Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Issue Information
Review Article
Synergistic Acceleration of Adsorbent Material Development by DFT and ML for CO2 Capture
- First Published: 09 June 2025
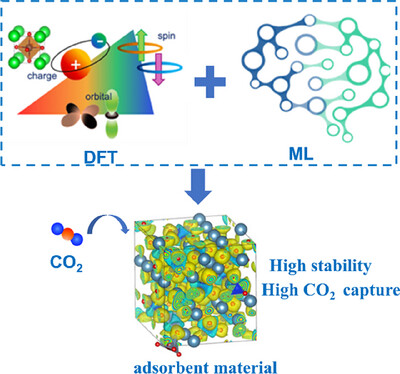
Addressing climate change necessitates the rapid discovery of efficient CO2 adsorbents. This review examines the synergistic integration of density functional theory (DFT) and machine learning (ML), emphasizing how their combination accelerates the design, screening, and optimization of solid amine, metalorganic framework (MOF), and calcium-based adsorbents.
Research Article
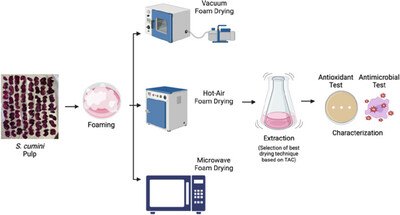
Effect of Foam Mat Drying on Extraction of Anthocyanins from Syzygium cumini (Jamun)
- First Published: 06 December 2024
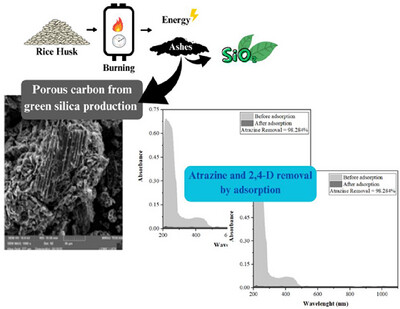
Pesticides Adsorption by a Sustainable Porous Carbon: Modeling and River Water Decontamination
- First Published: 04 May 2025
Improving the Efficiency of a Bioreactor Equipped With Mixed-Flow Impellers
- First Published: 04 May 2025

The present work investigated the biological performance of mixed-flow impellers. To the authors’ knowledge, this is the first experimental study on such impellers in a fermentation process using A. vinelandii, which was chosen as a microorganism due to its high oxygen demand. Results showed that the mixed-flow impellers performed better in high-viscosity media than the Rushton turbines.
Numerical Investigation of Liquid Jet Breakup in Rotary Atomizer
- First Published: 29 May 2025
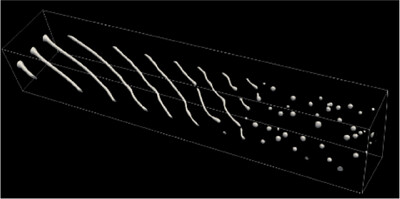
This study presents a numerical analysis of liquid jet breakup in rotary atomization. By comparing different boundary conditions and focusing on gas–liquid interactions, the simulation reveals nonlinear instabilities that govern droplet formation. The findings offer insights into breakup behavior beyond the scope of conventional linear theories.
Superhydrophobicity of PTFE-HFM with PDMS/Nano-SiO2 Composite Coating Used in Waste Oil Purification
- First Published: 28 May 2025
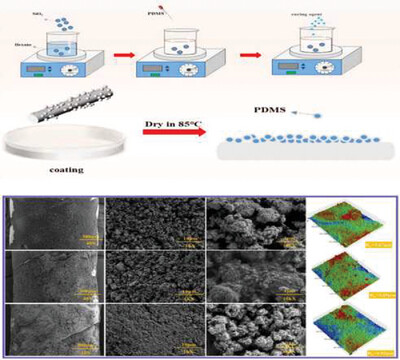
This study presented a superhydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene hollow fiber membrane (PTFE-HFM) modified with a PDMS/nano-SiO2 composite coating for high-temperature waste oil purification. By integrating interfacial engineering and thermal stabilization, the membrane achieved tunable hydrophobicity (water contact angle up to 158°) and hierarchical roughness via controlled SiO2 loading. At 2 wt.% SiO2, the optimized membrane exhibited exceptional performance: superior high-temperature permeation flux (162.38 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1 at 150 °C), and remarkable anti-fouling stability (flux attenuation reduced to 7.35 % over 200 h). The synergistic PDMS/SiO2 coating enhanced mechanical robustness while maintaining structural integrity under dynamic conditions. The membrane demonstrated efficient separation of water-in-oil emulsions (96.78 % rejection) and sustained operational stability in high-temperature environments, offering a promising solution for industrial oily wastewater treatment.
Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Cymbopogon citratus (lemon grass) Leaf Extract for Antibacterial and Antidiabetic Activity
- First Published: 08 June 2025
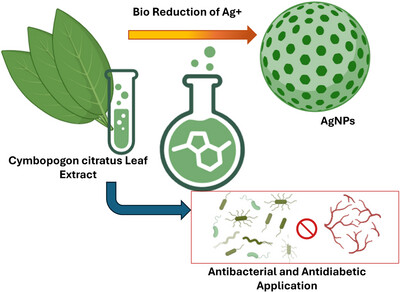
This study reports the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Cymbopogon citratus (lemon grass) leaf extract. The bio-reduction of Ag⁺ ions was visually confirmed by a color change from light yellow to dark brown and characterized by a distinct surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak at 447 nm. Various analytical techniques, including FTIR, XRD, SEM, and TEM, confirmed the formation of crystalline, spherical nanoparticles with an average size of 26 nm. The biosynthesized AgNPs exhibited significant antibacterial activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as dose-dependent inhibition of α-amylase enzyme, indicating antidiabetic potential. This eco-friendly synthesis approach supports future applications of AgNPs in antimicrobial and therapeutic domains.
Entropy Analysis of Al2O3–TiO2/H2O Hybrid Nanofluid Flow over an Exponential Stretching Sheet with Thermal Dissipation and Chemical Reactions
- First Published: 08 June 2025
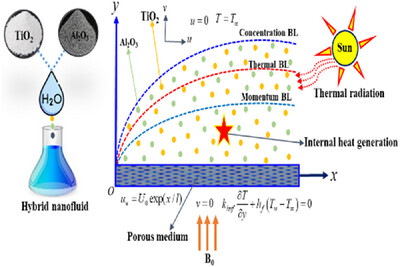
This study presents valuable perspectives that can be applied to various sectors, ranging from thermal engineering to nanotechnology and fluid dynamics. The practical implications of these perspectives can enhance HT processes in industries like nuclear power generation, aerospace technology, microfluidics, and manufacturing. Moreover, integrating dissipation and radiative impacts into HNF flow models introduces a fresh outlook on comprehending HT mechanisms, opening doors for progress in related research areas.
Ag–Fe3O4 Nanofluids via Ultrasound-Assisted Minireactor for Enhanced Heat Transfer in Pinched Pipe
- First Published: 08 June 2025
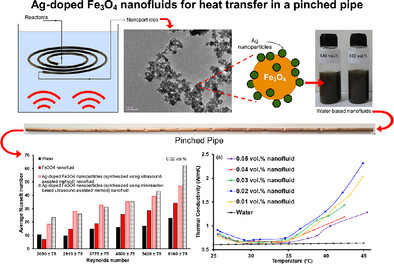
The incorporation of Ag-doped Fe3O4 nanofluids leads to a marked enhancement in heat transfer performance within compact thermal systems. This work offers insights into how nanoparticle design and synthesis routes can be strategically used to unlock new levels of efficiency in convective heat exchange in enhanced tubes.
Experimental and Speciation Analysis of Biphasic TETA/TMEDA Blend for CO2 Capture
- First Published: 09 June 2025

This study presents a novel biphasic aqueous solvent system using TETA and TMEDA for energy-efficient post-combustion CO2 capture. The optimized blend achieved 22% lower regeneration energy and 62% higher cyclic capacity than MEA, with stable performance over multiple cycles and rapid phase separation.
Pore Diffusion in the Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Limitation or Advantage in Multi-Tubular Reactors?
- First Published: 08 June 2025
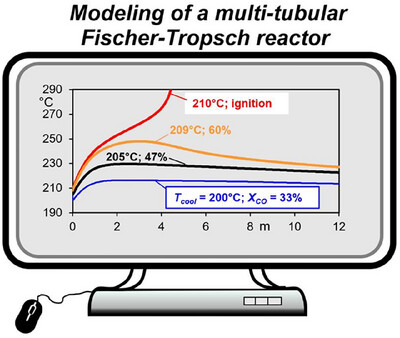
Pore diffusion limitations in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis are typically seen as detrimental due to lower reaction rates. This study shows that they reduce thermal sensitivity and increase reactor stability. A 2D model demonstrates how these limitations enable higher conversions in multi-tubular reactors—turning a drawback into a process advantage.
Cannabigerol Extraction from a Cannabis Cultivar Using a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Process
- First Published: 08 June 2025
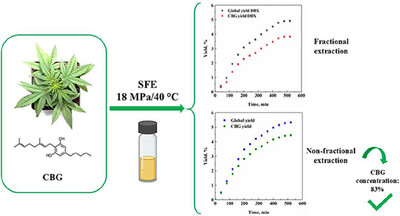
The aim of this work was to assess for the first time the supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) process feasibility to obtain a CBG-rich extract from Cannabis. Extraction experiments highlighted that CBG can be properly extracted at 18 MPa and 40 °C and the extraction plant scheme affected CBG recovery and purity.
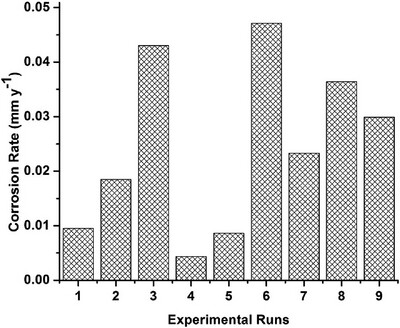
Copper Corrosion in Blended Diesel-Biodiesel: Corrosion Rate Evaluation and Characterization
- First Published: 12 June 2025
Co-Pyrolysis of Calophyllum inophyllum Seeds and Polypropylene: Thermokinetics and Batch Studies
- First Published: 09 June 2025
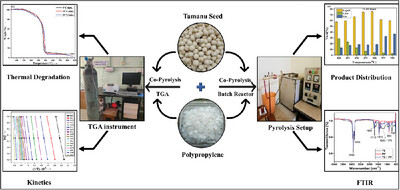
This study explores co-pyrolysis of Tamanu seed (TS) and waste polypropylene (PP) from saline bottles for sustainable energy. Process optimization, product characterization, kinetic modeling (isoconversional and model-fitting methods), thermodynamic analysis, and reaction mechanism evaluation were performed. Synergistic effects improved degradation behavior, oil yield, quality, and composition.
Resolution of Double Salts via Crystallization-Induced Diastereomeric Transformation (CIDT)
- First Published: 09 June 2025
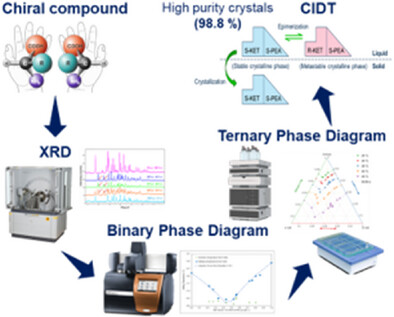
Crystallization-induced diastereomeric transformation (CIDT) was used to separate (S)-ketoprofen-(S)-phenylethylamine salts with high purity. A mixed solvent system and phase diagrams guided the process, while DBU emerged as the best catalyst. The study shows how CIDT, aided by DBU's dual role, offers a method for enantioseparation in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Multi-Slip Effect on the Radiative Micropolar Williamson Hybrid Nanofluid Flow on a Rotating Frame
- First Published: 28 June 2025
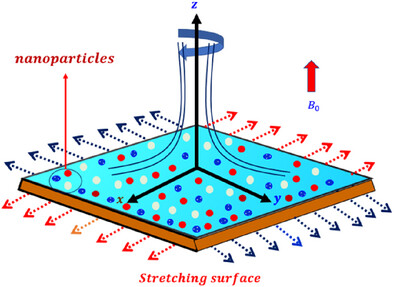
This study examines multiple-slip effects in a micropolar Williamson hybrid nanofluid influenced by an exponential heat source and inertial drag within a rotating porous medium. By including thermal radiation and medium permeability, the model accounts for velocity and thermal slip and is solved numerically using the Runge–Kutta method.
A Reference Material for Bulk Solid Investigations
- First Published: 28 June 2025
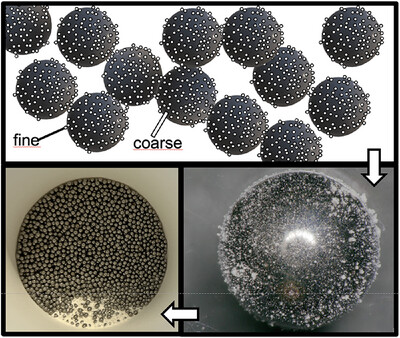
This article deals with the invention of a reference material representing a bulk material with its main parts, the fine and the coarse fraction. The idea is to use this material to support and improve further research dealing with the prediction of dust emissions when handling coarsely dispersed bulk materials.
Numerical Simulation on Gas–Solid Flow Characteristics in Circulating Fluidized Bed Desulfurization Tower
- First Published: 28 June 2025
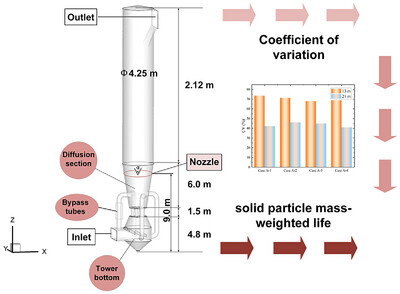
CFD analyzes gas-solid flow characteristics in CFB-FGD towers affected by key components including bottom design, diffusion section, and bypass tubes. Two indices (CV value, particle mass-weighted life) evaluate distribution uniformity and residence time. Findings reveal optimization pathways for enhanced flue gas distribution and desulfurization efficiency, offering crucial design insights.
How Real-Life Vibration and Variable Flow Affects Filtration Efficiency in Automotive Applications
- First Published: 28 June 2025
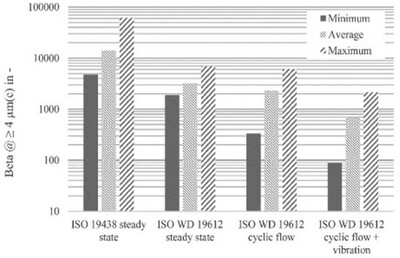
Fuel filters are necessary to prevent damage of the fuel injection system caused by particles and water. To take real operational conditions into the test labs the ISO 19612 is currently in work. The article provides insights of the filtration performance when simulating real-life fuel flow and vibration, highlighting the most dominant influencing parameters.
Production of Fine Crystalline Particles Using Vapor–Aeration Method in Anti-Solvent Crystallization
- First Published: 28 June 2025
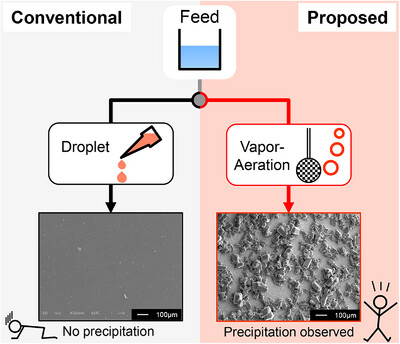
This study proposes a vapor–aeration (V–A) method to produce fine crystalline particles with a narrow size distribution. The V–A method successfully induced nucleation even under low supersaturation conditions where nucleation was not observed using the conventional method. Furthermore, it produced fine particles with improved size distribution due to its nucleation enhancement.
Perfluoro(butylcyclohexane)–Cis-Perfluorodecalin Mixture Separation by Heteroazeotropic Distillation
- First Published: 30 June 2025
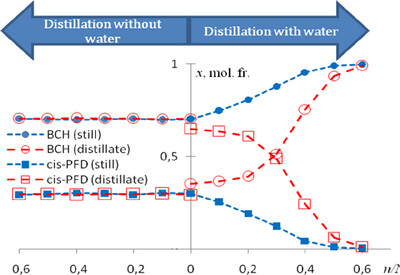
A new method for separating perfluorodecalin – perfluoro(butylcyclohexane) mixture by heteroazeotropic distillation is proposed. Water is used as a heteroazeotrope-forming agent. This approach allows the isolation of perfluoro(butylcyclohexane) with a purity of more than 0.99 mol.fr. The efficiency of this method is experimentally demonstrated on laboratory and semi-industrial scales.
Continuous Trichloroethylene Removal in Internally Recirculating Fluidized Bed of Activated Carbon
- First Published: 30 June 2025
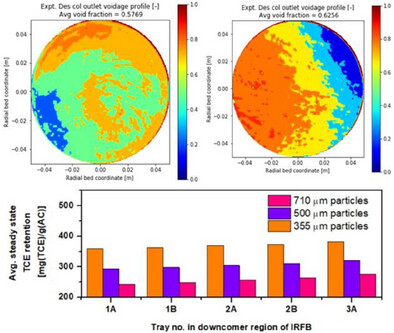
This work integrates moving bed adsorption and fluidized bed desorption processes in one chemical engineering equipment by using internally recirculating fluidized bed (IRFB) technology. The in-house-developed IRFB prototype uses activated carbon as an adsorbent to continuously remove trichloroethylene (known to be mutagenic and a suspected carcinogen) from gaseous streams.
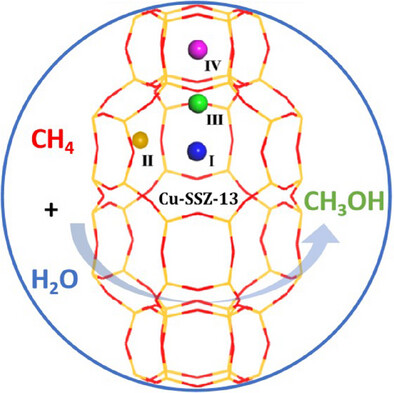
Optimization of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite for Selective Oxidation of Methane to Methanol
- First Published: 30 June 2025
The Impact of Partial Cake Reslurrying on Displacement Washing
- First Published: 30 June 2025
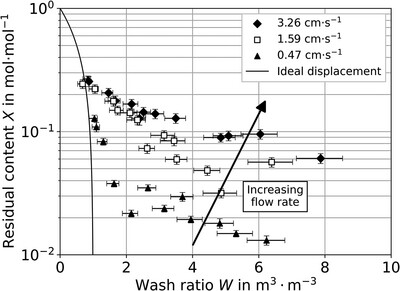
Displacement washing improves product quality by removing contaminants from filter cakes, but its efficiency is limited by partial reslurrying of the cake surface, which unintentionally contaminates the wash liquid. This study presents experimental wash curves demonstrating this previously undescribed limitation and introduces the cake reslurry ratio φ to quantify its impact. Process parameters influencing washing outcomes are evaluated, leading to recommendations for optimizing displacement washing.
Copper Oxide Nanoparticles: Characterization, Photocatalysis, and Biomedical Applications
- First Published: 30 June 2025
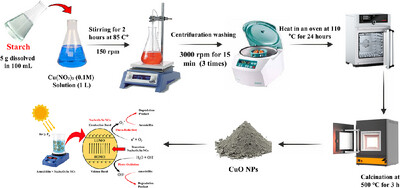
Discover a sustainable approach to synthesizing copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO NPs) using potato starch as a green reducing and stabilizing agent. This method yields CuO NPs with a 13.92 nm crystallite size, flake-like structures, and a 2.95 eV bandgap, showcasing enhanced photocatalytic and antimicrobial properties. Achieving 99.2 % degradation of Evans Blue dye in 140 min and complete atrazine removal in 160 min, alongside significant inhibition zones (up to 26 mm for bacteria, 14 mm for fungi), these NPs offer a promising, eco-friendly solution for environmental cleanup and antimicrobial applications.
Review Article
Direct Membrane Filtration of MWW: Membrane Module, Fouling Control, and Anaerobic Treatability
- First Published: 30 June 2025
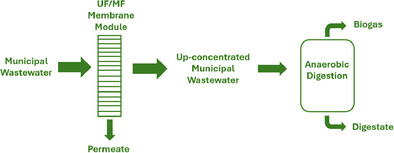
This review article discusses the role of Direct Membrane Filtration (DMF) in up-concentrating municipal wastewater (MWW). DMF is a promising alternative to the conventional aerobic wastewater treatment processes, wherein we can recover energy from MWW. Different membrane module configurations and fouling control strategies are also discussed. Finally, the possibility of treating the up-concentrated wastewater anaerobically is also presented.
Research Article
LaCoxMn1−xO3 Perovskite Oxide: Its Synthesis and Catalytic Application in Thermal Study of AP
- First Published: 01 July 2025
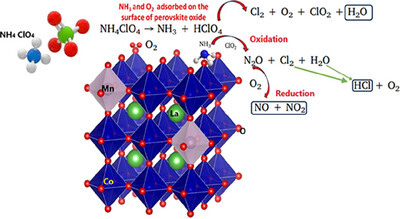
At low temperature, Ammonium perchlorate undergoes decomposition and forms ammonium ion and perchlorate ion. Then proton transfer takes place to form NH3 molecules which are adsorbed on the surface of AP to inhibit the further decomposition process. Catalyst provide the necessary surface area to the NH3 molecules and relieve AP free to decompose further.
Elucidation of Droplet Formation Mechanisms by Vibrating Mesh Atomizers
- First Published: 03 July 2025
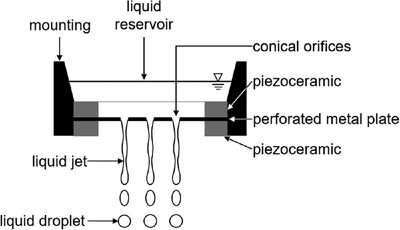
The knowledge about the functionality of atomizers is of fundamental importance for their application. In case of the metal mesh atomizers, the operating principle is highly discussed. This study examines the dependencies, such as volume flow rate, droplet size distribution, and efficiency, on the operating conditions of this type of atomizer and shows the related droplet formation mechanism.
Reactor Modeling to Evaluate the Effect of Reactions Mass Balances on Sulfur Removal in Gasoil HDT
- First Published: 08 July 2025
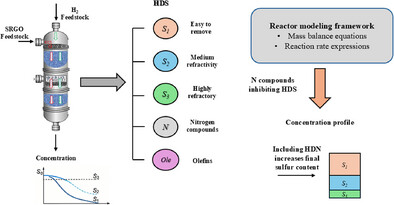
Understanding how each mass balance equation affects the sulfur removal is relevant for proper simulation of HDT reactor. This study uses reactor modeling to assess the individual and combined effects of HDT reaction mass balances on HDS performance, offering insights into inhibition phenomena and hydrogen consumption critical for ULSD production.
Review Article
Research Article
Improving the Physical and Chemical Specification of Diesel Fuel Using Solvent Extraction Technology
- First Published: 08 July 2025
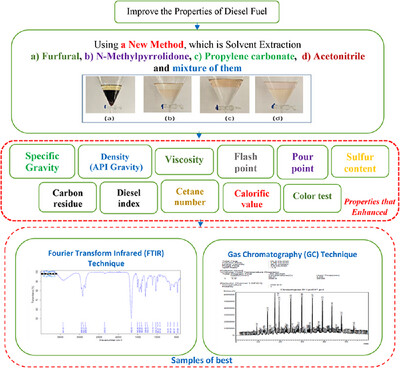
This study present a new structured methodology for improving diesel fuel properties through solvent extraction. Diesel fuel is analyzed using an experimental approach, including solvent selection, extraction, phase separation, and characterization. Optimizing extraction conditions and evaluating fuel quality using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) and Gas Chromatography (GC) techniques.Serves as a guide for systematically designing and executing research on fuel enhancement, the results demonstrating solvent extraction as a viable method for refining diesel fuel properties.
Adsorption and Enrichment of Ag(I) from Wastewater Using Wheat Bran-Derived Biosorbent
- First Published: 08 July 2025
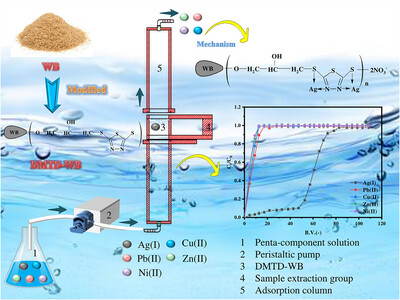
This study develops a novel and reusable wheat-bran-derived adsorbent (DMTD-WB), exhibiting outstanding selectivity and a high removal efficiency of 98.15 % for Ag(I) from a mixed Ag(I)–Cu(II)–Pb(II)–Zn(II)–Ni(II) effluent. The findings provide a sustainable strategy for the simultaneous recovery of silver and the valorization of agricultural waste in environmental remediation.
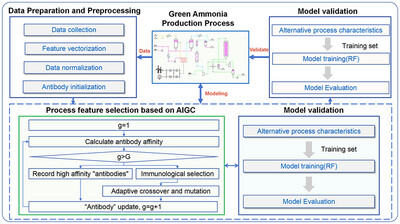
Adaptive Feature Selection and Random Forest Modeling for Green Ammonia Production Process
- First Published: 08 July 2025
Short Communication
Impact of Heating Modes on Thermochemical Behavior of Wood Pyrolysis Process
- First Published: 08 July 2025
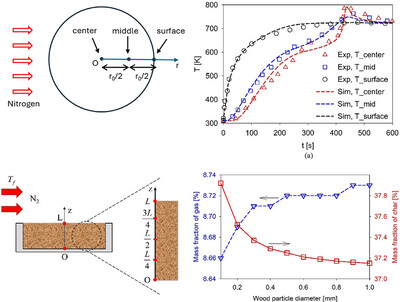
Impact of conductive heating on the thick layer of sawdust pyrolisis is investigated. The conductive heating from the substrate tray accelerates pyrolysis and increases tar and gas yields, whereas a perfectly insulated substrate tray results in a slow heat transfer, delaying temperature stabilization but producing denser, higher yield char.
Research Article
Simulation of Azelaic Acid Crystallization Process Based on MATLAB and Aspen Plus
- First Published: 08 July 2025
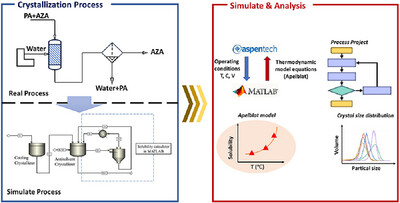
A novel coupled model integrating MATLAB and Aspen Plus is developed to simulate azelaic acid's cooling-antisolvent crystallization. Overcoming Aspen Plus's limitation in dynamic solubility tracking. Validated via crystal size distribution, this tool accurately captures process dynamics, aiding optimization of antisolvent crystallization for enhanced industrial efficiency.
High-Conversion Microreactor for Hydrogenation of Organic Waste
- First Published: 08 July 2025
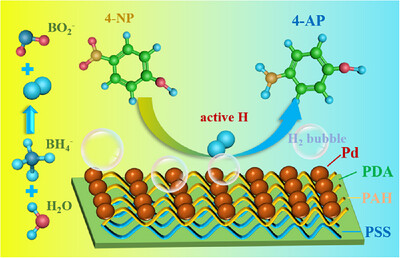
In this research, a highly efficient and stable catalytic layer loaded with palladium nanoparticles was successfully prepared in a microchannel reactor by layer-by-layer self-assembly and ion exchange–in situ reduction technology. This method achieved an even and stable distribution of the catalyst on the inner wall of the microreactor. Reactant molecules were transferred from the main solution to the catalyst surface through convection and diffusion, enhancing mass transfer and further improving the reaction efficiency.
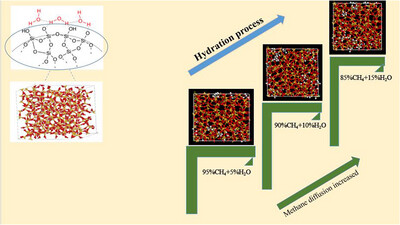
Simulating the Dehydration Process by Adsorption and Diffusion of H2O and CH4 on the Silica
- First Published: 15 July 2025
Modeling Iron Ore Breakage with the Tavares Model and DEM Simulation of a Laboratory Jaw Crusher
- First Published: 15 July 2025
Sustainable Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment: Template-Free Mesoporous Silica from Coal Fly Ash
- First Published: 17 July 2025
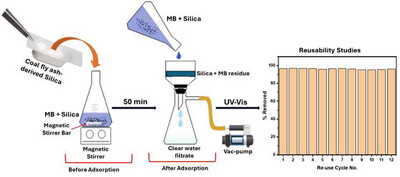
This study demonstrates highly effective and reusable methylene blue (MB) removal using coal fly ash-derived silica. Over 12 cycles, consistent 97 % MB removal was achieved, surpassing other reported silica adsorbents. This highlights the material's economic potential and promotes sustainable waste repurposing for environmental remediation.
Functional Coating of NPK Granules with Pyrolysis Oils for Enhanced Slow-Release Performance
- First Published: 17 July 2025
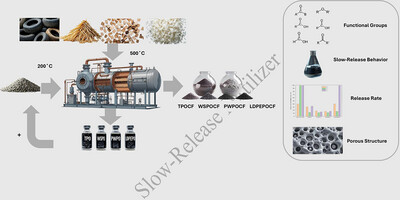
Four types of slow-release NPK fertilizers were prepared by coating granules with pyrolysis oils derived from both bio-based and petroleum-based polymeric waste materials. The functional groups present in these oils played a crucial role in strong chemical interactions with ions of the fertilizer, leading to the formation of porous coatings. This porous structure effectively slowed the release of nutrients. Among the coatings, those made from lignocellulosic feedstocks exhibited improved nitrogen retention and a more controlled release profile. This approach demonstrates how waste streams can be transformed into efficient agricultural inputs, offering an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic coatings and advancing sustainable nutrient management practices.
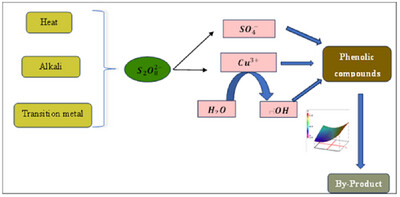
Phenolic Compound Removal from Olive Mill Wastewater by Sulfate Radical SR/AOP: RSM-CCD Optimization
- First Published: 21 July 2025
Gas–Liquid Mass Transfer in a Three-Staged Contactor Consisting of Venturi and Cyclone
- First Published: 26 July 2025
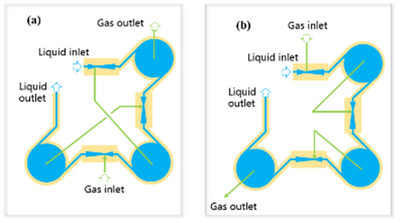
A three-staged contactor combining Venturi and cyclone achieves gas-liquid co-current and countercurrent modes by adjusting gas channels. Countercurrent mode, operable at 7.5–17.5 L min−1 liquid flow, outperforms co-current in mass transfer within a critical gas flow range. It features gas self-suction, efficient bubble dispersion, and low gas consumption, offering promising potential for sewage deoxygenation and volatile organic compound separation. This novel design bridges mixing-separation processes, enhancing mass transfer efficiency in chemical engineering.