Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
- First Published: 27 December 2022

The cover image is based on the Original Article Natural remedies medicine derived from flaxseed (secoisolariciresinol diglucoside, lignans, and α-linolenic acid) improve network targeting efficiency of diabetic heart conditions based on computational chemistry techniques and pharmacophore modeling by Fatemeh Hajibabaie et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.14480.
A comprehensive review on modulation of SIRT1 signaling pathways in the immune system of COVID-19 patients by phytotherapeutic melatonin and epigallocatechin-3-gallate
- First Published: 03 June 2022
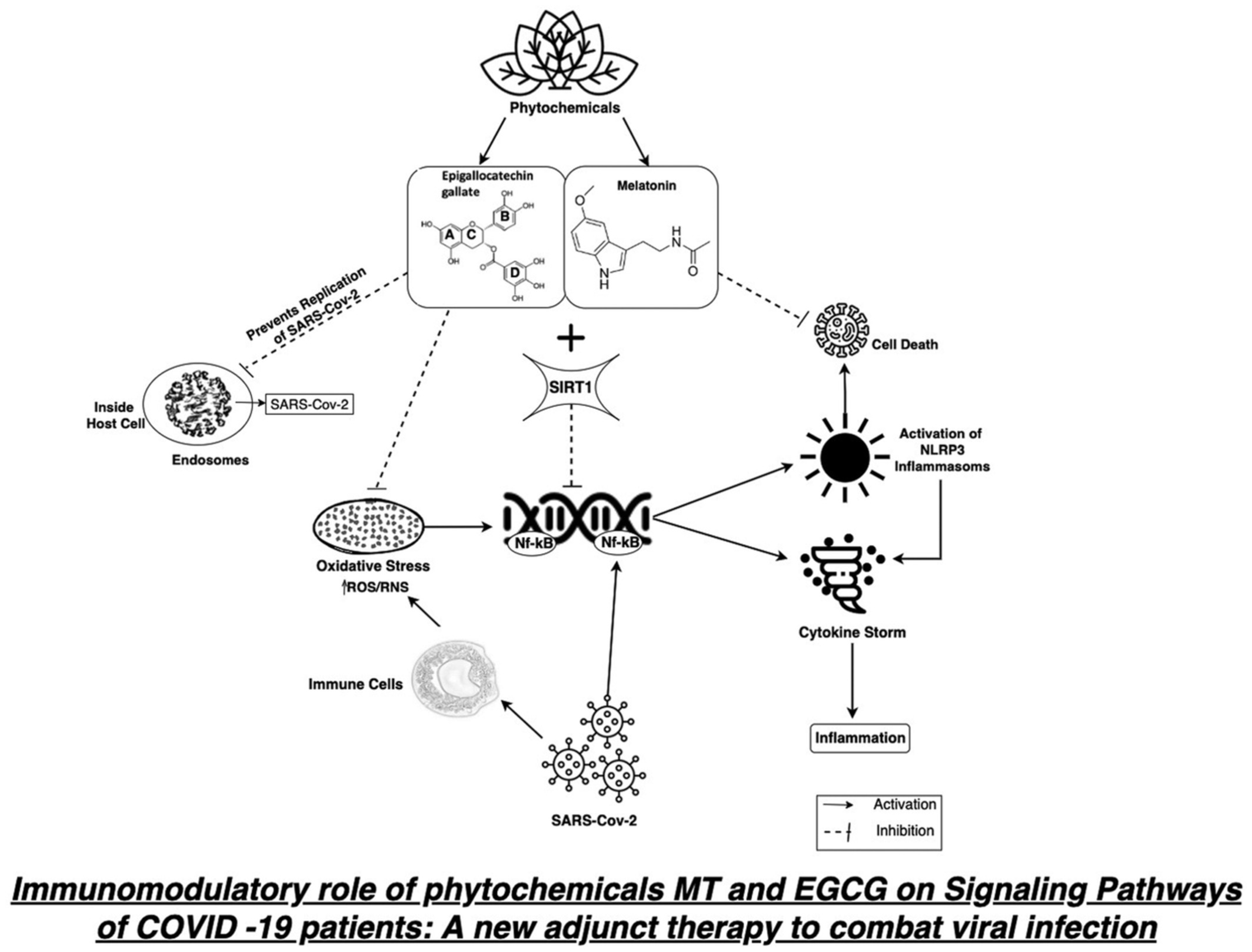
The mechanism of action of Melatonin and EGCG nutraceuticals in alleviating severe symptoms of COVID-19 illness by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation is elucidated in this review. Both phytochemicals provide a safe alternative to medications for preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection and increasing patients' immunity by modifying signaling pathways via upregulation of Sirtuin1 protein.
Phenolic compounds can induce systemic and central immunomodulation, which result in a neuroprotective effect
- First Published: 28 May 2022
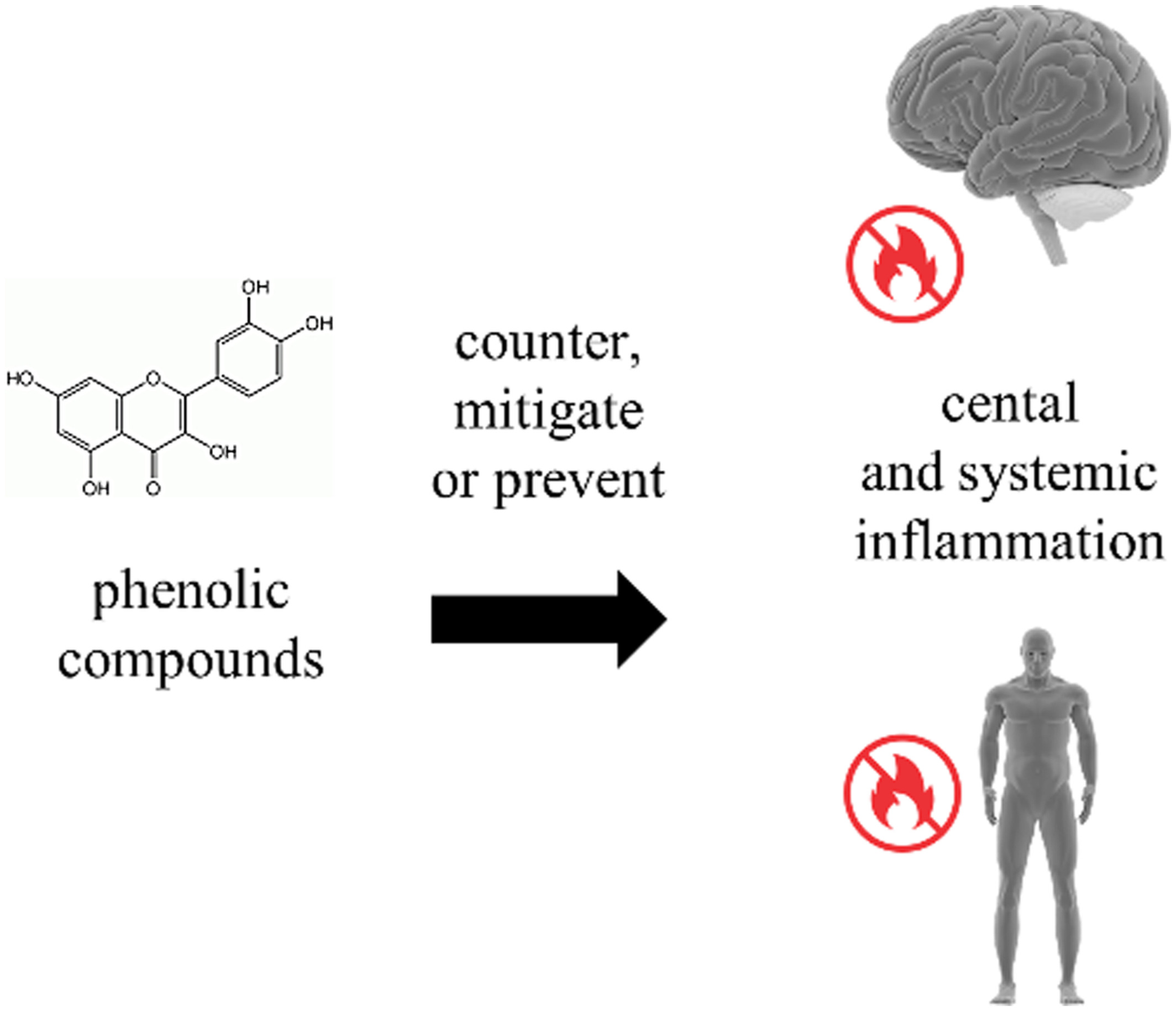
The literature shows that phenolic compounds maintain an adequate immune response, by regulating the expression and activity of pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators in various organs and tissues. Their activities in the central nervous system are particularly notable since uncontrolled central inflammation can be potentially life-threatening. Some compounds can even act therapeutically, if administered within hours of an acute inflammatory event.
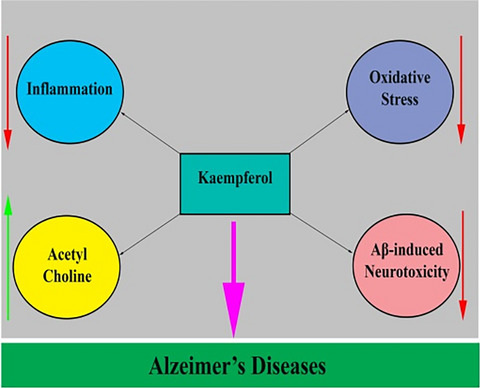
Kaempferol as a potential neuroprotector in Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 05 August 2022
Virtual screening analysis of natural flavonoids as trimethylamine (TMA)-lyase inhibitors for coronary heart disease
- First Published: 09 August 2022
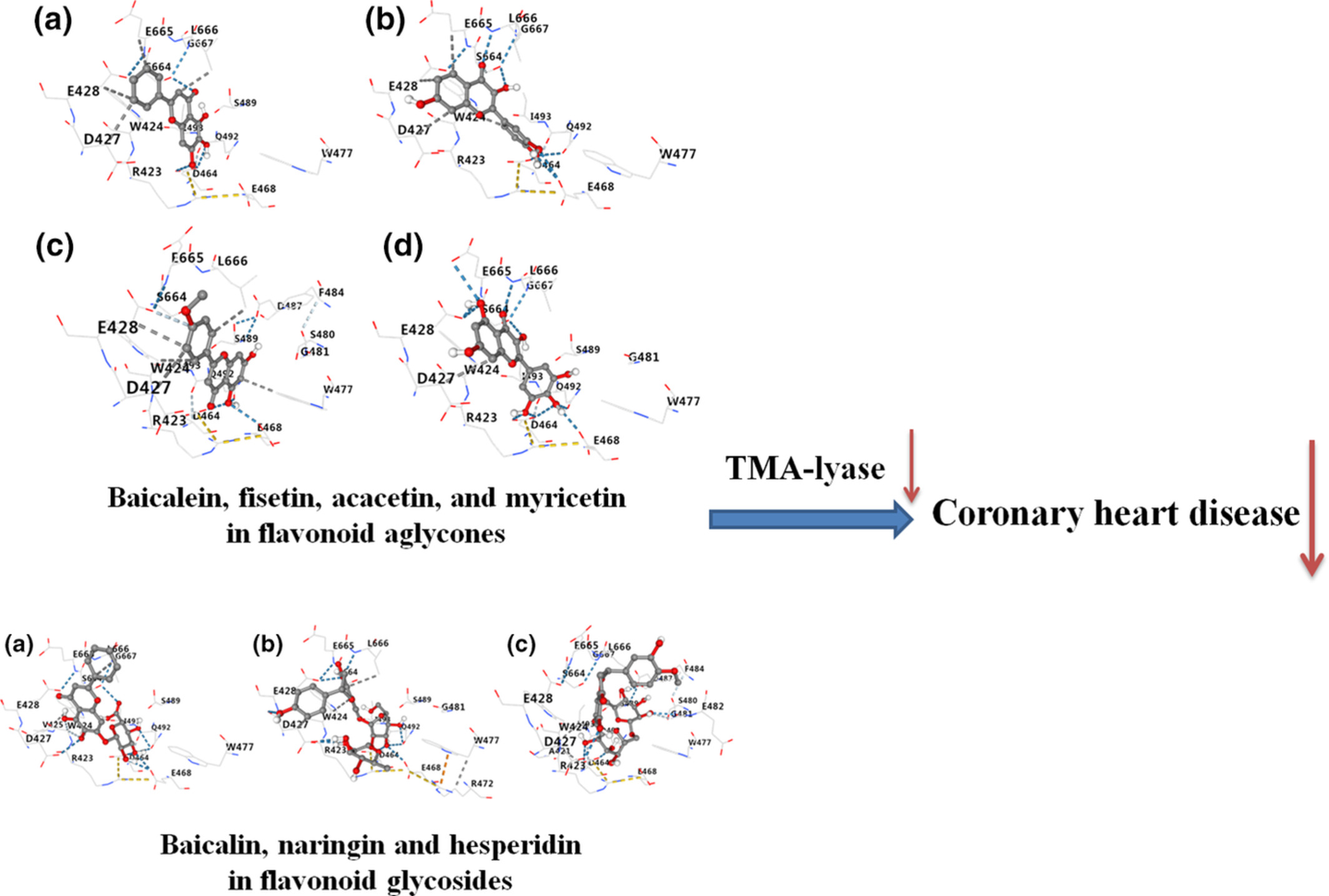
The TMA/TMAO pathway represents one of many microbe-dependent pathways that will ultimately be linked to CHD pathogenesis Molecular docking results found that baicalein, fisetin, acacetin, and myricetin in flavonoid aglycones, and baicalin, naringin and hesperidin in flavonoid glycosides had good binding effects on TMA-lyase, which were the most active and could be used as lead compounds for structural modification.
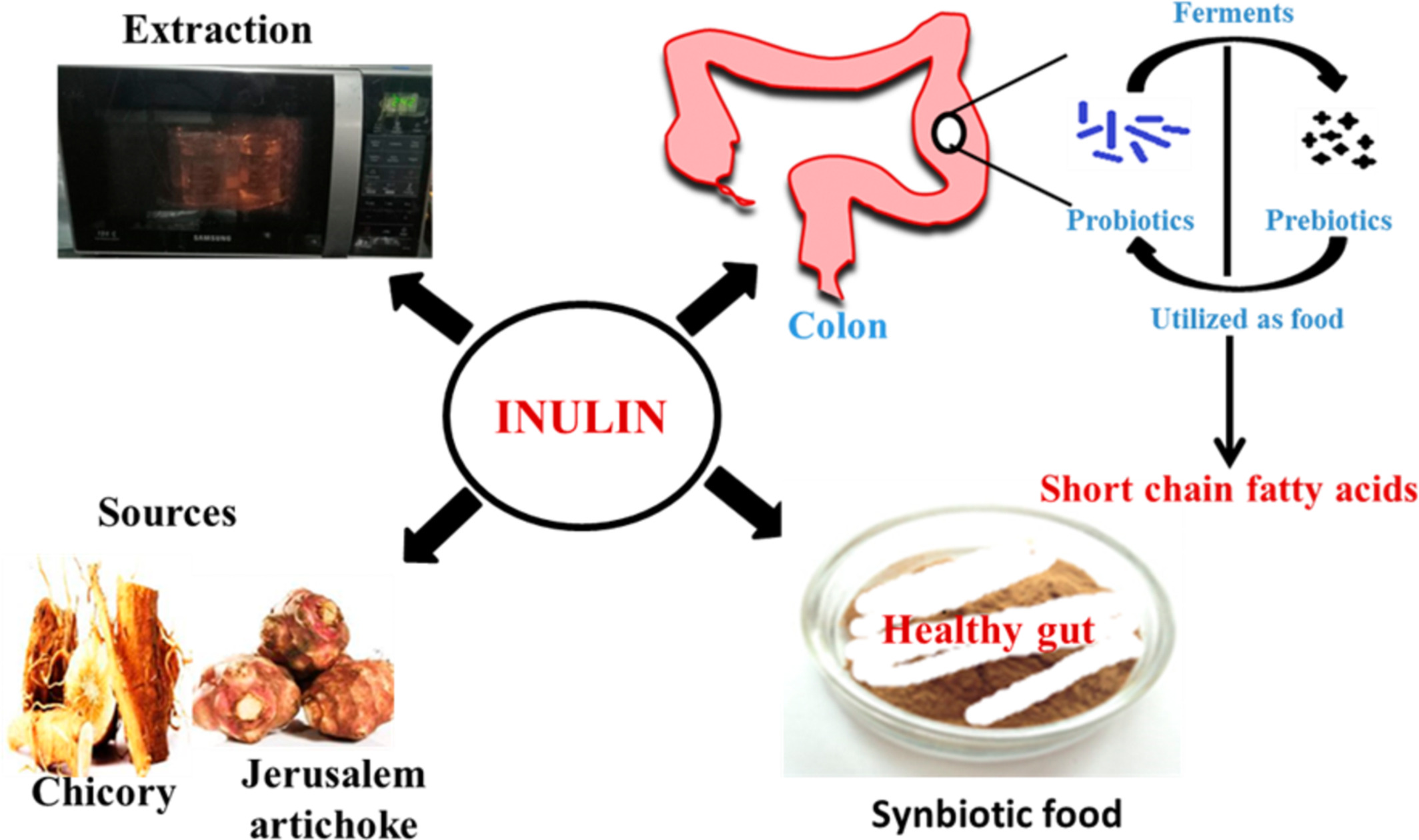
Inulin-A polysaccharide: Review on its functional and prebiotic efficacy
- First Published: 27 September 2022
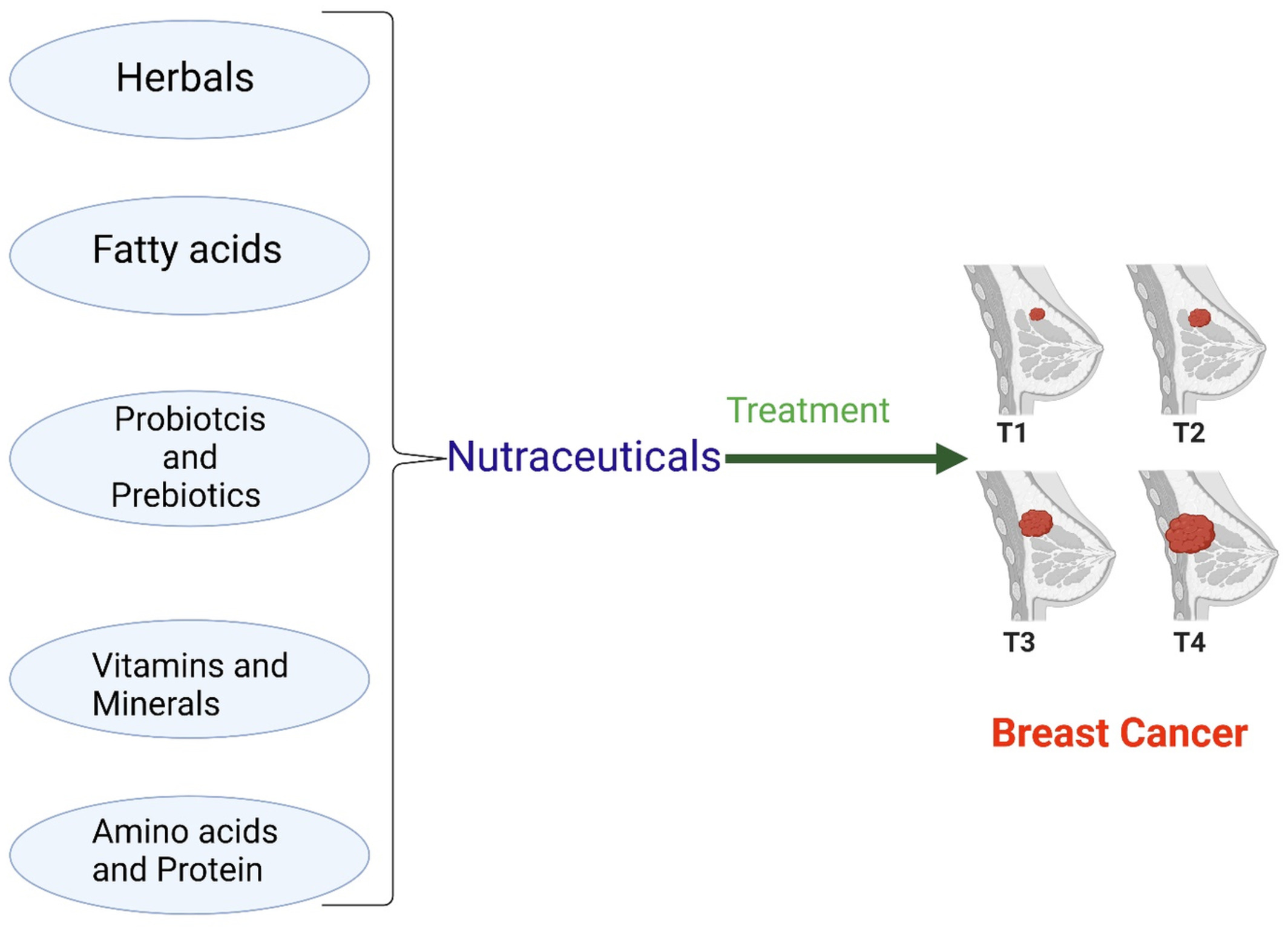
Role of Medicinal plant-derived Nutraceuticals as a potential target for the treatment of breast cancer
- First Published: 19 September 2022
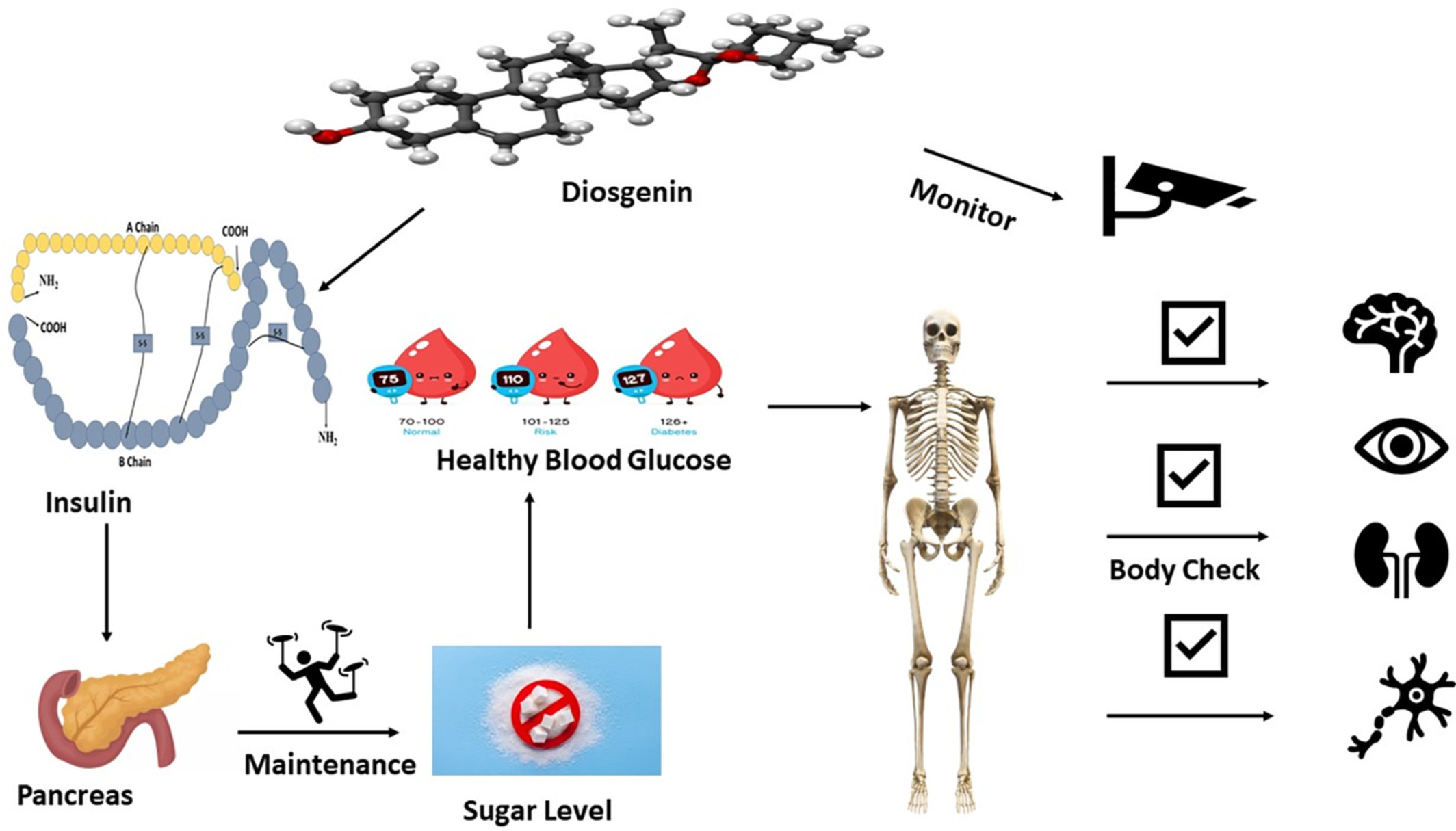
Diosgenin: An ingress towards solving puzzle for diabetes treatment
- First Published: 15 September 2022
Research progress in the preparation, structural characterization, bioactivities, and potential applications of sulfated agarans from the genus Gracilaria
- First Published: 22 September 2022
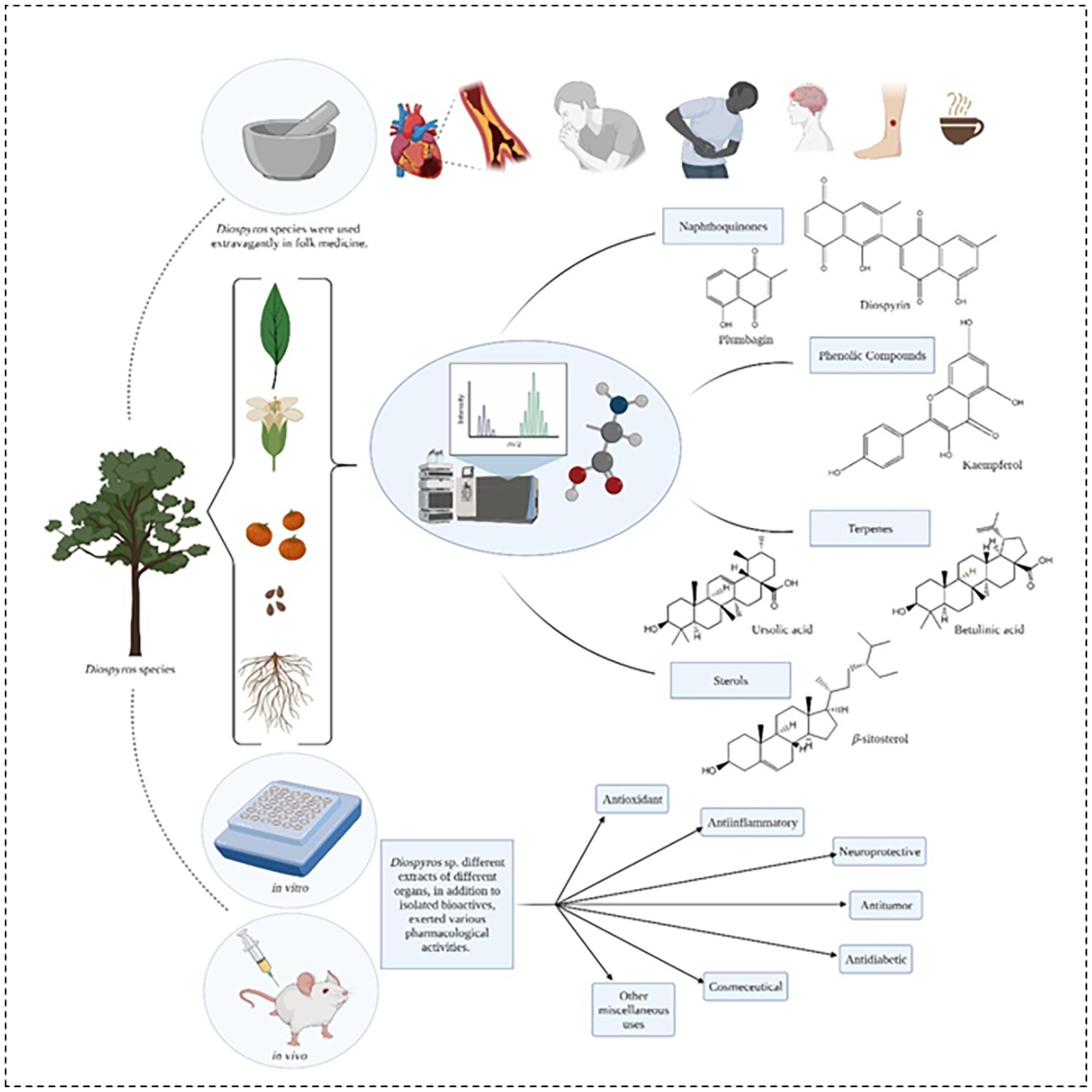
Unveiling major ethnopharmacological aspects of genus Diospyros in context to its chemical diversity: A comprehensive overview
- First Published: 22 September 2022
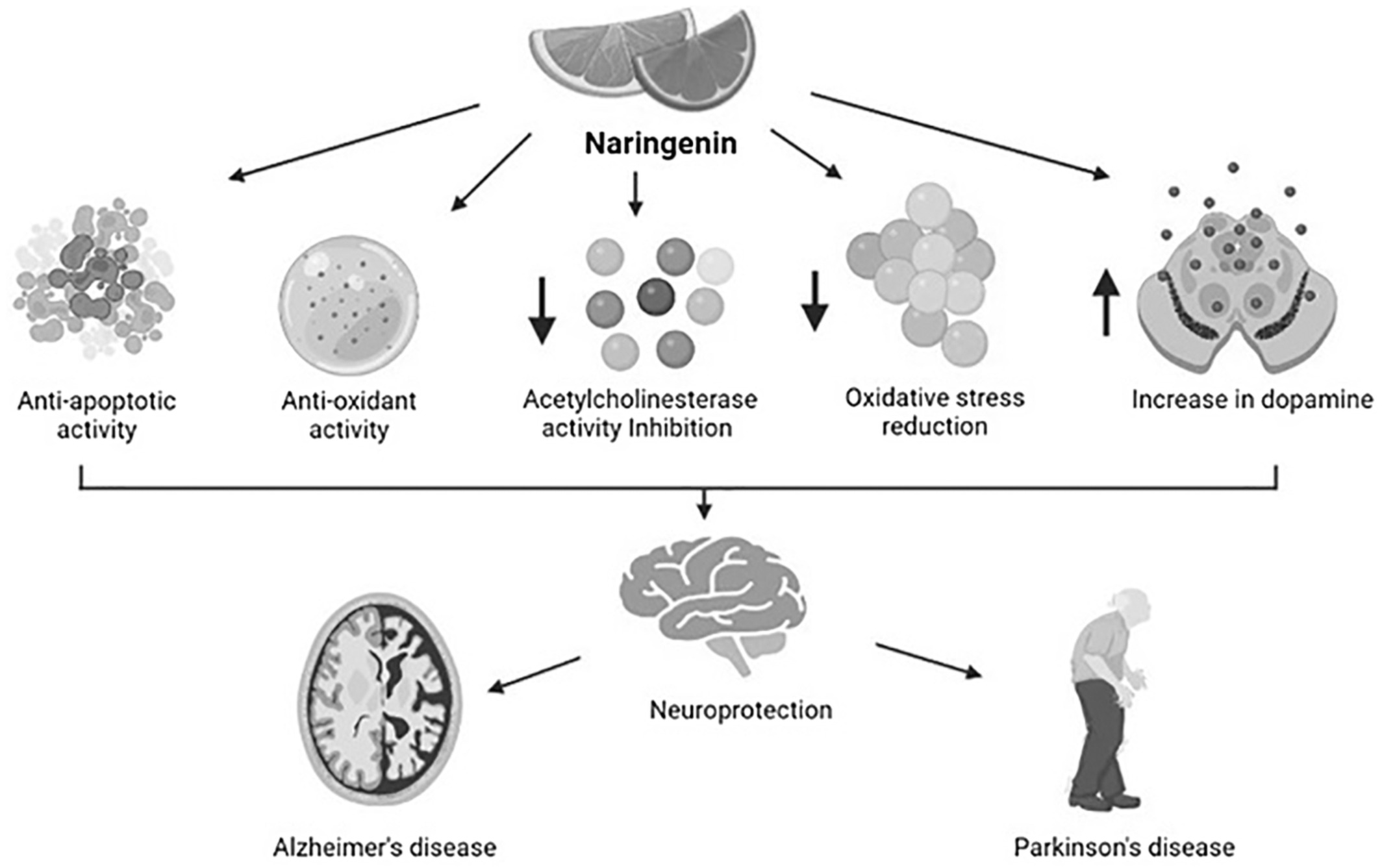
Naringenin: A prospective therapeutic agent for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 15 September 2022
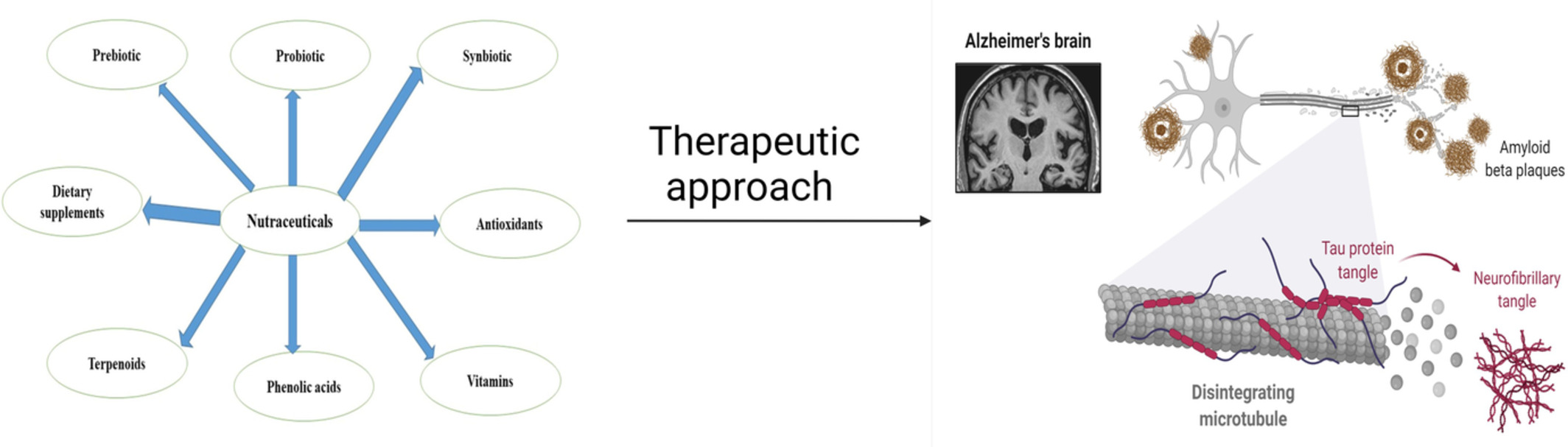
Therapeutic approaches of nutraceuticals in the prevention of Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 28 September 2022
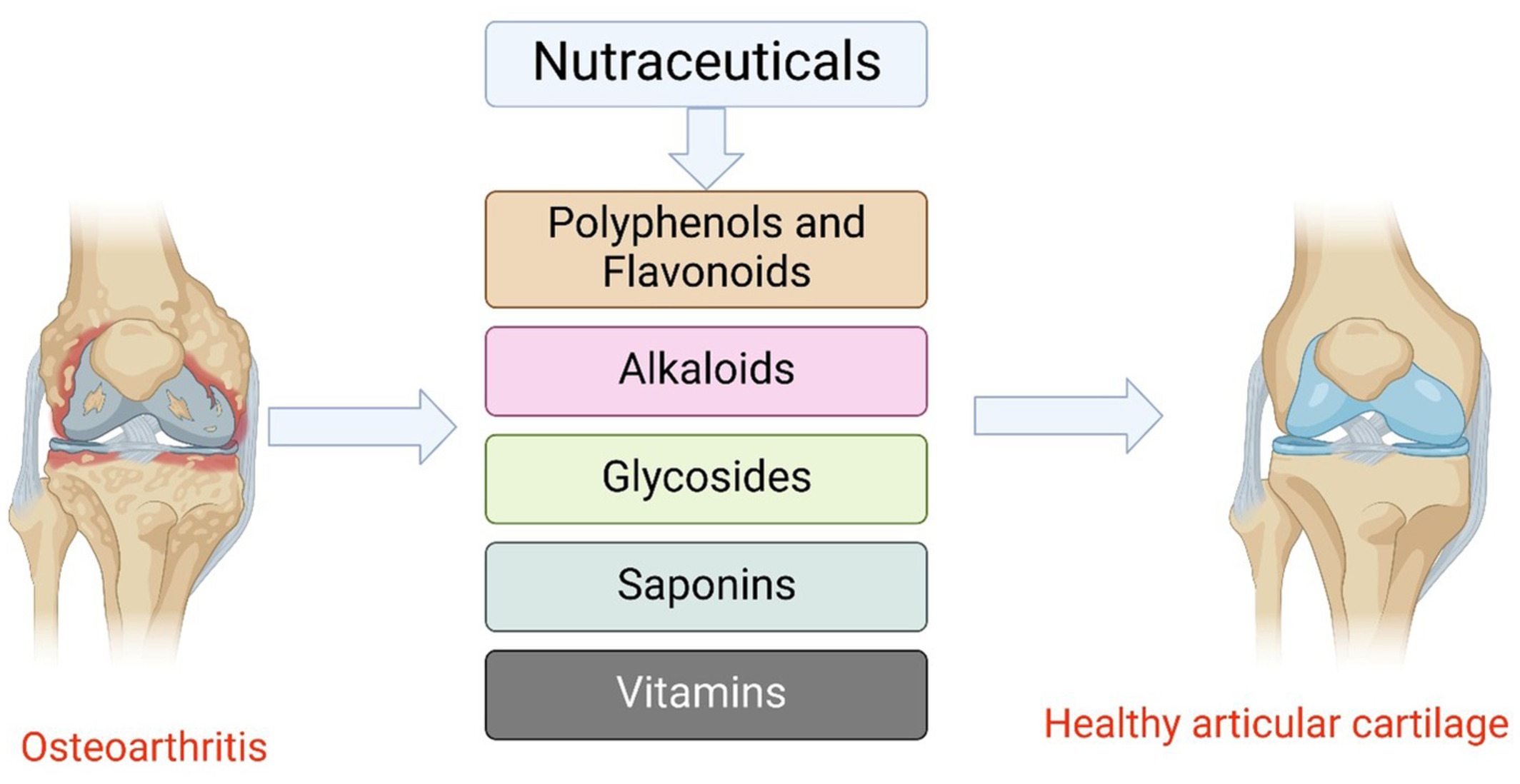
Potential role of nutraceuticals via targeting a Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB pathway in treatment of osteoarthritis
- First Published: 27 September 2022
The effects and underlying mechanisms of medicine and food homologous flowers on the prevention and treatment of related diseases
- First Published: 27 September 2022
Hovenia acerba Lindl.: An insight into botany, phytochemistry, bioactivity, quality control, and exploitation
- First Published: 02 October 2022
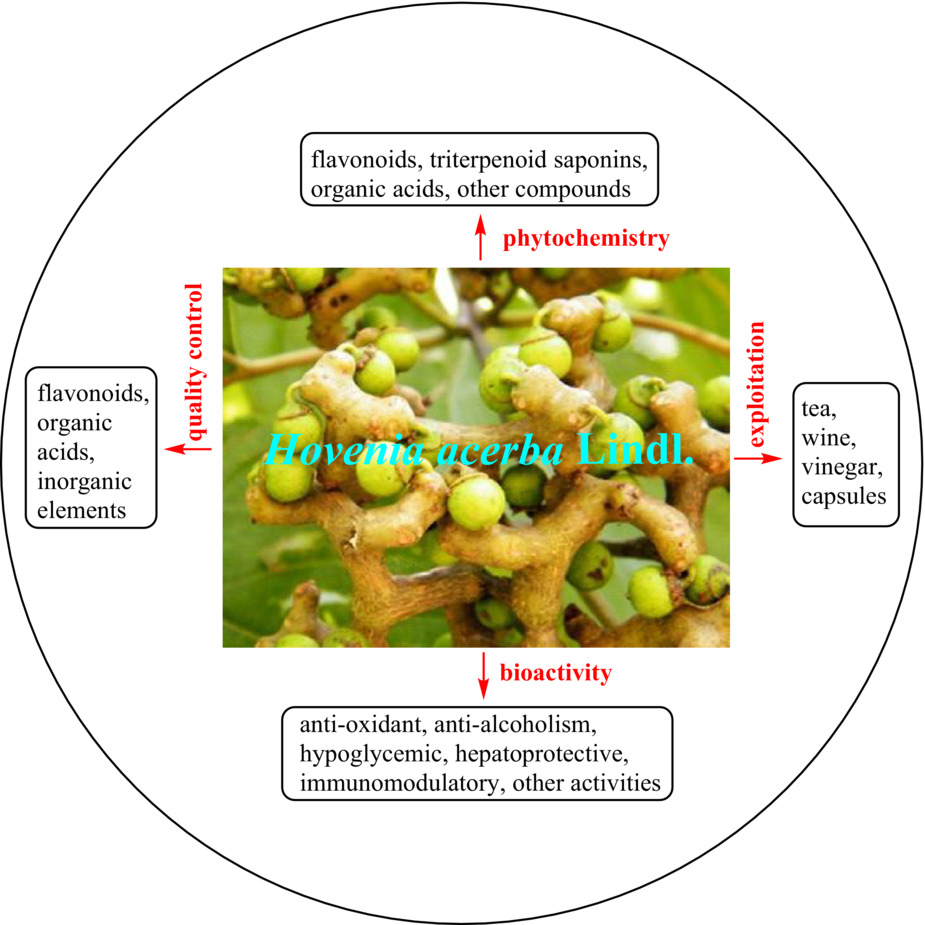
Hovenia acerba Lindl. contains abundant phytochemicals (flavonoids, triterpenoid saponins, organic acids, other compounds) and possesses multiple biological activities (anti-alcoholism, hepatoprotective, anti-oxidant, hypoglycemic, immunomodulatory, and other activities). This review may provide essential guidance for the further utilization of H. acerba Lindl. in food and pharmaceutical industry.
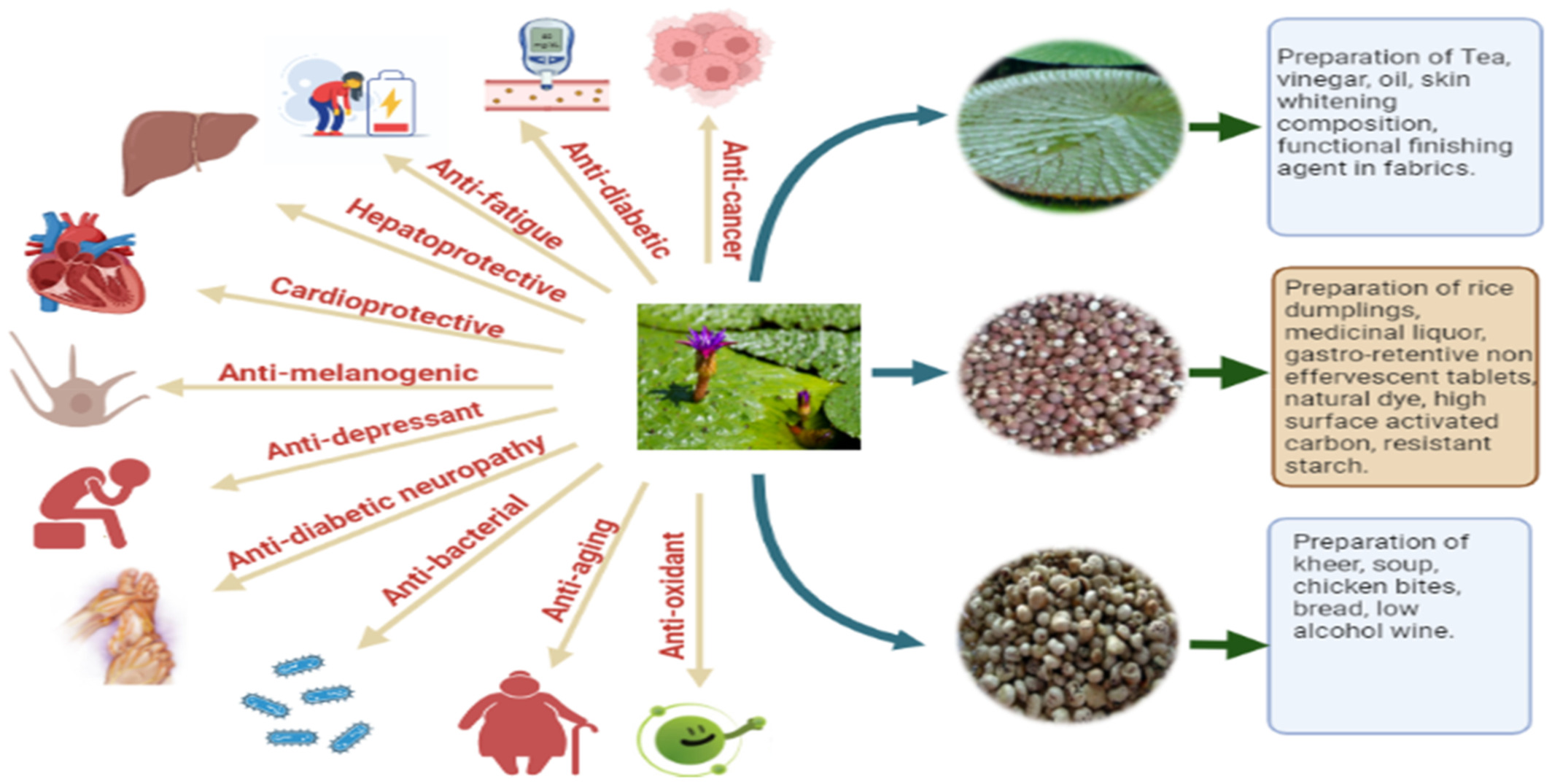
Euryale ferox, a prominent superfood: Nutritional, pharmaceutical, and its economical importance
- First Published: 01 October 2022
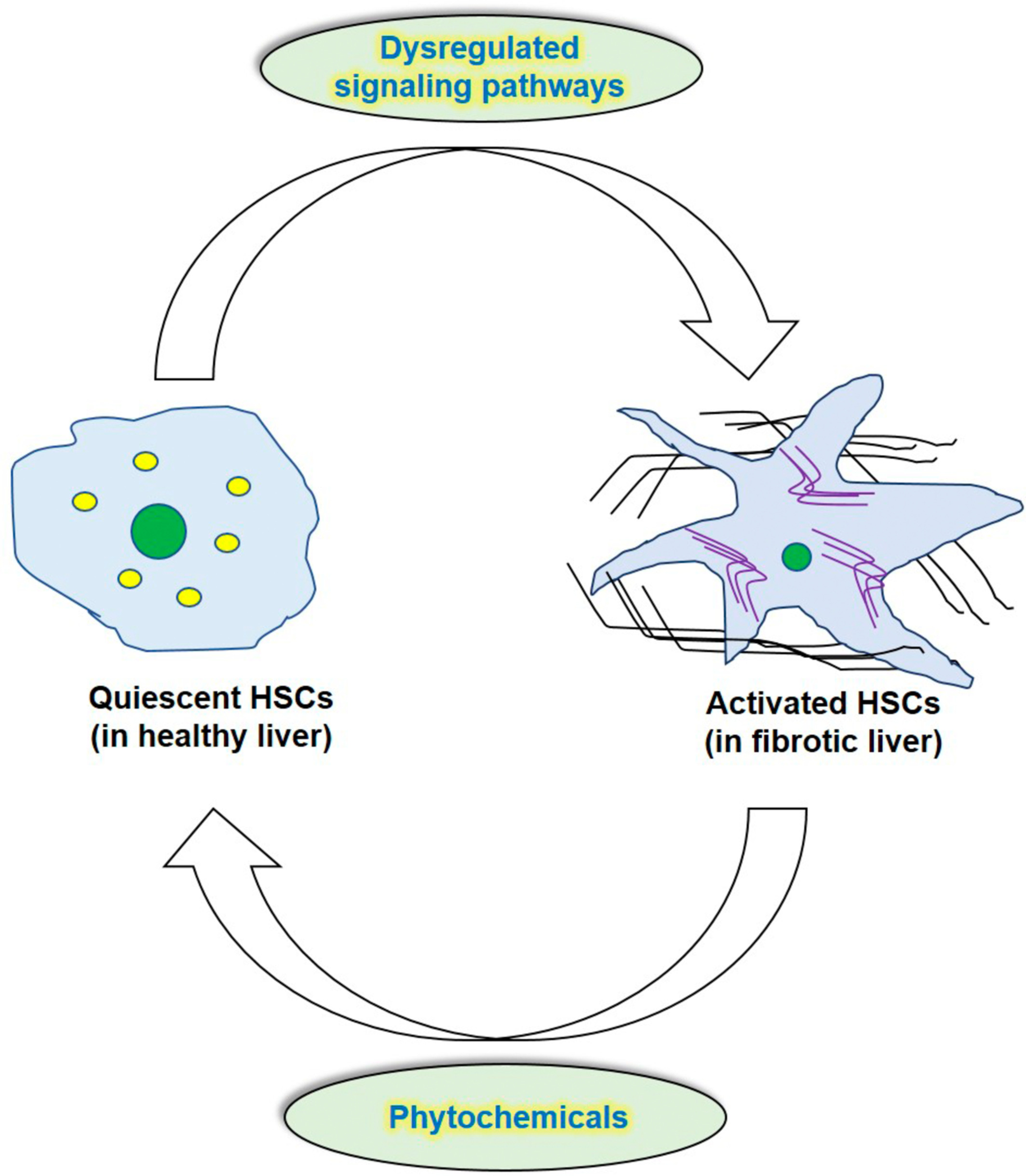
A critical review on anti-fibrotic phytochemicals targeting activated hepatic stellate cells
- First Published: 09 October 2022
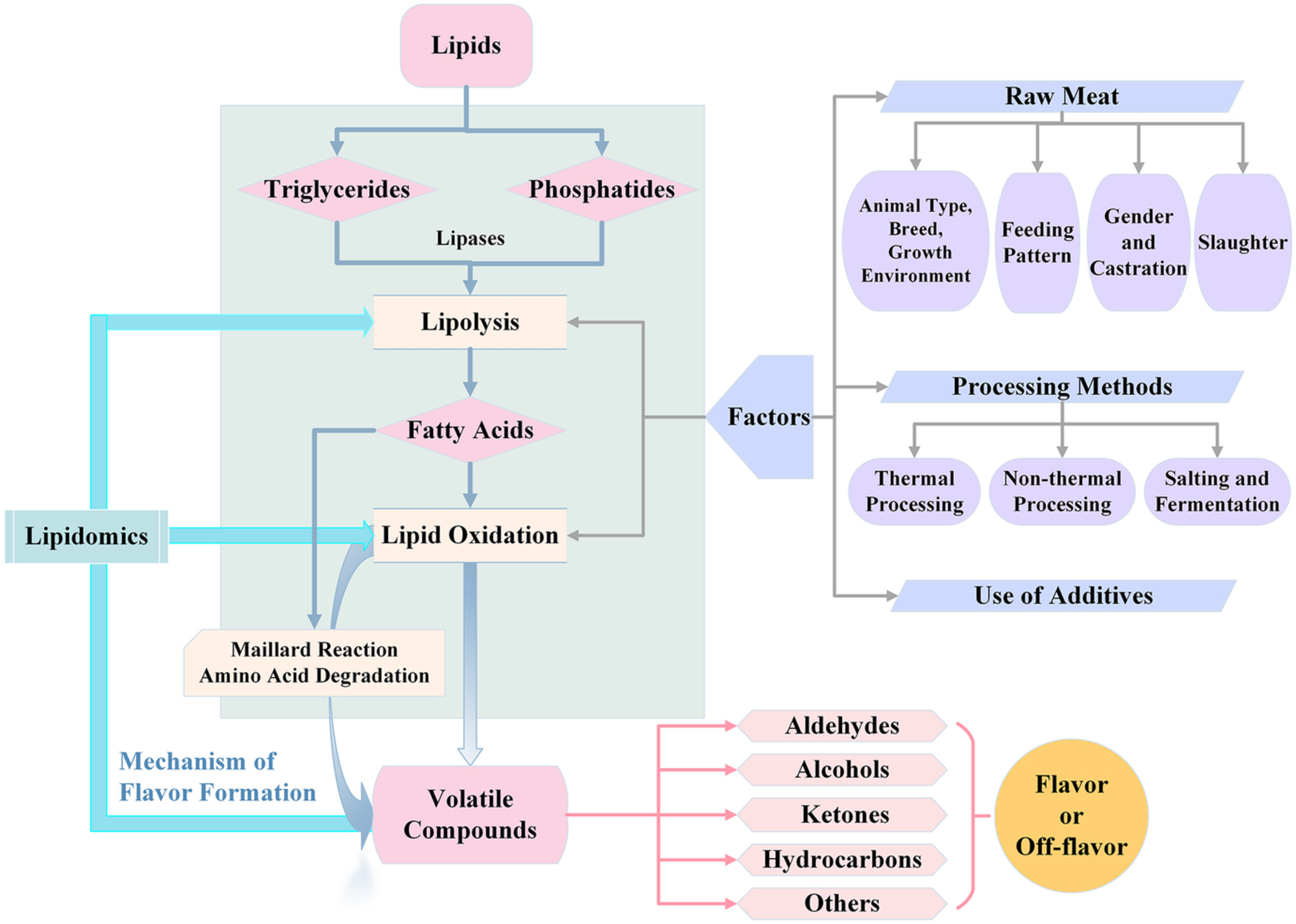
Flavor formation based on lipid in meat and meat products: A review
- First Published: 01 October 2022
Ethno-pharmacological and industrial attributes on the underutilized Arenga species in India
- First Published: 06 October 2022
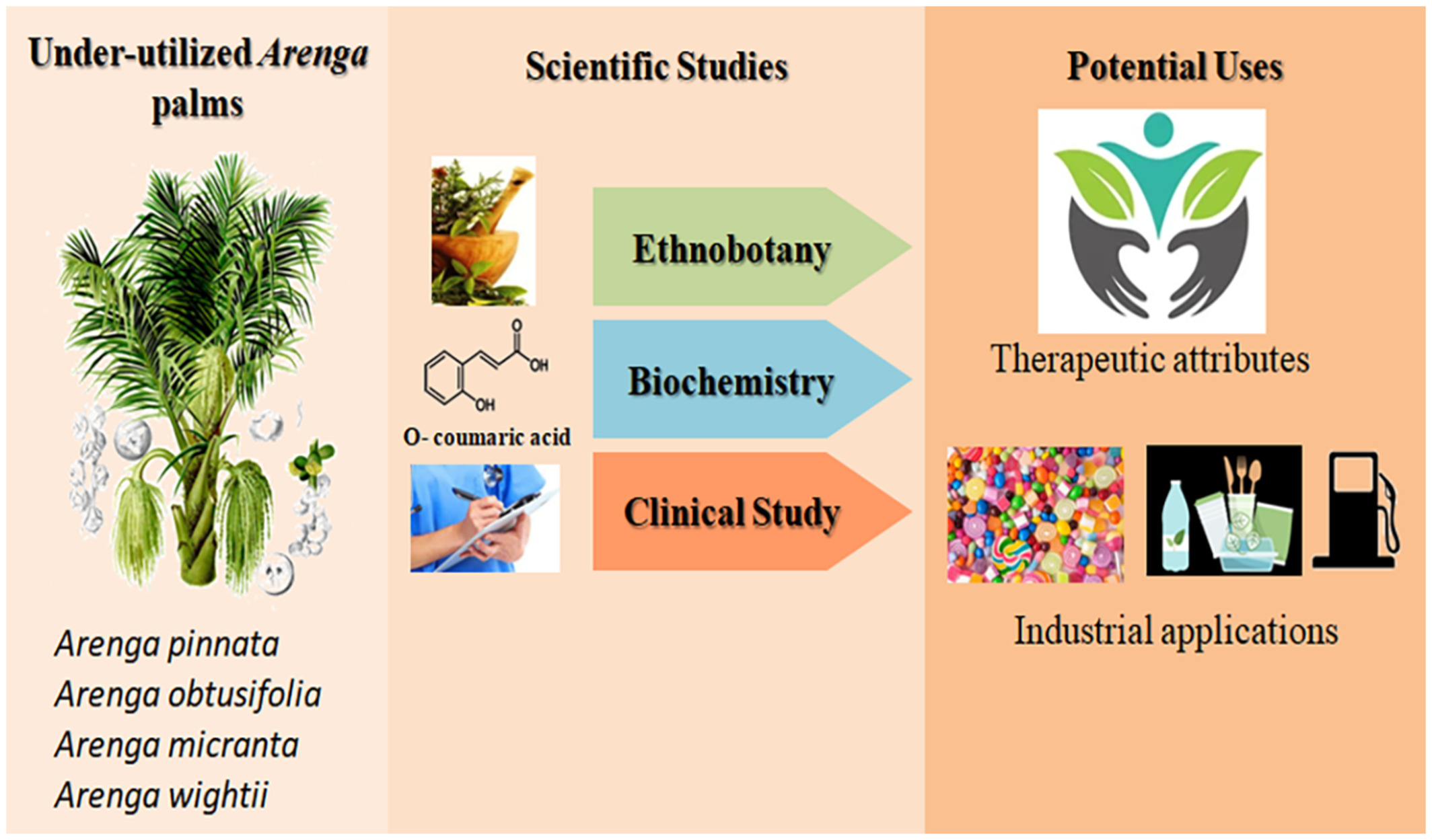
In many regions of India, Arenga pinnata and its allied species are used as food, household products, medicines, pharmaceuticals, fiber, and many more. However, they have not received proper recognition in conventional commercial markets as researchers and policymakers do not consider them so-called industrial crops. But scientists in many different countries have done a lot of clinical, biochemical, and application-based tests on them, and the results have led to them being widely used as medicine and industrial crops.
Nutraceuticals and COVID-19: A mechanistic approach toward attenuating the disease complications
- First Published: 14 October 2022
Regular consumption of such nutraceuticals has been shown to boost the immune system and prevent viral infections. Nutraceuticals such as vitamins, amino acids, flavonoids like curcumin, and probiotics have been studied for their beneficial effects in the prevention of COVID-19 symptoms such as fever, pain, malaise, and dry cough. As such, various nutraceutical-based products such as compounds could be promising agents for the effective management of COVID-19 symptoms and complications.
Neuroprotective potential of Moringa oleifera mediated by NF-kB/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway: A review
- First Published: 07 October 2022
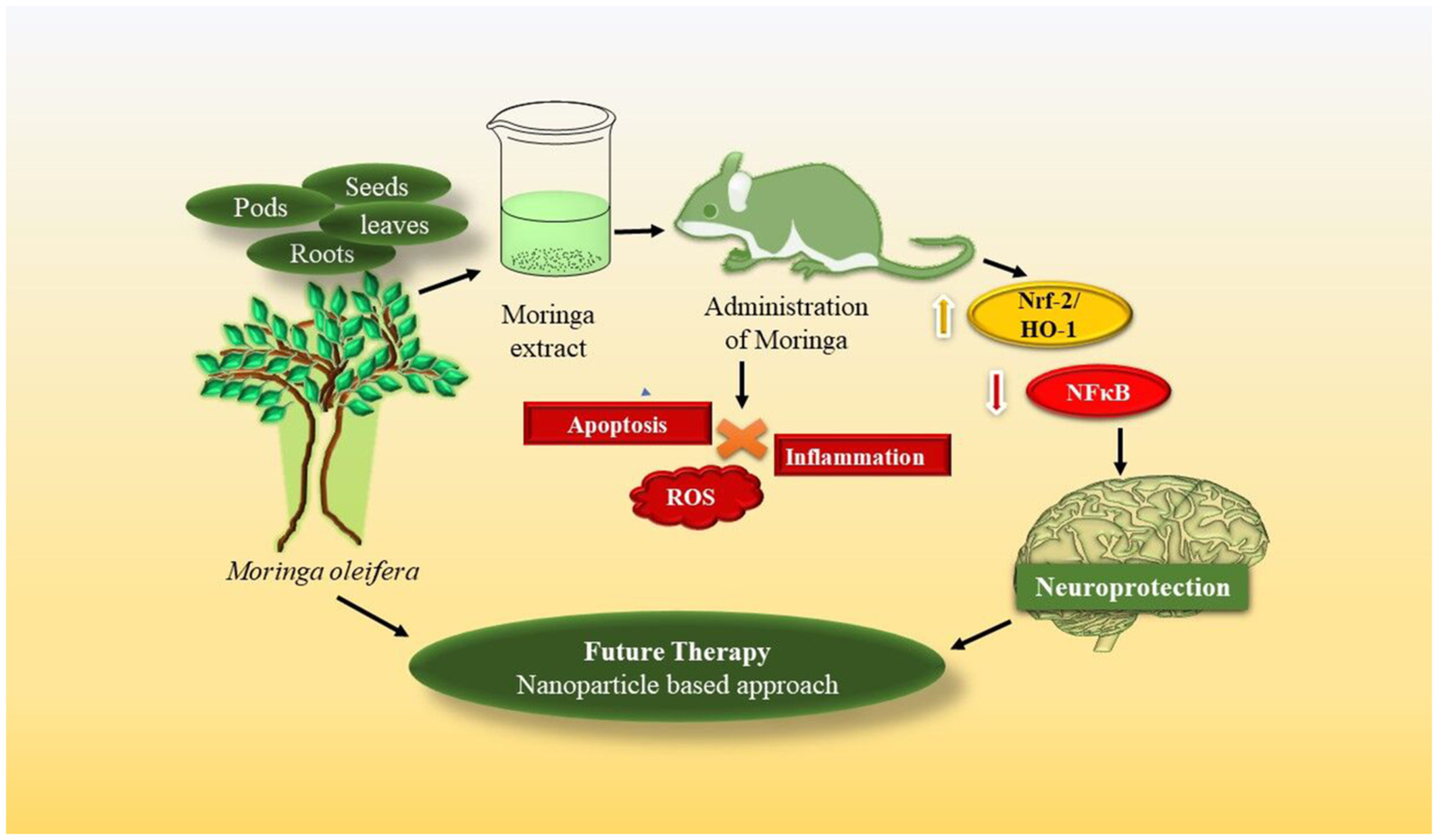
Moringa oleifera extract was prepared using various parts of the moringa plant, and oral administration in rats produced neuroprotective action against various neurological disorders via increasing the expression of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and decreasing NFκB expression. As a result, it inhibits ROS generation, apoptosis, and inflammation. In the future, for enhancing the bioavailability of moringa, nanoparticle-based approach could be used to treat brain disorders.
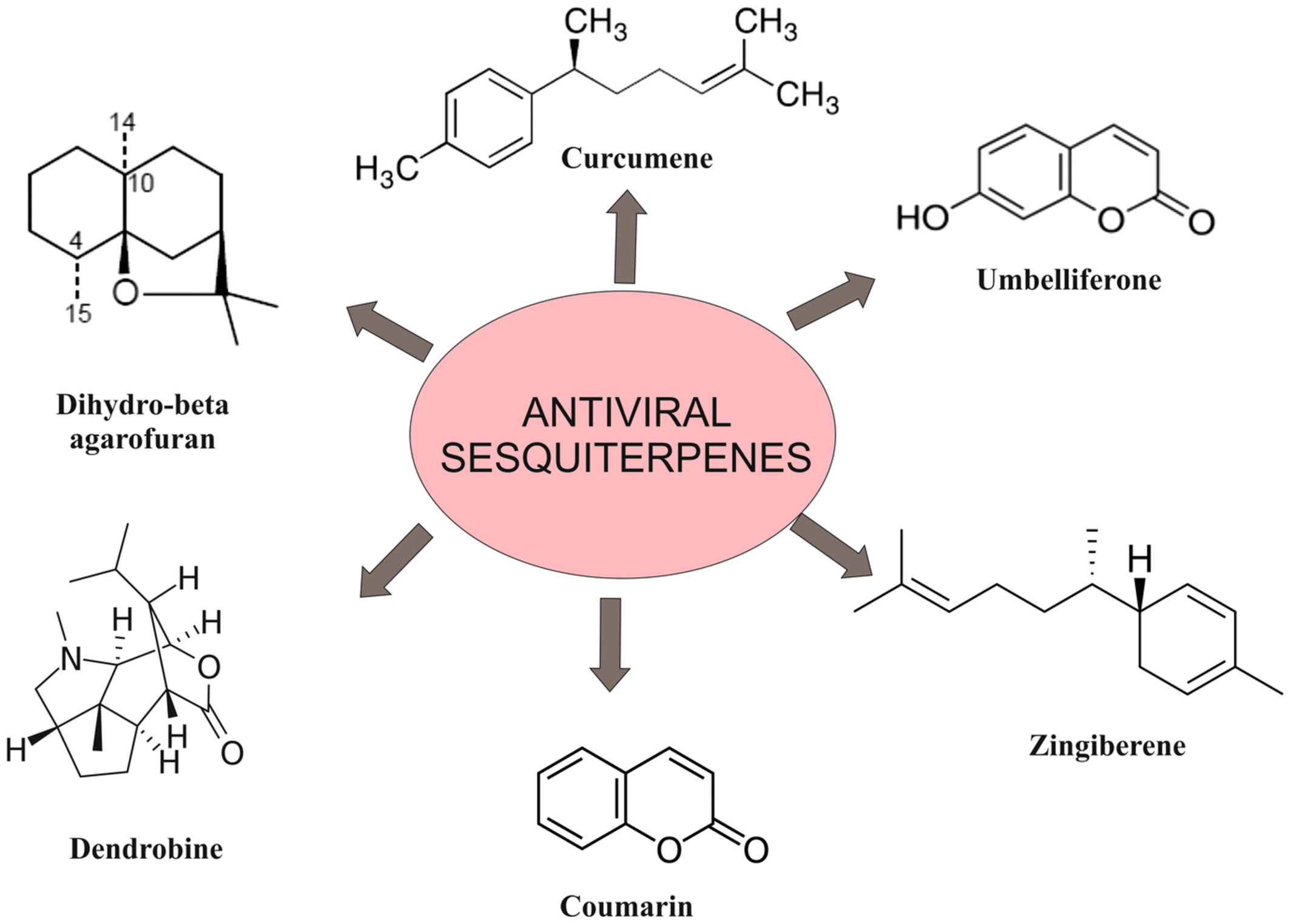
Mechanistic elucidations of sesquiterpenes ameliorating viral infections: A review
- First Published: 27 September 2022
Quercetin improves pancreatic cancer chemo-sensitivity by regulating oxidative-inflammatory networks
- First Published: 01 October 2022

Quercetin is a flavonoid widely found in numerous vegetables, fruits, and foods and has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Quercetin improves chemotherapy sensitivity of pancreatic cancer. Quercetin prevents chemotherapy resistance of pancreatic cancer by regulating oxidative-inflammatory networks, which induce immune escape of cancer cells.
A study of the molecular mechanism of quercetin and dasatinib combination as senolytic in alleviating age-related and kidney diseases
- First Published: 21 October 2022
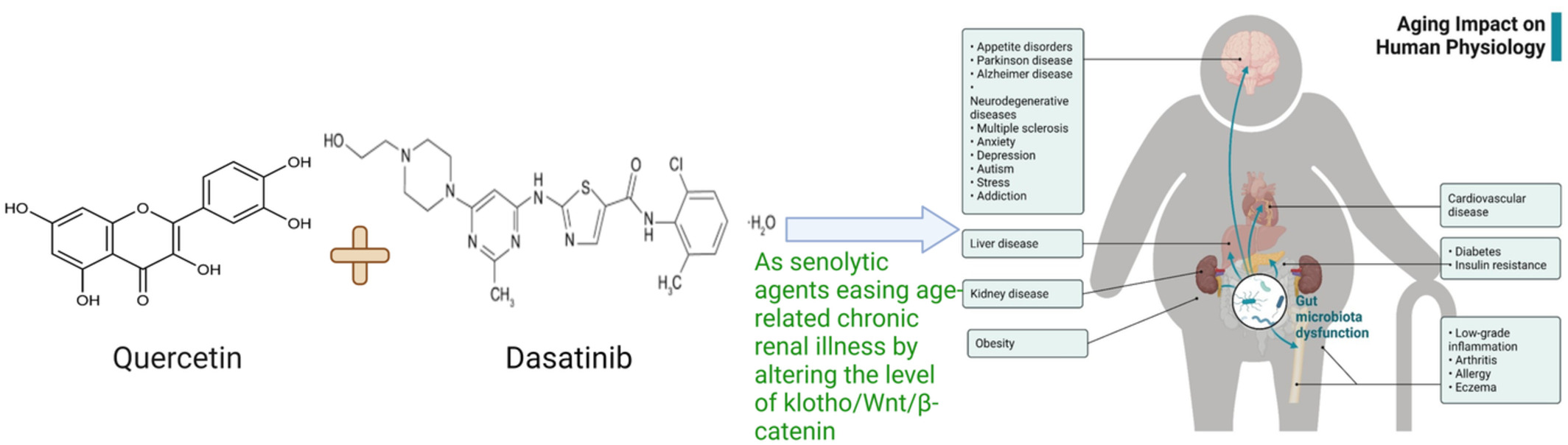
- Aging is a significant risk factor for the majority of prevalent human illnesses.
- α-klotho upregulation extends life and slows the onset of many age-related illnesses.
- We studied the mechanism of the combination of quercetin and dasatinib as senolytic.
- Senolytic drugs boost aging animals' adipose and cardiac progenitor cell activity.
Amazonian fruits with potential effects on COVID-19 by inflammaging modulation: A narrative review
- First Published: 14 October 2022
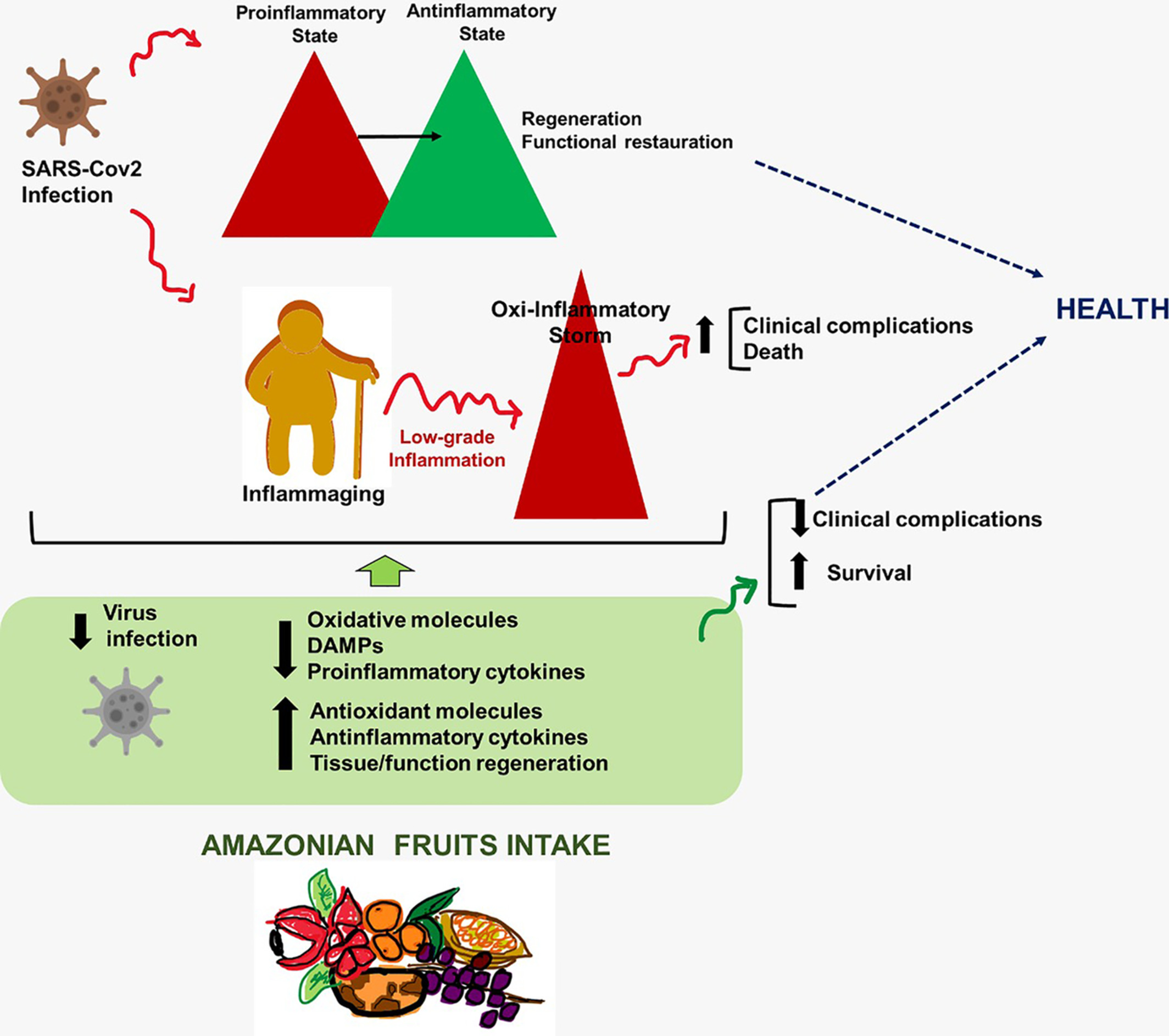
Amazonian fruits have bioactive molecules, which present antioxidant activity, modulate inflammatory cytokines and assist in tissue regeneration and functions. Thus, they can help reduce the clinical complications caused by aging and aggravated by COVID-19, and may even decrease SARS-COV-2 infection.
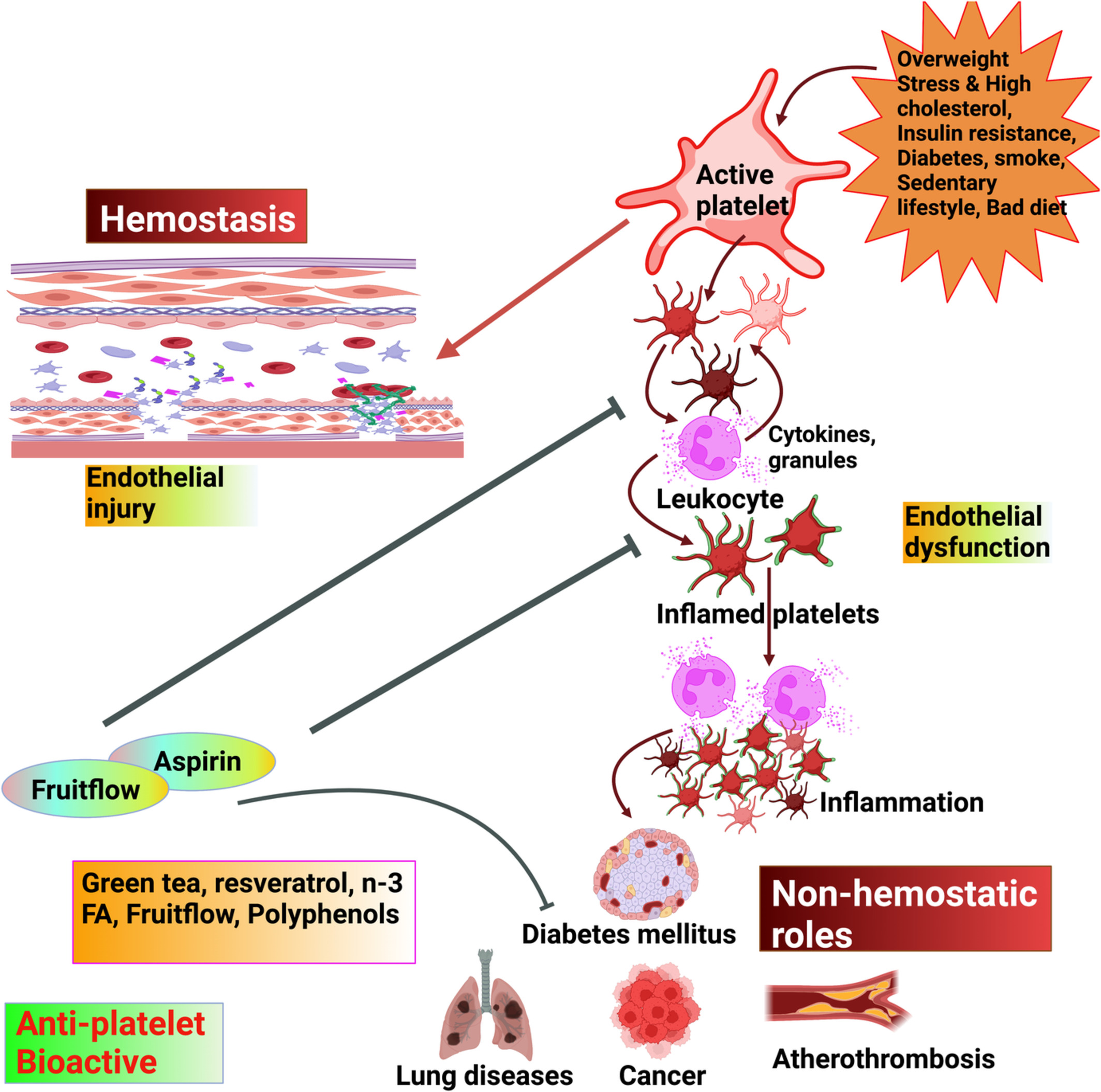
Bioactive food components and their inhibitory actions in multiple platelet pathways
- First Published: 11 October 2022
Recent developments in plant-derived edible nanoparticles as therapeutic nanomedicines
- First Published: 21 October 2022
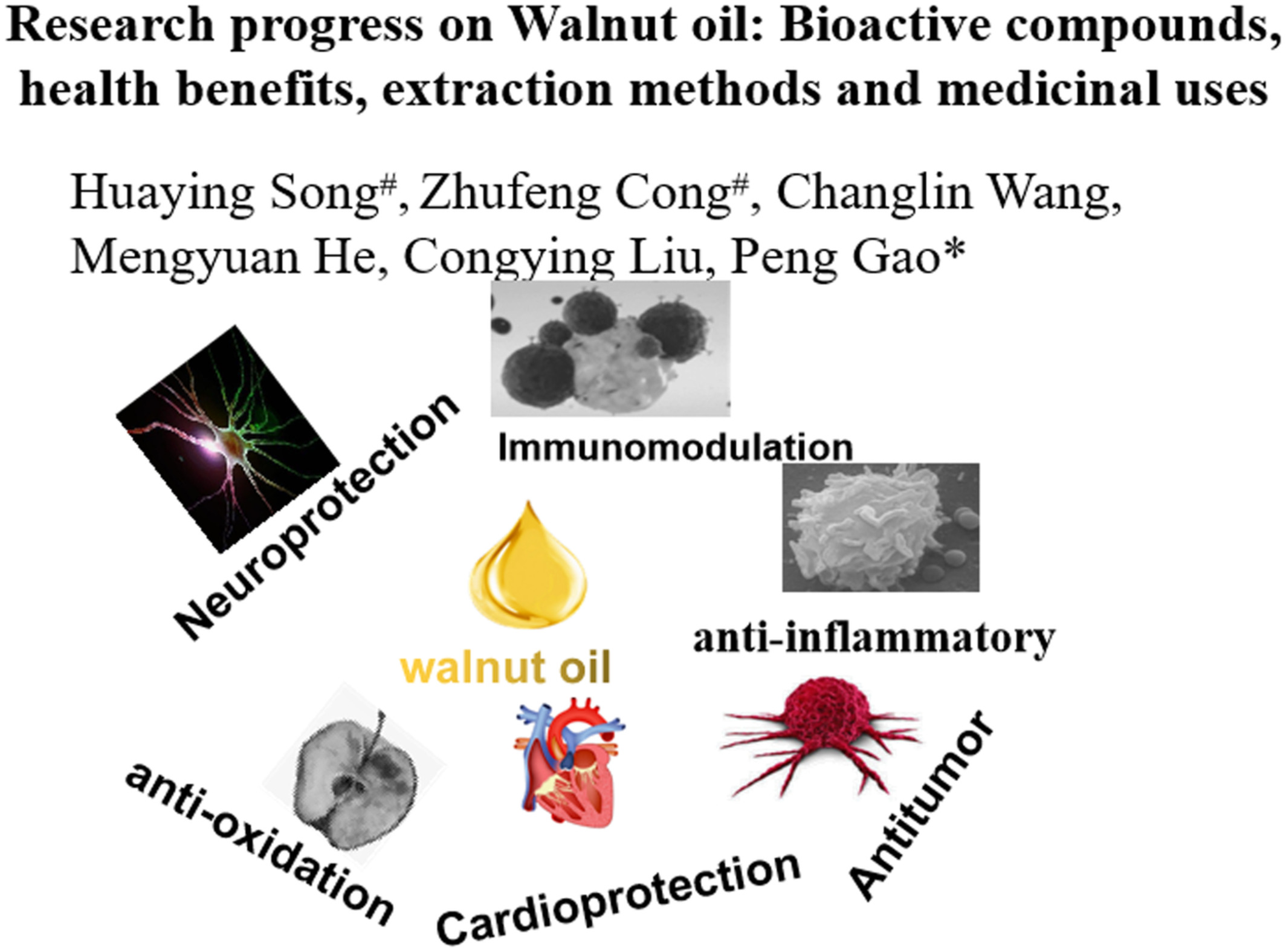
Research progress on Walnut oil: Bioactive compounds, health benefits, extraction methods, and medicinal uses
- First Published: 12 November 2022
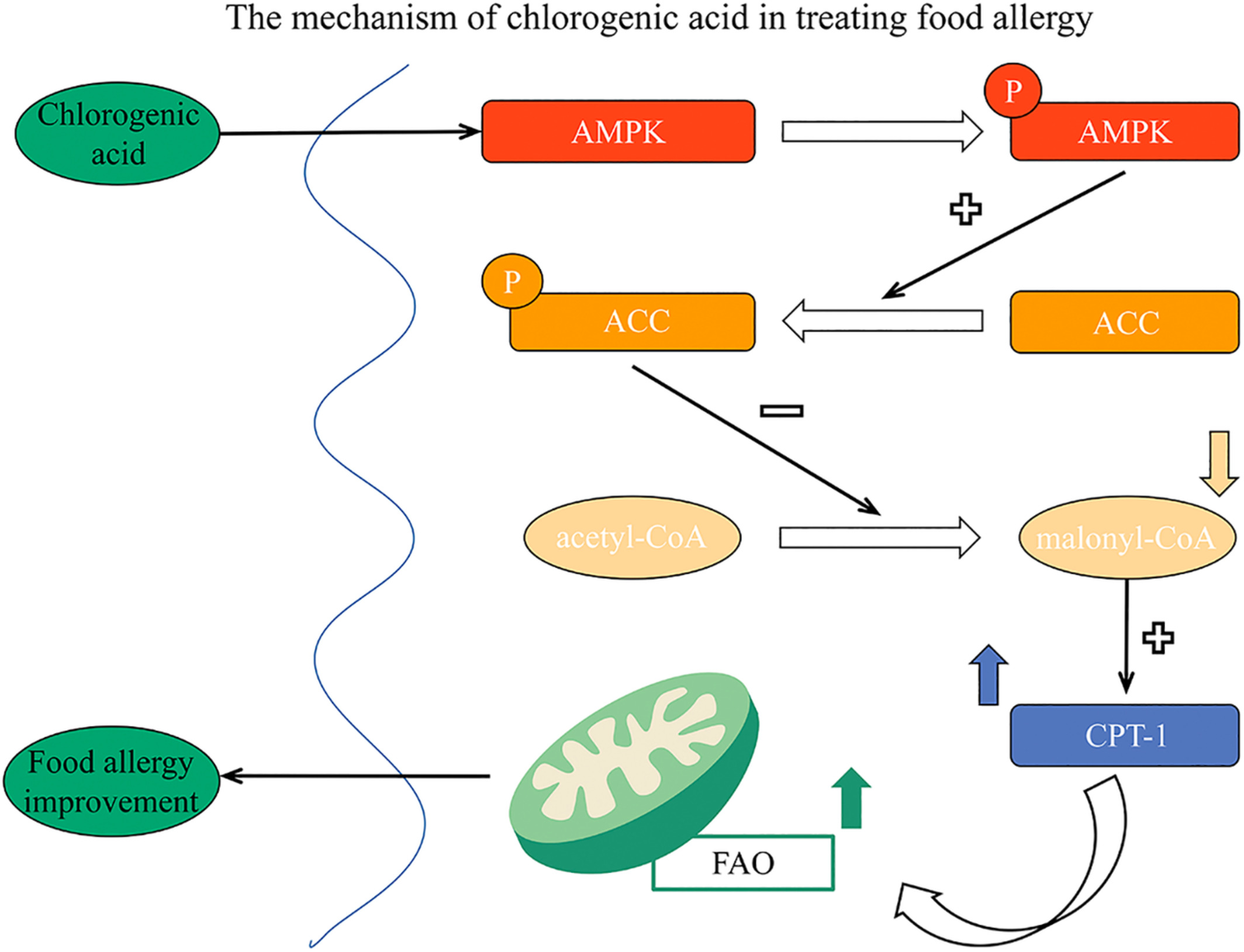
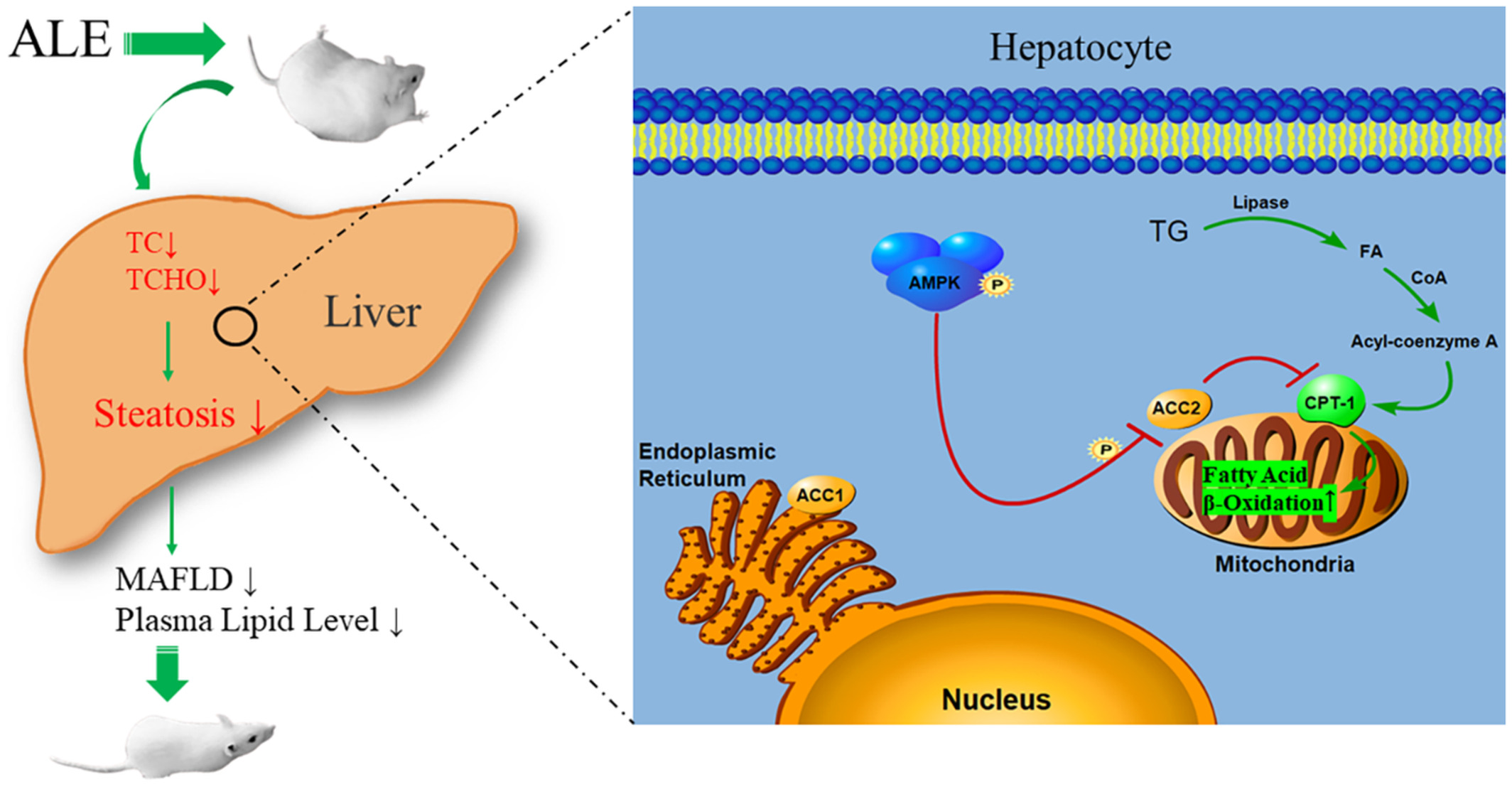
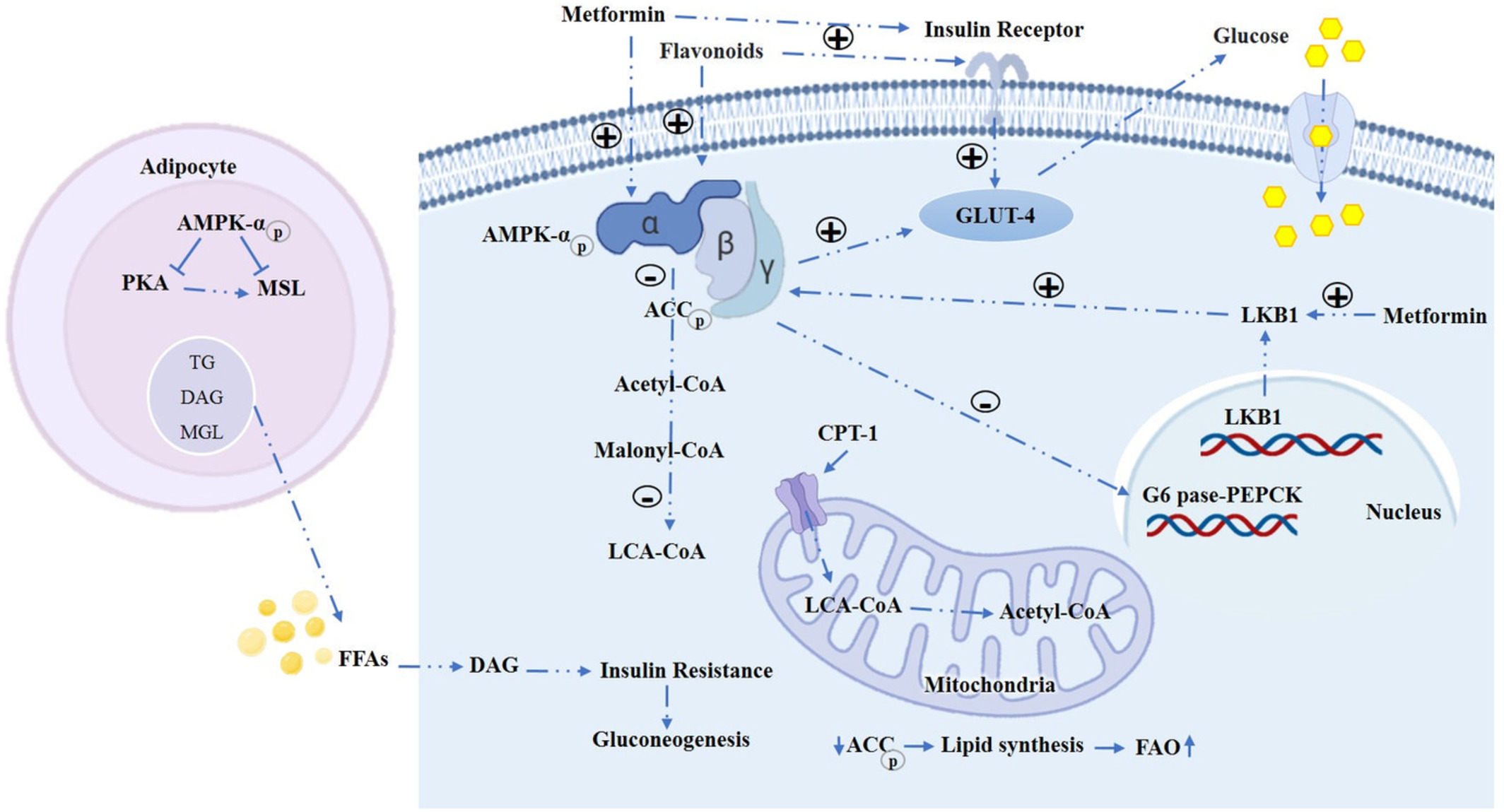
Chlorogenic acid improves food allergy through the AMPK/ACC/CPT-1 pathway
- First Published: December 2022
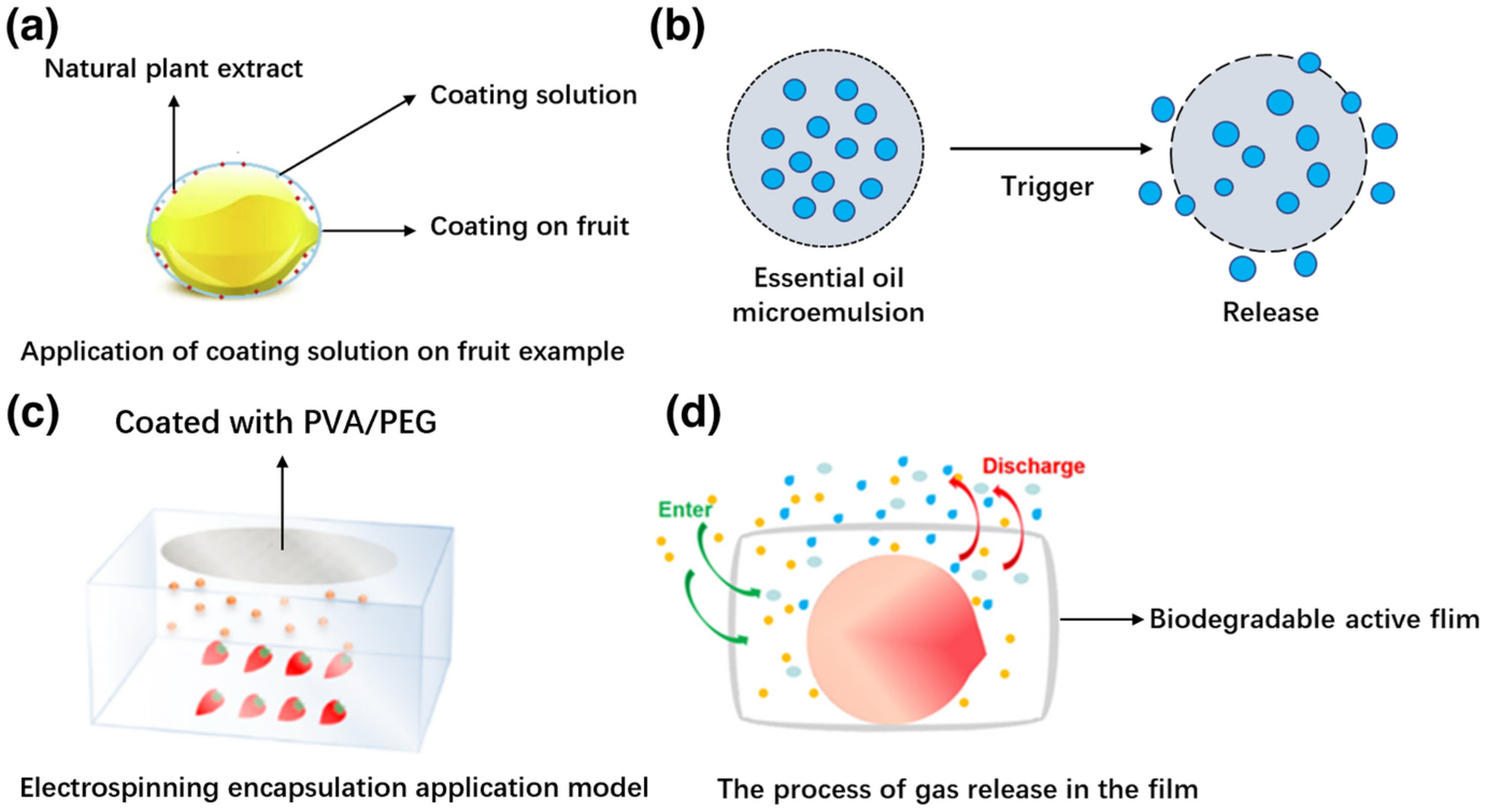
The role of essential oils in maintaining the postharvest quality and preservation of peach and other fruits
- First Published: 17 November 2022
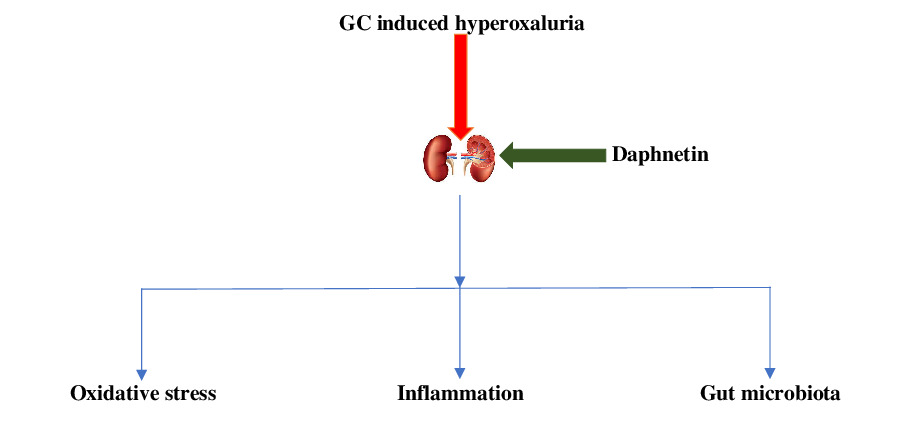
Nephro-protective effect of Daphnetin in hyperoxaluria-induced rat renal injury via alterations of the gut microbiota
- First Published: 22 August 2022
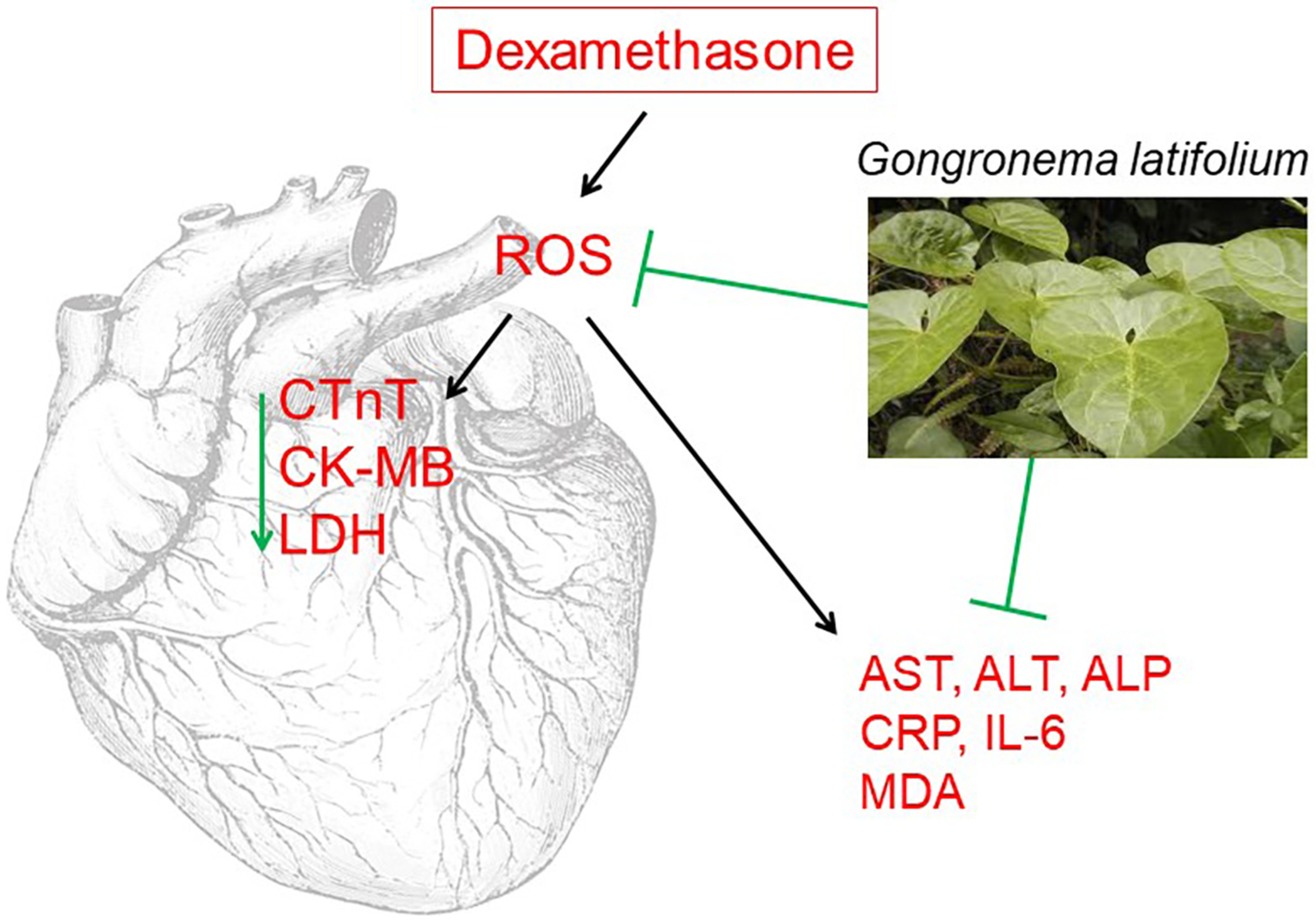
Gongronema latifolium leaf extract protects against dexamethasone-induced myocardial cell injury via cardiac oxido-inflammatory molecules modulation
- First Published: 17 August 2022
Chrysin improves diabetic nephropathy by regulating the AMPK-mediated lipid metabolism in HFD/STZ-induced DN mice
- First Published: 17 August 2022
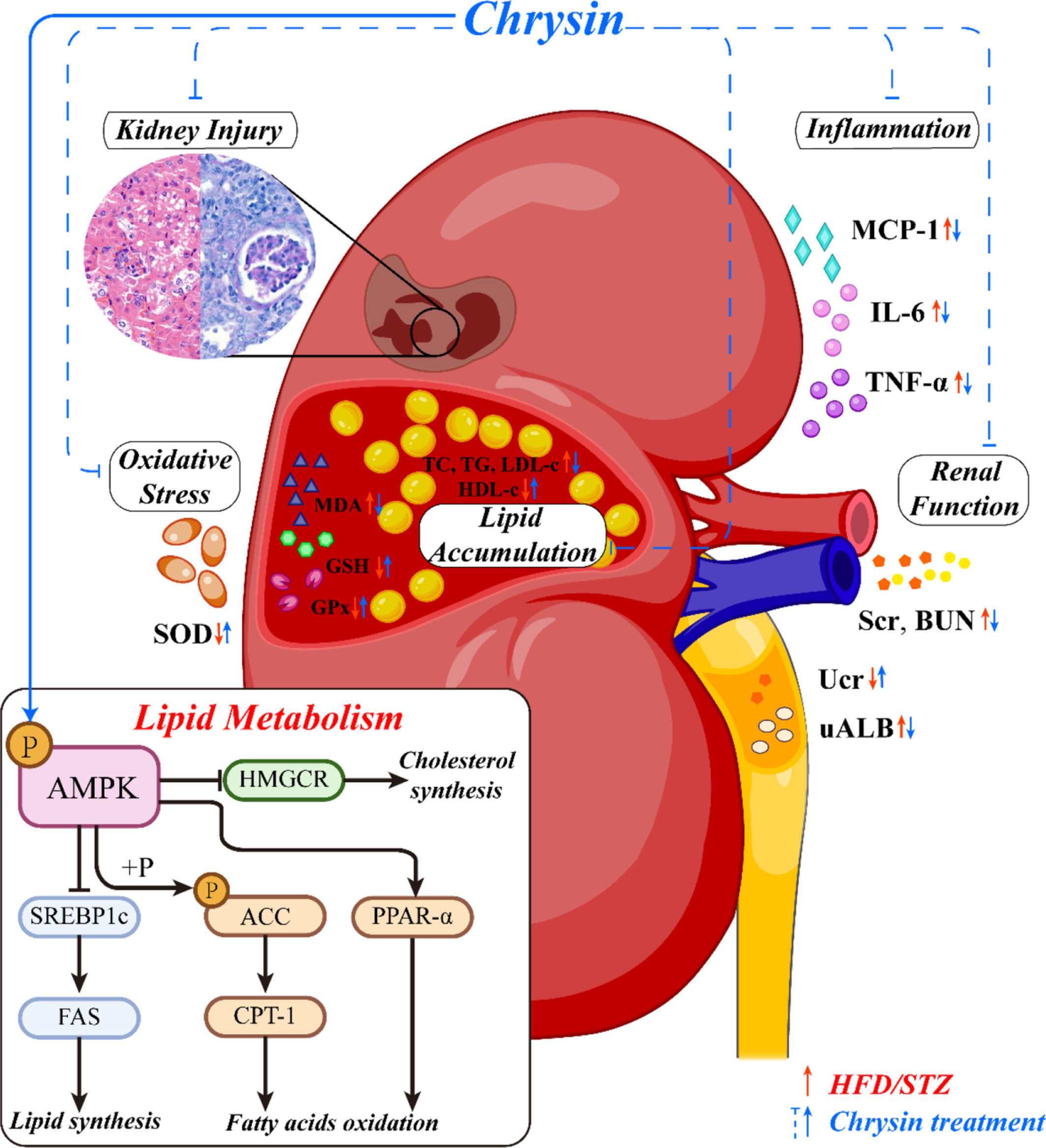
Chrysin ameliorated obesity, insulin resistance, kidney injury, decreased renal function, lipid accumulation, inflammation, and oxidative stress, commonly found in DN. Chrysin could modulate lipid metabolism and regulate the AMPK signaling pathway in the kidney and it is necessary for the effects of chrysin on DN. Chrysin improved DN by regulating lipid metabolism, and the effects partially depend on the activation of AMPK.
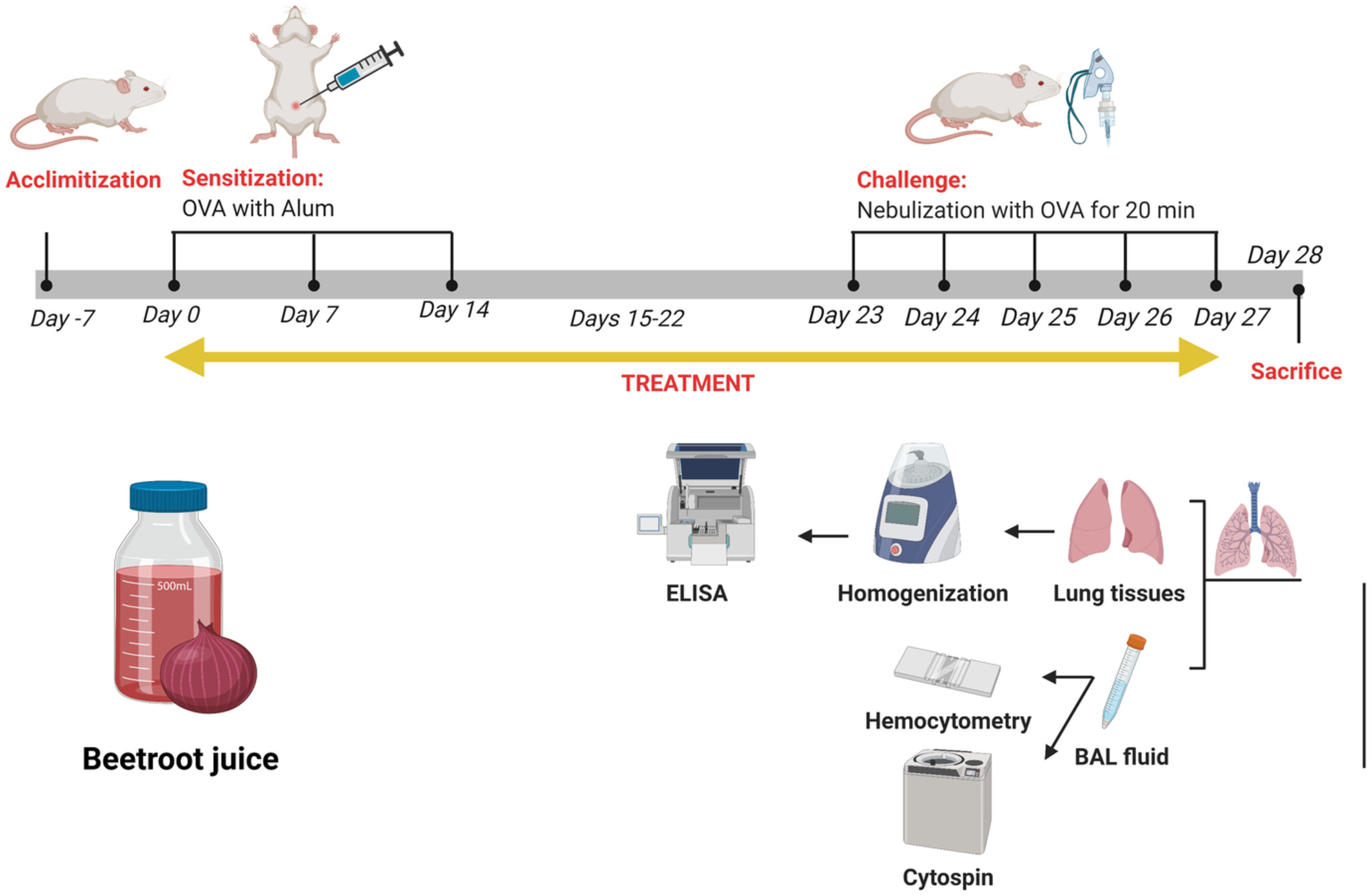
The effect of beetroot juice on airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma
- First Published: 17 August 2022
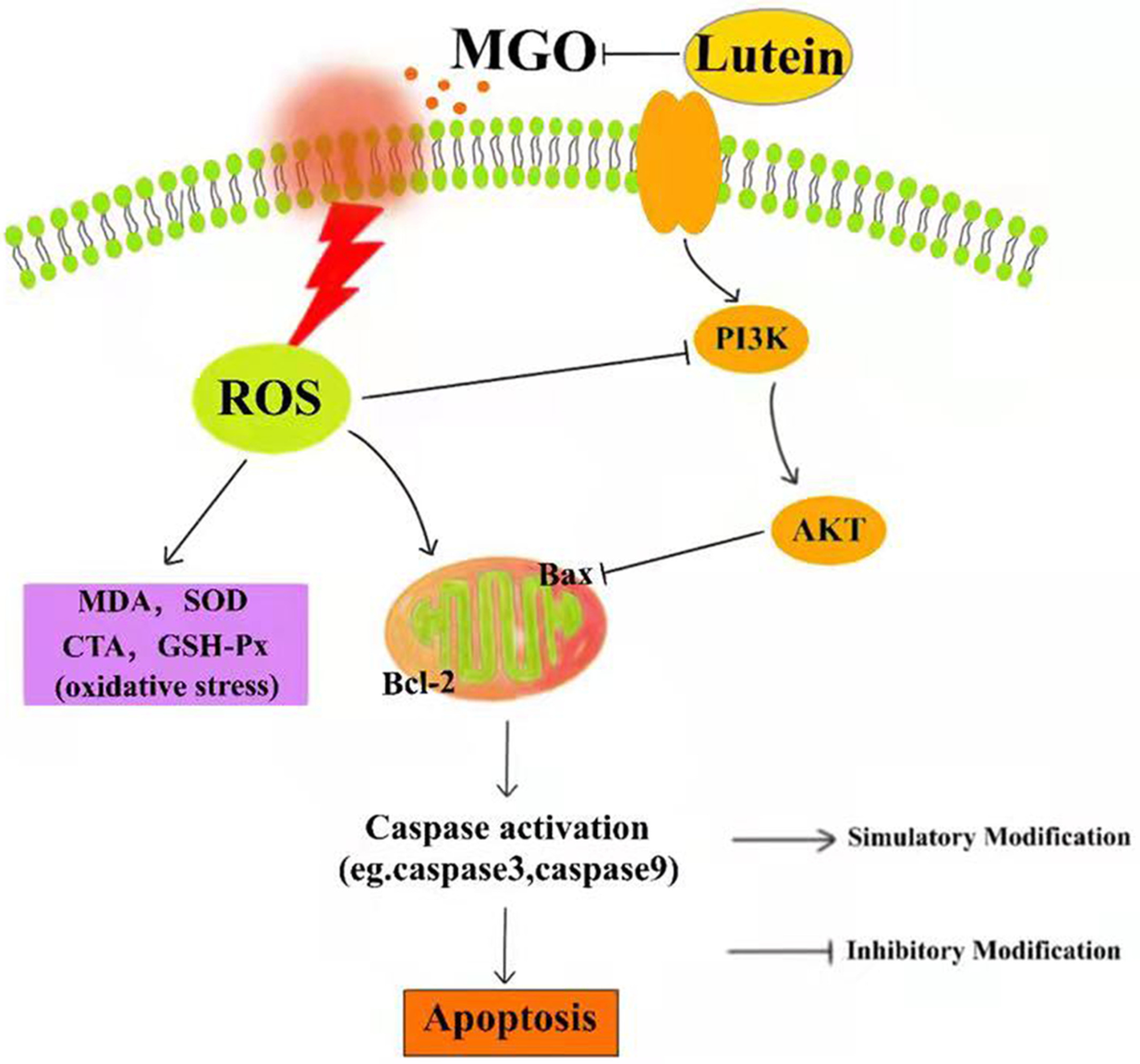
Lutein attenuated methylglyoxal-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in PC12 cells via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
- First Published: 26 August 2022
In vitro inhibition of glucose gastro-intestinal enzymes and antioxidant activity of hydrolyzed collagen peptides from different species
- First Published: 01 October 2022
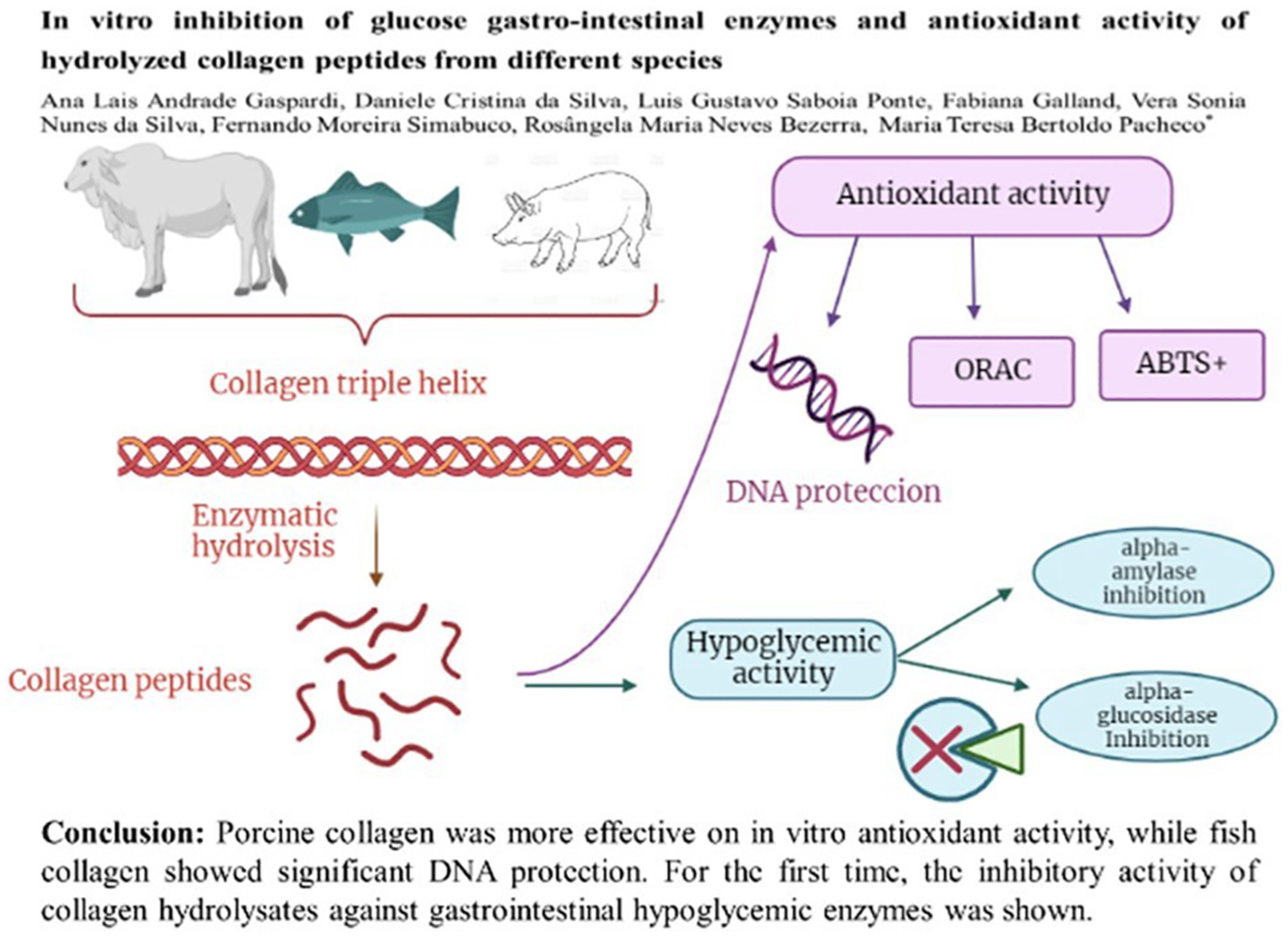
Different commercial sources of hydrolyzed collagen (fish, porcine, and bovine) showed antioxidant bioactivity, analyzed by ORAC, ABTS, and DNA protection; and inhibition of glucose gastrointestinal enzymes (alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase inhibition). Porcine collagen was more effective on in vitro antioxidant activity, while fish collagen showed significant DNA protection. For the first time, the inhibitory activity of collagen hydrolysates against gastrointestinal hypoglycemic enzymes was shown.
A new and efficient method for producing food ingredients high in l-ornithine using unused parts of white cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata)
- First Published: 07 September 2022
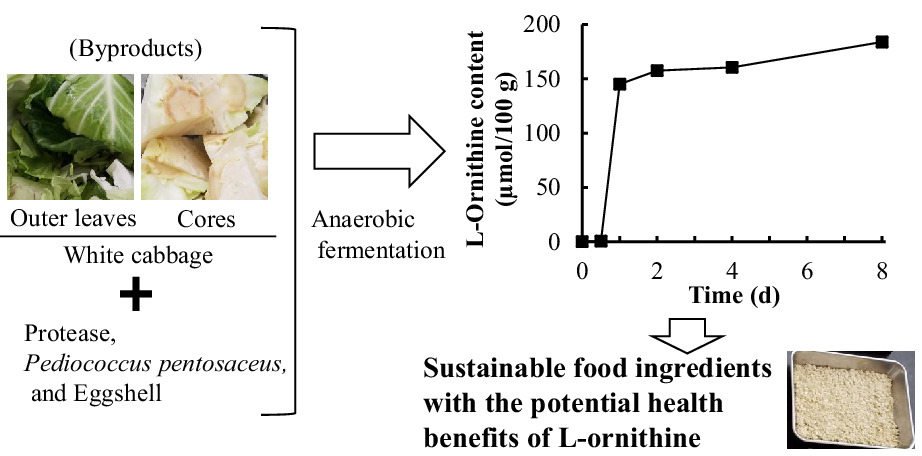
A surplus of unused parts of vegetables (e.g., white cabbage cores and outer leaves) is generated daily by factories of fresh-cut vegetables. Anaerobic fermentation of these vegetable residues with protease (Sumizyme FP) and Pediococcus pentosaceus did not produced l-ornithine, however, when eggshell was added to them, large amounts of l-ornithine were stably produced. These fermented products are sustainable food ingredients with the potential health benefits of l-ornithine.
A popular fermented soybean food of Northeast India exerted promising antihyperglycemic potential via stimulating PI3K/AKT/AMPK/GLUT4 signaling pathways and regulating muscle glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 07 September 2022
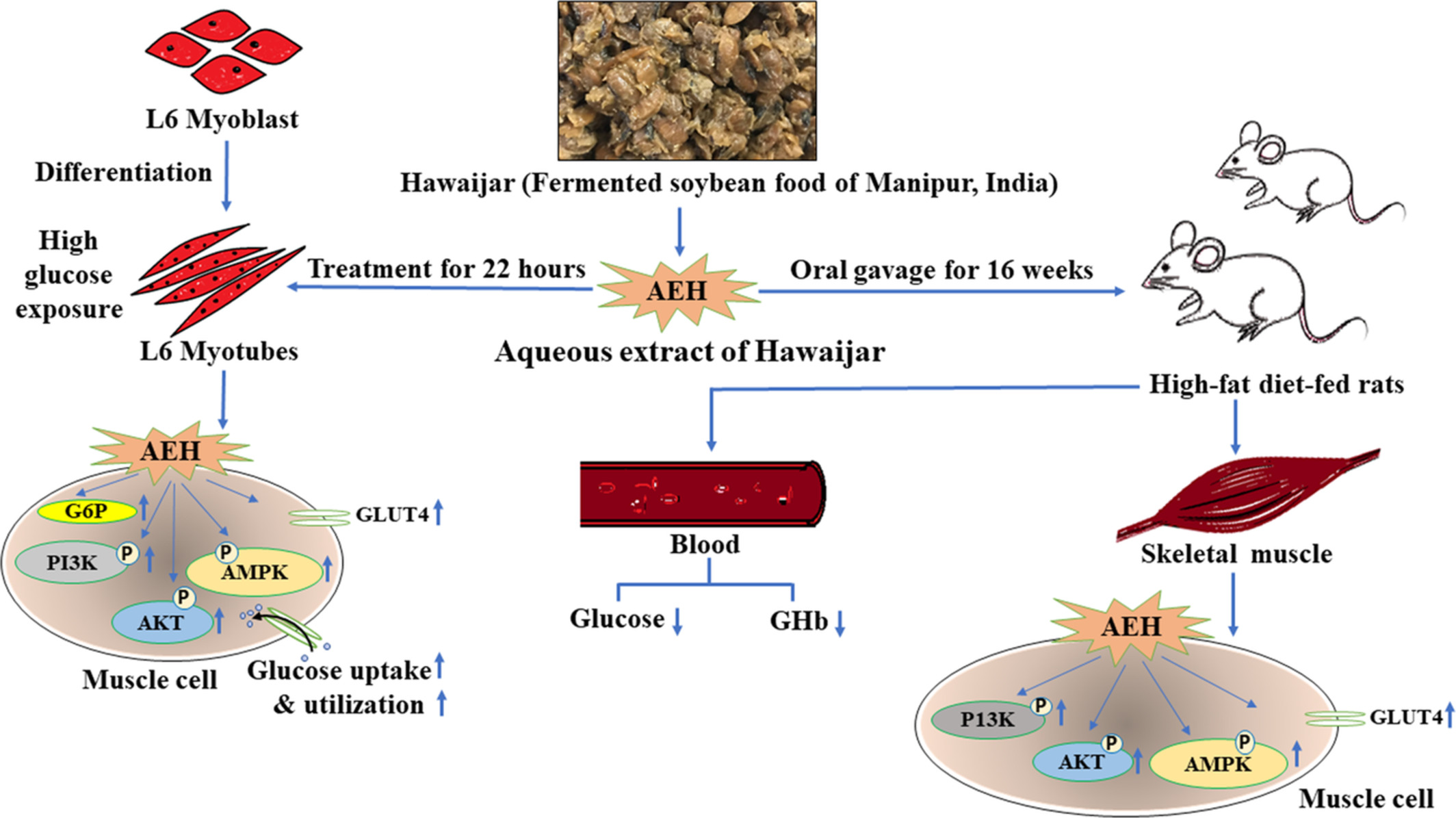
This study for the first time reported antidiabetic potential of Hawaijar, an indigenous fermented soybean food of Northeast India. Supplementation with aqueous extract of Hawaijar stimulated phospho-PI3K/phospho-AKT/phospho-AMPK/GLUT4 signaling cascades of glucose metabolism in high-glucose-treated cultured myotubes and muscle tissues of high-fat-diet-fed diabetic rats. Higher abundance of bioactive compounds (isoflavones/proteins/peptides) in Hawaijar may be responsible for the alleviation of impaired glucose metabolism associated with diabetes. This finding may be helpful for the development of a novel antidiabetic therapeutic.
Anti-inflammatory potential of berberine-rich extract via modulation of inflammation biomarkers
- First Published: 19 September 2022
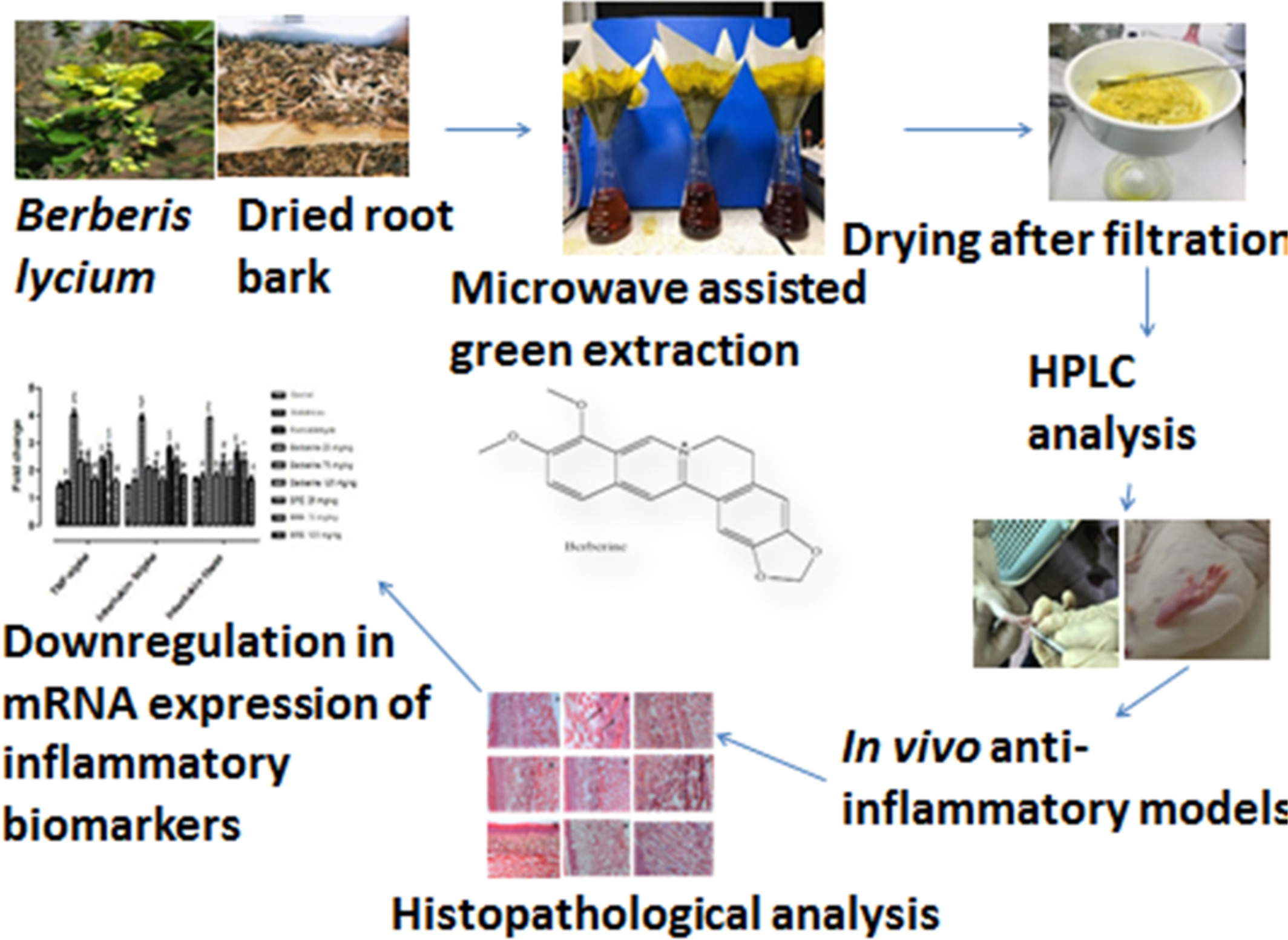
BRE from Berberis lycIum and berberine markedly decreased the paw diameter and inflammatory mediators in carrageenan and formaldehyde-induced inflammation. The levels of antioxidant enzymes were recovered with remarkable downregulation in mRNA and protein expression of inflammatory biomarkers. It is suggested that BRE obtained by microwave-assisted extraction technique is a natural, green, and therapeutically bioequivalent to berberine that could be used as an economical phytomedicine in the treatment of inflammatory disorders.
An investigation of correlation between structural and functional properties of Nigella sativa protein isolate
- First Published: 21 September 2022
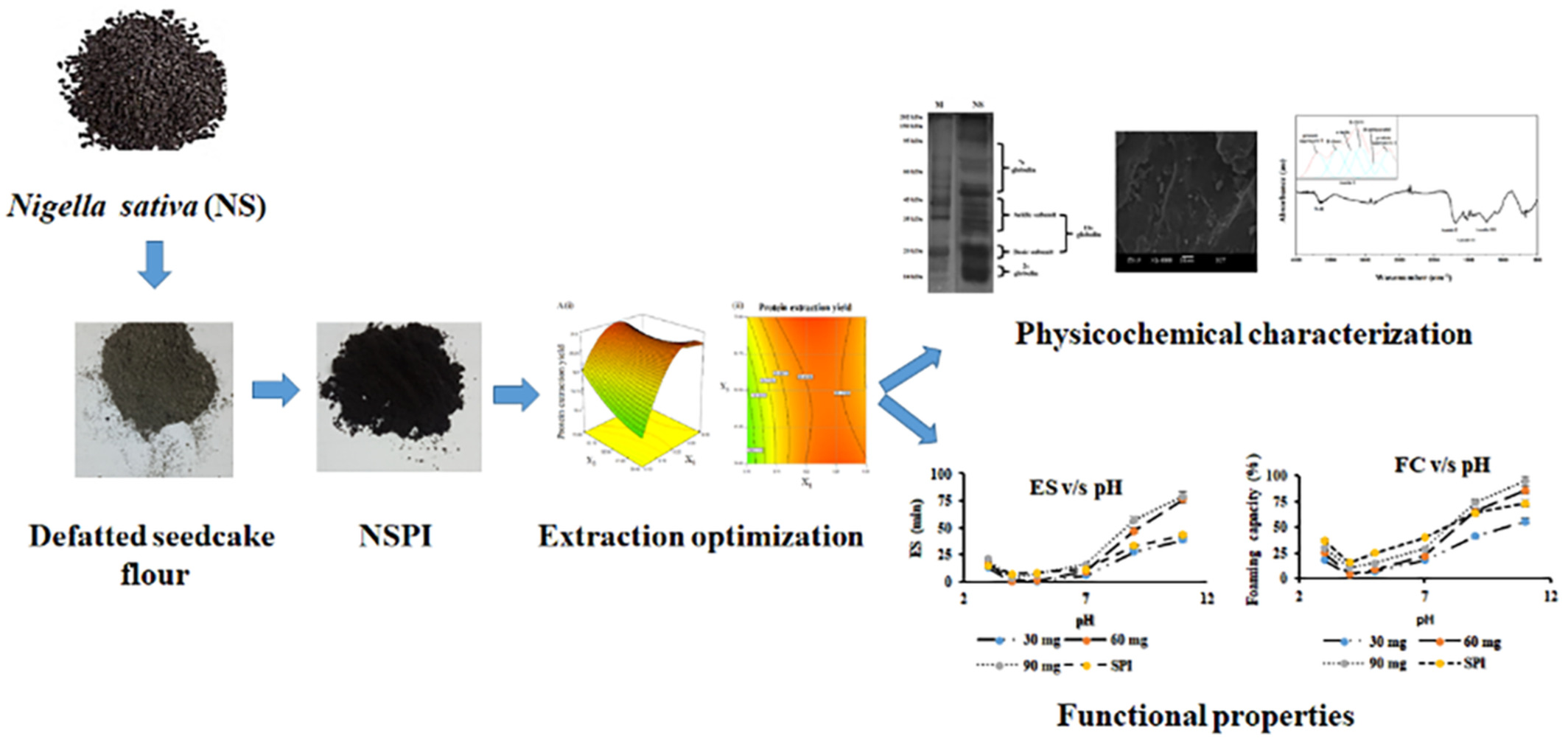
This project aims to optimize the NSPI extraction process and evaluate its physicochemical and functional properties for potential applications in the food industry. The methodology used ground Nigella sativa seeds, which underwent Soxhlet extraction to produce defatted seedcake flour. The NSPI extraction from defatted seedcake flour was optimized using the RSM approach, and the final product was characterized for its properties.
Holothuria Leucospilota polysaccharides alleviate hyperlipidemia via alteration of lipid metabolism and inflammation-related gene expression
- First Published: 16 September 2022
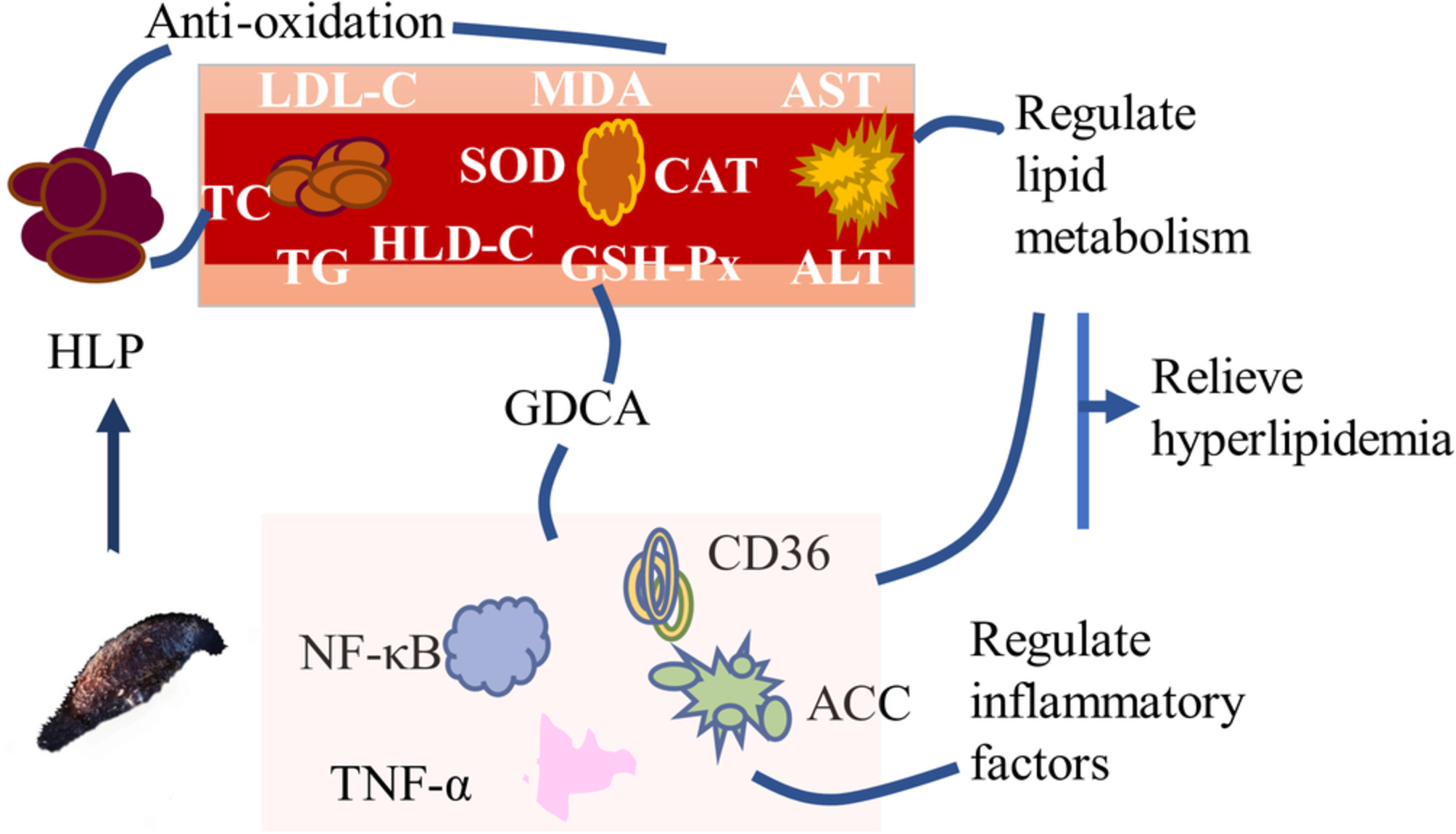
After being fed with sea cucumber polysaccharides, the serum levels of TC, TG, LDL-C and MDA in the high-fat group were significantly increased, the serum levels of HDL-C, SOD, CAT, GSH-Px, ALT and AST were decreased; HLP inhibited the expression of ACC, CD36, TNF-α and NF-κB, decreased the accumulation of lipid and the secretion of inflammatory factors in liver. HLP relieved hyperlipidemia mainly by regulating lipid metabolism and regulating inflammatory factors.
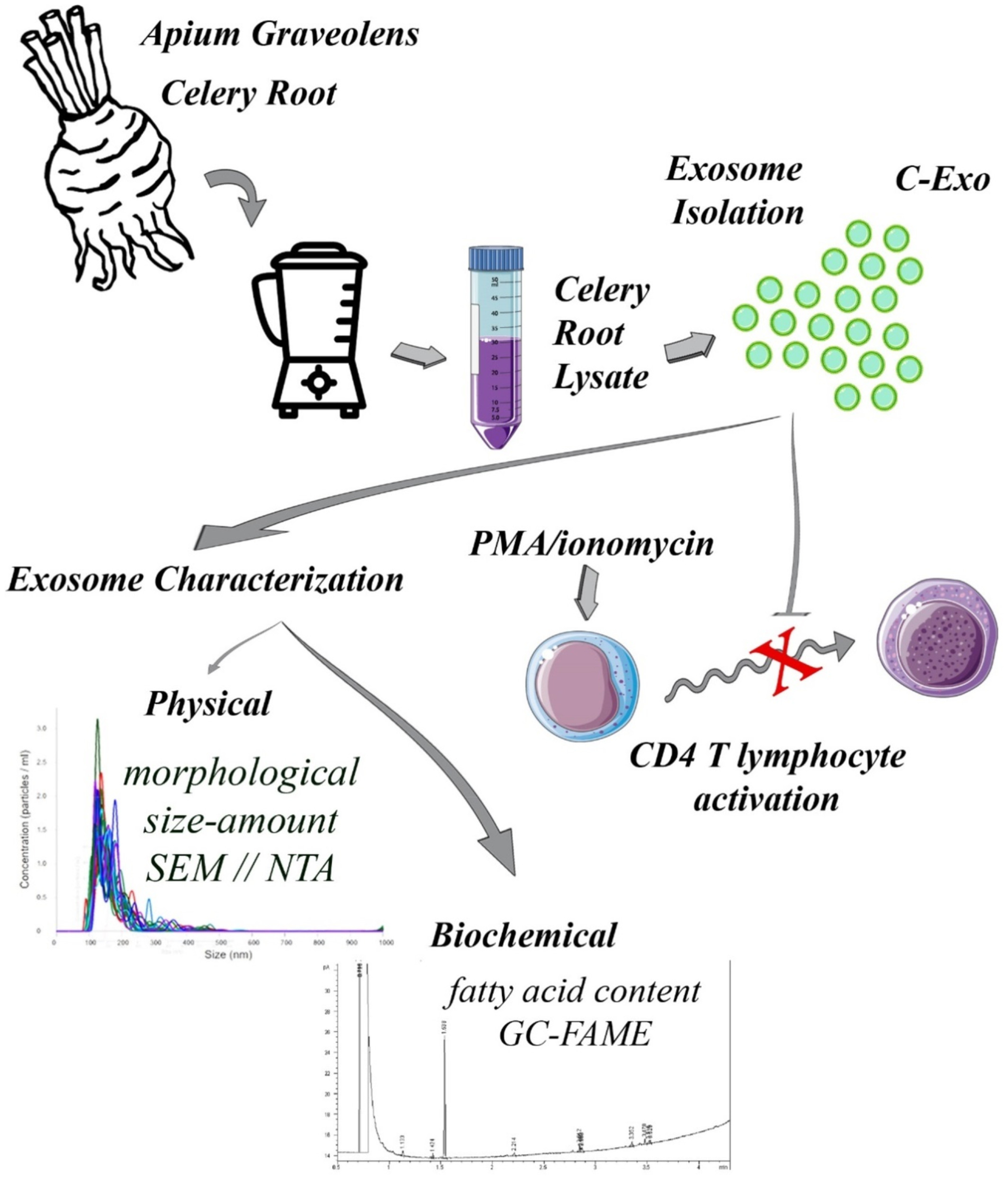
Usage of celery root exosome as an immune suppressant; Lipidomic characterization of apium graveolens originated exosomes and its suppressive effect on PMA/ionomycin mediated CD4+ T lymphocyte activation
- First Published: 01 October 2022
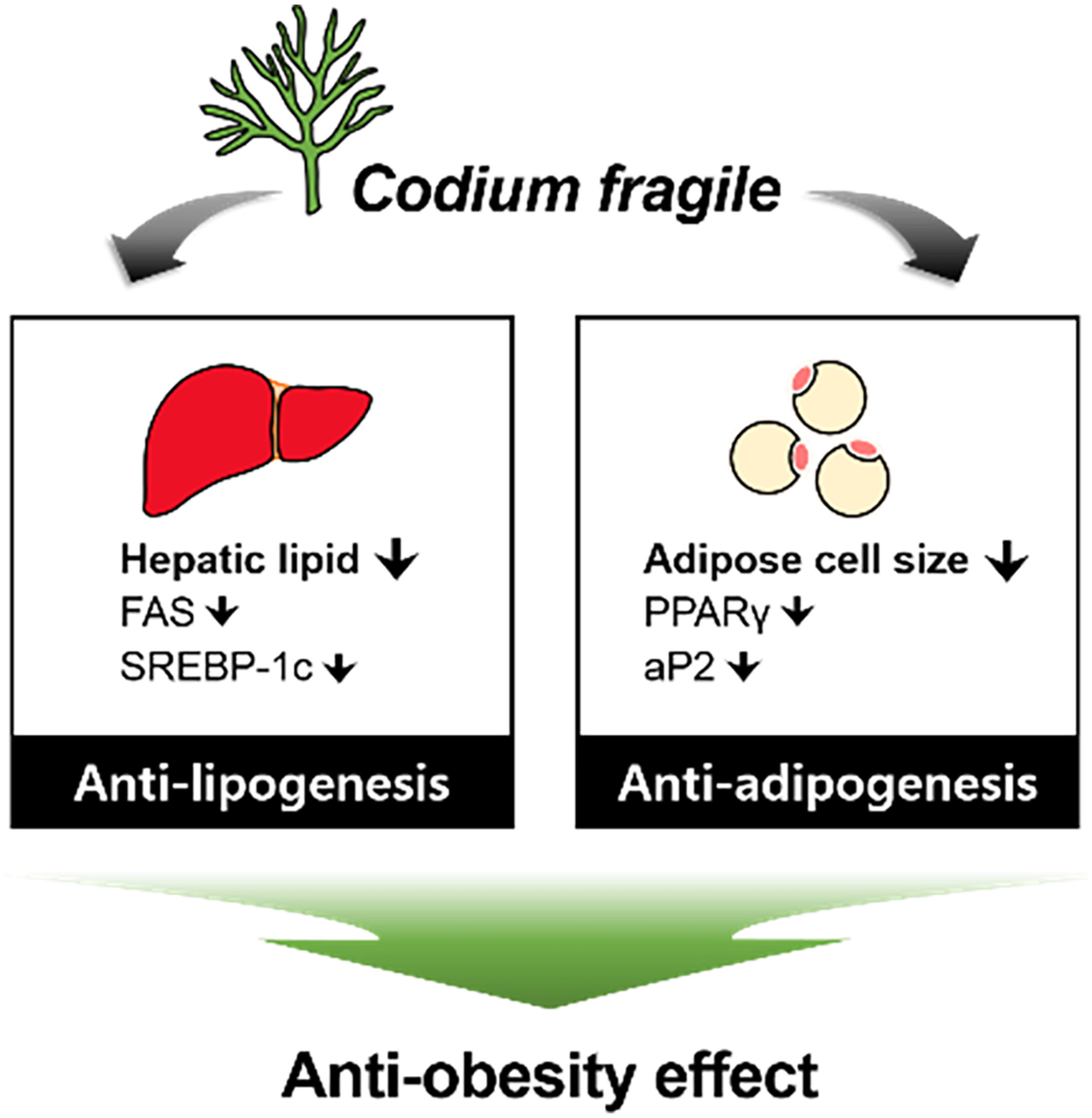
Codium fragile reduces adipose tissue expansion and fatty liver incidence by downregulating adipo- and lipogenesis
- First Published: 12 September 2022
A network pharmacology strategy combined with in vitro experiments to investigate the potential anti-inflammatory mechanism of Prunus cerasifera Ehrhart
- First Published: 28 September 2022
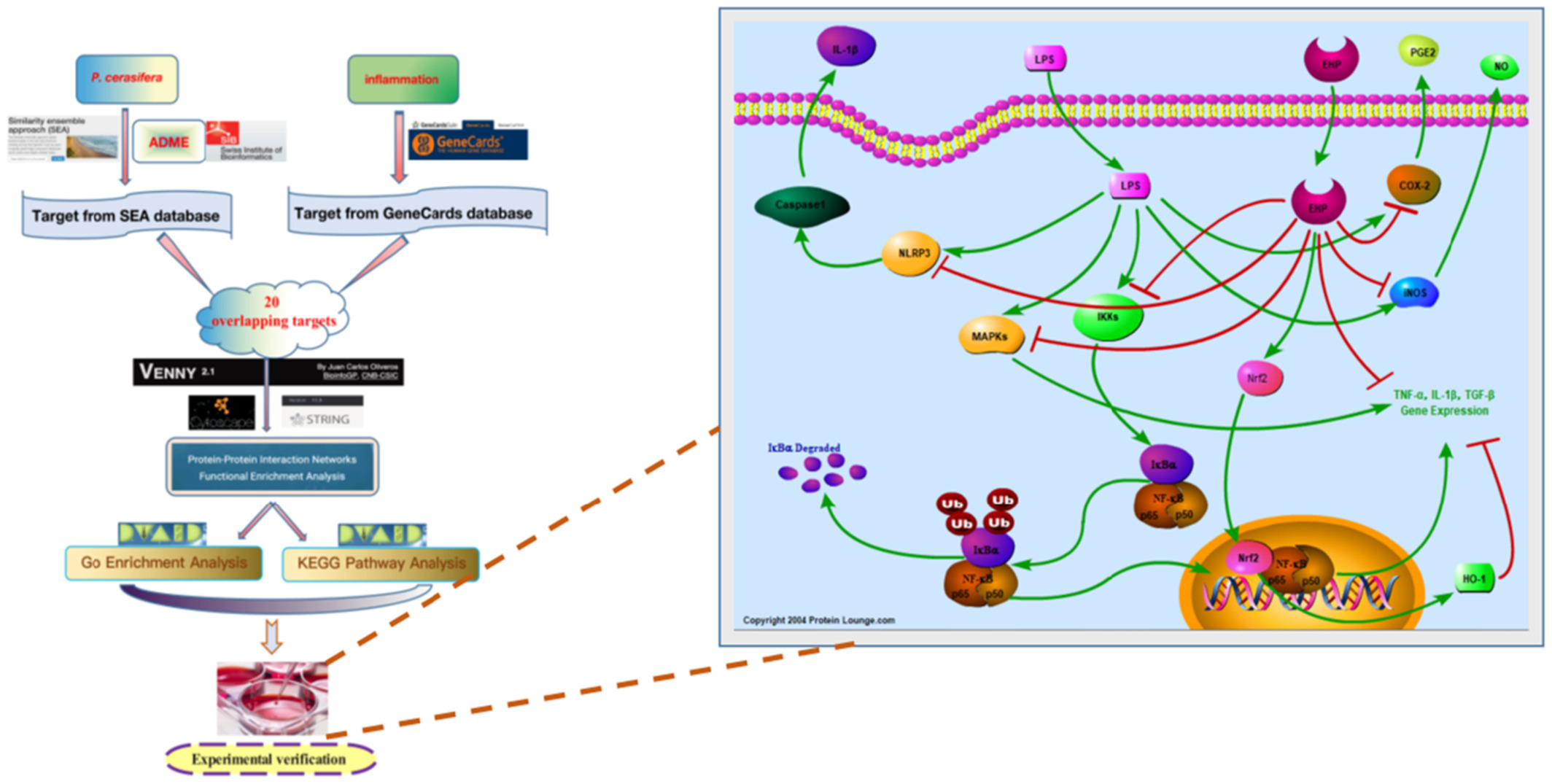
The underlying anti-inflammatory mechanism of Prunus cerasifera Ehrhart was investigated through network pharmacology in combination with Western Blot and ELISA experiments. The Network pharmacology analysis results indicated that P. cerasifera was related to TNF signaling pathway, inflammatory cytokine, and MAPK signaling pathway. In vitro experiment results showed that P. cerasifera exerted anti-inflammatory effect via NF-κB (p65), MAPKs, cell pyrolysis, and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. It could be further applied as a safe anti-inflammatory agent from the natural source.
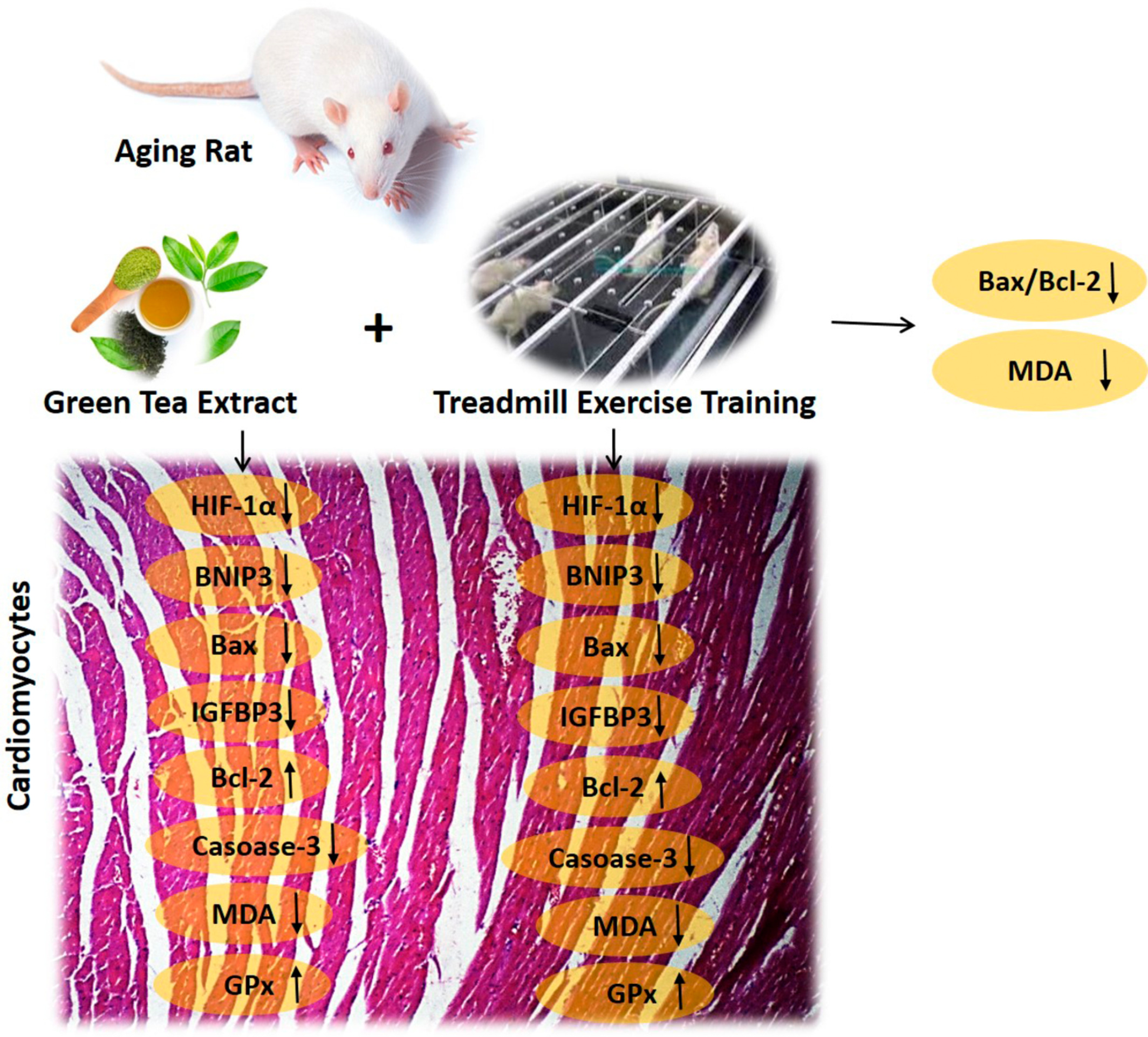
Twelve weeks of treadmill exercise training with green tea extract reduces myocardial oxidative stress and alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis in aging rat: The emerging role of BNIP3 and HIF-1α/IGFBP3 pathway
- First Published: 07 September 2022
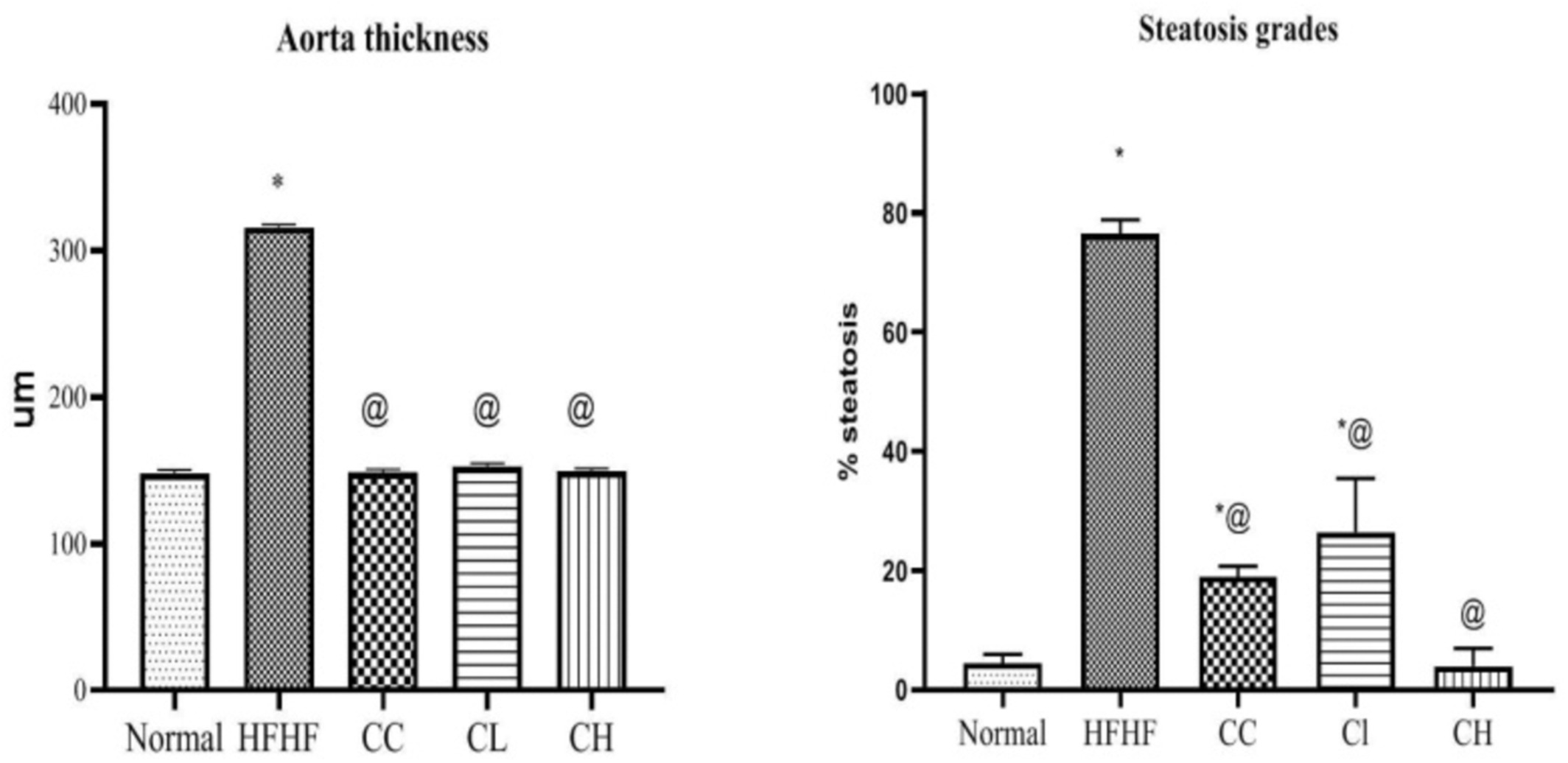
Green tea could improve elderly hypertension by modulating arterial stiffness, the activity of the renin/angiotensin/aldosterone axis, and the sodium–potassium pumps in old male rats
- First Published: 30 September 2022
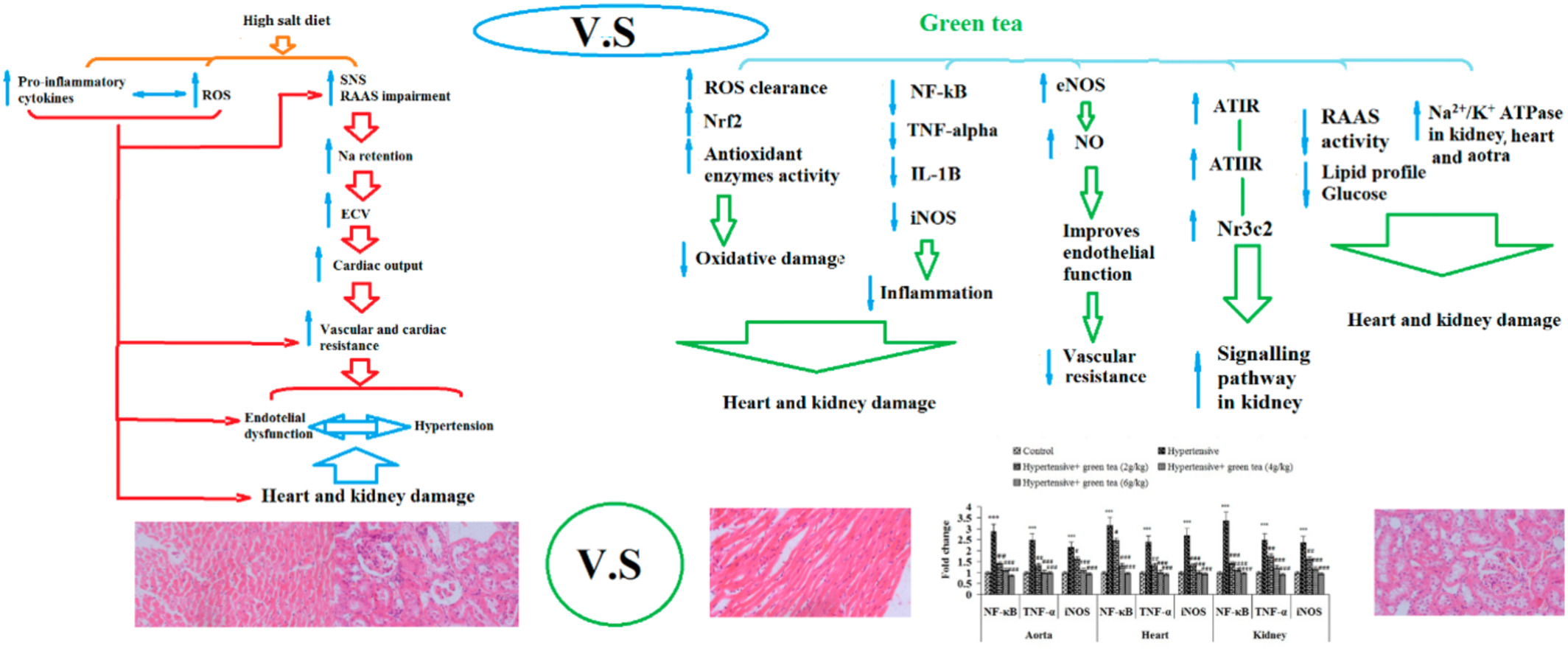
- The expression of sodium–potassium pump in heart, kidney, and aortic tissues
- The activity of renin–angiotensin II–aldosterone system in kidney
- Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in the heart, aorta, and kidneys, and metabolic factors.
- The expression of eNOS and increase in NO bioavailability
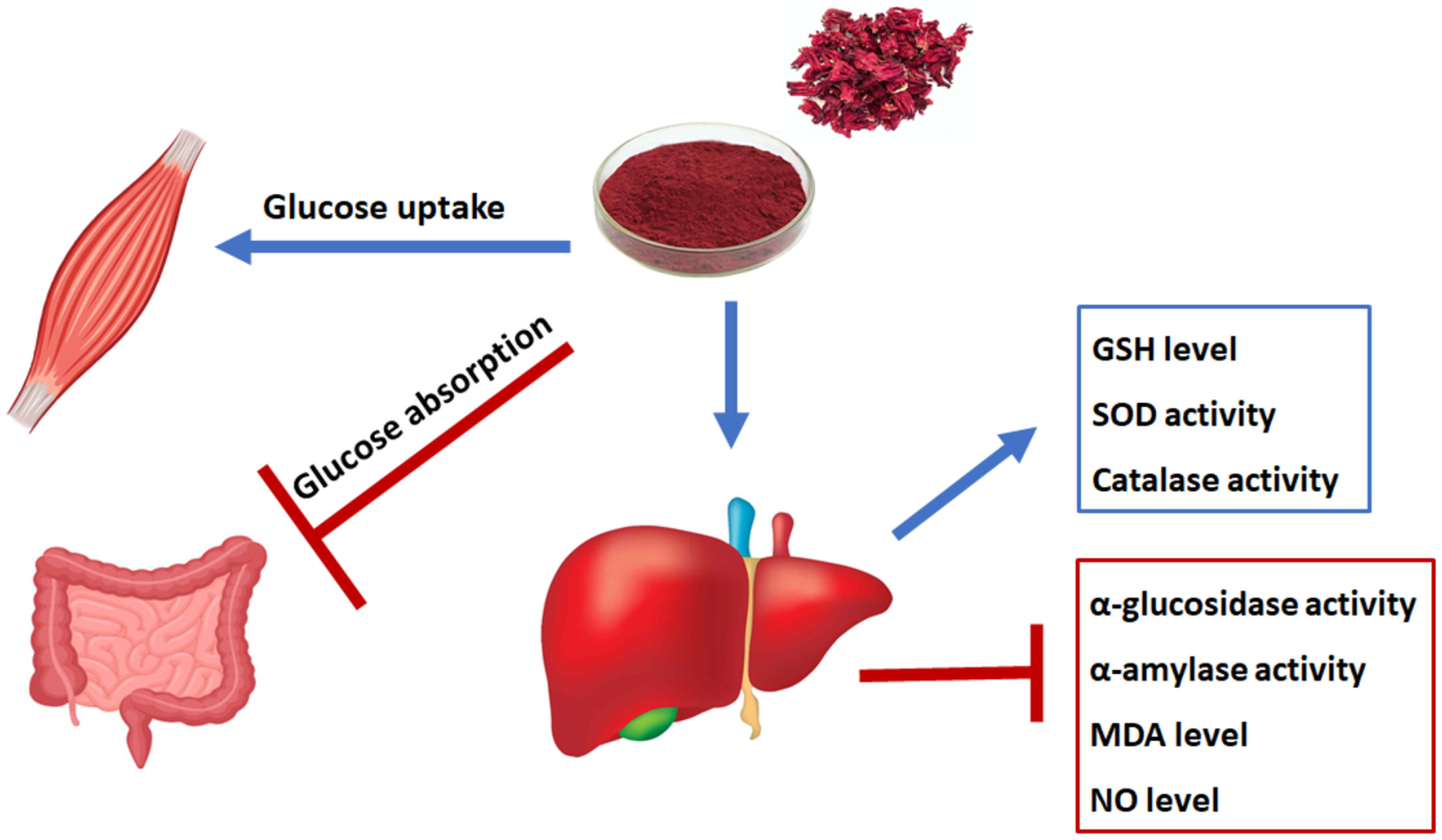
Hibiscus sabdariffa L. polyphenolic-rich extract promotes muscle glucose uptake and inhibits intestinal glucose absorption with concomitant amelioration of Fe2+-induced hepatic oxidative injury
- First Published: 18 October 2022
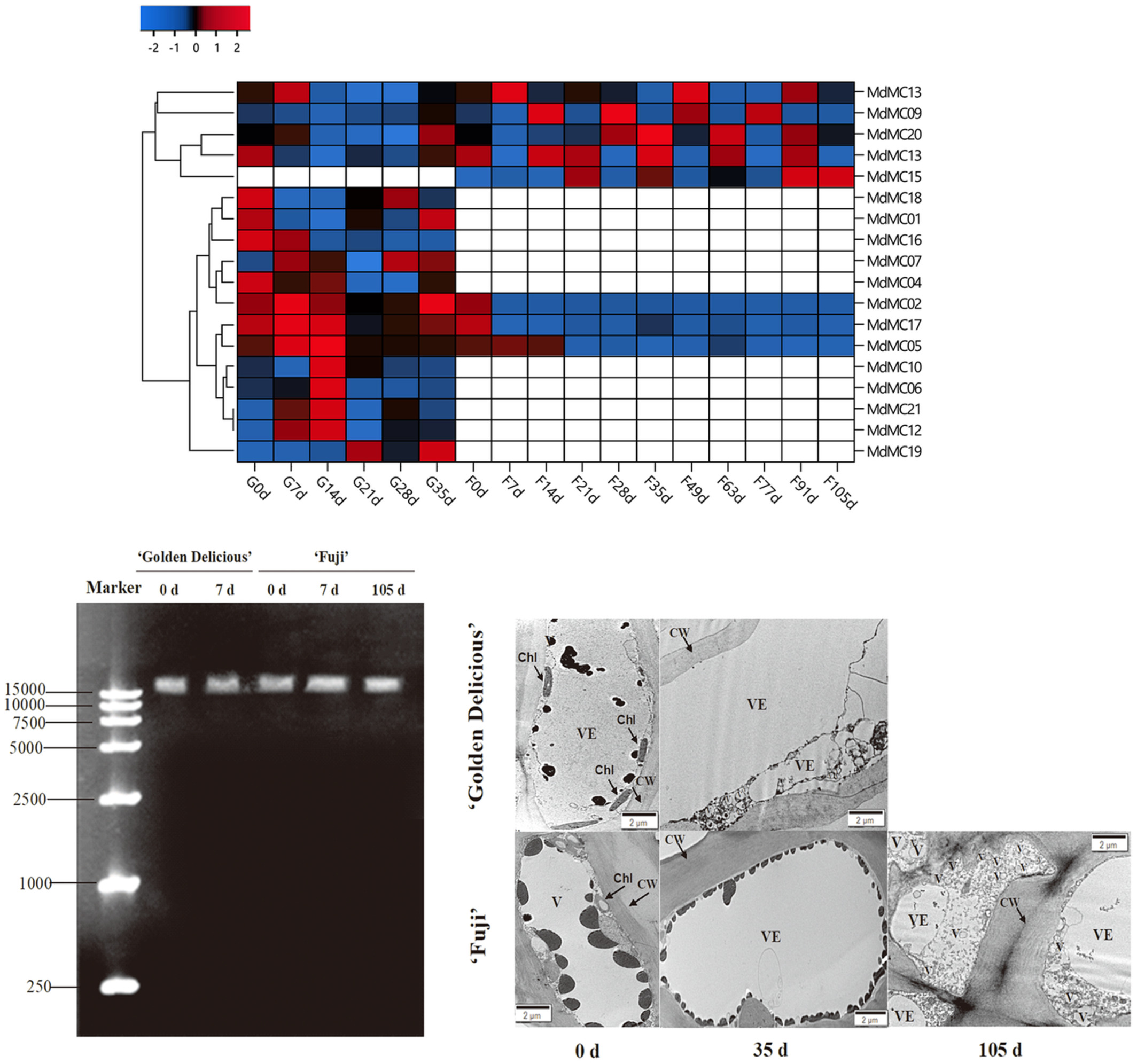
Comparative analysis of expression profiles of metacaspase (MC) genes between two apple (Malus domestica) cultivars with distinct ripening behavior
- First Published: 12 September 2022
Aqueous extract of Polygonatum sibiricum ameliorates glucose and lipid metabolism via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
- First Published: 13 October 2022
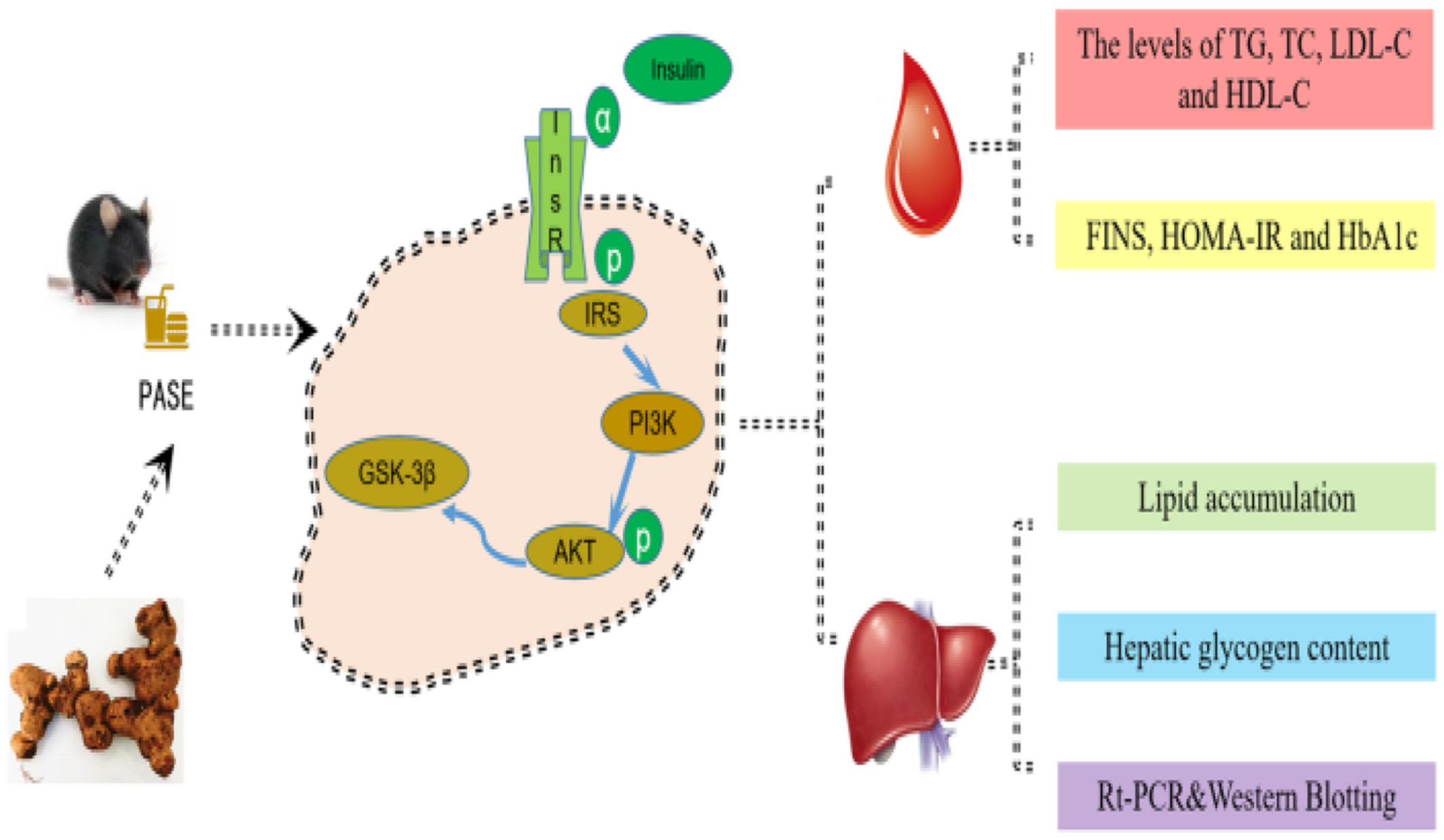
PSAE showed protective effects on the indicators of glycolipid metabolism. PSAE significantly increased the protein levels of p-IRS1, PI3K, p-AKT, and p-GSK3β in a dose-dependent manner in the model mice. PSAE can effectively regulate glucose and lipid metabolism during the development of T2DM in mice via regulation of IRS1/PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway.
Hypoglycemic and antioxidative activity evaluation of phenolic compounds derived from walnut diaphragm produced in Xinjiang
- First Published: 19 September 2022
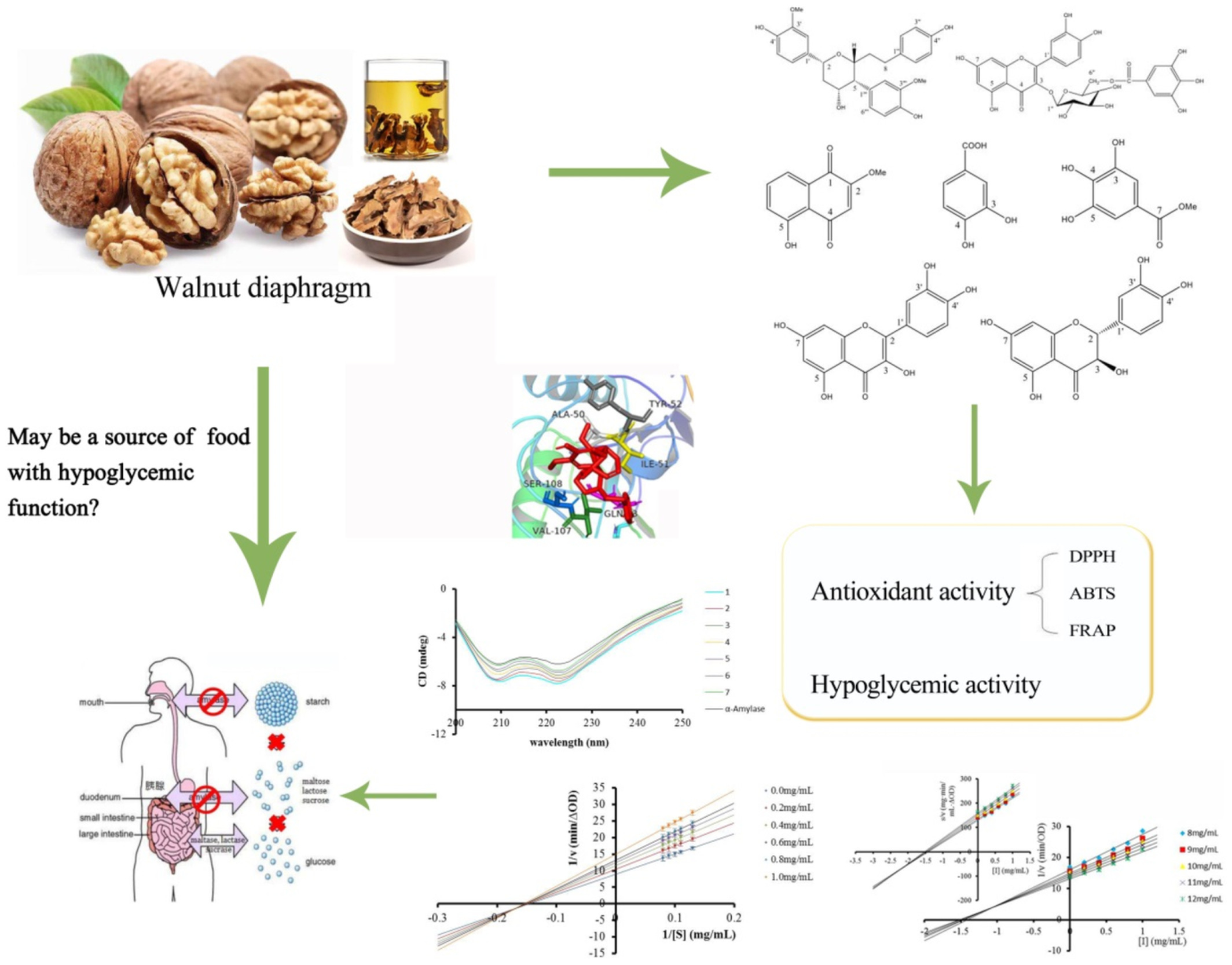
In order to provide a basis for application of Walnut diaphragm in functional food, the chemical constituents and activities of it were conducted. Seven phenolic compounds were isolated and activity experiments showed that compounds 1 and 2 had the strongest inhibitory activity against α-amylase in a mixed-competitive inhibition manner.
Exploring the mechanism of citric acid for treating glucose metabolism disorder induced by hyperlipidemia
- First Published: 20 September 2022
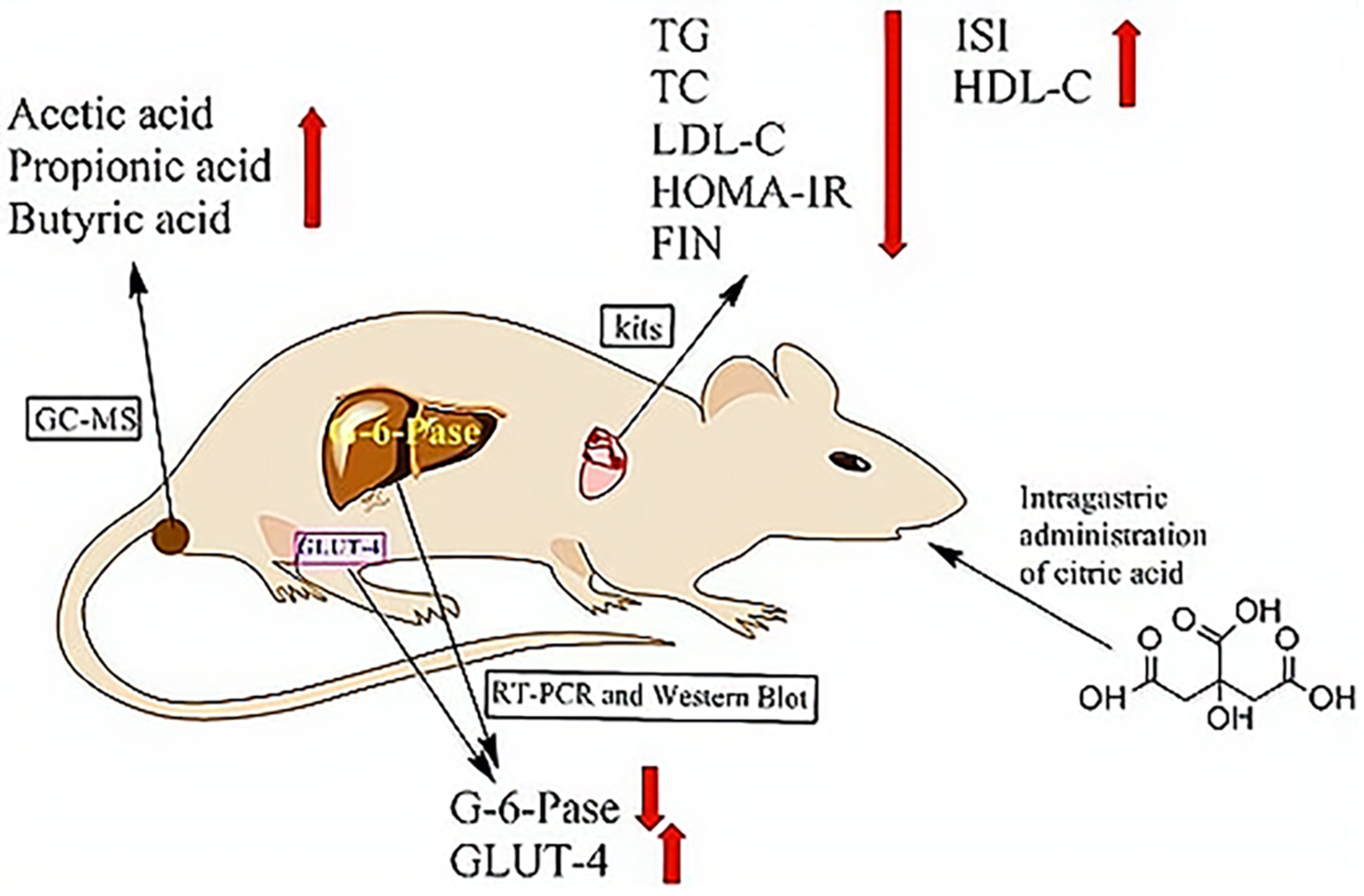
Citric acid decreased liver index, HDL-C blood, glucose and insulin resistance index, while reduced levels of TG, TC and LDL-C. Citric acid down-regulated mRNA and protein expression levels of G-6-Pase, while up-regulated mRNA and protein expression levels of GLUT-4. Citric acid increased the contents of acetic, propionic and butyric acids.
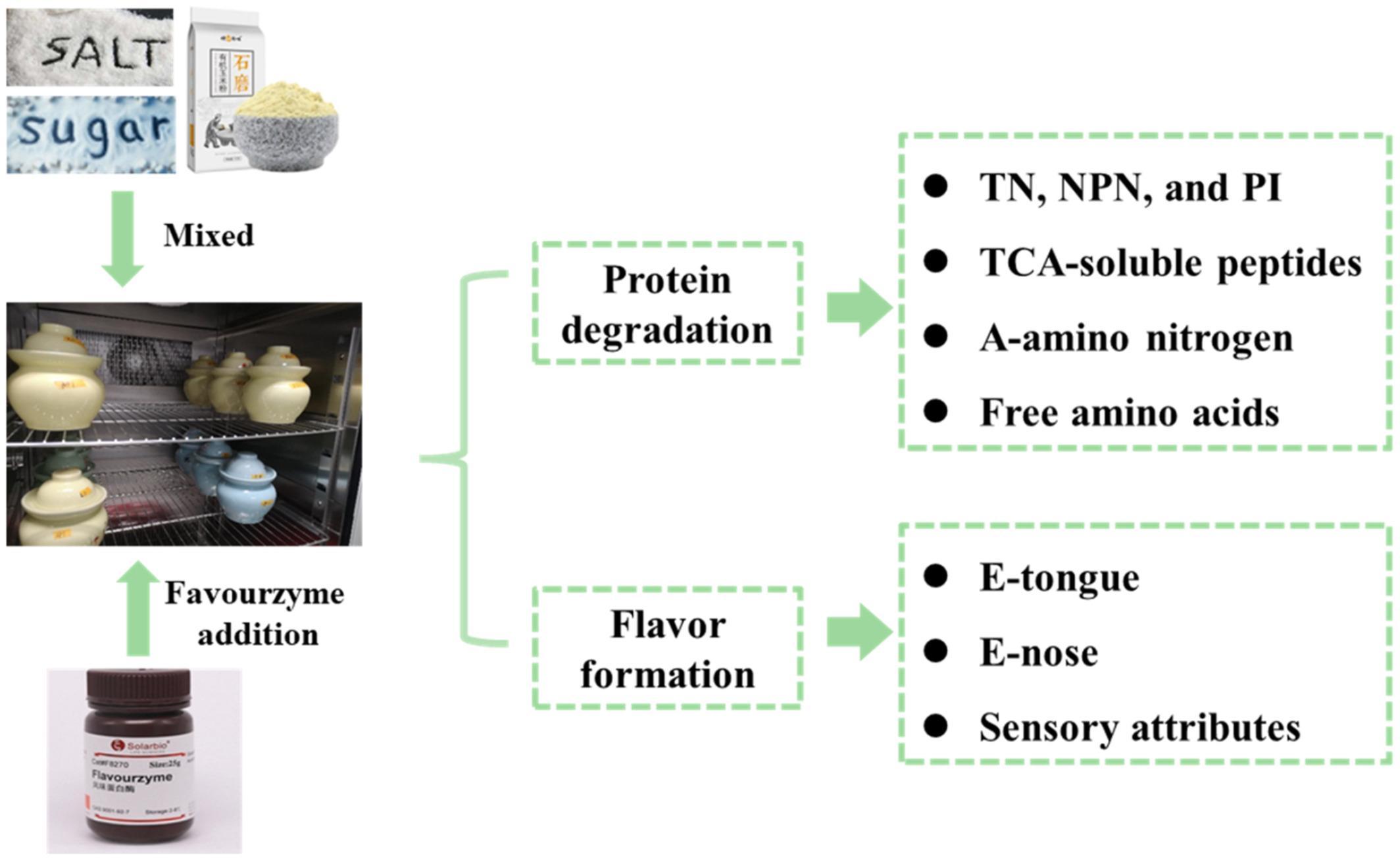
Effects of flavourzyme addition on protein degradation and flavor formation in grass carp during fermentation
- First Published: 19 September 2022
Preparation of Black pepper (Piper nigrum L.) essential oil nanoparticles and its antitumor activity on triple negative breast cancer in vitro
- First Published: 19 September 2022

To achieve effective encapsulation of black pepper essential oil and an excellent anti-triple negative breast cancer activity, nanoparticles loaded with BP-EO were prepared using Eudragit L100 as the carrier by the nanoprecipitation method. The results showed that the developed nanoparticles had an average size of around 178 nm, a zeta-potential of −57 mV, and an encapsulation efficiency equal to 89% with a loading capacity of 0.46 mg·mg−1. The in vitro study revealed that BP-EO NPs inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells via inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway.
The ketogenic diet could improve the efficacy of curcumin and Oldenlandia diffusa extract in the treatment of gastric cancer by increasing miR340 expression and apoptosis mediated by autophagy, oxidative stress, and angiogenesis
- First Published: 11 October 2022
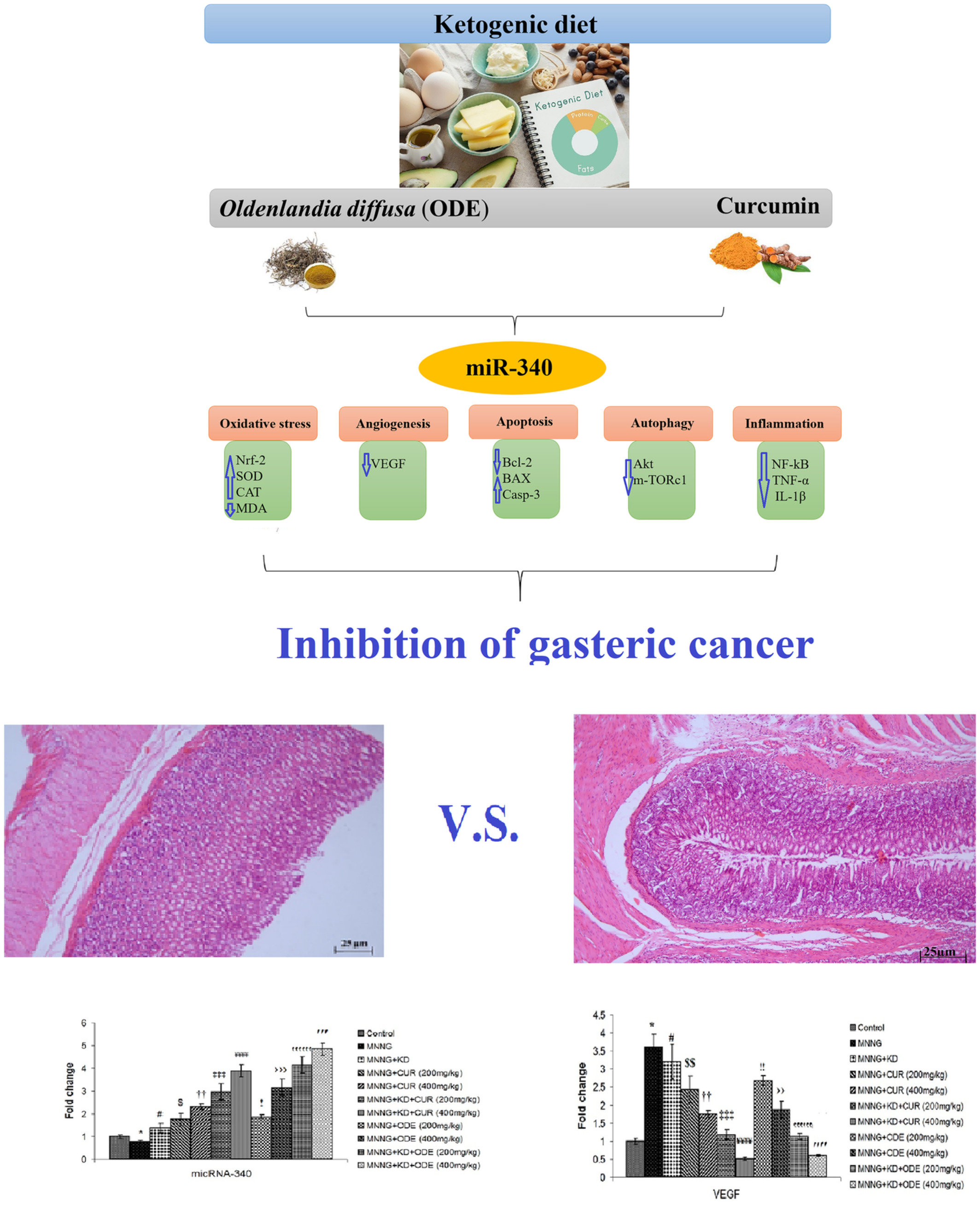
- The ketogenic diets (KD) and different doses of curcumin and Oldenlandia diffusa extract (ODE) could induce apoptosis and the Akt/mTORC1 pathway and inhibit inflammation, oxidative damage, and angiogenesis in the gastric tissue.
- The KD could significantly increase the efficacy of ODE and curcumin which may be due to an increase in miR-340 expression.
- It suggested that the KD as adjunctive therapy along with conventional therapies in traditional medicine could be considered a useful solution to prevent and treat gastric cancer.
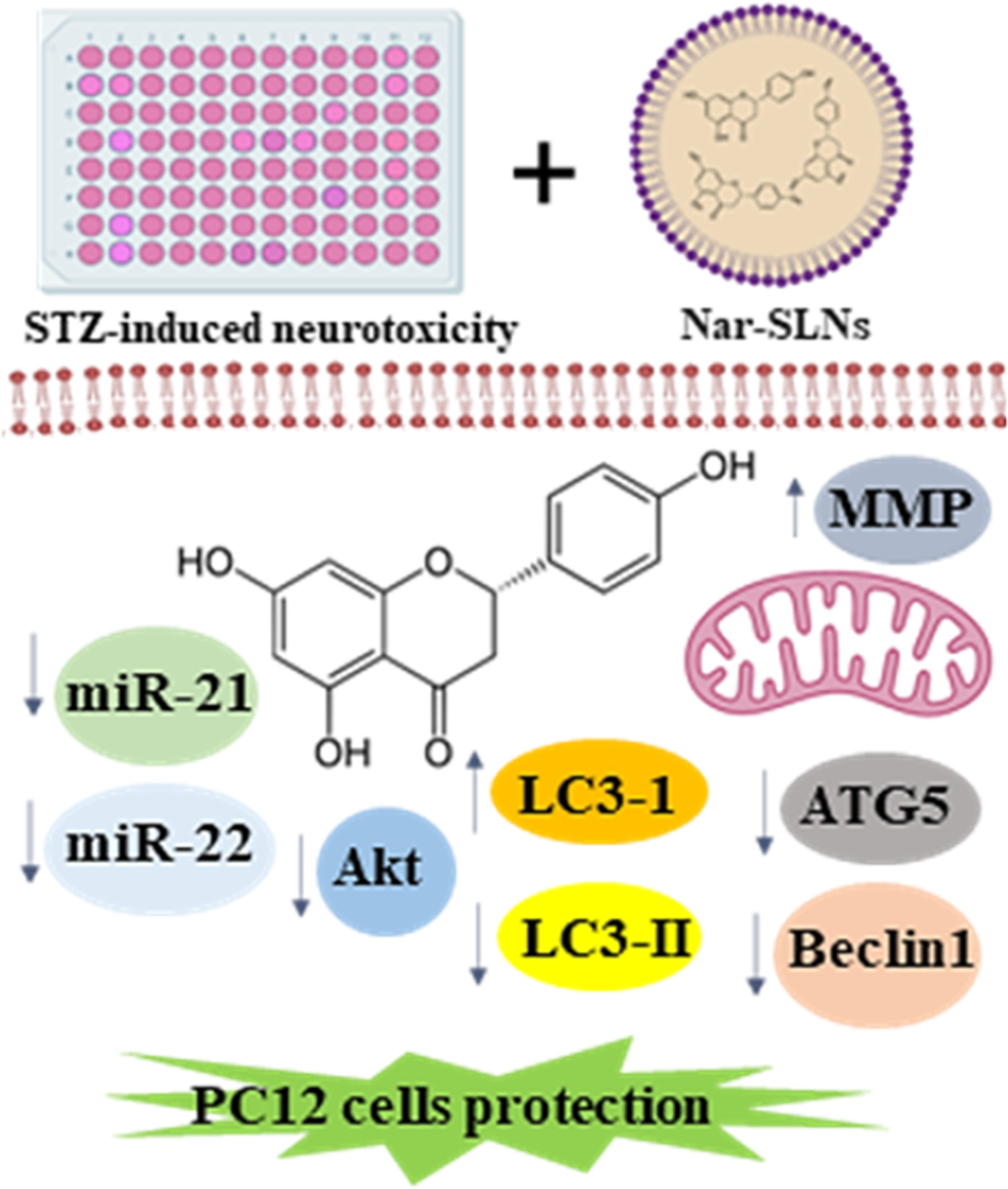
Neuroprotective effect of naringenin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles against streptozocin-induced neurotoxicity through autophagy blockage
- First Published: 21 September 2022
Material basis and action mechanism of Euryale Ferox Salisb in preventing and treating diabetic kidney disease
- First Published: 27 September 2022
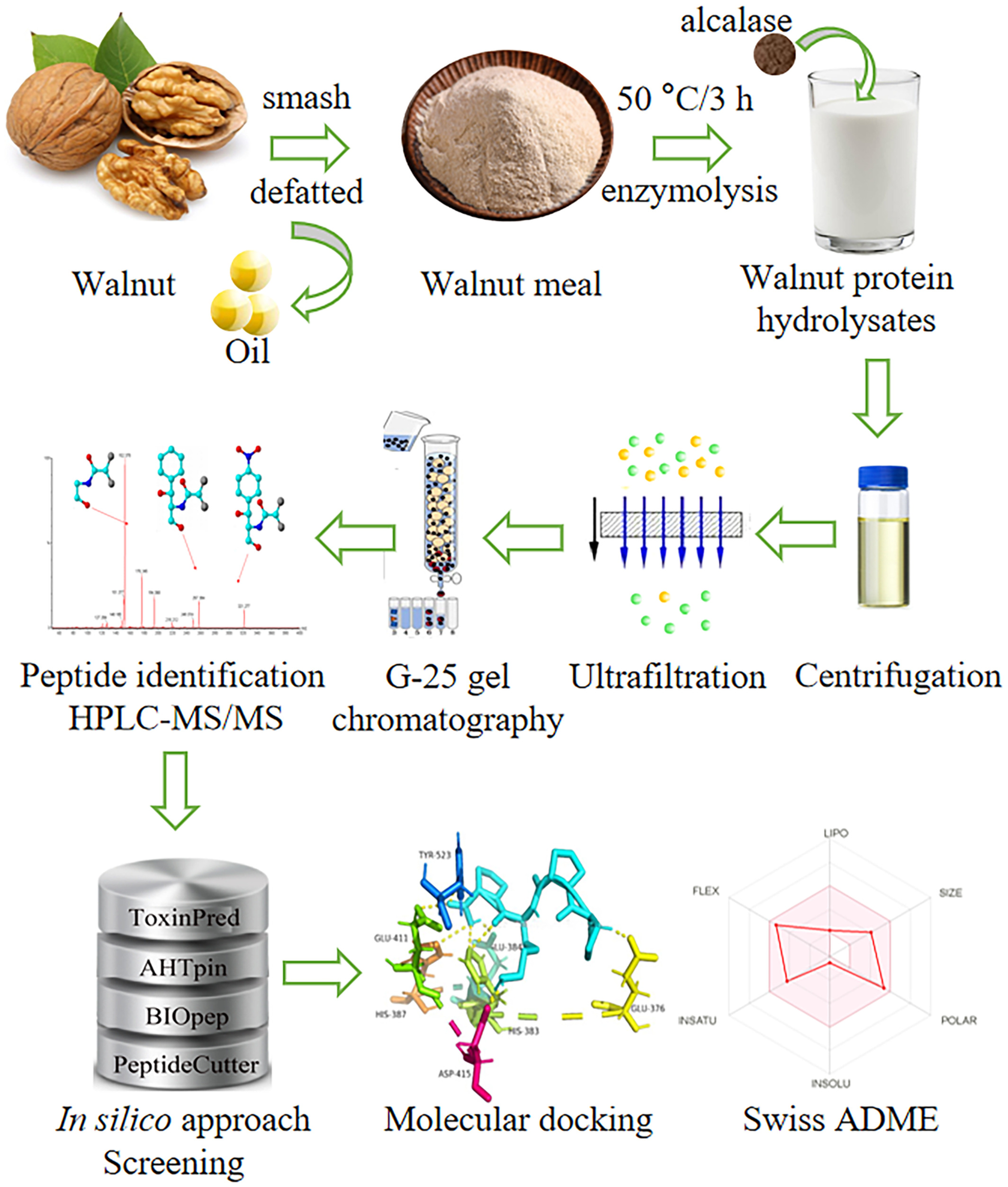
Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from walnut protein isolate: Separation, identification and molecular docking study
- First Published: 19 September 2022
Isolation and characterization of fucoidan from four brown algae and study of the cardioprotective effect of fucoidan from Sargassum wightii against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells
- First Published: 19 September 2022
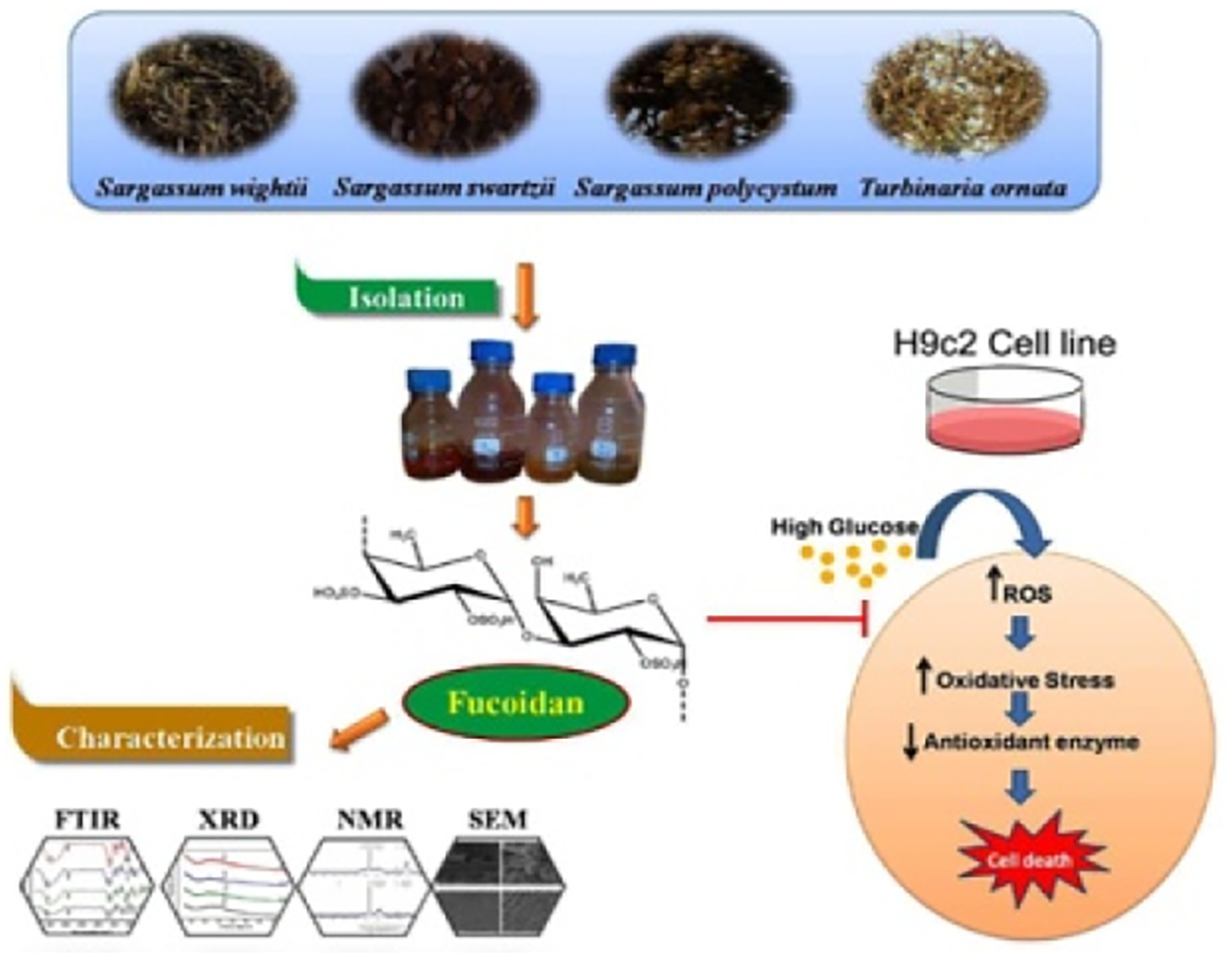
- Fucoidans from four different brown seaweeds have been isolated studied for cardioprotective properties.
- Fucoidan from S. wightii increased the cytoprotection through increasing Nrf2 and its regulated genes expression against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in H9c2 cells.
- Fucoidan from S. wightii protected the cells via increasing the MMP by decreasing the intracellular ROS generation.
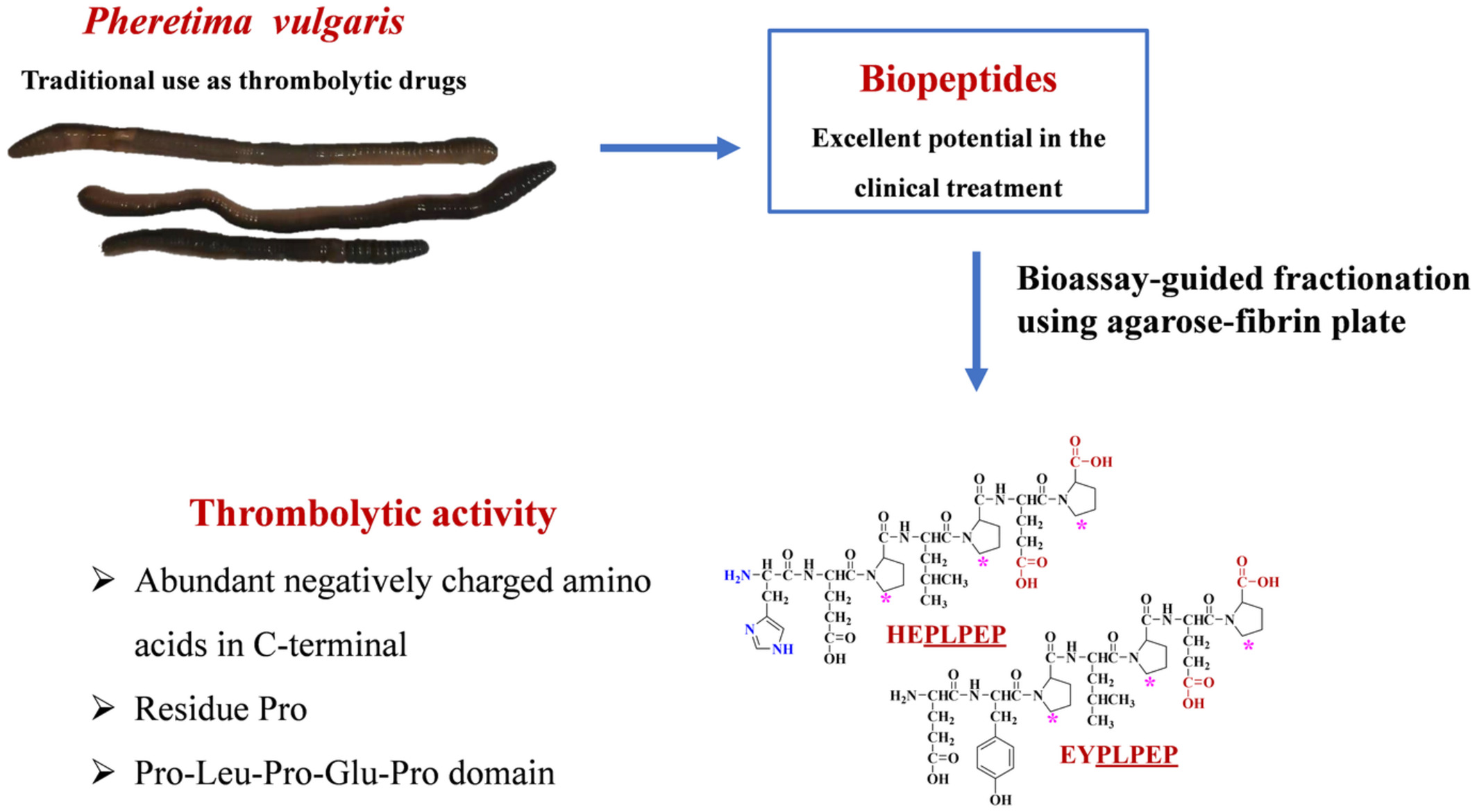
Purification and identification of thrombolytic peptides from enzymatic hydrolysate of Pheretima vulgaris
- First Published: 19 September 2022
Cross-linking effects of EGCG on myofibrillar protein from common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and the action mechanism
- First Published: 15 September 2022
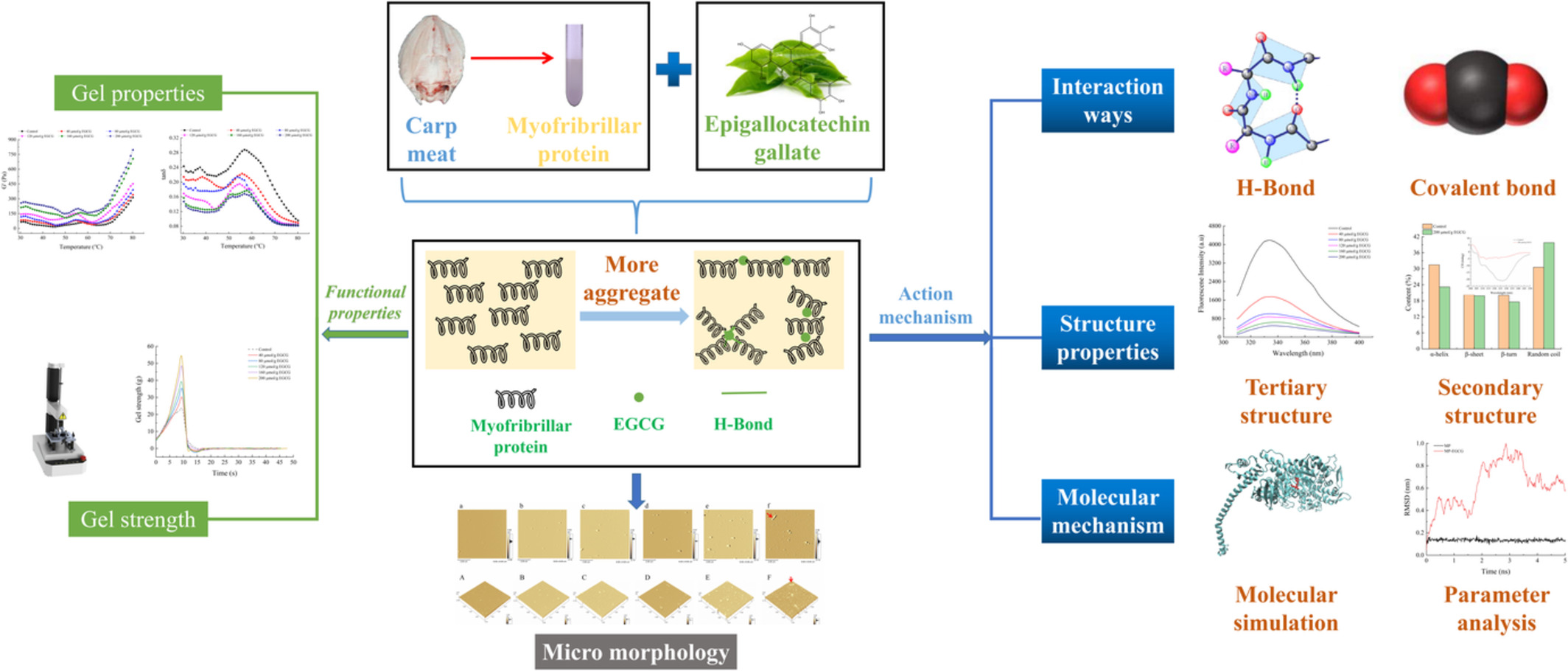
In the present study, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) showed the significant cross-linking effects on carp myofibrillar protein and further improved its physicochemical properties. All results suggested that EGCG had the potential to increase the cross-linking degree of fish myofibrillar protein and improve its properties, so as to ameliorate the quality of fish meat during processing and storage.
Effects of hemp seed alone and combined with aerobic exercise on metabolic parameters, oxidative stress, and neurotrophic factors in young sedentary men
- First Published: 17 September 2022
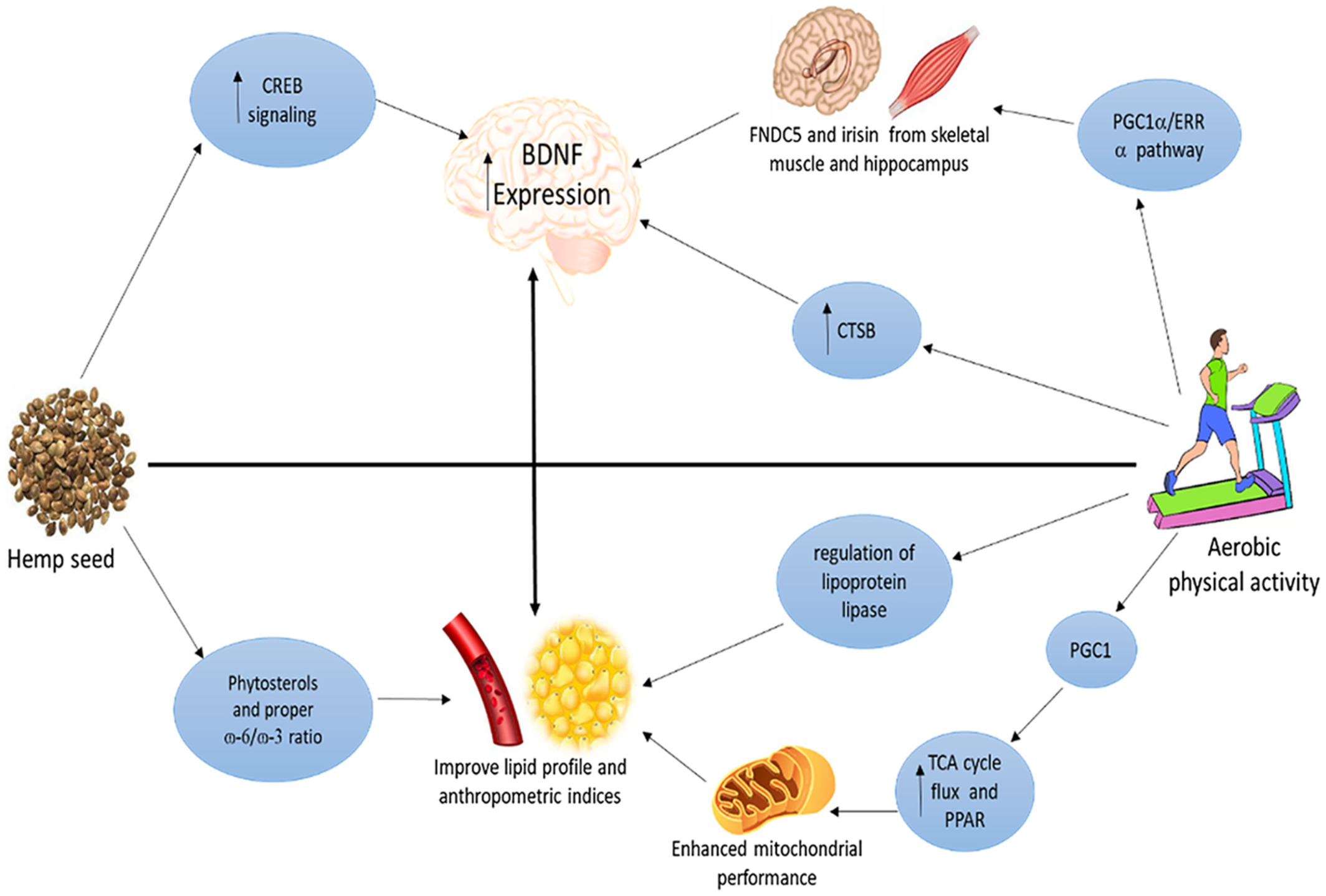
Mechanisms of health benefits of physical activity and hemp seed: 1. Exercise a) could improve the lipid profile and anthropometric indices by regulating lipoprotein lipase, diminishing lipid stress by increasing TCA cycle flux and coupling ligand-induced PPAR activity with PGC1 mediated remodeling of downstream metabolic pathways, leading to an enhanced mitochondrial performance in restoring insulin sensitivity; b) enhance BDNF expression in the hippocampus 2. Hemp seed a) may modulate lipid profile by its high content of phytosterols and proper ɷ-6/ɷ-3 ratio b) upregulate BDNF expression.
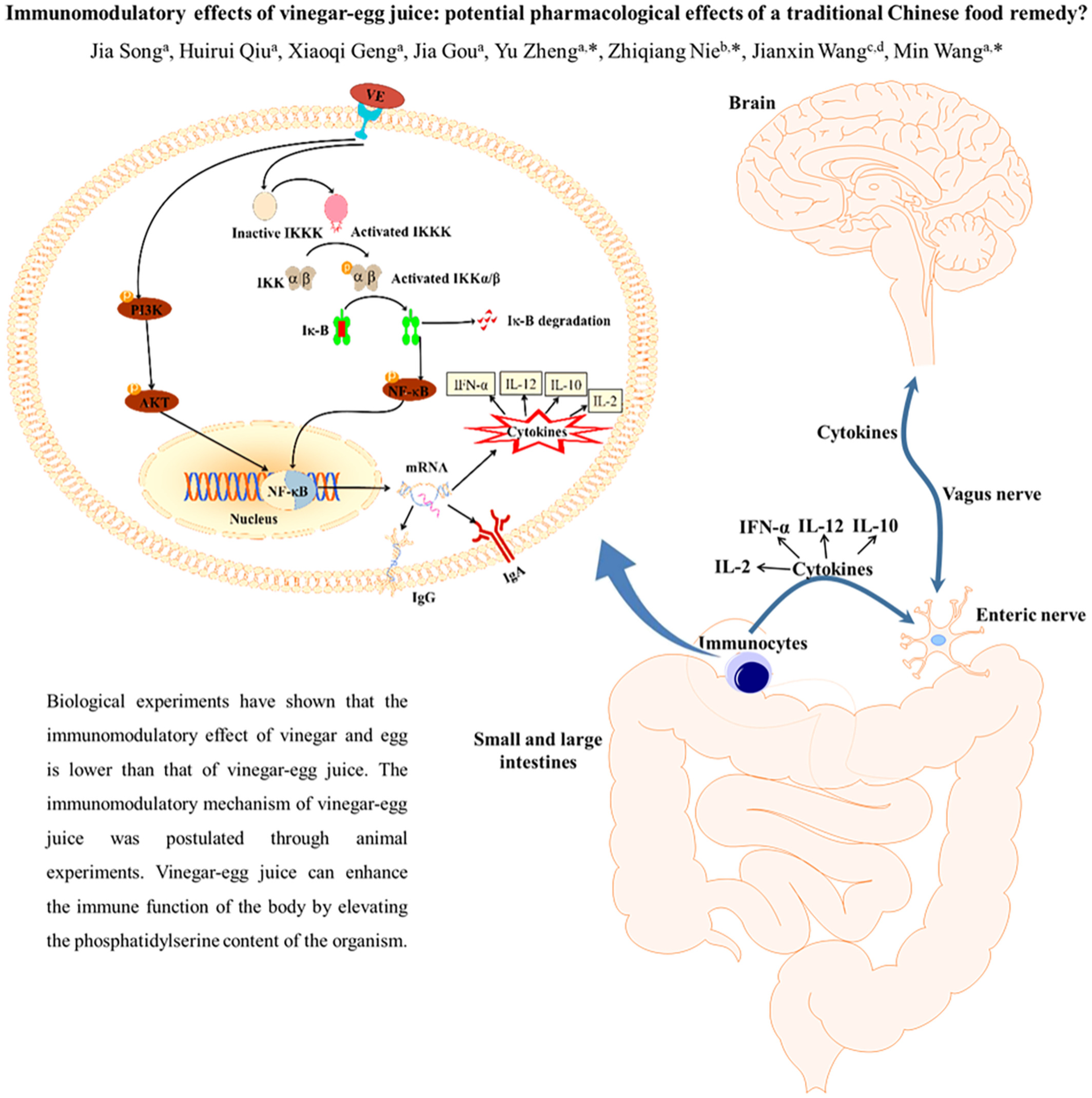
Immunomodulatory effects of vinegar-egg juice: Potential pharmacological effects of a traditional Chinese food remedy?
- First Published: 26 September 2022
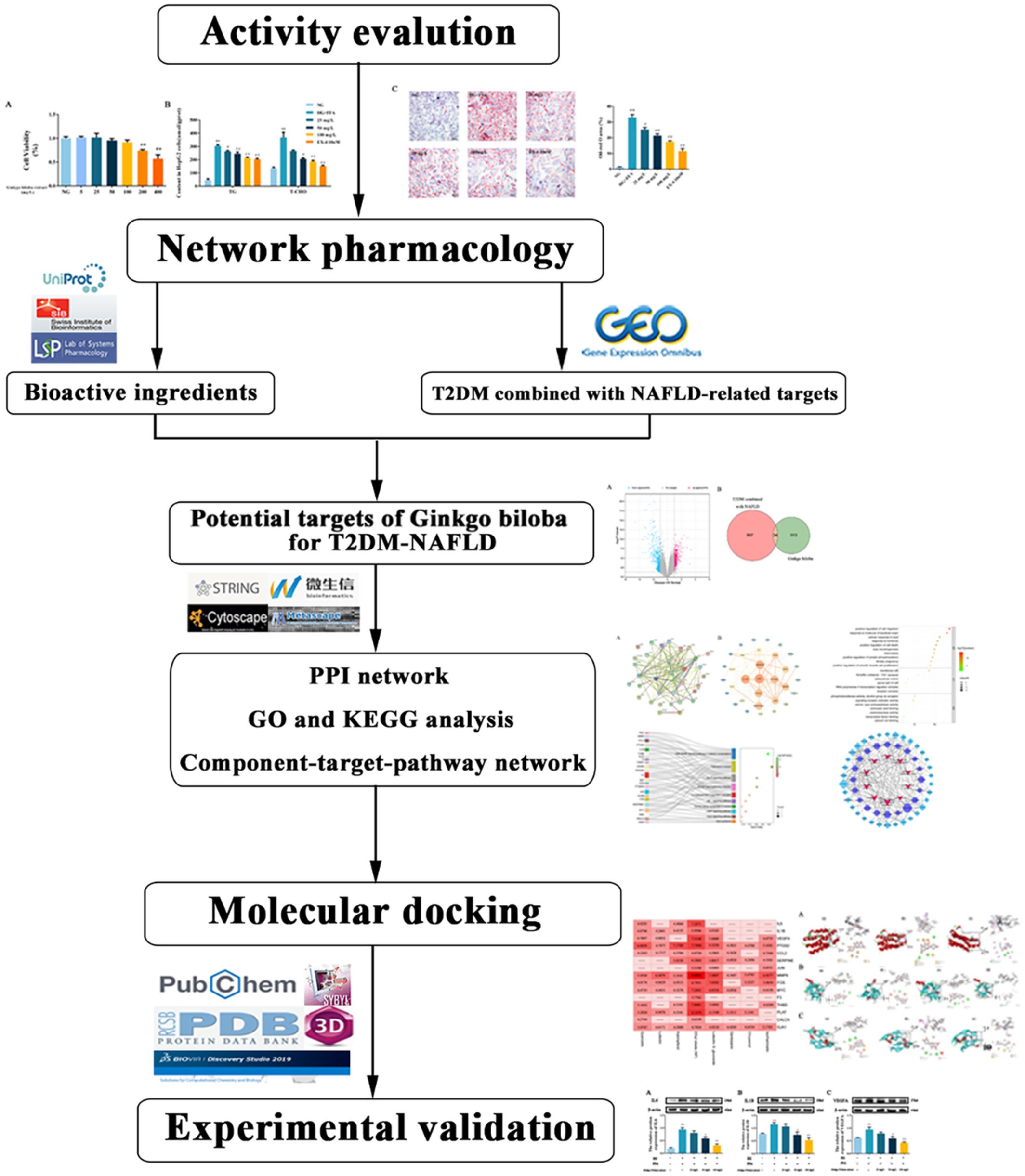
Molecular mechanism of Ginkgo biloba in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental evaluations
- First Published: 19 September 2022
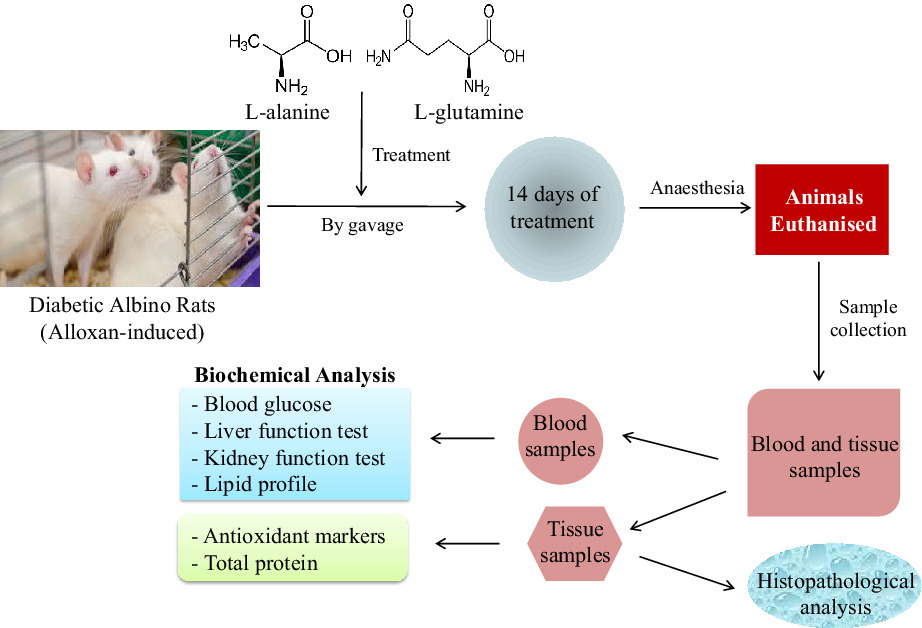
Coadministration of L-alanine and L-glutamine ameliorate blood glucose levels, biochemical indices and histological features in alloxan-induced diabetic rats
- First Published: 20 September 2022
GABA-enriched rice bran inhibits inflammation in LPS-stimulated macrophages via suppression of TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB signaling cascades
- First Published: 19 September 2022
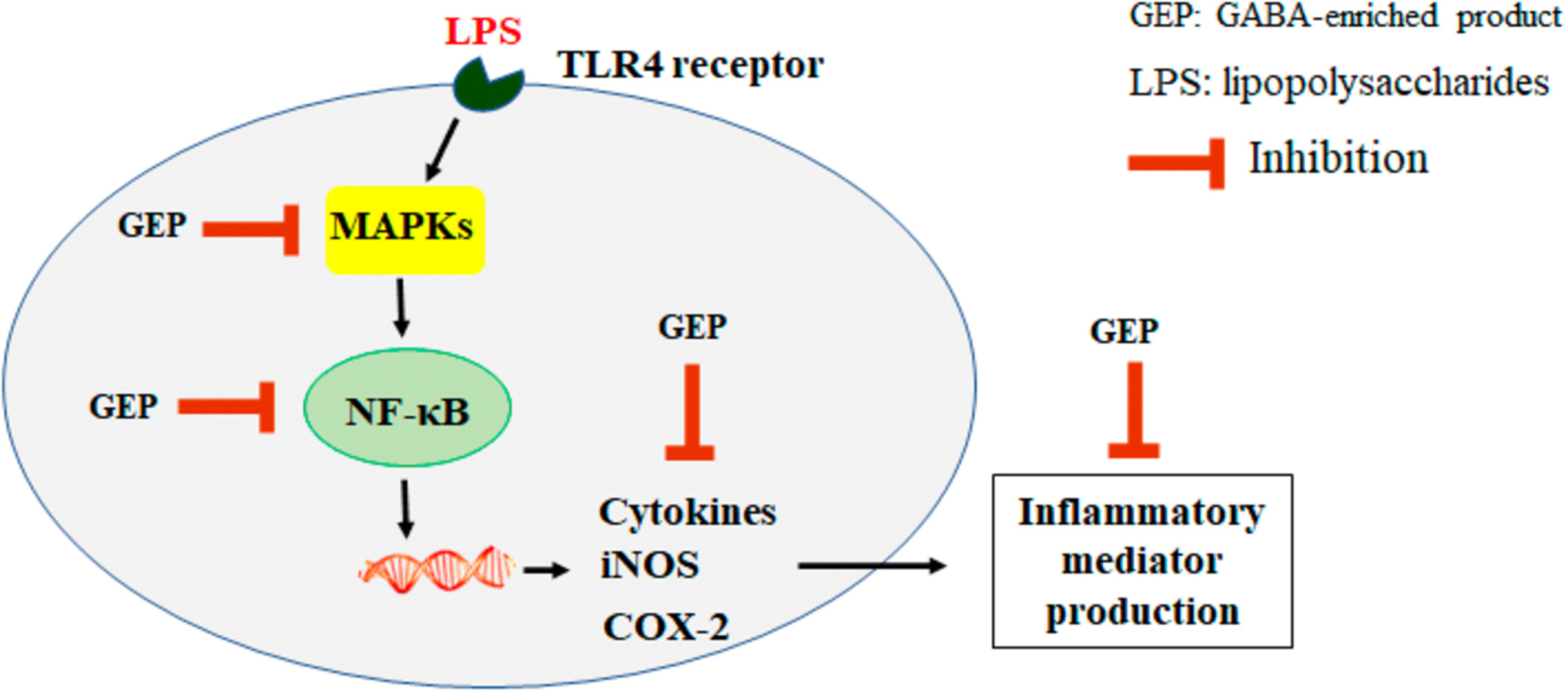
In this study, anti-inflammatory activity of GEP from Lactobacillus fermentum-fermented water solution of rice bran was evaluated on lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophage model. The anti-inflammatory activity of GEP was determined due to suppressing Toll-like receptor 4-mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor-κB signaling cascades, leading to the attenuation of inflammatory mediator production.
6- shogaol suppresses AOM/DSS-mediated colorectal adenoma through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in mice
- First Published: 20 September 2022
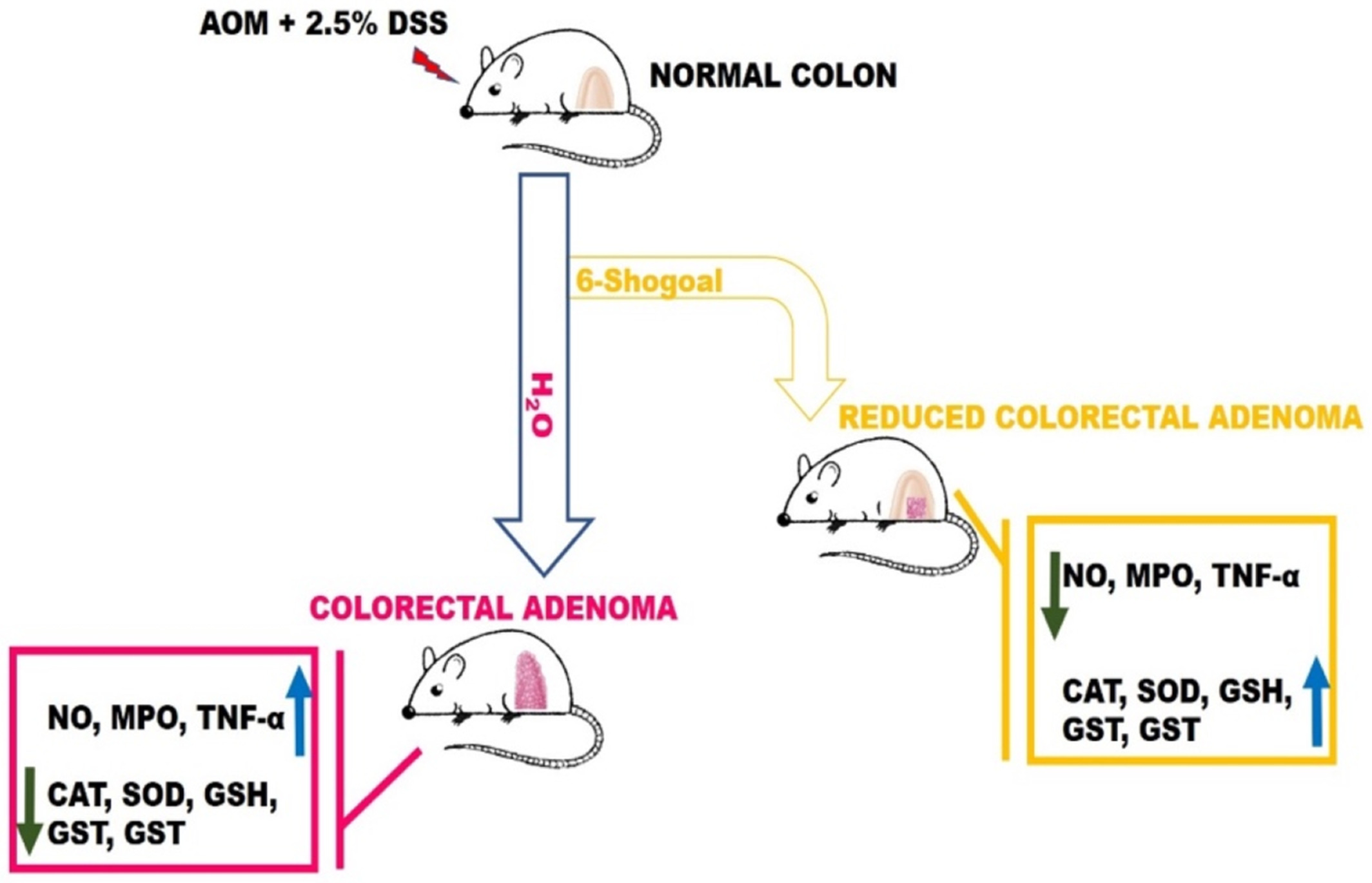
This paper reported the chemoprotective effect of 6- Shogaol, 6-[S] derived from ginger extract on azoxymethane (AOM) and dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced colorectal adenoma in mice. Treatment with 6-[S] prevented tubular adenoma and dysplasia in the colon of AOM/DSS treated Mice. 6S prevented colonic oxidative stress in AOM/DSS treated mice as well as colonic inflammation in AOM/DSS treated mice.
Tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus L.) and date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruit blend mitigates hyperglycemia, insulin resistance and oxidative complications in type-2 diabetes models
- First Published: 20 September 2022
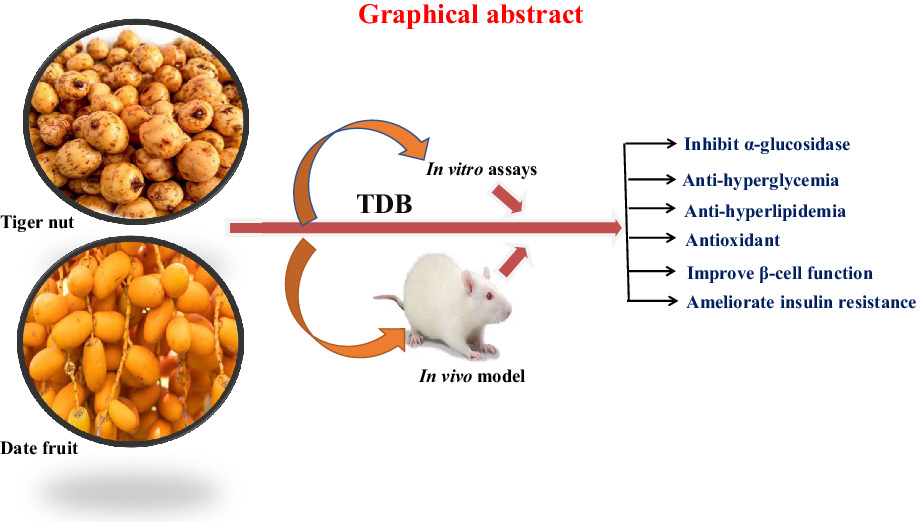
The antidiabetic activity of tiger nut and date fruit blend (TDB) was reported in both in vitro and in vivo models. At the end of the study, TDB demonstrated promising anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic and antioxidant activities, as well as improved pancreatic β-cell function and ameliorated insulin resistance. In addition, TDB showed potent inhibition against the α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities.
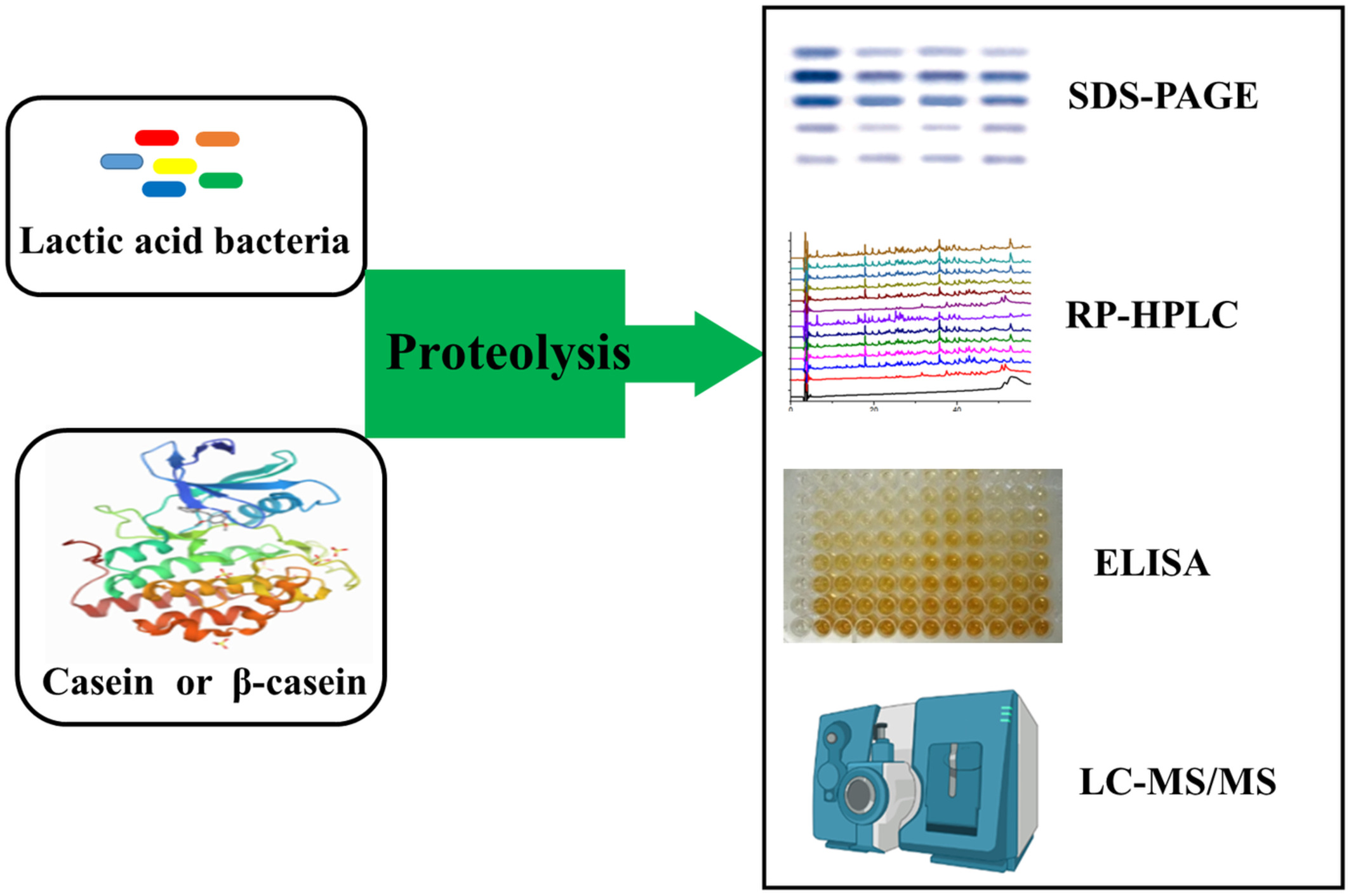
Potential allergenicity and hydrolysis assessment of bovine casein and β-casein by treatment with lactic acid bacteria
- First Published: 05 October 2022
Effects of Rosa roxburghii Tratt glycosides and quercetin on D-galactose-induced aging mice model
- First Published: 20 September 2022
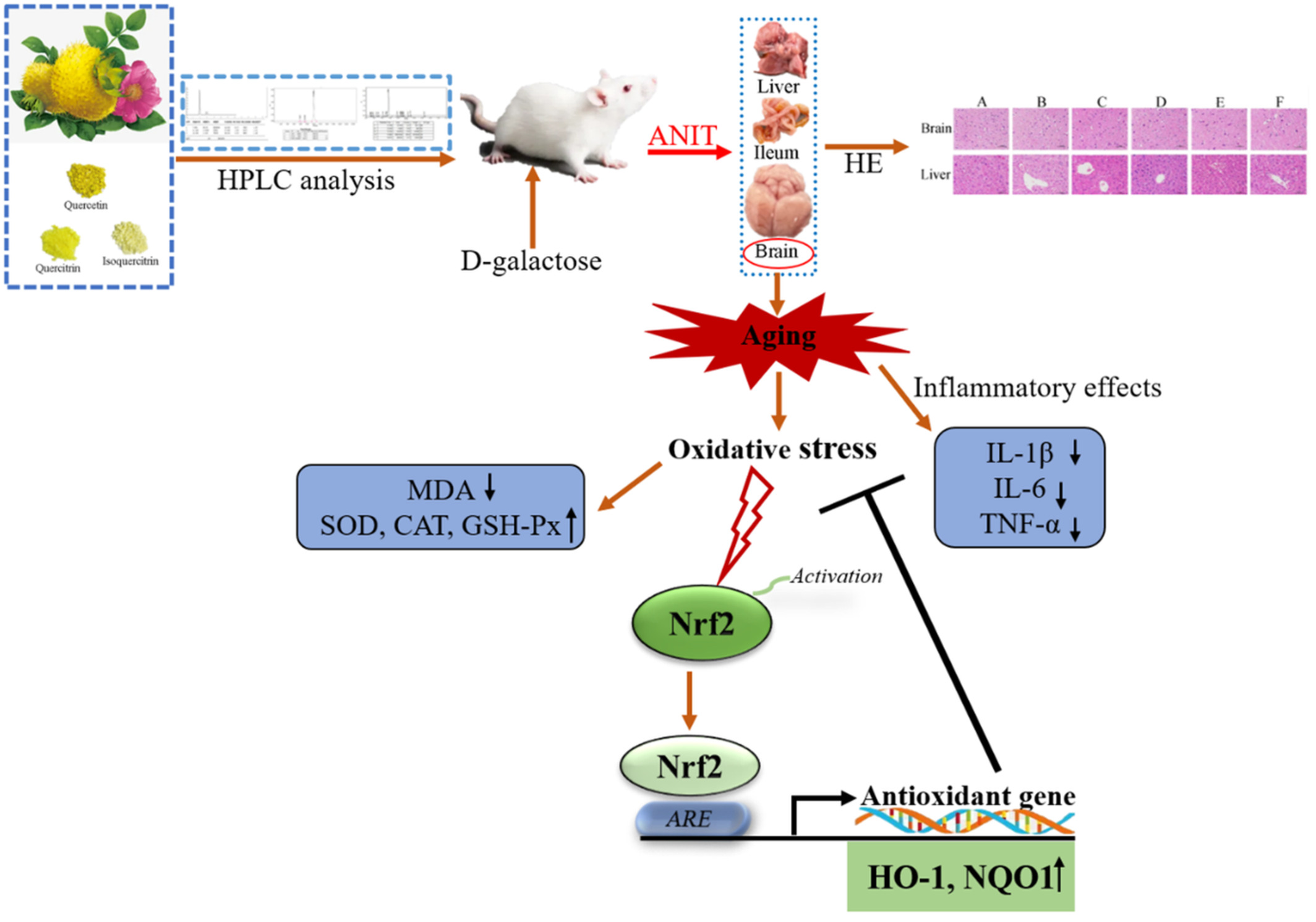
In this study, a D-galactose-induced aging mouse model was used to investigate the effects and potential mechanisms of RRT glucosides and quercetin on antioxidant stress and inflammation in aging, as well as to assess their protective effect in conjunction with pathological sections of the liver and brain. The results show that the anti-aging activity of RRT glycoside and quercetin could be linked to the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
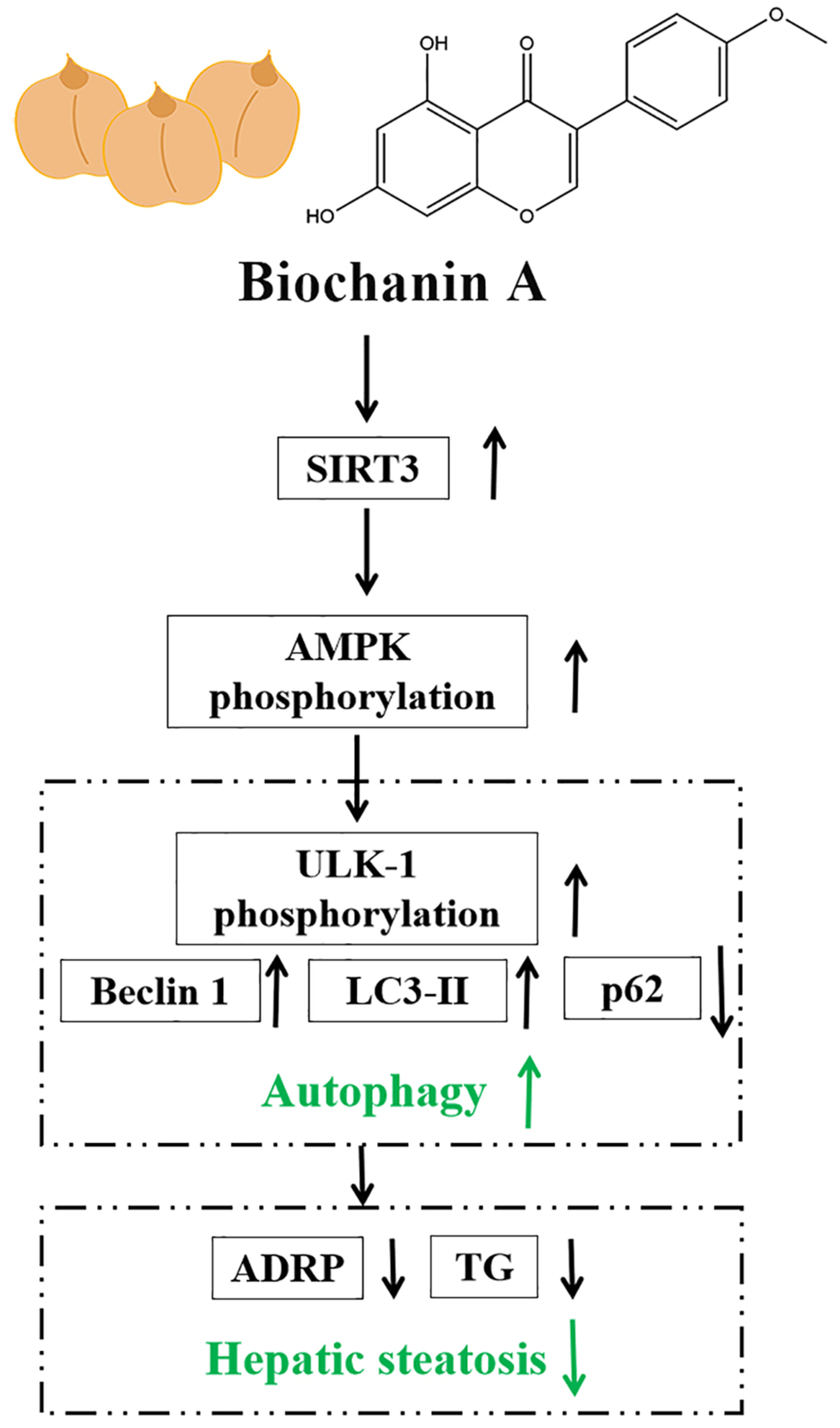
Biochanin A ameliorated oleate-induced steatosis in HepG2 cells by activating the SIRT3/AMPK/ULK-1 signaling pathway
- First Published: 20 September 2022
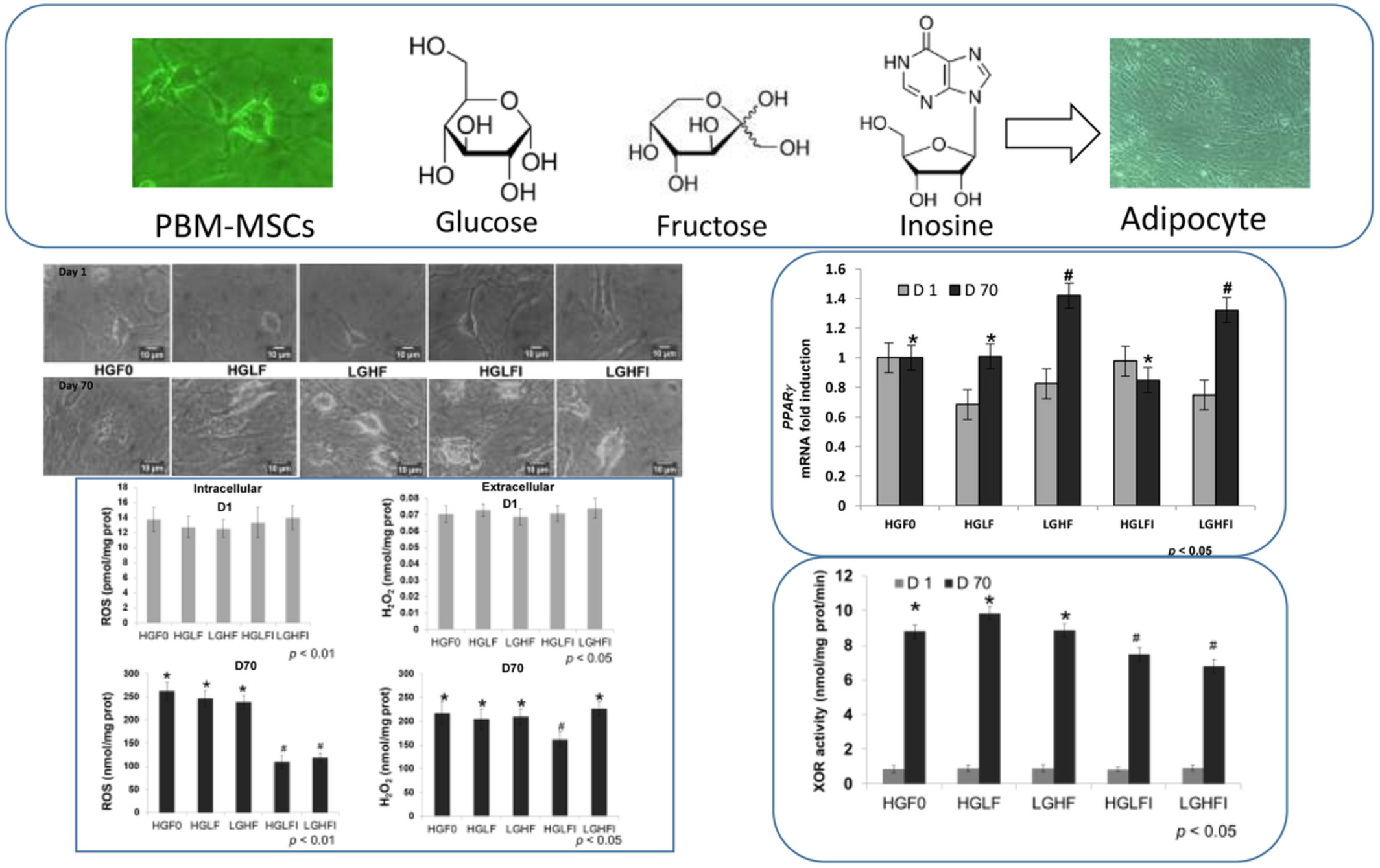
Fructose promotes more than glucose the adipocytic differentiation of pig mesenchymal stem cells
- First Published: 25 September 2022
Diet supplemented with boiled unripe plantain (Musa paradisiaca) exhibited antidiabetic potentials in streptozotocin-induced Wistar rats
- First Published: 06 October 2022
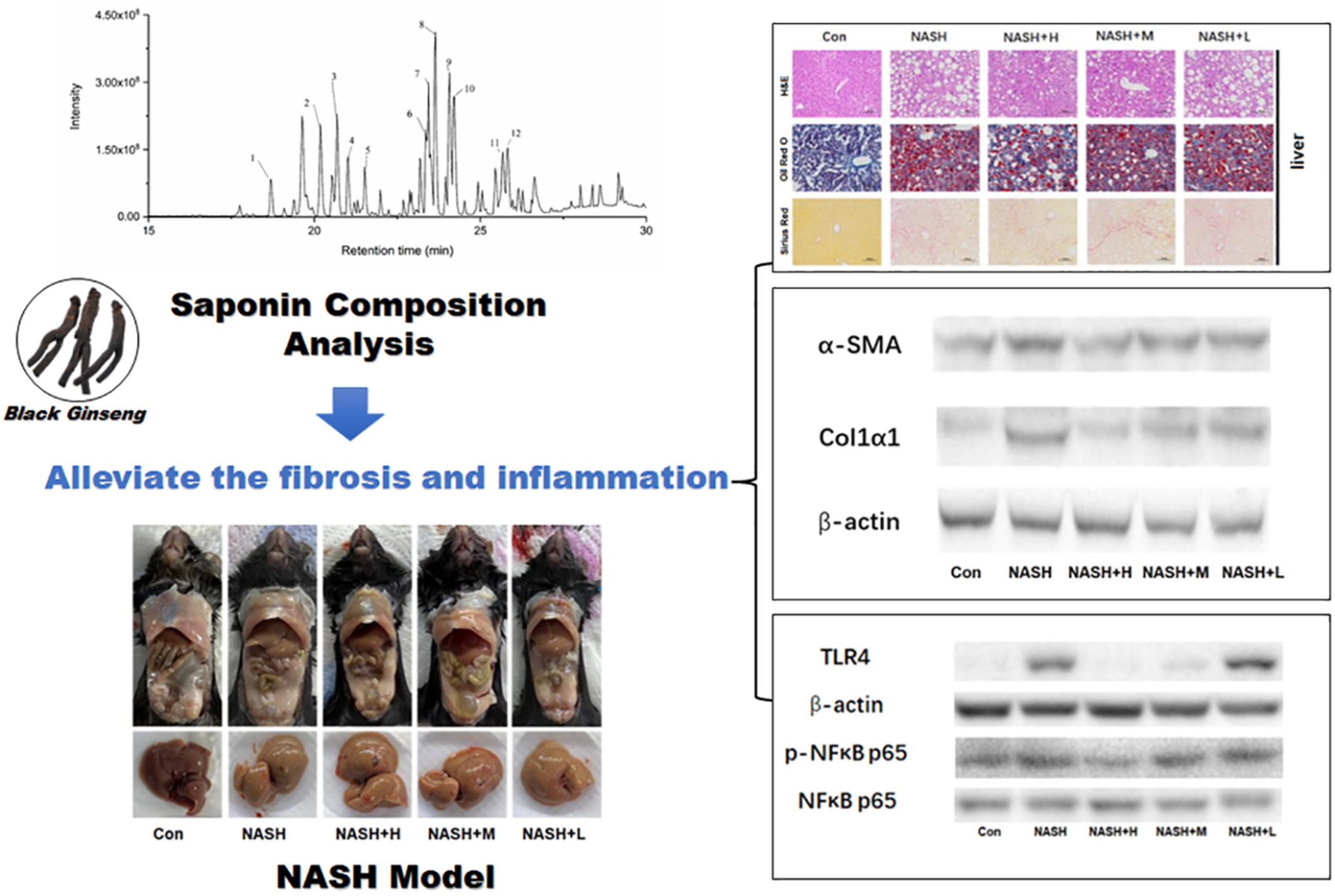
Black ginseng protects against Western diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by modulating the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in mice
- First Published: 01 October 2022
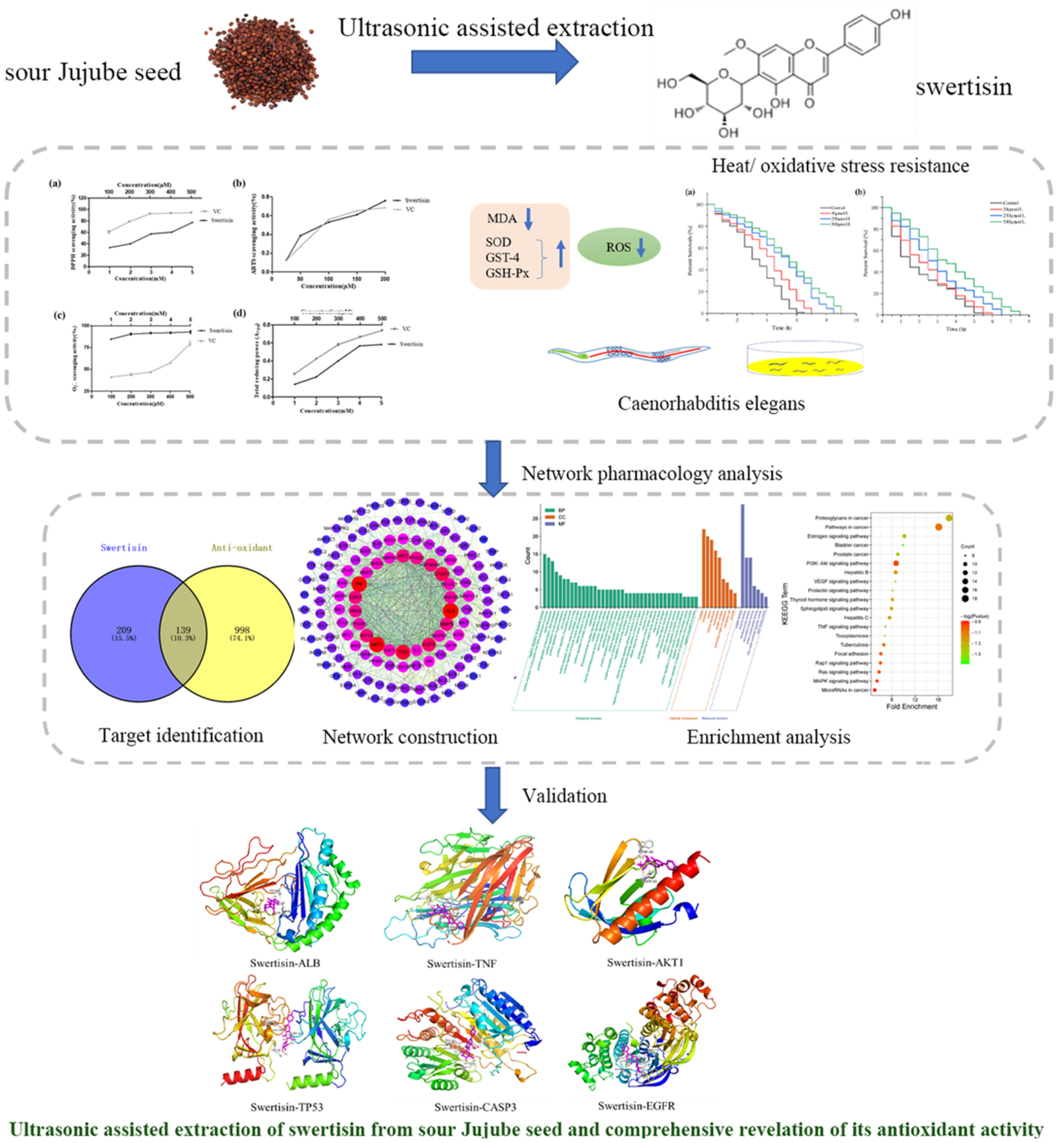
Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of swertisin from sour Jujube seed and comprehensive revelation of its antioxidant activity
- First Published: 05 October 2022
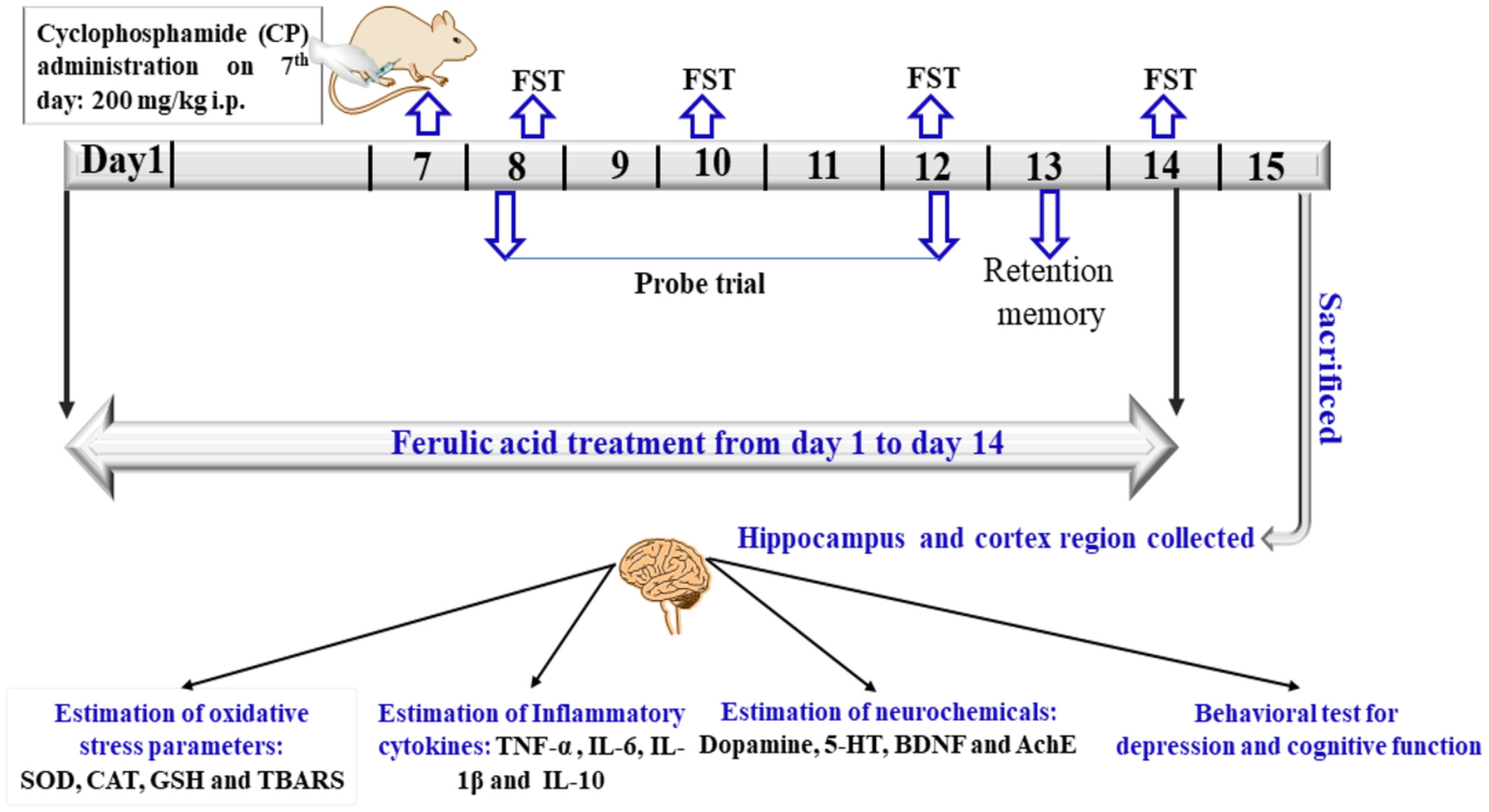
Neuroprotective potential of ferulic acid against cyclophosphamide-induced neuroinflammation and behavioral changes
- First Published: 27 September 2022
Transcriptome analyses and virus-induced gene silencing identify HuWRKY40 acting as a hub transcription factor in the preservation of Hylocereus undatus by trypsin
- First Published: 13 October 2022
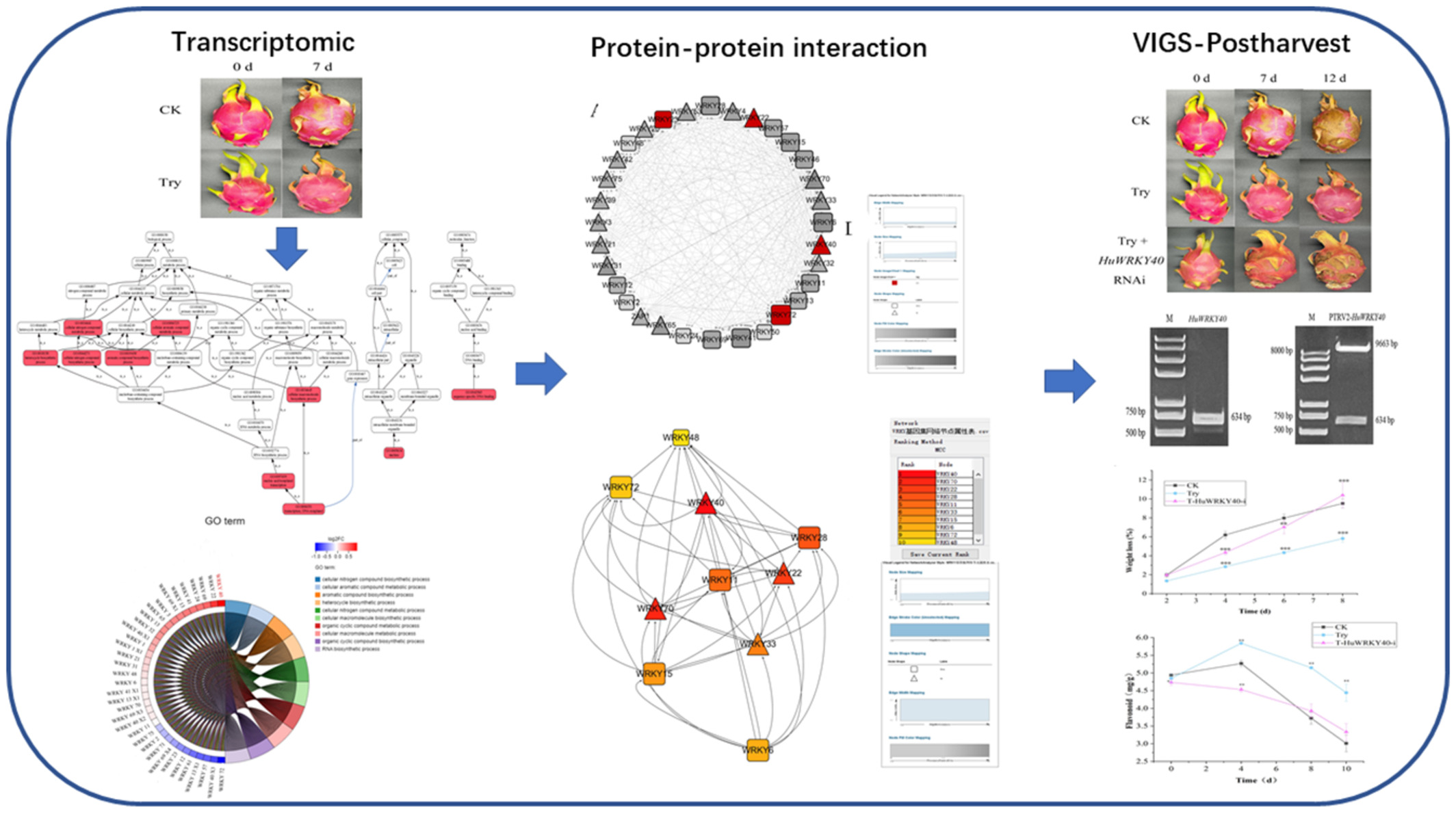
The mechanism of trypsin on the WRKY TFs during H. undatus storage was investigated. To verify the hub WRKY gene of H. undatus in trypsin preservation, joint analysis of transcriptome and protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was carried out, and virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) was conducted.
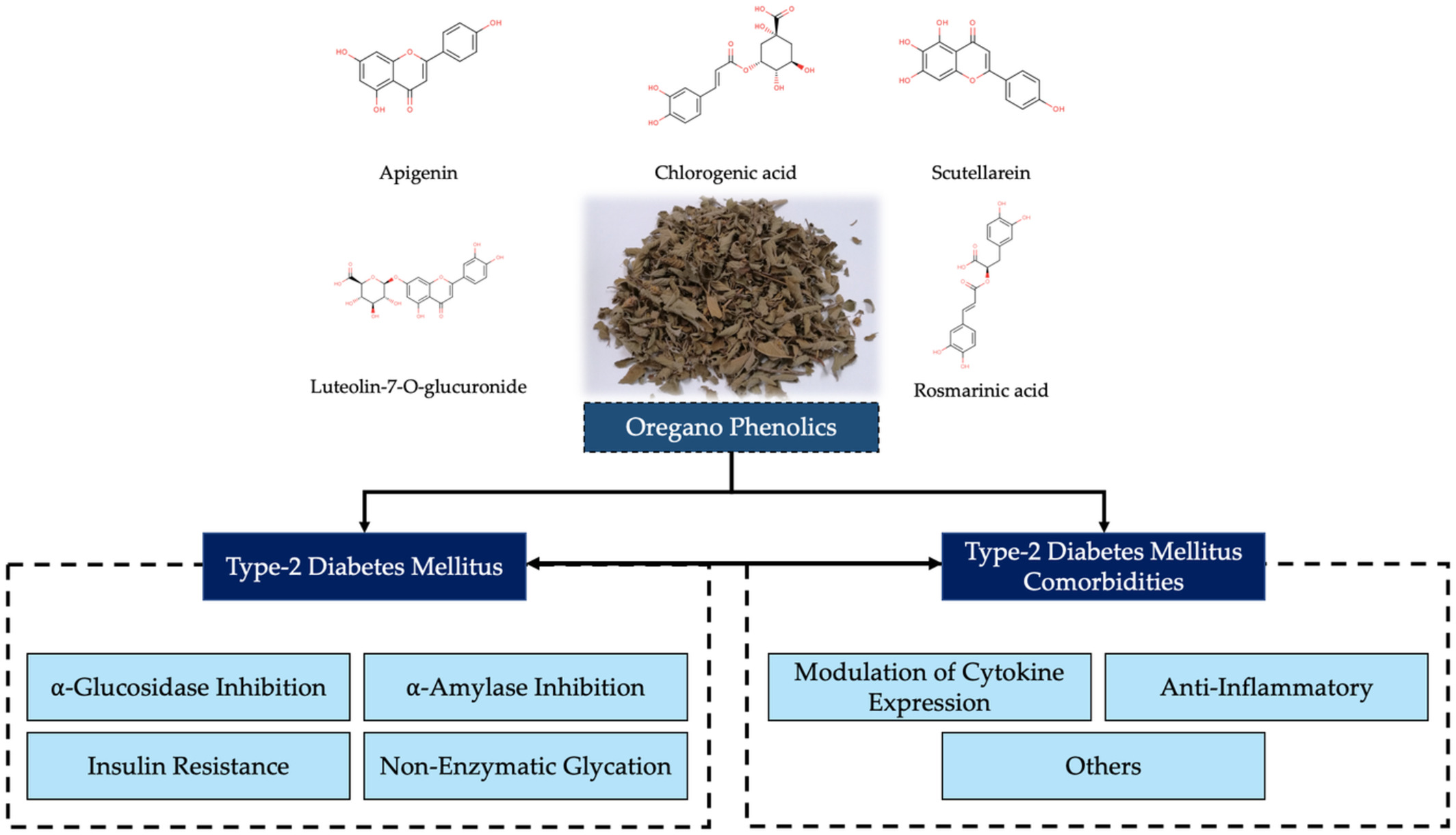
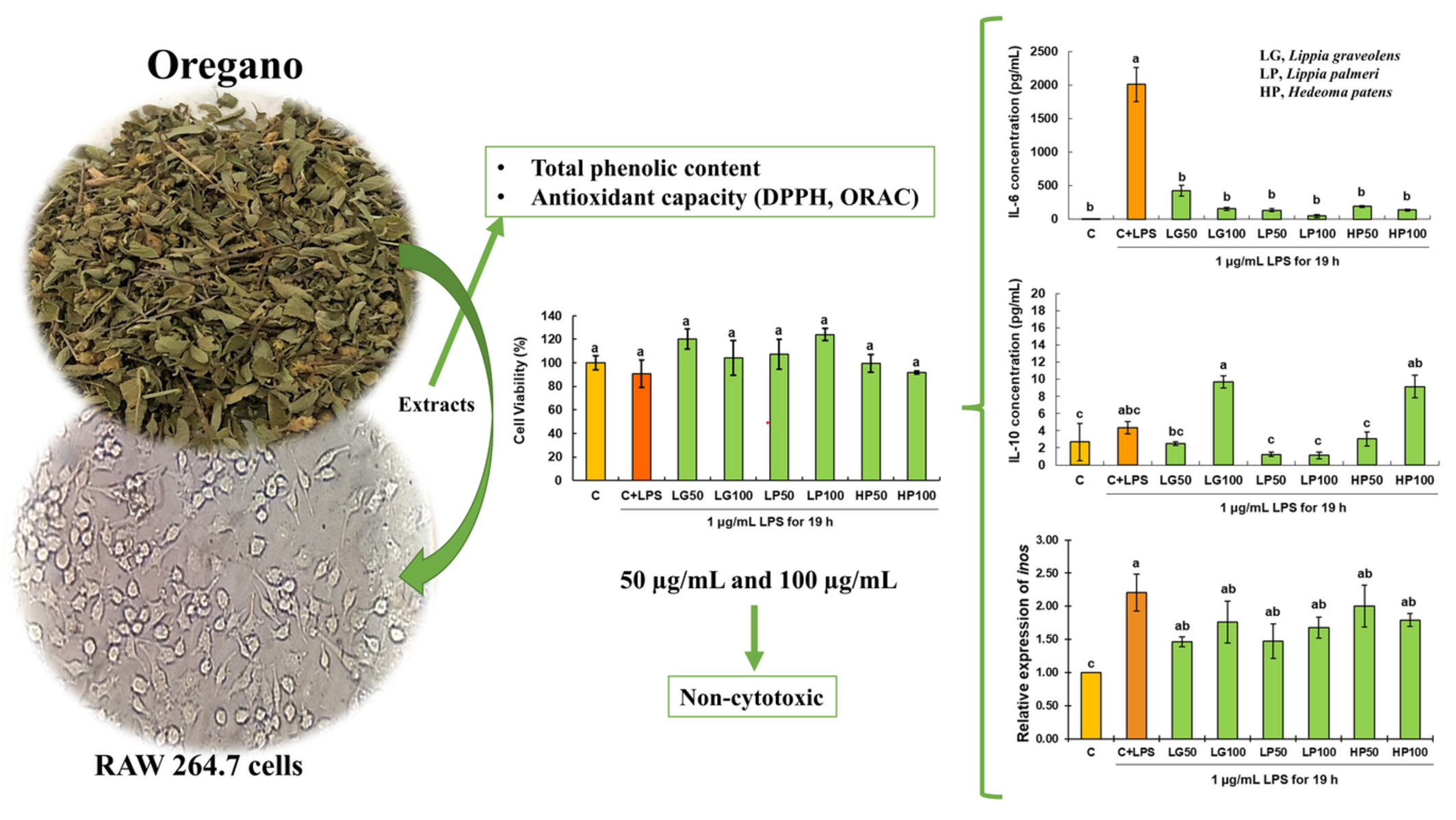
Antioxidant potential, cytokines regulation, and inflammation-related genes expression of phenolic extracts from Mexican oregano
- First Published: 28 September 2022
Curcumin nanoemulsion counteracts hepatic and cardiac complications associated with high-fat/high-fructose diet in rats
- First Published: 27 September 2022
Identification of off-flavor compounds and deodorizing of cattle by-products
- First Published: 28 September 2022
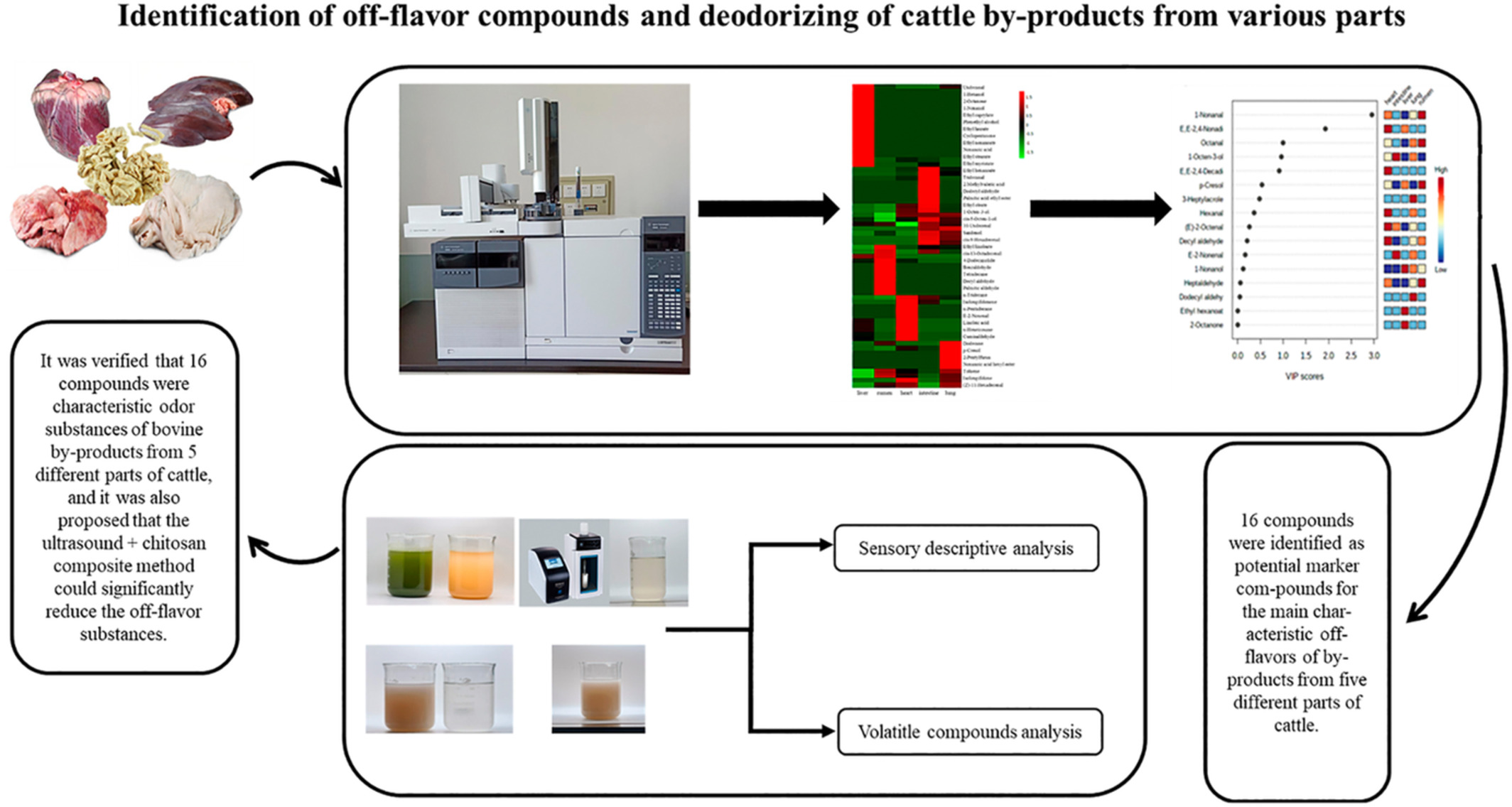
This study investigated the volatile flavor substances of cattle by-products from various parts (heart, liver, lung, rumen and intestine) by HS-SPEM/GC-MS. 16 volatile compounds were labeled as the major characteristic off-flavor substances in 5 different parts of cattle. The best deodorization effect of ultrasound + chitosan composite method.
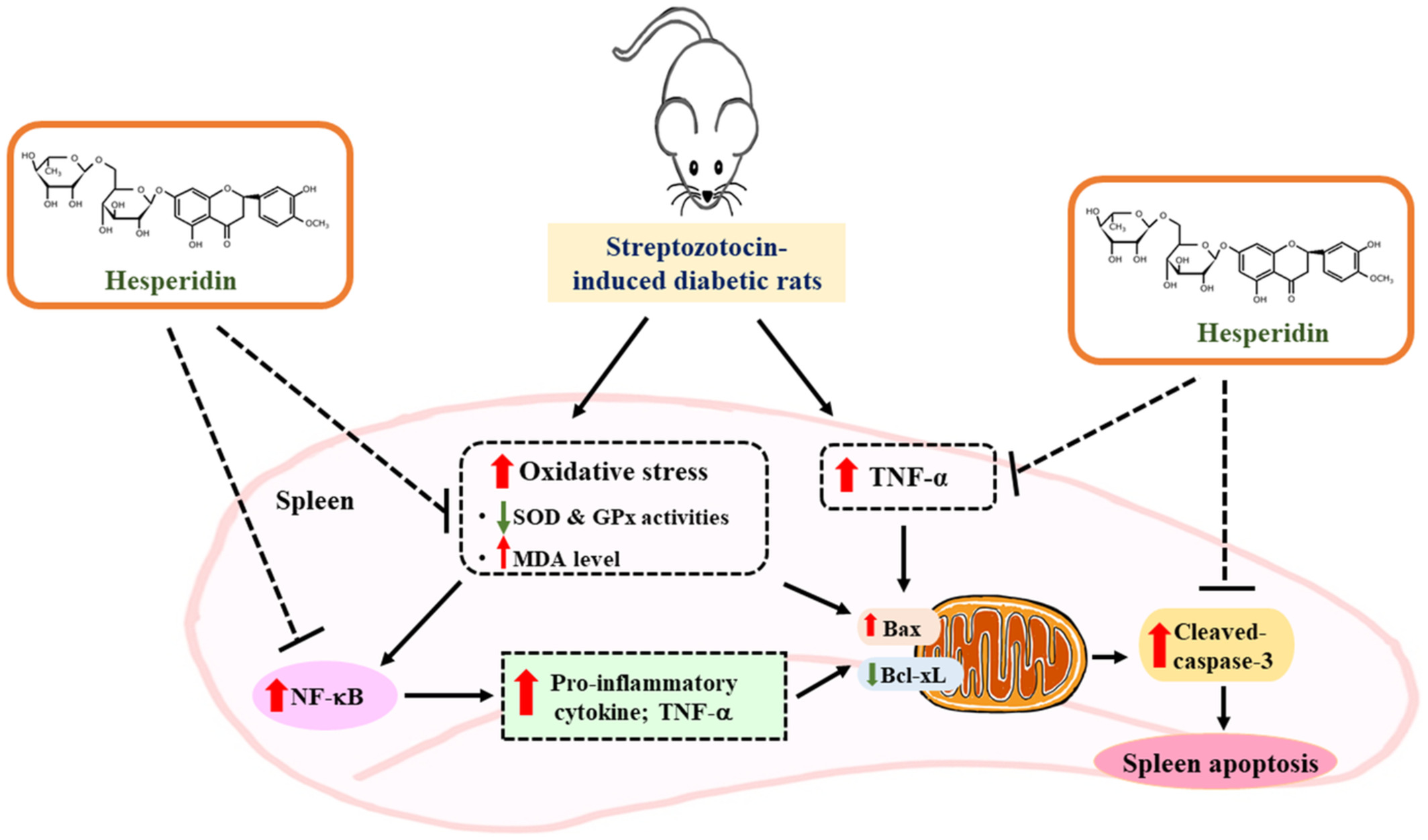
Protective role of hesperidin against diabetes induced spleen damage: Mechanism associated with oxidative stress and inflammation
- First Published: 27 September 2022
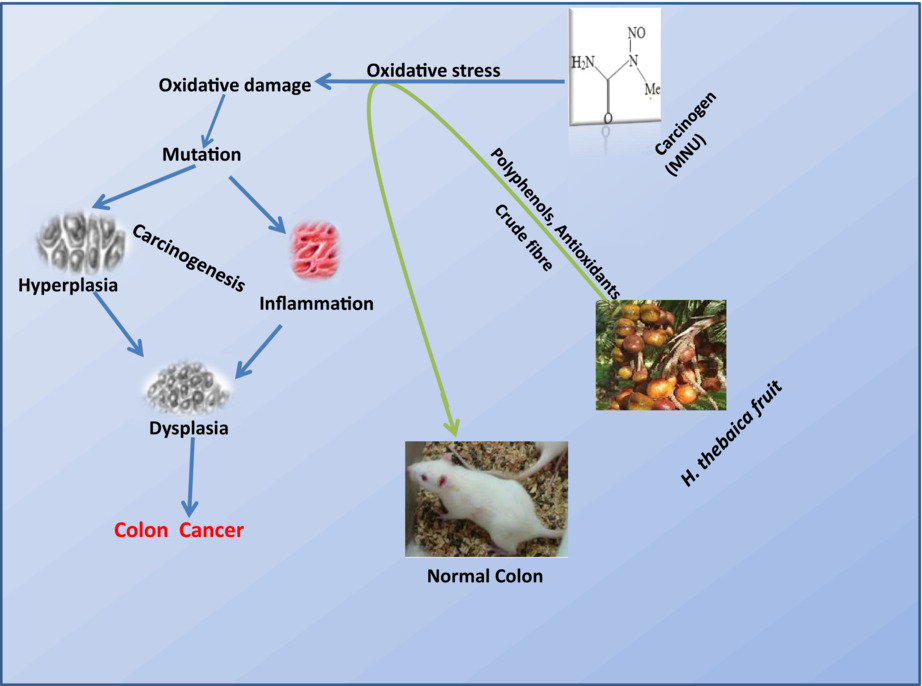
Evaluation of the preventive potential of graded dietary inclusion of Hyphaene thebaica (Linn) fruit in rat model of colon carcinogenesis
- First Published: 02 October 2022
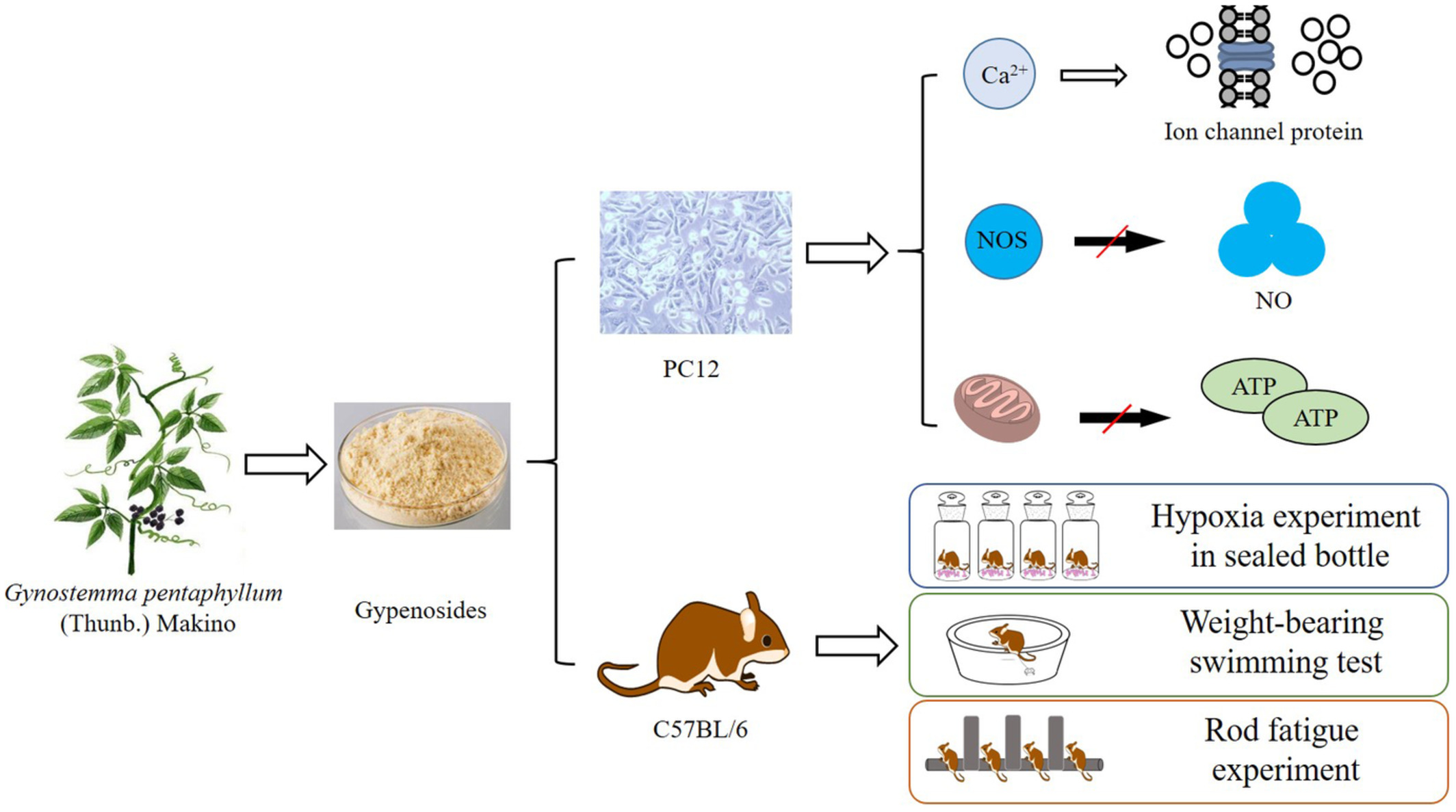
Gypenosides (GPs) alleviates hypoxia-induced injury in PC12 cells and enhances tolerance to anoxia in C57BL/6 mice
- First Published: 13 October 2022
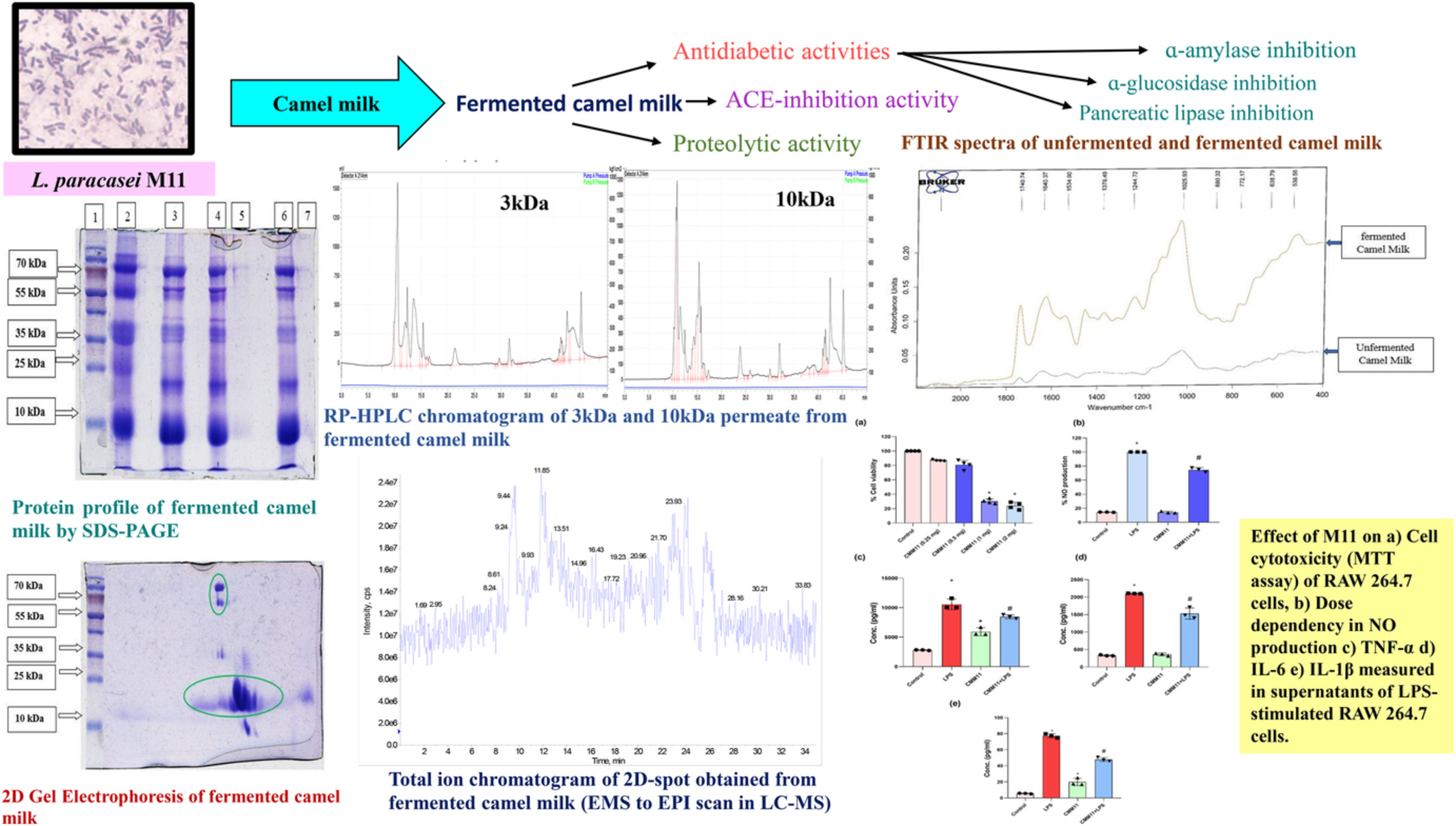
Exploring the potential of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei M11 on antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and ACE inhibitory effects of fermented dromedary camel milk (Camelus dromedaries) and the release of antidiabetic and anti-hypertensive peptides
- First Published: 07 October 2022
The effect of insulin-loaded gold and carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles on gene expression of glucokinase and pyruvate kinase in rats with diabetes type 1
- First Published: 11 October 2022
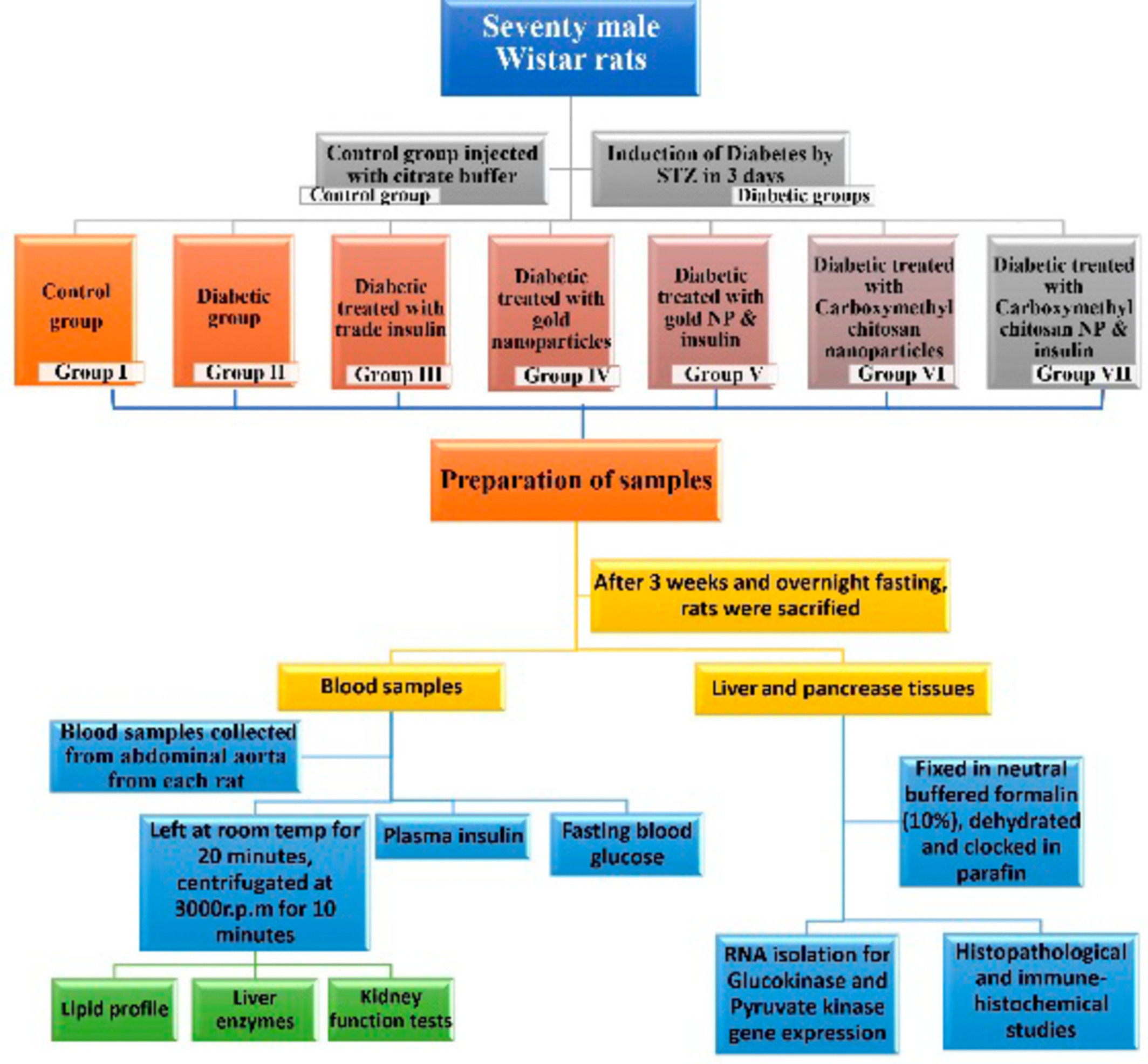
In comparison to subcutaneous insulin, CMCNPs and AuNPs showed a favorable effect on pyruvate kinase and Glucokinase gene expressions. Additionally, we found that conjugating insulin to CMCNPs and AuNPs enables controlled bioavailability by protecting insulin from the physiological barriers. We also focused at their histological effects on the liver and pancreas and numerous other criteria. Revealed that both had a considerable impact in vivo, enabling glucose level management, and enhancing the functions of the rats' organs.
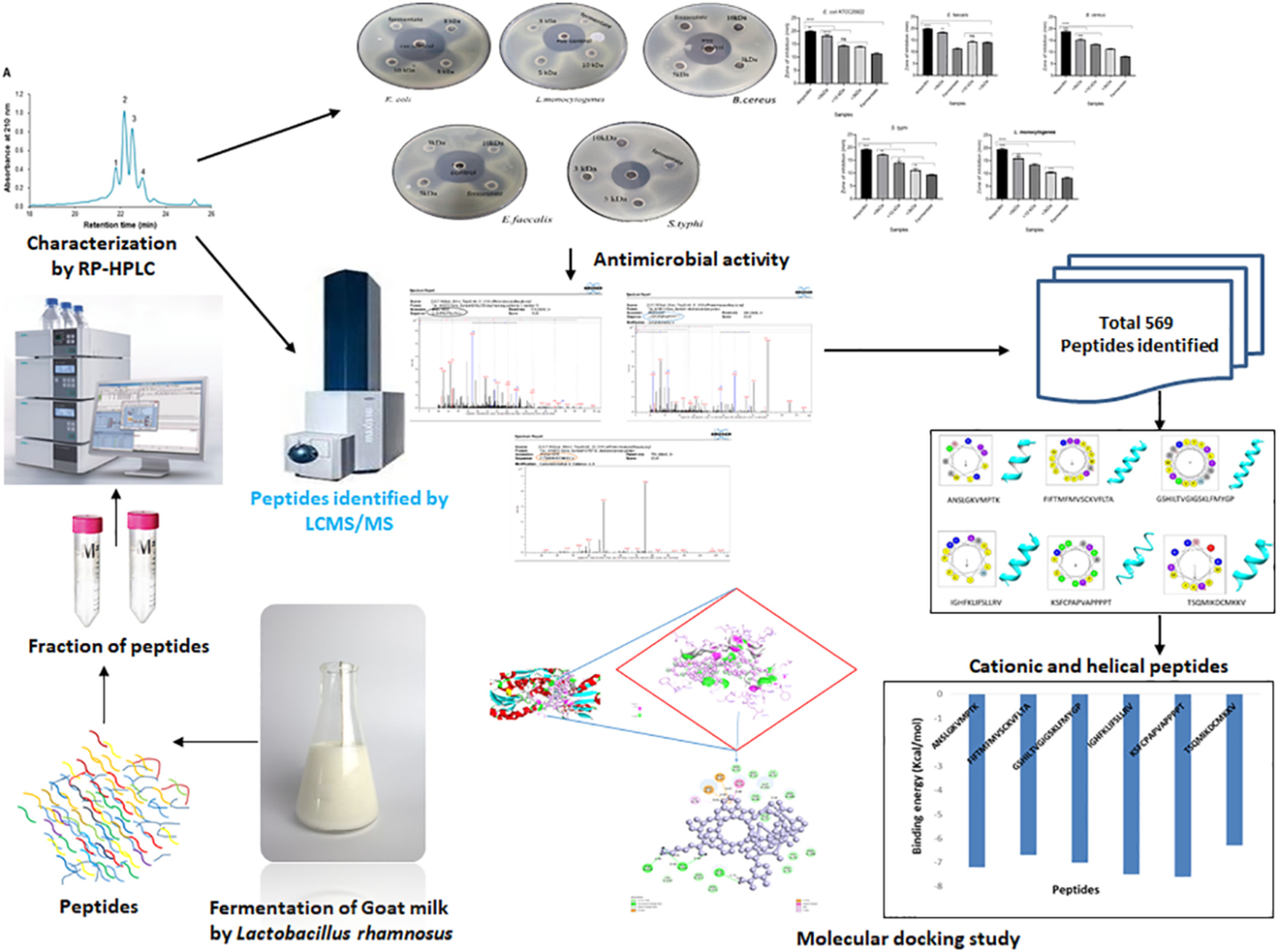
Peptidomics-based identification of an antimicrobial peptide derived from goat milk fermented by Lactobacillus rhamnosus (C25)
- First Published: 13 October 2022
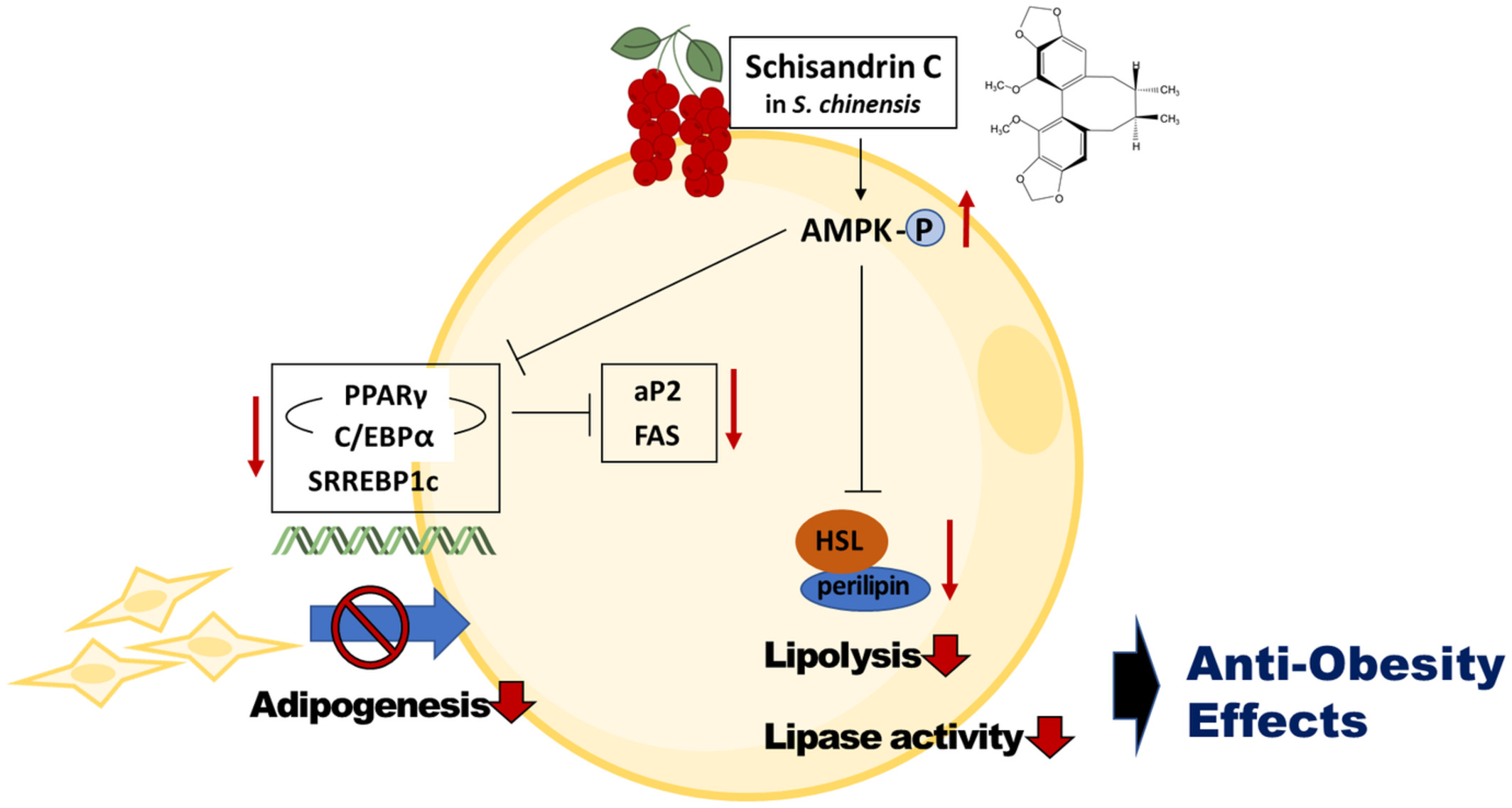
Schisandrin C isolated from Schisandra chinensis fruits inhibits lipid accumulation by regulating adipogenesis and lipolysis through AMPK signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
- First Published: 06 October 2022
Ethanolic extract of root from Arctium lappa L ameliorates obesity and hepatic steatosis in rats by regulating the AMPK/ACC/CPT-1 pathway
- First Published: 01 October 2022
Responses of bitter melon saponins to oxidative stress and aging via the IIS pathway linked with sir-2.1 and hlh-30
- First Published: 13 October 2022

Our data demonstrated that bitter melon saponins exerted the anti-aging and anti-oxidation abilities represented by strengthening the locomotive activities, delaying muscle fiber damage with age, reducing ROS accumulation, and improving the SOD and CAT levels, accompanied by the extension of lifespan. The mechanistic study revealed that the IIS pathway linked with sir-2.1 and hlh-30 transcriptional factors jointly to activate the downstream targets to increase the survival rate under oxidative stress.
Elucidation of active ingredients and mechanism of action of hawthorn in the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis
- First Published: 06 October 2022
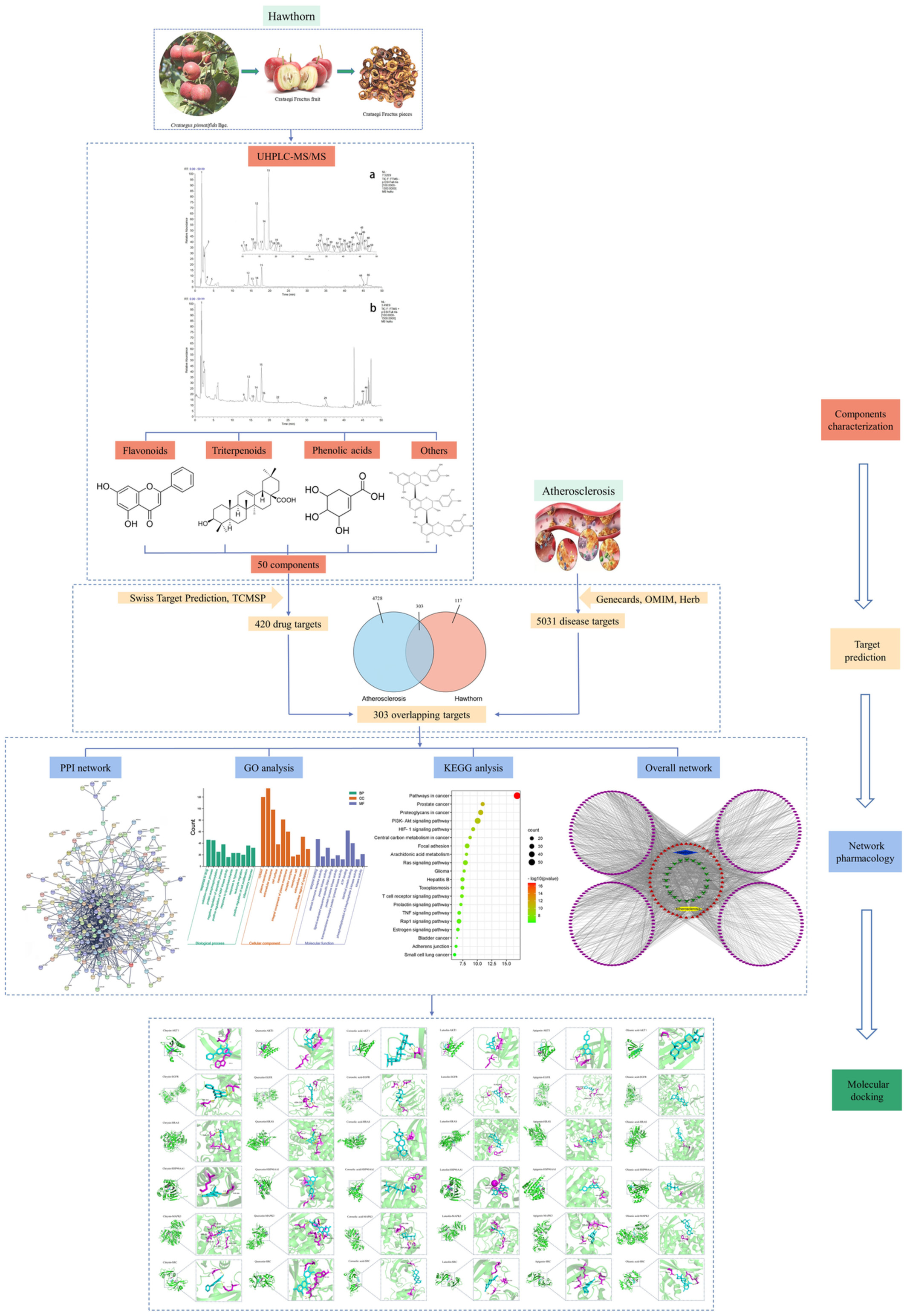
- A total of 50 compounds were detected and tentatively identified in a methanol–water (60:40, v/v) extract of hawthorn.
- A feasible compound–target–pathway network pharmacology model was established.
- The potential core active compounds, targets, and pathways of hawthorn in the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis were screened.
- Further molecular docking results indicated that the potential core active compounds had strong hydrogen bonding abilities with the core targets.
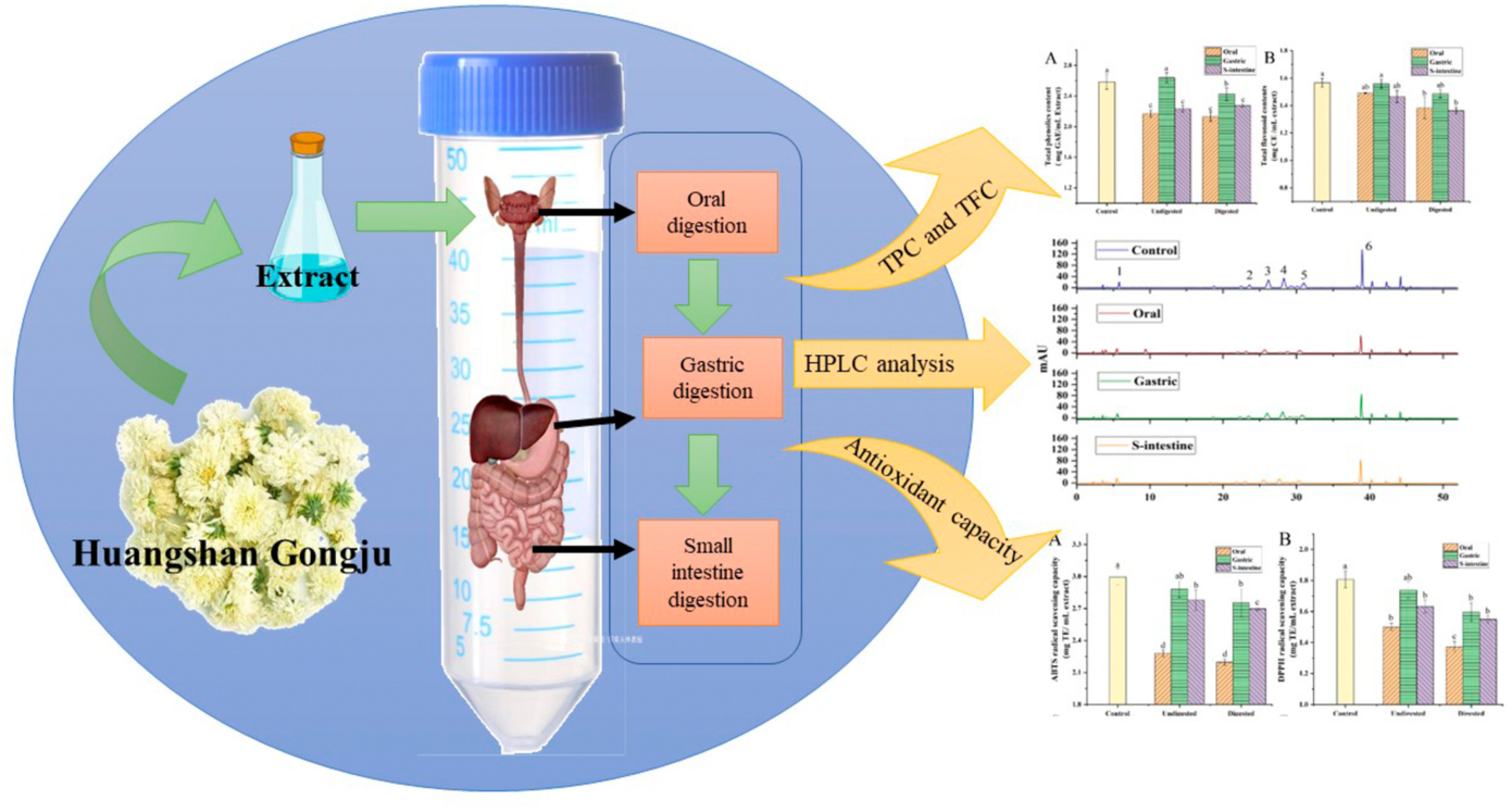
Profile and activity of phenolic antioxidants in chrysanthemum (Huangshan Gongju) as affected by simulated digestions
- First Published: 20 October 2022
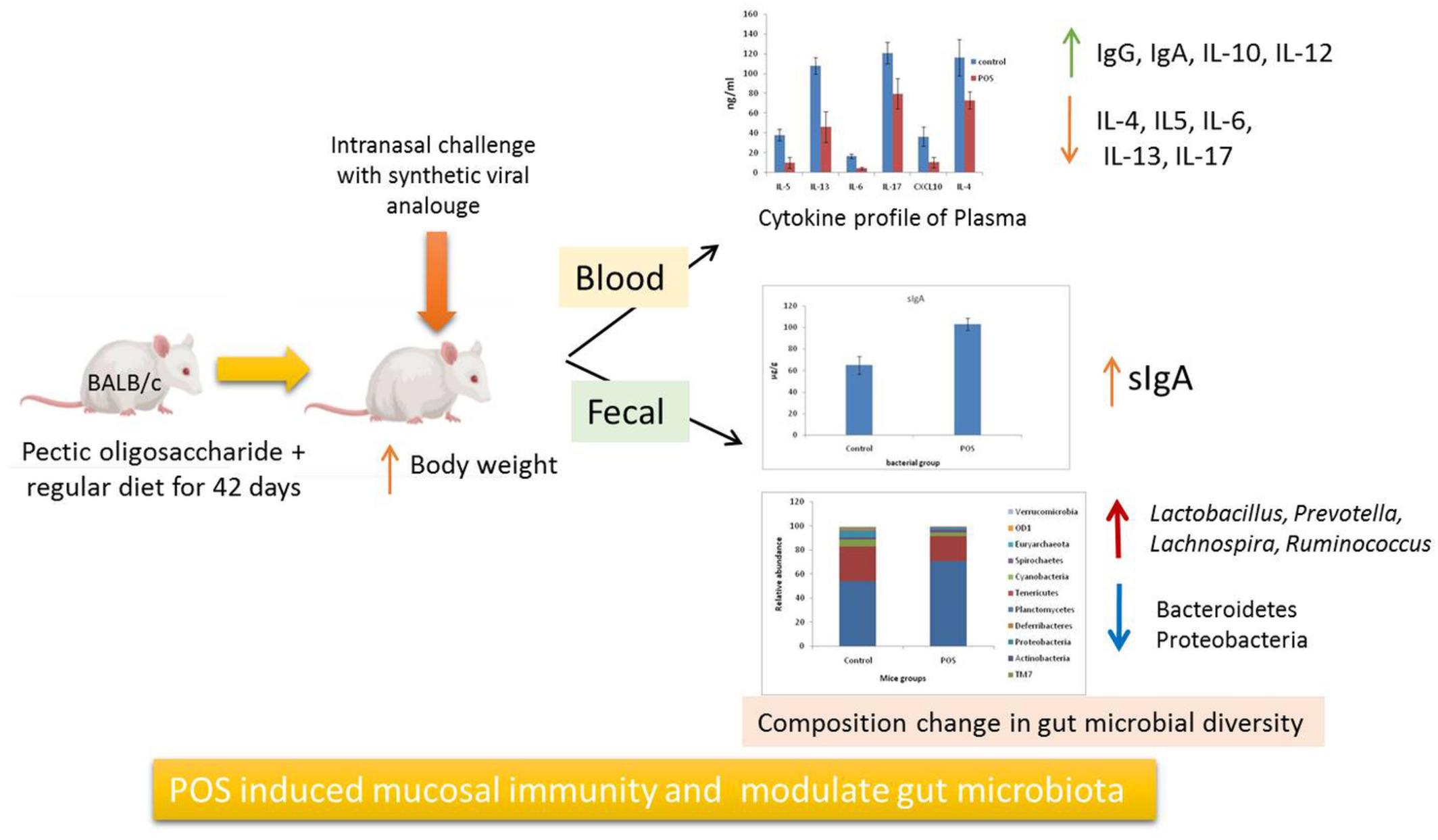
Prophylactic effect of pectic oligosaccharides against poly I: C- induced virus-like infection in BALB/c mice
- First Published: 14 October 2022
Phillygenin from Forsythia suspensa leaves exhibits analgesic potential and anti-inflammatory activity in carrageenan-induced paw edema in mice
- First Published: 06 October 2022
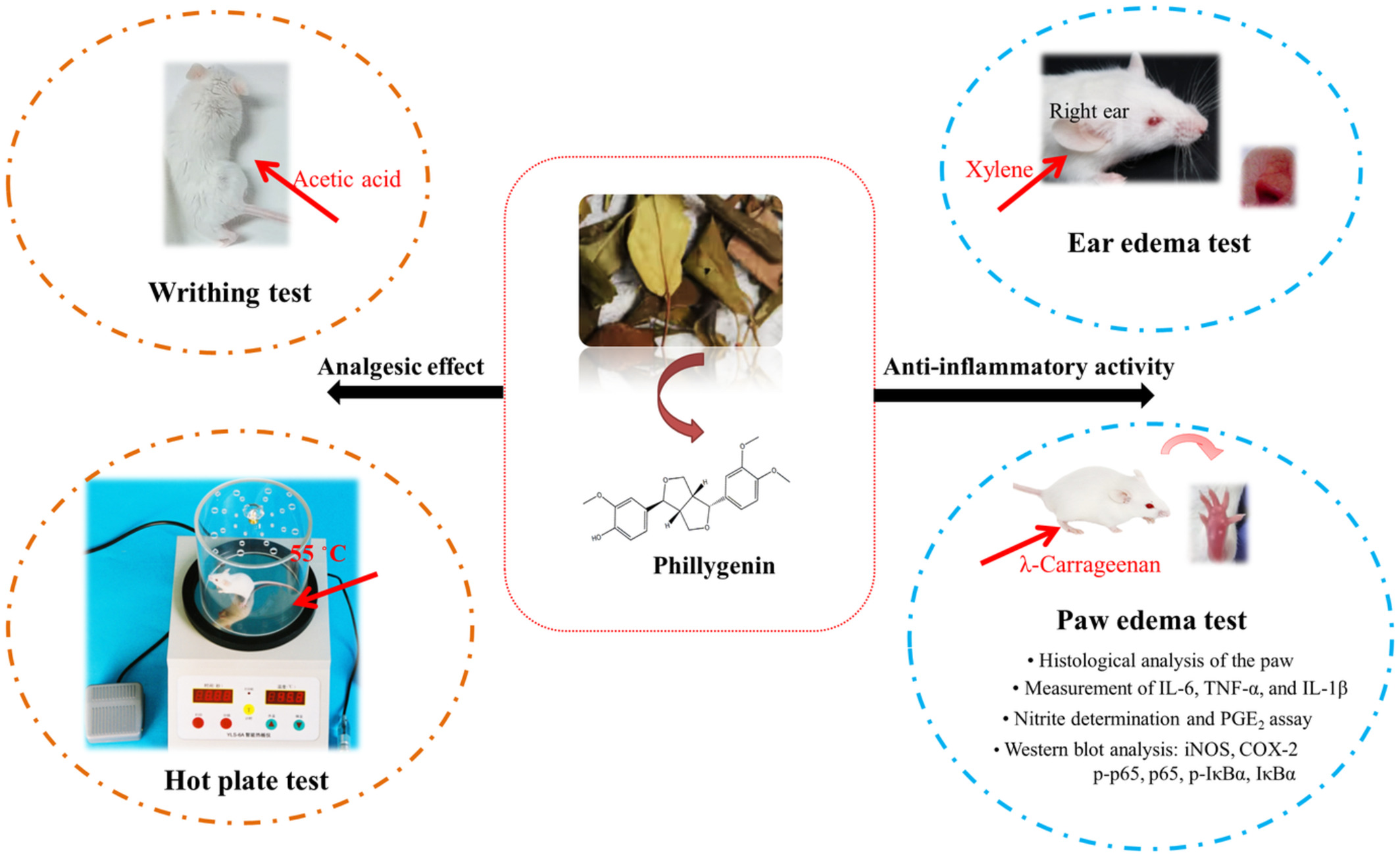
Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl (Oleaceae) leaves are valuable sources of phillygenin. Phillygenin was successfully extracted and isolated from F. suspensa leaves after fermentation and reduced the number of writhing induced by acetic acid, prolonged the latency period in the hot plate test, inhibited the xylene-induced ear edema and carrageenan-induced paw edema, decreased inflammatory mediators production, and regulated iNOS and COX-2 and NF-κB signal proteins expressions. Our study suggest that phillygenin may contribute to managing pain and inflammation-mediated disorders.
Dietary tea seed saponin combined with aerobic exercise attenuated lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD)
- First Published: 06 October 2022
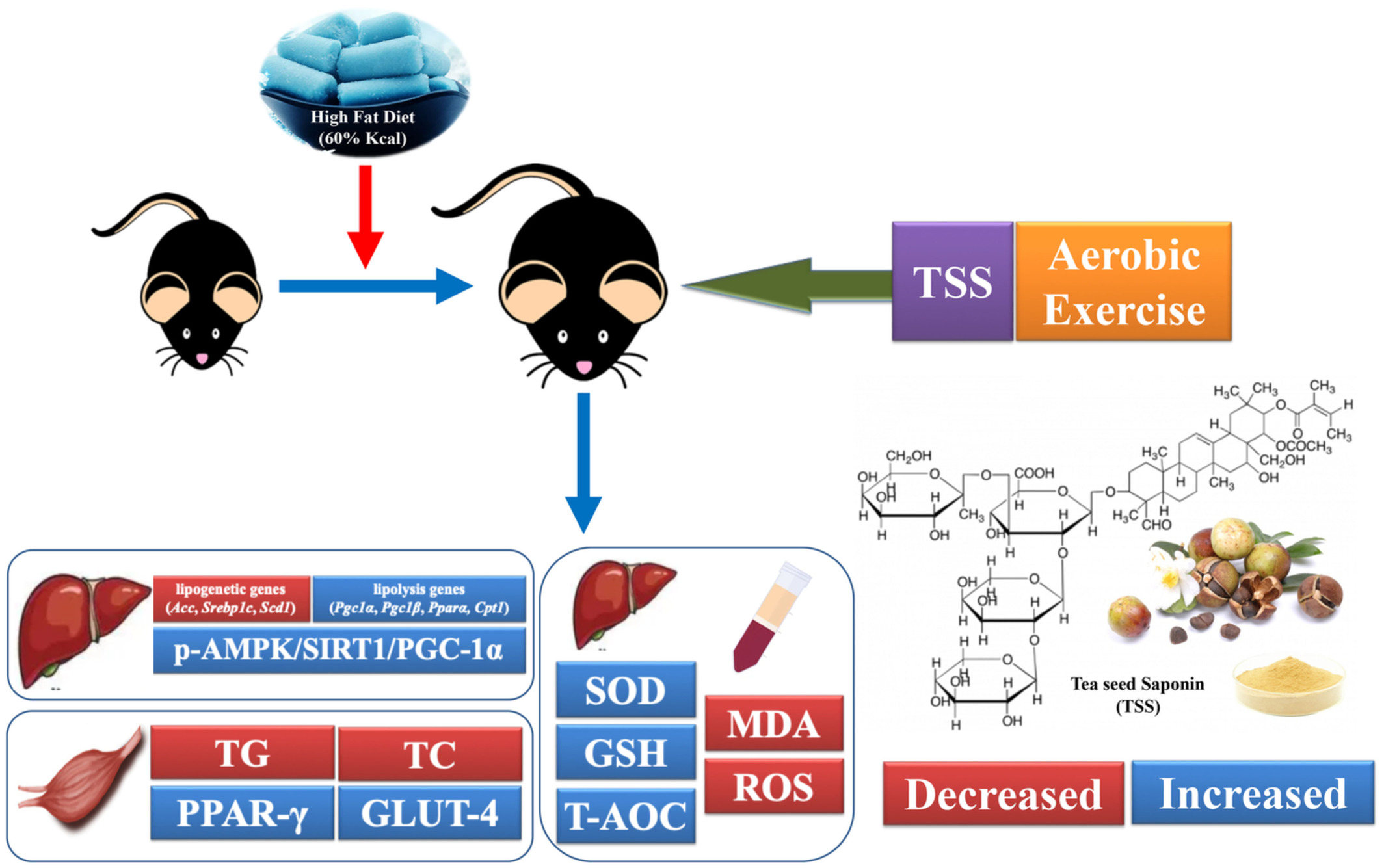
Dietary modifications combined with aerobic exercise are currently an effective method for weight loss. Tea seed saponins (TSS) are a variety of biologically active oleanolane-type pentacyclic triterpenoid saponins that naturally exist in tea seeds. In this study, the high fat diet-induced obese mice model to explore the mechanism of TSS with aerobic exercise (AE) in regulating lipid metabolism and its associated oxidative stress damage will help provide reliable data for the application of dietary nutrition combined with AE in anti-obesity.
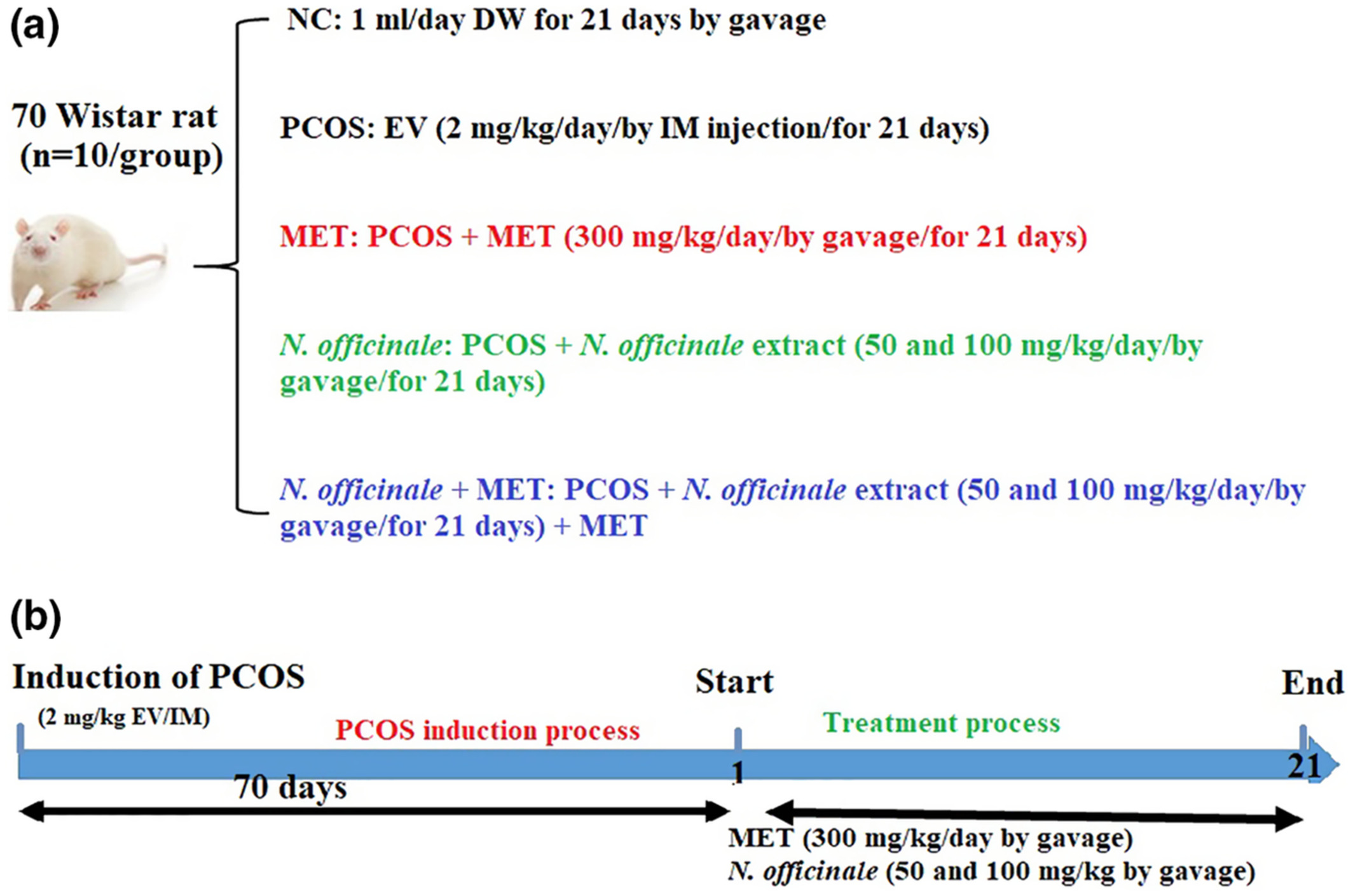
Nasturtium officinale L. and metformin alleviate the estradiol- induced polycystic ovary syndrome with synergistic effects through modulation of Bax/Bcl-2/p53/caspase-3 signaling pathway and anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects
- First Published: 09 November 2022
Resveratrol inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by regulating autophagy and apoptosis through the SIRT1 and JNK signaling pathways
- First Published: 31 October 2022
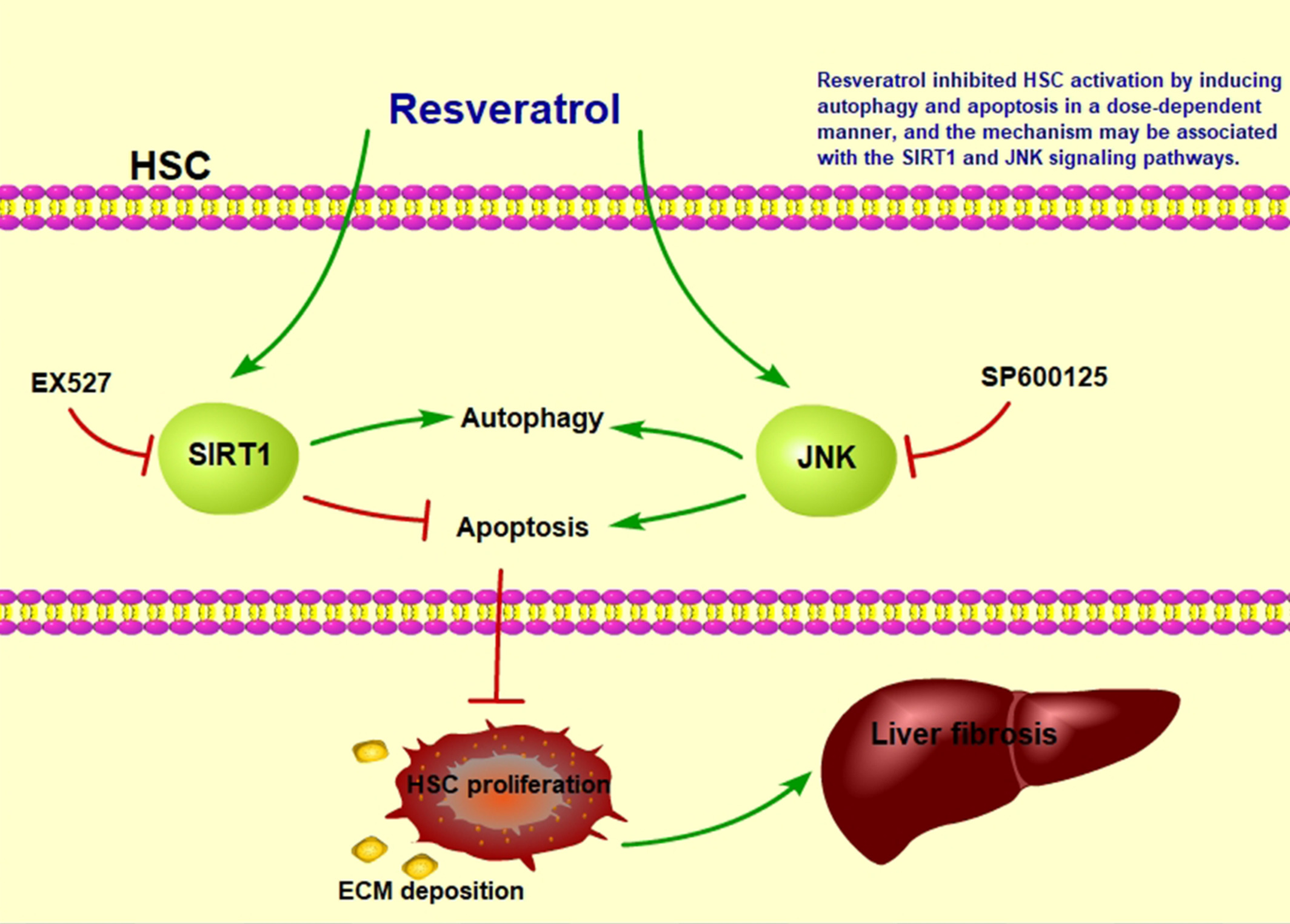
Resveratrol inhibited hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) activation by inducing autophagy and apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. The Sirtuin1 (SIRT1) inhibitor EX527 reversed autophagy, and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) inhibitor SP600125 reversed both autophagy and apoptosis induced by resveratrol. These findings suggest that the SIRT1 and JNK signaling pathways may be involved in the resveratrol-mediated inhibition of HSC activation by regulating autophagy and apoptosis.
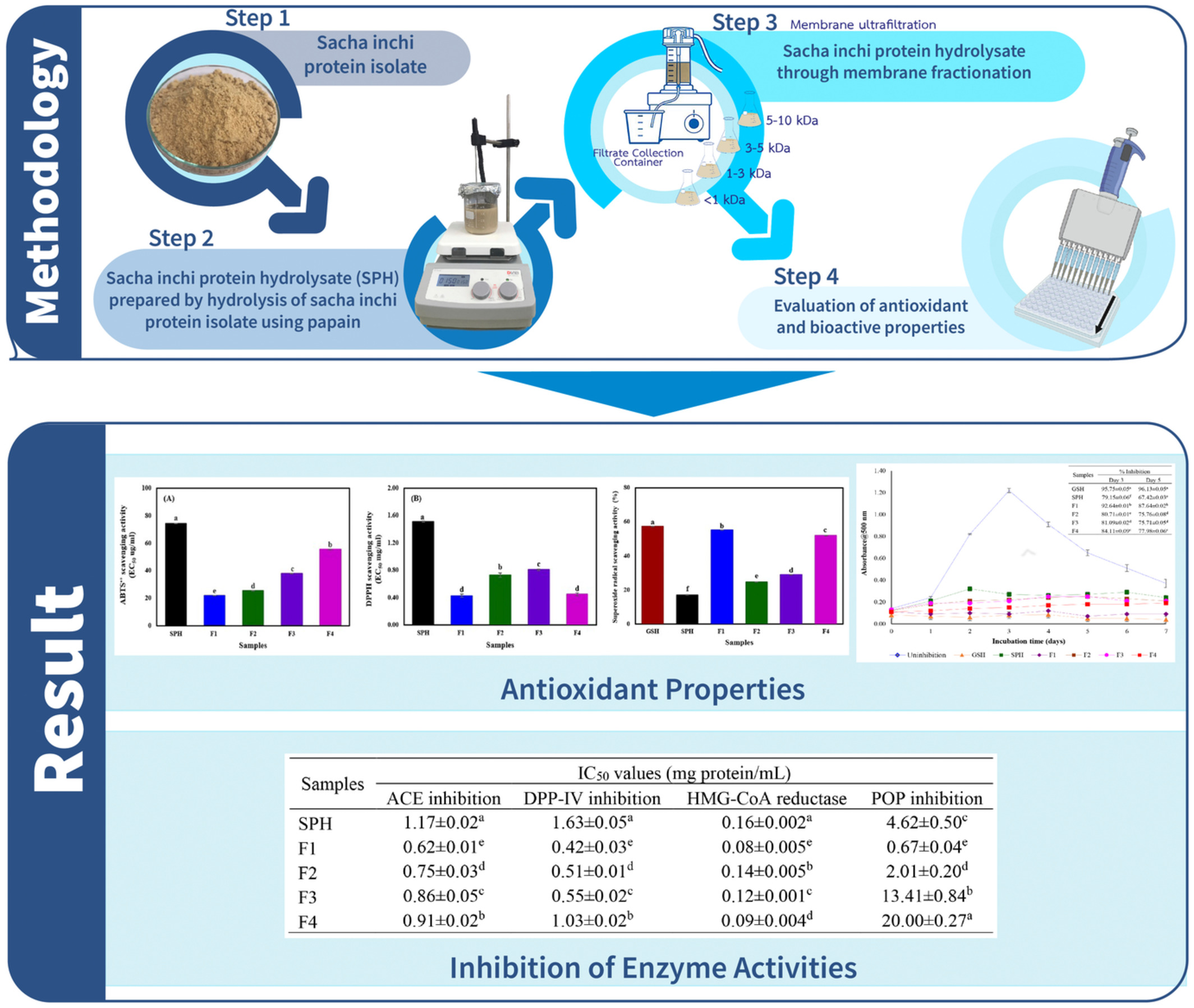
Antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory properties of sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis) protein hydrolysate and its peptide fractions
- First Published: 03 October 2022
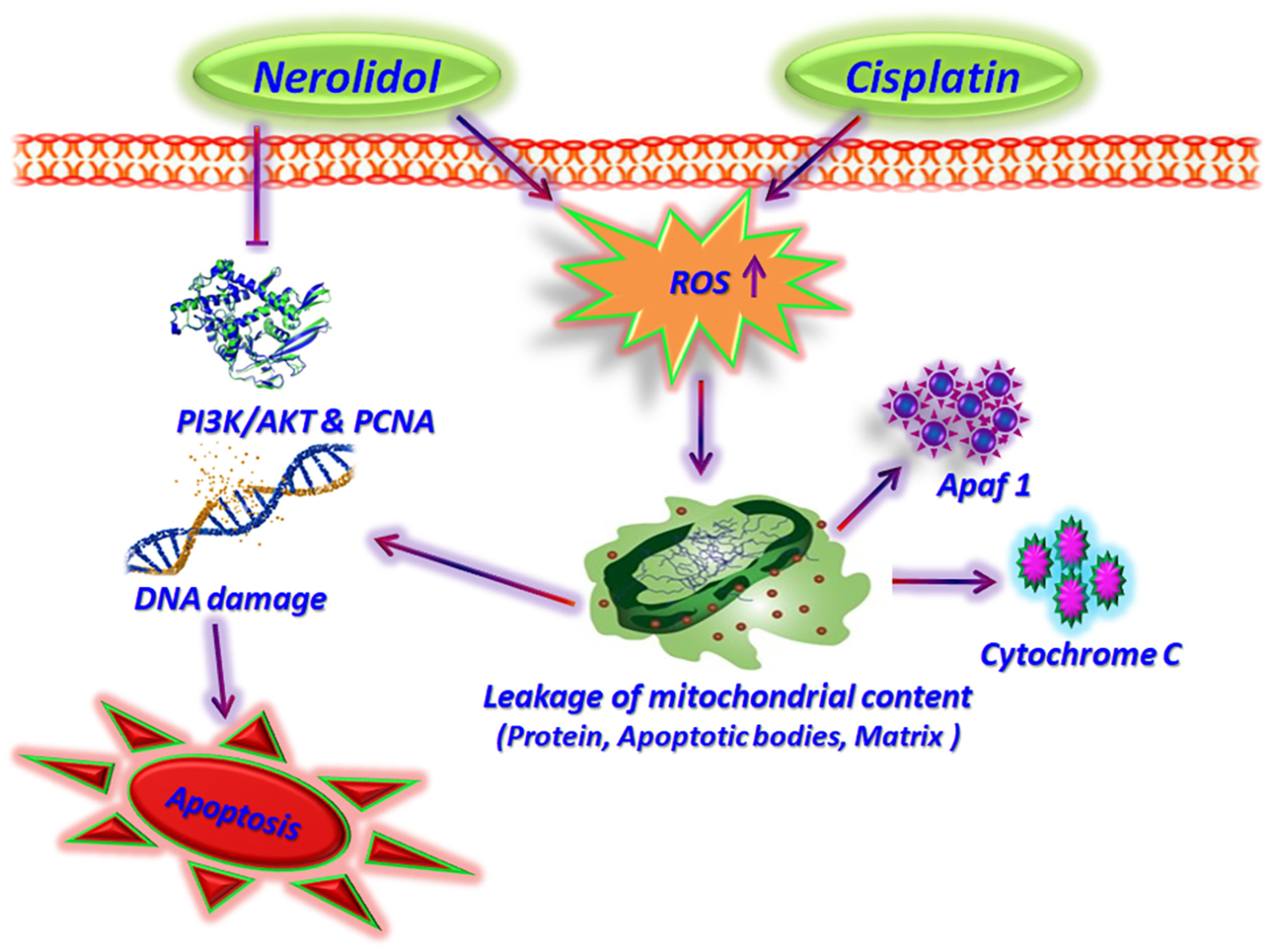
Nerolidol assists Cisplatin to induce early apoptosis in human laryngeal carcinoma Hep 2 cells through ROS and mitochondrial-mediated pathway: An in vitro and in silico view
- First Published: 13 October 2022
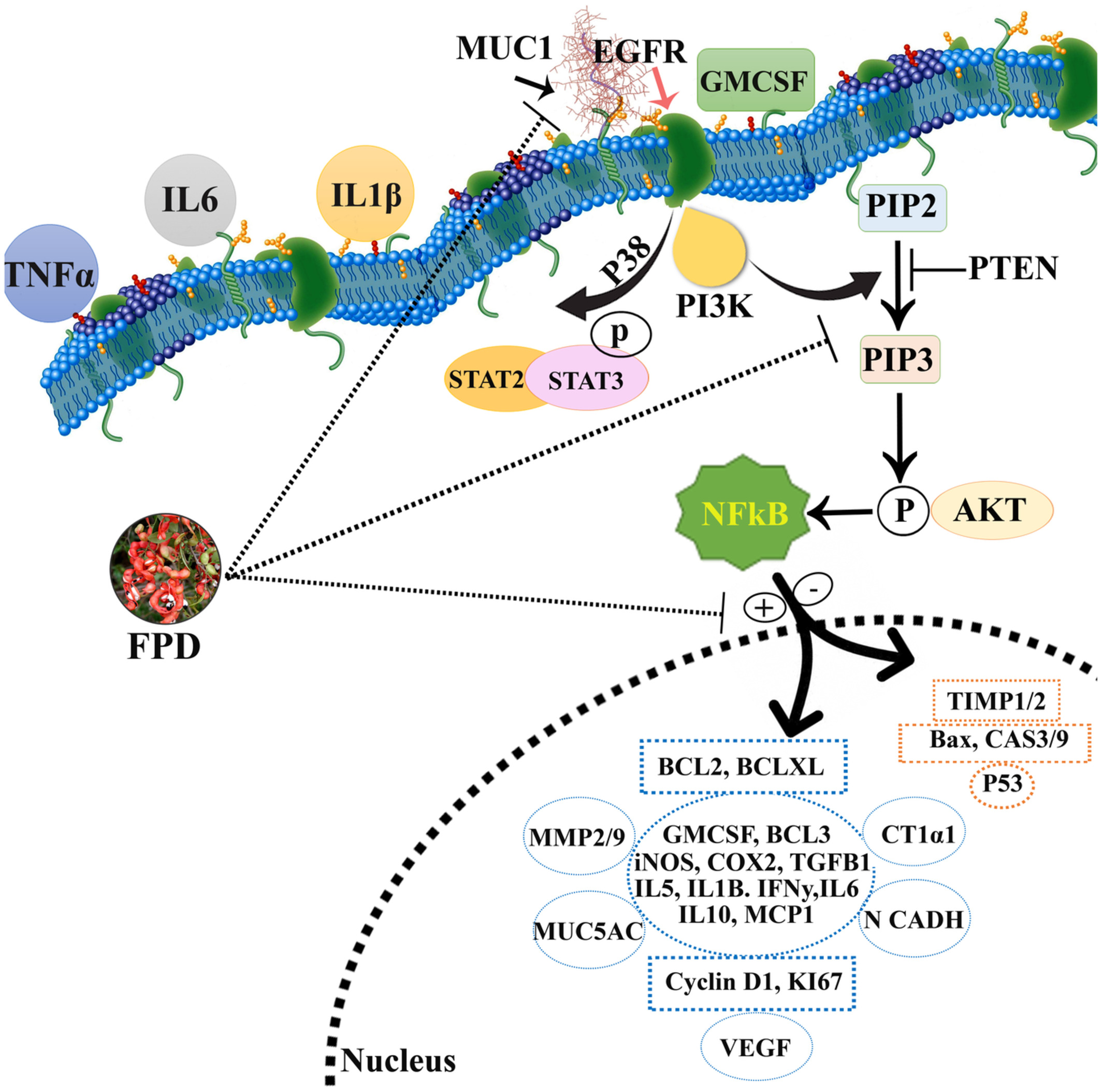
Pithecellobium dulce inhibits pulmonary metastasis induced by B16F10 melanoma cells in C57BL/6 via regulating EGFR/STAT/ NFκB /AKT signaling axis
- First Published: 11 October 2022
Synergistic properties of garlic and Citrullus colocynthis on reproductive injury caused by diabetes in male rats: Structural and molecular evidence
- First Published: 11 October 2022
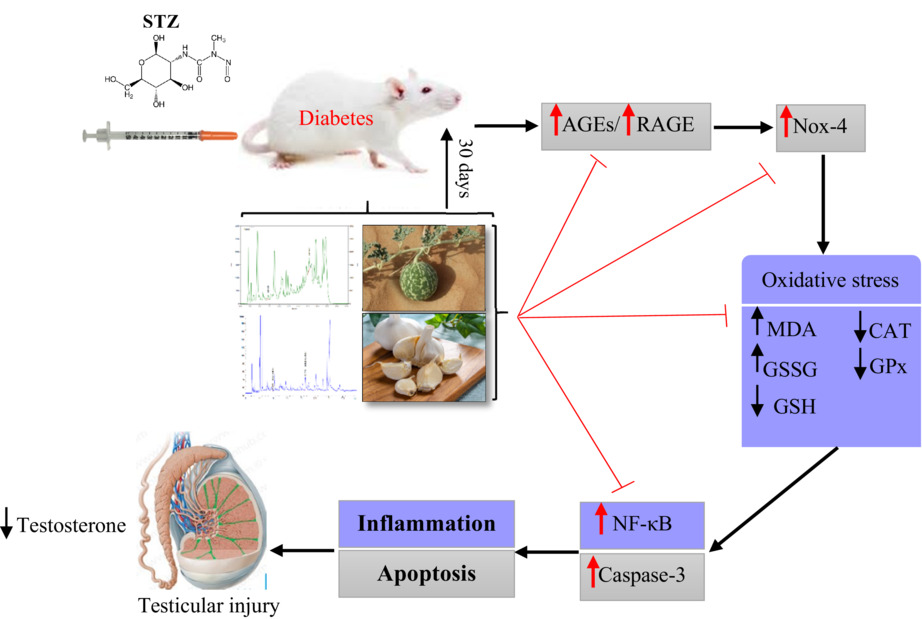
Figure 10. Schematic representation of the mechanisms by which garlic and Citrullus colocynthis reduce testicular damage in diabetic rats. Diabetes mellitus causes testicular damage through AGEs/RAGE/Nox-4 pathway and subsequent oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. The combination of garlic and C. colocynthis could significantly inhibit this pathway and the resulting complications.
β-Caryophyllene oxide inhibits metastasis by downregulating MMP-2, p-p38 and p-ERK in human fibrosarcoma cells
- First Published: 03 October 2022
In vitro immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects of oligopeptides and four characteristic peptides in black-bone silky fowl (Gallus gallus domesticus Brisson)
- First Published: 07 October 2022
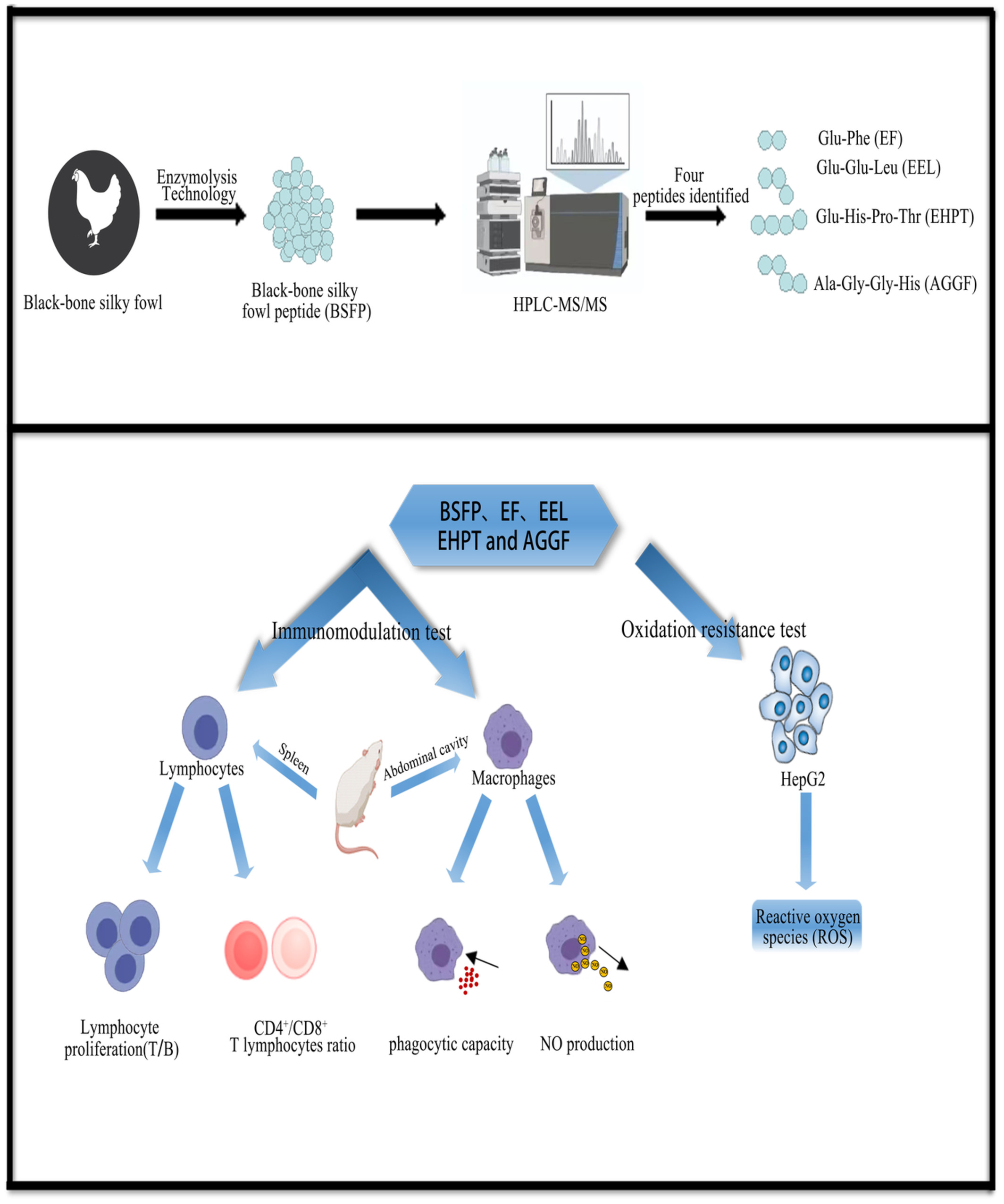
The black-bone silky fowl peptide (BSFP) was produced by enzymatic digestion of black-bone silky fowl. The peptide sequences in BSFP were identified by HPLC-MS/MS technique and found to contain four peptides (EF, EEL, EHPT, and AGGF). The positive effects of BSFP and the four characteristic peptides in antioxidant and immunomodulation were verified experimentally.
Effects of altitude on meat quality difference and its relationship with HIF-1α during postmortem maturation of beef
- First Published: 26 October 2022
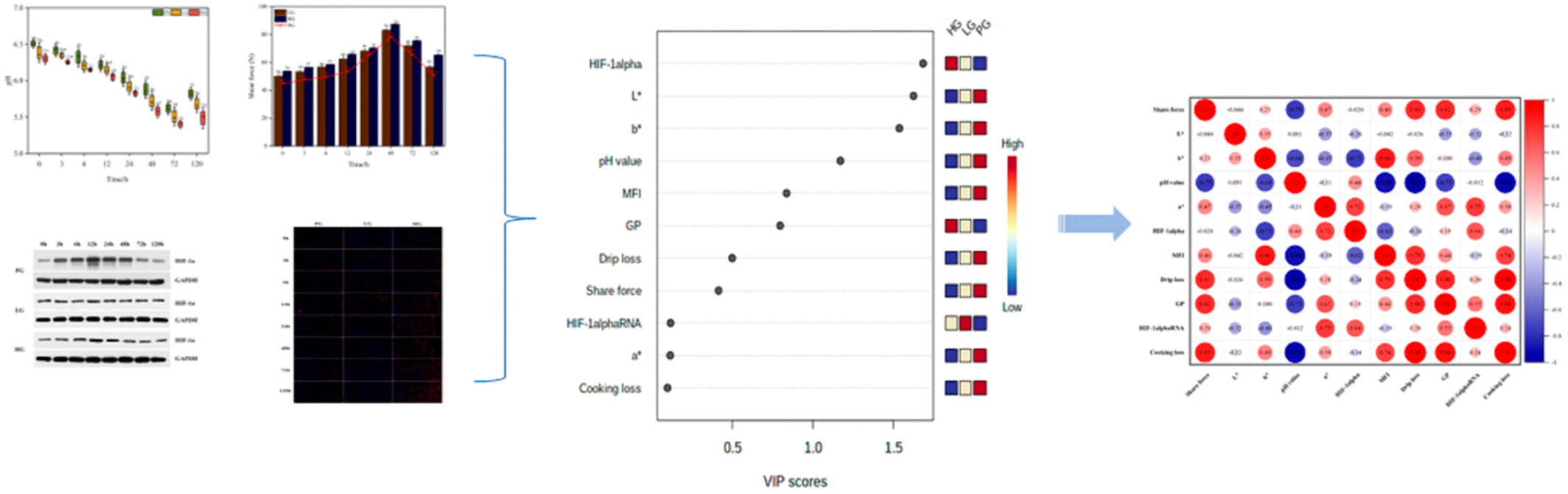
This study investigated the differences in meat quality during postmortem aging of yak meat at different altitudes and the relationship between hypoxic factor HIF-1α release and meat quality. As Journal of Food Biochemistry has a long-standing interest in publishing research related to the meat quality field, we feel your readership will be interested in this study that contributes to further understanding changes in meat quality during aging.
Tert-butylhydroquinone abrogates fructose-induced insulin resistance in rats via mitigation of oxidant stress, NFkB-mediated inflammation in the liver but not the skeletal muscle of high fructose drinking rats
- First Published: 17 October 2022
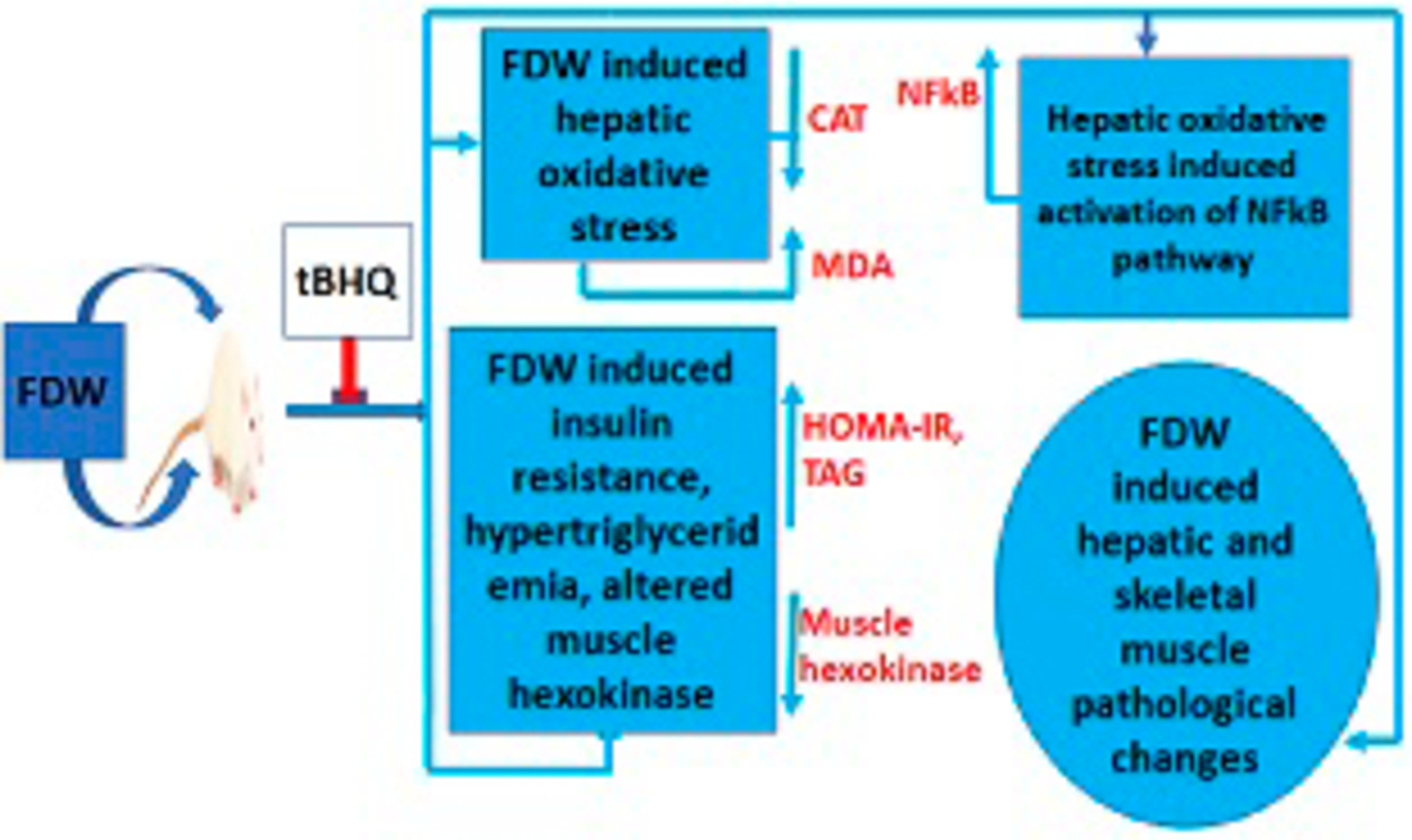
Fructose drinking water (FDW) altered the serum leptin, triacylglycerol, and C-reactive protein levels of the rats, inducing hypertriglyceridemia, oxidative stress, and inflammation in their liver (but not their skeletal muscle) and insulin resistance which was modulated by tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ). These biochemical findings were corroborated by liver and muscle histology.
Beneficial role of Boehmeria nivea in health and phytochemical constituents
- First Published: 09 October 2022
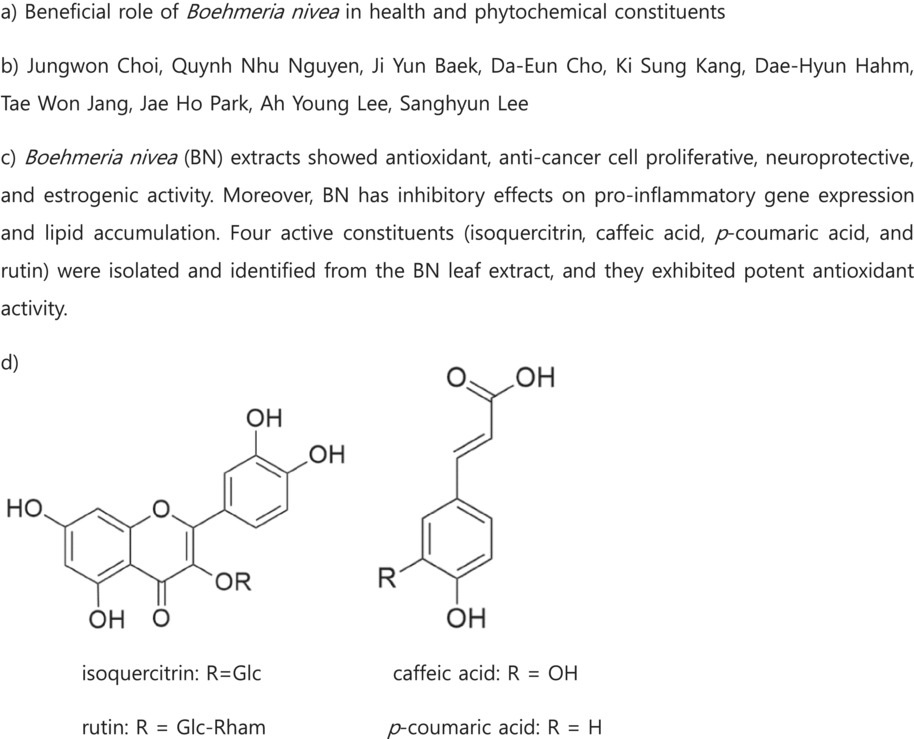
Boehmeria nivea (BN) extracts showed antioxidant, anti-cancer cell proliferative, neuroprotective, and estrogenic activity. Moreover, BN has inhibitory effects on pro-inflammatory gene expression and lipid accumulation. Four active constituents (isoquercitrin, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, and rutin) were isolated and identified from the BN leaf extract, and they exhibited potent antioxidant activity.
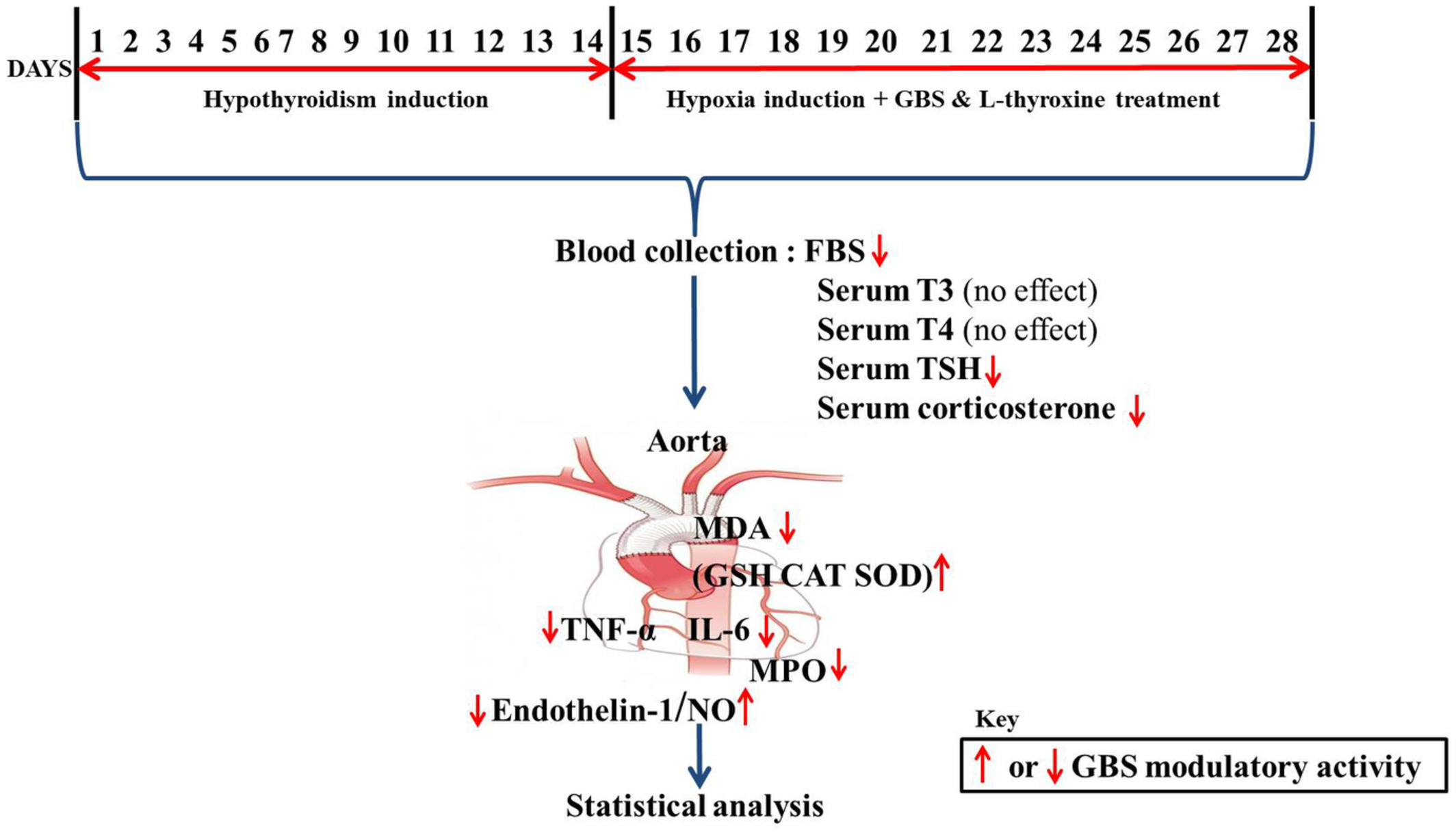
Treatment with Ginkgo biloba supplement modulates oxidative disturbances, inflammation and vascular functions in oxygen deprived hypothyroid mice: Involvement of endothelin-1/NO signaling pathways
- First Published: 13 October 2022
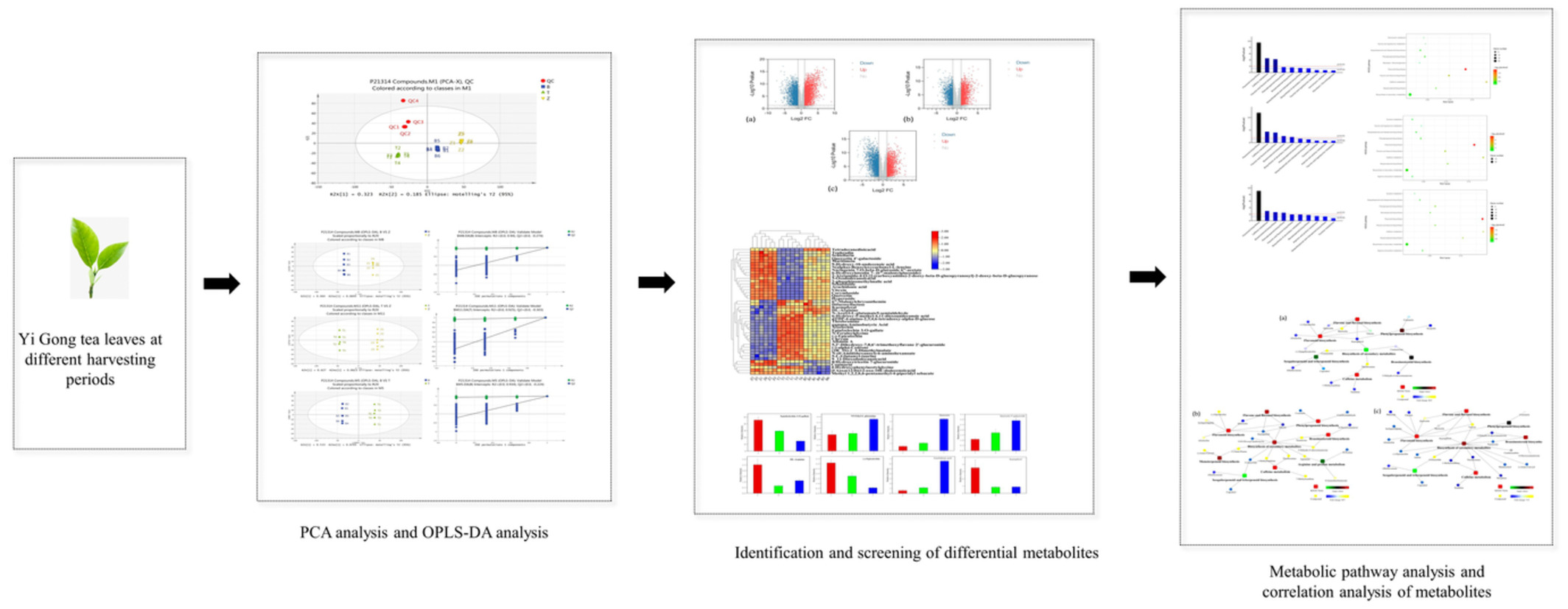
Metabolomic analysis reveals the quality characteristics of Yi Gong tea leaves at different harvesting periods
- First Published: 14 October 2022
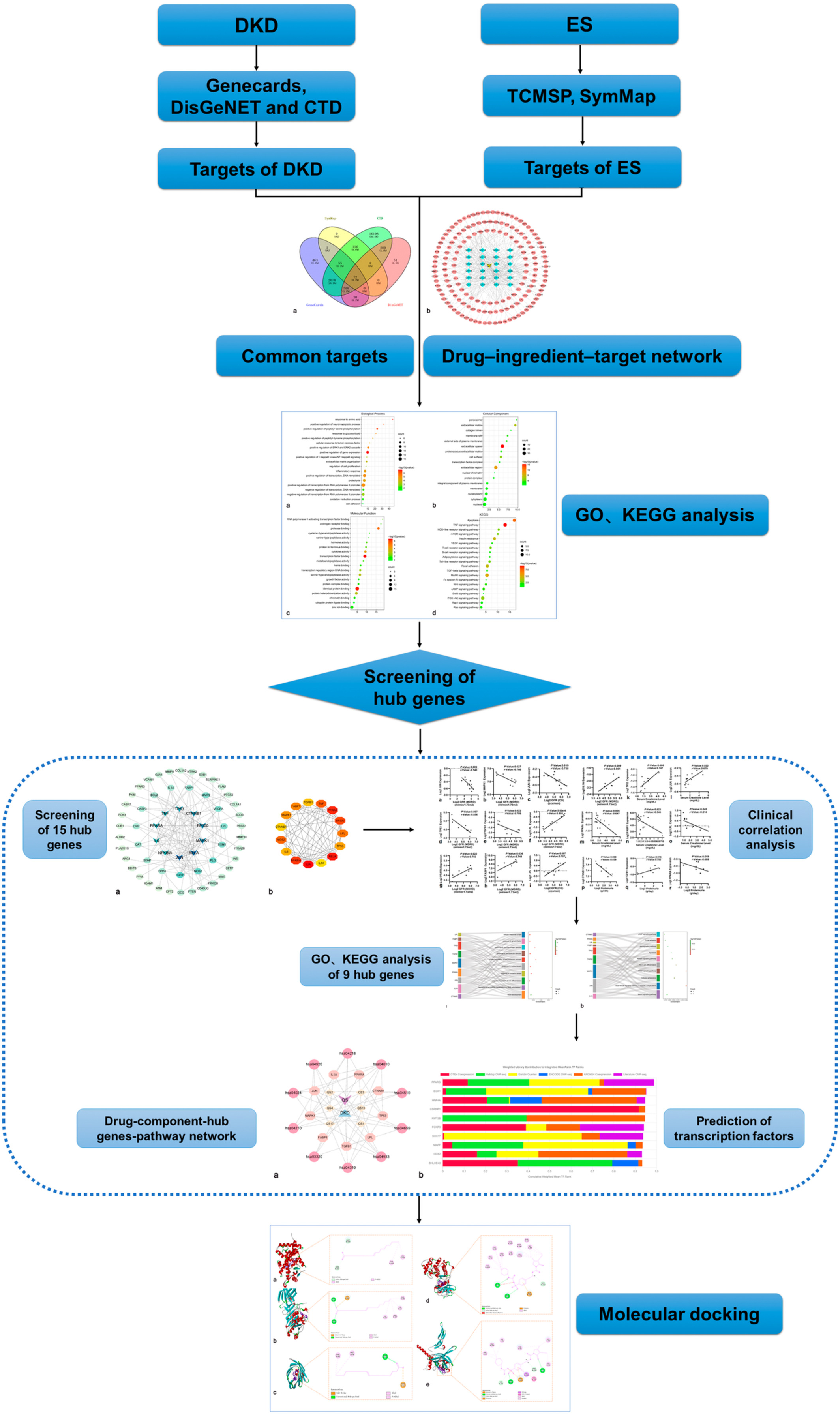
Natural remedies medicine derived from flaxseed (secoisolariciresinol diglucoside, lignans, and α-linolenic acid) improve network targeting efficiency of diabetic heart conditions based on computational chemistry techniques and pharmacophore modeling
- First Published: 14 October 2022
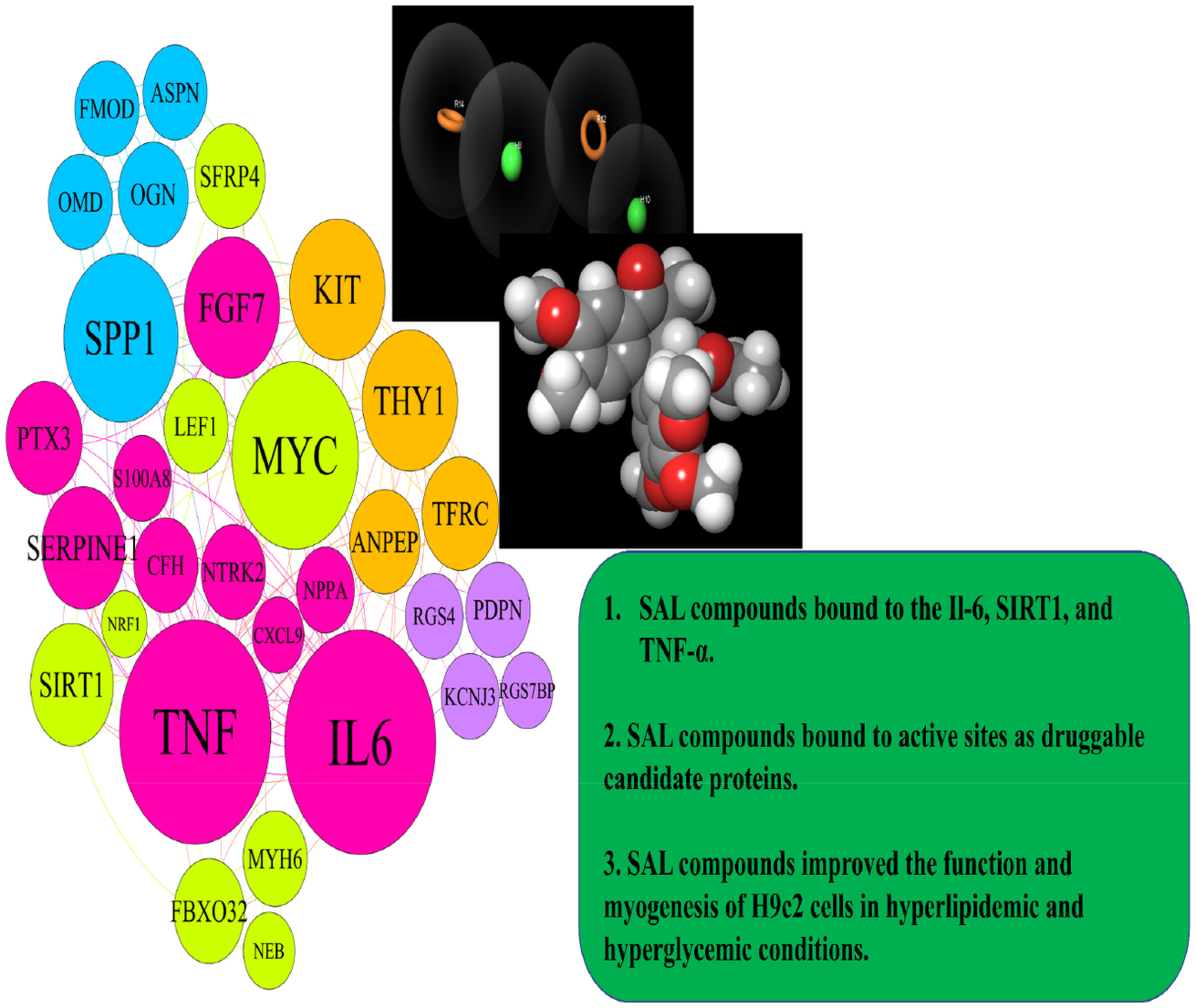
This study explored that SAL compounds improved the function and myogenesis of H9c2 cells in hyperlipidemic and hyperglycemic conditions. Our data suggested that phytochemicals obtained from flaxseed might have proposed potential complementary treatment or preventive strategies for MI. Moreover, we found druggable candidate proteins based on the chemoinformatics analysis. This study displayed that the TNF-α, IL6, SIRT1, NRF1, NPPA, and FGF7 are vital hub genes in MI induced by hyperlipidemic and hyperglycemic.
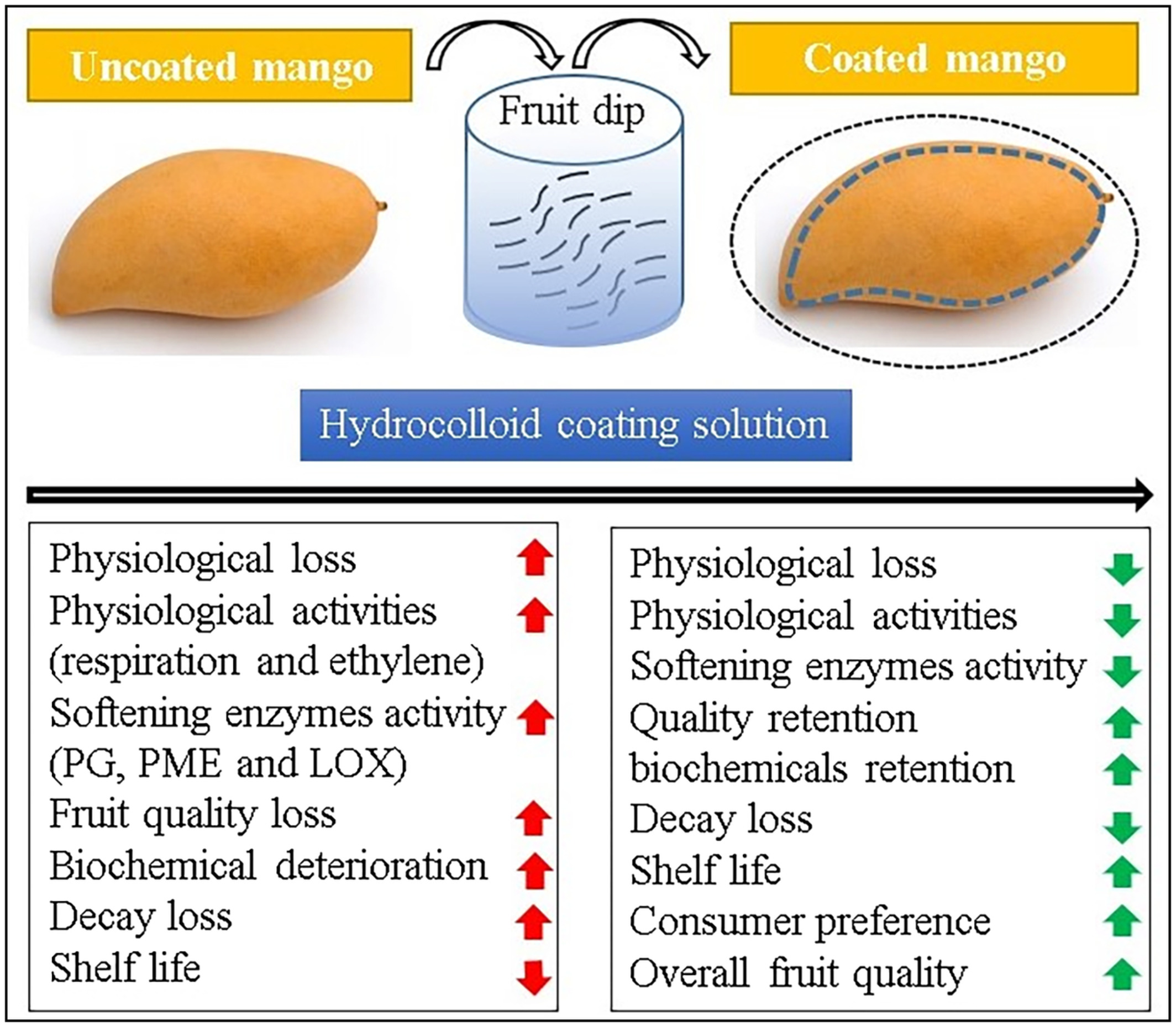
Hydrocolloid edible coatings extend shelf life, reduce postharvest decay, and maintain keeping quality of mango fruits (Mangifera indica L.) under ambient storage
- First Published: 13 October 2022
Protective effects of volatile components of aged garlic extract against ultraviolet B-induced apoptosis in human skin fibroblasts
- First Published: 11 October 2022
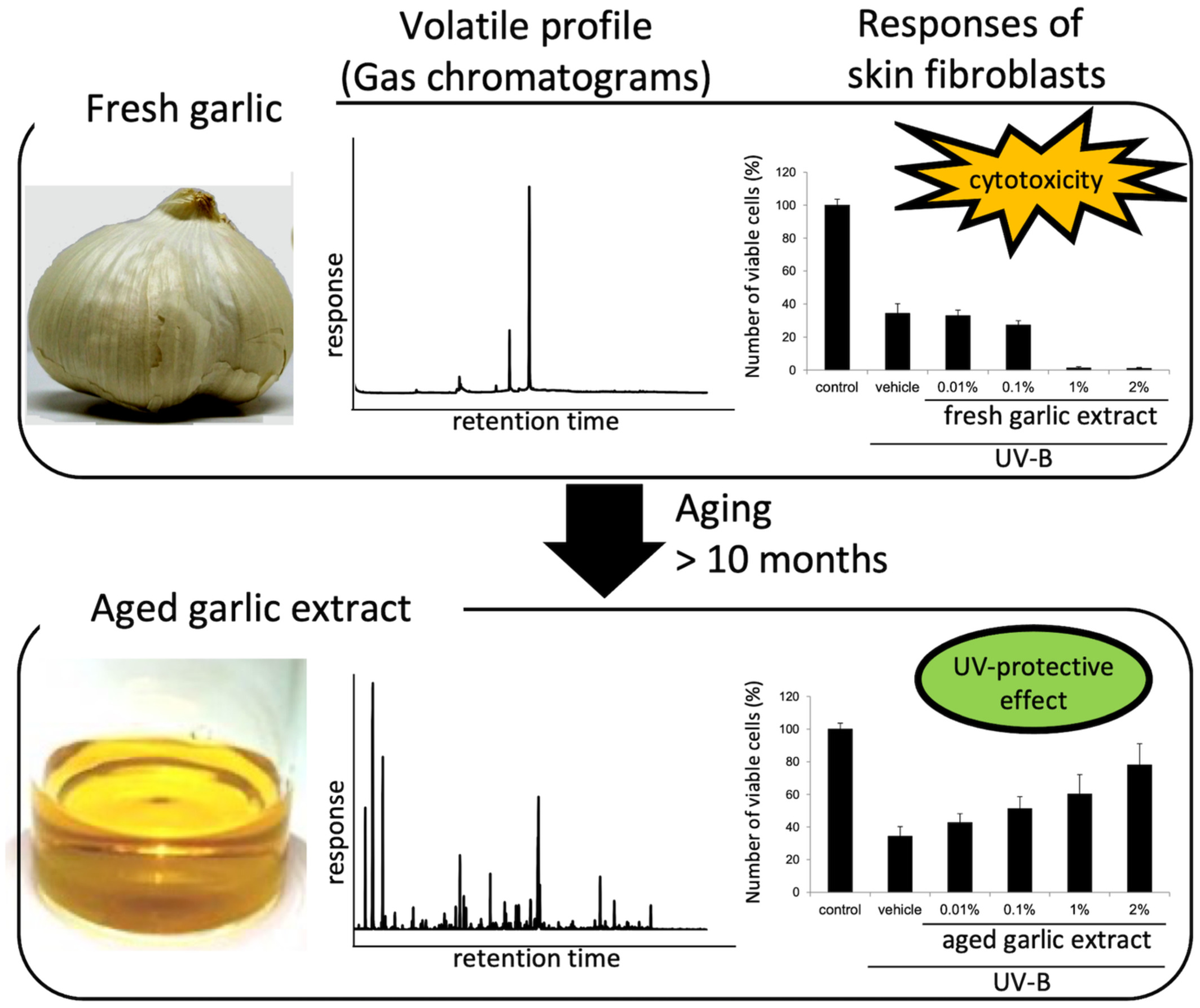
Treatment of cultured skin fibroblasts with fresh garlic extract enhanced the UV-B-induced reduction of cell viability, whereas that with aged garlic extract (AGE) inhibited the reduction of cell viability. The protective effects against UV-B-induced cell death were observed not only in the non-volatile fraction but also in the volatile fraction of AGE. This is the first report demonstrating that characteristic volatile compounds generated during the aging process of garlic have a high potency for improving skin health.
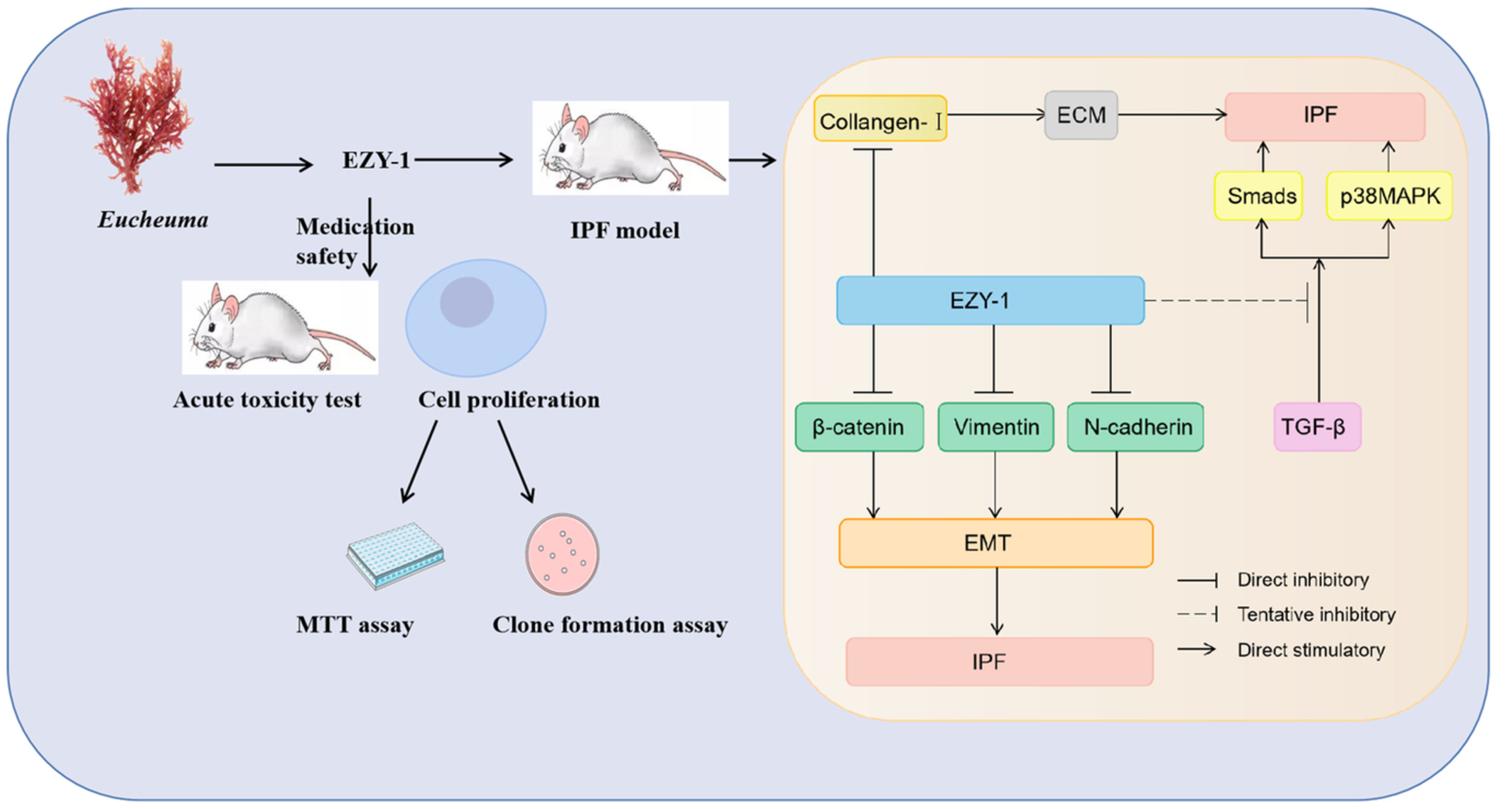
Acute toxicological study: EZY-1 with potent therapeutic effects of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and its mechanisms
- First Published: 13 October 2022
Inhibition characteristics and mechanism of tyrosinase using five citrus flavonoids: A spectroscopic and molecular dynamics simulation study
- First Published: 14 October 2022
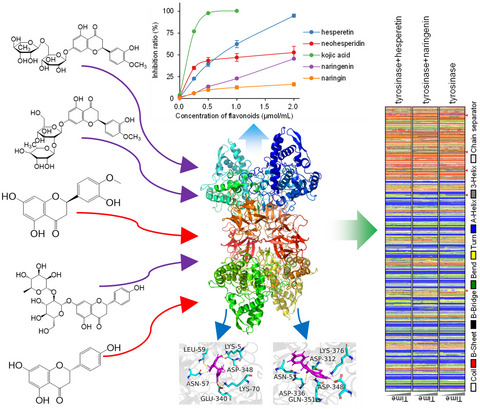
Hesperetin, neohesperidin, naringenin and naringin exhibited higher inhibitory activities than kojic acid. Hesperetin and naringenin were reversible inhibitors on tyrosinase in the mixed-type manner. H-bond and hydrophobic interactions were found to drive the binding of tyrosinase with hesperetin or naringenin, which subsequently decreased the α-helix ratio and increased the β-turn, β-sheet and random coil ratio in tyrosinase.
Pigeon pea penta- and hexapeptides with antioxidant properties also inhibit renin and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme activities
- First Published: 17 October 2022
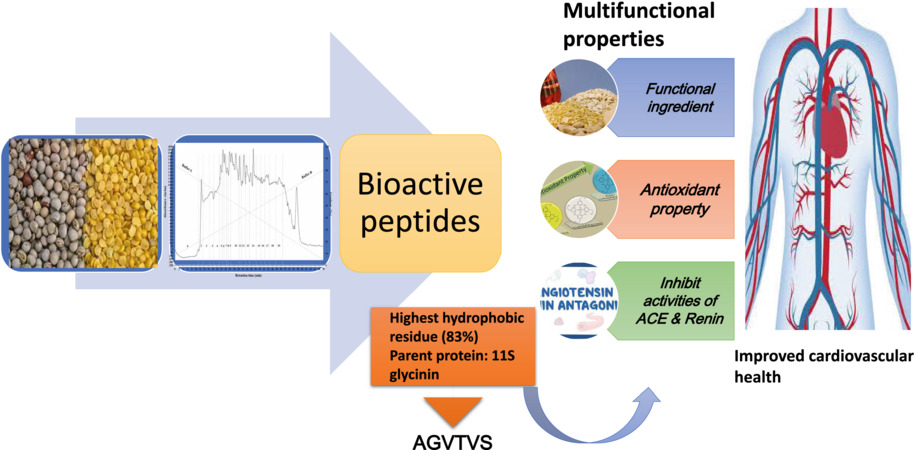
Pigeon pea was hydrolyzed and subjected to high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) purification and sequencing to obtain bioactive peptides which possesses multifunctional properties namely functional ingredient, antioxidant property and ability to inhibit activities of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and Renin.
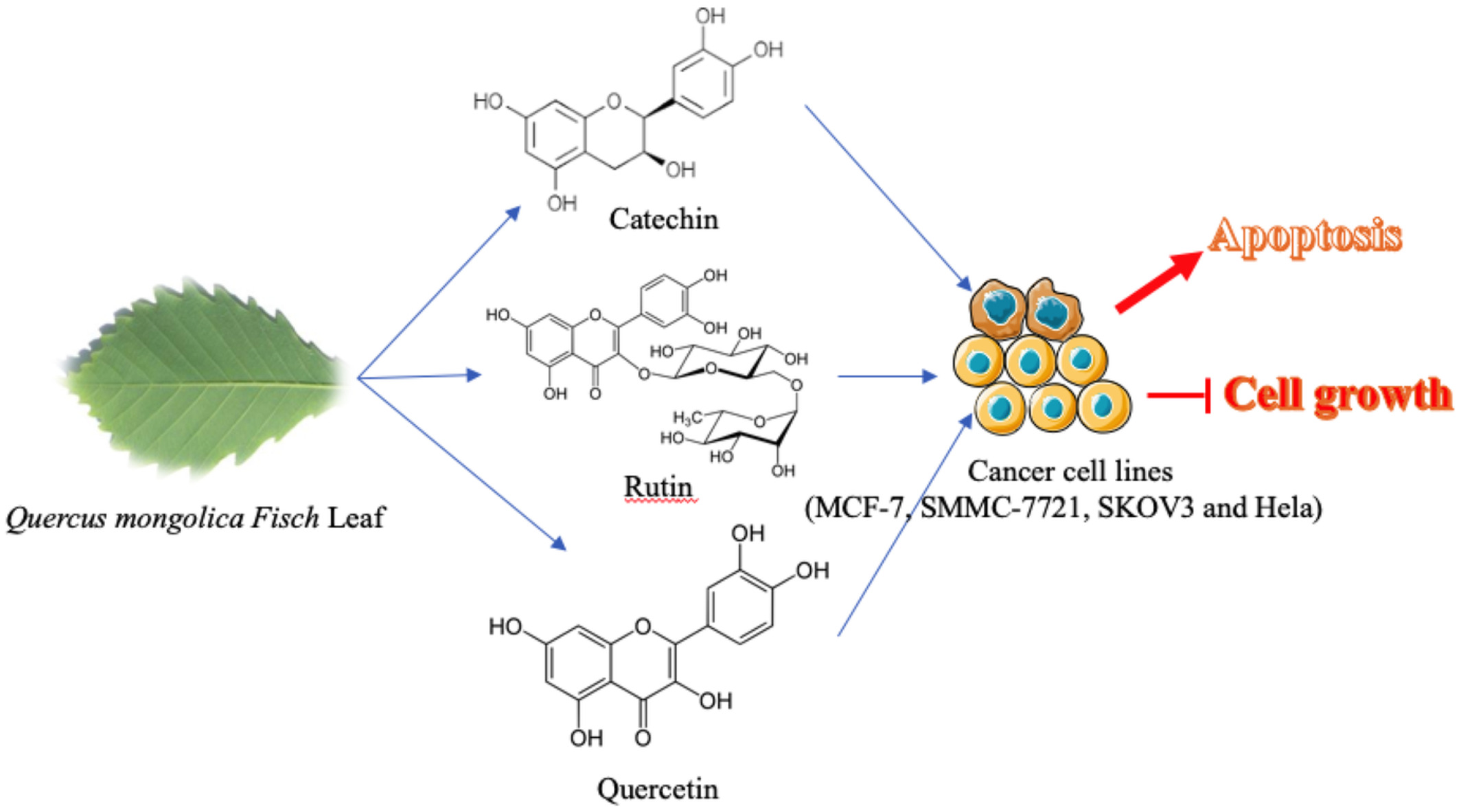
Catechin, rutin and quercetin in Quercus mongolica Fisch leaves exert inhibitory effects on multiple cancer cells
- First Published: 09 November 2022
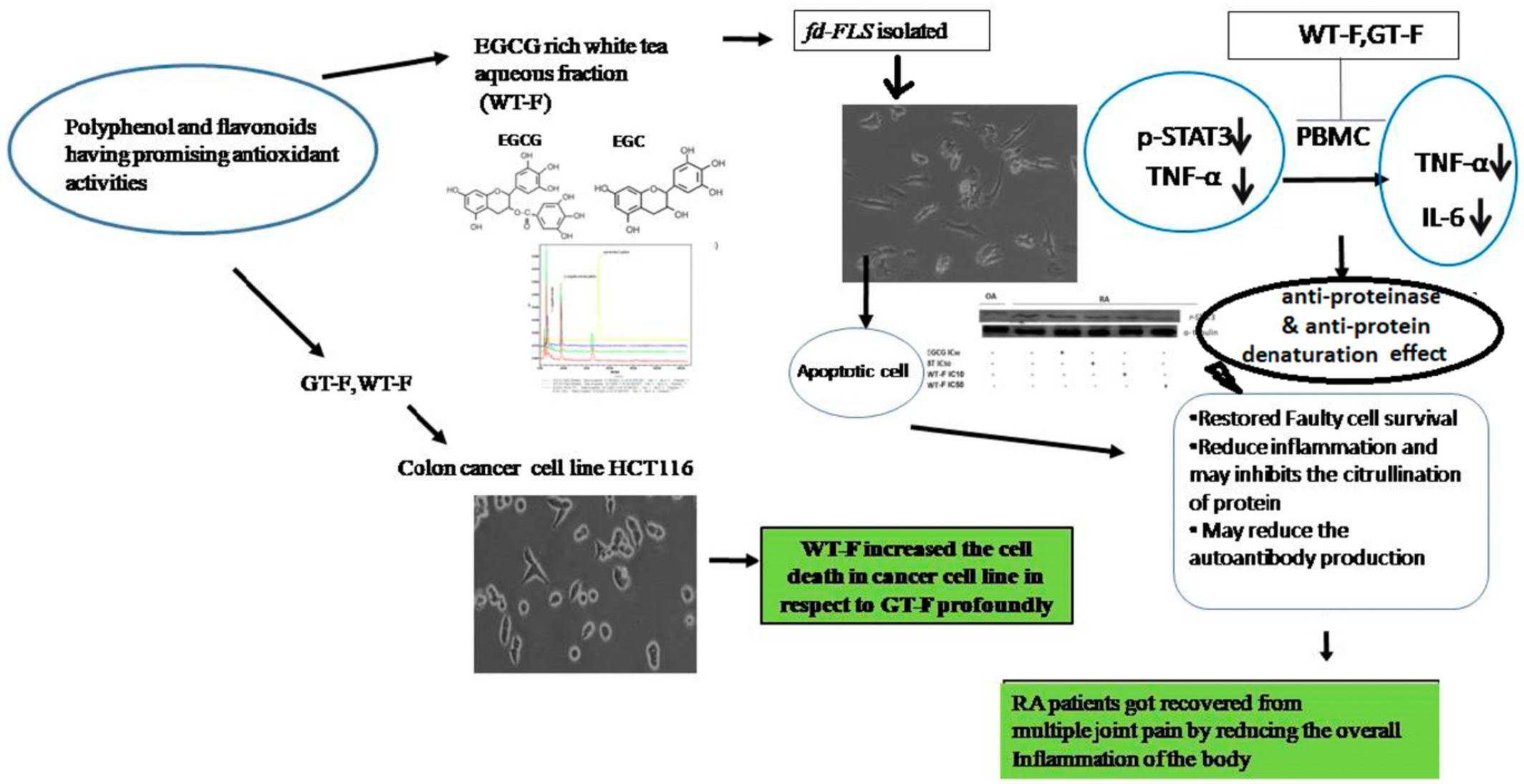
Validation of antioxidant, antiproliferative, and in vitro anti-rheumatoid arthritis activities of epigallo-catechin-rich bioactive fraction from Camellia sinensis var. assamica, Assam variety white tea, and its comparative evaluation with green tea fraction
- First Published: 30 October 2022
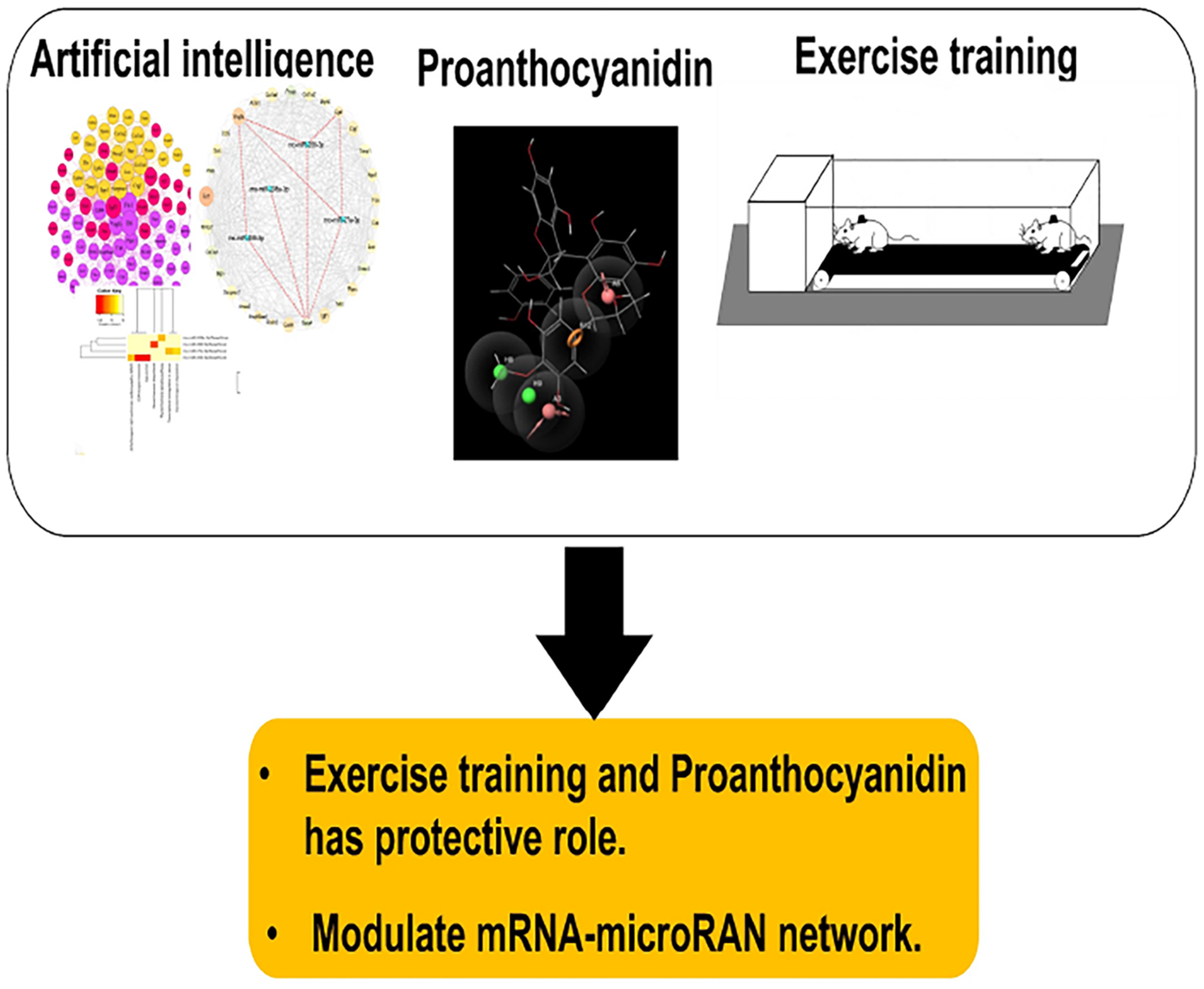
Alternation of heart microRNA-mRNA network by high-intensity interval training and proanthocyanidin in myocardial ischemia rats: Artificial intelligence and validation experimental
- First Published: 21 October 2022
Extraction optimization, purification, and biological properties of polysaccharide from Chinese yam peel
- First Published: 26 October 2022
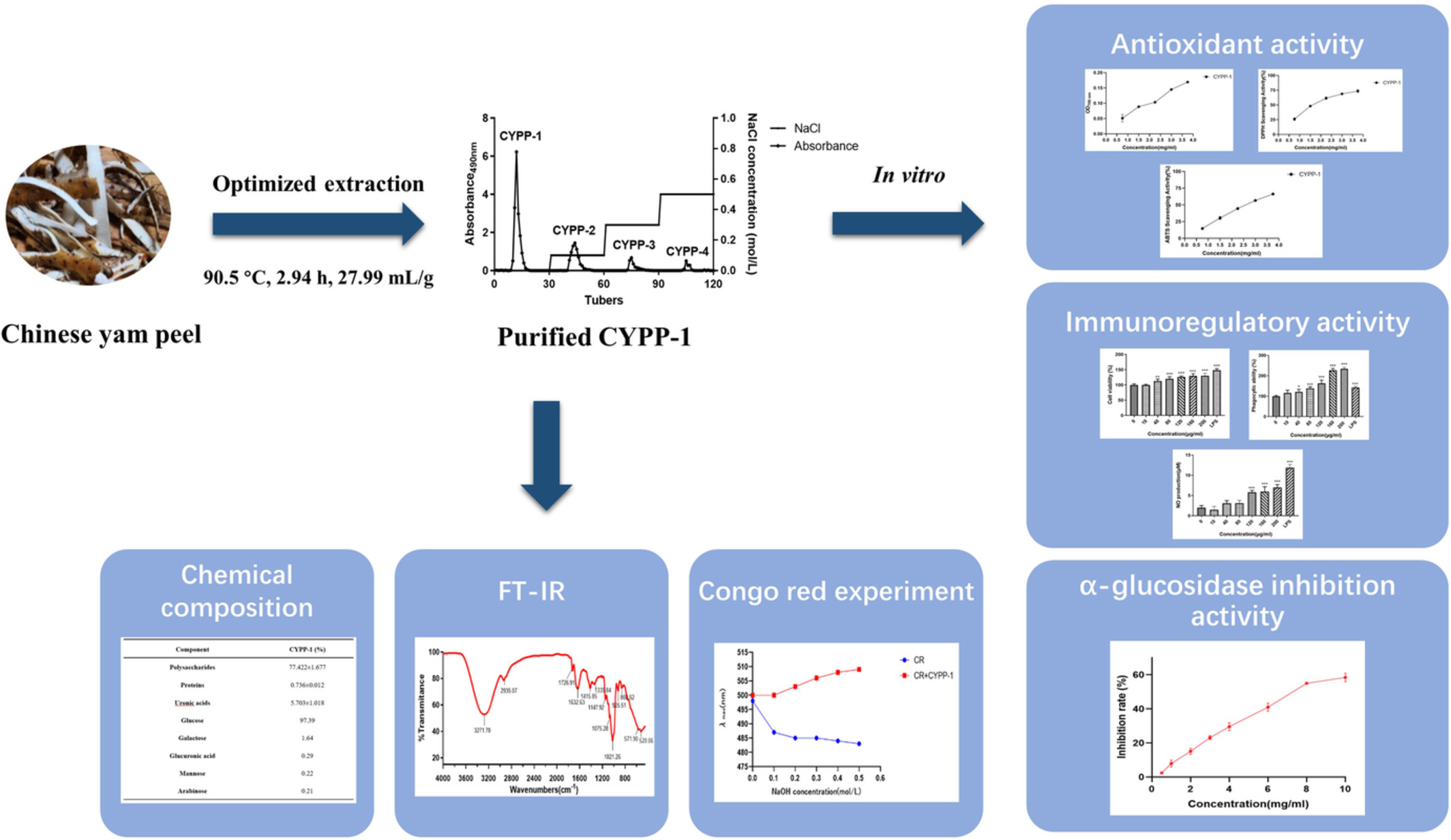
The study mainly includes three key findings: (1) The extraction rate of Chinese yam peel polysaccharides (CYPP) was up to 8.81 ± 1.48% after optimization; (2) CYPP-1 was the main purified peak of CYPP, and its physicochemical properties were researched; and (3) CYPP-1 showed excellent antioxidant, immunoregulatory, and hypoglycemic effects in vitro.
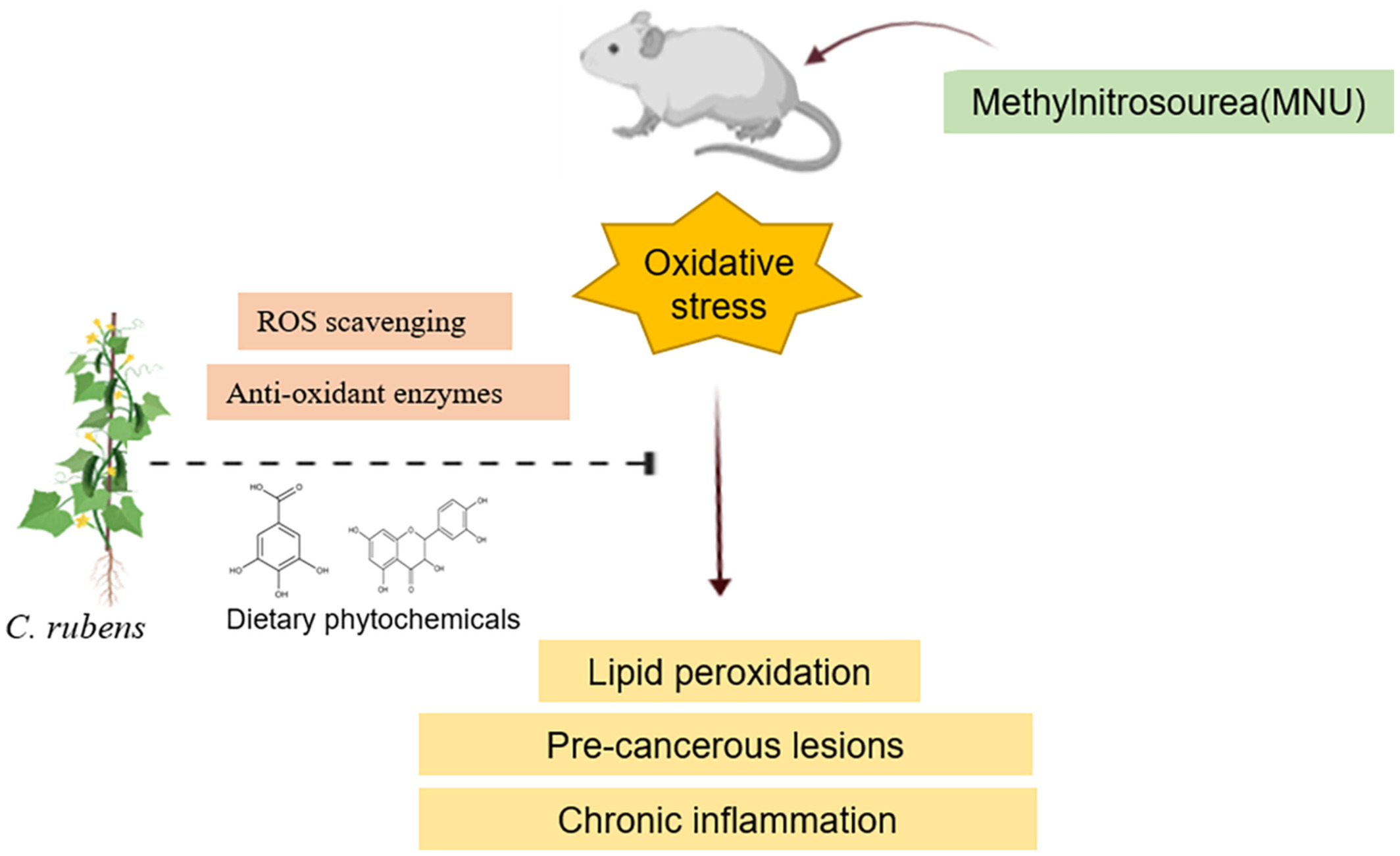
Crassocephalum rubens (Juss Ex Jacq) leaf diets ameliorate systemic oxidative stress and tissue damage in a Wistar rat model
- First Published: 30 October 2022
Systems pharmacology-based drug discovery and active mechanism of phlorotannins for type 2 diabetes mellitus by integrating network pharmacology and experimental evaluation
- First Published: 17 November 2022
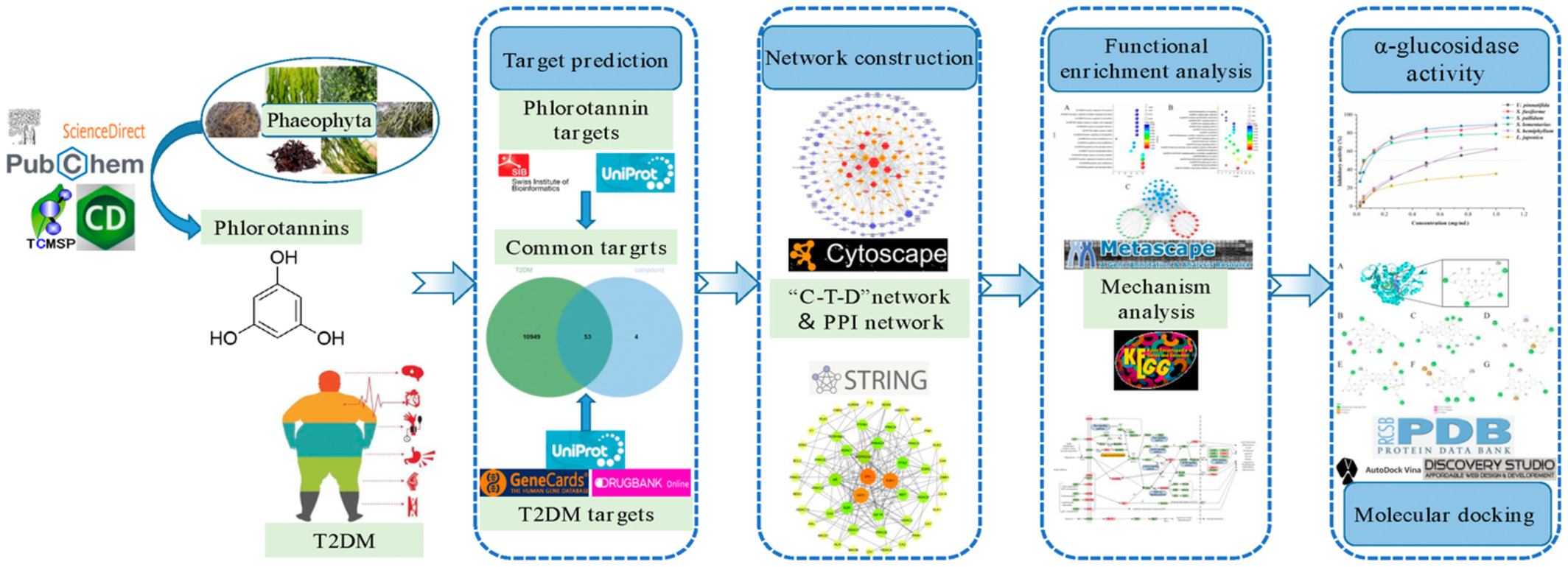
Based on the basic theory, the combination of network pharmacology and experimental evaluation, this study demonstrated the superiority of phlorotannins in the effective substance of T2DM through multi-target and multi-channel comprehensive regulation. Exploring the potential functional factors and mechanisms of action in seaweeds can provide a new way to develop new biological agents for treating on T2DM.
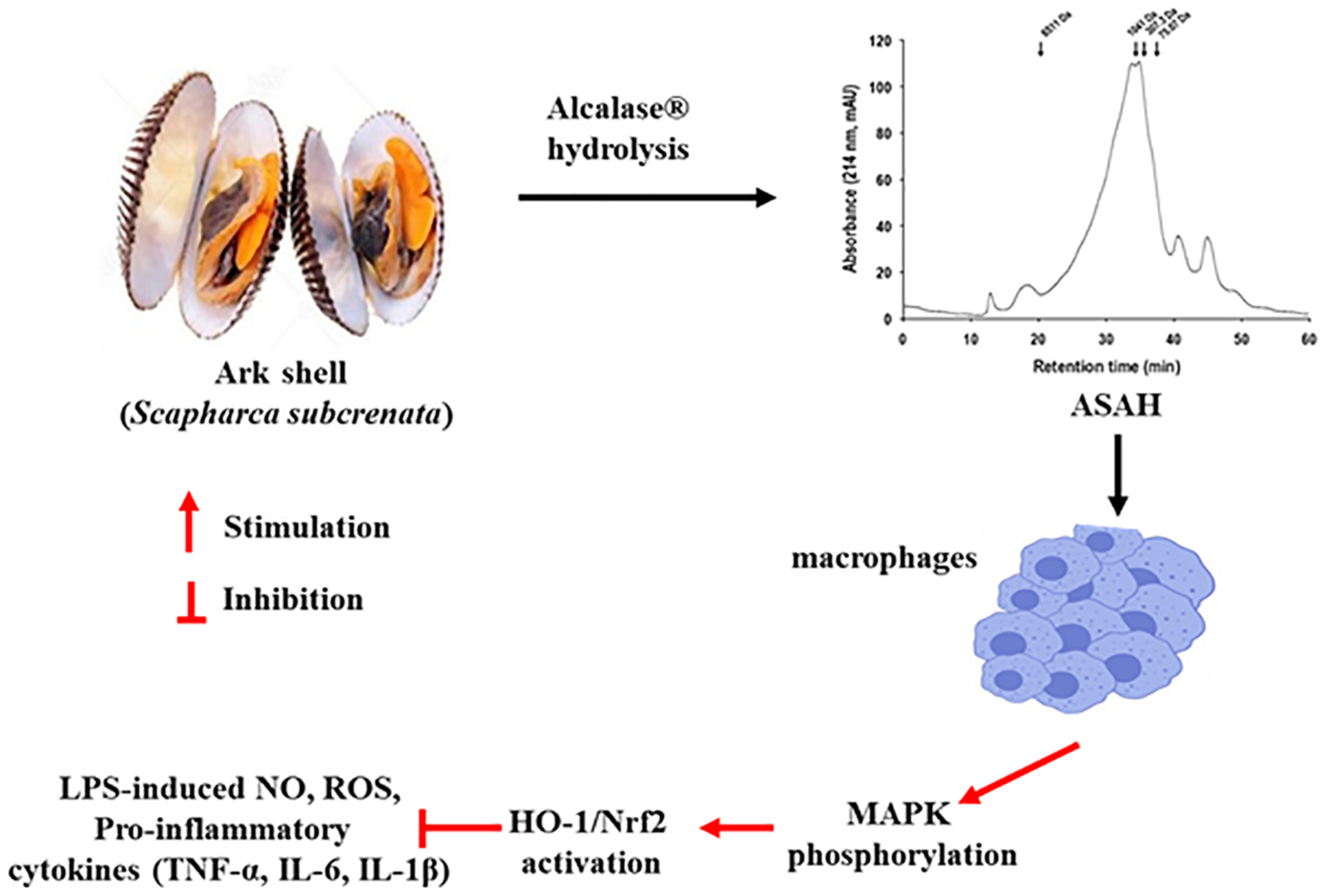
Anti-inflammatory action of ark shell (Scapharca subcrenata) protein hydrolysate in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 murine macrophages
- First Published: 30 October 2022
Cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis were attenuated by olive leaf extract treatment in a rat model of diabetes
- First Published: 02 November 2022
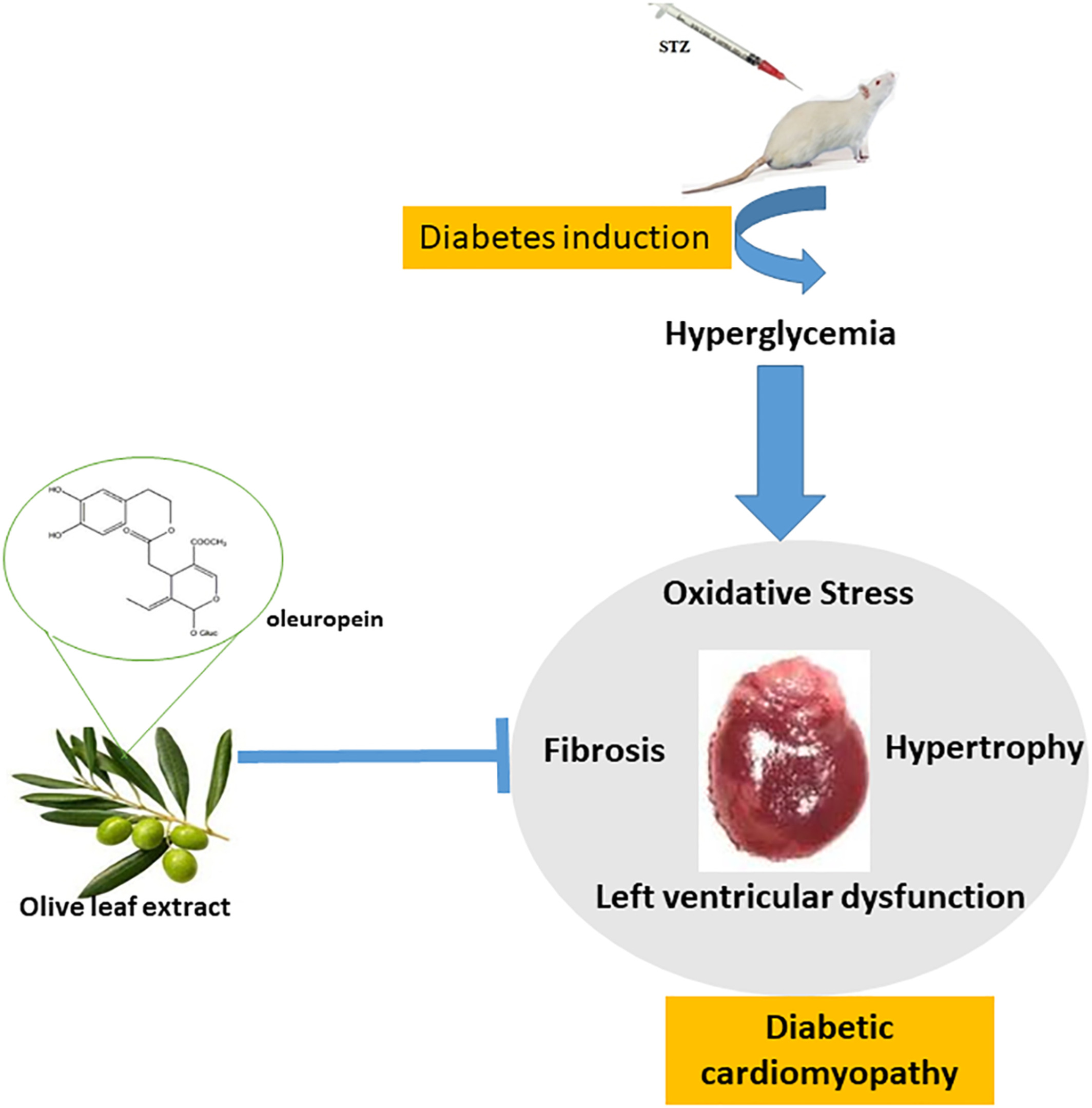
The effects of olive leaf extract in diabetic cardiomyopathy were evaluated. Diabetes was induced by single dose STZ-injection in rats. FBS and Heart-to-body weight ratio were reduced in all treated rats. Olive leaf extract ameliorated oxidative stress in heart tissue of diabetic rats. Cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis were diminished in treated rats. Left ventricular dysfunction was improved in treated rats.
Comprehensive proteome and lysine acetylome analysis after artificial aging reveals the key acetylated proteins involved in wheat seed oxidative stress response and energy production
- First Published: 02 November 2022
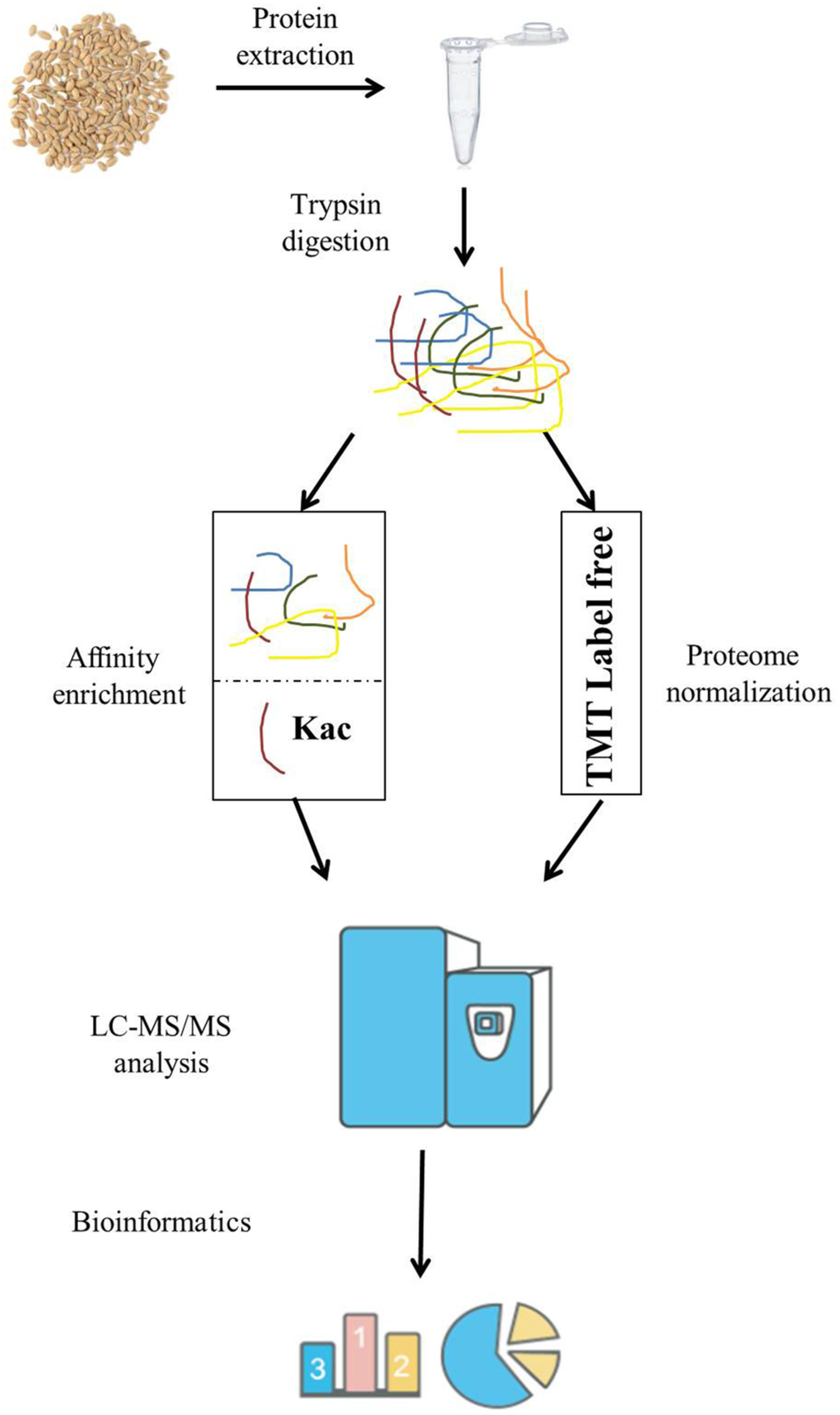
This study reports the first large-scale acetylome analysis of wheat seeds after artificial aging treatment. The results show that lysine-acetylation results in a weaker oxidative stress response and lower energy production efficiency, resulting in the apoptosis of wheat seed cells, insufficient energy supply, and consequently, marked loss of seed vigor.
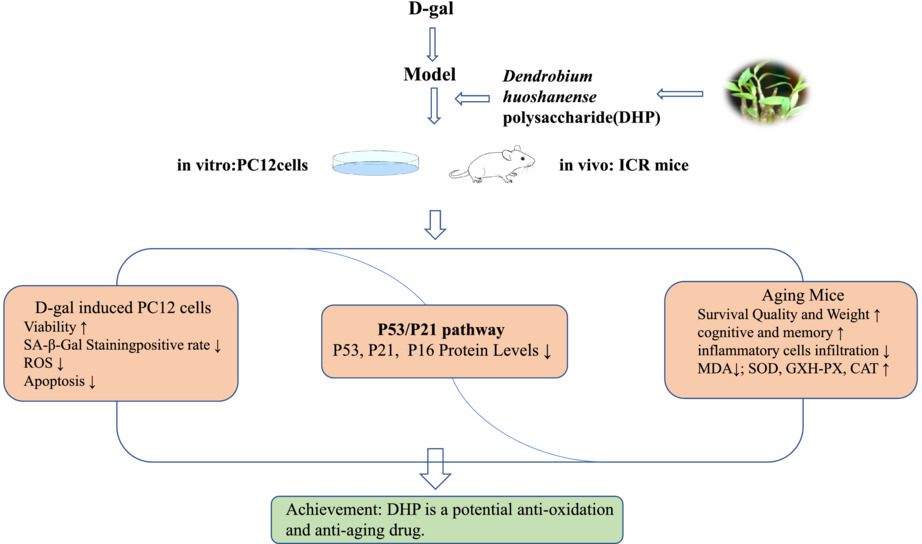
Protective effects of Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide on D-gal induced PC12 cells and aging mice, in vitro and in vivo studies
- First Published: 09 November 2022
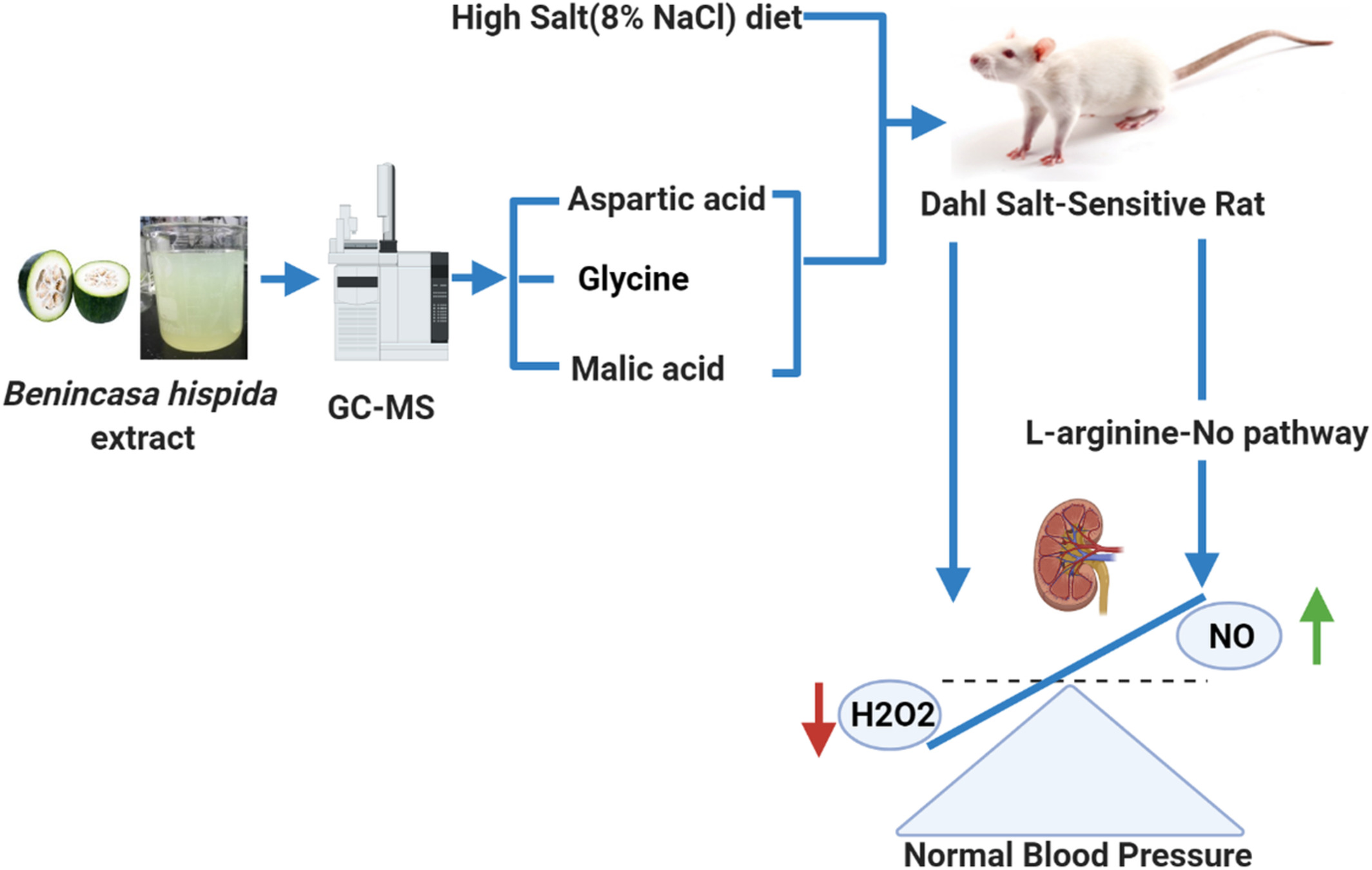
Benincasa hispida extracts positively regulated high salt-induced hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rats: Impact on biochemical profile and metabolic patterns
- First Published: 31 October 2022
Antiproliferative and apoptosis-inducing effects of aqueous extracts from Ecklonia maxima and Ulva rigida on HepG2 cells
- First Published: 09 November 2022
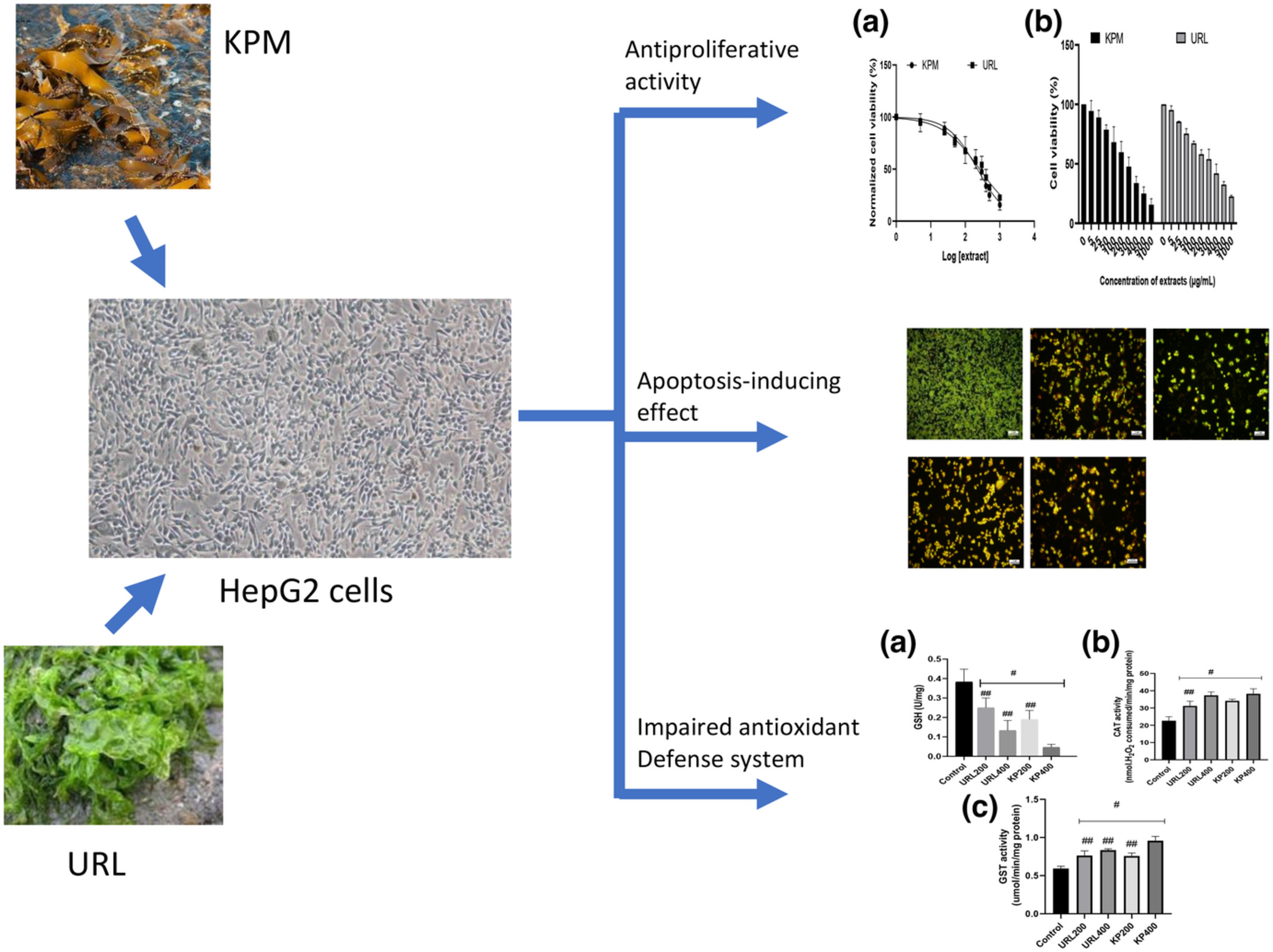
Aqueous extracts from Ecklonia maxima and Ulva rigida exhibited antiproliferative and apoptotic-inducing effects by exerting cytotoxic effects, inhibiting uncontrollable cell proliferation, induction of apoptosis, production of reactive oxygen species, reduction mitochondria membrane potential and alteration in antioxidant defense mechanism.
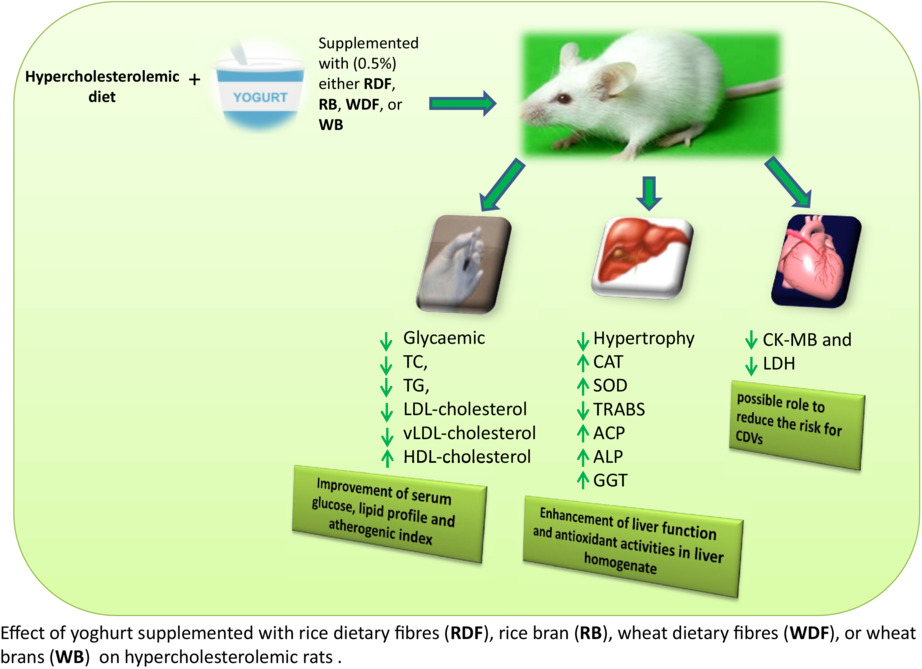
The ability of yoghurt supplemented with dietary fibers or brans extracted from wheat or rice to reduce serum lipids and enhance liver function in male hypercholesterolemic rats
- First Published: 09 December 2022
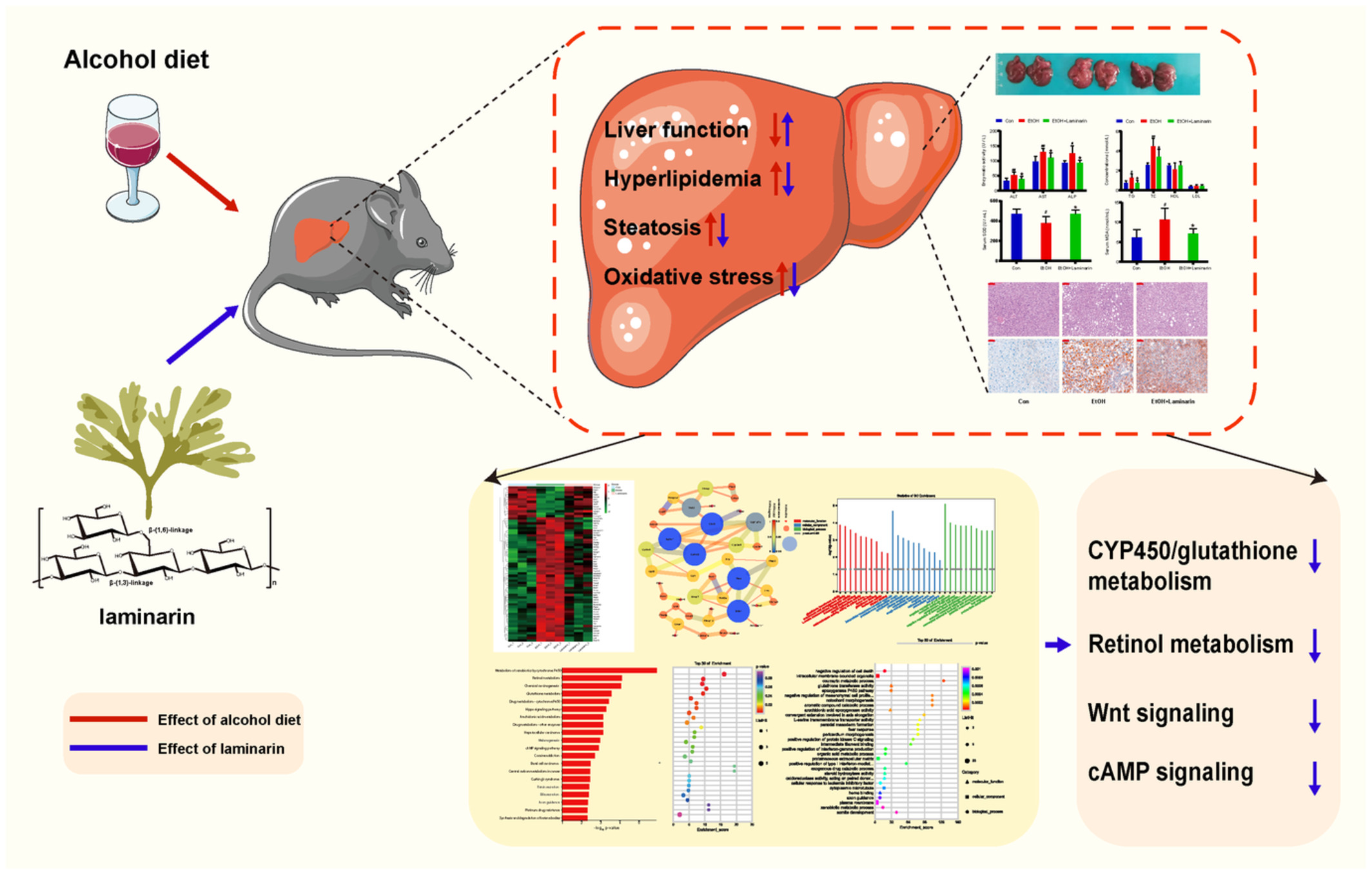
Laminarin ameliorates alcohol-induced liver damage and its molecular mechanism in mice
- First Published: 14 December 2022
Anti-adiposity and lipid-lowering effects of schisandrol A in diet-induced obese mice
- First Published: 04 November 2022
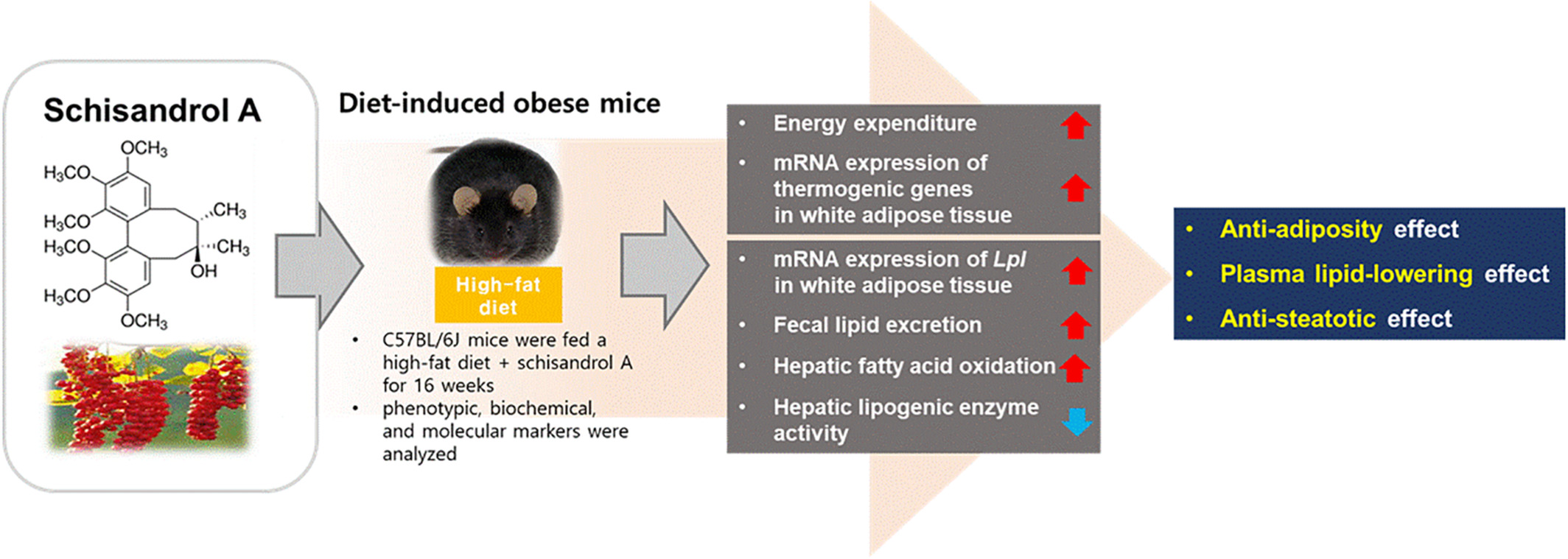
This study examined the anti-obesity effect of schisandrol A (SolA), a lignan derived from the fruit of Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill., in obese mice that were fed a high-fat diet. SolA supplementation reduced visceral adiposity by increasing energy expenditure and mRNA expression of thermogenic genes in white adipose tissue (WAT). Moreover, SolA decreased hepatic lipogenic enzyme activity and increased hepatic fatty acid oxidation, fecal lipid excretion and WAT lipoprotein lipase mRNA expression, which could confer protection from dyslipidemia and hepatic steatosis.
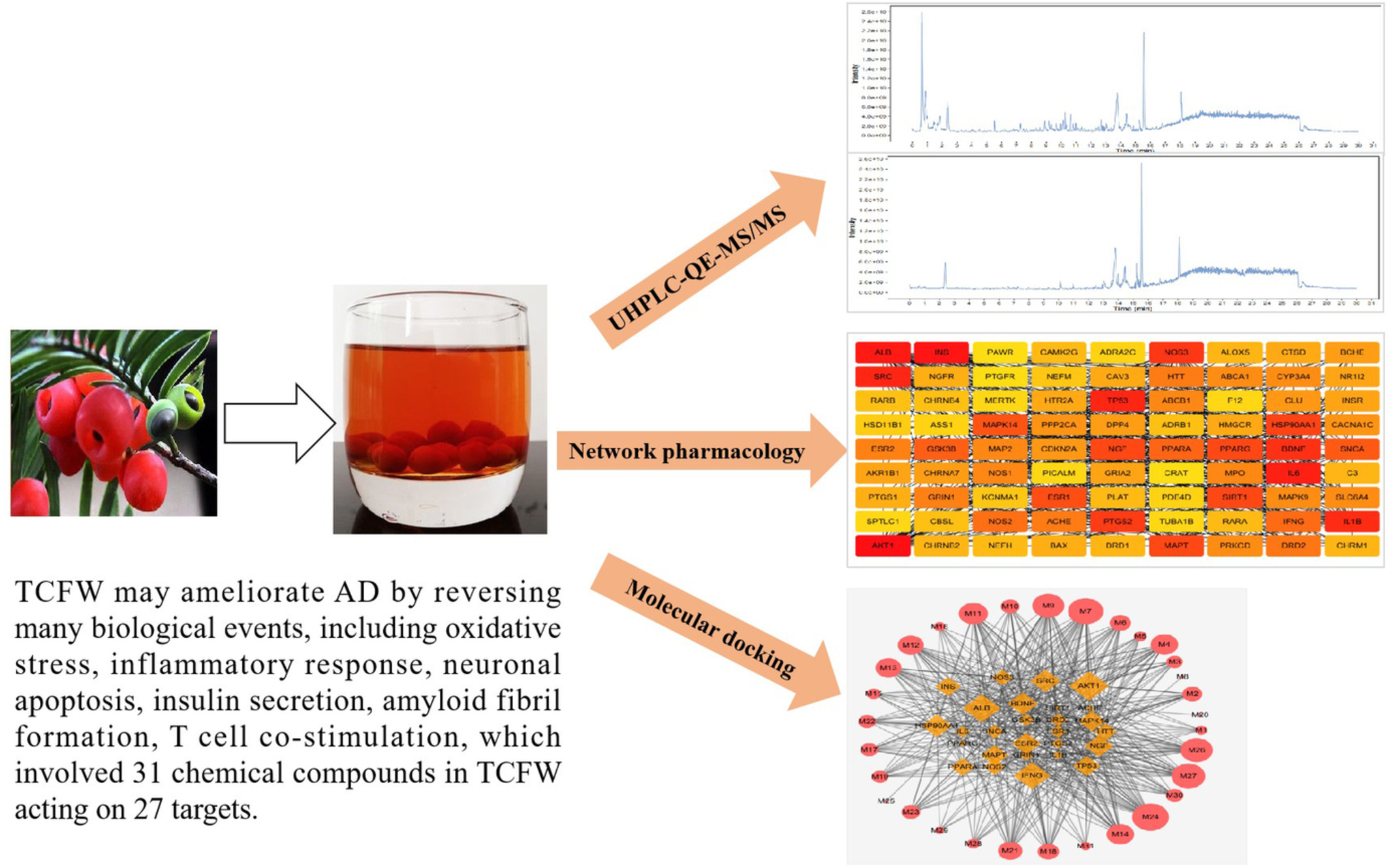
Discovery of Taxus chinensis fruit wine as potentially functional food against Alzheimer's disease by UHPLC-QE-MS/MS, network pharmacology and molecular docking
- First Published: 17 November 2022
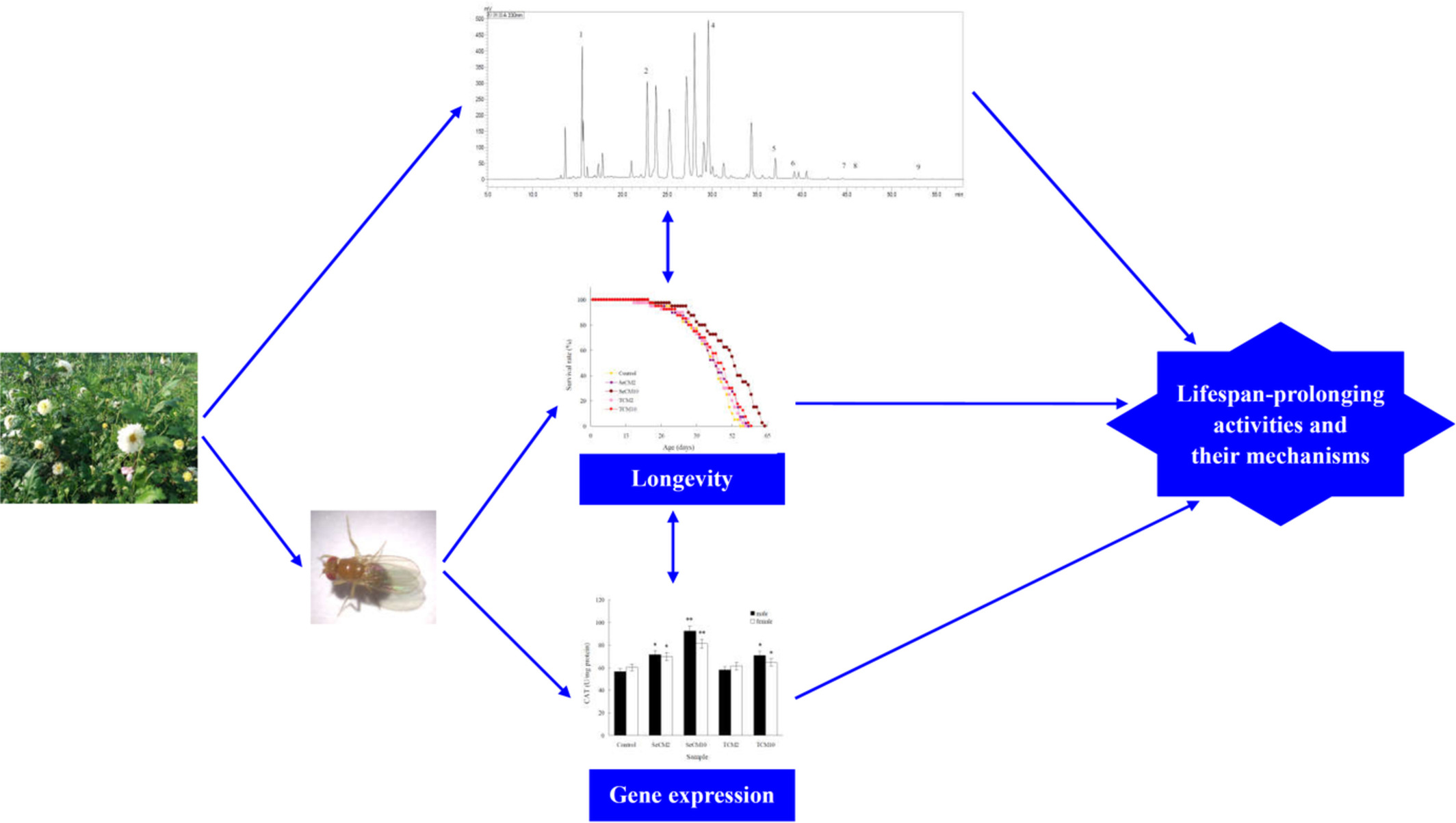
Effects of Se-enriched Chrysanthemum morifolium on lifespan and antioxidant defense-related gene expression of Drosophila melanogaster model
- First Published: 04 November 2022
Effect of quercetin and Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench on lipids metabolism and blood glucose through AMPK-α in diabetic rats (HFD/STZ)
- First Published: 12 November 2022
Protective effect of isoflavone enriched soy β-conglycinin on osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats
- First Published: 05 November 2022
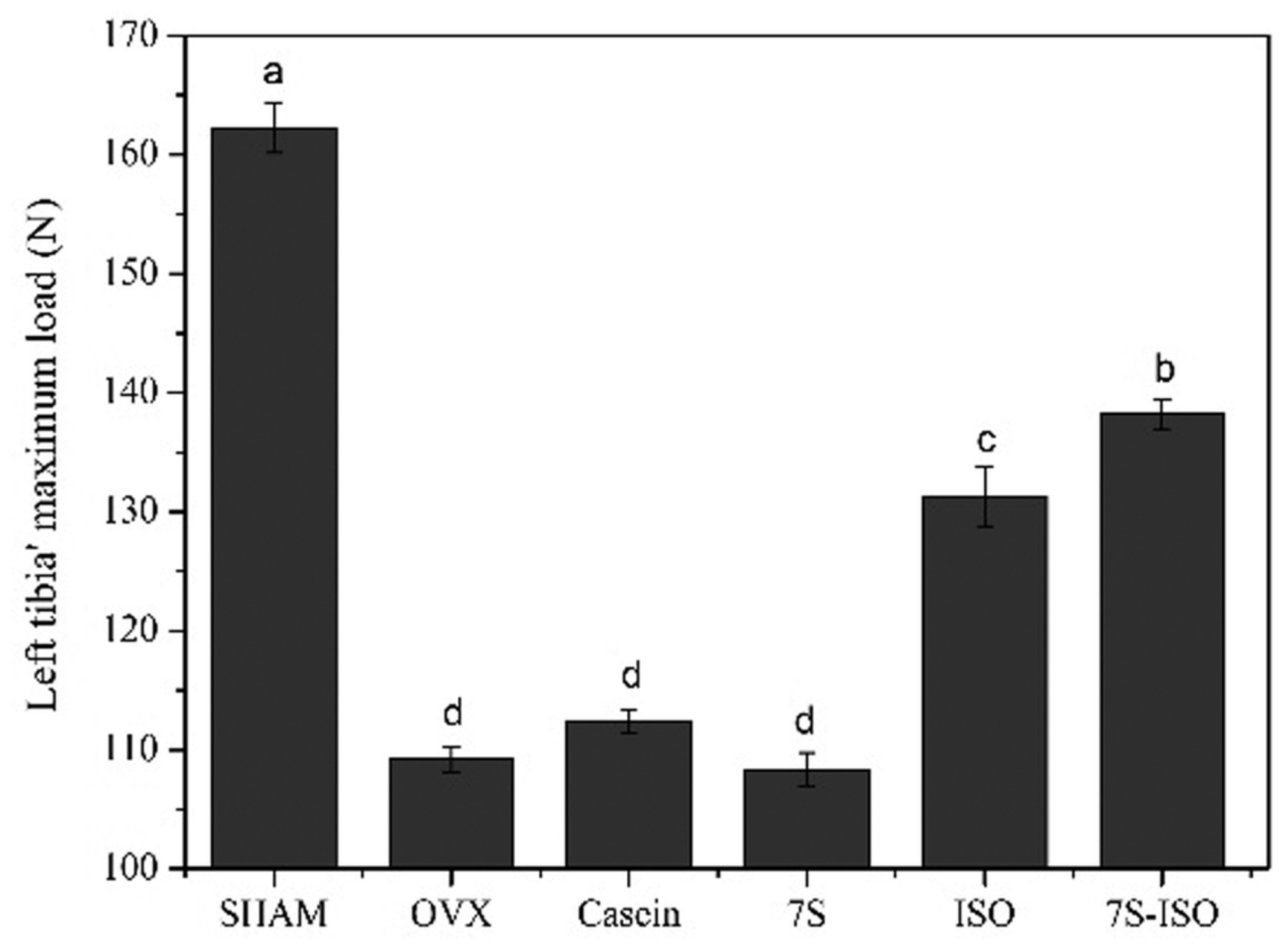
Different complex of soy β-conglycinin (7S) and isoflavones (7S-ISO) were used in ovariectomized rats. Bone biomechanics results of left tibia' maximum load data were collected. Empirical data indicate that intragastric administration of 7S-ISO is potential to prevent the downtrend of biomechanics properties in the left femora in ovariectomized rats.
Effect of partially hydrolyzed guar gum on the composition and metabolic function of the intestinal flora of healthy mice
- First Published: 04 November 2022
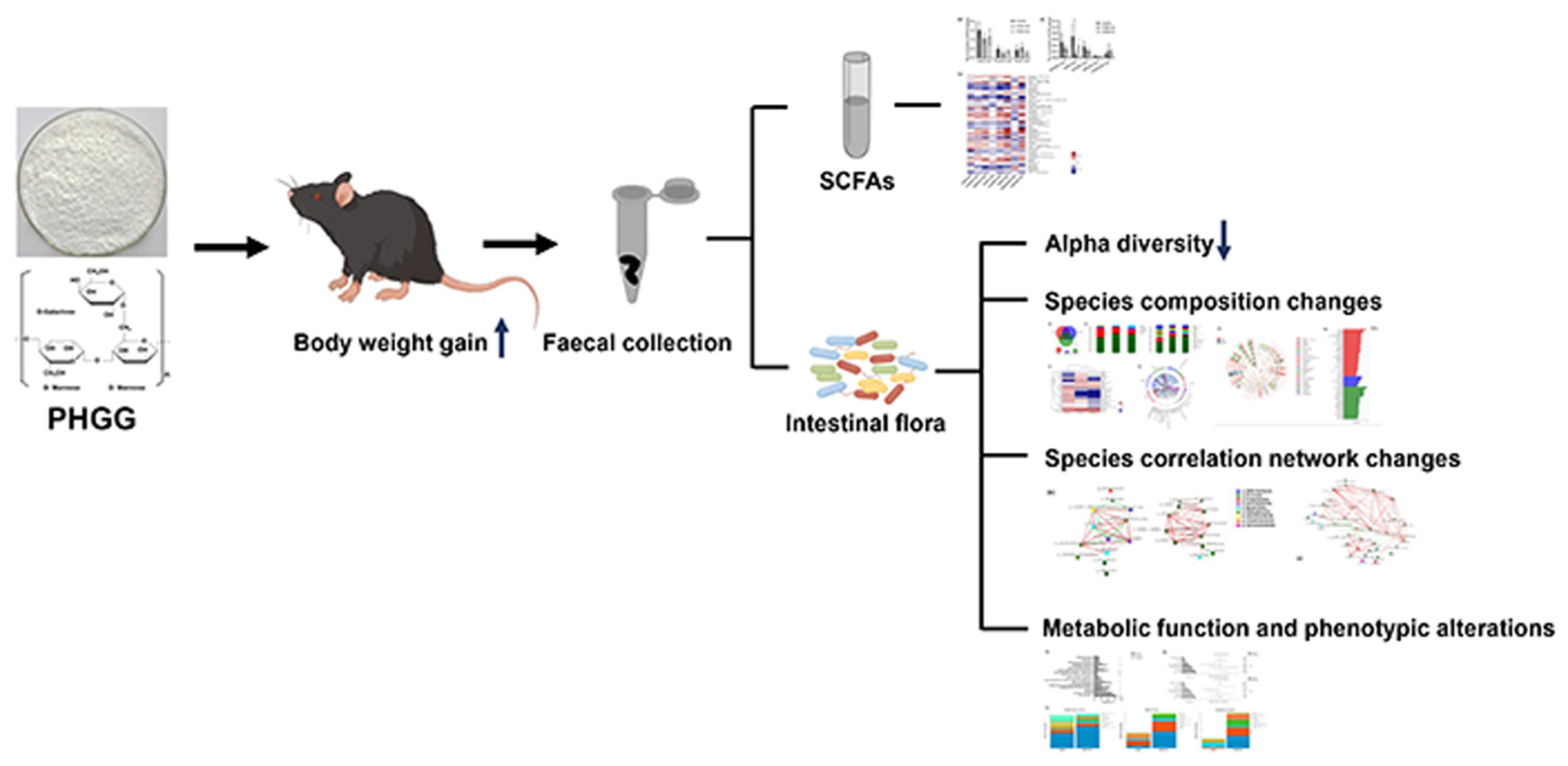
In healthy mice, long-term addition of PHGG to the diet did not increase fecal concentrations of short-chain fatty acids. However, it led to a decrease in alpha diversity and significantly altered the composition structure and metabolic function of the intestinal flora. In addition, the impact of PHGG on intestinal flora varied with the duration of addition.
Protective effect of probiotic and prebiotic fermented milk containing Lactobacillus fermentum against obesity-induced hepatic steatosis and inflammation
- First Published: 05 November 2022
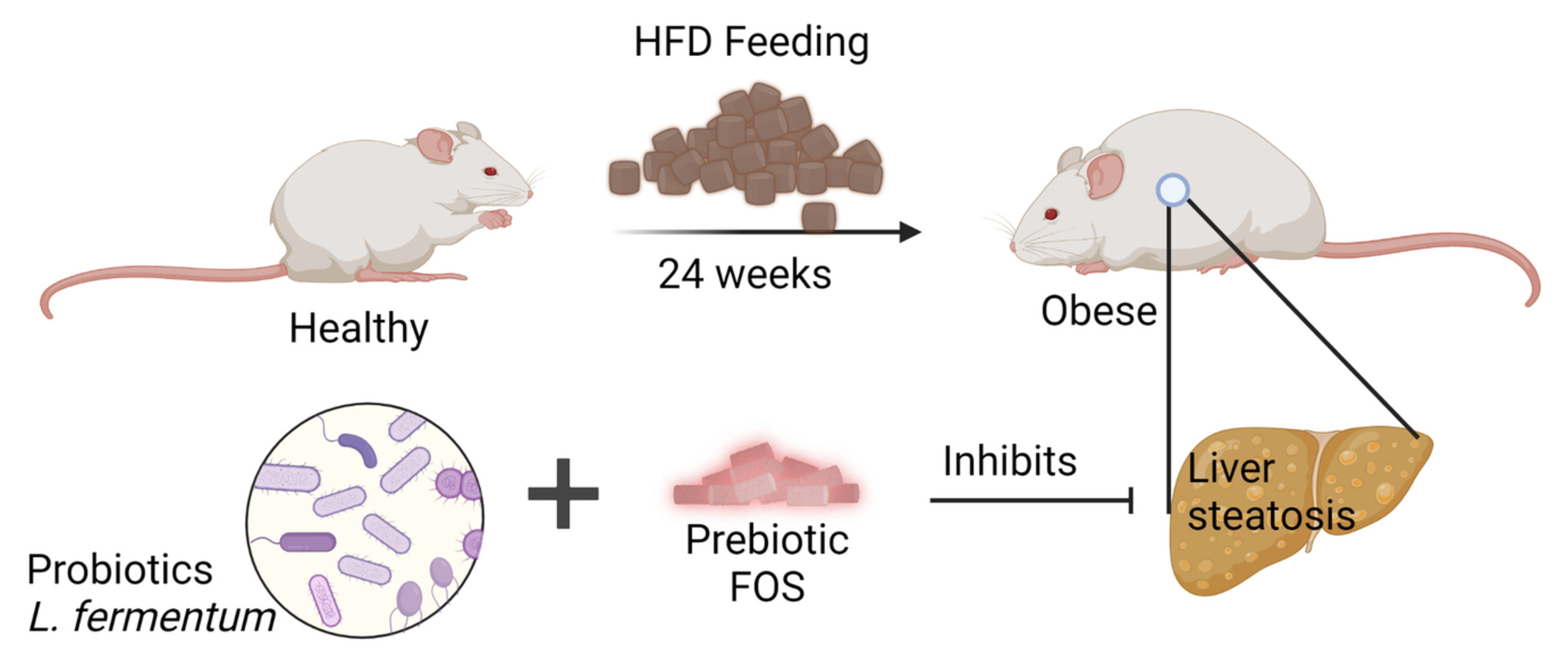
All the animals (C57BL/6 mice) were fed with high-fat diet, probiotic fermented milk, FOS, Dahi, and synbiotic fermented milk diets for 24 weeks. High-fat diet feeding causes obesity in animals which finally resulted into hepatic steatosis, inflammation, disturbed glucose homeostasis, and lipid profile. Co-feeding of probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum NCDC 400 and FOS fiber in different combinational diet forms improve the animal's health by preventing obesity-induced adverse effects.
Polygonatum sibiricum ameliorated cognitive impairment of naturally aging rats through BDNF–TrkB signaling pathway
- First Published: 14 November 2022
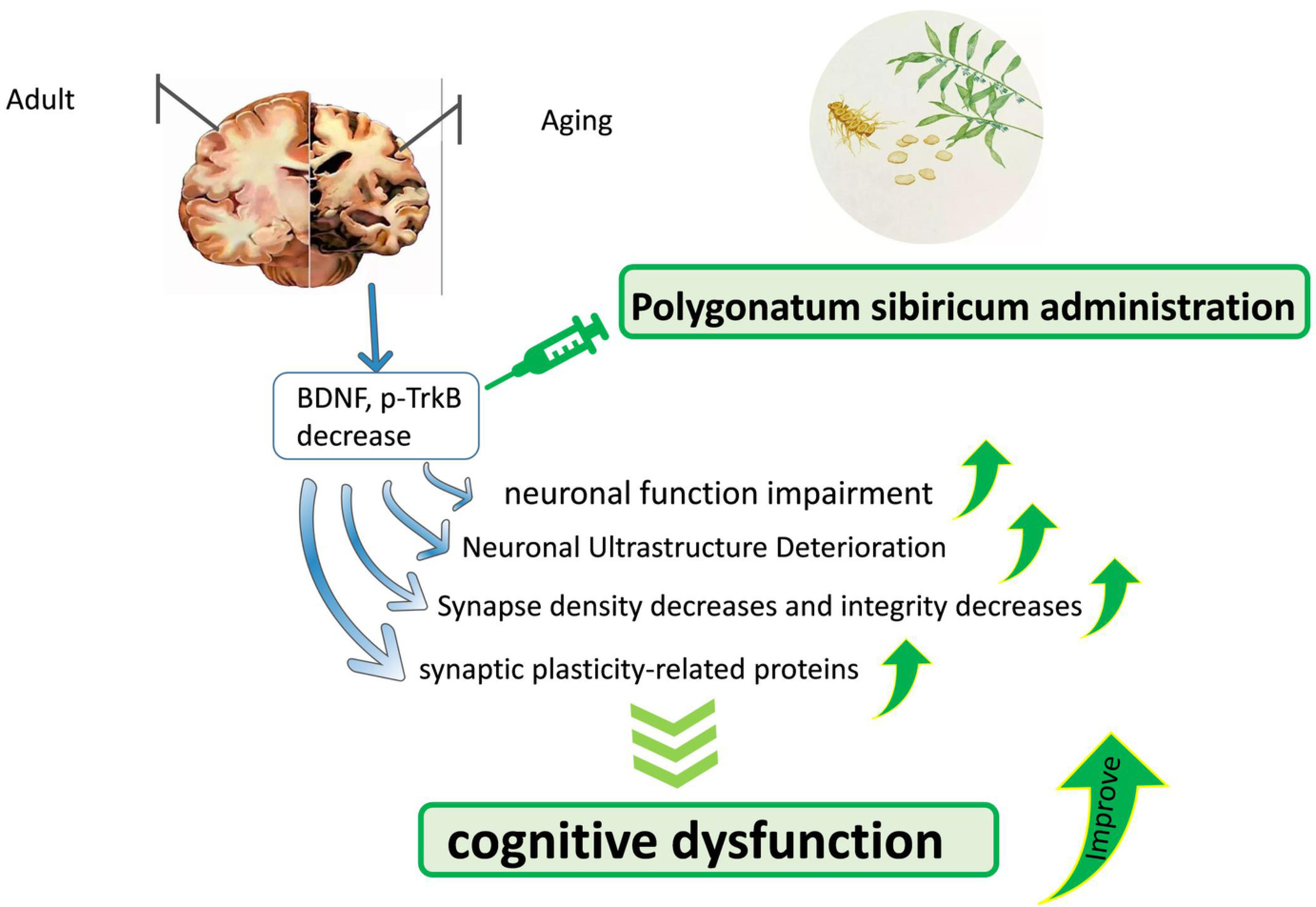
In this study, we demonstrated that polygonatum sibiricum effectively ameliorated the spatial learning and memory function of naturally aging rats. In addition, polygonatum sibiricum can improve neuronal function, increase the number of synapses in aging rats and enhance structural integrity. The underlying mechanism is mainly related to PS increases the expression of BDNF–Trkb signaling pathway and enhances synaptic plasticity.
Glycemic indices and effect of bitter leaf (Vernonia amygdalina) flavored non-alcoholic wheat beer (NAWB) on key carbohydrate metabolizing enzymes in high fat diet fed (HFD)/STZ-induced diabetic Wistar rats
- First Published: 12 November 2022
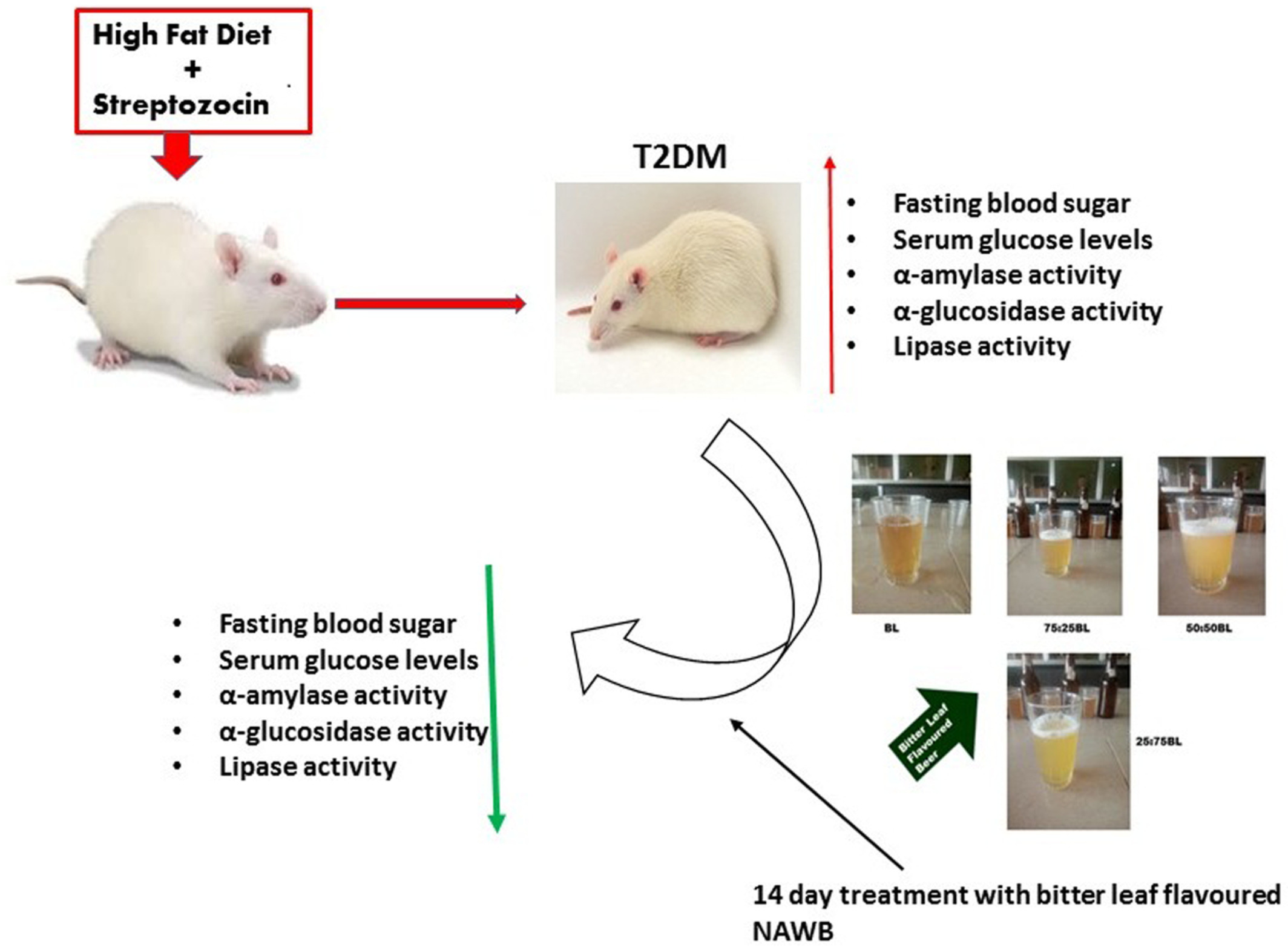
Bitter leaf flavored non-alcoholic wheat beer (NAWB) improved hyperglycemic conditions in the high-fat diet fed (HFD)/STZ-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Increased inclusion of bitter leaf in the beer samples, however, causes a reduction in phenolic contents, a raised glycemic index and a lower inhibitory activity on α-amylase when compared to the rest of the samples. Conclusively, bitter leaf flavored NAWB could be a viable dietary intervention in the management of type 2 diabetes.
Cocoa presents cytotoxicity against melanoma cancer cell lines (A-375 e B16-F10) and improves chemotherapy activity by increasing oxidative stress
- First Published: 04 November 2022
Thermally oxidized sunflower oil diet alters leptin/ghrelin balance and lipid profile in rats: Possible role of reactive aldehydes in dyslipidemia
- First Published: 15 November 2022
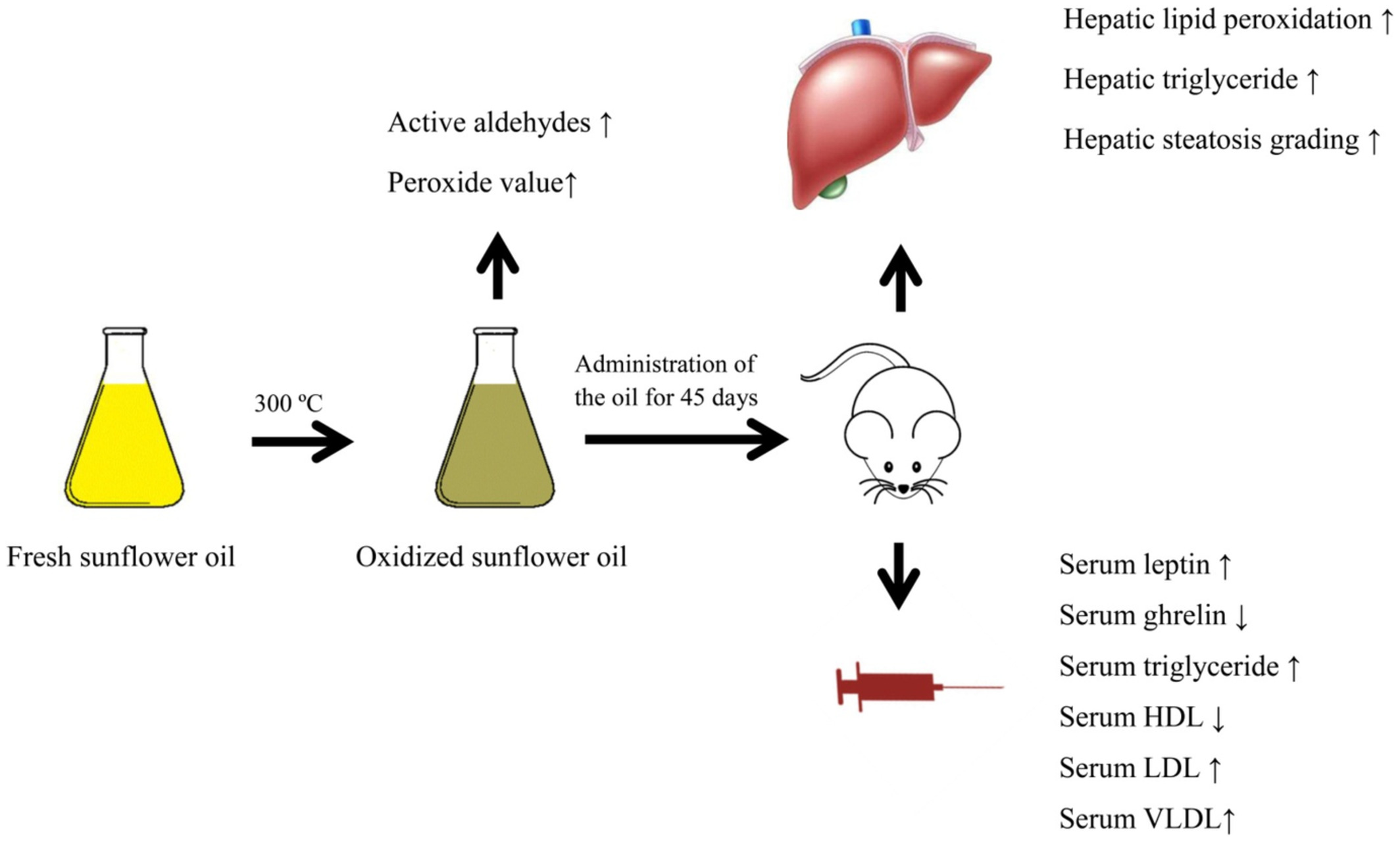
Increasing time of heating enhanced the peroxide value and formation of active aldehydes in sunflower oil. Administration of oxidized oils could increase serum leptin, LDL, VLDL and triglycerides levels, and decrease serum ghrelin and HDL levels in the rats. These changes were associated with the accumulation of triglycerides and lipid peroxidation in the hepatic tissue.
Erratum to “Infused aqueous curry tea extracts ameliorate Nω-Nitro-l-Arginine Methyl Ester-induced liver dysfunction in male albino Wistar rats”
- First Published: 20 October 2022