Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Titelbild
Titelbild: Stabilization of Undercooled Metals via Passivating Oxide Layers (Angew. Chem. 11/2021)
- Page: 5633
- First Published: 02 February 2021

Kühle Frustration. Variieren der Zusammensetzung in einer dünnen Oberflächenoxidschicht eines Metallpartikels und deren Stabilisierung durch geeignete Liganden führen zu einer starken Oberflächenspannung, die die Erstarrung vereitelt. Chemische Potentialgradienten durch induktive Effekte der Liganden tragen zur Stabilisierung eines metastabilen Zustands bei. Es bildet sich ein unterkühltes flüssiges Metallteilchen, was ein neues Konzept für das gezielte Engineering der Energielandschaft eines Materials unter Verwendung einer dünnen Oberflächenschicht aufzeigt, wie Martin Thuo et al. in ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 5993 beschreiben.
Innentitelbild: Nanoskaliger hybrider amorph/graphitischer Kohlenstoff als Schlüssel zur nächsten Generation von kohlenstoffbasierten Katalysatoren für oxidative Dehydrierungen (Angew. Chem. 11/2021)
- Page: 5634
- First Published: 01 February 2021

Kristallinität ist der Schlüssel für das Design einer neuen Generation kohlenstoffbasierter Katalysatoren für die oxidative Dehydrierung von Ethanol zu Acetaldehyd. In ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 5962 berichten Bastian J. M. Etzold und Mitarbeiter über die Synthese eines neuartigen Kohlenstoffkatalysators, der eine vergleichsweise große Partikelgröße (100 μm) aufweist und gleichzeitig eine leicht zugängliche kristalline Nanostruktur besitzt. Mit diesem neuen Katalysatorsystem konnten im Vergleich zu Kohlenstoff-Nanoröhren um eine Größenordnung höhere Raum-Zeit-Ausbeuten erzielt werden.
Innenrücktitelbild: Electrochemical Polymerization Provides a Function-Integrated System for Water Oxidation (Angew. Chem. 11/2021)
- Page: 6251
- First Published: 04 January 2021

Die Wasseroxidation ist eine Schlüsselreaktion in der natürlichen und künstlichen Photosynthese. In ihrem Forschungsartikel auf S. 6030 berichten Mio Kondo, Shigeyuki Masaoka et al. über eine einfache Strategie zur Integration von katalytischen Zentren und Lochtransportsystemen, ähnlich wie beim natürlichen Wasseroxidationskatalysator. Ein Metallkomplex-Vorläufer wurde elektrochemisch polymerisiert, und das erhaltene Polymermaterial zeigt eine ausgezeichnete Lochtransportfähigkeit und katalysiert die Wasseroxidation mit hoher Leistung.
Rücktitelbild: Light-Triggered Transformable Ferrous Ion Delivery System for Photothermal Primed Chemodynamic Therapy (Angew. Chem. 11/2021)
- Page: 6252
- First Published: 01 February 2021

Ein lichtgetriggertes Fe2+-Freisetzungssystem (LET-6) für die photothermische chemodynamische Therapie wird im Forschungsartikel von Jing Lin und Mitarbeitern auf S. 6112 beschrieben. Die thermische Expansion von LET-6 durch 808-nm-Laserbestrahlung bricht LET-6 in kleine Fragmente auf und löst die Freisetzung von Fe2+ sowie die Erzeugung von .OH für eine verbesserte CDT aus.
Frontispiz
Frontispiz: Das riechende Prinzip des Vetiveröls, aufgeklärt durch chemische Synthese
- First Published: 01 March 2021

Duftstoffchemie In der Zuschrift auf S. 5728 stellen Philip Kraft, Benjamin List et al. eine kurze stereoselektive Totalsynthese von (+)-2-epi-ziza-6(13)en-3-on vor.
Frontispiz: Die entscheidende Rolle von lokalen Ladungsfluktuationen beim Wachstum von Dendriten auf Lithium-Elektroden
- First Published: 01 March 2021

Batterien Im Forschungsartikel auf S. 5940 erläutern Elizabeth Santos und Wolfgang Schmickler die zentrale Rolle von lokalen Überschussladungen beim Dendritwachstum auf Lithiumelektroden.
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis: Angew. Chem. 11/2021
- Pages: 5637-5660
- First Published: 01 March 2021
Berichtigungen
Berichtigung: Synthesis of Polybenzoacenes: Annulative Dimerization of Phenylene Triflate by Twofold C−H Activation
- Page: 5659
- First Published: 01 March 2021
Berichtigung: Deep Eutectic Supramolecular Polymers: Bulk Supramolecular Materials
- Page: 5660
- First Published: 01 March 2021
Berichtigung: Sulfur(IV)-Mediated Unsymmetrical Heterocycle Cross-Couplings
- Page: 5660
- First Published: 01 March 2021
Kurzaufsätze
Synthetic Biology
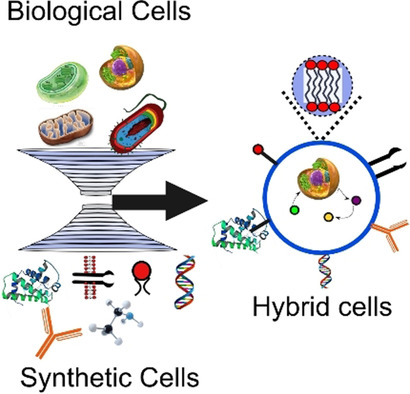
Interfacing Living and Synthetic Cells as an Emerging Frontier in Synthetic Biology
- Pages: 5662-5671
- First Published: 10 September 2020
Metal–Organic Frameworks
2D Conductive Metal–Organic Frameworks: An Emerging Platform for Electrochemical Energy Storage
- Pages: 5672-5684
- First Published: 25 May 2020
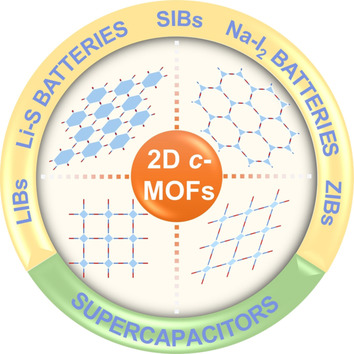
Thanks to their predesigned structure, intrinsic porosity and decent conductivity, 2D c-MOFs have attracted considerable attention especially in electrochemical energy storage. In this Minireview, the progress of 2D c-MOFs is surveyed with a focus on the structural design principles, electrical properties and potential applications in supercapacitors and batteries.
Aufsätze
Tumortherapeutika
Zielgerichtete Wirkstoffe für die Krebstherapie: Aktuelle Entwicklungen und Perspektiven
- Pages: 5686-5705
- First Published: 24 February 2020
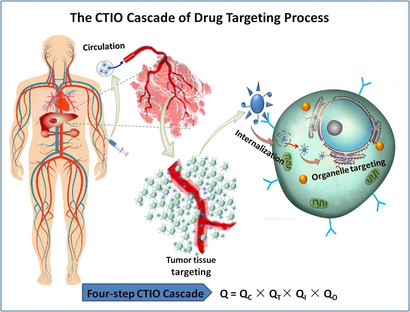
Schwerwiegende Nebenwirkungen und mangelhafte therapeutische Wirksamkeit sind die hauptsächlichen Nachteile der derzeitigen Krebsmedikamente. Diese Problematik kann durch gezielte Ansteuerung, sogenanntes Targeting, minimiert werden, jedoch ist die zielgerichtete Wirksamkeit gegenwärtiger Medikamente noch dürftig und benötigt dringend Verbesserungen.
Biokatalyse
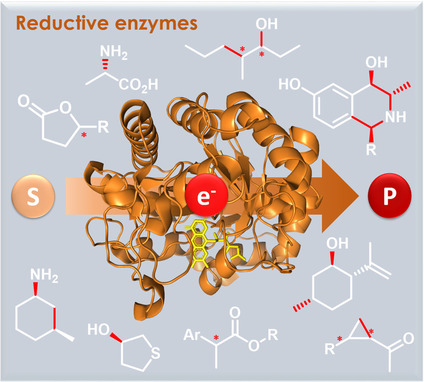
Biokatalytische Reduktionen aus der Sicht eines Chemikers
- Pages: 5706-5727
- First Published: 24 April 2020
Zuschriften
Riechstoffchemie | Hot Paper
Das riechende Prinzip des Vetiveröls, aufgeklärt durch chemische Synthese
- Pages: 5728-5735
- First Published: 14 December 2020

Trotz des Fortschritts der modernen Analytik ist das riechende Prinzip des Vetiveröls aufgrund seiner äußerst komplexen Matrix aus über 150 Komponenten immer noch unbekannt. Eine stereoselektive Totalsynthese beweist, dass (+)-2-epi-Ziza-6(13)en-3-on der Schlüssel zur quasi-pheromonartigen Aura von Vetiver ist, die auf magische Weise der von Iso E Super ähnelt.
Supramolekulare Chemie | Hot Paper
Teerfarben-basierte Koordinationskäfige und -helikate
- Pages: 5736-5741
- First Published: 27 November 2020
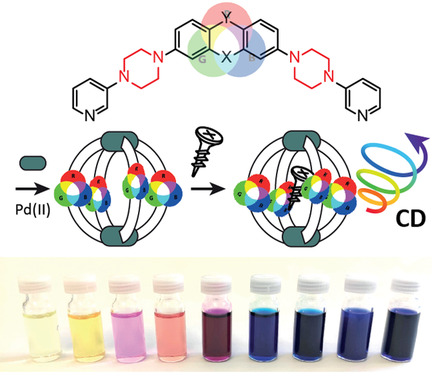
Eine Familie lange bekannter organischer Farbstoffe wurde mittels einer neuartigen Piperazin-Linker-Strategie unter Erhaltung auxochromer Substituenten in dreidimensionale, selbstassemblierte Nanoobjekte integriert. Die dynamische Natur der laternenförmigen Käfige und Helikate erlaubt die Erkennung enantiomerenreiner Gäste über Chiralitätstransfer auf den Wirt, gemessen über CD-Spektrsokopie bis weit ins sichtbare Spektrum.
Schwefelsäure-Analogon
Tetraimidoschwefelsäure H2S(NtBu)4 – isovalenzelektronisch zu H2SO4
- Pages: 5742-5746
- First Published: 22 January 2021
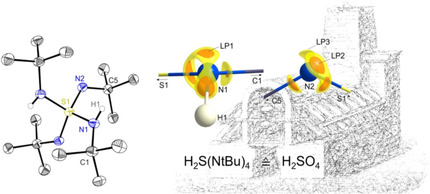
H2S(NtBu)4 wurde synthetisiert, isoliert und mittels NMR-Spektroskopie und hochaufgelöster Röntgenladungsdichteanalyse charakterisiert. Die topologischen Parameter ρ(r), ∇2ρ(r) und ϵ beschreiben die zwei unterschiedlichen Amido-S-N(H)tBu- und Imido-S-NtBu-Bindungen als stark polarisierte Einfachbindungen. Die komplette SN4-Einheit kann sich dabei leicht an unterschiedliche elektronische Anforderungen anpassen.
Sulfathydride
Na3SO4H – ein erster Vertreter der Materialklasse der Sulfathydride
- Pages: 5747-5751
- First Published: 13 January 2021
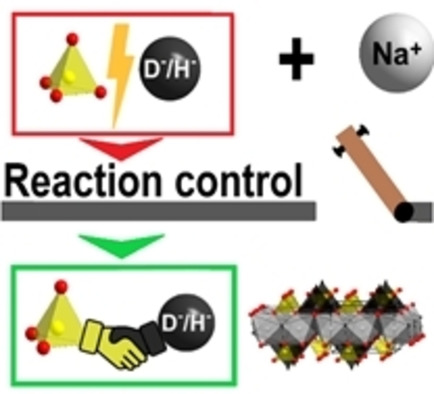
Mittels exakter Reaktionskontrolle konnte ein neuartiges Sulfathydrid – der erste Vertreter einer neuen Materialklasse – hergestellt werden. Eine Reihe an verschiedenen Methoden, wie Neutronen- und Röntgenbeugung, Festkörper-NMR, Schwingungsspektroskope und Dichtefunktionalberechnungen, wird angewendet.
C-H-Aktivierung | Hot Paper
Regioselektive und redox-neutrale Cp*IrIII-katalysierte allylische C-H-Alkinylierung
- Pages: 5752-5756
- First Published: 05 January 2021
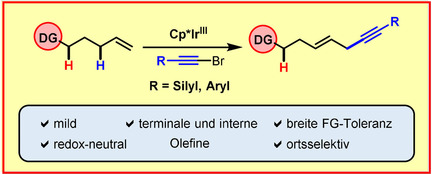
Iridium-Allyl-Paar! Hierin beschreiben wir eine Cp*IrIII-katalysierte hochregioselektive und redoxneutrale Alkinylierung von unaktivierten Olefinen mit Bromalkinen über allylische C-H-Aktivierung. Diese undirigierte C-H-Funktionalisierung war bevorzugt gegenüber anderen typischerweise verwendeten dirigierenden Gruppen, einschließlich Ketonen, Estern und stark koordinierenden Oximen.
C−H Activation
Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed Synthesis of Skipped Enynes via C(sp3)–H Alkynylation of Terminal Alkenes
- Pages: 5757-5762
- First Published: 06 January 2021
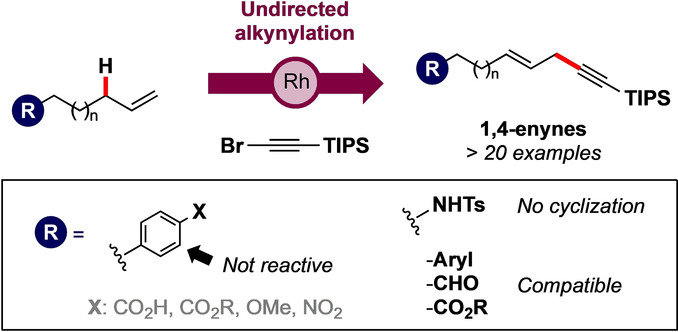
Non-activated olefins react with TIPS-bromoacetylene under directing group-free RhIII catalysis to afford 1,4-enynes in a linear-selective fashion. The developed protocol performs on mild conditions and a vast array of functional groups are tolerated, including weak aryl-directing groups and disubstituted olefins, where no over functionalization is observed. Additionally, α,β- and β,γ-unsaturated amides provide Z-enynes and E- enediynes.
Imaging Agents | Hot Paper
A Functional Chemiluminescent Probe for in Vivo Imaging of Natural Killer Cell Activity Against Tumours
- Pages: 5763-5767
- First Published: 10 December 2020
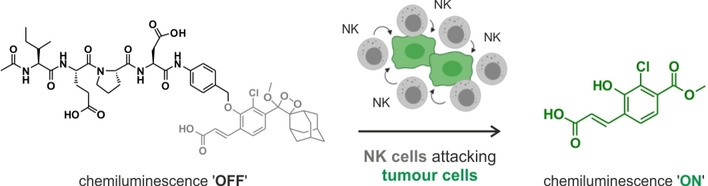
In vivo detection of natural killer (NK) cell activity against tumours was achieved with an activatable chemiluminescent probe containing a granzyme B-reactive peptide substrate linked to a phenoxydioxetane scaffold through a p-aminobenzyl alcohol linker. The rapid and specific chemiluminescence response of the probe was used to detect NK cell activity against breast cancer cells in living mice.
Enzyme Mechanisms | Very Important Paper
Structural Characterization of Two CO Molecules Bound to the Nitrogenase Active Site
- Pages: 5768-5771
- First Published: 14 December 2020
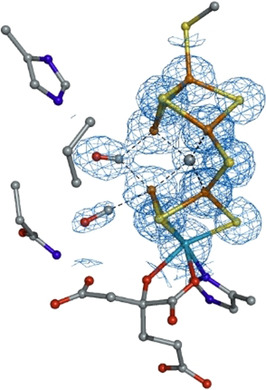
Besides reducing dinitrogen, nitrogenases reduce CO to hydrocarbons, mediating C−C bond formation between multiple CO-derived ligands. To shed light on how multiple C-based ligands bind to the active site, we report a 1.33 Å resolution crystal structure of two CO ligands coordinated to the FeMo-cofactor of molybdenum nitrogenase (see picture). The second CO ligand is coordinated to Fe6 in a previously unreported ligand binding mode.
Reaction Mechanisms | Very Important Paper
Spectroscopic Verification of Adsorbed Hydroxy Intermediates in the Bifunctional Mechanism of the Hydrogen Oxidation Reaction
- Pages: 5772-5775
- First Published: 16 December 2020
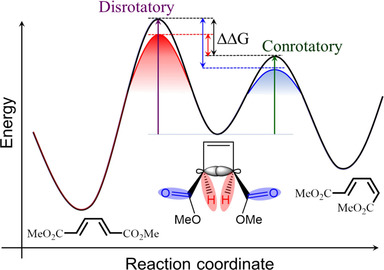
Strong Coupling | Hot Paper
Modifying Woodward–Hoffmann Stereoselectivity Under Vibrational Strong Coupling
- Pages: 5776-5781
- First Published: 11 December 2020
Energy Storage | Hot Paper
Ammonium-Ion Storage Using Electrodeposited Manganese Oxides
- Pages: 5782-5786
- First Published: 15 December 2020
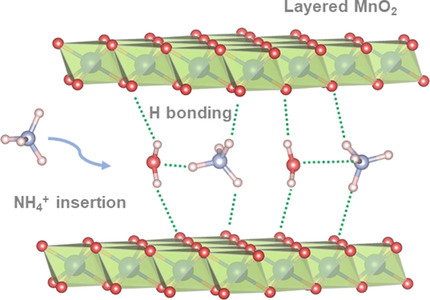
NH4+ storage using electrodeposited manganese oxides (MnOx) is studied for the first time. MnOx exhibits structural transformation during charge/discharge in dilute ammonium acetate (NH4Ac) electrolyte. Experimental and theoretical results suggest that the reversible NH4+ insertion/deinsertion in layered MnOx is associated with hydrogen-bond formation/breaking between NH4+ and the MnOx layers.
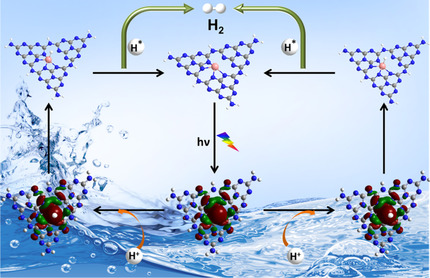
Hydrogen Generation | Hot Paper
Reactivity and Mechanisms of Photoactivated Heterometallic [RuIINiII] and [RuIINiIIRuII] Catalysts for Dihydrogen Generation from Water
- Pages: 5787-5792
- First Published: 14 December 2020
![Reactivity and Mechanisms of Photoactivated Heterometallic [RuIINiII] and [RuIINiIIRuII] Catalysts for Dihydrogen Generation from Water](/cms/asset/cdc5ef52-aae0-45f6-be45-c37aad25748b/ange202013678-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Two new heterometallic photocatalysts were probed for water reduction. While the bimetallic [RuIINiII] requires an external photosensitizer to be catalytic, the trinuclear heterometallic [RuIINiIIRuII] produces dihydrogen when irradiated with blue light. Mechanisms are proposed to account for these observations.
Metal–Organic Frameworks | Hot Paper
Synthesis of Polycarboxylate Rhodium(II) Metal–Organic Polyhedra (MOPs) and their use as Building Blocks for Highly Connected Metal–Organic Frameworks (MOFs)
- Pages: 5793-5797
- First Published: 11 December 2020
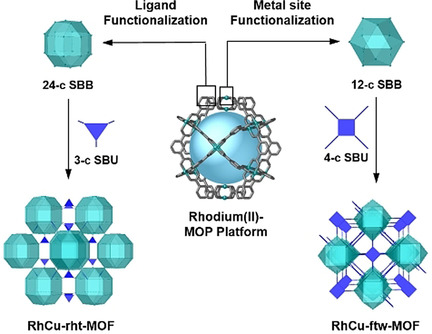
Two different post-synthetic routes have been followed to functionalize pre-synthesized RhII-based cuboctahedral metal–organic polyhedra (MOPs) with carboxylic acid groups, either on their 12 metal sites (vertices) or on their 24 linkers (edges). Such isolated MOPs serve as highly connected (12-c and 24-c) supermolecular building blocks, for the formation of two new bimetallic RhCu-MOF structures.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Highly Potent MRI Contrast Agent Displaying Outstanding Sensitivity to Zinc Ions
- Pages: 5798-5802
- First Published: 23 November 2020
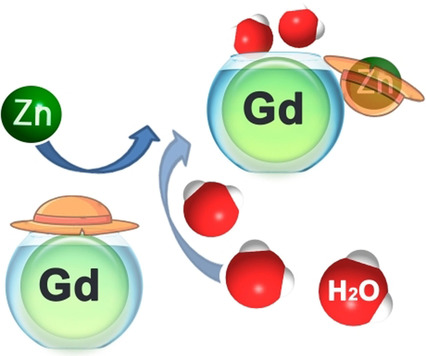
A highly potent MRI contrast agent based on paramagnetic Gd3+ was developed to selectively recognize Zn2+ over other abundant endogenous metal ions. The interaction with Zn2+ modulates the hydration of the complex, leading to a significant increase in its longitudinal relaxivity. The new responsive platform is highly suitable for studying the Zn-related physiological processes at high magnetic fields.
Theranostics | Hot Paper
Concentration-Dependent Subcellular Distribution of Ultrasmall Near-Infrared-Emitting Gold Nanoparticles
- Pages: 5803-5807
- First Published: 18 December 2020
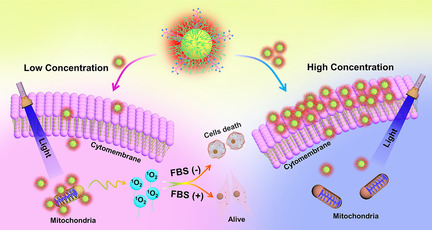
Ultrasmall NIR-emitting CR-AuNPs showed strong membrane binding in high concentration but more mitochondria targeting in lower concentration. This concentration-dependent subcellular distribution performed large advances for photocytotoxicity to tumour cells in a relatively low concentration region, providing the deeper understanding of the ultrasmall luminescent AuNPs in biomedicine.
Colloids
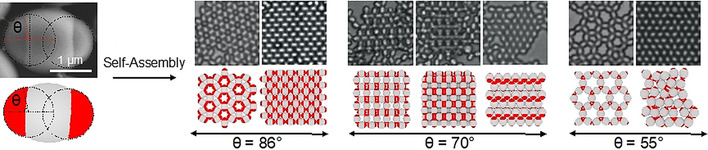
Two-Dimensional (2D) or Quasi-2D Superstructures from DNA-Coated Colloidal Particles
- Pages: 5808-5812
- First Published: 07 December 2020
Biocatalysis
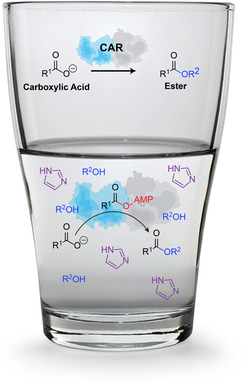
Carboxylic Acid Reductase Can Catalyze Ester Synthesis in Aqueous Environments
- Pages: 5813-5817
- First Published: 28 November 2020
Enzyme Mechanisms
Cysteine Nucleophiles in Glycosidase Catalysis: Application of a Covalent β-l-Arabinofuranosidase Inhibitor
- Pages: 5818-5822
- First Published: 02 February 2021
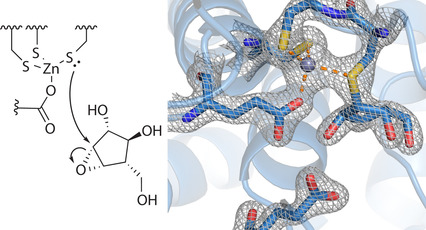
β-l-arabinofuranosidases are thought to make use of a unique zinc-associated cysteine nucleophile to catalyze glycoside hydrolysis. Using a bespoke synthetic covalent inhibitor, this proposed mechanism is put to the test. Mass spectrometry, X-ray crystallography, and mechanistic simulations support the formation of a thioglycosyl enzyme intermediate and reveal how the enzyme facilitates CS bond cleavage.
Cell Surface Engineering
In Situ Synthesis of Photoactive Polymers on a Living Cell Surface via Bio-Palladium Catalysis for Modulating Biological Functions
- Pages: 5823-5829
- First Published: 28 November 2020
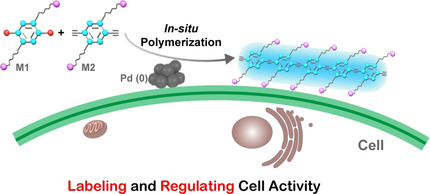
An in situ polymerization strategy to modify cell surface with conjugated polymers was developed by a bio-Pd nanoparticle catalyst on a cell surface. The in situ formed PPE traces the polymerization process, exhibits enhanced antibacterial activity against E. coli, and augments the ATP synthesis of C. pyrenoidosa.
Macrocycles
Azobenzene-Based Macrocyclic Arenes: Synthesis, Crystal Structures, and Light-Controlled Molecular Encapsulation and Release
- Pages: 5830-5834
- First Published: 09 December 2020
Electrocatalysis
Alloying Nickel with Molybdenum Significantly Accelerates Alkaline Hydrogen Electrocatalysis
- Pages: 5835-5841
- First Published: 16 December 2020

Ni4Mo alloy nanoparticles were prepared from the reduction of molybdate-intercalated Ni(OH)2 nanosheets. They exhibited the highest mass activity among all non-precious-metal-based electrocatalysts for the hydrogen-oxidation reaction in our best knowledge as well as a superb hydrogen-evolution-reaction performance in alkaline solution.
Organophosphorus Compounds
Phosphinylation of Non-activated Aryl Fluorides through Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution at the Boundary of Concerted and Stepwise Mechanisms
- Pages: 5842-5846
- First Published: 02 December 2020
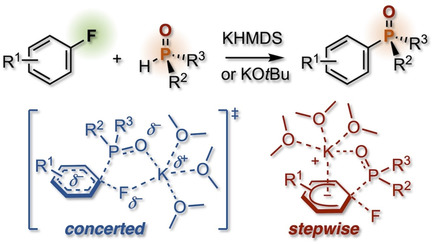
Both electron-neutral and electron-rich non-activated aryl fluorides reacted with potassium diorganophosphinites through a nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) reaction. Even substantially stabilized anionic P nucleophiles reacted to form the corresponding tertiary phosphine oxides. Quantum chemical calculations suggested a nucleophile-dependent mechanism involving both concerted and stepwise SNAr reaction pathways (see scheme).
siRNA Delivery
Cell-Selective siRNA Delivery Using Glycosylated Dynamic Covalent Polymers Self-Assembled In Situ by RNA Templating
- Pages: 5847-5851
- First Published: 08 December 2020
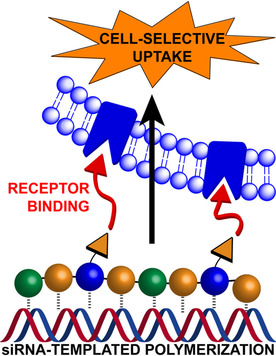
Dynamic covalent polymers are expressed at low concentration by siRNA templating from peptide-based dynamic covalent libraries. Using a glycosylated building block, we show that this templated polymerization further translates into the multivalent presentation of carbohydrate ligands, which subsequently promotes cell uptake and even cell-selective siRNA delivery.
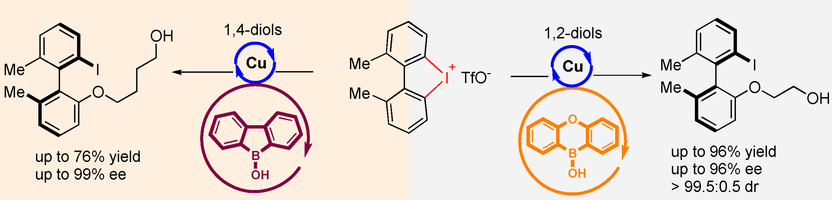
Asymmetric Catalysis
Diols Activation by Cu/Borinic Acids Synergistic Catalysis in Atroposelective Ring-Opening of Cyclic Diaryliodoniums
- Pages: 5852-5857
- First Published: 13 December 2020
Batteries
Rechargeable Aqueous Aluminum Organic Batteries
- Pages: 5858-5863
- First Published: 13 December 2020
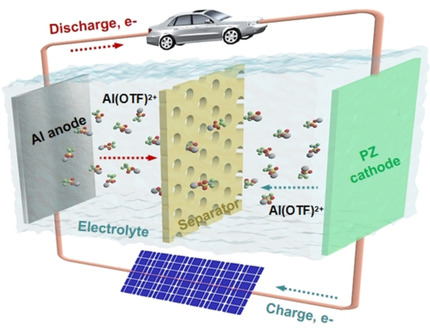
A highly rechargeable aqueous aluminum-organic battery system based on phenazine has been developed. The phenazine cathode undergoes a reversible electrochemical redox with high structural stability to accommodate the large-size aluminum-complex ions (de)insertion, and shows a strikingly stable aluminum storage capacity for promising large-scale energy applications.
Heterogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
Tunable eg Orbital Occupancy in Heusler Compounds for Oxygen Evolution Reaction
- Pages: 5864-5869
- First Published: 10 December 2020
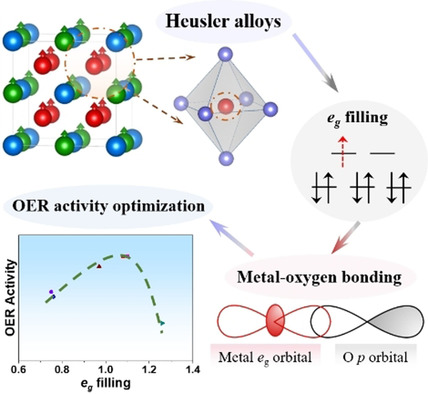
Heusler compounds (Co2YZ) with mechanical robustness, metallic conductivity, and wide tunability in the electronic structure and element compositions, are studied as a new class of oxygen evolution electrocatalysts. The eg orbital filling of active Co sites was precisely regulated by varying the Y and Z sites of the Co2YZ compounds, where the higher catalytic current was achieved for eg orbital filling approaching unity.
Asymmetric Catalysis | Hot Paper
Regiodivergent Synthesis of Spirocyclic Compounds through Pd-Catalyzed Regio- and Enantioselective [3+2] Spiroannulation
- Pages: 5870-5874
- First Published: 20 January 2021
![Regiodivergent Synthesis of Spirocyclic Compounds through Pd-Catalyzed Regio- and Enantioselective [3+2] Spiroannulation](/cms/asset/4672a5ca-8bd0-45e5-9c61-948c4fb98c06/ange202016439-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A Pd0-catalyzed highly regio- and enantioselective [3+2] spiroannulation reaction has been developed for rapid assembly of [5,5] spirocyclic carbo- and heterocycles. The regioselectivity could be dominated by fine-tuning the Pd-π-allyl intermediate. An array of coupling partners could be well-tolerated with excellent regio-, and enantioselectivities. Potential application of the reaction was exemplified by several further transformations.
Metal–Organic Frameworks | Very Important Paper
Fe-O Clusters Anchored on Nodes of Metal–Organic Frameworks for Direct Methane Oxidation
- Pages: 5875-5879
- First Published: 09 November 2020
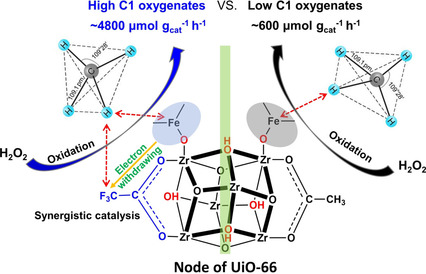
Fe-O clusters are synthesized on nodes of UiO-66 simultaneously coordinated with trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) or acetic acid (AA) for direct methane oxidation. The TFA group coordinated with Zr6 node of UiO-66 enhances the oxidation state of adjacent Fe-O cluster, promotes the activation of C−H bond of methane, and increases its selective conversion into C1 oxygenates.
Carbenes | Hot Paper
Thermally Activated n-Doping of Organic Semiconductors Achieved by N-Heterocyclic Carbene Based Dopant
- Pages: 5880-5884
- First Published: 24 November 2020
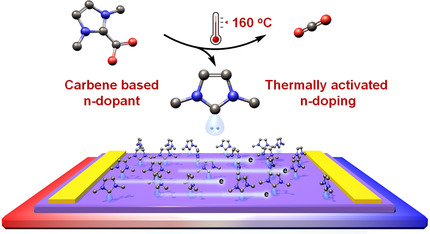
Based on N-heterocyclic carbene, a thermally activated n-dopant with excellent air stability and high n-doping efficacy is developed. It can regenerate N-heterocyclic carbene in situ by decarboxylation for the subsequent n-doping. The thermally activated n-doping increases the air stability of n-dopants and permits n-dopants to be co-processed with polymer FBDPPV noninteractively before heating in air.
Batteries
Transition of the Reaction from Three-Phase to Two-Phase by Using a Hybrid Conductor for High-Energy-Density High-Rate Solid-State Li-O2 Batteries
- Pages: 5885-5890
- First Published: 25 November 2020
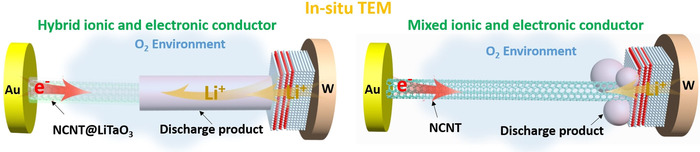
A hybrid electronic and ionic conductor was proposed to build a solid-state air electrode that transforms the solid-state Li-O2 battery electrochemical mechanism from a three-phase to a two-phase process and further enhances the battery performance. The electrochemical effect of the hybrid conductor was shown by an in situ environmental transmission electron microscopy process.
Sensors
Long-Range Exciton Migration in Coassemblies: Achieving High Photostability without Disrupting the Electron Donation of Fluorene Oligomers
- Pages: 5891-5896
- First Published: 16 December 2020

Long-range exciton migration in coassembled superstructural microspheres (SMS) leads to embedding a small number of energy acceptors to afford efficient energy communication with energy donors, which not only creates high photostability but also preserves the properties of energy donors. The advantages of the coassembled SMS are illustrated in the sensitive fluorescence detection of trace explosives.
Polyoxometalates
Accurate Determination of the Quantity and Spatial Distribution of Counterions around a Spherical Macroion
- Pages: 5897-5901
- First Published: 09 December 2020
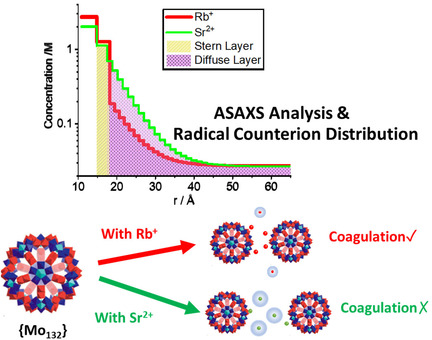
Anomalous small-angle scattering measurements accurately and quantitatively determine the spatial distribution of counterions around a rigid, spherical charged cluster {Mo132}42−, which reveal the secret behind the unusual high solubility of {Mo132} with divalent counterions in comparison to the monovalent ones.
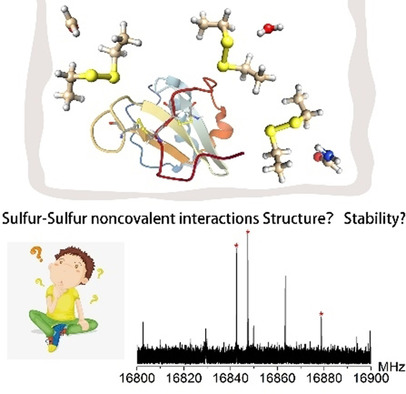
Disulfide-Centered Hydrogen Bonds
The Characteristics of Disulfide-Centered Hydrogen Bonds
- Pages: 5902-5906
- First Published: 30 November 2020
Asymmetric Catalysis
Iridium-Catalyzed Regio- and Enantioselective Borylation of Unbiased Methylene C(sp3)−H Bonds at the Position β to a Nitrogen Center
- Pages: 5907-5911
- First Published: 16 December 2020

Unbiased methylene C(sp3)−H bonds at the position β to a nitrogen center were borylated in an enantioselective manner in the presence of a catalytic amount of a chiral bidentate boryl ligand and an iridium precursor (see scheme). The method tolerated a broad spectrum of functional groups to furnish a variety of C(sp3)−H functionalized products in good yields with excellent enantioselectivity.
Lipid Nanoparticles | Hot Paper
A Systematic Study of Unsaturation in Lipid Nanoparticles Leads to Improved mRNA Transfection In Vivo
- Pages: 5912-5917
- First Published: 10 December 2020
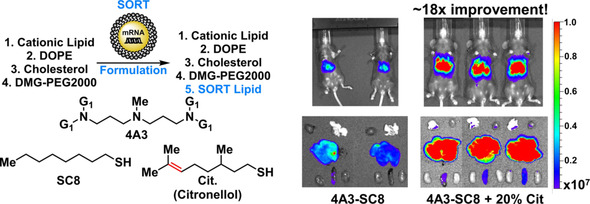
Unsaturated amino lipids were synthesized to study the role of unsaturation in lipid nanoparticle (LNP)-mediated mRNA delivery. A lipid series with a Citronellol tail (4A3-Cit) was identified from a library screen. Employing 4A3-Cit in new Selective ORgan Targeting (SORT) formulation resulted in an 18-fold increase in mRNA expression over saturated LNPs. The findings provide insights into how unsaturation and SORT mixing can promote mRNA delivery.
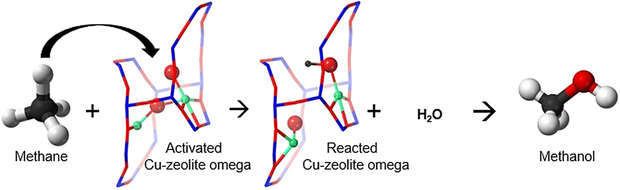
Zeolites
Paired Copper Monomers in Zeolite Omega: The Active Site for Methane-to-Methanol Conversion
- Pages: 5918-5922
- First Published: 08 December 2020
DNA Nanotechnology | Hot Paper
Light-Responsive Dynamic DNA-Origami-Based Plasmonic Assemblies
- Pages: 5923-5927
- First Published: 15 December 2020

The spatial configuration and optical properties of non-photoresponsive DNA-origami-based plasmonic assemblies can be controlled with light using a photoresponsive medium. Upon exposure to visible light, the medium's pH decreases, inducing the formation of DNA triplex links in the plasmonic assemblies, leading to their spatial reconfiguration, which can be reversed by turning the light off.
Nanomaterials
Analogous Mixed Matrix Membranes with Self-Assembled Interface Pathways
- Pages: 5928-5934
- First Published: 10 November 2020
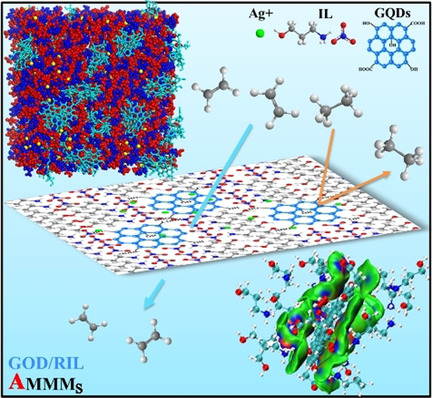
A series of analogous mixed matrix membranes with self-assembled interface pathways were constructed via molecular-level hybridization by utilizing a reactive ionic liquid (RIL) as the continuous phase and graphene quantum dots (GQD) as nanofiller for sub-angstrom-scale ethylene/ethane (0.416 nm/0.443 nm) separation. Importantly, the interfacial pathway structure was visualized and the self-assembly mechanism was revealed.
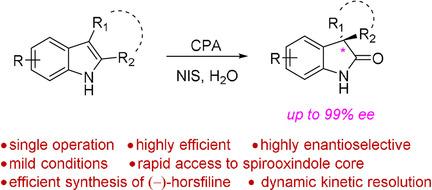
Asymmetric Catalysis | Hot Paper
Catalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of Spirooxindoles by Oxidative Rearrangement of Indoles
- Pages: 5935-5939
- First Published: 06 December 2020
Forschungsartikel
Lithiumbatterien | Hot Paper
Die entscheidende Rolle von lokalen Ladungsfluktuationen beim Wachstum von Dendriten auf Lithium-Elektroden
- Pages: 5940-5945
- First Published: 12 January 2021
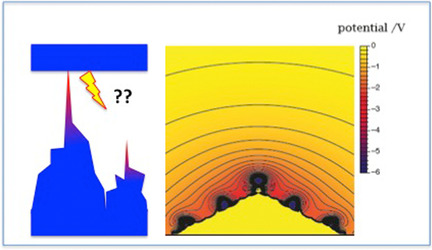
Batterien mit reinem Li als Elektrodenmaterial versprechen eine höhere Energiedichte als Li-Ionen-Batterien, bei denen die Ionen in Graphit gespeichert werden. Jedoch bilden sich an reinen Li-Elektroden Dendriten, die zum Kurzschluss führen können. Rechnungen zeigen, dass sich Überschussladung auf der Spitze kleiner Unebenheiten konzentriert, wo sie ein starkes elektrisches Feld erzeugt, das Li+ anzieht, die Spitze weiter wachsen lässt und schließlich zur Bildung von Dendriten führt.
Rhodiumhydride
Synthese und Hydrierung schwerer Homologe eines Rhodium-Carbins: [(Me3P)2(Ph3P)Rh≡E-Ar*] (E=Sn, Pb)
- Pages: 5946-5953
- First Published: 13 January 2021
![Synthese und Hydrierung schwerer Homologe eines Rhodium-Carbins: [(Me3P)2(Ph3P)Rh≡E-Ar*] (E=Sn, Pb)](/cms/asset/c4ac5421-599f-44c4-b296-1dbe21a5cbee/ange202015725-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Schwere Homologe eines Rhodium-Carbins mit einer Rh≡Sn- oder Rh≡Pb-Dreifachbindung wurden durch Dehydrierung der entsprechenden Rhodiumdihydridkomplexe [(Ph3P)2RhH2SnAr*] und [(Ph3P)2RhH2PbAr*] synthetisiert. Die Synthese erfolgte durch Umsetzung des nukleophilen Organodihydridostannats mit [(Ph3P)3RhCl] oder in einer Hydridtransferreaktion zwischen [(Ph3P)3RhH] und Organoelementhydriden des Zinns oder Bleis.
CO-Oxidation
Nanopartikel auf subnanometer dünnen oxidischen Filmen: Skalierung von Modellsystemen
- Pages: 5954-5961
- First Published: 08 December 2020
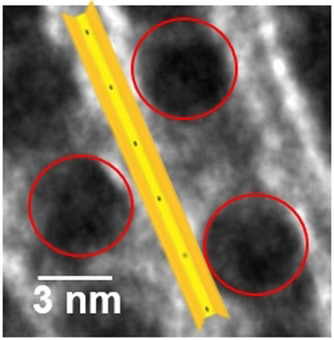
Palladium-Nanopartikel wurden teilweise von subnanometerdicken Schichten aus Hectorit bedeckt. Aufgrund elektronischer Wechselwirkungen zwischen den Nanopartikeln und den ultradünnen Schichten waren die Nanopartikel positiv geladen. Dies wiederum erhöhte die Aktivität in der Oxidation von Kohlenmonoxid.
Heterogene Katalyse
Nanoskaliger hybrider amorph/graphitischer Kohlenstoff als Schlüssel zur nächsten Generation von kohlenstoffbasierten Katalysatoren für oxidative Dehydrierungen
- Pages: 5962-5971
- First Published: 26 January 2021
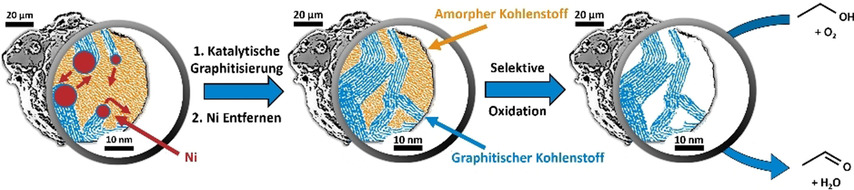
Ein amorph/graphitisches Hybridmaterial wurde synthetisiert, indem nanoskalige Graphitkristallite in einem polymer-abgeleiteten „Nicht-nano“-Kohlenstoff durch katalytische Graphitisierung gezüchtet wurden. Ein aktiver Dehydrierungskatalysator wurde durch das Erzeugen von Zugänglichkeit zu diesen graphitischen Domänen durch selektive Oxidation erhalten. Der Katalysator bietet 10-fach höhere Raum-Zeit-Ausbeuten bei der oxidativen Ethanol-Dehydrierung als ein CNT-Benchmark.
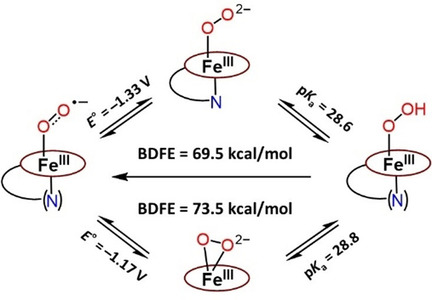
Ferric Heme Complexes | Hot Paper
Ferric Heme Superoxide Reductive Transformations to Ferric Heme (Hydro)Peroxide Species: Spectroscopic Characterization and Thermodynamic Implications for H-Atom Transfer (HAT)
- Pages: 5972-5977
- First Published: 21 December 2020
Biocatalysis | Very Important Paper
In Vivo Assembly of Artificial Metalloenzymes and Application in Whole-Cell Biocatalysis
- Pages: 5978-5985
- First Published: 11 January 2021
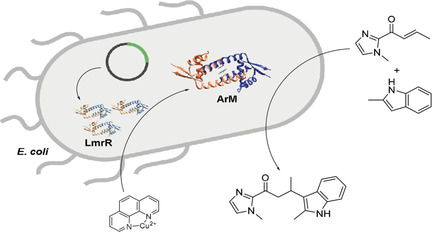
Artificial metalloenzymes were created by supramolecular assembly in the cytoplasm of E. coli cells. The cells were then applied to the enantioselective biocatalysis of a Friedel–Crafts alkylation of indoles (see picture) and a Diels–Alder reaction. Directed evolution of the artificial metalloenzymes inside the cells provided improved variants for both whole-cell biocatalytic reactions.
Fluorescent Probes | Very Important Paper
Activatable Polymeric Nanoprobe for Near-Infrared Fluorescence and Photoacoustic Imaging of T Lymphocytes
- Pages: 5986-5992
- First Published: 10 December 2020
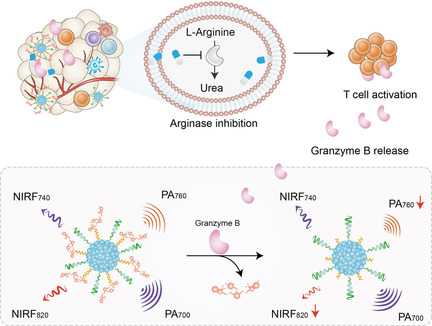
An activatable semiconducting polymer nanoprobe (SPNP) is synthesized for near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) and photoacoustic (PA) detection of granzyme B, a biomarker related to activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. SPNP actively targets the tumor and reacts with granzyme B to release the dye-labeled peptide, leading to ratiometric NIRF/PA imaging of T lymphocytes during cancer immunotherapy.
Phase Transformation
Stabilization of Undercooled Metals via Passivating Oxide Layers
- Pages: 5993-6000
- First Published: 30 December 2020
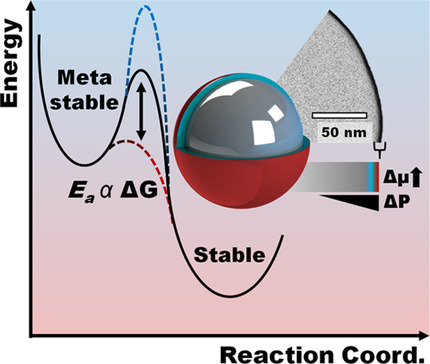
The potential effect of the static surface tensor for metal alloy surfaces is found to be significantly larger than size-related effects as demonstrated by oxide shell and stabilizing ligand composition. Considering these finds, the free-energy equation related to solid–liquid phase transformation, under the classical nucleation theory, is extended to incorporate the stress-component resulting from the passivating shell.
Zeolites | Hot Paper
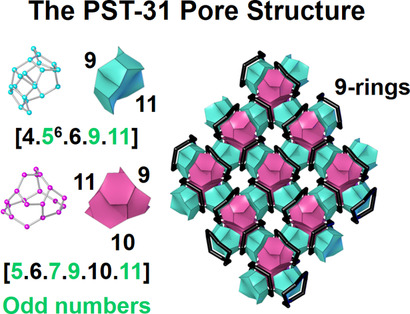
An Aluminosilicate Zeolite Containing Rings of Tetrahedral Atoms with All Odd Numbers from Five to Eleven
- Pages: 6001-6005
- First Published: 14 December 2020
Supramolecular Chemistry
Masked Alkyne Equivalents for the Synthesis of Mechanically Interlocked Polyynes
- Pages: 6006-6012
- First Published: 30 November 2020
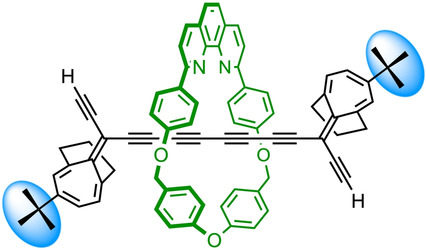
Active-metal-template synthesis has been used to prepare a [2]rotaxane in which the whole dumbbell component is a masked C16H2 polyyne. t-Butyl substituents make the photo-labile terminal groups bulky enough to act as stoppers and prevent unthreading of the macrocycle. Rotaxanes of this type are promising intermediates in the synthesis of mechanically interlocked carbon-rich architectures, such as cyclocarbon catenanes and carbyne polyrotaxanes.
DNA Nanomachine
Endogenous mRNA Triggered DNA-Au Nanomachine for In Situ Imaging and Targeted Multimodal Synergistic Cancer Therapy
- Pages: 6013-6023
- First Published: 02 December 2020
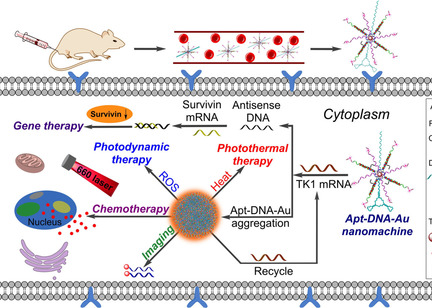
A multifunctional DNA-Au nanomachine which can be triggered by endogenous tumor growth-related TK1 mRNA has been devised as the combinatorial theranostic agent for fluorescence imaging-guided chemo, genic, photodynamic, and photothermal synergistic targeted therapy of breast cancer. This theranostic nanoplatform achieves the significant inhibition of tumor growth and improvement of therapeutic efficacy through in situ imaging.
Nanoclusters | Hot Paper
Carboranealkynyl-Protected Gold Nanoclusters: Size Conversion and UV/Vis–NIR Optical Properties
- Pages: 6024-6029
- First Published: 14 December 2020

A carboranealkynyl-protected gold nanocluster Au28 possessing an open-shell electronic structure with 13 valence electrons was isolated through a facile self-reduction method in which it undergoes a complete transformation in methanol into a smaller-sized cluster Au23 bearing 12 valence electrons and crystal-field-like split superatomic 1D orbitals. Au28 and Au23 both display optical absorption covering the UV/Vis–NIR range and NIR emission.
Electrocatalysis | Hot Paper
Electrochemical Polymerization Provides a Function-Integrated System for Water Oxidation
- Pages: 6030-6034
- First Published: 30 November 2020
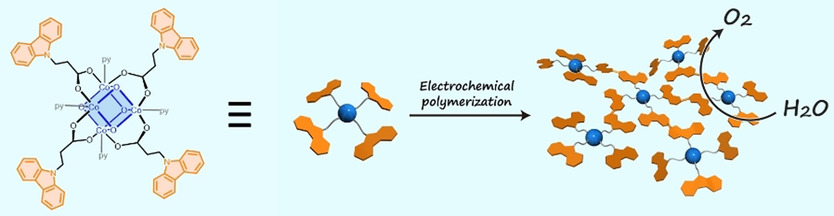
Four-electron oxidation of water with a function-integrated polymer is reported. Electrochemical polymerization provided a material with molecule-based active sites and hole-transporting moieties (see picture). Electrochemical impedance analysis revealed that the hole-transporting polymer reduced charge-transfer resistance. The material catalyzed electrochemical water oxidation with high faradaic efficiency and a low overpotential.
Semiconductors
One-Step Sixfold Cyanation of Benzothiadiazole Acceptor Units for Air-Stable High-Performance n-Type Organic Field-Effect Transistors
- Pages: 6035-6042
- First Published: 14 December 2020
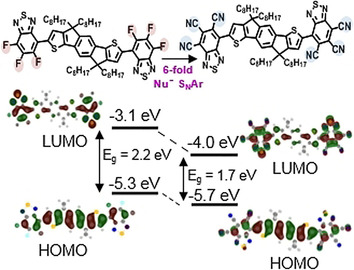
A new strongly electron-accepting end group, 2,1,3-benzothiadiazole-4,5,6-tricarbonitrile (TCNBT), has been prepared by a one-step sixfold nucleophilic substitution reaction. Cyanation results in a significant enhancement of the electron affinity in comparison to the fluorinated analogue, and the material demonstrates promising n-type performance in solution processed organic field-effect transistors with excellent stability.
Battery Materials | Hot Paper
Deeply Cycled Sodium Metal Anodes at Low Temperature and in Lean Electrolyte Conditions
- Pages: 6043-6048
- First Published: 30 November 2020

An ether–ionic liquid composite electrolyte with fast ion transport, superior desolvation capability, and high electrochemical stability is exploited to suppress sodium dendrite growth at low temperatures ranging from 0 to −40 °C. This composite electrolyte enables a stable sodium metal anode to be deeply cycled with an ultrahigh reversible capacity of 50 mAh cm−2 for 500 hours at −20 °C in lean electrolyte (1.0 μL mAh−1) conditions.
Electrocatalysis
Artificial Heterointerfaces Achieve Delicate Reaction Kinetics towards Hydrogen Evolution and Hydrazine Oxidation Catalysis
- Pages: 6049-6058
- First Published: 11 December 2020
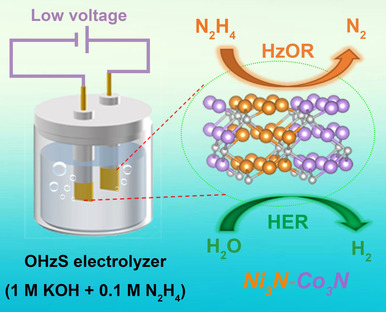
An efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst toward hydrazine-assisted H2 production was designed by constructing the Ni3N-Co3N heterointerfaces on Ni foam (Ni3N-Co3N PNAs/NF). The catalyst can achieve energy-saving hydrogen production in an overall hydrazine splitting (OHzS) unit, showing its potential for practical applications.
Copolymers
Enantioselective, Stereoconvergent Resolution Copolymerization of Racemic cis-Internal Epoxides and Anhydrides
- Pages: 6059-6067
- First Published: 03 December 2020
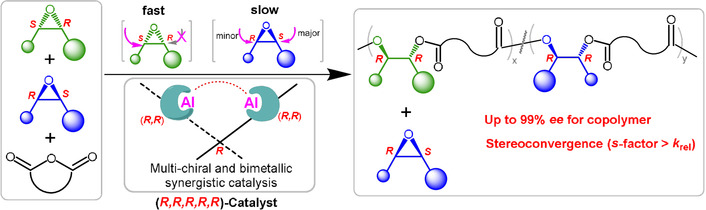
Stereoconvergence is observed in the enantioselective resolution copolymerization of racemic cis-internal epoxides and anhydrides mediated by dinuclear aluminum complexes with multiple chirality, where the selectivity factor for chiral copolymer formation significantly exceeds the kinetic resolution coefficient based on the unreacted substrate at various conversions.
Ring-Opening Polymerization
Unimolecular Anion-Binding Catalysts for Selective Ring-Opening Polymerization of O-carboxyanhydrides
- Pages: 6068-6077
- First Published: 02 December 2020

An effective unimolecular anion-binding organocatalysis is described. Herein, 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine is anchored to a thiourea for ring-opening polymerization of O-carboxyanhydrides (OCAs), which well addresses the formidable challenge of synthesizing high molecular weight stereoregular polyesters.
Donor–Acceptor Systems
Donor/Acceptor Pairs Created by Electrostatic Interaction: Design, Synthesis, and Investigation on the Exciplex Formed Within the Pair
- Pages: 6078-6085
- First Published: 16 December 2020
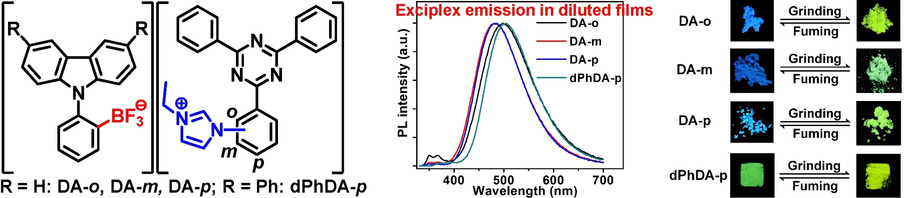
Donor/acceptor pairs are created by electrostatic interaction between an anionic donor and a cationic acceptor, which afford an isolated exciplex with thermally activated delayed fluorescence in a diluted film. Interactions between donor and acceptor are changed by varying the anchoring position of the imidazolium cation in the acceptor. The pairs show mechanochromic luminescence in the solid state and promising performances in light-emitting devices.
Nucleic Acids
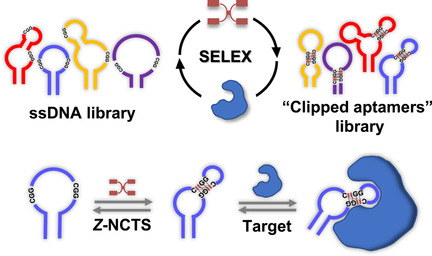
Activation of Aptamers with Gain of Function by Small-Molecule-Clipping of Intramolecular Motifs
- Pages: 6086-6093
- First Published: 18 November 2020
Enzyme Inhibition
Inhibition of Urease, a Ni-Enzyme: The Reactivity of a Key Thiol With Mono- and Di-Substituted Catechols Elucidated by Kinetic, Structural, and Theoretical Studies
- Pages: 6094-6100
- First Published: 27 November 2020
The inhibition of urease by mono- and dimethyl-substituted catechols was investigated. The results reveal the occurrence of an irreversible inactivation of urease by means of a radical-based autocatalytic multistep mechanism and indicate that, among all tested catechols, the mono-substituted 3-methyl-catechol is the most efficient inhibitor.
OLEDs
Novel Series of Mononuclear Aluminum Complexes for High-Performance Solution-Processed Organic Light-Emitting Devices
- Pages: 6101-6106
- First Published: 14 December 2020
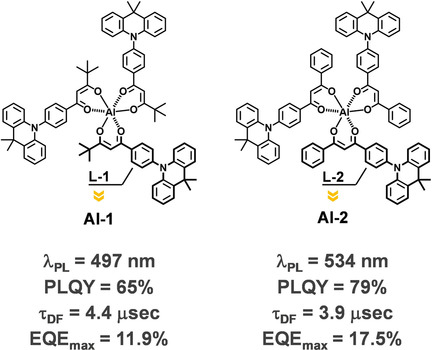
A high photoluminescence quantum yield of up to 79 % with a short delayed fluorescence lifetime of approximately 4 μs in the solid state is possible with a novel series of mononuclear aluminum complexes. Solution-processed organic light-emitting devices based on these Al complexes achieve a high external quantum efficiency of 17.5 % at 100 cd m−2.
Single-Molecule Magnets
Bis-Cyclooctatetraenyl Thulium(II): Highly Reducing Lanthanide Sandwich Single-Molecule Magnets
- Pages: 6107-6111
- First Published: 08 December 2020
The highly reactive divalent sandwich (Cot)2Tm{K(18-c-6)}2 exhibits slow magnetic relaxation in absence of a DC field, an unprecedented report for f13 configuration. The variation of the counter-cation influences the magnetic relaxation in line with the overall stability of the organometallic sandwich complex.
Antitumor Agents | Hot Paper
Light-Triggered Transformable Ferrous Ion Delivery System for Photothermal Primed Chemodynamic Therapy
- Pages: 6112-6119
- First Published: 16 December 2020
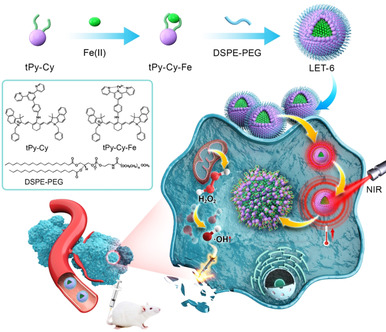
A light-triggered transformable ferrous ion (Fe2+) delivery agent (LET-6) was developed for photothermal primed chemodynamic therapy (CDT). Thermal expansion caused by 808 nm laser irradiation triggers the transformation of LET-6 to expose Fe2+, which primes the catalytic breakdown of endogenous H2O2 within the tumor microenvironment, thus generating .OH for enhanced CDT. This high-performance Fe2+ delivery system provides a sound basis for future synergistic metal-ion-mediated cancer therapy.
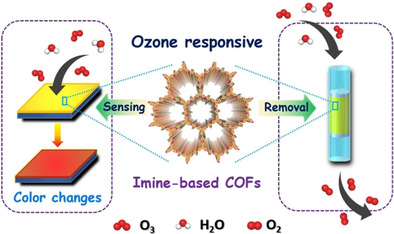
Smart Materials | Very Important Paper
Rational Fabrication of Crystalline Smart Materials for Rapid Detection and Efficient Removal of Ozone
- Pages: 6120-6125
- First Published: 15 December 2020
Gasotransmitters | Hot Paper
Targeted Delivery of Persulfides to the Gut: Effects on the Microbiome
- Pages: 6126-6132
- First Published: 29 January 2021
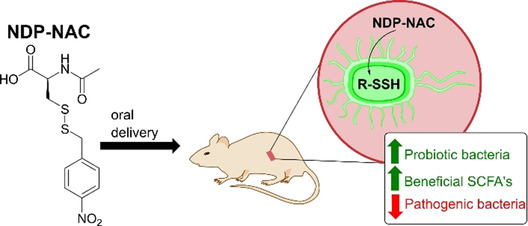
The persulfide donor NDP-NAC (see structure) was synthesized and found to decompose in response to E. coli nitroreductase with the release of N-acetyl cysteine persulfide (NAC-SSH). NDP-NAC elicited gastroprotective effects in mice by the upregulation of beneficial small- and medium-chain fatty acids, by increasing growth of Turicibacter sanguinis, a beneficial gut bacterium, and by decreasing populations of pathogenic Synergistales bacteria.
Analytical Methods | Hot Paper
Dried Blood Spot Self-Sampling with Automated Capillary Electrophoresis Processing for Clinical Analysis
- Pages: 6133-6140
- First Published: 09 December 2020
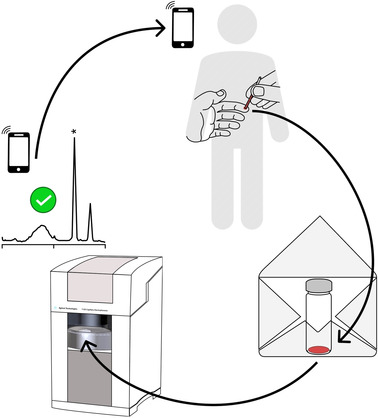
An all-in-one concept is presented, which enables at-home dried blood spot (DBS) self-sampling, DBS transport to a clinical laboratory by mail, and a fully automated DBS elution/analysis. It provides an elegant analytical tool for personalized health monitoring and clinical analyses in pandemic situations; moreover, it could help shift the current sick-care-based healthcare system to a prevention-based one.
Proton Exchange Membranes | Hot Paper
Precise Molecular-Level Modification of Nafion with Bismuth Oxide Clusters for High-performance Proton-Exchange Membranes
- Pages: 6141-6150
- First Published: 09 December 2020
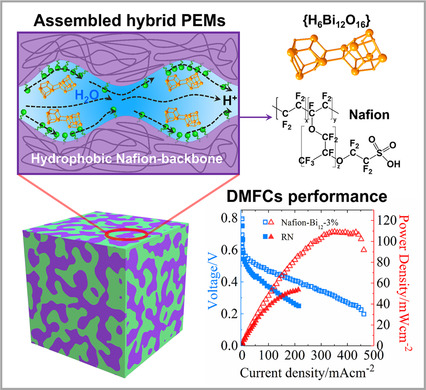
A hybrid membrane (Nafion-Bi12-3 %) used as a high-performance proton exchange membrane (PEM) is fabricated through molecular-level doping of {H6Bi12O16} clusters into ionic phase of Nafion. The clusters combine with anionic side chains of Nafion and optimize the hydrophilic/hydrophobic nano-phases, resulting in hybrid membranes with high proton conductivity, ideal mechanical and chemical stability, and low methanol permeability.
Crystal Engineering | Hot Paper
Confinement-Driven Enantioselectivity in 3D Porous Chiral Covalent Organic Frameworks
- Pages: 6151-6158
- First Published: 09 December 2020
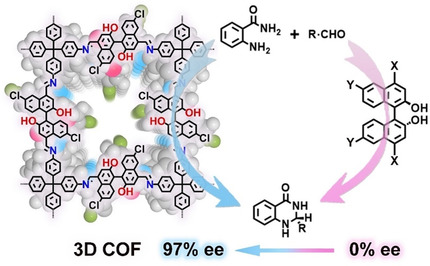
Chiral 3D COFs with interpenetrated open frameworks were synthesized from tetrahedral tetraamine and enantiopure BINOL dialdehydes. The resulting 3D COF was capable of inducing chiral molecular catalysts from non-enantioselective to highly enantioselective under confinement effect in catalyzing important organic transformation with high catalytic activity and good recyclability.
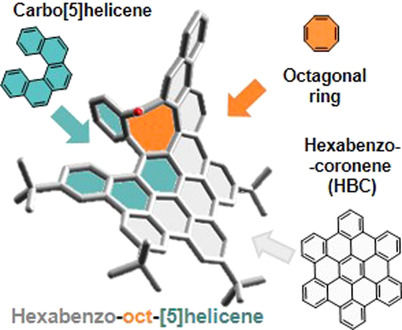
Nanographenes | Hot Paper
Octagon-Embedded Carbohelicene as a Chiral Motif for Circularly Polarized Luminescence Emission of Saddle-Helix Nanographenes
- Pages: 6159-6165
- First Published: 18 December 2020
Antiviral Agents
Translation of Mycobacterium Survival Strategy to Develop a Lipo-peptide based Fusion Inhibitor
- Pages: 6166-6171
- First Published: 26 November 2020
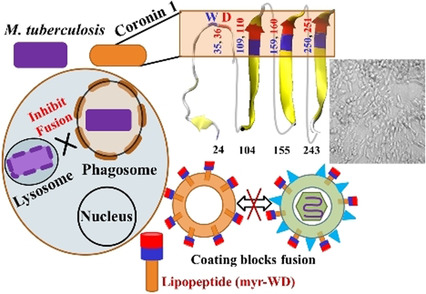
The survival mechanism of mycobacterium inside the phagosome was translated to develop a new class of fusion inhibitor. The mycobacterium inspired simple lipo-dipeptide (myr-WD) inhibits the membrane fusion and protects cells from lethal type 1 influenza virus (H1N1) and murine coronavirus challenge as a potential broad-spectrum antiviral agent.
Electrochemistry
Nickel-Catalyzed Electrochemical C(sp3)−C(sp2) Cross-Coupling Reactions of Benzyl Trifluoroborate and Organic Halides
- Pages: 6172-6181
- First Published: 07 December 2020
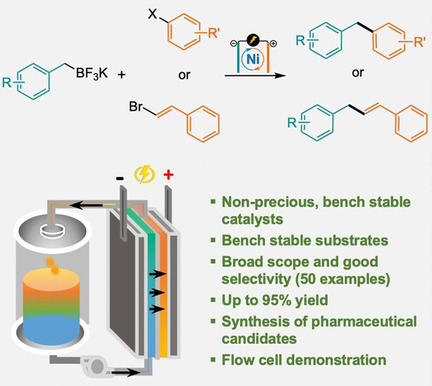
A redox-neutral electrochemical C(sp2)−C(sp3) cross-coupling method is developed using bench-stable substrates and Ni catalysts. The Ni-catalyzed electrochemical cross-coupling exhibits good reaction efficiency, has practical applications, and expands the synthetic toolbox to forge carbon–carbon bonds.
Porous Frameworks
Anionic Polymerization in Porous Organic Frameworks: A Strategy to Fabricate Anchored Polymers and Copolymers
- Pages: 6182-6188
- First Published: 01 December 2020
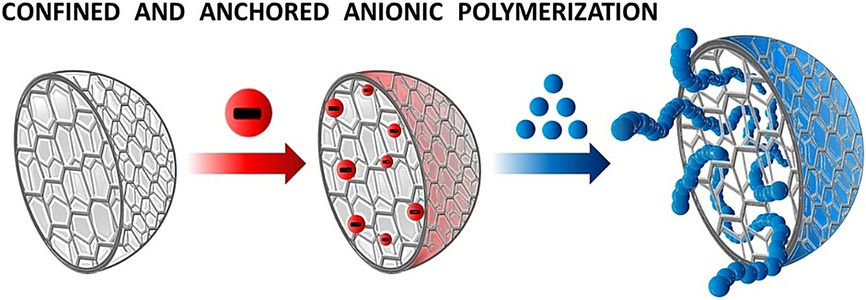
Porous organic frameworks provide the suitable hydrocarbon cavities for anionic polymerization and copolymerization of isoprene and methylmethacrylate, forming core–shell nanostructured materials. Lithiation reaction on the frameworks generated multiple anion initiators which promoted the growth of anchored chains.
Photocatalysis
Photocatalyst for High-Performance H2 Production: Ga-Doped Polymeric Carbon Nitride
- Pages: 6189-6194
- First Published: 20 January 2021
An all-in-one photocatalyst, Ga-doped carbon nitride (CN), with an H2 production rate at 9900 μmol h−1 g−1, is prepared by a one-step calcination. Ga exists in the GaN4 form on CN, and serves as the H2 production center. The excited electron prefers the GaN4 site, which adsorbs the proton in the excited state and tends to desorption of H* in the ground state, thus enhancing the H2 production.
Optical Barcodes
Lanthanide-Based Molecular Cluster-Aggregates: Optical Barcoding and White-Light Emission with Nanosized {Ln20} Compounds
- Pages: 6195-6201
- First Published: 09 December 2020
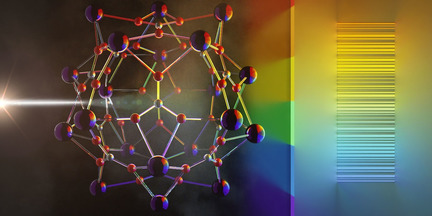
The control of the energy transfer and the emission colour is demonstrated for the first time in molecular cluster-aggregates. Moreover, through the targeted choice of the lanthanide composition, a novel pure white-light emitting cluster-aggregate was isolated. This approach can pave new avenues into the future of efficient optical anti-counterfeiting technologies.
Quantum Dots | Hot Paper
Zn-Cu-In-S-Se Quinary “Green” Alloyed Quantum-Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells with a Certified Efficiency of 14.4 %
- Pages: 6202-6209
- First Published: 30 November 2020
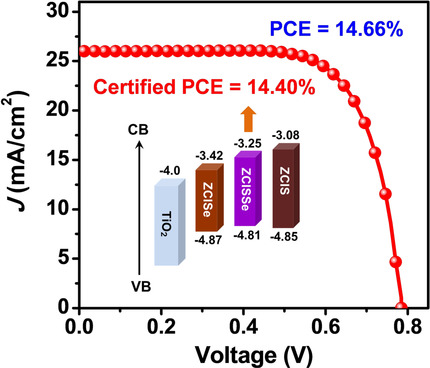
A cation/anion co-alloying strategy is applied to prepare Zn0.4Cu0.7In1.0SxSe2−x (ZCISSe) quinary alloyed quantum dots (QDs). The band gap, conduction band energy level, and density of defect trap states of the QDs can be conveniently tailored through composition engineering. The quinary alloyed QDs deliver a new certified efficiency record of 14.4 % for quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells.
Homogeneous Catalysis | Hot Paper
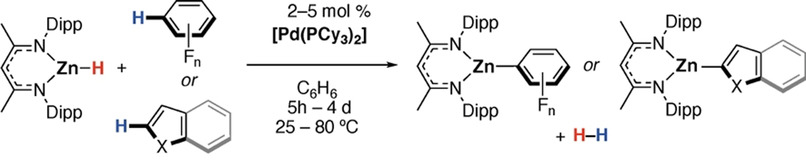
Palladium-Catalysed C−H Bond Zincation of Arenes: Scope, Mechanism, and the Role of Heterometallic Intermediates
- Pages: 6210-6218
- First Published: 04 December 2020
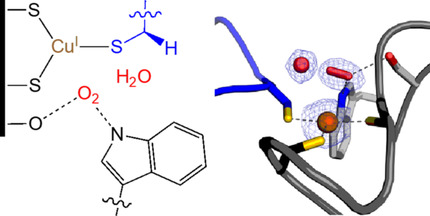
Oxygen Activation | Very Important Paper
Non-Coordinative Binding of O2 at the Active Center of a Copper-Dependent Enzyme
- Pages: 6219-6224
- First Published: 27 November 2020
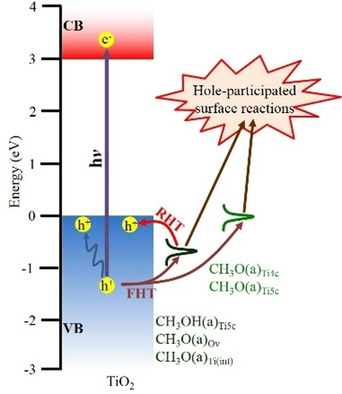
Surface Chemistry
Site Sensitivity of Interfacial Charge Transfer and Photocatalytic Efficiency in Photocatalysis: Methanol Oxidation on Anatase TiO2 Nanocrystals
- Pages: 6225-6234
- First Published: 07 December 2020
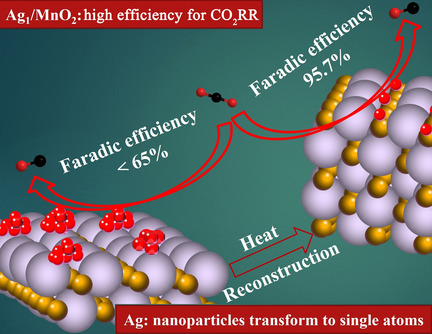
Single-Atom Catalysis | Very Important Paper
Silver Single-Atom Catalyst for Efficient Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Synthesized from Thermal Transformation and Surface Reconstruction
- Pages: 6235-6241
- First Published: 04 December 2020
C−H Insertion | Hot Paper
β-Diazocarbonyl Compounds: Synthesis and their Rh(II)-Catalyzed 1,3 C−H Insertions
- Pages: 6242-6249
- First Published: 04 December 2020
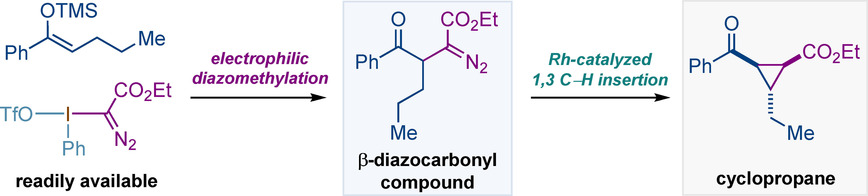
The first electrophilic diazomethylation of ketone silyl enol ethers with diazomethyl-substituted hypervalent iodine reagents that gives access to unusual β-diazocarbonyl compounds is described. The potential of this unexplored class of diazo compounds for the development of new reactions was demonstrated by the discovery of a rare Rh-catalyzed intramolecular 1,3 C−H carbene insertion that led to complex cyclopropanes with excellent stereocontrol.