Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
A Review of Biomass Resources and Thermochemical Conversion Technologies
- First Published: 21 February 2022
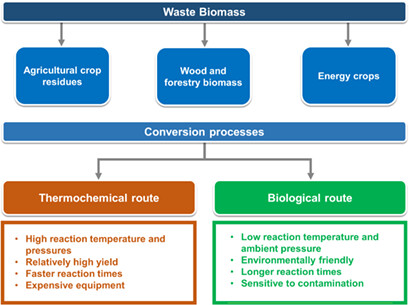
Agricultural crop residues, energy crops, and woody biomass are potential feedstocks for biofuel production through thermochemical and biological conversion technologies. Bio-oil, bio-crude oil, biodiesel, biochar, syngas, biohydrogen, biomethane, bioethanol, and biobutanol are promising biofuel products from waste biomass.
Extraction of Sugars and Cellulose Fibers from Cannabis Stems by Hydrolysis, Pulping, and Bleaching
- First Published: 28 January 2022

Subcritical water hydrolysis of cannabis stems was used to recover sugars from hydrolytic hemicellulose degradation and followed by pulping and bleaching to remove lignin and extract microfibrillated cellulose. Design of experiments was used optimize process conditions such as temperature, reaction time, and feed concentration for subcritical water hydrolysis with maximum cellulose recovery.
Polysulfide Synthesis Using Waste Cooking Palm Oil via Inverse Vulcanization
- First Published: 21 March 2022

Elemental sulfur is an industrial by-product from petrochemical industries. The increasing threat of abundant elemental sulfur can be diminished via sustainable inverse vulcanization. The first application of waste cooking palm oil in inverse vulcanization is presented, being utilized as a potential comonomer. The produced high-sulfur-content polymer showed satisfactory characteristics.
Synthesis of Active Hybrid Films Reinforced with Cellulose Nanofibers as Active Packaging Material
- First Published: 28 April 2022

Active food packaging was developed by reinforcing films made from semi-refined carrageenan derived from seaweed with cellulose nanofibers made from empty fruit bunch to improve thermal properties and incorporating α-tocopherol as antioxidant. Release of the antioxidant was studied in a food simulant and fresh meat and found to delay lipid oxidation of the food product during 16 d of refrigeration.
Simulation of an Integrated Anaerobic Digestion and Combined Heat and Power System for Food Waste Utilization
- First Published: 28 April 2022
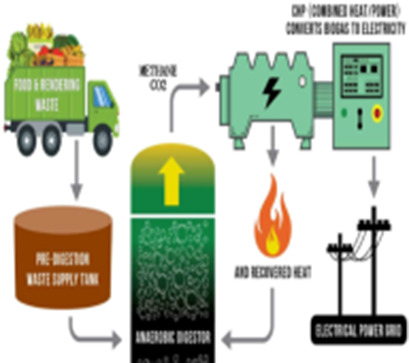
Integrating the anaerobic digestion process with a combined heat and power system is a potential technology in managing municipal solid waste by the waste-to-energy approach. Process simulation to transform food waste into energy in the form of heat and electricity was performed. The model agrees well with typical biogas compositions and can predict the energy output for various process conditions.
Optimization of Culture Conditions of Immobilized Cells for Enzyme Excretion and Cell Lysis
- First Published: 02 May 2022
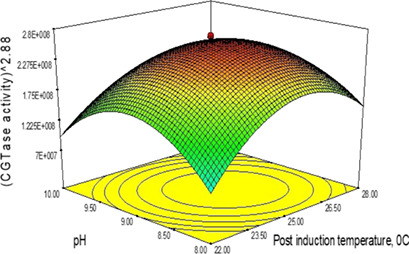
The optimization of culture conditions such as post induction temperature, inducer, and pH of immobilized cells on enzyme excretion and cell lysis was successfully carried out. High enzyme excretion and low cell lysis were observed applying the optimized culture conditions. The immobilized cells represent a suitable system to be employed for high production levels of a desired product.
Modeling of Volatile Composition during Heating and Isothermal Stages of the Torrefaction Process
- First Published: 02 May 2022

The current two-stage mechanism kinetic model is applicable for predicting solid and volatile evolution under isothermal condition only. Thus, this kinetic model is extended for covering heating and isothermal stages during the torrefaction process. It is able to describe the decomposition behavior of solid biomass and to predict volatile components released during the torrefaction process.
Applicability of Deep Eutectic Solvents in Oil and Gas Processing Fields for CO2 Control
- First Published: 24 May 2022
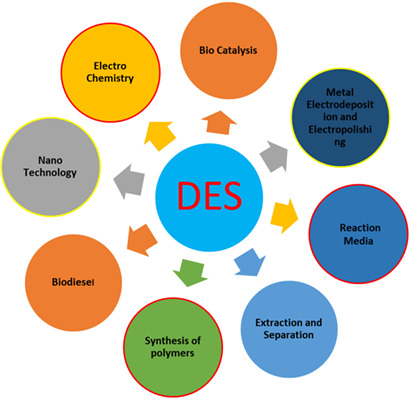
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are a novel generation of viable green solvents with good CO2 capture performance. An overview is given on the possible and beneficial usage of DESs for contaminated CO2 capture in the petroleum and gas industry. Their physicochemical properties, potential applications, chemical structures, preparation, and experimental solubilities of CO2 are evaluated and discussed.
Immobilization Method to Separate Microalgae Biomass for Fatty Acid Methyl Ester Production
- First Published: 18 May 2022
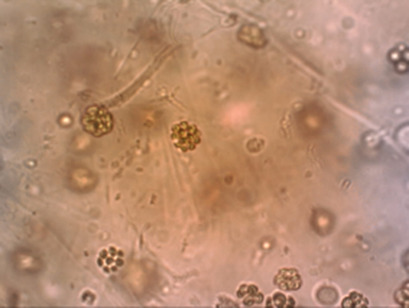
The bead immobilization method simplifies the harvesting of microalgae biomass from culture media. Mixed-matrix beads are shown to solve problems like bead leakage, instable structures, and oversaturation. The mixed matrix achieves higher cell numbers and higher lipid yields than the single matrix, providing an efficient method to harvest microalgae biomass for sustainable biodiesel production.
Development of a Prediction Model for Gas Hydrate Formation in Multiphase Pipelines by Artificial Intelligence
- First Published: 30 May 2022
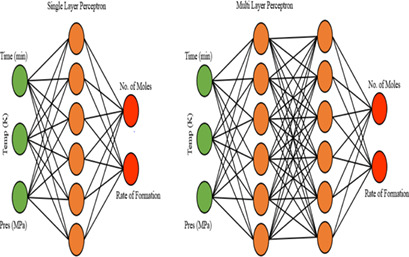
A prediction model was developed by means of artificial neural networks (ANNs) to determine the gas hydrate formation kinetics in multiphase gas dominant pipelines with crude oil. The results let conclude that the application of ANNs could be a potential solution for the accurate prediction model development to forecast the reaction kinetics of gas hydrate formation and dissociation.









