋅ h−1.
Chemical Biology
Click-and-Release Formation of Urea Bonds in Living Cells Enabled by Micelle Nanoreactors
- First Published: 23 December 2024
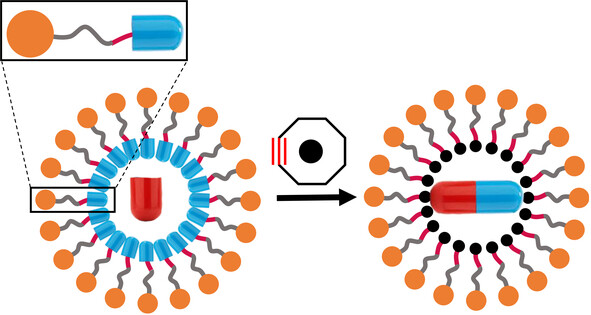
Behind bioorthogonal chemistry: micelles constructed with amphiphiles bearing bioorthogonal reactants allowed non-bioorthogonal chemistry in a confined environment. Application of this strategy was made with the synthesis of an FDA-approved anticancer drug inside living cells. Apart from this application, this strategy could represent a change of paradigm, allowing an extension of the concept of bioorthogonal chemistry.
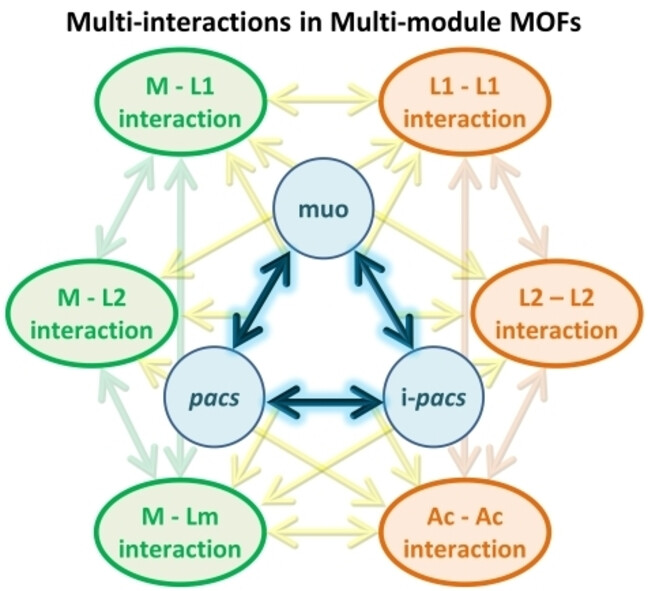
MOFs | Hot Paper
Isoreticular Tolerance and Phase Selection in the Synthesis of Multi-Module Metal–Organic Frameworks for Gas Separation and Electrocatalytic OER
- First Published: 20 January 2025
Biocatalysis | Hot Paper
Artificial Metalloenzymes with Two Catalytic Cofactors for Tandem Abiotic Transformations
- First Published: 06 January 2025
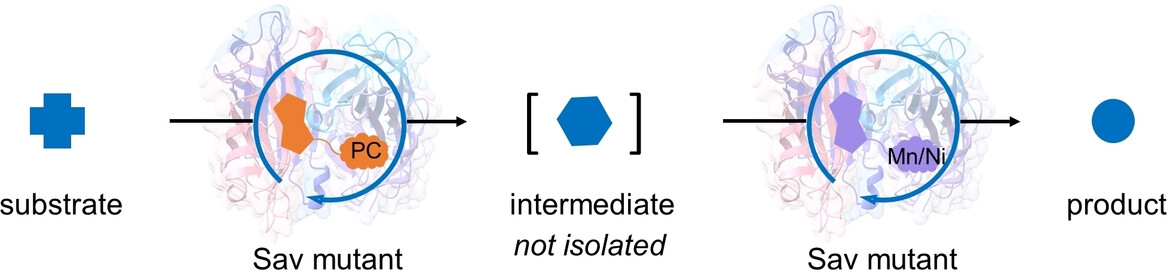
Sequential incorporation of an organic photocatalytic cofactor and a metal cofactor into streptavidin leads to artificial metalloenzymes (ArMs) that catalyze tandem abiotic transformations such as enantioselective formal C−H hydroxylation and photooxidation-Michael addition. This work introduces a programmable approach for the construction of ArMs that can catalyze tandem abiotic reactions.
Ammonia Synthesis | Hot Paper
Photo-Driven Ammonia Synthesis via a Proton-Mediated Photoelectrochemical Device
- First Published: 07 January 2025
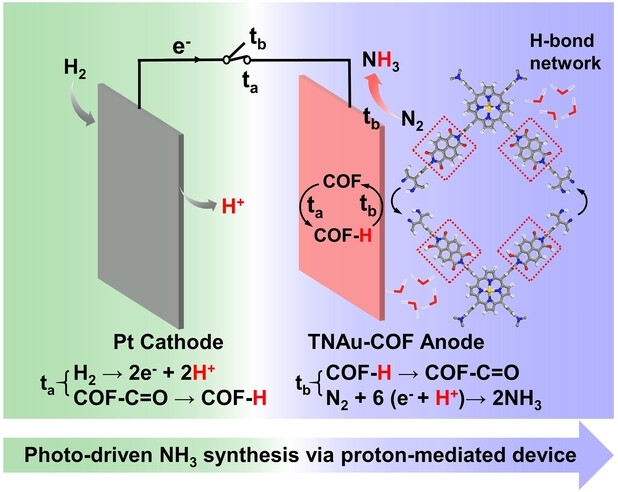
A strategy of photo-driven N2 reduction to NH3 via a proton-mediated photoelecrochemical device is proposed and achieved. This strategy with a two-electrode cell system uses a covalent organic framework (COF) anode with Au single-atom catalytic sites and −OH redox functions, which enables protons to be stored and transferred to catalytic sites. It achieved proton promoted N2 reduction reaction and the ammonia synthesis.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Synthesis of γ-Amino Amides by Iridium-Catalyzed Enantioselective Hydroamination of Internal Alkenes Directed by an Amide
- First Published: 16 December 2024
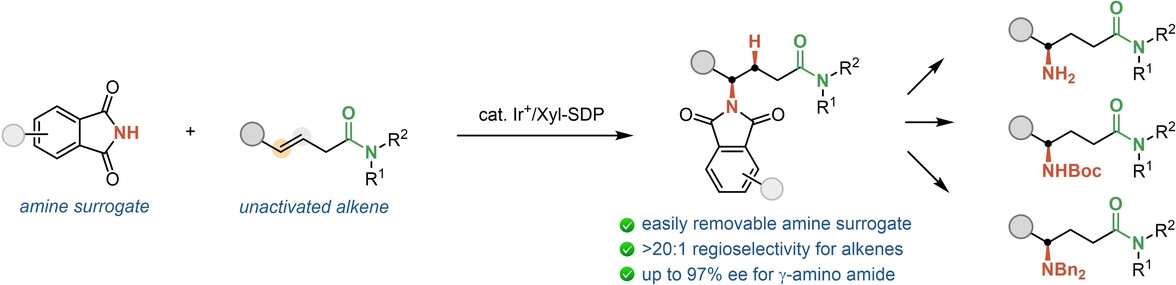
Unactivated internal alkenes were found to undergo enantioselective hydroamination catalyzed by a cationic iridium complex. An amide group effectively directs the catalyst to control the regioselectivity to over 20 : 1 and the enantioselectivity to up to 97 % ee. This coordination assistance enables hydroamination to occur selectively at the remote position, delivering valuable enantioenriched γ-amino acid derivatives that are otherwise challenging to access.
Polyoxometalate
A Highly Biocompatible Polyoxotungstate with Fenton-like Reaction Activity for Potent Chemodynamic Therapy of Tumors
- First Published: 16 December 2024
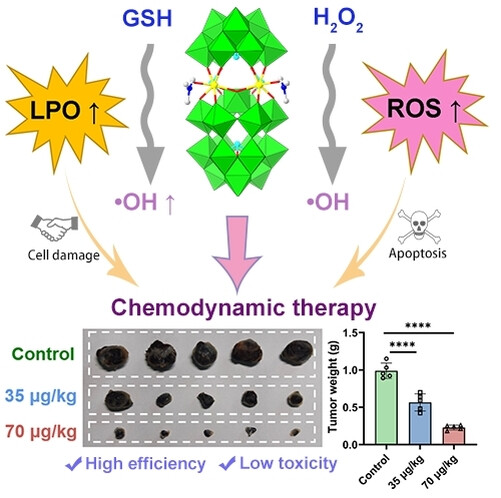
A new polyoxotungstate has been made and found to show excellent solubility, stability, and biocompatibility in aqueous solutions and physiological conditions. Remarkably, it can catalyze the decomposition of H2O2 to generate toxic hydroxyl radicals, and thus exhibit high cytotoxicity and selectivity towards B16-F10 mouse melanoma cancer cells. Moreover, it exhibits excellent antitumor efficacy with good biosafety against melanoma growth in vivo. This makes it a promising candidate as a cancer chemodynamic therapy agent
Foldamere
DNA-Mimikry-Foldamer-Erkennung eines chromosomalen Proteins
- First Published: 23 December 2024
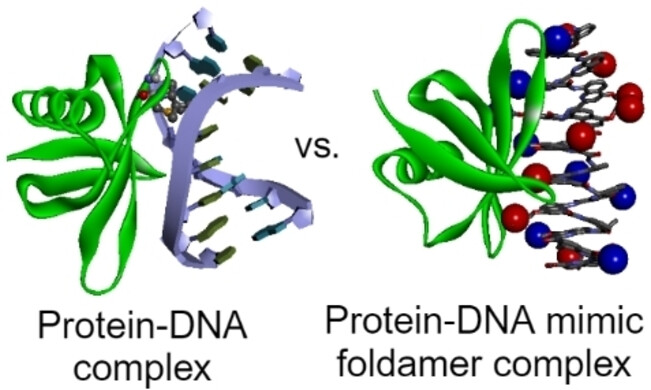
Biomolekulare Mimikry sollen ihre natürlichen Gegenstücke übertreffen. Die Nachahmung von B-DNA-Oberflächen, die auf DNA-bindende Proteine abzielen, ist jedoch lange Zeit unterentwickelt geblieben. Wir haben helikale aromatische Foldamere eingeführt, die die Form und Ladungsverteilung von B-DNA nachahmen und an einige DNA-bindende Proteine besser binden als die DNA selbst. Am Beispiel des chromosomalen Proteins Sac7d geben wir nun die ersten strukturellen Einblicke in die Wechselwirkungen zwischen DNA-Mimikry-Foldameren und Proteinen.
NLO Materials
Unprecedented Deep Ultraviolet (DUV) Birefringence in Fluorides Constructed from Linear π-Group Anisotropic Structure Building Units
- First Published: 23 December 2024
Cascade Reactions
Hydrogen-Borrowing-Based Methods for the Construction of Quaternary Stereocentres
- First Published: 09 January 2025
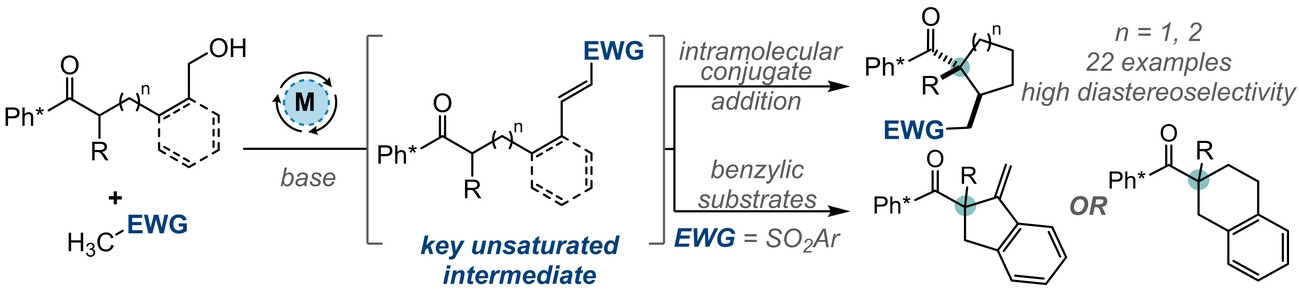
Use of the hydrogen borrowing manifold to access α-quaternary ketones through a tandem acceptorless dehydrogenation-cyclisation cascade is presented. This new application of the methodology results in the formation of five- and six-membered carbocycles with a high degree of diastereoselectivity. Interestingly, benzylic alcohol substrates behaved anomalously and eliminated sulfinate in situ to give a set of rearranged α-quaternary ketone products.
Copper Catalysis | Hot Paper
Building Three-Dimensional Complexity by Intramolecular 2-Aminoallyl Cation−Diene (4+3) Cycloaddition
- First Published: 14 January 2025
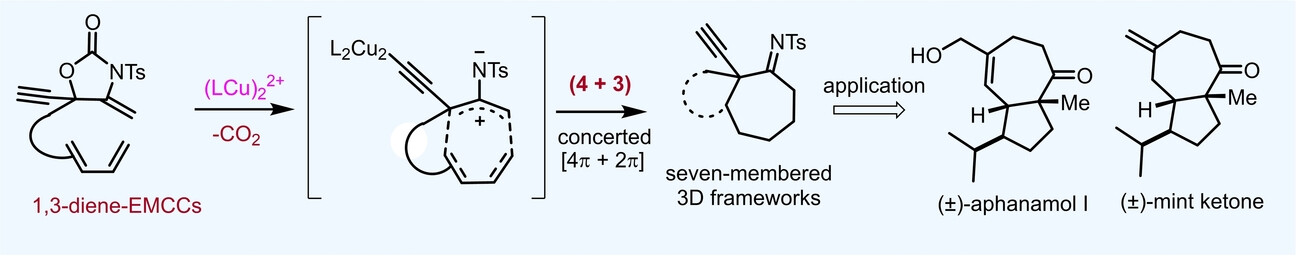
A copper-catalyzed intramolecular [4π+2π] cycloaddition of 2-aminoallyl cations with 1,3-dienes was achieved. This transformation utilized various 1,3-diene-tethered ethynyl methylene cyclic carbamates (1,3-diene-EMCCs) as substrates, providing rapid access to diverse seven-membered 3D frameworks. By employing this cycloaddition as a key step, the total synthesis of (±)-aphanamol I and (±)-mint ketone was demonstrated.
Photoelectrochemical Devices
Hybrid CIGS-Cobalt Quaterpyridine Photocathode with Backside Illumination: A New Paradigm for Solar Fuel Production
- First Published: 31 December 2024
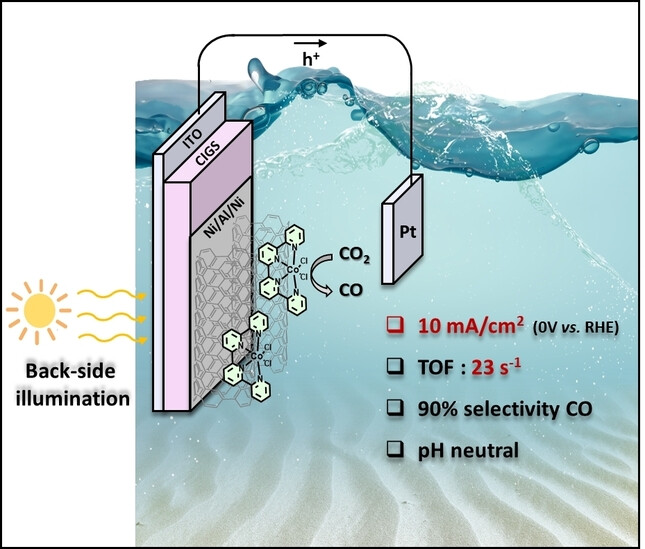
An efficient and selective solar-driven conversion of CO2 to CO has been achieved using a Cu(In,Ga)S2 chalcopyrite-based photocathode, coated with a cobalt molecular catalyst and operated under backside illumination. This innovative design addresses the challenges associated with the absorption properties of the catalyst and the protection layer, paving the way for high-performance and versatile photoelectrochemical (PEC) devices.
Sustainable 3D Printing
Reprocessable and Recyclable Materials for 3D Printing via Reversible Thia-Michael Reactions
- First Published: 20 January 2025
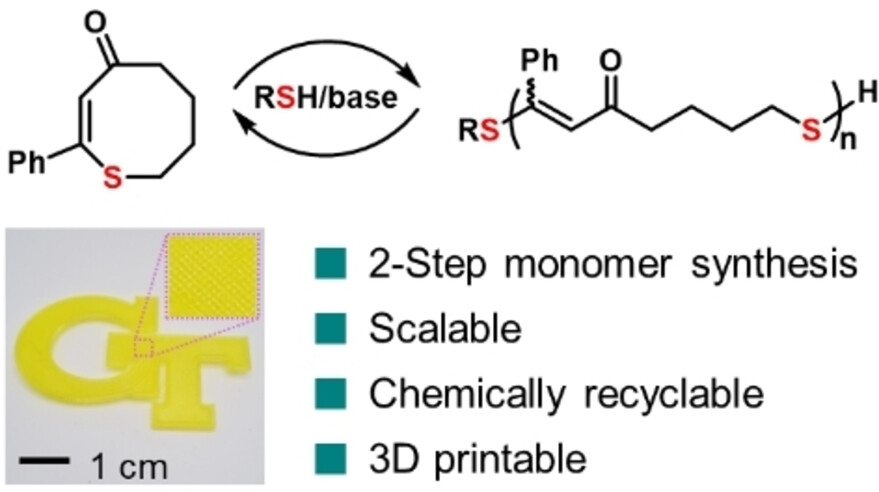
A 3D printing material platform based on polythioenones (PCTE) is introduced. The thioenone monomers are synthesized in a scalable two-step process and are readily amenable to diversification. PCTE−Ph exhibits excellent tensile strength, machinability, and recyclability, achieving 90 % depolymerization yield in a closed-loop polymerization/depolymerization cycle. Its performance in fused-filament fabrication (FFF) highlights its potential for advanced additive manufacturing.