Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Titelbild
Titelbild: A Macromolecular Drug for Cancer Therapy via Extracellular Calcification (Angew. Chem. 12/2021)
- Page: 6253
- First Published: 15 February 2021

Ein makromolekularer Wirkstoff , Polysialinsäure konjugiert mit Folat (Folat-polySia), wurde von Ruikang Tang, Ben Wang und Mitarbeitern in ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 6583 als extrazelluläres Chemotherapeutikum gegen maligne Tumorerkrankungen entwickelt. Der neuartige Wirkstoff verbindet sich mit dem Folatrezeptor und induziert über die Aufnahme von Kalzium aus dem Blut selektiv die biogene Mineralbildung auf Tumorzellen, was zur pathologischen Verkalkung von Tumoren führt. Die Verabreichung von Folat-polySia hemmt das Tumorwachstum und verbesserte die Überlebensraten von Mäusen dramatisch.
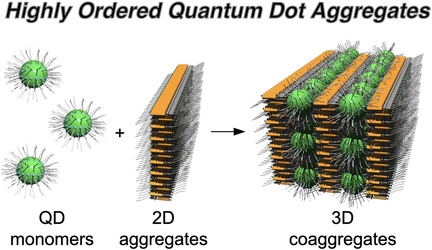
Innentitelbild: A Highly Ordered Quantum Dot Supramolecular Assembly Exhibiting Photoinduced Emission Enhancement (Angew. Chem. 12/2021)
- Page: 6254
- First Published: 01 February 2021

Hochgeordnete Koaggregate aus Quantenpunkten (QDs) und Azobenzol-Derivaten wurden von Mitsuaki Yamauchi, Seiya Yamamoto und Sadahiro Masuo in ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 6547 konstruiert. Die einzigartigen Koaggregate haben eine gleichmäßig angeordnete Struktur, und ihre photophysikalischen Eigenschaften können durch Bestrahlung gesteuert werden.
Innenrücktitelbild: An Enzyme-Activatable Engineered DNAzyme Sensor for Cell-Selective Imaging of Metal Ions (Angew. Chem. 12/2021)
- Page: 6903
- First Published: 04 February 2021

Ein zellselektives Imaging von Metallionen wird von Lele Li et al. in ihrer Zuschrift auf S. 6370 durch den Einsatz einer enzymaktivierbaren DNAzym-Sensortechnologie erreicht. Im Bild ist die Sensoraktivität in normalen Zellen stumm und kann in Krebszellen durch ein überexprimiertes Enzym durch ortsspezifische Spaltung wiederhergestellt werden. Der DNAzym-Sensor ermöglichte die Unterscheidung von Metallionensignalen in Tumorzellen und gesunden Zellen sowohl in vitro als auch in vivo.
Rücktitelbild: An Efficient Turing-Type Ag2Se-CoSe2 Multi-Interfacial Oxygen-Evolving Electrocatalyst (Angew. Chem. 12/2021)
- Page: 6904
- First Published: 15 February 2021
Turing-Muster sind in lebenden Systemen weithin bekannt, dennoch bleibt die Synthese von chemischen Turing-Strukturen in anorganischen Nanomaterialien eine große Herausforderung. In ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 6627 konstruierten Min-Rui Gao und Mitarbeiter stationäre Ag2Se-Turing-Muster auf CoSe2-Nanogürteln über diffusionsgetriebene Instabilität. Das neue Material enthält zahlreiche Ag2Se-CoSe2-Grenzflächen, die als aktive Zentren die Chemisorption von sauerstoffhaltigen Spezies an der Oberfläche ermöglichen, was zu einer verbesserten Energetik für die Sauerstoffentwicklungsreaktion führt.
Frontispiz
Frontispiz: Intramolecular Electric Field Construction in Metal Phthalocyanine as Dopant-Free Hole Transporting Material for Stable Perovskite Solar Cells with >21 % Efficiency
- First Published: 08 March 2021
Perowskit-Solarzellen In der Zuschrift auf S. 6364 berichten Jing Cao et al. über die Herstellung eines Nickelphthalocyanins mit vier Methoxyethoxy-Gruppen und dessen Anwendung als Lochtransportmaterial in Perowskit-Solarzellen.
Frontispiz: Tracking Reactions of Asymmetric Organo-Osmium Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysts in Cancer Cells
- First Published: 08 March 2021
Tumortherapeutika In ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 6536 untersuchen Paul D. Quinn, Carlos Sanchez-Cano, Peter J. Sadler et al. Reaktionen von Organoosmium-Komplexen, die asymmetrische Transferhydrierungen katalysieren, in Krebszellen.
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis: Angew. Chem. 12/2021
- Pages: 6257-6278
- First Published: 08 March 2021
Kurzaufsätze
Hybridmaterialien
Kombination von DNA-Origami und Polymeren: Eine leistungsstarke Methode zum Aufbau definierter Nanostrukturen
- Pages: 6282-6294
- First Published: 10 July 2020
Die Kombination von DNA-Origami mit synthetischen Polymeren führt zu einer neuen Klasse von Materialien mit interessanten Eigenschaften und Merkmalen. Dieses Verfahren ist genauer als herkömmliche Nanofabrikationsverfahren, wie die Positionierung einzelner Polymerstränge. In diesem Kurzaufsatz fassen wir die mögliche Herstellung von Nanostrukturen von Polymeren mit zwei- und dreidimensionalem DNA-Origami zusammen.
Dyes
Explorations into the Effect of meso-Substituents in Tricarbocyanine Dyes: A Path to Diverse Biomolecular Probes and Materials
- Pages: 6295-6306
- First Published: 22 September 2020
Aufsätze
Präbiotische Chemie
Coenzyme und ihre Rolle in der Evolution des Lebens
- Pages: 6308-6337
- First Published: 16 January 2020
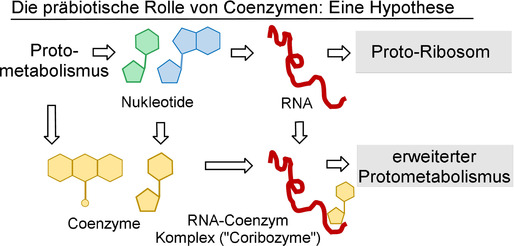
Obwohl Coenzyme im biotischen Metabolismus eine Schlüsselrolle spielen, standen sie als Beteiligte am Protometabolismus nicht im Mittelpunkt des Interesses, noch wurde ihre mögliche präbiotische Erzeugung ausführlich diskutiert. Dieser Aufsatz bietet einen konzeptionellen Überblick über die Rolle von Coenzymen mit Blick auf bekannte Theorien des Protometabolismus und ihre Aufnahme in die RNA-Welthypothese.
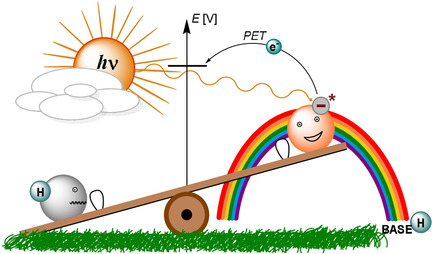
Photochemie
Photoangeregte Anionen in organischen Reaktionen
- Pages: 6338-6363
- First Published: 01 October 2020
Zuschriften
Perovskite Solar Cells | Hot Paper
Intramolecular Electric Field Construction in Metal Phthalocyanine as Dopant-Free Hole Transporting Material for Stable Perovskite Solar Cells with >21 % Efficiency
- Pages: 6364-6369
- First Published: 20 January 2021
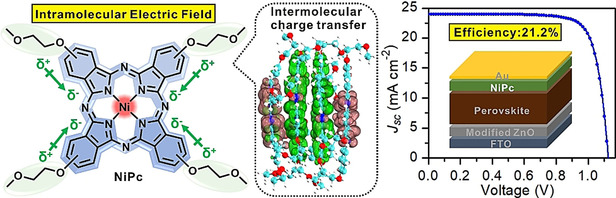
A Ni phthalocyanine (NiPc) decorated by four methoxyethoxy units with a strong intramolecular electric field is prepared and used as hole-transporting materials (HTMs) in perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The best PSCs with NiPc as dopant-free HTM show a record efficiency of 21.23 % (certified 21.03 %). The PSCs also exhibit the excellent stability.
Bioimaging | Hot Paper
An Enzyme-Activatable Engineered DNAzyme Sensor for Cell-Selective Imaging of Metal Ions
- Pages: 6370-6374
- First Published: 03 January 2021
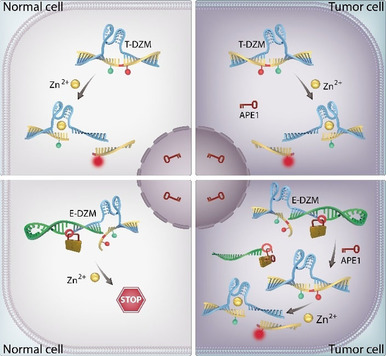
An enzyme-activatable engineering strategy was developed to generate a new DNAzyme sensor technology. The catalytic sensing probe remained silent in normal cells but could be reactivated by a cancer-specific enzyme, thus enabling metal-ion signals to be identified as occurring in tumor cells as opposed to normal cells both in vitro and in vivo (see picture).
Asymmetric Carbonylation
Asymmetric Hydroesterification of Diarylmethyl Carbinols
- Pages: 6375-6379
- First Published: 16 December 2020
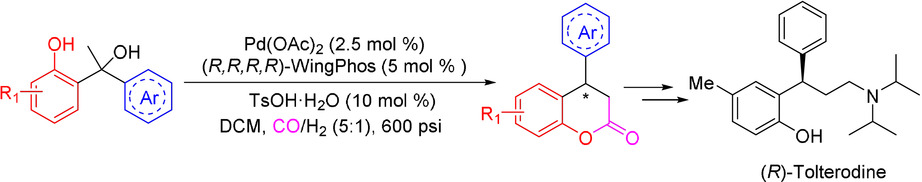
An efficient asymmetric hydroesterfication of diarylmethyl carbinols is developed with a Pd-WingPhos catalyst, resulting in a series of chiral 4-aryl-3,4-dihydrocoumarins in excellent enantioselectivities and good yields. The method features mild reaction conditions, a broad substrate scope, use of easily accessible starting materials, and low palladium loadings. A plausible stereochemical model is proposed with the Pd-WingPhos catalyst.
Imaging Agents
Multi-Color, Bleaching-Resistant Super-Resolution Optical Fluctuation Imaging with Oligonucleotide-Based Exchangeable Fluorophores
- Pages: 6380-6383
- First Published: 10 December 2020
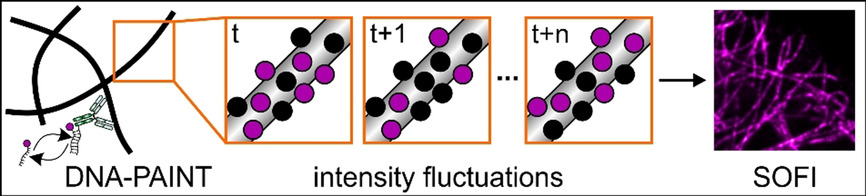
Fluorophore labels that transiently bind to and unbind from a protein target allow photobleaching in super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI) to be circumvented. Using short fluorophore-labeled DNA oligonucleotides, we demonstrate high-contrast, low-background, and multi-color super-resolution imaging with SOFI.
C−H Amination
Efficient Amination of Activated and Non-Activated C(sp3)−H Bonds with a Simple Iron–Phenanthroline Catalyst
- Pages: 6384-6389
- First Published: 10 December 2020
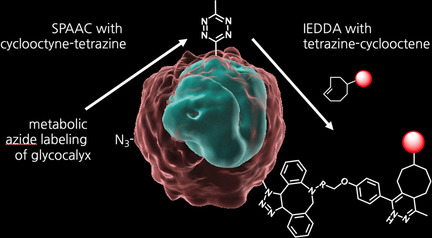
Bioorthogonal Chemistry | Very Important Paper
Covalent Cell Surface Conjugation of Nanoparticles by a Combination of Metabolic Labeling and Click Chemistry
- Pages: 6390-6395
- First Published: 23 December 2020
Carbon | Very Important Paper
Locally Ordered Graphitized Carbon Cathodes for High-Capacity Dual-Ion Batteries
- Pages: 6396-6402
- First Published: 22 December 2020

Locally ordered graphitized carbon (LOGC), interconnected with disordered carbon, is able to weaken the van der Waals interactions between adjacent graphene sheets and thus reduce the anion-intercalating voltage. Conversely, disordered carbon not only interconnects the dispersed nanographite but also partially buffers severe anion–anion repulsions and offers extra capacitive anion storage sites.
Self-Assembly
Light-Triggered, Non-Centrosymmetric Self-Assembly of Aqueous Arylazopyrazoles at the Air–Water Interface and Switching of Second-Harmonic Generation
- Pages: 6403-6408
- First Published: 21 December 2020
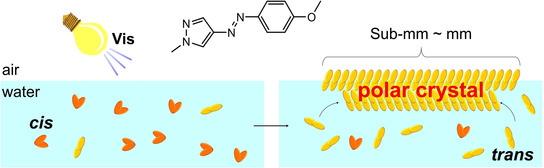
Macroscopically oriented, large polar crystalline films were fabricated at the air–water interface by photoisomerization of a cis-arylazopyrazole derivative dissolved in the aqueous phase. The trans-film formed on the solid substrate showed reversible photo-induced phase changes between the polar crystal and liquid phase, which lead to an on/off photo-switching of the second-harmonic-generation intensity.
Nanomaterials | Hot Paper
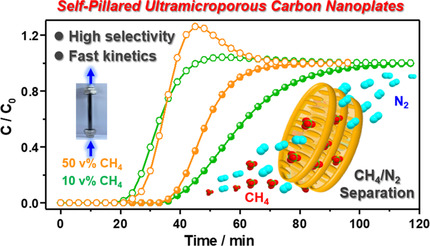
Self-Pillared Ultramicroporous Carbon Nanoplates for Selective Separation of CH4/N2
- Pages: 6409-6413
- First Published: 16 December 2020
Photochemistry | Hot Paper
Cocrystal Engineering: Toward Solution-Processed Near-Infrared 2D Organic Cocrystals for Broadband Photodetection
- Pages: 6414-6420
- First Published: 17 December 2020
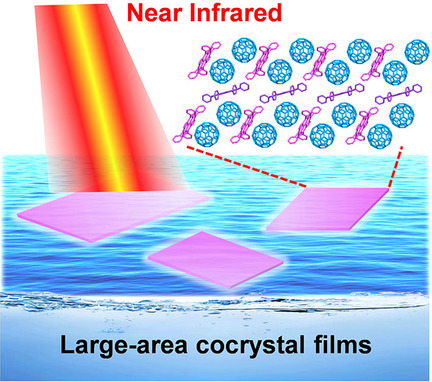
A large-area cocrystal film is designed and fabricated in a low-cost solution-processed method. Attributed to the enhanced charge-transfer absorption in the NIR region, the generation of long-lived free carriers, and the device configuration optimization, the cocrystal film-based photodetector exhibits a high responsivity to a wide spectra range, coupled with fast response times and large EQE.
Cluster Compounds | Hot Paper
Boosting CO2 Electrochemical Reduction with Atomically Precise Surface Modification on Gold Nanoclusters
- Pages: 6421-6426
- First Published: 21 December 2020
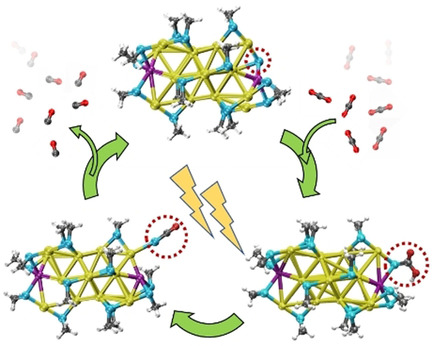
Surface modification with Cd atom doping generates the Au19Cd2(SR)16 nanocluster, which exhibits significantly boosted CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) performance, doubling that of the undoped Au23. DFT calculations reveal that local surface Cd doping leads to a dynamic behavior of the sulfur active site on Au19Cd2 when interacting with CO, contributing to the energetically favorable formation of CO on the exposed sulfur active site that facilitates the overall CO2RR.
Deuterated Pharmaceuticals
Room-Temperature Palladium-Catalyzed Deuterogenolysis of Carbon Oxygen Bonds towards Deuterated Pharmaceuticals
- Pages: 6427-6431
- First Published: 17 December 2020
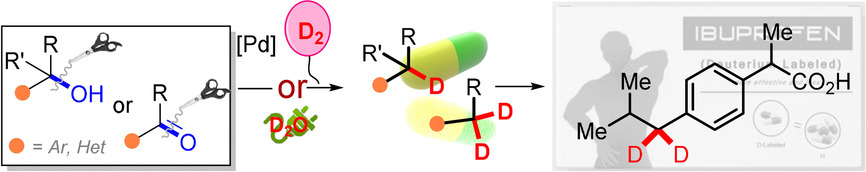
An operationally simple and easily scalable protocol for deuterogenolysis of carbon oxygen bonds was developed, which leads to a practical approach to synthetically valuable benzyl-deuterated building blocks and deuterium medicines, including atomoxetine, tesmilifene, amiodarone, and ibuprofen. Combining the in situ electrocatalytic heavy water-splitting, this protocol enables the direct utilization of D2O for construction of high value-added deuterated chemicals and pharmaceuticals from low costing and easily available alcohols and ketones.
Metal-Organic Frameworks
Topological-Distortion-Driven Amorphous Spherical Metal-Organic Frameworks for High-Quality Single-Mode Microlasers
- Pages: 6432-6436
- First Published: 14 December 2020
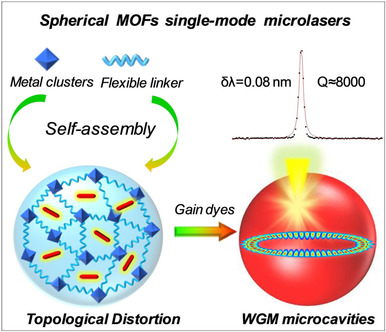
Amorphous spherically-shaped metal-organic framework (MOF) microcavities have been constructed by amorphizing MOFs with a topological distortion network through introducing flexible building blocks, which possess a Q factor as high as ≈104 and can provide sufficient feedback for high-quality single-mode lasing oscillations. The results will pave an avenue for the construction of new types of flexible MOFs-based photonic components.
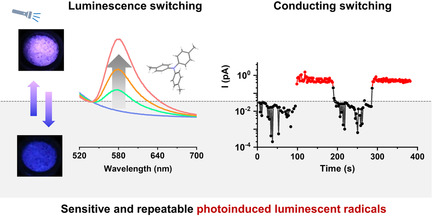
Luminescence | Hot Paper
Sensitive and Repeatable Photoinduced Luminescent Radicals from A Simple Organic Crystal
- Pages: 6437-6441
- First Published: 03 December 2020
Catalysis | Hot Paper
Reactivity and Selectivity in Ruthenium Sulfur-Chelated Diiodo Catalysts
- Pages: 6442-6446
- First Published: 12 February 2021

A diiodo trifluoromethyl sulfur-chelated ruthenium benzylidene complex was synthesized as precatalyst for olefin metathesis, allowing ring-opening metathesis of dicyclopentadiene in the presence of a methylene donor to produce 1,3-divinyl-hexahydropentalenes and depolymerization of polybutadiene upon green light irradiation. The selectivity displayed by the catalyst is attained through a fine balance between its rate of pre-activation and deactivation.
Oxidation Catalysis
Pt/MnO2 Nanoflowers Anchored to Boron Nitride Aerogels for Highly Efficient Enrichment and Catalytic Oxidation of Formaldehyde at Room Temperature
- Pages: 6447-6451
- First Published: 20 December 2020
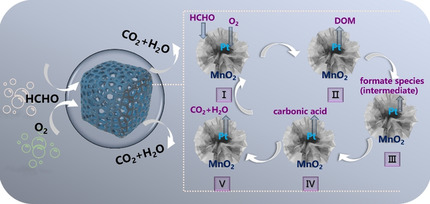
A three-dimensional monolithic Pt/MnO2-BN catalyst was prepared by anchoring Pt/MnO2 nanoflower on boron nitride (BN) aerogels. The as-formed porous aerogels catalyst offers a combination of adsorption and oxidation to efficiently remove formaldehyde at room temperature, as well as easier recycling and reuse in comparison with powdery catalysts.
Catalysis
Selective Oxidation of Anilines to Azobenzenes and Azoxybenzenes by a Molecular Mo Oxide Catalyst
- Pages: 6452-6455
- First Published: 17 December 2020
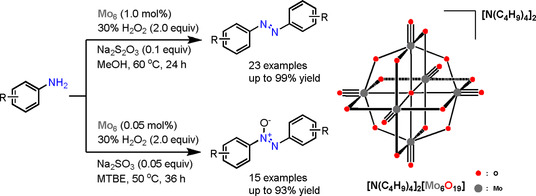
Selective synthesis of azobenzene compounds and azoxybenzene compounds with N=N bonds was performed by a molecular molybdenum oxide compound [N(C4H9)4]2[Mo6O19] (simplified as Mo6) under mild conditions. A series of symmetric and asymmetric azobenzenes and azoxybenzenes were produced in high yield and selectivity by changing additive and solvent. Moreover, the catalytic mechanism of the reaction system was also assumed appropriately.
Nonlinear Optical Crystals
Nonlinear Optical Oxythiophosphate Approaching the Good Balance with Wide Ultraviolet Transparency, Strong Second Harmonic Effect, and Large Birefringence
- Pages: 6456-6460
- First Published: 20 December 2020
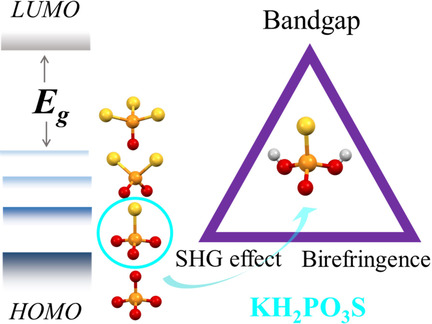
Based on first-principles and experimental studies, the design strategy from (PO4)3− to (PO3S)3− is confirmed to enhance the birefringence and second harmonic generation (SHG) effect while maintaining large band gap. The oxythiophosphate KH2PO3S with novel motif of (H2PO3S)− is accordingly predicted to exhibit better UV NLO balance than KH2PO4, including larger birefringence, stronger SHG effect, and shorter phase-matching SHG wavelength.
Fluorides | Hot Paper
Searching for Monomeric Nickel Tetrafluoride: Unravelling Infrared Matrix Isolation Spectra of Higher Nickel Fluorides
- Pages: 6461-6464
- First Published: 10 December 2020
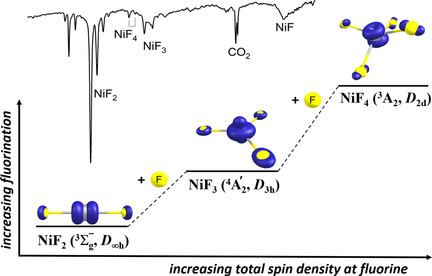
Molecular NiF3 and NiF4 are the missing tri- and tetrafluorides of the otherwise known binary first-row transition-metal fluorides that are predicted to be stable. These elusive high-valent molecular nickel fluorides were identified in rare-gas matrices aided by high-level quantum chemical electronic structure calculations. They are among the most powerful known fluorination and oxidation agents.
Flow Chemistry | Hot Paper
Flow Technology for Telescoped Generation, Lithiation and Electrophilic (C3) Functionalization of Highly Strained 1-Azabicyclo[1.1.0]butanes
- Pages: 6465-6469
- First Published: 16 December 2020
![Flow Technology for Telescoped Generation, Lithiation and Electrophilic (C3) Functionalization of Highly Strained 1-Azabicyclo[1.1.0]butanes](/cms/asset/1fd9326c-ef06-402f-836d-85538abbe3b6/ange202014881-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Strained….in Flow! The first telescoped continuous flow protocol for the generation, lithiation, and electrophilic trapping of 1-azabicyclo[1.1.0]butane is reported. Several structurally unique C3-functionalized 1-azabicyclo[1.1.0]butanes were prepared using this strategy starting from readily available starting materials.
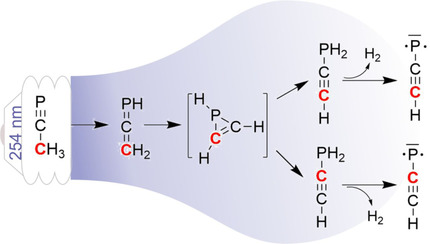
Phosphorus Compounds
An Efficient Photochemical Route Towards Triplet Ethynylphosphinidene, HCCP
- Pages: 6470-6472
- First Published: 15 December 2020
Supramolekulare Chemie | Hot Paper
Rückgrat-verknüpfte Liganden erhöhen die Vielfalt in heteroleptischen Koordinationskäfigen
- Pages: 6473-6478
- First Published: 28 October 2020
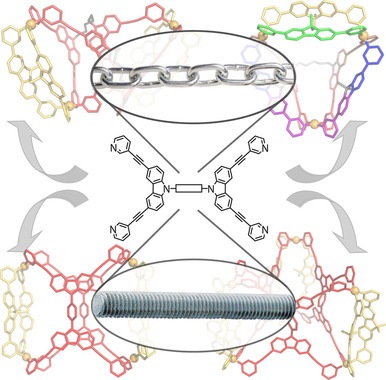
Eine reiche strukturelle Vielfalt an formkomplementären, metallo-supramolekularen Strukturen wird durch die Verbrückung von Liganden über ihre Zentraleinheiten erreicht. Es konnte eine Reihe neuer heteroleptischer Gebilde erhalten werden, von dimeren Käfigen über eine prismatische Struktur bis hin zu einem Pseudotetraeder. Der Einfluss von Linker-Flexibilität, Lösungsmittel und Gastmolekülen wurde untersucht.
Biomimetische Klebstoffe | Hot Paper
Die nächste Generation synthetischer Muschelkleberpolymere durch muschelinspirierte Polymerisation
- Pages: 6479-6484
- First Published: 28 January 2021
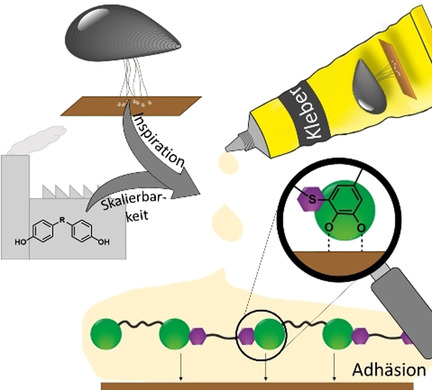
Die Herstellung muschelkleberinspirierter Polymere auf Basis großtechnisch verfügbarer Monomere eröffnet vielfältige Möglichkeiten. Vorgestellt wird ein chemischer Oxidationsweg über den Dichinone erhalten werden, die anschließend in Michael-Polyadditionen mit verschiedenen Dithiolen umgesetzt werden. Der modulare Ansatz ergibt eine Klebstoff-Bibliothek mit Thiol-Catechol-Haftfunktionalitäten und interessanten Unterwasser-Klebeigenschaften.
Distannabenzol | Hot Paper
Ein offenschaliges Singulett-SnI-Diradikal und H2-Spaltung
- Pages: 6485-6489
- First Published: 18 January 2021
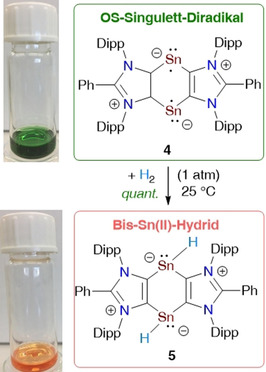
Das 1,4-Distannabenzol-Derivat 4 mit zweifach koordinierten SnI-Atomen wurde als grüner, kristalliner Feststoff isoliert. Der Grundzustand von 4 ist ein offenschaliges Singulett (OS) mit der Singulett-Triplett-Energielücke (ΔEOS–T) von 4.4 kcal mol−1 (nach CASSCF, ΔES–T=6.6 kcal mol−1). Folglich zeigt 4 ein Halbfeld-EPR-Signal bei 100 K und addiert H2-Gas bei Raumtemperatur, wobei quantitativ das SnII-Hydrid 5 als orangefarbener Feststoff entsteht.
Elektrochemie | Hot Paper
Elektrooxidative Rhodium-katalysierte [5+2]-Anellierung durch C-H/O-H-Aktivierung
- Pages: 6490-6495
- First Published: 20 January 2021
Asymmetrische Katalyse | Hot Paper
Unterbrochene Pyridin-Hydrierung: asymmetrische Synthese von δ-Lactamen
- Pages: 6496-6500
- First Published: 18 January 2021
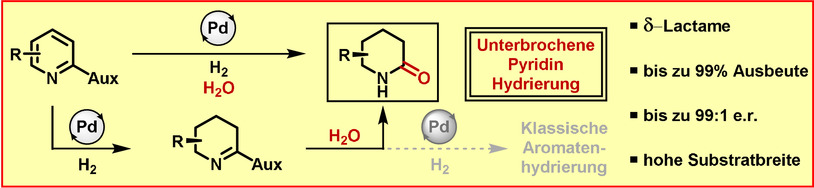
Die Metall-katalysierte Hydrierung von Aromaten ist eine effiziente Transformation, um gesättigte Carbo- und Heterocyclen zu erhalten, die allerdings auf die Bildung von C-H- und N-H-Bindungen beschränkt ist. Wir stellen hier die Synthese von enantioangereicherten δ-Lactamen aus leicht verfügbaren Oxazolidinon-substituierten Pyridinen vor. Entscheidend für diese Reaktion ist die Unterbrechung der Aromatenreduktion durch nukleophile Substitution.
Organokatalyse
Eine chirale pentafluorierte Isopropylgruppe durch Iod(I)/(III)-Katalyse
- Pages: 6501-6506
- First Published: 11 January 2021
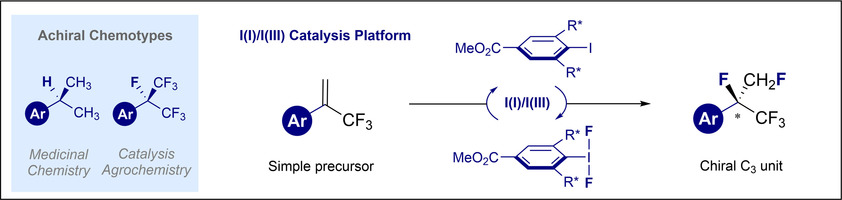
Die Iod(I/III)-katalysierte Konstruktion eines enantioangereicherten fluorierten Isoster der Isopropylgruppe wird beschrieben. Die in situ Generierung einer chiralen ArIF2-Spezies ermöglicht die Difluorierung von leicht zugänglichen α-CF3-Styrolen, um ein Stereozentrum mit den Substituenten F, CH2F und CF3 aufzubauen (bis zu 95 %, >20:1 vic:gem Difluorierung). Zur Validierung der Enantioselektivität wurde eine Katalysatoroptimierung durchgeführt.
Phosphaorganische Gerüste
Zugang zu (tBuCP)n-Gerüsten (n=2, 4) durch P-C-Bindungsspaltung von Di-tert-butyldiphosphatetrahedran
- Pages: 6507-6512
- First Published: 05 January 2021
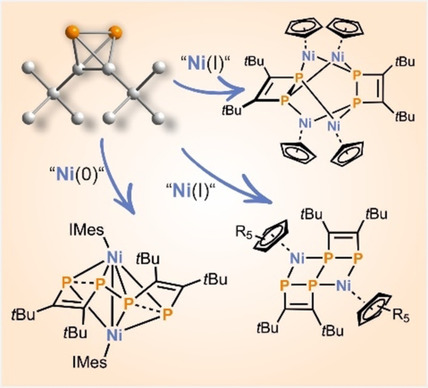
Reaktionen von (tBuCP)2 mit N-heterocyclischen Carbenkomplexen von Nickel führen zur P-C-Bindungsspaltung und der Verknüpfung zweier (tBuCP)2-Einheiten. Die so gebildeten Metallkomplexe weisen ungewöhnliche phosphaorganische Gerüste auf und zeigen eine bemerkenswerte Folgechemie. Die Ergebnisse zeigen, dass (tBuCP)2 als Baustein für die Synthese ungewöhnlicher Phosphaorganometallverbindungen genutzt werden kann.
Bismutchemie
Bismutamide als einfache Vermittler hochselektiver Pn−Pn-Radikal-Kupplungsreaktionen (Pn=N, P, As)
- Pages: 6513-6518
- First Published: 14 December 2020

Bismutamide des Typs [Bi(NAr2)3] wurden synthetisiert und charakterisiert. Sie können Aminylradikale [NAr2]. freisetzen und durch Radikalkupplung die hochselektive Generierung von Hydrazinen [NAr2]2 induzieren. Zudem vermitteln sie die selektive Dehydrokupplung von HPnR2 (Pn=N, P, As), auch von schwierig zu kuppelnden Substraten. Dabei sind die Reaktionsbedingungen, der Mechanismus und die Substratbreite komplementär zu oder günstiger als bei etablierten Methoden.
Thiazolthiazole
Intensiv farbige Bor-dotierte Thiazolthiazole durch reduktive Dimerisierung von Borisothiocyanaten
- Pages: 6519-6524
- First Published: 25 January 2021
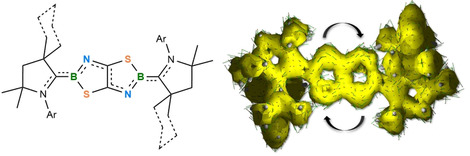
Während die Reduktion cyclischer Alkyl(amino)carben-stabilisierter Borisothiocyanate in der Gegenwart einer Lewis-Base dreifach koordinierte Isothiocyanatoborylene ergibt, liefert die Reduktion in Abwesenheit einer Lewis-Base die ersten Beispiele für intensiv blaue, Bor-dotierte, aromatische Thiazolthiazole.
Dehydrierende C-N-Kupplung
Tellur(II)/Tellur(III)-katalysierte dehydrierende C-N-Bindungsbildung
- Pages: 6525-6530
- First Published: 15 December 2020
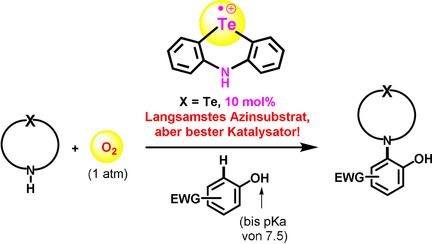
Eine TeII/TeIII-katalysierte dehydrierende C-H-Phenothiazinierung von anspruchsvollen Phenolen mit elektronenziehenden Substituenten unter milden, aeroben Bedingungen liefert hohe Ausbeuten. Diese unerwarteten TeII/TeIII-radikalkatalytischen Eigenschaften wurden mithilfe von Cyclovoltammetrie, ESR-Spektroskopie, kinetischen Experimenten und DFT-Rechnungen untersucht.
Germanium-Chemie
“Überschuss”-Elektronen in LuGe
- Pages: 6531-6535
- First Published: 25 November 2020
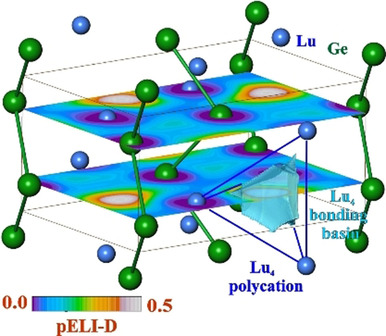
Das Germaniummonogermanid wird durch Hochdruck- und Hochtemperatur-Synthese dargestellt. Die chemische Bindung in LuGe wird als kovalent gebundene Zickzackketten von Ge-Atomen und Lu4-Polykationen beschrieben, die mit Hilfe „überschüssiger“ Elektronen im Sinne der Zintl-Bilanz Lu3+(2b)Ge2− × 1 e− gebildet werden. Die homonukleare Bindung in dem Polykation in LuGe ähnelt der Bindungssituation in Ga2Se2.
Forschungsartikel
Anticancer Complexes | Hot Paper
Tracking Reactions of Asymmetric Organo-Osmium Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysts in Cancer Cells
- Pages: 6536-6546
- First Published: 15 February 2021
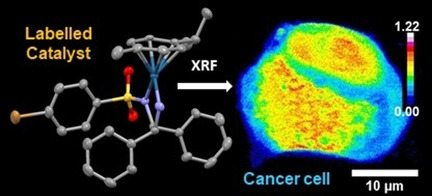
This chiral organo-osmium complex catalyses enantioselective reduction of pyruvate to lactate in cancer cells. The bromine tag on the chelated ligand and osmium have been jointly mapped in cells by X-ray fluorescence and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, revealing facile displacement of the ligand and its translocation to the nucleus.
Supramolecular Chemistry | Hot Paper
A Highly Ordered Quantum Dot Supramolecular Assembly Exhibiting Photoinduced Emission Enhancement
- Pages: 6547-6553
- First Published: 23 December 2020
Protein–DNA Interactions
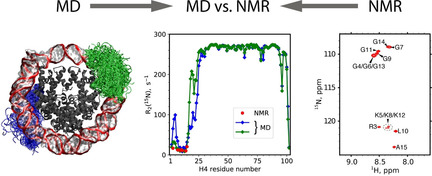
Histone H4 Tails in Nucleosomes: a Fuzzy Interaction with DNA
- Pages: 6554-6561
- First Published: 31 January 2021
Sensors
Spatiotemporal Measurement of Osmotic Pressures by FRET Imaging
- Pages: 6562-6569
- First Published: 14 November 2020
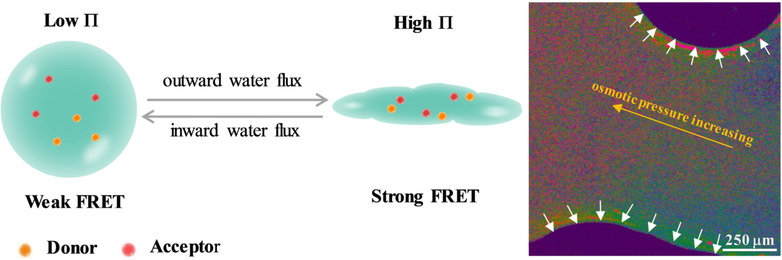
A novel osmotic pressure sensor based on liposomes loaded with FRET dyes is developed, which experience volume changes responding to osmotic pressure due to water outflux through their semipermeable membrane. With FRET microscopy, measurement of osmotic pressures in situ with spatiotemporal resolution is demonstrated, which has not been achieved so far.
Synthetic Biology
Non-Equilibrium Large-Scale Membrane Transformations Driven by MinDE Biochemical Reaction Cycles
- Pages: 6570-6576
- First Published: 07 December 2020
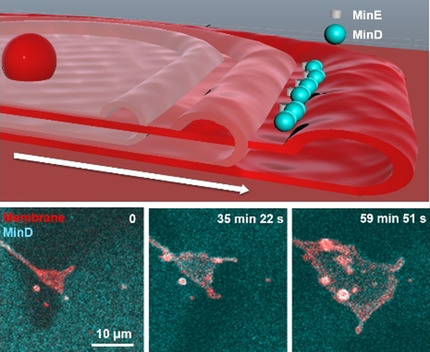
We are demonstrating a new model membrane system, flat vesicles on top of a supported lipid bilayer. By reconstituting a paradigmatic biological pattern-forming system, ATP-dissipating MinDE proteins, dynamic „breathing“ deformations of the soft membrane vesicles and progressive membrane spreading are achieved, confirming that under this specific condition, MinDE reaction cycles can result in work performed on the biological membrane.
Membrane Biophysics
Probing Membrane Protein Association Using Concentration-Dependent Number and Brightness
- Pages: 6577-6582
- First Published: 22 December 2020
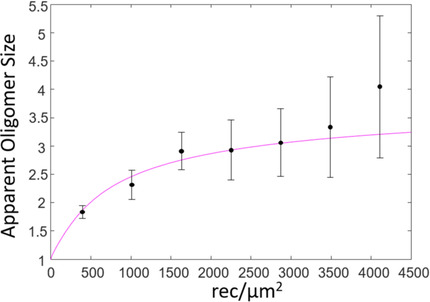
Concentration-dependent number and brightness (cdN&B) is a fluorescence fluctuation technique that can be implemented on a standard confocal microscope and report on the thermodynamics of membrane protein association in the native plasma membrane. cdN&B uses transient transfection to enable measurements of oligomer size as a function of receptor concentration over a broad range, yielding the association constant.
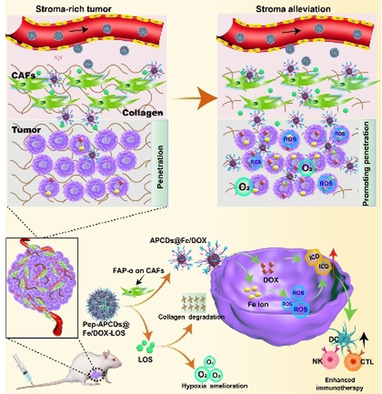
Cancer Therapy | Hot Paper
A Macromolecular Drug for Cancer Therapy via Extracellular Calcification
- Pages: 6583-6591
- First Published: 11 January 2021
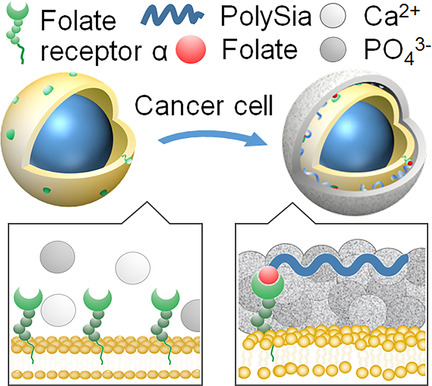
We propose a macromolecular-drug-induced extracellular chemotherapy involving biomineralization by absorbing calcium from blood. Polysialic acid combined with folate, which spontaneously induces biogenic mineral formation on cancer cells rich in folate receptors, leads to targeted pathological calcification and cell death. Systemic administration of folate-polySia improves survival rates of tumor-bearing mice with negligible side effects.
Donor-Acceptor Systems | Hot Paper
Tuning Photoinduced Electron Transfer in POM-Bodipy Hybrids by Controlling the Environment: Experiment and Theory
- Pages: 6592-6599
- First Published: 22 December 2020
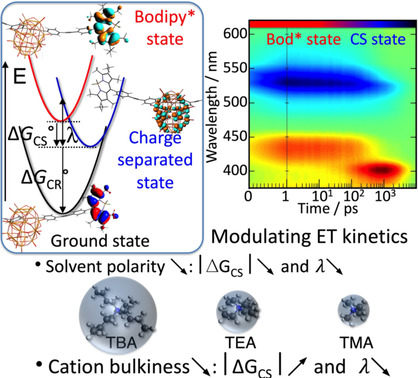
The intramolecular photoinduced electron transfer of a series of polyoxometalate (POM)-bodipy hybrids was examined. The data show that both solvents and counterions have a major impact on the relaxation dynamics of the excited states by modifying the solvation shell around the POM. The experimental findings were corroborated with a computational investigation combining DFT and molecular dynamics simulation methods.
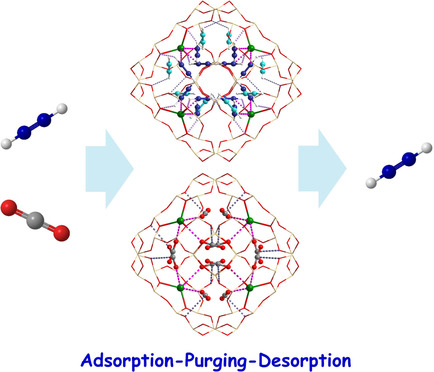
Zeolites | Hot Paper
Efficient Separation of Acetylene and Carbon Dioxide in a Decorated Zeolite
- Pages: 6600-6606
- First Published: 23 December 2020
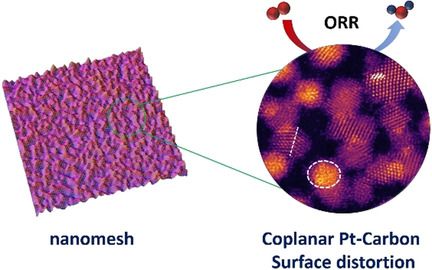
Electrocatalysis | Hot Paper
Coplanar Pt/C Nanomeshes with Ultrastable Oxygen Reduction Performance in Fuel Cells
- Pages: 6607-6612
- First Published: 22 December 2020
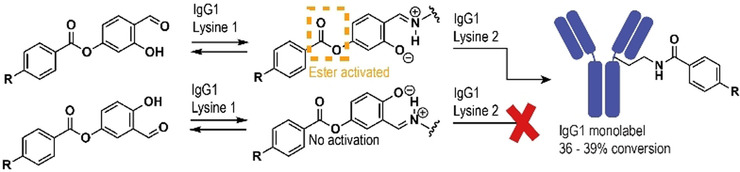
IgG1 Antibodies | Hot Paper
A Reagent for Amine-Directed Conjugation to IgG1 Antibodies
- Pages: 6613-6618
- First Published: 11 December 2020
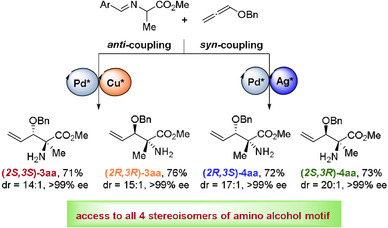
Synthetic Methods | Hot Paper
Diastereodivergent Synthesis of β-Amino Alcohols by Dual-Metal-Catalyzed Coupling of Alkoxyallenes with Aldimine Esters
- Pages: 6619-6626
- First Published: 03 December 2020
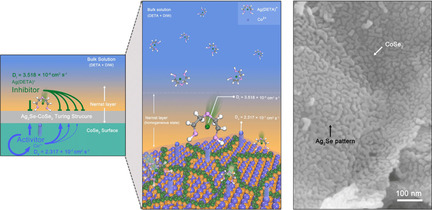
Oxygen Evolution | Hot Paper
An Efficient Turing-Type Ag2Se-CoSe2 Multi-Interfacial Oxygen-Evolving Electrocatalyst
- Pages: 6627-6634
- First Published: 12 January 2021
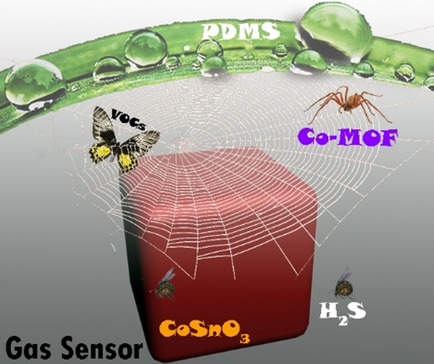
Sensors | Hot Paper
Surface Functionalized Sensors for Humidity-Independent Gas Detection
- Pages: 6635-6640
- First Published: 22 December 2020
Inhibitor Peptides | Hot Paper
Conformational Plasticity of Cyclic Ras-Inhibitor Peptides Defines Cell Permeabilization Activity
- Pages: 6641-6646
- First Published: 11 January 2021
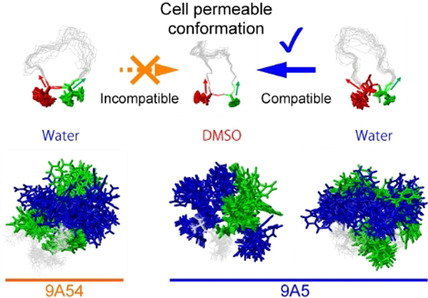
Conformational plasticity defines cell permeabilization activity: Cell permeabilization activities of cyclic Ras-inhibitor peptides are determined by the ability to adopt a cell-permeable amphipathic conformation, in which aromatic residues (green) are converged on one side and the Arg residues (blue) surround the aromatic residues, in a low polarity environment.
Drug Delivery
Drug-Sponge Lipid Nanocarrier for in Situ Cargo Loading and Release Using Dynamic Covalent Chemistry
- Pages: 6647-6654
- First Published: 07 December 2020
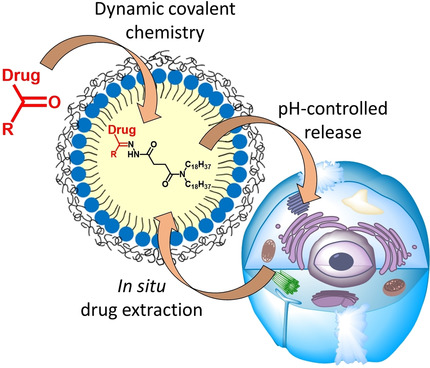
A drug-sponge nanocarrier that reversibly captures and releases drugs or contrast agents under pH control is developed using dynamic covalent chemistry. Inside this lipid droplet nano-reactor, lipophilic capture molecules transform free cargo-ketones into encapsulated hydrazone prodrugs, enabling the controlled release of active cargos and also their extraction from cells and tissues for detoxification.
Antitumor Therapy
Transformable Honeycomb-Like Nanoassemblies of Carbon Dots for Regulated Multisite Delivery and Enhanced Antitumor Chemoimmunotherapy
- Pages: 6655-6666
- First Published: 11 December 2020
Microporous Materials
Leveraging Free Volume Manipulation to Improve the Membrane Separation Performance of Amine-Functionalized PIM-1
- Pages: 6667-6673
- First Published: 05 December 2020
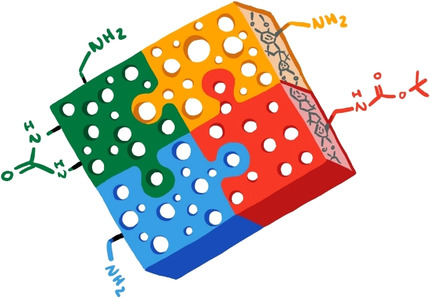
A protection/deprotection strategy was developed to enhance the separation performance of amine-functionalized PIM-1. Thermal deprotection yielded a synergistic boost in size-sieving and CO2 diffusion, ultimately surpassing the H2/CH4, O2/N2 and H2/N2 upper bounds and boosting CO2 permeability by 200 %.
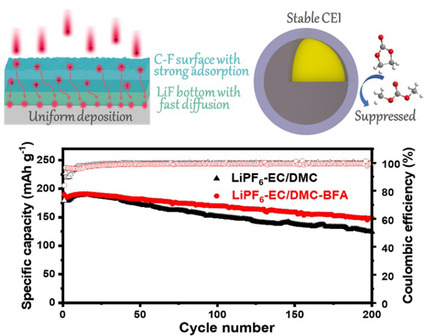
Lithium Batteries
Gradient Solid Electrolyte Interphase and Lithium-Ion Solvation Regulated by Bisfluoroacetamide for Stable Lithium Metal Batteries
- Pages: 6674-6682
- First Published: 11 December 2020
Molecular Electronics
Single-Molecule Conductance of 1,4-Azaborine Derivatives as Models of BN-doped PAHs
- Pages: 6683-6690
- First Published: 21 December 2020
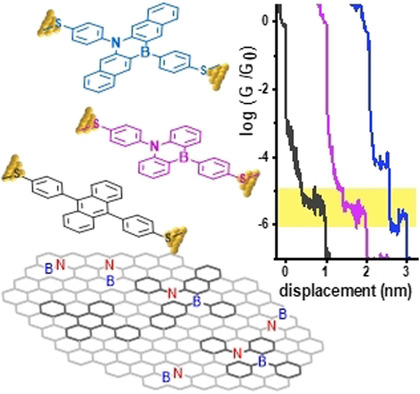
Single-molecule conductance of 1,4-azaborine acene-type compounds was studied using the scanning tunneling microscope break-junction technique. This substitution ensures an unambiguous electron path through both heteroatoms. A moderate change in conductance is observed when compared to the parent all-carbon structure. State-of-the-art transport calculations support the experimental results.
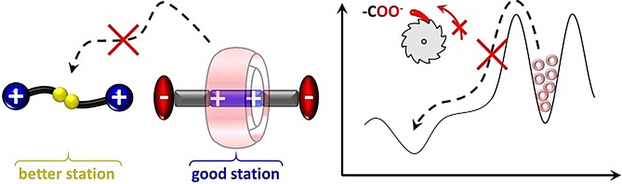
Molecular Machines
Guest Exchange by a Partial Energy Ratchet in Water
- Pages: 6691-6697
- First Published: 23 December 2020
DNA Nanostructures
Probing Transient DNA Conformation Changes with an Intercalative Fluorescent Excimer
- Pages: 6698-6704
- First Published: 13 December 2020
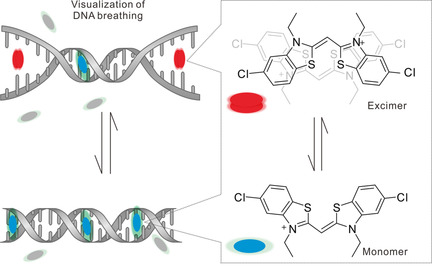
A DNA intercalator, K21, can form transient excimers on the surface of DNA. The ratiometric emission of monomer and excimer was strongly correlated to DNA transient conformation stability. The K21 excimer can probe transient DNA conformation changes in DNA structures with various length and shape. This label-free method can also probe the transient conformation change in single plasmid under supercoiled and open-circular states.
Organocatalysis
1,5,7-Triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene Enhances Activity of Peroxide Intermediates in Phosphine-Free α-Hydroxylation of Ketones
- Pages: 6705-6712
- First Published: 01 December 2020
![1,5,7-Triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene Enhances Activity of Peroxide Intermediates in Phosphine-Free α-Hydroxylation of Ketones](/cms/asset/43ee0699-723a-4c59-af18-89d8a5698009/ange202014478-toc-0001-m.jpg)
The dual catalytic role of 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene (TBD) was revealed for the aerobic α-hydroxylation of ketones under a metal- and phosphine-free method. By means of a double-proton-transfer process, TBD activates the α-C(sp3)−H bond of ketones, avoiding the necessity of an alkali metal. Most importantly, TBD enhances the activity of the peroxide intermediate through the double hydrogen bonds, allowing reduction by DMSO in the absence of a phosphine reductant.
Natural Products
Self-Resistance in the Biosynthesis of Fungal Macrolides Involving Cycles of Extracellular Oxidative Activation and Intracellular Reductive Inactivation
- Pages: 6713-6719
- First Published: 14 December 2020
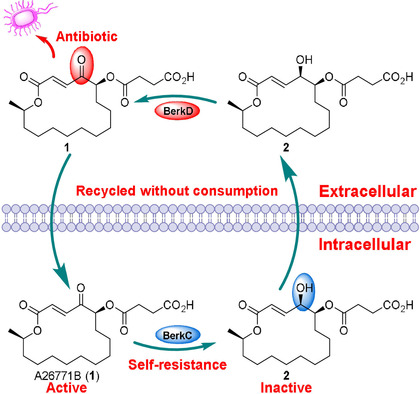
A self-resistance mechanism involving a cycle of extracellular oxidative activation and intracellular reductive inactivation was revealed by identifying the biosynthesis pathway of the macrolide antibiotic A26771B (1). This finding not only expands the understanding of resistance toward macrolide antibiotics, but also guides efforts to develop new antibiotics.
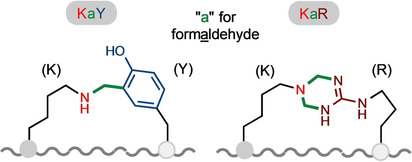
Peptide Macrocycles
Cooperative Stapling of Native Peptides at Lysine and Tyrosine or Arginine with Formaldehyde
- Pages: 6720-6726
- First Published: 18 December 2020
Chemotypes
Piptides: New, Easily Accessible Chemotypes For Interactions With Biomolecules
- Pages: 6727-6733
- First Published: 14 December 2020
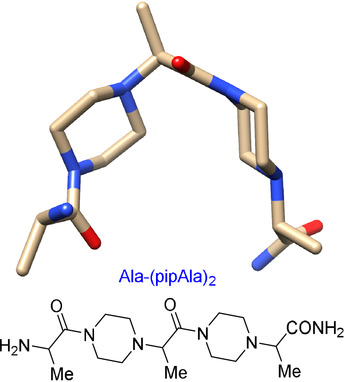
Piptides, a new form of chemotype, are accessible from natural amino acids in either configuration, hence can conveniently display all the side chain pharmacophores found in peptides and proteins. They can be made in solution or on supports and are proteolytically-/pH-robust. Piptide-based disruption of EGF⋅EGFR was chosen as an initial challenge and Exploring Key Orientations (EKO) was used to evaluate candidates.
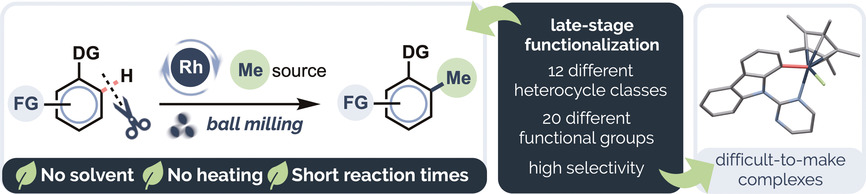
C−H Functionalization | Hot Paper
Mechanochemical Solvent-Free Catalytic C−H Methylation
- Pages: 6734-6740
- First Published: 08 October 2020
Nanostructures
Growth of Colloidal Nanocrystals by Liquid-Like Coalescence
- Pages: 6741-6746
- First Published: 16 December 2020
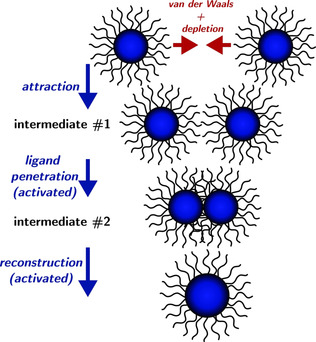
Ligand-capped PbS colloidal nanoparticles grow by liquid-like coalescence rather than Ostwald ripening in the absence of supersaturation. The effective activation energy of the coalescence process is associated with two factors: one is proportional to the contact area between the ligand shells of two colliding particles and the other is related to the reconstruction. The model successfully predicts the growth kinetics of nanoparticles.
Heterojunctions | Hot Paper
Two-Dimensional Porous Molybdenum Phosphide/Nitride Heterojunction Nanosheets for pH-Universal Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- Pages: 6747-6755
- First Published: 17 December 2020
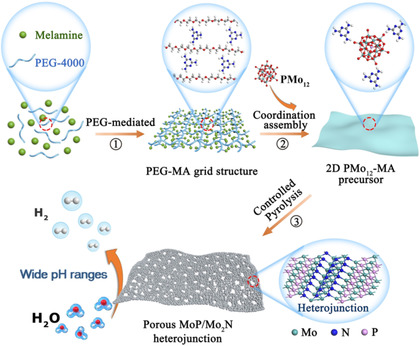
2D porous MoP/Mo2N heterojunction nanosheets have been created based on a PEG-mediated assembly strategy, which exhibit outstanding performance for HER over wide pH ranges even out-performing the Pt/C benchmark at large current density. A series of tests and DFT calculations shows the synergy of the heterojunctions, pores and 2D nanosheets for promoting the HER performance.
Carbodicarbenes
Carbodicarbene Bismaalkene Cations: Unravelling the Complexities of Carbene versus Carbone in Heavy Pnictogen Chemistry
- Pages: 6756-6764
- First Published: 08 December 2020
Photoelectrochemistry | Hot Paper
Unveiling the Hydration Structure of Ferrihydrite for Hole Storage in Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation
- Pages: 6765-6772
- First Published: 19 December 2020
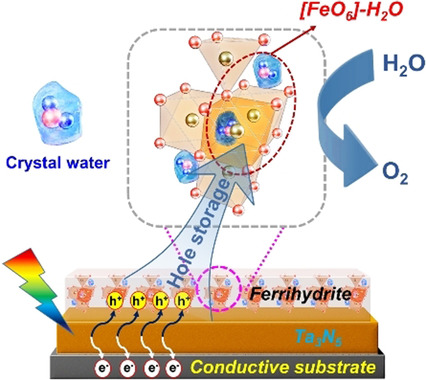
The [FeO6] polyhedral hydration structure of ferrihydrite is responsible for its hole storage function. With the continuous loss of three molecules of crystal water, the quantity of stored photogenerated holes for PEC water oxidation gradually decreases, accompanied by the destruction of the hydration structure.
Cluster Compounds
Enriching Structural Diversity of Alkynyl-Protected Gold Nanoclusters with Chlorides
- Pages: 6773-6777
- First Published: 17 December 2020
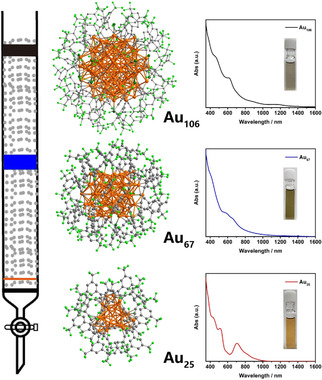
The combination of chloride and alkynyl as protecting agents leads to the formation of large gold nanoclusters. Silica gel column chromatography results in the successful isolation and crystallization of atomically precise gold nanoclusters [HNEt3]3[Au67L32Cl4] (Au67), [HNEt3]4[Au106L40Cl12] (Au106), where L=3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)-phenylacetylide. They are all superatomic clusters, and show size-dependent electrochemical properties.
Cancer Stem Cells
The Discrete Breast Cancer Stem Cell Mammosphere Activity of Group 10-Bis(azadiphosphine) Metal Complexes
- Pages: 6778-6783
- First Published: 03 December 2020

Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are associated to cancer relapse and metastasis. Herein, the breast CSC activities of Group 10-bis(azadiphosphine) complexes under exclusively three-dimensional cell culture conditions, are systematically compared. Breast CSC mammosphere inhibition and potency was highly dependent on the Group 10 metal present.
Recycling
Selective Chemical Upcycling of Mixed Plastics Guided by a Thermally Stable Organocatalyst
- Pages: 6784-6791
- First Published: 18 December 2020

The energetic differences for the glycolysis of BPA-PC and PET in the presence of a protic ionic salt TBD:MSA catalyst enable the selective and sequential depolymerisation of these two commonly employed polymers. Functionalised cyclic carbonates can be obtained from both mixed plastic wastes and industrial polymer blend.
Solid-State Batteries | Hot Paper
Lithium-Metal Anode Instability of the Superionic Halide Solid Electrolytes and the Implications for Solid-State Batteries
- Pages: 6792-6797
- First Published: 14 December 2020
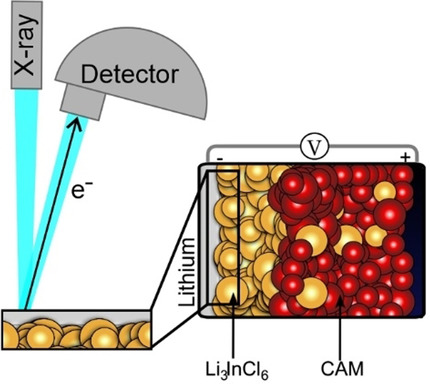
Superionic halide solid electrolytes show excellent cathodic electrolyte properties in solid state batteries, but they are unstable in contact with the lithium metal anode. The forming solid electrolyte interphase is analyzed herein, using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and impedance spectroscopy. Additionally, the hetero-interface between Li3InCl6 and Li6PS5Cl is analyzed to highlight the concept of hybrid electrolyte cells.
Supramolecular Assembly
Embedment of Quantum Dots and Biomolecules in a Dipeptide Hydrogel Formed In Situ Using Microfluidics
- Pages: 6798-6806
- First Published: 06 December 2020
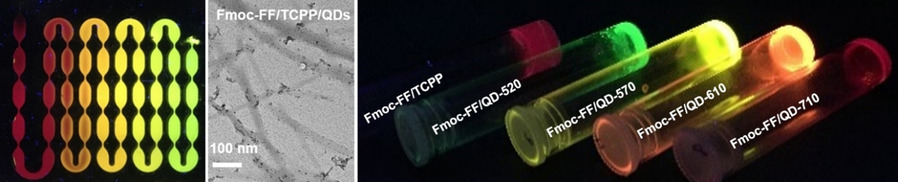
A dipeptide hydrogel was obtained by dynamic assembly in the confined space of continuous-flow microfluidics. Organic porphyrins and inorganic quantum dots (QDs) were integrated in the system for energy transfer, and dynamic structural control over hydrogel formation and QD integration occurred within the microchannel network (see picture).
DNA Nanotechnology | Hot Paper
Scan and Unlock: A Programmable DNA Molecular Automaton for Cell-Selective Activation of Ligand-Based Signaling
- Pages: 6807-6817
- First Published: 16 December 2020
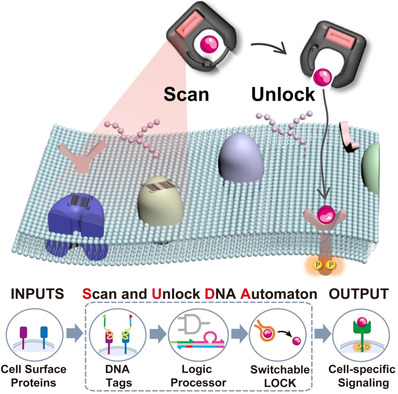
An intelligent molecular-lock device of signaling ligand proteins, termed „scan and unlock“ DNA automaton (SUDA), is presented. The SUDA employs DNA chemical reaction networks to autonomously scan and logically evaluate the cell-surface-protein profile of the designated cell type, selectively unlocking the signaling ligand–receptor interactions for cell-specific signaling.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Adaptive Chirality of an Achiral Cucurbit[8]uril-Based Supramolecular Organic Framework for Chirality Induction in Water
- Pages: 6818-6825
- First Published: 01 December 2020
![Adaptive Chirality of an Achiral Cucurbit[8]uril-Based Supramolecular Organic Framework for Chirality Induction in Water](/cms/asset/67be4275-f54d-4421-a339-31192034cc13/ange202012681-toc-0001-m.jpg)
An achiral supramolecular organic framework (SOF) exhibits adaptive chirality with dual circular dichroism and circularly polarized luminescence responses when meeting various chiral guests, including L-/D-Phe, adenosine derivatives, and peptides/proteins via chirality induction in water. The adaptive chirality of the SOF can be used as a chiroptical platform to determine the enantiopurity, develop aqueous CPL materials, and distinguish peptides/proteins.
Bioinorganic Chemistry | Hot Paper
A Pseudotetrahedral Terminal Oxoiron(IV) Complex: Mechanistic Promiscuity in C−H Bond Oxidation Reactions
- Pages: 6826-6830
- First Published: 21 December 2020
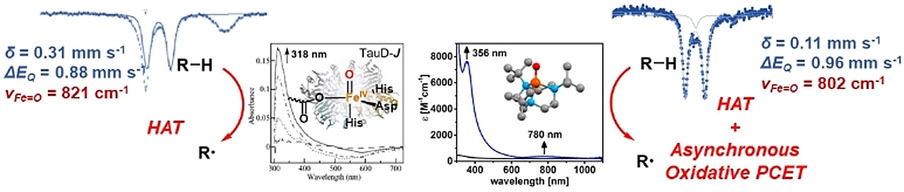
A highly reactive S=2 pseudotetrahedral oxoiron(IV) complex 2 supported by a sterically demanding 1,4,7-tri-tert-butyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane ligand has been synthesized and spectroscopically characterized as one of the best electronic and functional models for a biological oxoiron(IV) intermediate of taurine dioxygenase (TauD-J).
Frustrated Lewis Pairs
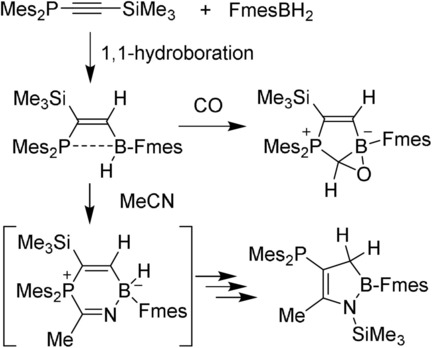
Alkyne 1,1-Hydroboration to a Reactive Frustrated P/B-H Lewis Pair
- Pages: 6831-6837
- First Published: 11 December 2020
Self-Assembly
Ultra-Low Molecular Weight Photoswitchable Hydrogelators
- Pages: 6838-6844
- First Published: 09 December 2020
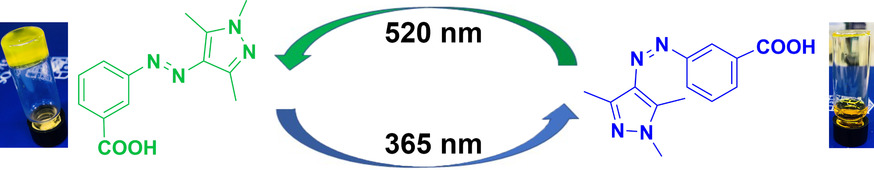
Small, photoswitchable (MW 258 g mol−1) arylazopyrazoles form self-assembled gels in water that can be reversibly cycled between a gel and solution state using two different excitation wavelengths that cause „thinning“ of the gel fibers upon the light induced E to Z isomerisation. These materials could be used for light-controlled cargo release.
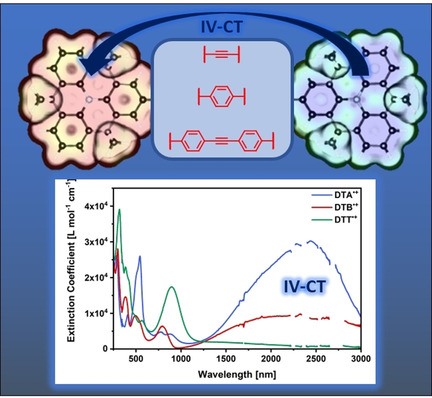
N-Heterotriangulene
Vorplanarisierte Triphenylamin-basierte lineare gemischtvalente Ladungstransfersysteme
- Pages: 6845-6851
- First Published: 11 December 2020
Kreuzkupplungen
Kupplung von Reformatsky-Reagenzien und Arylchloriden ermöglicht durch Ylid-funktionalisierte Phosphanliganden
- Pages: 6852-6858
- First Published: 11 January 2021
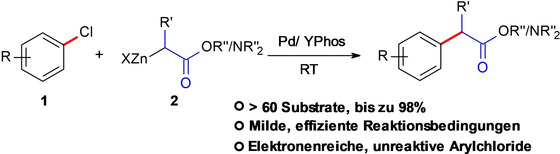
Ylid-funktionalisierte Phosphane wurden für die Anforderungen von Negishi-Kupplungen von Arylchloriden bei Raumtemperatur maßgeschneidert. Der YPhos/Pd-Katalysator ist hocheffizient für die Kupplung mit Arylchloriden im Allgemeinen, und die Reaktion zeigt eine ausgezeichnete Kompatibilität gegenüber funktionellen Gruppen. Dies ermöglicht die selektive Kupplung von Arylelektrophilen in konkurrierenden Reaktionen, wie bei der Synthese von Ibuprofen demonstriert.
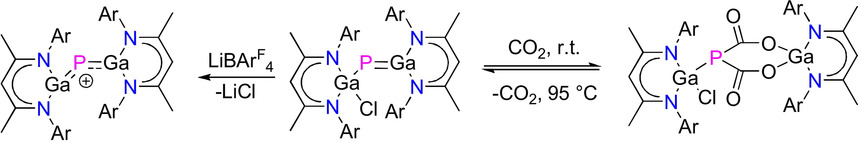
Hauptgruppenelemente | Hot Paper
Vielseitiges Gallaphosphen: Von einem Ga-P-Ga-Heteroallylkation über CO2-Speicherung hin zu C(sp3)-H-Bindungsaktivierung
- Pages: 6859-6865
- First Published: 24 December 2020
Magnetresonanztomographie | Hot Paper
Singulett-Kontrast-Magnetresonanztomographie: Freisetzung der Hyperpolarisation durch den Metabolismus
- Pages: 6866-6873
- First Published: 19 December 2020
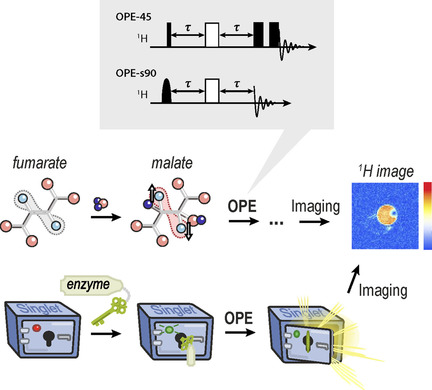
Der durch Hydrierung mit Parawasserstoff erzeugte 1H-Singulettzustand von Fumarate wird durch enzymatische Konversion in Malat umgewandelt, was die hyperpolarisierten NMR-Signale freisetzt. Wir demonstrieren zwei „Out-of-Phase Echo“ Pulssequenzen die den I1zI2z Zustand in 1H-Nettomagnetisierung umwandeln und zeigen die Anwendung in der hyperpolarisierten 1H-Bildgebung.
Chemische Sonden | Hot Paper
Eine Strategie zur Ligandenselektion identifiziert chemische Sonden für die Markierung von SARS-CoV-2-Proteasen
- Pages: 6874-6881
- First Published: 21 December 2020
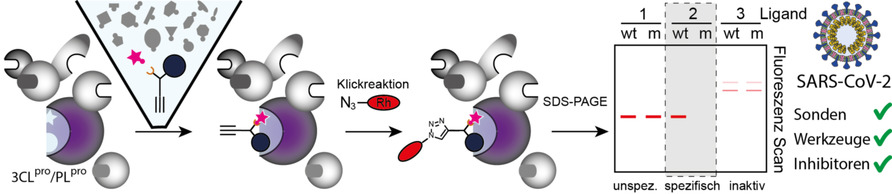
Die Feinabstimmung der Ligandenstruktur ermöglicht es, chemische Sonden schnell auf Wirksamkeit und Spezifität für das aktive Zentrum von Proteasen zuzuschneiden. Eine Anwendung zur Ligandenselektion wird durch die Entwicklung von Sonden für die beiden nicht homologen, aber essentiellen Proteasen von SARS-CoV-2 demonstriert, womit komplementäre chemische Werkzeuge für die proteomische Markierung und die Entdeckung von Inhibitoren verfügbar gemacht werden.
Katalyse
Ameisensäure-unterstützte selektive Hydrogenolyse von 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural zu 2,5-Dimethylfuran über bifunktionale Pd-Nanopartikel auf N-dotiertem mesoporösem Kohlenstoff als Träger
- Pages: 6882-6891
- First Published: 07 December 2020
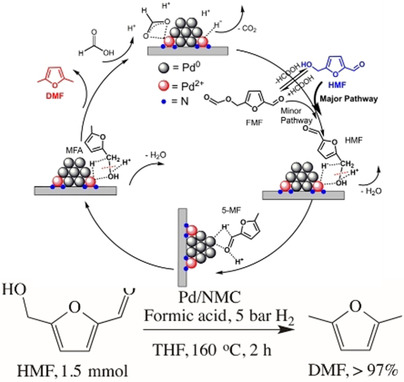
Die quantitative Umwandlung von HMF zu DMF wurde in Gegenwart von Ameisensäure und H2 über dem bifunktionellen Pd/NMC-Katalysator innerhalb von 2 h erreicht. Experimentelle Untersuchungen und DFT-Berechnungen ergaben, dass Ameisensäure die Reaktionsgeschwindigkeit deutlich erhöht und den dominanten Reaktionsweg von der Hydrierung der Aldehydgruppe zur Hydrogenolyse der Hydroxymethylgruppe über deren Protonierung verschiebt.
Schwarzer Phosphor / Phosphoren | Hot Paper
Bildungsmechanismen für Phosphoren und SnIP
- Pages: 6892-6899
- First Published: 29 January 2021
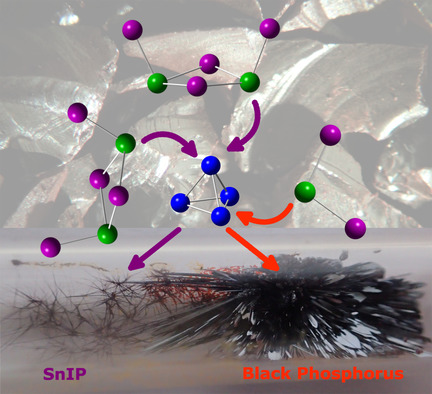
Doppelhelikales 1D-SnIP und 2D-Phosphoren entstehen in einer Gasphasenreaktion aus weißem Phosphor (P4) und SnI2. Mittels P4-Aktivierung wird das Helix-Wachstum oder die Phosphorenbildung initiiert. Sn2I4-Dimere koordinieren die freien Elektronenpaare des Phosphors beim SnIP, während eine direkte Sn-Insertion in die P-P-Bindung zur Phosphorenbildung führt. Beide Reaktionswege werden zwischen 0 K und den jeweiligen Synthesetemperaturen beleuchtet.






![Elektrooxidative Rhodium-katalysierte [5+2]-Anellierung durch C-H/O-H-Aktivierung](/cms/asset/1f4e1a65-0af4-4b06-9135-a978db7f3615/ange202016895-toc-0001-m.jpg)
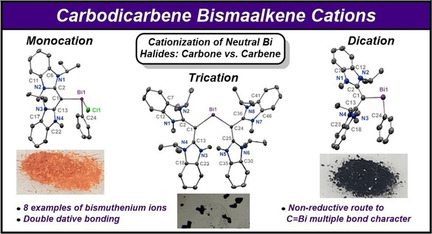
 Bi double dative bonds. The synthesis of these compounds represents a unique non-reductive route to C=Bi double-bond character.
Bi double dative bonds. The synthesis of these compounds represents a unique non-reductive route to C=Bi double-bond character.