Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Elderberries as a potential supplement to improve vascular function in a SARS-CoV-2 environment
- First Published: 03 February 2022
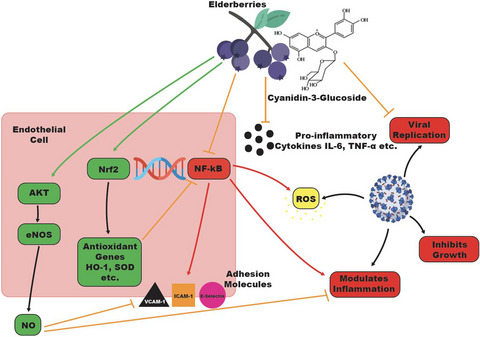
Elderberry extract (EE) can target both viral infection and vascular dysfunction which could be a useful strategy to reduce morbidity and mortality relating to COVID-19. Literature looks promising and builds a suggestion for investigating EE against COVID-19. However, further in vitro and in vivo research is required to fully evaluate elderberries as a supplement to aid current therapies.
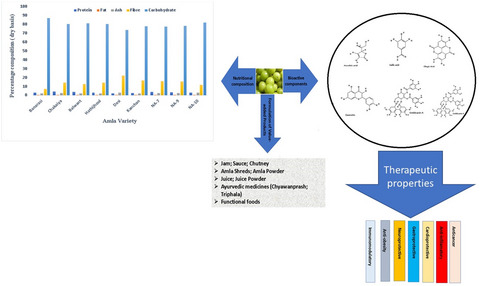
Insight about the biochemical composition, postharvest processing, therapeutic potential of Indian gooseberry (amla), and its utilization in development of functional foods—A comprehensive review
- First Published: 27 March 2022
Mulberry plant as a source of functional food with therapeutic and nutritional applications: A review
- First Published: 31 May 2022

Mulberry is a potential source of alkaloids, glycosides, polysaccharides, terpenoids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, and tannins that exerts various biological activities including anticancer, antidiabetic, hypolipidemic, hepatoprotective, neuroprotective, nephroprotective, and antimicrobial. Mulberry has potential applications for the food industry and animal husbandry mainly due to its flavonoids.
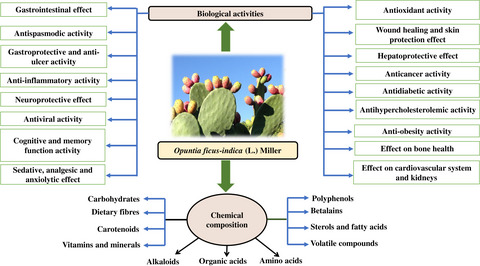
An overview and update on the chemical composition and potential health benefits of Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Miller
- First Published: 02 July 2022
Health-promoting foods and food crops of West-Africa origin: The bioactive compounds and immunomodulating potential
- First Published: 30 November 2022
Shallot-enriched amaranth-based extruded snack influences blood glucose levels, hematological parameters, and carbohydrate degrading enzymes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- First Published: 06 February 2022
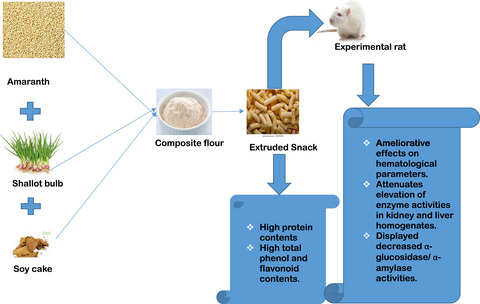
Developed shallot-enriched amaranth-based extruded snacks possess high protein contents and exhibited high total phenol and flavonoid contents. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats fed with the extruded snacks showed ameliorative effects on hematological parameters, attenuates elevation of enzyme activities in kidney and liver homogenates, and displayed decreased α-glucosidase/α-amylase activities. The extruded snack might be a functional snack appropriate for the management of hyperglycemia and prevention of its complication.
Amino acid composition, mineral profile, free radical scavenging ability, and carbohydrase inhibitory properties of Moringa oleifera seed globulin, hydrolysates, and membrane fractions
- First Published: 24 March 2022
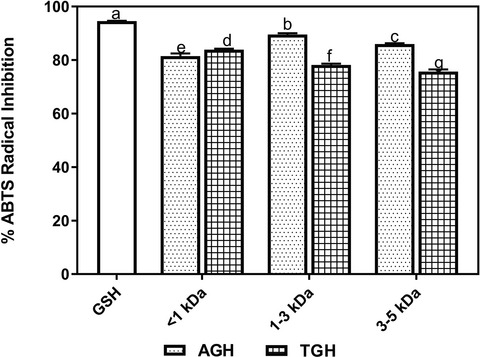
The nutritional—amino acid profile and mineral element of Moringa oleifera seed globulin (GLO) and its hydrolysates, as well as the in vitro bioactive properties—antioxidant, alpha-amylase, and alpha-glucosidase inhibition of the GLO, hydrolysates, and membrane fractions were evaluated. The result showed that M. oleifera seed peptide fraction (<3 kDa) from the alcalase-derived hydrolysate contains potent antioxidants but relatively low in vitro antidiabetic properties.
In silico identification of antidiabetic and hypotensive potential bioactive peptides from the sheep milk proteins—a molecular docking study
- First Published: 29 March 2022
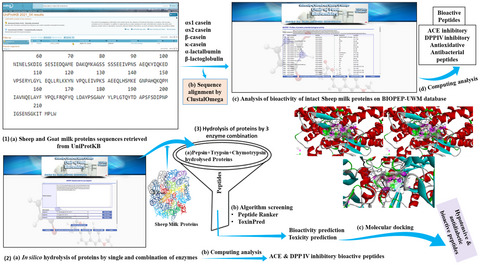
- Sheep milk intact proteins have the potential to produce various biological peptides.
- In silico proteolysis of sheep milk proteins using an enzyme combination produced ACE-I and DPP-IV inhibitory BAPs.
- Molecular docking was used to identify BAPs that inhibit ACE-I and DPP-IV.
- An enzyme combination used in silico proteolysis gives guidance for lab-based protein hydrolysis for the generation of BAPs.
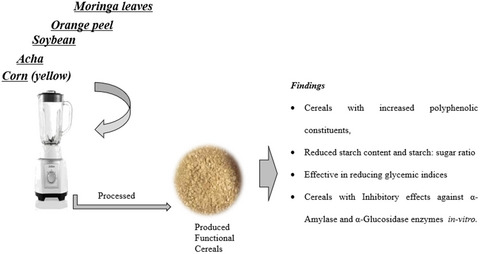
Functional cereals' anti-diabetic property, phenolic composition, and role on glycemic indices in-vitro
- First Published: 25 March 2022
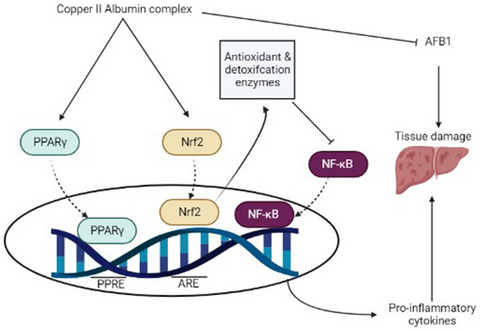
Protective effect of copper II-albumin complex against aflatoxin B1- induced hepatocellular toxicity: The impact of Nrf2, PPAR-γ, and NF-kB in these protective effects
- First Published: 25 March 2022
The immune-enhancing effect and in vitro antioxidant ability of different fractions separated from Colla corii asini
- First Published: 12 April 2022
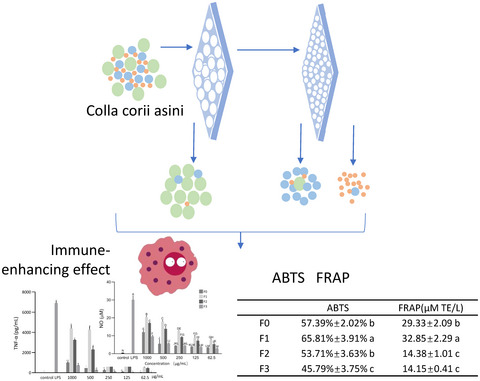
- Colla corii asini (CCA) was fractionated into three fractions with different molecular weights using ultracentrifugation equipment.
- The immunomodulatory activity of CCA fractions was investigated using RAW264.7 cell model and their antioxidant abilities were evaluated by 2′-Azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonate) (ABTS) and ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay.
- Components with a molecular weight of >10 kDa in CCA had stronger immunomodulatory and antioxidant ability, which would be helpful to guide the industrial processing and manufacturing of CCA and to develop the health food based on CCA.
Grapefruit peel extract mitigates paroxetine-induced erectile dysfunction in rats through stimulation of erectile response, antioxidant status, and inhibition of key enzymes related with impaired penile erection
- First Published: 23 April 2022
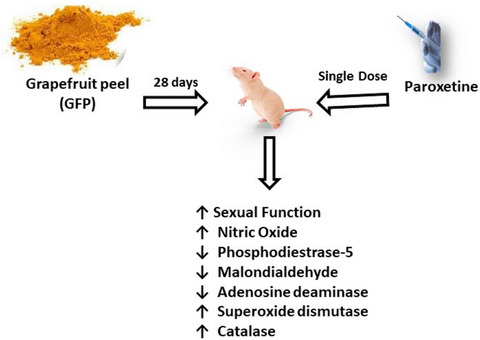
Erectile dysfunction was induced in rats with paroxetine administration. Grapefruit peel infusions improved sexual function and antioxidant status in the rats. Nitric oxide levels and the activities of catalase and superoxide dismutase were increased while phosphodiesterase-5 and adenosine deaminase activities were inhibited.
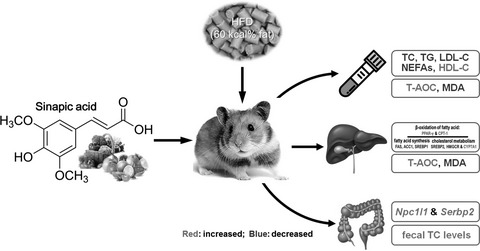
Dietary sinapic acid attenuated high-fat diet-induced lipid metabolism and oxidative stress in male Syrian hamsters
- First Published: 26 April 2022
Parquetina nigrescens and Spondias mombin protects against neurochemical alterations in the scopolamine model of cognitive dysfunction
- First Published: 27 April 2022
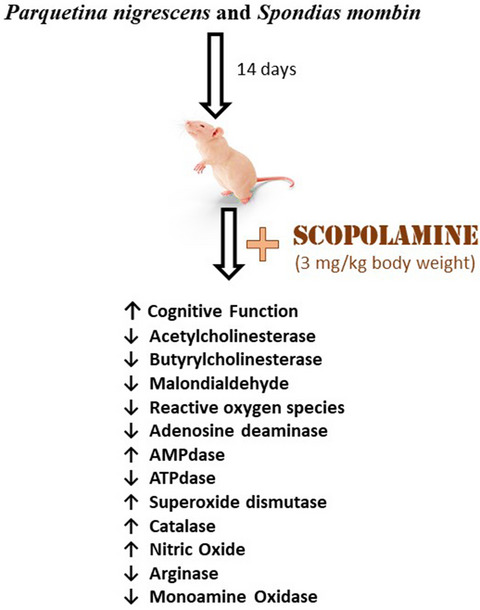
Memory impairment was induced in rats with scopolamine administration after they were pre-treated with Hog plum (Spondias mombin) and Ogbo (Parquetina nigrescens) leaves extracts. Pre-treatment with the extracts prevented cognitive dysfunction in the rats. Increased cholinesterases, adenosine deaminase (ADA), ATP hydrolysis, monoamine oxidase (MAO), and arginase activities induced by scopolamine were significantly reduced in rats treated with the extracts.
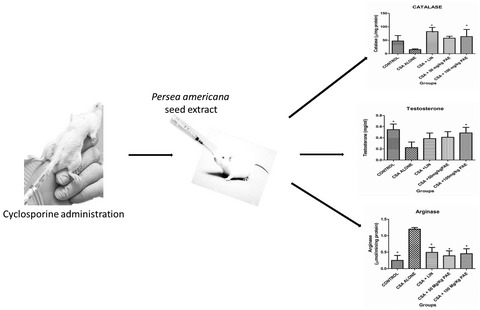
Persea americana seed extract restores defective sperm quality and biochemical parameters relevant to reproduction in male wistar rats treated with cyclosporine A
- First Published: 13 May 2022
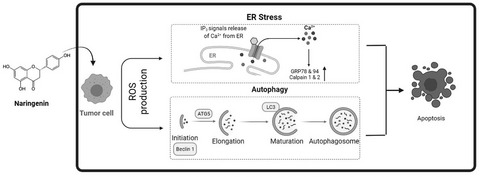
Naringenin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated cell apoptosis and autophagy in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- First Published: 21 May 2022
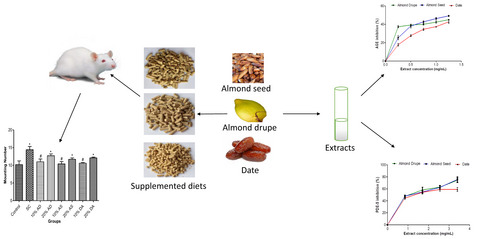
Almond and date fruits enhance antioxidant status and have erectogenic effect: Evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies
- First Published: 29 May 2022
Plantain peels restore sexual performance, hormonal imbalance, and modulate nitric oxide production and key enzymes of penile function in paroxetine-sexually impaired male rats
- First Published: 24 May 2022
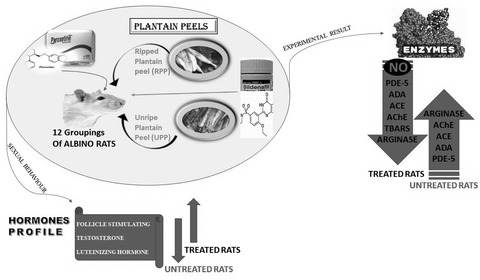
Plantain peels, which is regarded as a waste product, could be channelled towards improving sexual vigor, testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)], and as a control agent of enzymes [acetylcholinesterase (AChE), phosphodiesterase-5′ (PDE-5), arginase, angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE), ecto-5′neucleotidase, adenosine deaminase (ADA)] involves in erectile dysfunction.
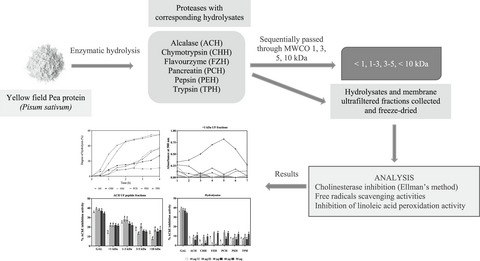
Acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of antioxidant peptides obtained from enzymatic pea protein hydrolysates and their ultrafiltration peptide fractions
- First Published: 27 June 2022
Comparing healing effect against ulcerative colitis and toxicological effects of Rosmarinus officinalis: A comprehensive in vivo study of an edible plant in rats
- First Published: 01 July 2022

Rosemary is one of the most used spices in the Mediterranean region. Since rosemary and its constituents possess several biological properties, it is examined for its potential healing capacity against UC disease in the present study. For this purpose, in vivo anti-ulcerative colitis effect of ROME was investigated comprehensively by histopathological studies, a number of in vivo anti-inflammatory activities and several in vivo antioxidant activities, in addition to in vitro antioxidant activities and biochemical analyses. In addition, the toxic effects of ROME on intestine, liver, and kidney were examined.
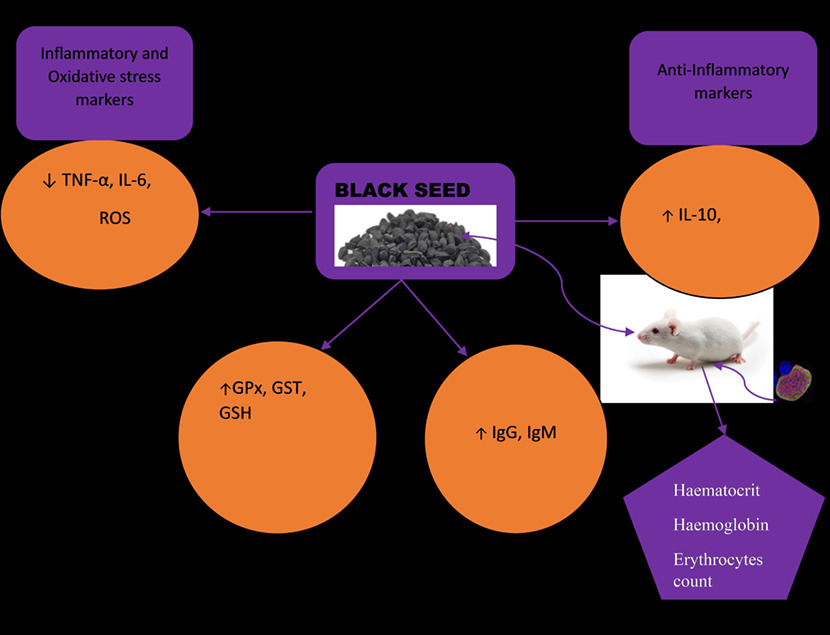
Effect of black seeds (Nigella sativa) on inflammatory and immunomodulatory markers in Plasmodium berghei-infected mice
- First Published: 14 July 2022
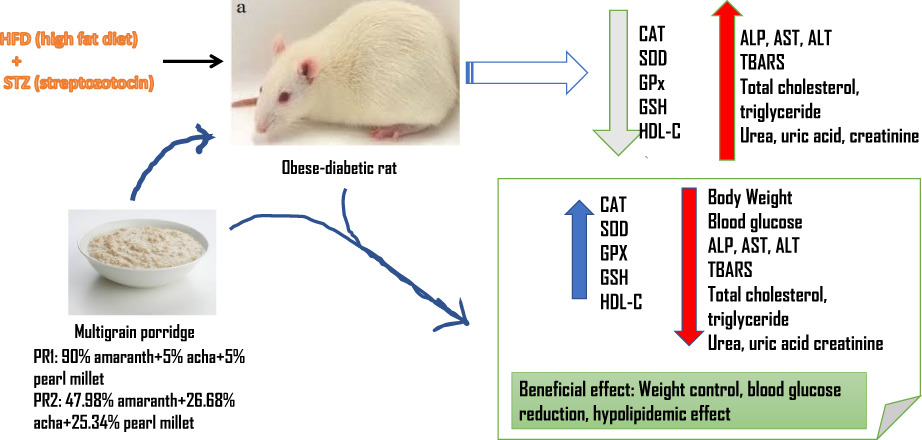
Multigrain porridge possesses superior nutritional quality, its consumption alleviates hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia and oxidative stress in obese-diabetic wistar rats
- First Published: 07 July 2022
Effect of chlorogenic acid plus donepezil on critical neurocortical enzyme activities, inflammatory markers, and synaptophysin immunoreactivity in scopolamine-assaulted rats, supported by multiple ligand simultaneous docking
- First Published: 05 July 2022
Phytochemical characterization of Morus nigra fruit ultrasound-assisted ethanolic extract for its cardioprotective potential
- First Published: 18 July 2022
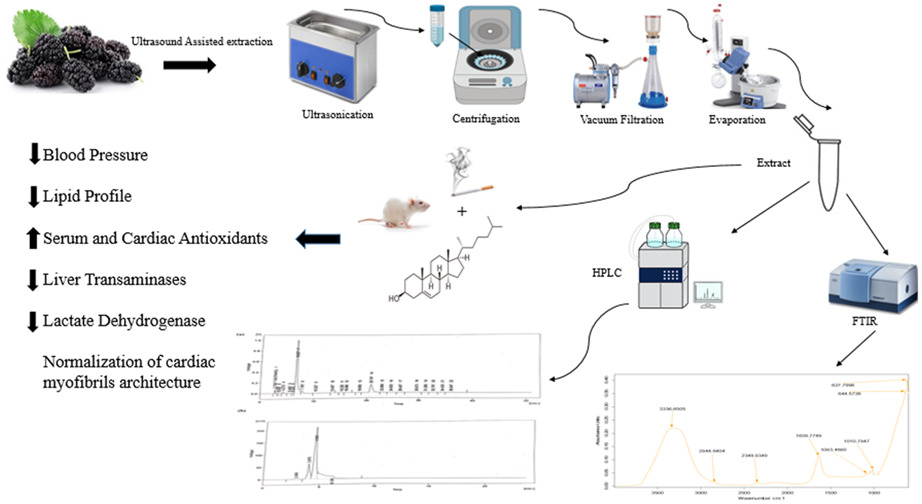
- FTIR analysis of Morus nigra fruit ultrasound-assisted ethanolic extract revealed the O-H, C-H, C=C, and C≡C functional groups containing biomolecules.
- Quercetin, gallic acid, vanillic acid, chlorogenic acid, syringic acid, cinnamic acid, sinapic acid, and kaempferol in M. nigra fruit were quantified using the HPLC system.
- The cardioprotective effect of ethanolic extract of M. nigra fruit was investigated.
- M. nigra exerted antioxidant, hypotensive, and hypolipidemic effects in cholesterol-fed and cigarette smoke exposed hypertensive rats.
Composite biscuits from sandpaper and acha flour restore the altered activity of arginase, cholinergic, and purinergic enzymes in hypertensive-diabetic rats
- First Published: 18 July 2022
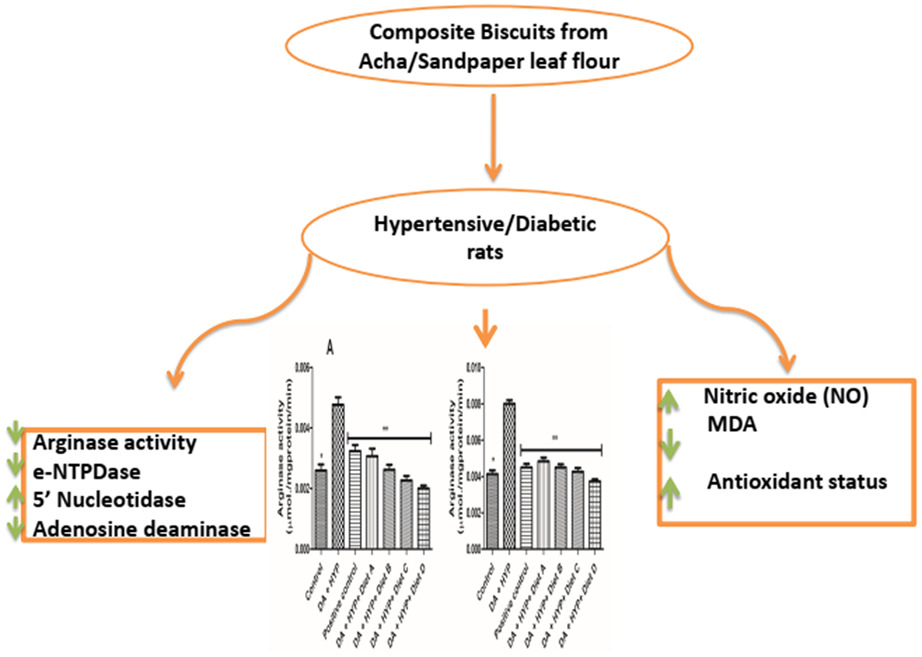
Composite biscuits reduce the elevated activity of arginase in streptozotocin (STZ)/L-NG-Nitro arginine methyl ester (L-NAME)-induced hypertensive/diabetic rats. Also, the modulated activity of the purinergic enzymatic cascade was restored in composite biscuits-treated rats. The antioxidant status of the hypertensive/diabetic rats was enhanced in the treated rats.
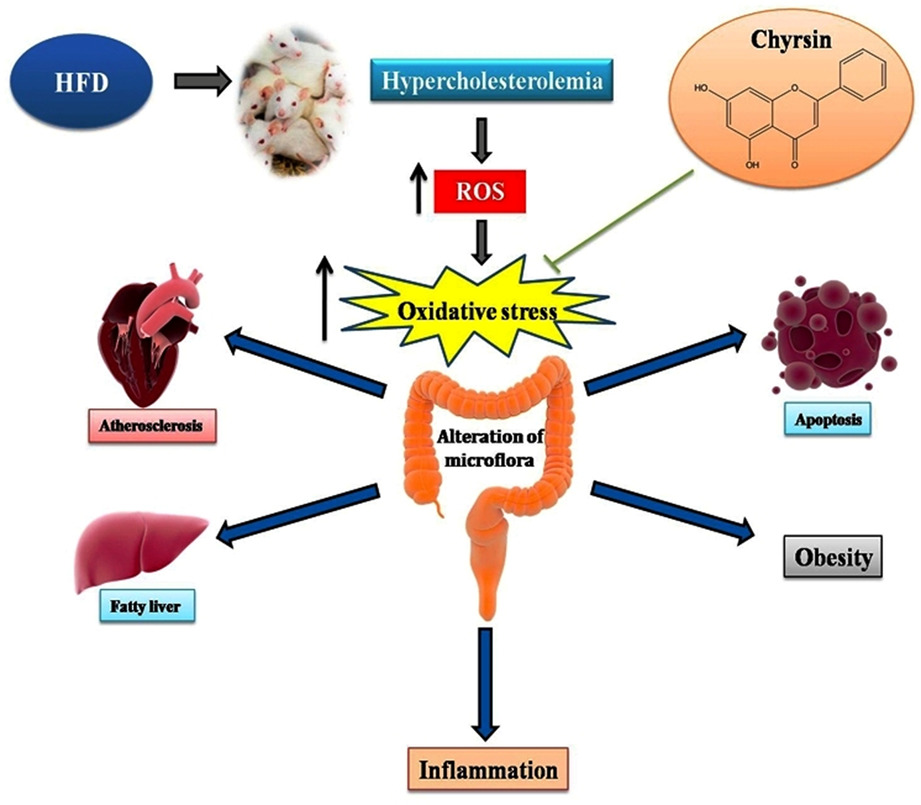
Chrysin reduces hypercholesterolemia-mediated atherosclerosis through modulating oxidative stress, microflora, and apoptosis in experimental rats
- First Published: 27 July 2022
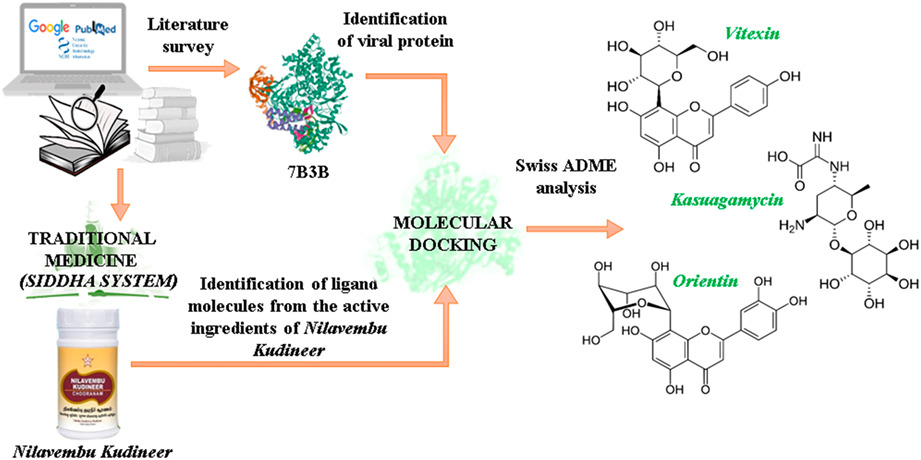
Evaluation of the active constituents of Nilavembu Kudineer for viral replication inhibition against SARS-CoV-2: An approach to targeting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)
- First Published: 22 August 2022
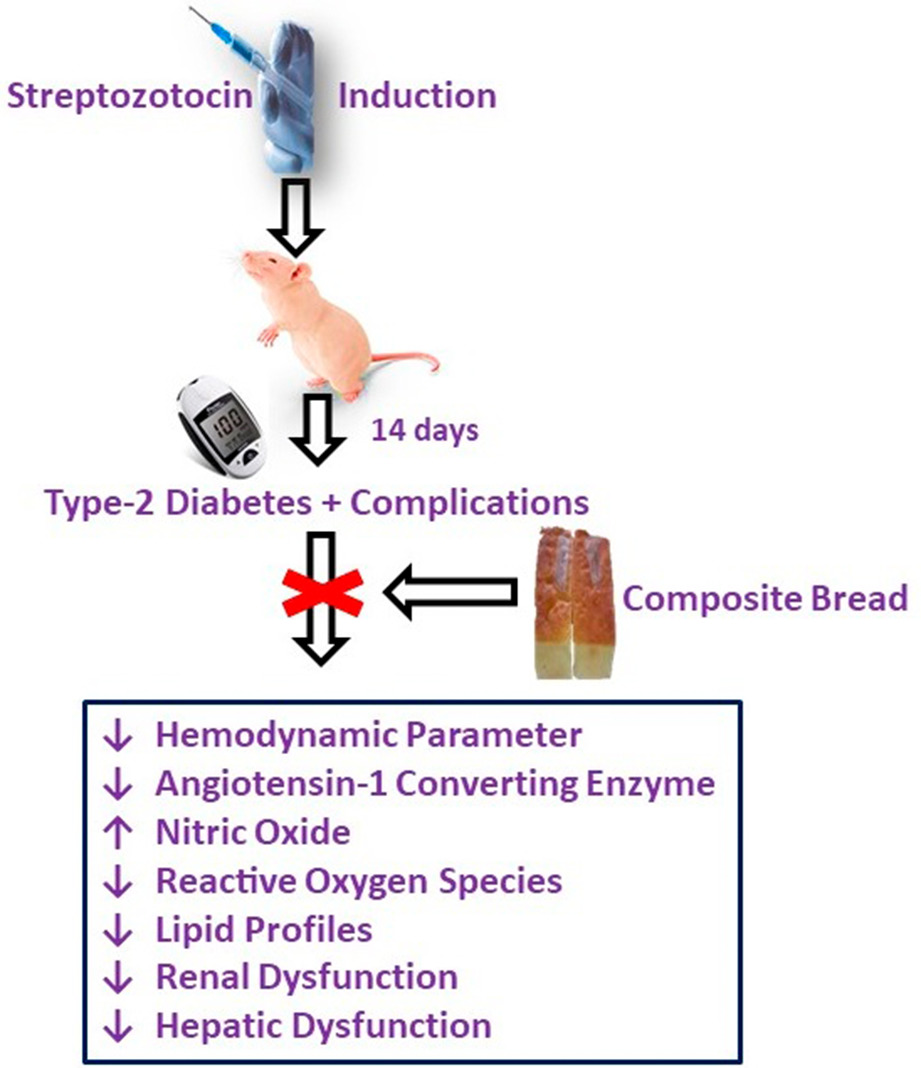
Effects of dietary inclusion of Bambara groundnut and sweet orange peels on streptozotocin/HFD type-2 induced diabetes mellitus complications and related biochemical parameters
- First Published: 07 August 2022
Synergistic cardioprotective ability of co-administration of Moringa supplemented diets and acarbose in diabetic cardiomyopathy involves attenuation of cholinergic, purinergic, monoaminergic, renin-angiotensin system, and antioxidant pathways
- First Published: 11 October 2022
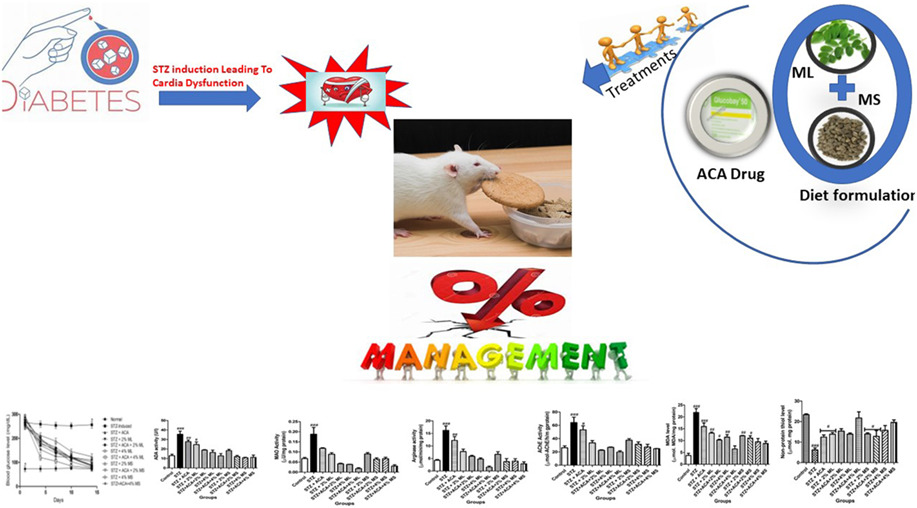
Moringa oleifera has been a vocal appetite in mitigating diabetic cardiomyopathy. For the first time, this report indicates that Moringa combines synergistically with acarbose to ameliorate diabetic cardiomyopathy by modulating cholinergic, purinergic, monoaminergic, renin-angiotensin systems, and antioxidant pathways.