Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Titelbild
Titelbild: Expanding the Toolbox of Target Directed Bio-Orthogonal Synthesis: In Situ Direct Macrocyclization by DNA Templates (Angew. Chem. 7/2023)
- First Published: 03 January 2023

The DNA-templated bioorthogonal synthesis of macrocyclic gene modulators is illustrated in the cover picture accompanying the Research Article (e202215245) by Jyotirmayee Dash and co-workers. DNA secondary structures present in the telomere and oncogene promoter proximally orient bifunctional alkyne and azide fragments, enabling bond formation by copper-free azide–alkyne cycloaddition in live cells. The high-affinity DNA binding macrocyclic ligand efficiently suppresses oncogene expression in cancer cells.
Innentitelbild: Boosting Electroreduction of CO2 over Cationic Covalent Organic Frameworks: Hydrogen Bonding Effects of Halogen Ions (Angew. Chem. 7/2023)
- First Published: 03 January 2023

A hydrogen bonding strategy for achieving an excellent electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction performance over an imidazolium-functionalized covalent organic framework (Co-iBFBim-COF-X) is reported by Yuan-Biao Huang and co-workers in their Research Article (e202215687). The halogen anions can form hydrogen bonds with intermediates (*COOH) and thus lower the energy barrier to the formation of CO. Moreover, the water–anion interactions can repel the contact of water with the active centers, thus inhibiting the occurrence of HER.
Innenrücktitelbild: Electronic Control of the Scholl Reaction: Selective Synthesis of Spiro vs Helical Nanographenes (Angew. Chem. 7/2023)
- First Published: 03 January 2023

Different electronic effects in the starting anthracene-containing polyphenylene substrate (bottom) afford two different nanographenes under Scholl reaction conditions, namely spironanographenes (R=H) on the left and a helically arranged molecular nanographene having two orthogonal aromatic moieties linked by an octafluoroanthracene core (R=F) on the right. The different stabilities of the intermediate trityl cations and the concomitant gain of aromaticity decide the fate of the reaction, as explained by Israel Fernández, Nazario Martín, and co-workers in their Research Article (e202215655).
Rücktitelbild: Optimizing Acetylene Sorption through Induced-fit Transformations in a Chemically Stable Microporous Framework (Angew. Chem. 7/2023)
- First Published: 19 January 2023

Optimizing acetylene (C2H2) sorption through induced-fit transformations of a metal–organic framework has been achieved. In their Research Article (e202215253), Qihui Chen, Daqiang Yuan, Maochun Hong, and co-workers describe the preparation of an adaptive ultramicroporous framework that effectively captures C2H2 with a record-high storage density but a very low adsorption enthalpy. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that the excellent adsorption performance is due to the synergism of active sites, a flexible framework, and matched pores.
Frontispiz
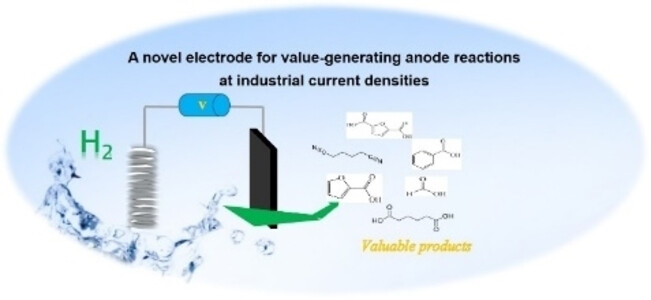
Frontispiz: A Novel Electrode for Value-Generating Anode Reactions in Water Electrolyzers at Industrial Current Densities
- First Published: 02 February 2023

Electrooxidation. A novel electrode for value-generating anode reactions in water electrolyzers at industrial current densities is reported by Yufeng Wu, Ferdi Schüth et al. in their Communication (e202215804).
Frontispiz: ZnF2-Riched Inorganic/Organic Hybrid SEI: in situ-Chemical Construction and Performance-Improving Mechanism for Aqueous Zinc-ion Batteries
- First Published: 02 February 2023

Zinc-Ion Batteries. Jing-Ping Zhang, Xing-Long Wu et al. report in their Research Article (e202216934) a ZnF2-rich hybrid solid-electrolyte interphase for aqueous zinc-ion batteries.
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis
Graphisches Inhaltsverzeichnis: Angew. Chem. 7/2023
- First Published: 02 February 2023
Berichtigungen
Berichtigung: Metal-Free Catalytic Hydrogenolysis of Silyl Triflates and Halides into Hydrosilanes
- First Published: 11 January 2023
Berichtigung: Mechanistic Studies on the Organocatalytic α-Chlorination of Aldehydes: The Role and Nature of Off-Cycle Intermediates
- First Published: 28 November 2022
Berichtigung: Ultralong Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Boric Acid
- First Published: 01 January 2023
Introducing …
Julian G. West
- First Published: 04 January 2023

“The most exciting thing about my research is helping others to grow as scientists and people … The best advice I have ever been given is ‘Always be on the lookout for the presence of wonder,’ a fantastic quote from E. B. White by way of Prof. Scott Miller …” Find out more about Julian West in his Introducing … Profile.
Team Profile
A Collaboration for Guiding the Rational Design of Multielement Solid Catalysts
- First Published: 30 December 2022

„After finishing two weeks of quarantine during a typical Finnish winter … we succeeded to have the setup working and perform a wide range of studies … Overall, the visits of Nina turned out to be challenging due to the special times, but also rewarding from a professional as well as cultural and social point of life.“ Find out more about the collaboration of Bert Weckhuysen and his co-workers in their Team Profile.
Scientific Perspectives
Nanomedicine
A Forward Vision for Chemodynamic Therapy: Issues and Opportunities
- First Published: 17 January 2023
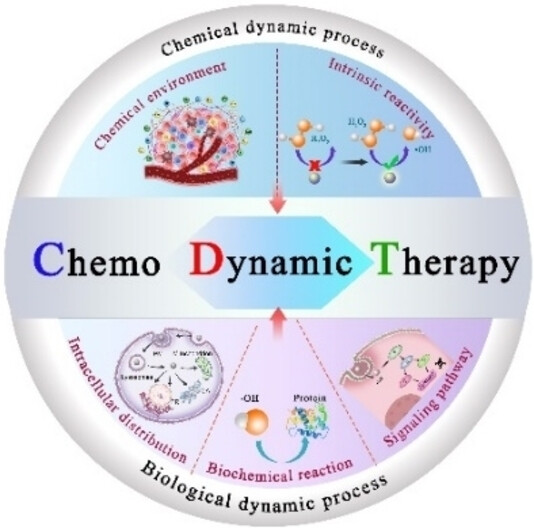
Chemodynamic therapy (CDT) that integrates Fenton chemistry and biomedicine provides strategies for cancer treatment with nanomedicine; however, the exact mechanism of CDT is not fully understood. In this Scientific Perspective, the conceptual framework of CDT is clarified and research approaches that illuminate its chemical and biological mechanisms are discussed. Beneficial outlooks for CDT are provided to inspire new advances in the field.
Kurzaufsätze
Fluorescent Probes
Single mRNA Imaging with Fluorogenic RNA Aptamers and Small-molecule Fluorophores
- First Published: 24 November 2022
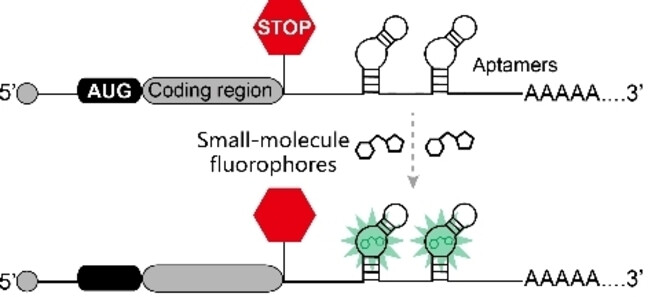
This Minireview covers the recent advances in the development of small-molecule fluorophores and fluorogenic RNA aptamers for single mRNA imaging. We summarized the pros and cons, and photochemical properties of five different RNA aptamers: small-molecule fluorophores systems and how they can be applied to single-molecule mRNA imaging.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Emerging Lithiated Organic Cathode Materials for Lithium-Ion Full Batteries
- First Published: 29 November 2022
This Minireview systematically summarizes the recent progress on emerging lithiated organic cathode materials, including their synthesis, stability, and half- and full-battery applications. The biggest advantage of lithiated organic cathode materials is that they can act as a Li reservoir to couple with Li-free anodes for lithium-ion full batteries.
Nonlinear Optical Materials
Aufsätze
Einzelatomkatalyse
Einzelatomkatalysatoren auf kovalenten Triazinnetzwerken: am Scheidepunkt zwischen homogener und heterogener Katalyse
- First Published: 15 September 2022
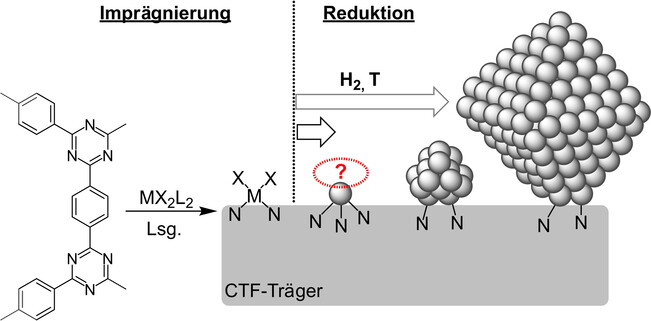
Dieser Aufsatz beleuchtet die Einzelatomkatalyse am Beispiel von kovalenten Triazinnetzwerken (CTFs) und konzentriert sich dabei auf die verfügbaren Erkenntnisse über Faktoren, die die Nuklearität und die Koordinationsumgebung von Metallspezies an CTFs beeinflussen, sowie auf die Auswirkungen auf die katalytische Aktivität.
Zuschriften
Hydrogen Evolution
A Novel Electrode for Value-Generating Anode Reactions in Water Electrolyzers at Industrial Current Densities
- First Published: 28 November 2022
Ionic Liquids
Luminescence | Hot Paper
A Configurationally Confined Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescent Two-Coordinate CuI Complex for Efficient Blue Electroluminescence
- First Published: 21 December 2022
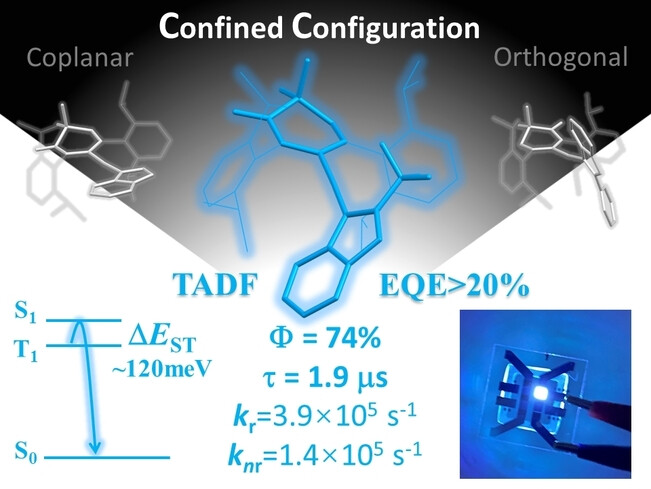
Efficient thermally activated delayed fluorescent (TADF) two-coordinate CuI complex is designed by configurationally confined strategy. With proper twist angle around 45° between ligands, fast radiative decay is achieved with balanced ΔEST and kr of S1, meanwhile, knr is also depressed. As demonstrated in efficient OLED with high EQE over 20 % and small efficiency roll-off less than 2 %, configurationally confined strategy is practical for developing novel CuI TADF emitters.
Palladium Catalysis | Hot Paper
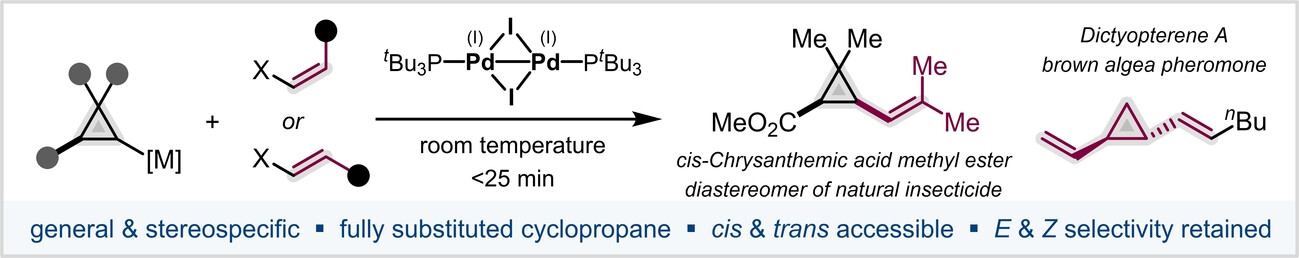
Rapid and Modular Access to Vinyl Cyclopropanes Enabled by Air-stable Palladium(I) Dimer Catalysis
- First Published: 13 October 2022
Enzyme Mechanisms
Mechanistic Insight into Peptidyl-Cysteine Oxidation by the Copper-Dependent Formylglycine-Generating Enzyme
- First Published: 22 December 2022
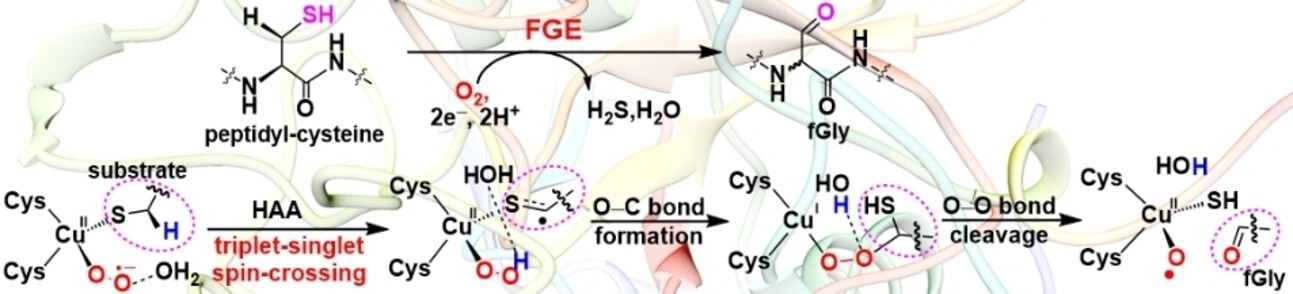
QM/MM calculations reveal the reaction mechanism of the FGE-catalyzed oxidative conversion of peptidyl-cysteines into formylglycine. Triplet-singlet crossing initiates the rate-limiting hydrogen atom abstraction from substrate to generate a CuII−OOH species. A nearby water molecule plays a vital role in the formation of the CuI-alkylperoxo intermediate, which is the key species that can undergo O−O bond cleavage to give formylglycine.
Imaging Agents
Unprecedented Relaxivity Gap in pH-Responsive FeIII-Based MRI Probes
- First Published: 22 December 2022
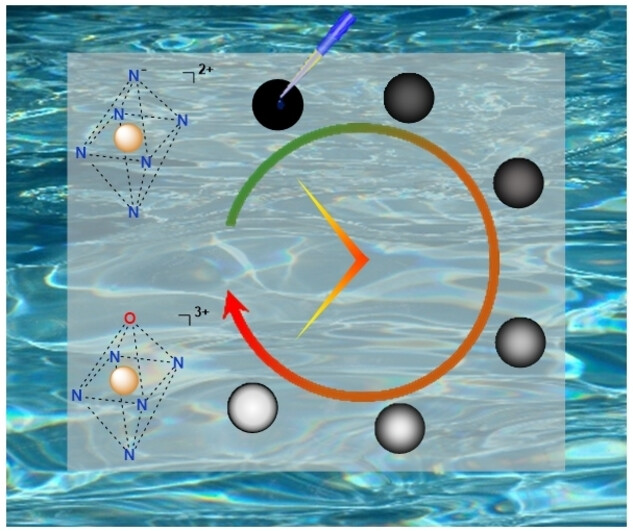
Two ferric chelates act as molecular probes for a changing pH by a 21- and 71-fold change in their relaxivity. This unprecedented performance became possible thanks to a pendant-arm design within the hexadentate ligand ensuring virtually complete coordination at high pH and de-coordination at low pH. Both probes do not show any detectable fatigue over several activation/de-activation cycles, underscoring the elevated robustness of the system.
Nucleic Acids
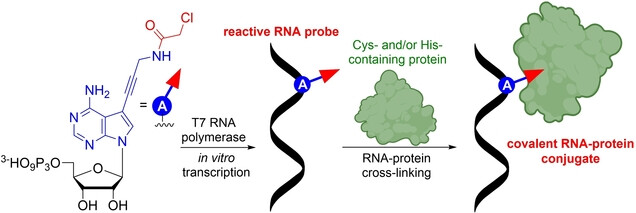
Chloroacetamide-Modified Nucleotide and RNA for Bioconjugations and Cross-Linking with RNA-Binding Proteins
- First Published: 19 December 2022
Photocatalysis
Direct Excitation of Aldehyde to Activate the C(sp2)−H Bond by Cobaloxime Catalysis toward Fluorenones Synthesis with Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 13 December 2022
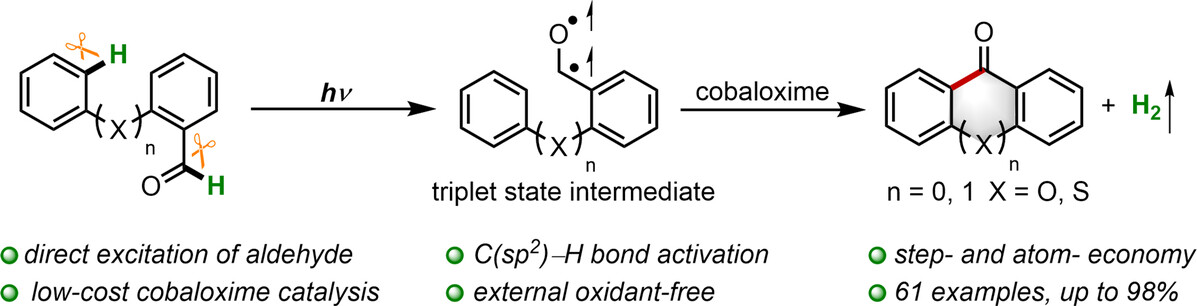
Direct excitation of aldehydes to activate their C (sp2)−H bond through cobaloxime catalysis has been successfully developed. Upon irradiation, the highly reactive photoexcited triplet state of aromatic aldehyde intermediates is intercepted by the catalyst in the ground state, thus leading to the synthesis of a series of fluorenones, xanthones and thioxanthones in good to excellent yields without any external oxidants and with hydrogen as the byproduct.
Biocatalysis
Chiral Alcohols from Alkenes and Water: Directed Evolution of a Styrene Hydratase
- First Published: 13 December 2022
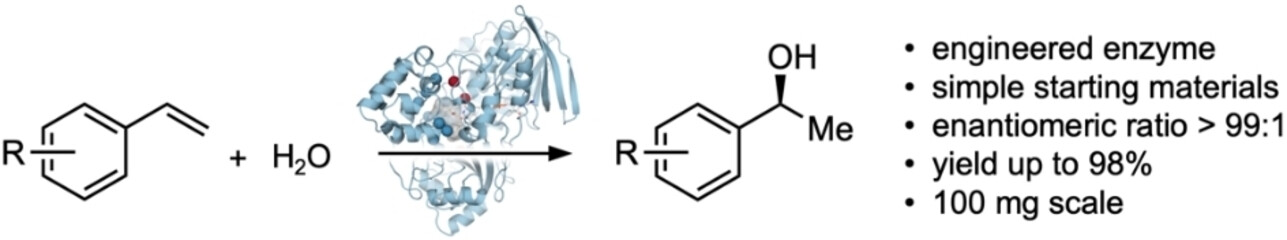
The enantioselective addition of water across unactivated alkenes is a much sought-after chemical transformation and a major challenge in catalysis. Now a promiscuous engineered fatty acid hydratase produces chiral alcohols with high enantioselectivity, also on a preparative scale, using simple alkenes and water as reactants.
Photoelectrochemical H2 Evolution
Monitoring Transformations of Catalytic Active States in Photocathodes Based on MoSx Layers on CuInS2 Using In Operando Raman Spectroscopy
- First Published: 21 December 2022
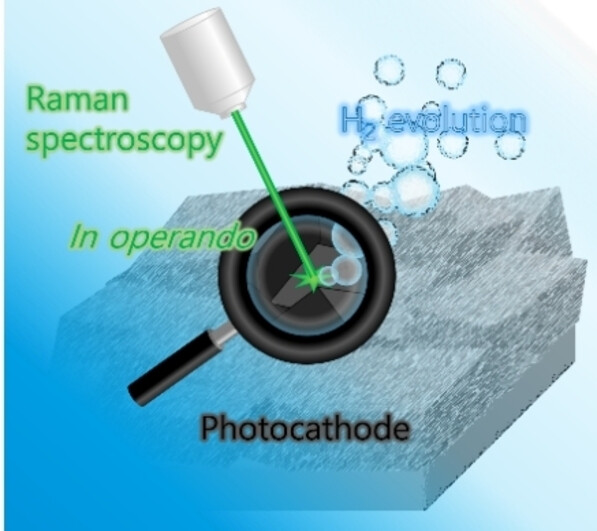
The chemical state of a CuInS2/MoSx photocathode surface was investigated by Raman spectroscopy under actual photoelectrochemical H2 evolution reaction conditions. In operando Raman spectroscopy revealed the nature of MoSx activation during PEC H2 evolution, which was not revealed by ex situ XPS or Raman spectroscopy. In operando Raman spectroscopy characterization is a promising tool for photoelectrochemical cells.
Cross-Coupling
Ligand-Controlled Nickel-Catalyzed Regiodivergent Cross-Electrophile Alkyl-Alkyl Couplings of Alkyl Halides
- First Published: 14 December 2022
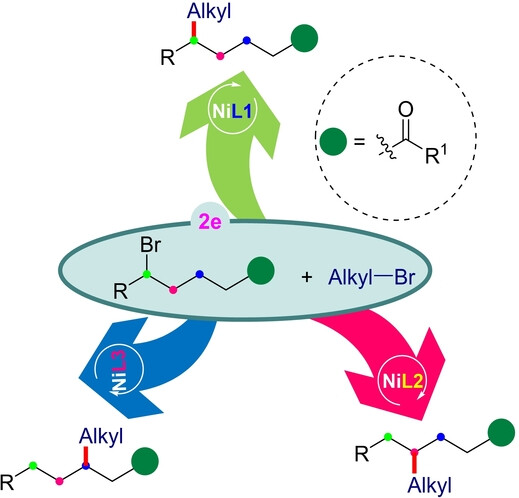
Herein, a unified protocol for the regiodivergent nickel-catalyzed cross-electrophile coupling of two distinct alkyl bromides has been established, providing access to β-, γ-, δ-alkylated amides. This catalytic protocol relies on a good practical regiocontrol for installing alkyl groups and provides orthogonal access to diverse branched architectures with remote saturated carbon centers while starting from identical substrates.
Organic Memristors
Redox-Active Azulene-based 2D Conjugated Covalent Organic Framework for Organic Memristors
- First Published: 12 December 2022
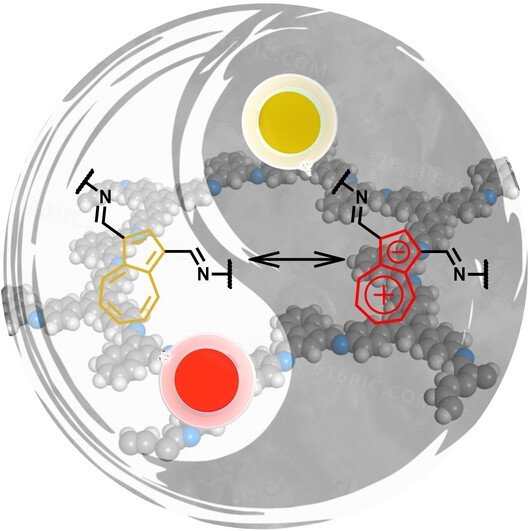
By using 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)-benzene and azulene-1,3-dicarbaldehyde as the starting materials, an azulene-based 2D conjugated covalent organic framework, COF-Azu, is prepared through liquid-liquid interface polymerization strategy. The as-fabricated Al/COF-Azu/ITO memristor shows typical non-volatile resistive switching performance. Associated with its unique memristive performance, a simple convolutional neural network is built for image recognition.
Imaging
Super-Resolution Tension PAINT Imaging with a Molecular Beacon
- First Published: 19 December 2022
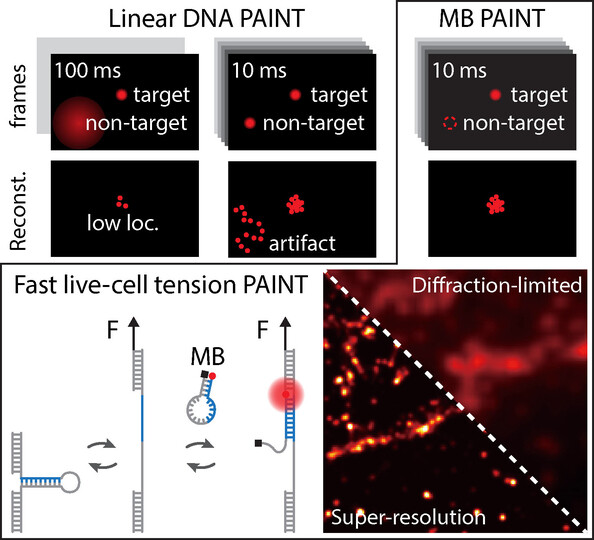
Constraints such as low imager concentration, thin illumination volume, and long exposure time limit the potential of traditional DNA-PAINT in fast live-cell imaging. MB-PAINT removes these constraints by eliminating background fluorescence and localization artifacts caused by free-diffusing imagers in traditional DNA-PAINT, thus enabling fast super-resolution imaging of living cells, and particularly in tension imaging.
Polymerization
Rapid and Selective Photo-degradation of Polymers: Design of an Alternating Copolymer with an o-Nitrobenzyl Ether Pendant
- First Published: 15 December 2022
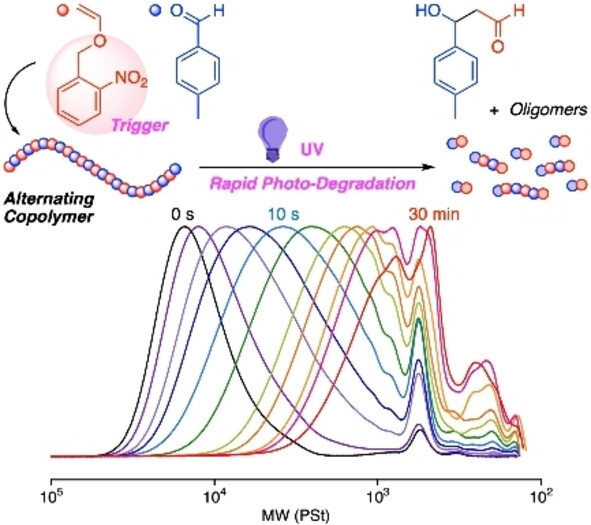
We designed a vinyl ether monomer with a photo-deprotectable o-nitrobenzyl pendant and synthesized an alternating copolymer with an oNBn-capped acetal backbone via cationic copolymerization with p-tolualdehyde. This copolymer rapidly degrades into lower-molecular-weight compounds upon exposure to UV irradiation, whereas it is stable toward heat and ambient light.
Zeolites
Impact of Mineralizing Agents on Aluminum Distribution and Acidity of ZSM-5 Zeolites
- First Published: 21 December 2022
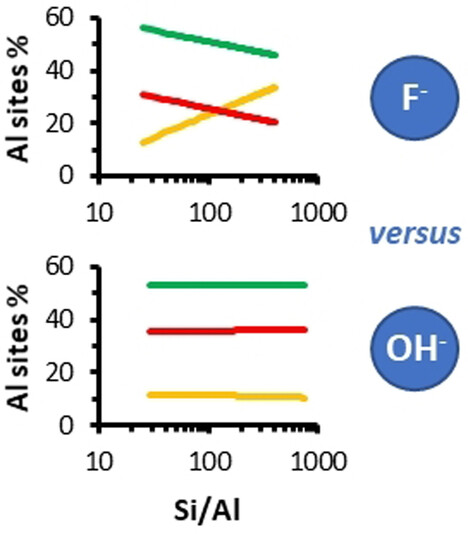
The mineralizing agents F− and OH− directly influence aluminum distribution in ZSM-5. The proportion of Al sites depends on the Si/Al ratio for F−, but remains identical for OH− (from Si/Al=30 to 760). This effect offers a simple and new opportunity to control zeolite acidity and further reactivity.
Asymmetric Catalysis
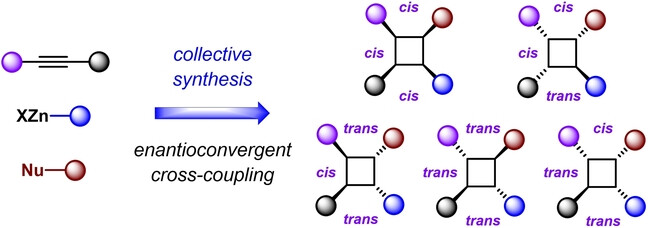
Collective Synthesis of Chiral Tetrasubstituted Cyclobutanes Enabled by Enantioconvergent Negishi Cross-Coupling of Cyclobutenones
- First Published: 20 December 2022
Biosynthesis
A Widely Distributed Biosynthetic Cassette Is Responsible for Diverse Plant Side Chain Cross-Linked Cyclopeptides
- First Published: 18 December 2022
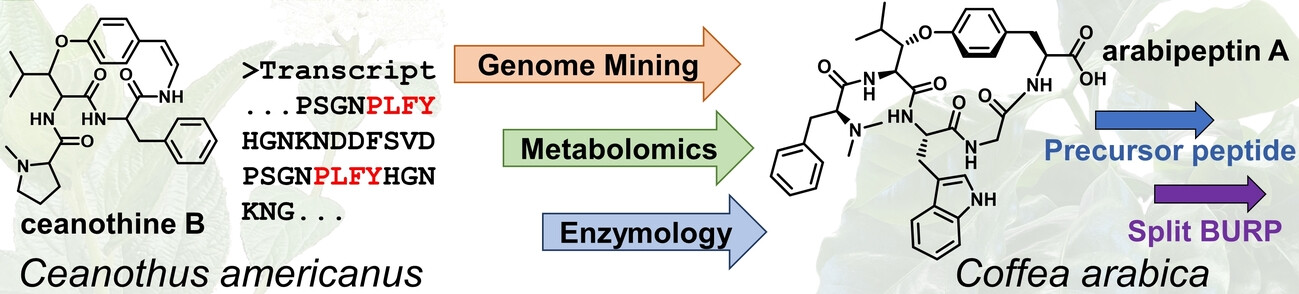
Cyclopeptide alkaloids are a diverse class of plants natural products, yet little is known of their biosynthesis. By combining transcriptomics and genome mining, we uncover a widespread biosynthetic cassette responsible for side chain cross-linked cyclopeptides. We validate these observations by isolating a new cyclopeptide from Coffea arabica and reconstituting enzymatic activity for the family defining split BURP peptide cyclase.
Asymmetrische Katalyse
Kupferkatalysierte, hochgradig enantioselektive Addition eines Siliciumnukleophils an 3-substituierte 2H-Azirine unter Verwendung eines Si-B-Reagenzes
- First Published: 12 December 2022
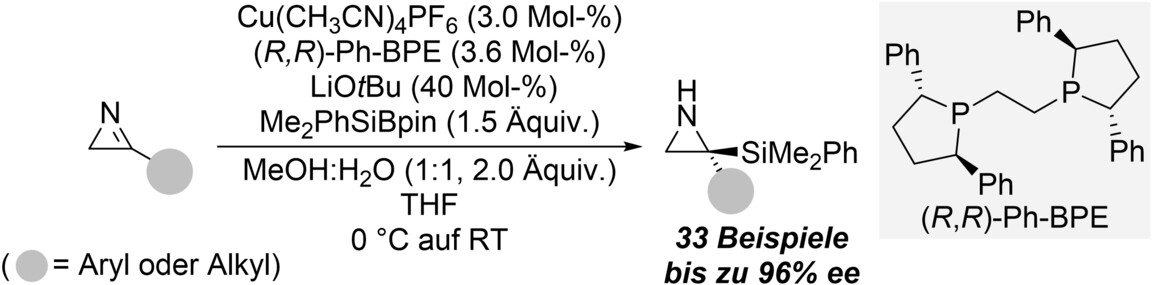
Die erste katalytische asymmetrische Synthese von C-silylierten, ungeschützten Aziridinen wurde erreicht. Unter Verwendung eines Silylboronsäureesters als latentes Siliciumnukleophil befähigt ein chiraler Kupferkatalysator zu dessen Addition an 3-substituierte 2H-Azirine in hohen Ausbeuten und mit hervorragenden Enantioselektivitäten. Diese Azirine können als gespannte cyclische und demzufolge reaktive Ketimine angesehen werden, für die eine erfolgreiche Silylierung noch unbekannt ist.
Enzymmechanismen
Die Bindung von Cyanid an [FeFe]-Hydrogenasen stabilisiert die alternative Konfiguration des Protonentransferpfads
- First Published: 04 December 2022
![Die Bindung von Cyanid an [FeFe]-Hydrogenasen stabilisiert die alternative Konfiguration des Protonentransferpfads](/cms/asset/cc31b35a-fb70-48ee-9749-7a8e51d3820e/ange202216903-toc-0001-m.jpg)
[FeFe]-Hydrogenasen sind hocheffiziente H2-Biokatalysatoren, die intrinsische CN− Liganden verwenden. Hier zeigen wir, dass extrinsisches CN− an die offene Koordinationsstelle des katalytischen Zentrums bindet. Darüber hinaus werden neue Konformationen innerhalb des Protonentransferpfads beobachtet, die komplementär zu denen im oxidierten Zustand Hox sind und so eine strukturelle Grundlage für das Verständnis der molekularen Mechanismen des schnellen Protonentransfers in Enzymen darstellen.
Forschungsartikel
Aqueous Zn Batteries | Very Important Paper
ZnF2-Riched Inorganic/Organic Hybrid SEI: in situ-Chemical Construction and Performance-Improving Mechanism for Aqueous Zinc-ion Batteries
- First Published: 07 December 2022
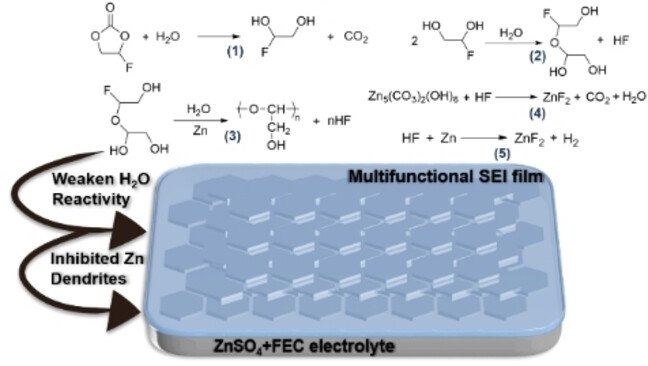
Multifunctional FEC is introduced into aqueous electrolyte to produce a ZnF2-riched inorganic/organic hybrid SEI (ZHS) layer on Zn metal anode (ZMA) surface. The hydrolysate of FEC can favorably regulate the solvated structure of Zn2+ to restrict the H2O-related parasitic reactions. The in situ formed ZHS layer not only realize uniform Zn deposition, but also suppresses ZMA corrosion.
Peptide Drug
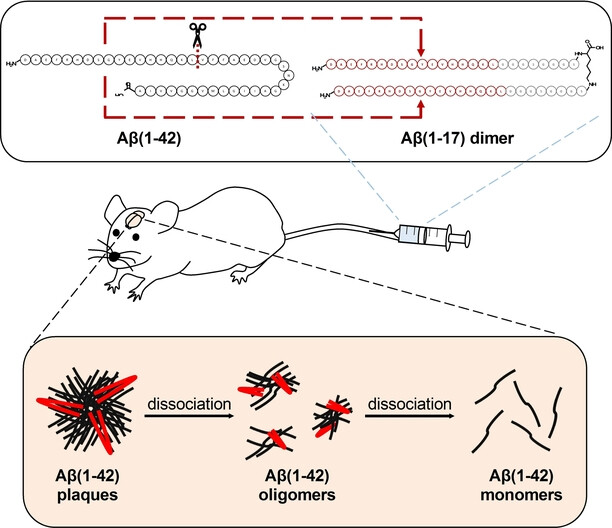
Amyloid Against Amyloid: Dimeric Amyloid Fragment Ameliorates Cognitive Impairments by Direct Clearance of Oligomers and Plaques
- First Published: 31 October 2022
Amyloid
Decreased Water Mobility Contributes To Increased α-Synuclein Aggregation
- First Published: 31 October 2022
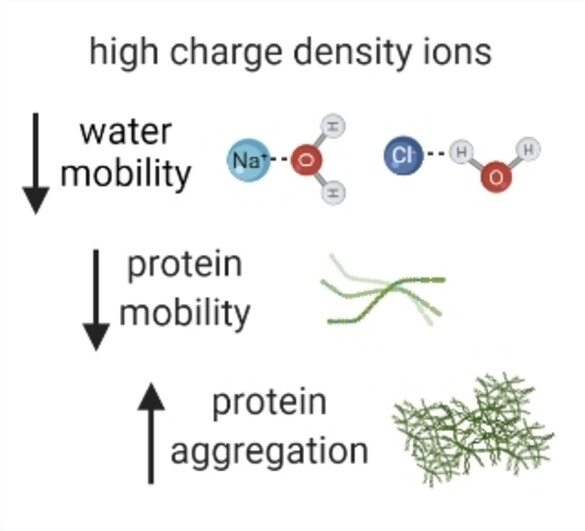
Ions can influence the mobility of water molecules in the solvation shell of a protein, which is important for folding and function. We show ions that decrease water mobility contribute to decreased protein mobility and subsequently to an increase in the self-association and aggregation rate. Alteration in water mobility may occur in ageing cells where ion concentrations become dysregulated and therefore promote αSyn aggregation.
Solid-State Batteries
Impact of the Chlorination of Lithium Argyrodites on the Electrolyte/Cathode Interface in Solid-State Batteries
- First Published: 23 November 2022
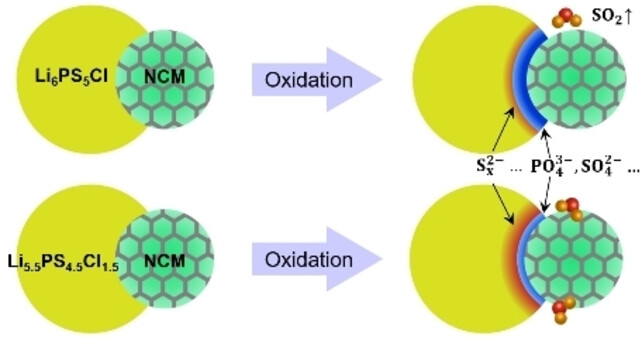
Lithium argyrodite-type electrolytes show high ionic conductivity and good processability, but they suffer from interfacial degradation. The influence of chlorination on the interfacial degradation is systematically evaluated here using electrochemical measurements, gas analysis and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry. This work highlights the importance of electrolyte modifications.
Peptides
Ranking Peptide Binders by Affinity with AlphaFold
- First Published: 21 December 2022
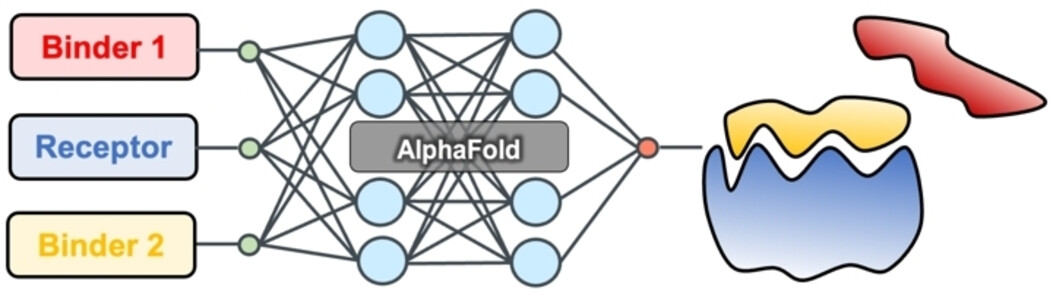
AlphaFold is transforming the field of protein structure prediction. Standing on its highly accurate mapping between protein sequence and structure, we discovered a novel way to predict the ranking of peptide binding affinities through a competitive binding assay. While there are still limitations, we anticipate this approach can be easily adopted for identifying higher affinity peptide binders.
Atomic-scale Qubits
Room Temperature Incorporation of Arsenic Atoms into the Germanium (001) Surface
- First Published: 09 December 2022
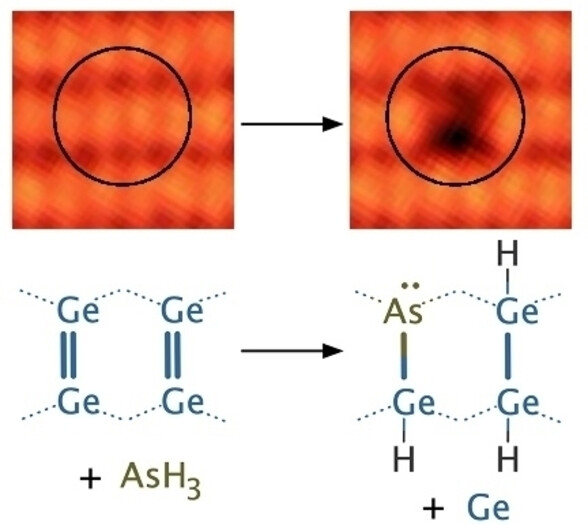
We report the discovery that arsenic atoms incorporate substitutionally into the (001) surface of germanium at room temperature when the surface is exposed to arsine (AsH3). We observe several types of incorporated arsenic structures that differ only in the locations of the three adsorbed hydrogen atoms. Arsenic incorporation causes germanium ad-atoms to be released onto the surface. These results provide a path toward atomic-scale dopant devices in germanium with clear advantages over silicon.
Single-Atom Nanozymes
Unraveling the Structure Transition and Peroxidase Mimic Activity of Copper Sites over Atomically Dispersed Copper-Doped Carbonized Polymer Dots
- First Published: 24 December 2022

Atomically dispersed copper-doped carbonized polymer dots (CPDs), Glu−Cu−CPDs, with excellent peroxidase-like activity were prepared from copper glutamate (Glu). The Cu binding sites in Glu−Cu−CPDs had a Cu−N2C2 structure, and Cu−O bonds were converted into Cu−C bonds under hydrothermal conditions. DFT calculations showed that H2O2 was cleaved by Glu−Cu−CPDs by a dual-site catalytic pathway. The Glu−Cu−CPDs enabled intracellular detection of H2O2.
Perovskites
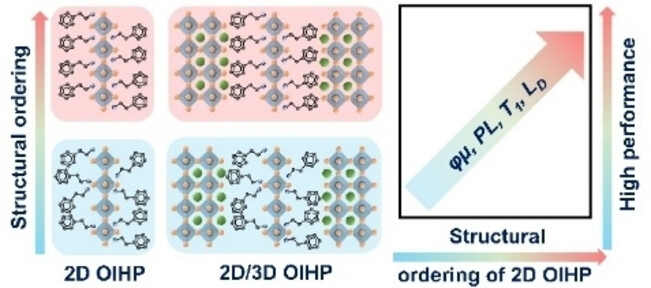
Boosting Charge Transport in a 2D/3D Perovskite Heterostructure by Selecting an Ordered 2D Perovskite as the Passivator
- First Published: 05 December 2022
Analytical Methods | Hot Paper
Quantitative Single-Molecule Electrochemiluminescence Bioassay
- First Published: 12 December 2022
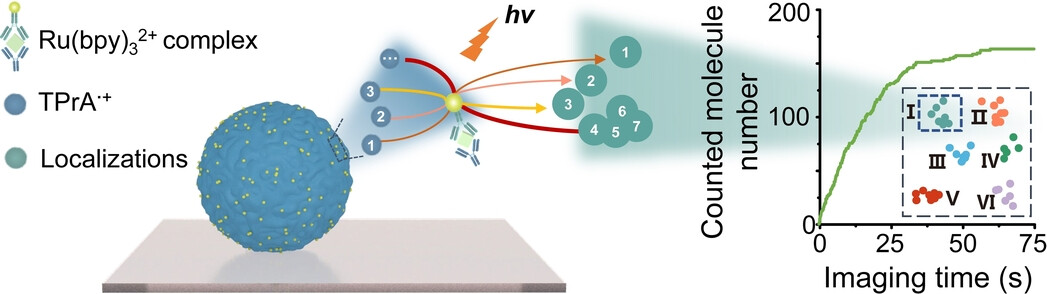
We developed a single-molecule electrochemiluminescence bioassay which allows imaging of single biomolecules with nanometer resolution based on localizing the repeated electrochemiluminescence reactions. Quantification of biomolecules is achieved by merging the clustered reactions at one molecule site and then counting the merged molecule numbers.
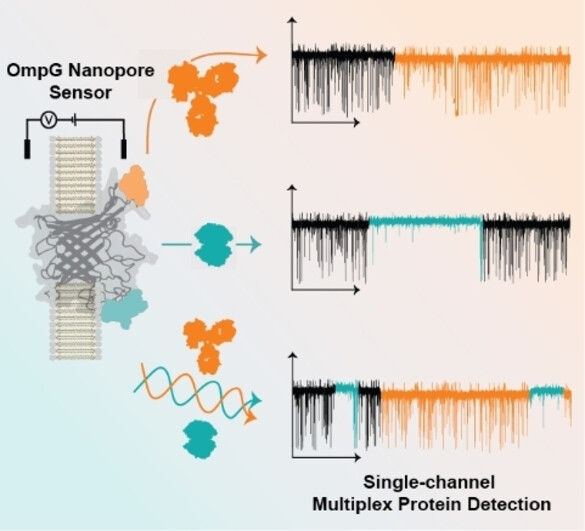
Biosensors
An Engineered OmpG Nanopore with Displayed Peptide Motifs for Single-Molecule Multiplex Protein Detection
- First Published: 01 December 2022
Coordination Polymers
Low-Frequency Sub-Terahertz Absorption in HgII−XCN−FeII (X=S, Se) Coordination Polymers
- First Published: 15 December 2022
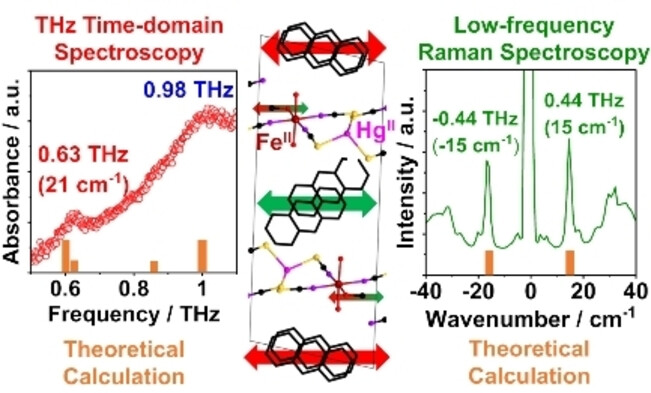
A new series of high-dimensional thiocyanate-/selenocyanate-bridged networks [Fe (L)m] [Hg (XCN)4]⋅solvents (L=phenazine/quinoxaline/4,4′-trimethylenedipyridine; X=S/Se) exhibits unique low-frequency terahertz absorbance and Raman scattering spectra. The phonon-mode analysis is supported by quantum chemical calculations, indicating the importance of heavy elements in these phenomena and demonstrating the potential of the ab initio method.
Inhibitors
A Versatile Strategy for Screening Custom-Designed Warhead-Armed Cyclic Peptide Inhibitors
- First Published: 19 December 2022
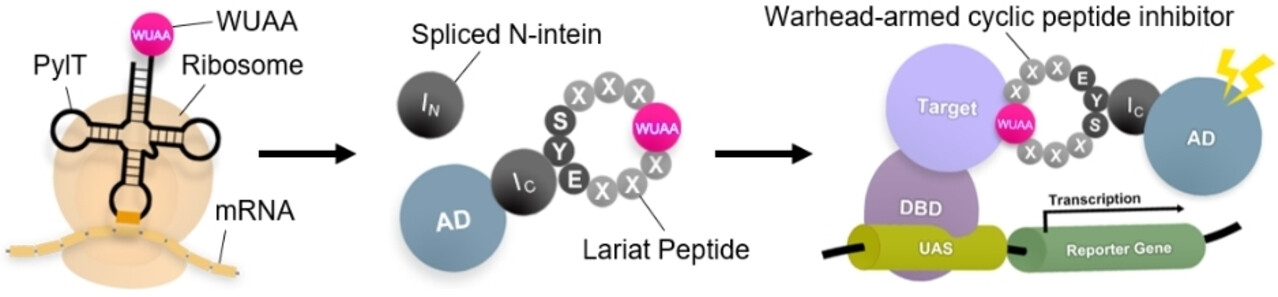
We developed a general strategy for a yeast-based screening platform that we call custom-designed warhead-armed cyclic peptide screening (or CWCPS). This platform has led to the discovery of a potent inhibitor CY5-6Q that targets human histone deacetylase 8 with a KD value in the double-digit nanomolar range. This strategy can be a versatile platform for peptide-based drug discovery.
Cage Compounds
Charge-Assisted Halogen Bonding in an Ionic Cavity of a Coordination Cage Based on a Copper(I) Iodide Cluster
- First Published: 14 December 2022
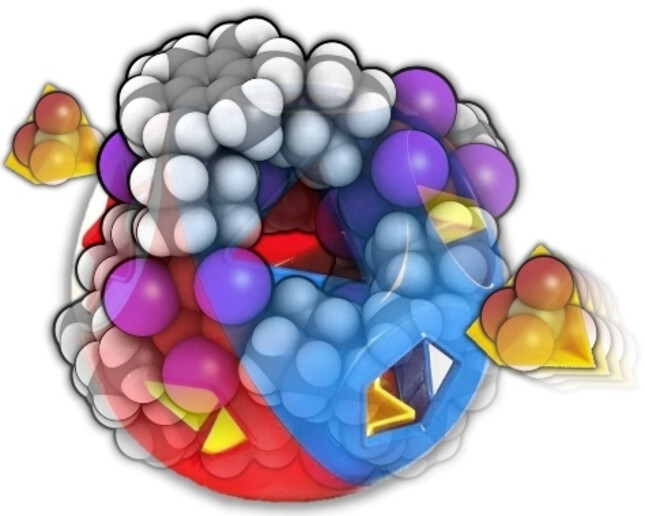
An unusual Cu3I4− based coordination cage was synthesized by a reaction between copper (I) iodide and a tripodal cationic ligand. X-ray structural evidence demonstrates that this cage can selectively encapsulate bromomethanes by concerted ligand-iodide-bromomethane ionic and halogen bonding interactions.
G-quadruplexes
Expanding the Toolbox of Target Directed Bio-Orthogonal Synthesis: In Situ Direct Macrocyclization by DNA Templates
- First Published: 27 November 2022
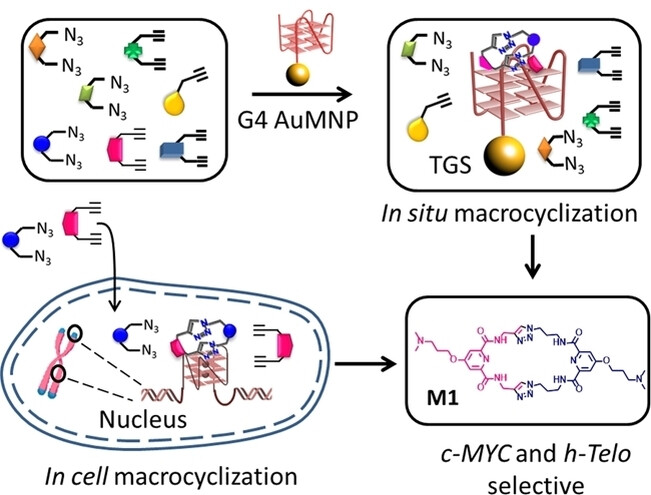
This work demonstrates the first instance of bioorthogonal macrocyclization directed by non-canonical DNAs as templates. The size complementarity of the macrocyclic core with the G-quartet of a G-quadruplex DNA plays a key role to drive the macrocyclization over oligomerization. In cellulo macrocyclization has also been established leading to a peptidomimetic macrocycle with promising therapeutic properties.
Nanographenes
Electronic Control of the Scholl Reaction: Selective Synthesis of Spiro vs Helical Nanographenes
- First Published: 10 December 2022
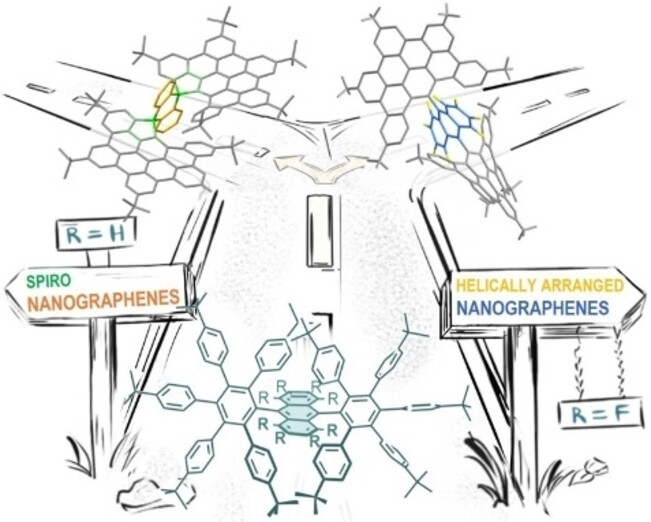
The electronic nature of the starting substrate decides the fate of the reaction: Anthracene-based polyphenylenes lead to less-known spiro (R=H) or helical (R=F) nanographenes under mild Scholl conditions, depending upon the substitution pattern on the anthracene core. DFT calculations reveal that the formation, or not, of the trityl cation is the key issue.
CO2 Reduction | Hot Paper
Boosting Electroreduction of CO2 over Cationic Covalent Organic Frameworks: Hydrogen Bonding Effects of Halogen Ions
- First Published: 24 November 2022
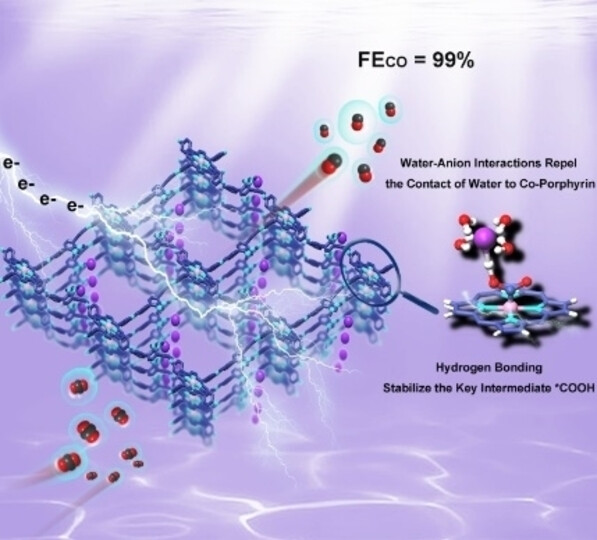
Charged imidazolium struts were integrated into two-dimensional cobalt porphyrin-based covalent organic frameworks (Co-iBFBim-COF-X) creating catalytic pockets with 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-aminophenyl)-porphinatocobalt centers and halogen counter ions (e.g., F−, Cl−, Br−, and I−). The free imidazolium anions in the proximity of the active Co sites in the Co-iBFBim-COF-X can stabilize the key intermediate *COOH and inhibit the occurrence of HER through hydrogen bonding.
Perovskites
A General Synthetic Route to High-Quality Perovskite Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Enhanced Solar Photocatalytic Activity
- First Published: 28 December 2022
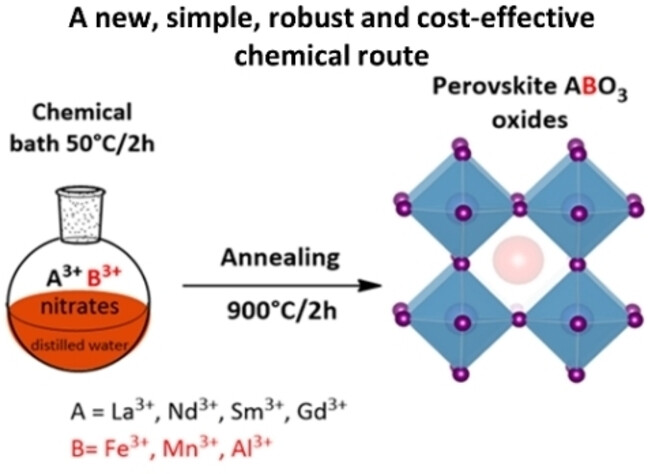
Generalization in preparing perovskite oxide nanomaterials with high purity and crystalline quality is crucial to permit their full study and widen their applicative potentials. We provide a generic and robust chemical bath route for synthesizing nano-shaped rare-earth-based REMO3 nanoparticles oxides (RE=La, Nd, Sm, Gd; M=Fe, Mn, Al) by simply changing the desired nitrate salts.
Microporous Materials | Very Important Paper
Optimizing Acetylene Sorption through Induced-fit Transformations in a Chemically Stable Microporous Framework
- First Published: 16 December 2022
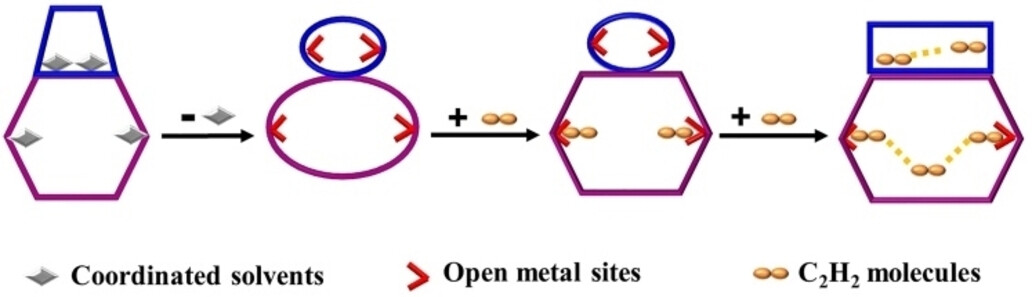
An acid/base-resistant framework with adaptive pores was prepared; it could effectively capture C2H2 with a record-high storage density but a very low adsorption enthalpy. Mechanism studies demonstrate that such excellent performance comes from the synergism of active sites, flexible framework, and matched pores, where the adsorbed-C2H2 can drive framework to undergo continuous induced-fit transformations, finally leading to dense packing of C2H2.
Molecular Computing
Computing Arithmetic Functions Using Immobilised Enzymatic Reaction Networks
- First Published: 23 December 2022
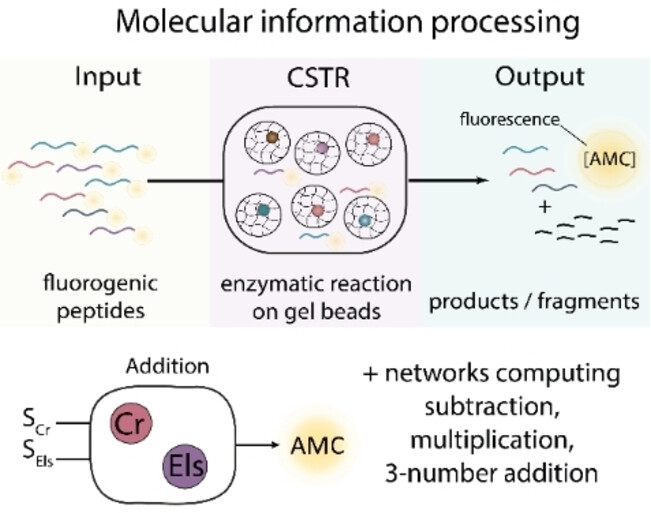
Enzymes immobilised in hydrogel beads and compartmentalised in a continuous tank reactor were shown to serve as a novel modular and reusable platform for molecular information processing. With small molecules (peptide-based substrates and inhibitors) as inputs, the robustness of the platform in performing the fundamental arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction and multiplication was demonstrated.
Plasmonic Catalysis
Simultaneous Harvesting of Multiple Hot Holes via Visible-Light Excitation of Plasmonic Gold Nanospheres for Selective Oxidative Bond Scission of Olefins to Carbonyls
- First Published: 16 December 2022
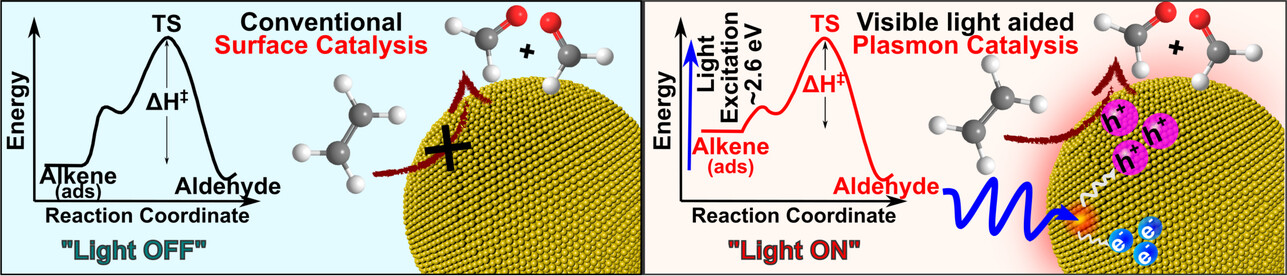
Harvesting of multiple hot holes has been demonstrated using Au nanospheres for the plasmonic photocatalytic oxidative scission of olefin to carbonyls through a step-down process. Interband photoexcitation of Au nanospheres beyond a threshold intensity leads to a spurt in hot-carrier generation, enabling multifold enhancement in substrate activation compared to a dark process.
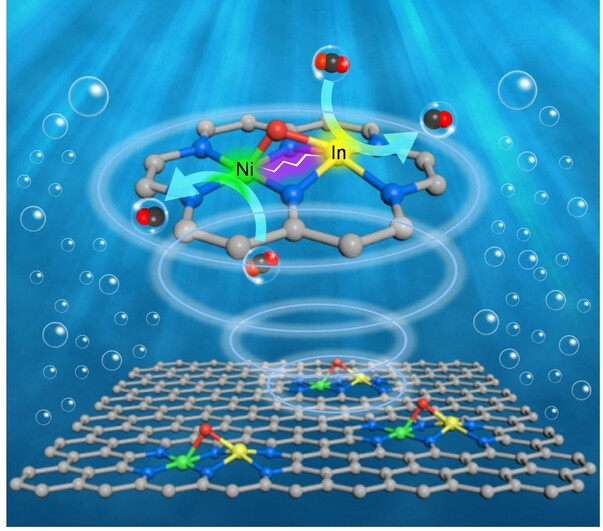
CO2 Reduction
Oxygen-Bridged Indium-Nickel Atomic Pair as Dual-Metal Active Sites Enabling Synergistic Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
- First Published: 15 December 2022
Fluorescent Probes | Hot Paper
An Activatable NIR-II Fluorescent Reporter for In Vivo Imaging of Amyloid-β Plaques
- First Published: 13 December 2022
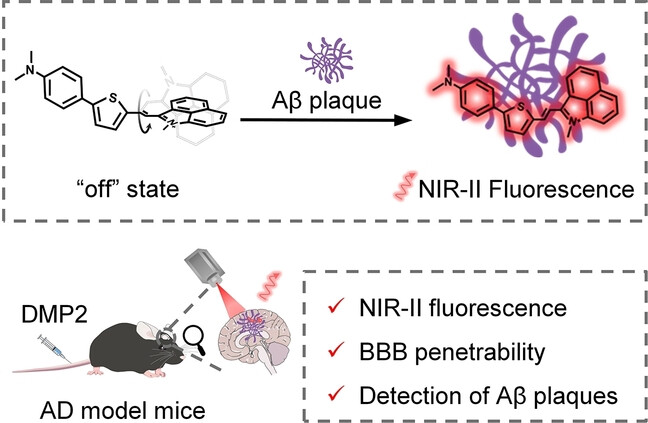
A NIR-II fluorescent reporter (i.e., DMP2) is designed to specifically activate its NIR-II fluorescence upon binding to amyloid-β (Aβ) fibrils via a suppressed twisted intramolecular charge transfer effect. Benefiting from high specificity in response to Aβ fibrils and suitable lipophilicity to penetrate BBB, DMP2 achieves in vivo visualization of Aβ plaques in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model.
Li-Ion Batteries | Hot Paper
Gradient Graphdiyne Induced Copper and Oxygen Vacancies in Cu0.95V2O5 Anodes for Fast-Charging Lithium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 14 December 2022
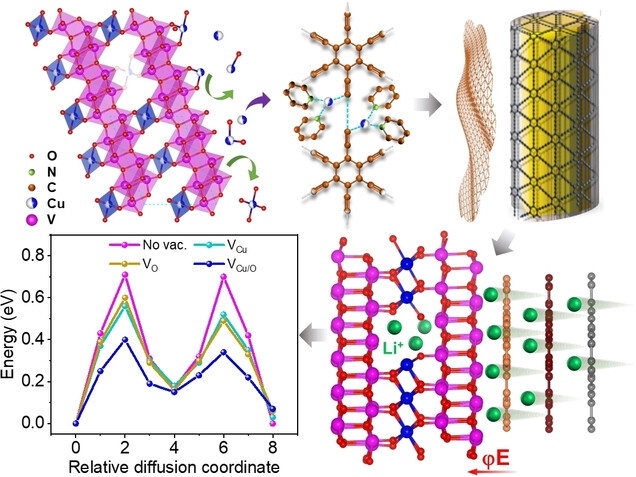
Cu0.95V2O5 self-catalyzes the growth of gradient GDY to generate Cu and O vacancies in Cu0.95V2O5@GDY heterostructure material. The rich Cu/O vacancies, outside-in self-expanded ion-transport channels enabled by gradient GDY, and synergistic effect of built-in electric field greatly enhance the Li-ion transport kinetics, the electrochemical reaction reversibility and the Li storage sites of Cu0.95V2O5, thus boosting its fast-charging performance.
Supramolecular Chemistry
Real-time Observation of Macroscopic Helical Morphologies under Optical Microscope: A Curious Case of π–π Stacking Driven Molecular Self-assembly of an Organic Gelator Devoid of Hydrogen Bonding
- First Published: 08 December 2022
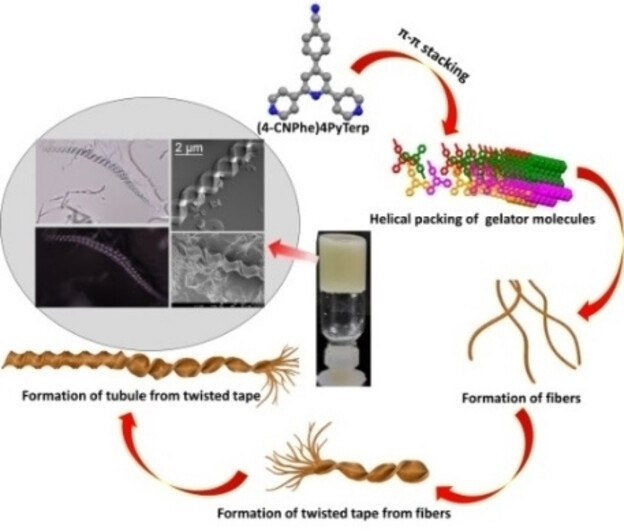
A DMSO gel of a terpyridine derivative produced macroscopic helical morphologies which could be observed under optical microscope, formation of which could be monitored by optical videography, stable enough to withstand acidic vapour, robust enough to display reversible gel↔sol in response to acidic and ammonia vapour and sturdy enough to be maneuvered with a needle. SXRD and MD simulation suggested π-π stacking behind the self-assembly process.
OLEDs | Hot Paper
Solution-Processable Pure-Red Multiple Resonance-induced Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence Emitter for Organic Light-Emitting Diode with External Quantum Efficiency over 20 %
- First Published: 13 December 2022
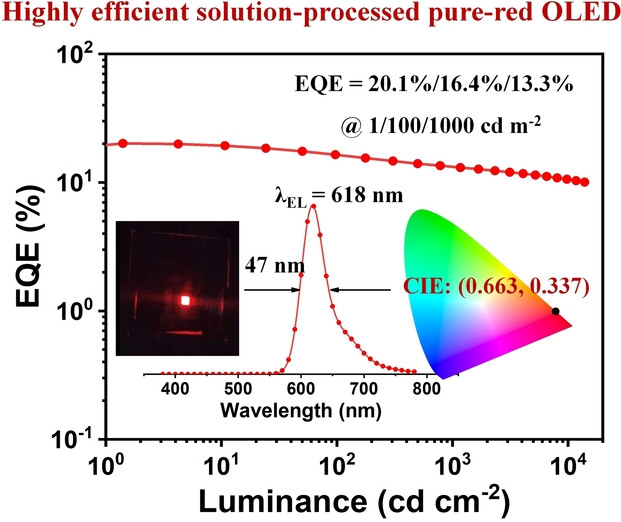
An universal strategy was proposed to develop red multiple resonance thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters by introducing auxiliary donor and acceptor moieties into the HOMO and LUMO distributed positions of B,N-containing multiple resonance skeleton simultaneously. The solution-processable pure-red OLED exhibits a state-of-the-art performance with external quantum efficiency over 20 %, high color purity and good operational lifetime.
Oxygen Evolution Reaction | Hot Paper
Non-Kinetic Effects Convolute Activity and Tafel Analysis for the Alkaline Oxygen Evolution Reaction on NiFeOOH Electrocatalysts
- First Published: 19 December 2022
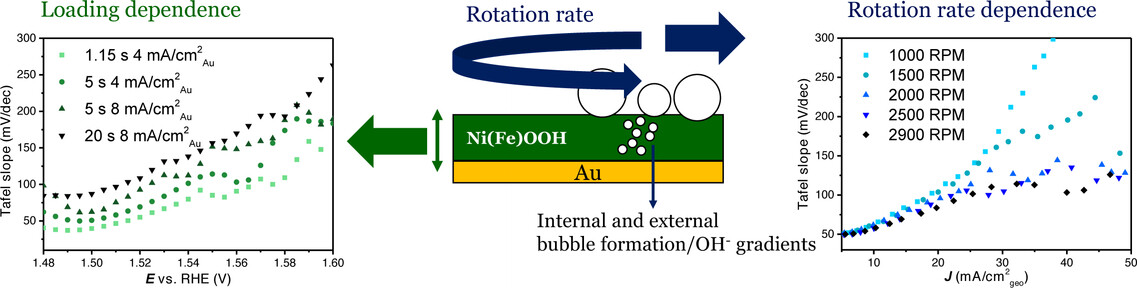
We studied NiFeOOH catalysts for the alkaline oxygen evolution reaction (OER) with different loading, varying rotation rate, hydroxide concentration and with and without sonication. We show that the Tafel slope initially is ≈30 mV dec−1 for NiFeOOH in 0.05–0.2 M KOH, and at higher polarization the Tafel slope continually increases due to bubbles, potential-dependent changes in ohmic resistance, and (internal) OH− gradients.
Luminescent Materials | Very Important Paper
A Melt-Quenched Luminescent Glass of an Organic–Inorganic Manganese Halide as a Large-Area Scintillator for Radiation Detection
- First Published: 11 December 2022
Atropisomerism
A Dynamic Kinetic Resolution Approach to Axially Chiral Diaryl Ethers by Catalytic Atroposelective Transfer Hydrogenation
- First Published: 19 December 2022
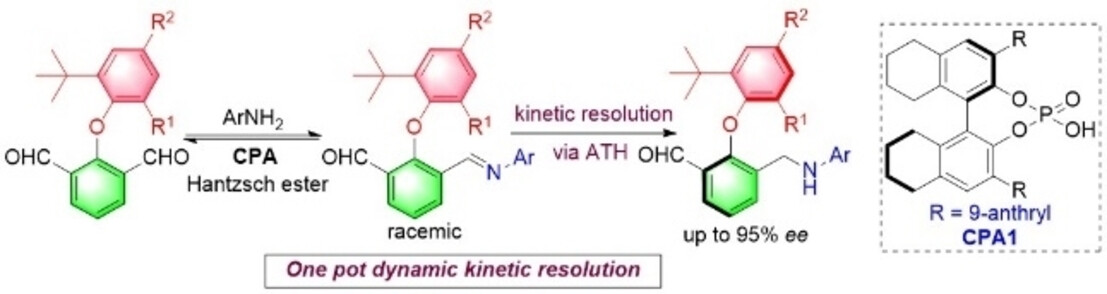
A dynamic kinetic resolution approach was developed for the synthesis of axially chiral diaryl ethers via a Brønsted acid catalyzed atroposelective transfer hydrogenation (ATH) reaction of dicarbaldehydes with anilines. The chiral phosphoric acid catalyzed dynamic kinetic resolution strategy has provided a modular platform for the synthesis of axially chiral diaryl ethers.
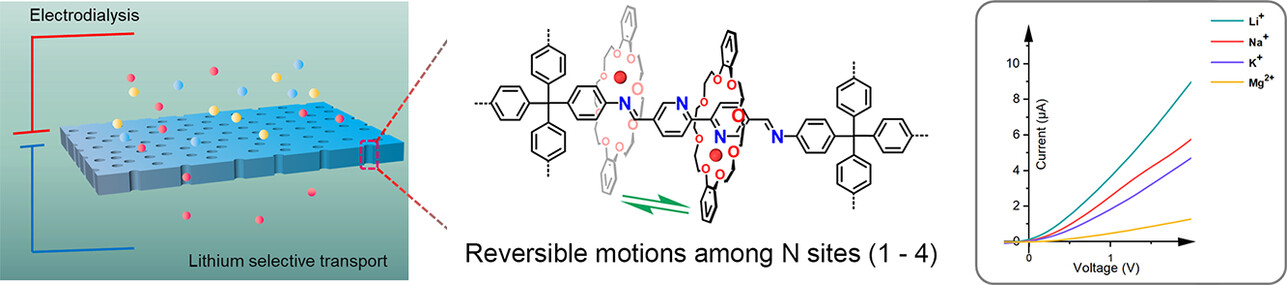
Porous Organic Frameworks
Constructing Mechanical Shuttles in a Three-dimensional (3D) Porous Architecture for Selective Transport of Lithium Ions
- First Published: 08 December 2022
Plasmonic Catalysis
Superlattice-based Plasmonic Catalysis: Concentrating Light at the Nanoscale to Drive Efficient Nitrogen-to-Ammonia Fixation at Ambient Conditions
- First Published: 12 December 2022
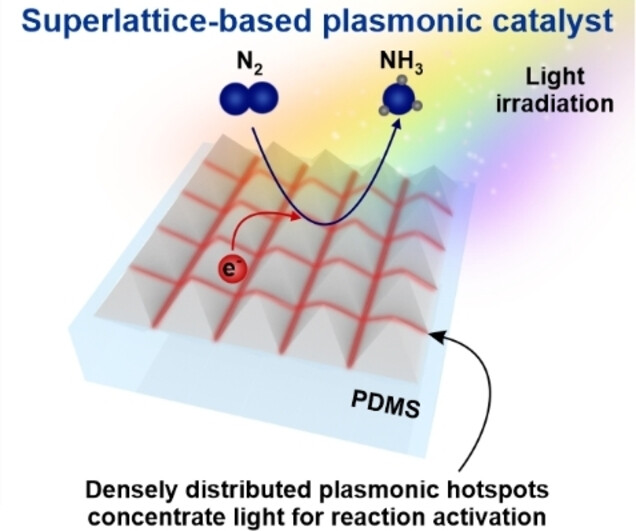
Organizing anisotropic plasmonic nanoparticles into a two-dimensional superlattice is important to intensify the electromagnetic field at both the single-particle and ensemble levels for efficient nitrogen-to-ammonia photoconversion at ambient conditions. Our unique superlattice-based plasmonic catalysts boost the ammonia formation rate and apparent quantum efficiency by up to ≈15-fold and ≈103-fold, respectively, when compared to traditional photocatalytic and hybrid plasmonic-photocatalytic designs.
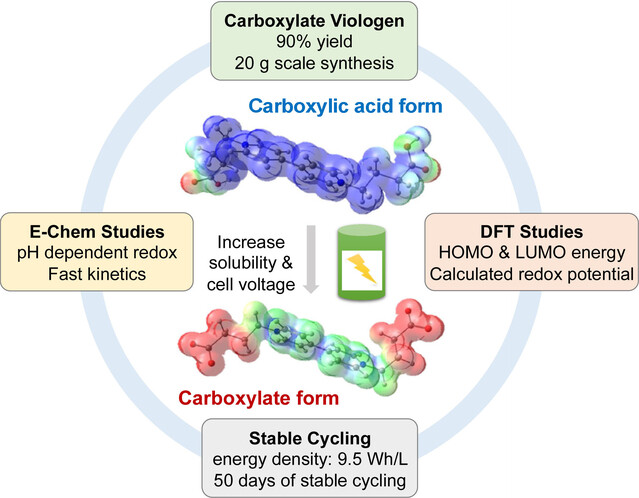
Redox Flow Batteries
A Highly Stable, Capacity Dense Carboxylate Viologen Anolyte towards Long-Duration Energy Storage
- First Published: 16 December 2022
Metal-Organic Frameworks | Hot Paper
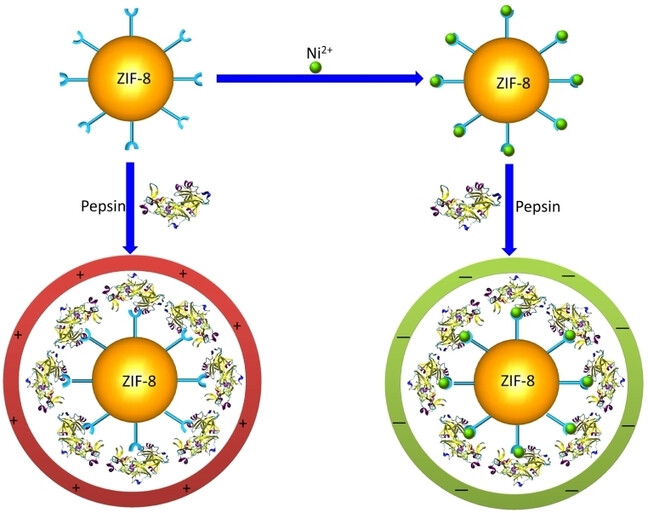
Enhanced Activity of Enzyme Immobilized on Hydrophobic ZIF-8 Modified by Ni2+ Ions
- First Published: 19 December 2022
CO2 Hydrogenation
Probing the Nature of Zinc in Copper-Zinc-Zirconium Catalysts by Operando Spectroscopies for CO2 Hydrogenation to Methanol
- First Published: 12 December 2022
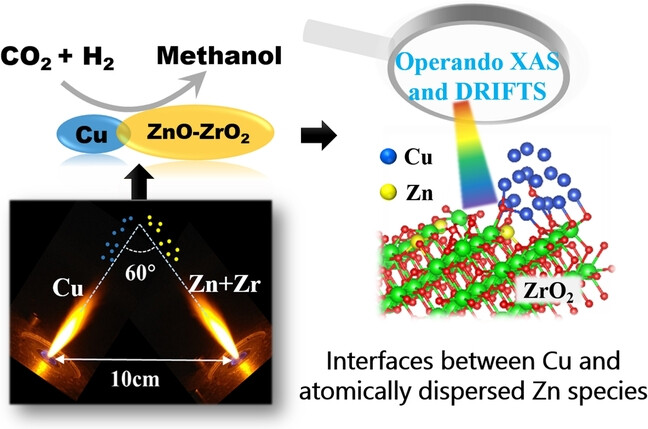
In Cu−Zn−Zr catalysts, interfaces between Cu and atomically dispersed Zn species are established by separating Zn and Zr from Cu in the double nozzles utilized during flame spray pyrolysis (FSP). Operando spectroscopies confirm that the structure is created during CO2 hydrogenation, and it boosts methanol production by suppressing formate decomposition to CO and decreasing the H2 dissociation energy.
Inorganic Electronic Structures
An Anomalous Electron Configuration Among 3d Transition Metal Atoms
- First Published: 20 December 2022
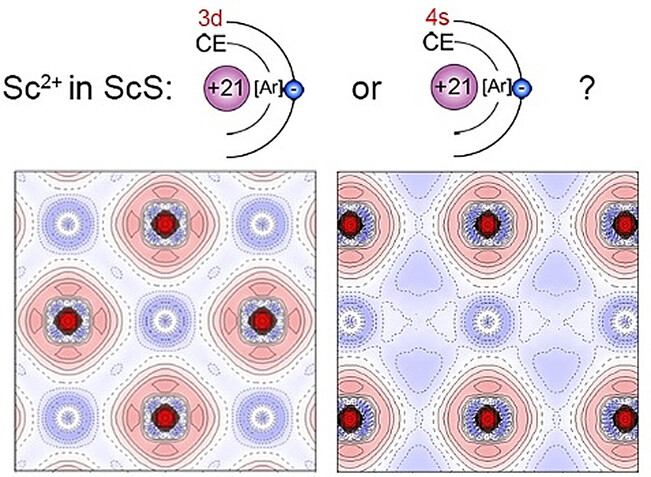
A special [Ar]4s1 electron configuration was revealed for Sc2+ in ScS, with no typical 3d orbital features and a bare population of t2g orbital from electron density reconstruction and orbital population analysis. Our work should be the first to report such anomalous electron structure with preferred 4s over 3d orbital for 3d transition metal atoms and may provide a new method to modulate material properties via artificial orbital adjustment.
Strained Molecules
Strain-Release Driven Epoxidation and Aziridination of Bicyclo[1.1.0]butanes via Palladium Catalyzed σ-Bond Nucleopalladation
- First Published: 12 December 2022
![Strain-Release Driven Epoxidation and Aziridination of Bicyclo[1.1.0]butanes via Palladium Catalyzed σ-Bond Nucleopalladation](/cms/asset/040f37a0-79da-4c1d-924e-b2d030fb292c/ange202217064-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Strained spirocyclic epoxides and aziridines were synthesized via three-component coupling between in situ generated 1-lithio bicyclo [1.1.0]butane, a broad variety of ketones, aldehydes and N-tosyl imines, and aryl triflates. The key step involves a highly diastereoselective palladium-catalyzed C−C σ-bond alkoxyarylation (or aminoarylation) of bicyclo [1.1.0]butyl carbinolate intermediates.
Fluorine Chemistry
Transition-Metal-Free Controllable Single and Double Difluoromethylene Formal Insertions into C−H Bonds of Aldehydes with TMSCF2Br
- First Published: 14 December 2022
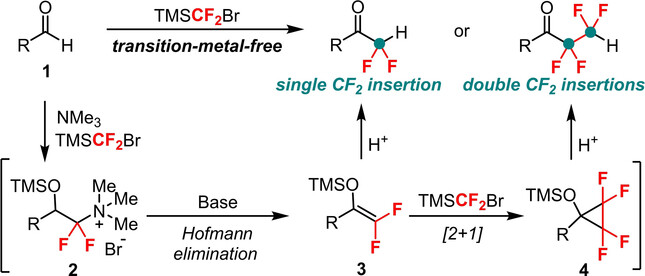
The unprecedented controllable single and double difluoromethylene (CF2) formal insertions into C−H bonds of aldehydes under transition-metal-free conditions with nearly full selectivity has been achieved, in which the well-defined formation of 2,2-difluoroenolsilyl ether and 2,2,3,3-tetrafluorocyclopropanolsilyl ether intermediates using difluorocarbene reagent TMSCF2Br (TMS=trimethylsilyl) is the key to the success.
Luminescence
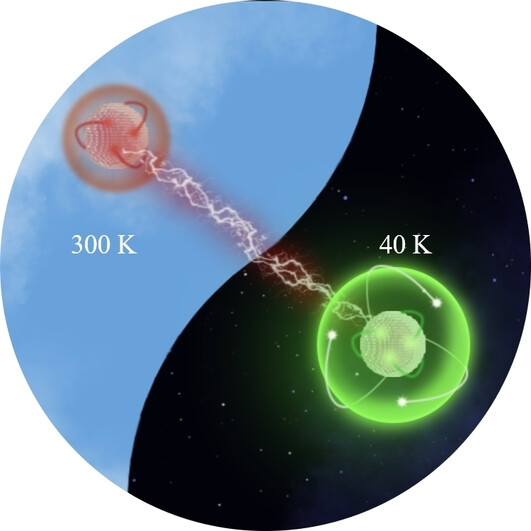
Significant Enhancement of the Upconversion Emission in Highly Er3+-Doped Nanoparticles at Cryogenic Temperatures
- First Published: 13 December 2022
Mesoporous Materials | Hot Paper
Stiffness-Transformable Nanoplatforms Responsive to the Tumor Microenvironment for Enhanced Tumor Therapeutic Efficacy
- First Published: 16 December 2022
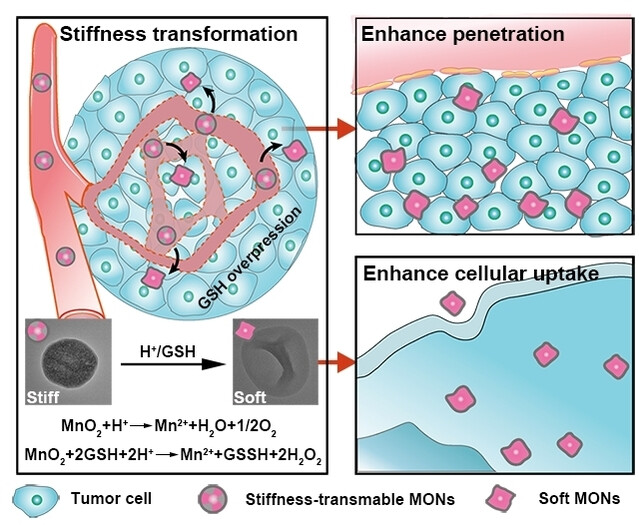
Stiffness-transformable nanoplatforms in response to a simulated tumor microenvironment (TME) were designed. The nanoplatforms maintain quasi-spherical shape in normal physiological conditions, which effectively reduces macrophage uptake and nonspecific liver/spleen distributions, and transform to soft nanocapsules in a TME, thus enhancing tumor penetration, cellular uptake and tumor accumulation.
Electrochemistry
Organoboron Reagent-Controlled Selective (Deutero)Hydrodefluorination
- First Published: 16 December 2022
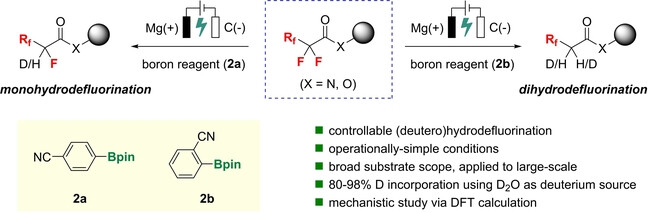
We herein reported an electrochemical selective (deutero)hydrodefluorination reaction of trifluoroacetamides. The reaction which exhibits a remarkable chemoselectivity control and delivers (deuterium-labeled) CF2H- and CFH2-products in good yields with high level of deuterium incorporation, respectively, is enabled by the addition of different organoboron sources and (deuterated)water as the deuterium or hydrogen source.
Polymer Films | Very Important Paper
Switchable and Highly Robust Ultralong Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Polymer-Based Transparent Films with Three-Dimensional Covalent Networks for Erasable Light Printing
- First Published: 13 December 2022
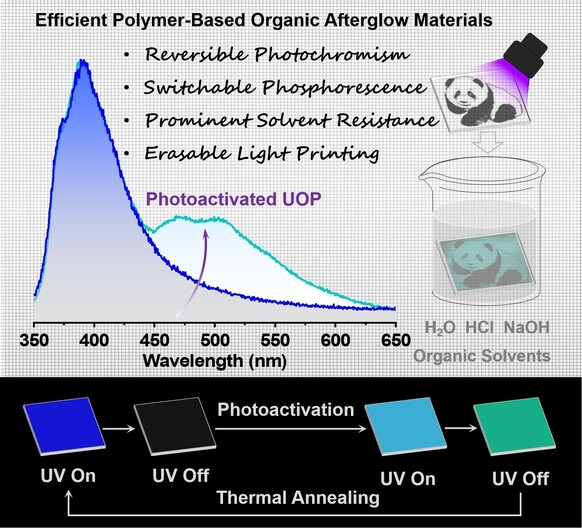
A series of efficient phosphorescence materials were developed by embedding phenothiazine, phenoxazine, and 10-ethyl-10H-phenoxazine into epoxy polymers. It is found that the polymer film involving phenoxazine shows reversible photochromism, switchable ultralong organic phosphorescence, and prominent water and chemical resistance simultaneously. In addition, its potential application in erasable light printing has also been demonstrated.
Metal-Organic Frameworks
Real-Time In Situ Volatile Organic Compound Sensing by a Dual-Emissive Polynuclear Ln-MOF with Pronounced LnIII Luminescence Response
- First Published: 13 December 2022
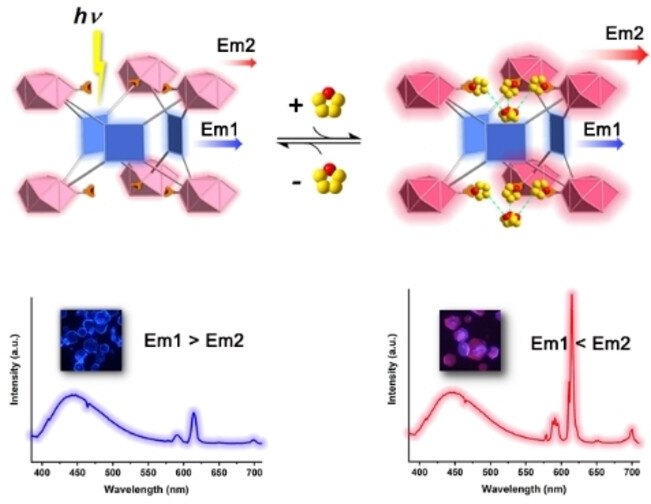
A dual-emissive polynuclear Eu-MOF enriched with abundant potential open metal sites was constructed. In terms of a novel recognition-transduction protocol, this material realized real-time in situ visual detection of THF vapor (<1 s) while showing a quantitative ratiometric response to vapor pressure with an ultralow limit of detection.
Li Metal Batteries | Hot Paper
A Stable Solid Polymer Electrolyte for Lithium Metal Battery with Electronically Conductive Fillers
- First Published: 12 December 2022
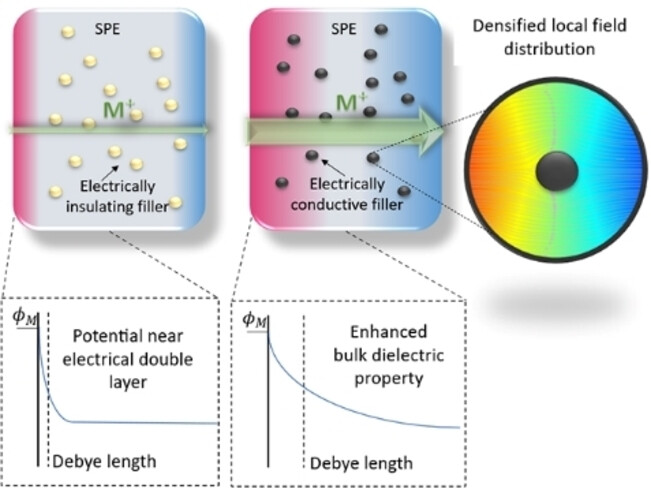
Electronically conductive materials are generally avoided in electrolyte designs to prevent charge leakage. However, it is found that with small amount of carbon filler, lower overpotential and better cycling stability could be achieved with lithium metal battery. This work proposes a novel perspective of the positive effect of introducing electronically conductive fillers by homogenizing the electric field distribution.
Organic Luminescence
Color-Tunable Dual-Mode Organic Afterglow from Classical Aggregation-Caused Quenching Compounds for White-Light-Manipulated Anti-Counterfeiting
- First Published: 20 December 2022
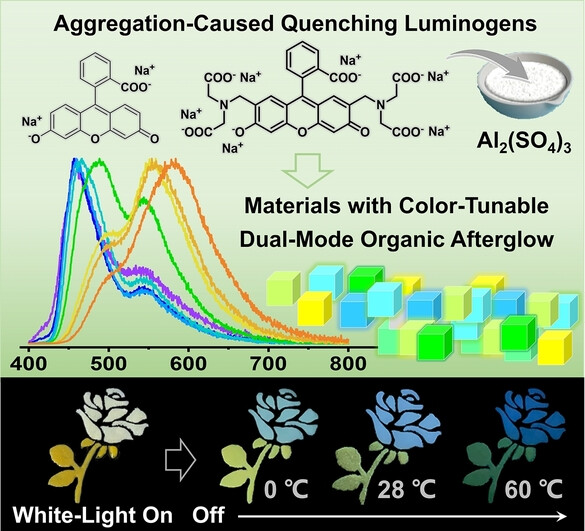
Luminescent materials with dual-mode organic afterglow composed of persistent thermally activated delayed fluorescence and ultralong organic phosphorescence were developed by doping fluorescein sodium and calcein sodium into aluminum sulfate, respectively. It is found that their afterglow can be excited by ultraviolet and white light, and the persistent luminescence colors can be tuned by varying temperatures and dopant concentrations.
Artificial Photosynthesis | Hot Paper
Folding-Induced Promotion of Proton-Coupled Electron Transfers via Proximal Base for Light-Driven Water Oxidation
- First Published: 13 December 2022
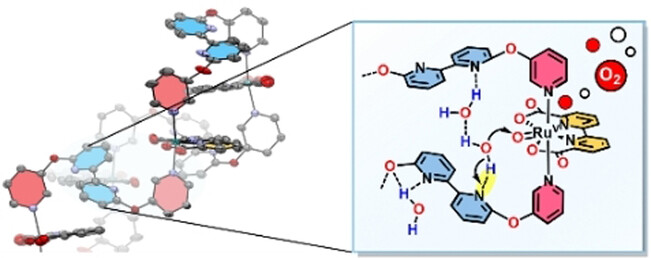
Structurally flexible, bipyridine-containing Ru macrocyles have shown a remarkable increase in turnover per Ru center in visible-light-driven water oxidation catalysis. Conformational studies in the solid state revealed an increased tendency of the auxiliary base close to the active centers of the larger complexes to undergo intramolecular folding and preorganization, which facilitates proton abstraction in the water nucleophilic attack (WNA) pathway.
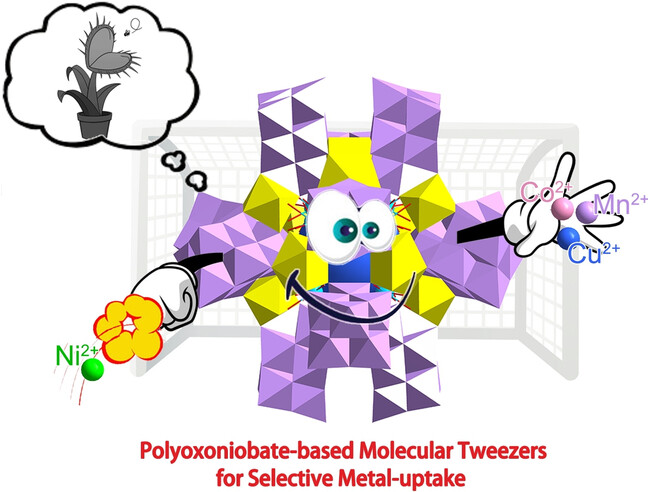
Polyoxometalates
Giant Polyoxoniobate-Based Inorganic Molecular Tweezers: Metal Recognitions, Ion-Exchange Interactions and Mechanism Studies
- First Published: 09 December 2022
NLO Materials | Very Important Paper
Na2Ba[Na2Sn2S7]: Structural Tolerance Factor-Guided NLO Performance Improvement
- First Published: 21 December 2022
![Na2Ba[Na2Sn2S7]: Structural Tolerance Factor-Guided NLO Performance Improvement](/cms/asset/6891dc92-3b73-4e40-8779-d4ca19b3a7ed/ange202218048-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Guided by the relationships between the structural tolerance factor and the dopant concentration and second-order susceptibility, a better balance between Eg and SHG is realized in Na2Ba [Na2Sn2S7] 1, which exhibits a large Eg of 3.42 eV and excellent NLO properties (SHG: 1.5×AGS; laser-induced damage threshold: 12×AGS), representing the best performance among the known Hg- or As-free sulfides to date.
Biokatalyse
Aerobe C-N-Bindungsknüpfung durch enzymatische Nitroso-En-Reaktionen
- First Published: 05 December 2022
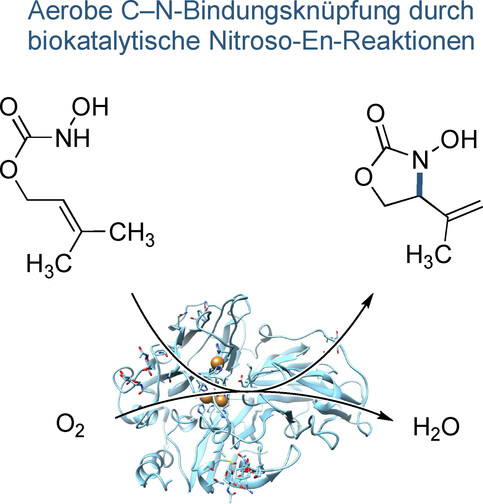
Katalytische Promiskuität ermöglicht eine neue synthetische Anwendung von Peroxidasen und Laccasen, welche über einen Nitroso-En-Mechanismus die C-N-Bindungsknüpfungen von acylierten Hydroxylamin-Derivaten vermitteln. Die ungewöhnliche biokatalytische Methode zur formalen, allylischen C-H-Aktivierung nutzt Luft als terminales Oxidationsmittel und liefert hohe Ausbeuten in intra- wie intermolekularen Aminierung.
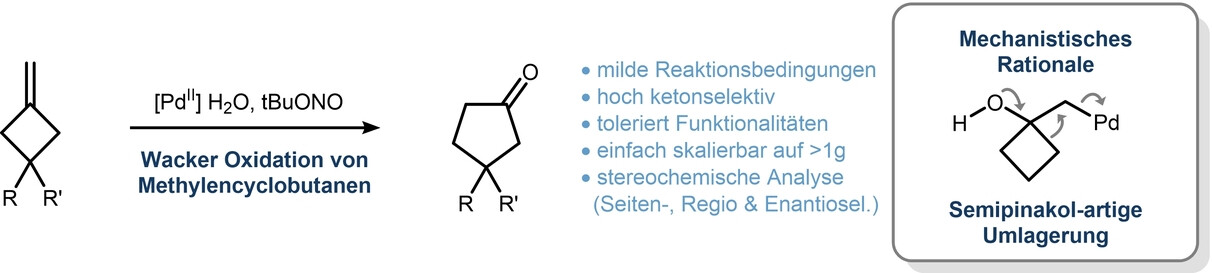
Homogene Katalyse
Wacker Oxidation von Methylencyclobutanen: Umfang und Selektivität in einer ungewöhnlichen Umgebung
- First Published: 23 November 2022
Glykomimetika | Hot Paper
Neutralisation der Auswirkungen des Virulenzfaktors LecA aus Pseudomonas aeruginosa auf Humanzellen durch neue glykomimetische Inhibitoren
- First Published: 18 November 2022
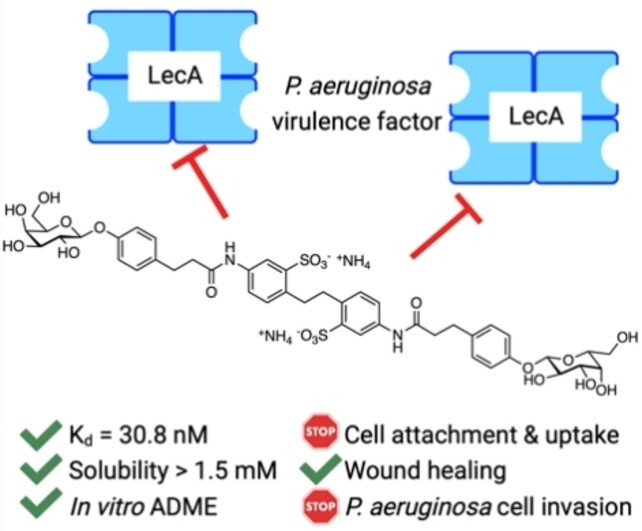
Inhibition of the bacterial lectin LecA is an alternative option to treat infections with the ESKAPE pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Optimization of divalent LecA ligands yielded ligands with good drug-like properties and high potency. Compound evaluation in functional cellular assays showed their ability to inhibit LecA-mediated virulence, demonstrating their suitability as pathoblockers.
Supramolekulare Chemie
Die Diantimonkomplexe [CpR2Mo2(CO)4(μ,η2-Sb2)] (CpR=C5H5, C5H4tBu) als unerwartete stabilisierende Liganden von Silber(I)n (n=1–4)-Monomeren, -Dimeren und -Ketten
- First Published: 05 December 2022
![Die Diantimonkomplexe [CpR2Mo2(CO)4(μ,η2-Sb2)] (CpR=C5H5, C5H4tBu) als unerwartete stabilisierende Liganden von Silber(I)n (n=1–4)-Monomeren, -Dimeren und -Ketten](/cms/asset/96a70706-f33c-41bb-ae6a-523d0747247c/ange202215650-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Die erste Studie zum Koordinationsverhalten tetraedrischer Sb-Donor-Komplexe gegenüber AgI-Salzen ergab 12 neuartige supramolekulare Aggregate als Monomere, Dimere sowie drei- und viergliedrige Ketten von AgI-Ionen. Basierend auf zahlreichen Lösungsstudien wurden Wege der Aggregierungsprozesse beschrieben und das Vorhandensein argentophiler Wechselwirkungen in Verbindungen, die zwei oder mehr AgI-Ionen enthalten, wurde mit Hilfe von DFT-Rechnungen bestätigt.