Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER
Cover Image, Volume 233, Number 5, May 2018
- Page: i
- First Published: 08 February 2018
ISSUE INFORMATION
Table of Contents, Editor's Choice, Highlights
- Pages: 3685-3694
- First Published: 08 February 2018
RAPID COMMUNICATIONS
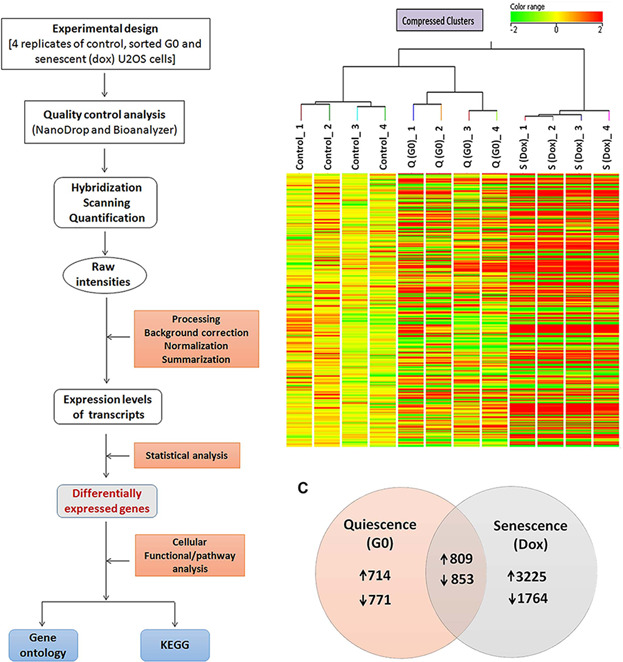
Differentially regulated gene expression in quiescence versus senescence and identification of ARID5A as a quiescence associated marker
- Pages: 3695-3712
- First Published: 17 October 2017
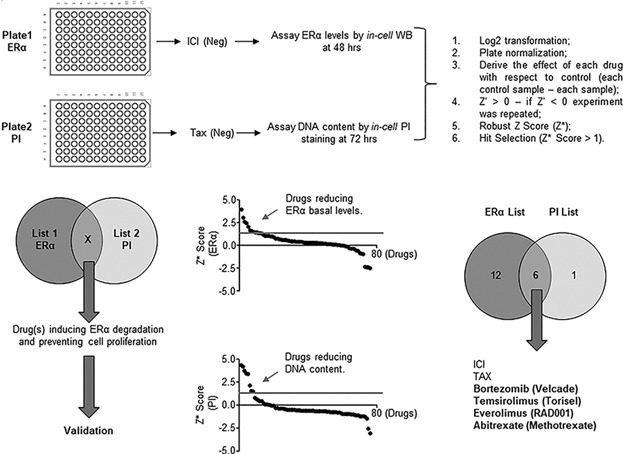
A high throughput method to study the physiology of E2:ERα signaling in breast cancer cells
- Pages: 3713-3722
- First Published: 01 November 2017
MINI-REVIEWS
Humanized mouse models: Application to human diseases
- Pages: 3723-3728
- First Published: 09 June 2017
Humanized mice are superior models to rodents for preclinical studies. Several human diseases including cancer, allergy, and GVHD can be recapitulated using humanized mice.
Aberrant miRNA promoter methylation and EMT-involving miRNAs in breast cancer metastasis: Diagnosis and therapeutic implications
- Pages: 3729-3744
- First Published: 03 August 2017
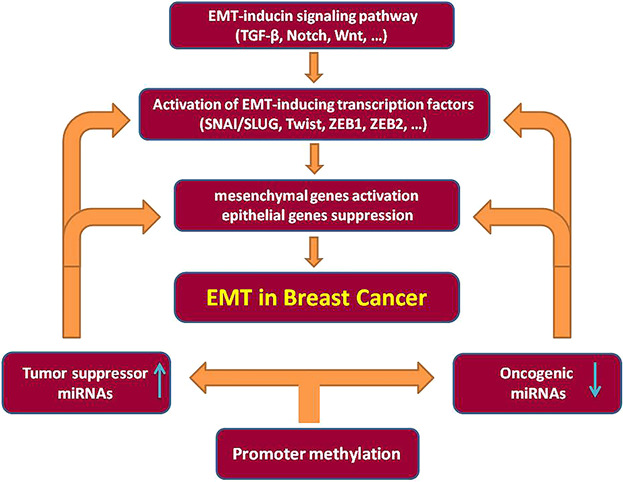
Breast cancer (BC) is the most prevalent cancer in women worldwide. Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) enables the invasion of metastatic cancer cells. Recent evidence demonstrates that aberrantly DNA methylation of miRNAs controls miRNA expression. Therefore, epigenetic controlling of EMT-involving miRNAs are important in diagnosis and therapeutic of BC.
The role of mitochondrial ROS in antibacterial immunity
- Pages: 3745-3754
- First Published: 03 August 2017
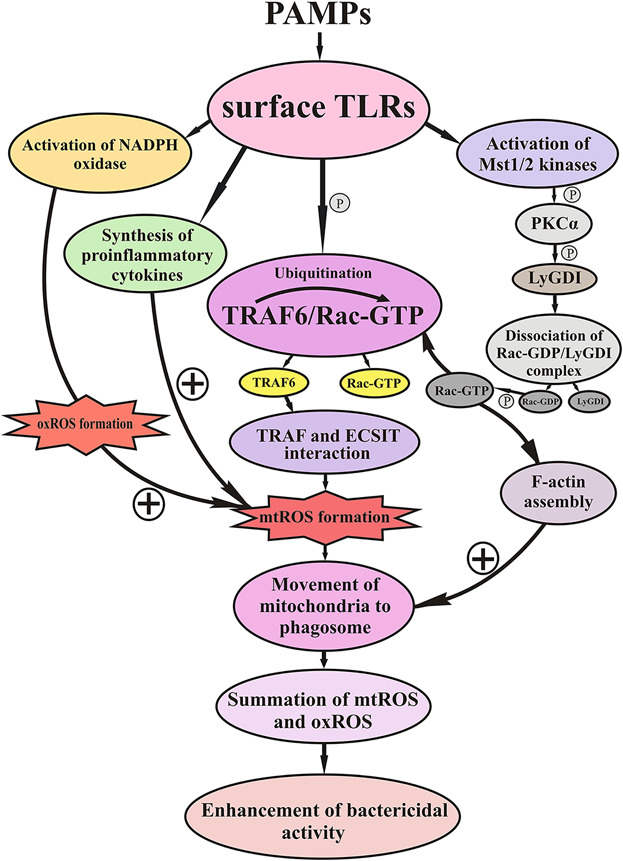
The present mini-review summarizes the most recent data on the role of mtROS in the antibacterial immunity. The principles of mtROS formation and possible mechanisms of their generation under the activation of innate immunity are highlighted in this review. We also speculate on the possibilities of using activators of mtROS production in clinical practice.
Mesenchymal stem cell differentiation: Control by calcium-activated potassium channels
- Pages: 3755-3768
- First Published: 04 August 2017
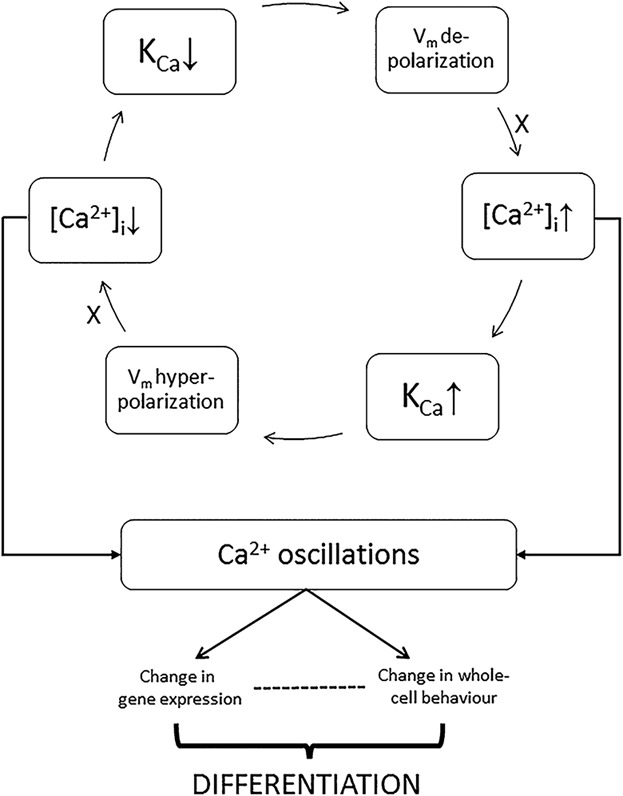
In this review, we evaluate the involvement of calcium-activated potassium channel subtypes in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. We propose a new model showing how intracellular calcium and membrane potential oscillations are generated and can contribute dynamically to the differentiation process. Finally, we highlight various mechanisms, including network interactions, fine tuning terminal differentiation.
Osteocalcin-dependent regulation of glucose metabolism and fertility: Skeletal implications for the development of insulin resistance
- Pages: 3769-3783
- First Published: 23 August 2017
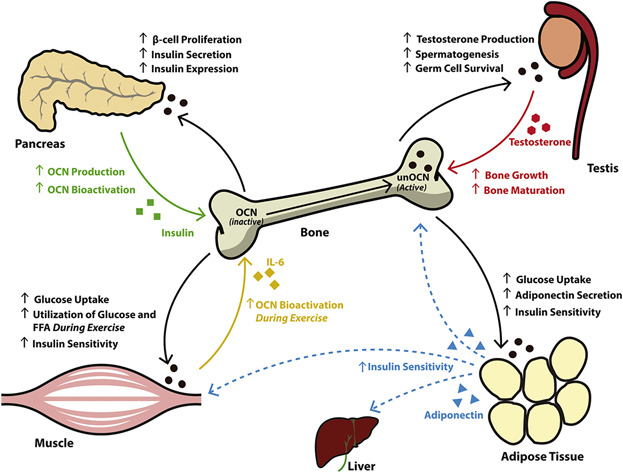
The skeleton has recently emerged as a critical insulin target tissue that regulates whole body glucose metabolism and male reproductive function. While our understanding of these new skeletal functions remains in its infancy, the bone-specific protein, osteocalcin, has been shown to be centrally involved in both processes. This review examines recent data emerging from transgenic mouse models and human clinical studies which have revealed a novel pancreas-bone-testis regulatory axis, and discusses the potential role of bone specific mTORC1 signaling in the regulation of systemic glucose metabolism.
Key-genes regulating the liposecretion process of mature adipocytes
- Pages: 3784-3793
- First Published: 19 September 2017
This review show some potential molecular mechanisms involved into the liposecretion process of human mature adipocytes.
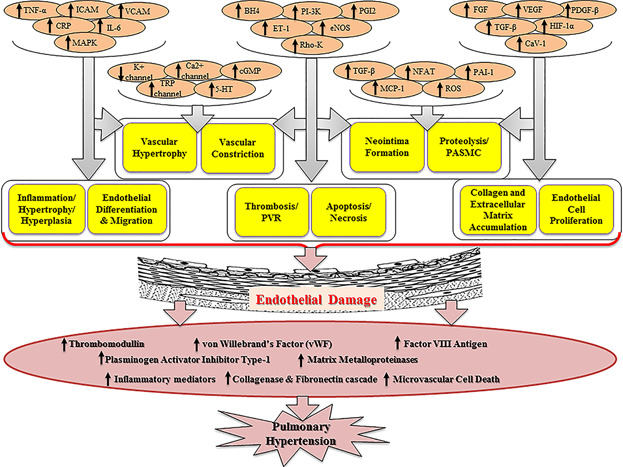
Pulmonary hypertension: Molecular aspects of current therapeutic intervention and future direction
- Pages: 3794-3804
- First Published: 19 September 2017
FROM THE BENCH
Application of a novel bioreactor for in vivo engineering of pancreas tissue
- Pages: 3805-3816
- First Published: 13 May 2017
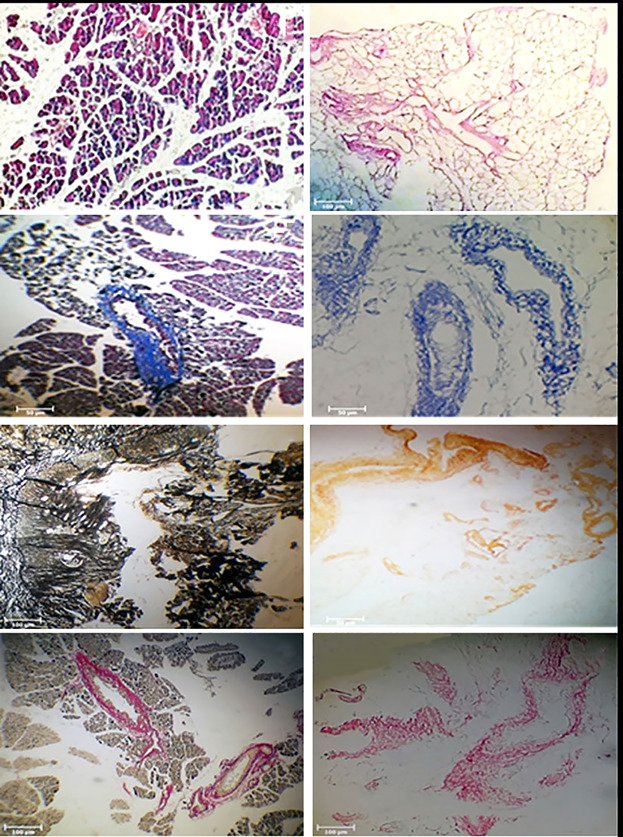
The current study was focused on bio-imitating the tissue engineering of the pancreas by employing an acellular pancreatic tissue as a non-immunogenic bioscaffold to be used as a novel surgical technique for in vivo tissue regeneration, as well as the unique utilization of the omentum as a bioreactor.
Establishment of in vitro model of corneal scar pathophysiology
- Pages: 3817-3830
- First Published: 28 June 2017
In the present study we attempted to develop an in vitro model of corneal scarring by simulating the myofibroblast differentiation of corneal keratocytes using a standardized cocktail of pro-fibrotic cytokines (TGF-β1, IL-6, and IL-8). The developed model can be used to acquire understanding about corneal scar pathophysiology and thus might be useful for designing the treatment modalities and efficacies for controlling scar formation.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Mesenchymal stem cells: A new platform for targeting suicide genes in cancer
- Pages: 3831-3845
- First Published: 13 July 2017
Current data indicate that cancer incidence is steadily increasing in the World. There is high mortality statistic available in current decades. All of these highlighted the urgent need for more safer and more effective therapies. One of the principal challenges along cancer treatment is how to destroy malignant tumors without damaging healthy cells. A new approach that shows great promise in this area is employment of a suicide gene. In this way, we need an appropriate carrier for therapeutic gene delivery specific to cancer site. The application of anti-cancer gene-expressing MSCs for targeted cancer therapy is a novel and promising strategy. MSCs with important characteristic such as strong tumor tropism, unlimited packaging capacity and unique immunologic tolerance, could overcome current obstacles and successfully deliver these suicide genes. Although MSCs have anticancer capacity but based on some reports could have positive role in tumor progression. Eventually more researches required to find novel insights into MSCs biology, potential clinical application, and molecular mechanism for homing to tumor site.
miRNAs and ovarian cancer: An overview
- Pages: 3846-3854
- First Published: 13 July 2017
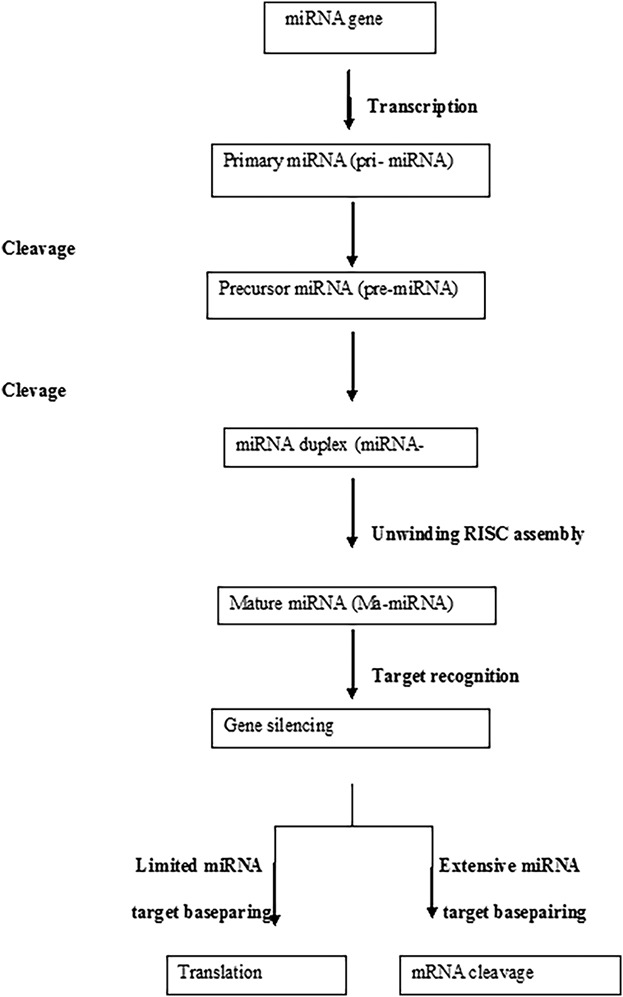
This review summarizes the current knowledge regarding the role of miRNAs expression in OC. It also provides information about potential clinical relevance of circulating miRNAs for OC diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics. The identification of functional targets for miRNAs represents a major obstacle in our understanding of microRNA function in OC, but significant progress is being made. The better understanding of the role of microRNA expression in ovarian cancer may provide new array for the detection, diagnosis, and therapy of the OC.
Basal progenitor cells bridge the development, malignant cancers, and multiple diseases of esophagus
- Pages: 3855-3866
- First Published: 04 August 2017
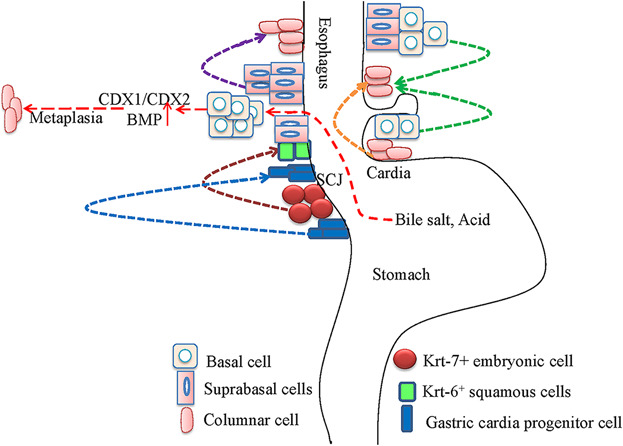
After abnormal regulation of these molecules in the basal cells of the esophagus occurs, multiple diseases, including esophageal atresia with or without tracheoesophageal fistula, Barrett esophagus, gastroesophageal reflux, and eosinophilic esophagitis, will take place as a result. Furthermore, expression changes of signal molecules or signal pathways in basal cells and the microenvironment around basal cells both can initiate the switch of malignant transformation.
Crosstalk of ER stress-mediated autophagy and ER-phagy: Involvement of UPR and the core autophagy machinery
- Pages: 3867-3874
- First Published: 04 August 2017
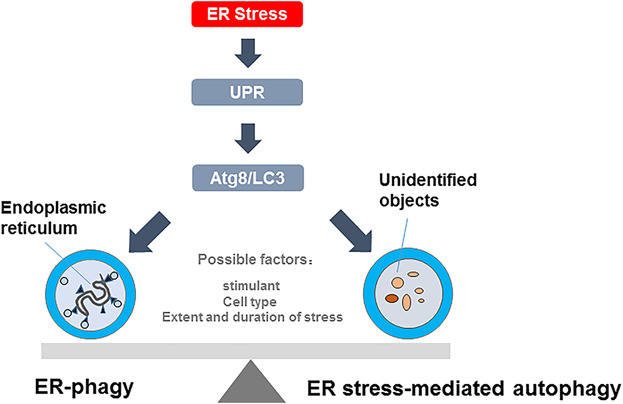
Under ER stress condition, the ER stress-mediated autophagy and ER-phagy can be activated, and both involved in UPR and the core autophagy machinery. However, the determined factors that control the changeover switch between ER stress-mediated autophagy and ER-phagy, are unclear. And we speculate that the type of cells and the extent of stimulation may be associated with the type of autophagy induced by ER stress.
CRISPR editing in biological and biomedical investigation
- Pages: 3875-3891
- First Published: 08 August 2017
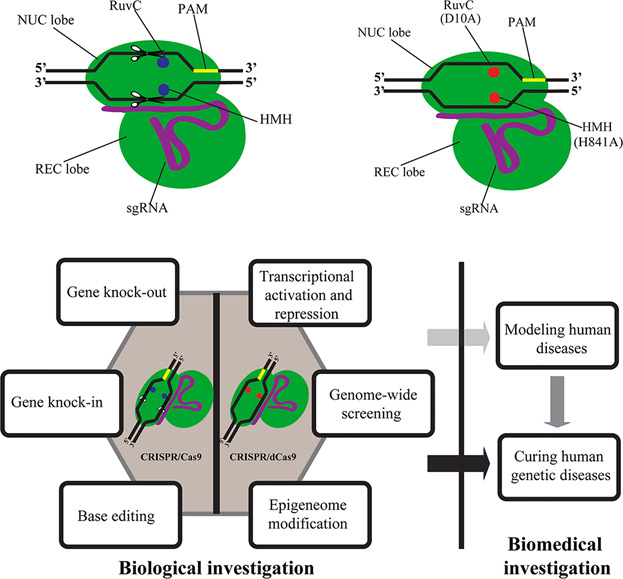
In this prospect article, after highlighting recent developments of CRISPR systems, we outline different applications and current limitations of CRISPR use in biological and biomedical investigation. Finally, we provide a perspective for future development and potential risks of this multifunctional technology.
Apelin/APJ system: A novel potential therapy target for kidney disease
- Pages: 3892-3900
- First Published: 10 August 2017
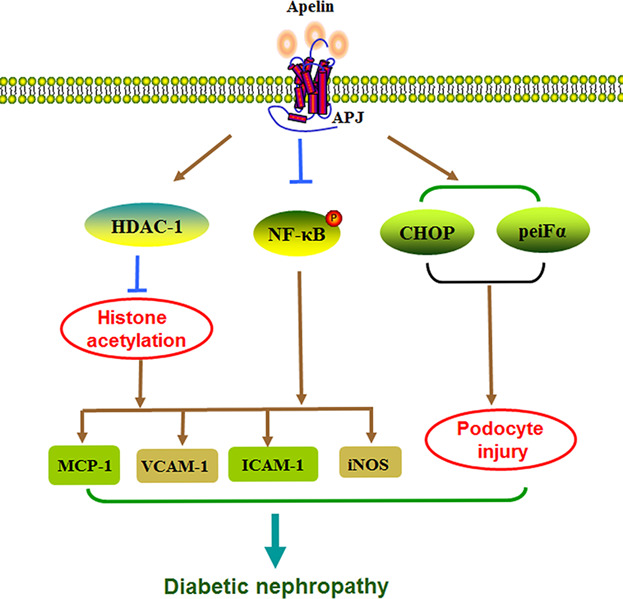
Studies show that apelin mRNA is highly expressed in the inner stripe of kidney outer medulla, which plays an important role in process of water and sodium balance. Additionally, more studies also indicate that apelin/APJ system may exerts a broad range of activities in kidney. Therefore, we review the role of apelin/APJ system in kidney diseases such as renal fibrosis, renal ischemia/reperfusion injury, diabetic nephropathy, polycystic kidney disease, and hemodialysis.
TRPC3-mediated Ca2+ signals as a promising strategy to boost therapeutic angiogenesis in failing hearts: The role of autologous endothelial colony forming cells
- Pages: 3901-3917
- First Published: 17 August 2017

Endothelial colony forming cells (ECFCs) isolated from peripheral blood display (PB-ECFCs) a lower pro-angiogenic response to VEGF as compared to those deriving from umbilical cord blood (UCB-ECFCs). The Ca2+ permeable channel TRPC3 initiates VEGF-induced pro-angiogenic Ca2+ oscillations in UCB-ECFCs. We discuss the possibility to use TRPC3 to improve the reparative potential of autlogous ECFCs in cell based therapy of failing heart.
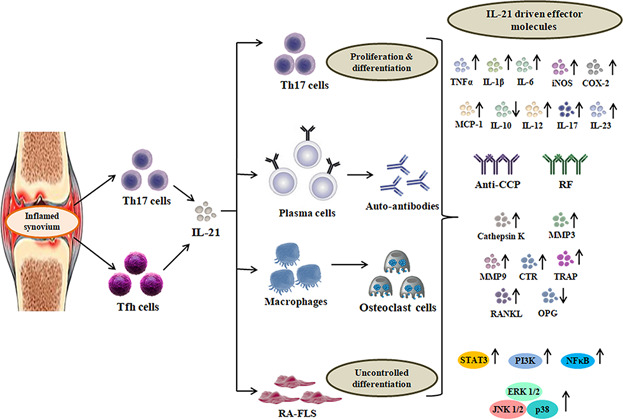
Multifaceted role of IL-21 in rheumatoid arthritis: Current understanding and future perspectives
- Pages: 3918-3928
- First Published: 18 August 2017
Mammalian target of rapamycin as a therapeutic target in osteoporosis
- Pages: 3929-3944
- First Published: 23 August 2017
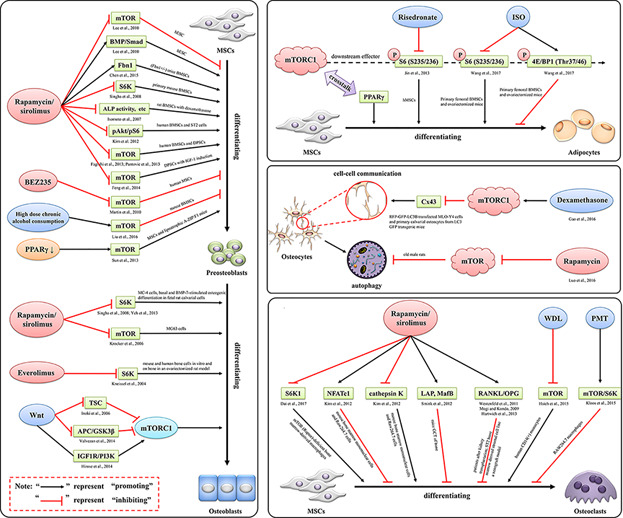
The activation/inhibition of mTOR signaling can positively/negatively regulate bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs)/osteoblasts-mediated bone formation, adipogenic differentiation, osteocytes homeostasis, and osteoclasts-mediated bone resorption, which result in the changes of bone homeostasis, thereby resulting in or protect against osteoporosis.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE
The inhibitory effect in Fraxinellone on oxidative stress-induced senescence correlates with AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent autophagy restoration
- Pages: 3945-3954
- First Published: 08 September 2017
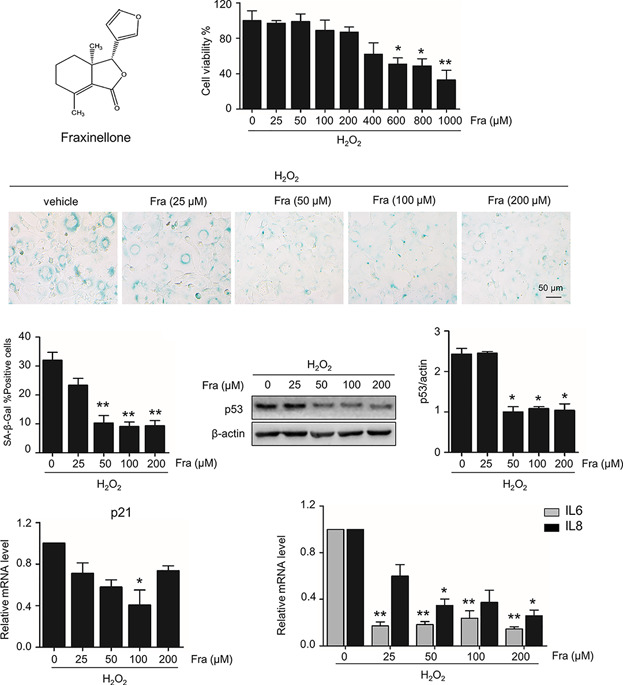
We found that fraxinellone administration caused growth arrest and certainly repressed the activity of senescence-associated β-galactosidase as well as the expression of senescence-associated genes. Interestingly, this effect of fraxinellone is closely correlated with the restoration of impaired autophagy and the activation of AMPK. Notably, fraxinellone reacts in an AMPK-dependent but mTORC1-independent manner.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Adult-onset brain tumors and neurodegeneration: Are polyphenols protective?
- Pages: 3955-3967
- First Published: 08 September 2017
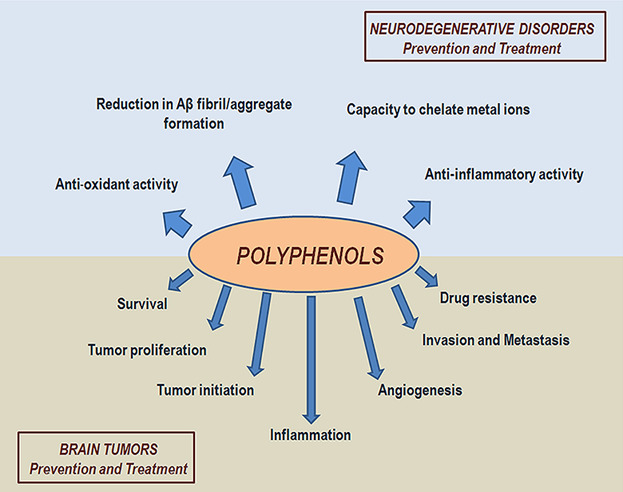
NDs and tumors are severe, disabling, progressive, and often incurable conditions, and represent a pressing problem in terms of human suffering and economic costs to the healthcare systems. Recently, the scientific community has focused on the beneficial effects of dietary antioxidant classes, such as polyphenols, in neurodegeneration and tumor prevention. Pre-clinical and clinical evidence shows that polyphenolic compounds are safe and able to interact in synergy with commonly used therapeutic treatment.
Comparison of genome-wide analysis techniques to DNA methylation analysis in human cancer
- Pages: 3968-3981
- First Published: 09 September 2017
Various commonly conducted techniques for this evaluation are reviewed in this paper. We provided a comparative description of the procedures, advantages, and drawbacks of genome-wide DNA methylation analysis methods and biological applications.
Functional role of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chronic neurodegenerative diseases
- Pages: 3982-3999
- First Published: 19 September 2017
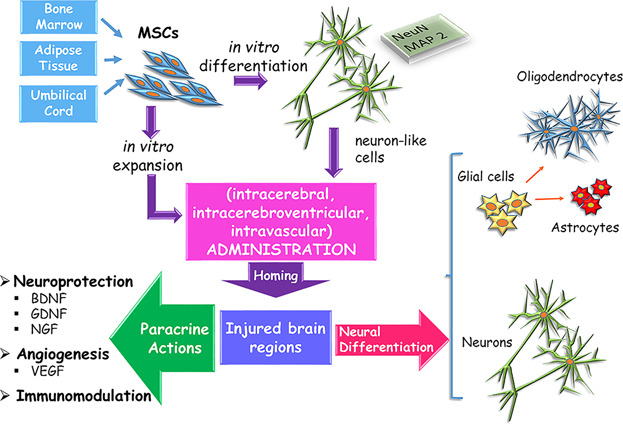
The review focuses on studies using Mesenchymal Stem Cells in therapeutic strategies for chronic neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Huntington's Disease, and Parkinson's Disease. The main findings obtained by in vitro and in vivo experiments, as well as in clinical trials are outlined. Possible stem cell mediated mechanisms of action are discussed.
Role of viruses in gastrointestinal cancer
- Pages: 4000-4014
- First Published: 19 September 2017
Gastrointestinal cancers are a global public health problem, which represent a vast majority of all cancer-caused deaths in both men and women. So in this respect, the present review has focused on the existing literature on the subject of viral involvement in gastrointestinal tumorgenesis.
Melatonin application in targeting oxidative-induced liver injuries: A review
- Pages: 4015-4032
- First Published: 12 October 2017
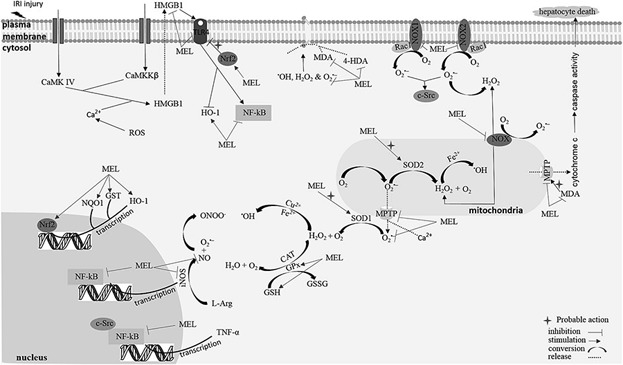
Melatonin is one of the best antioxidants that protects liver. Melatonin exerts its antioxidative function directly through its radical scavenging ability and indirectly through stimulation of antioxidant enzymes. This indoleamine is also an effective and promising antioxidative choice for targeting liver IRI, NAFLD, NASH, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and HCC.
Genetic and epigenetic factors influencing vitamin D status
- Pages: 4033-4043
- First Published: 14 October 2017
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
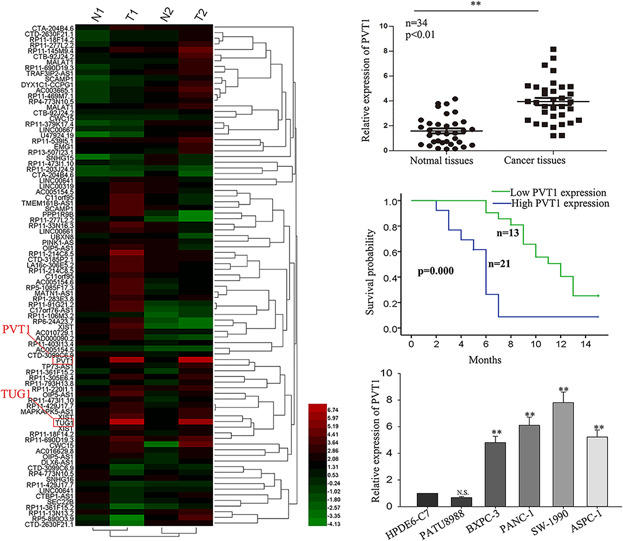
LncRNA-PVT1 promotes pancreatic cancer cells proliferation and migration through acting as a molecular sponge to regulate miR-448
- Pages: 4044-4055
- First Published: 28 June 2017
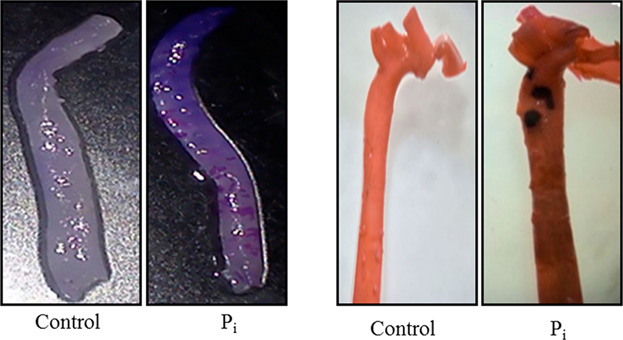
Characterization and assessment of potential microRNAs involved in phosphate-induced aortic calcification
- Pages: 4056-4067
- First Published: 04 August 2017
Systematic-analysis of mRNA expression profiles in skeletal muscle of patients with type II diabetes: The glucocorticoid was central in pathogenesis
- Pages: 4068-4076
- First Published: 08 September 2017
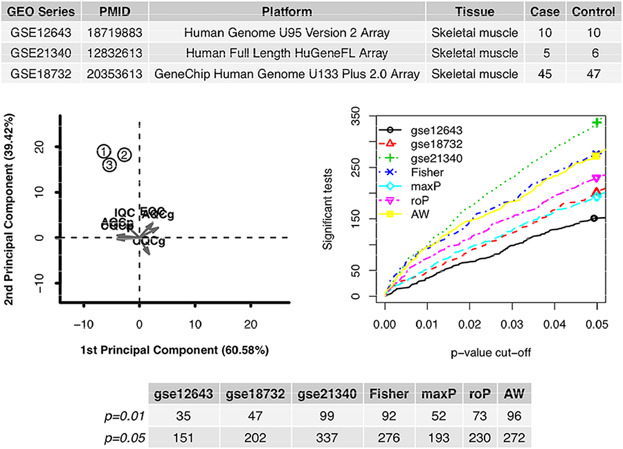
We identified 96 differentially expressed genes in patients with type II diabetes and these genes were enriched in the response to glucocorticoid. Seven genes belonging to this term, including UBE2L3, PTPRU, UCP3, TFAP4, CDKN1A, ATP2B1, and ZFP36L1, might play critical role in the progression of diabetes and they might perform as targets of treatment. The network-based analysis also suggested the existed drug might also work for diabetes.
Bone morphogenetic protein-7 inhibits endothelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary artery endothelial cell under hypoxia
- Pages: 4077-4090
- First Published: 19 September 2017
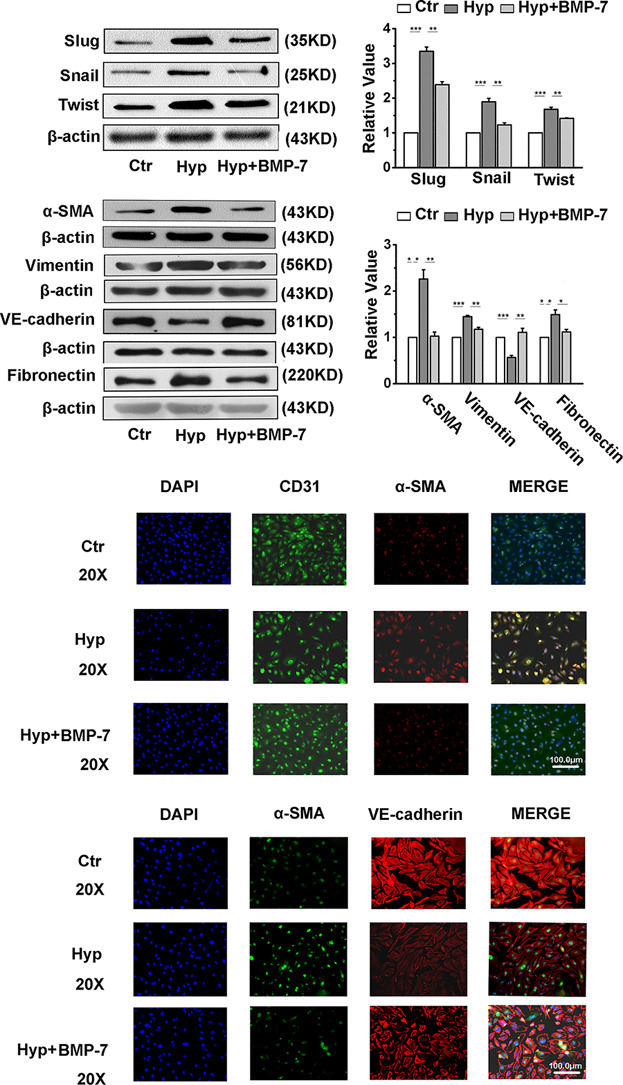
Our study demonstrate that BMP-7 attenuates the hypoxia-induced EndoMT and cell migration by suppressing the m-TORC1 signaling pathway. We revealed a novel mechanism underlying the hypoxia-induced EndoMT in pulmonary artery endothelial cells and suggested a new therapeutic strategy targeting EndoMT for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
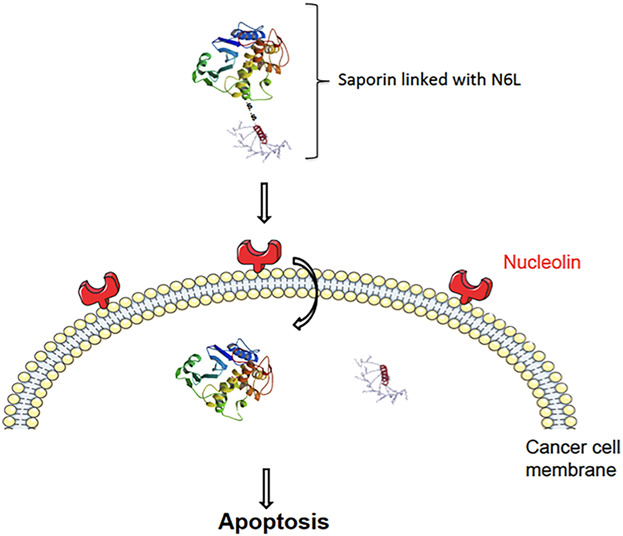
Targeted therapy of human glioblastoma via delivery of a toxin through a peptide directed to cell surface nucleolin
- Pages: 4091-4105
- First Published: 23 September 2017
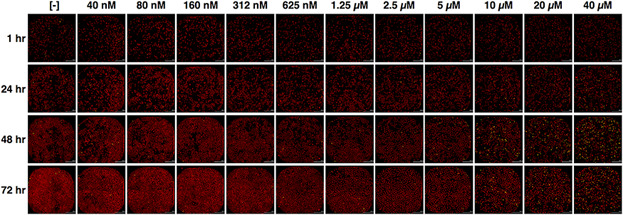
A new parameter of growth inhibition for cell proliferation assays
- Pages: 4106-4115
- First Published: 12 October 2017
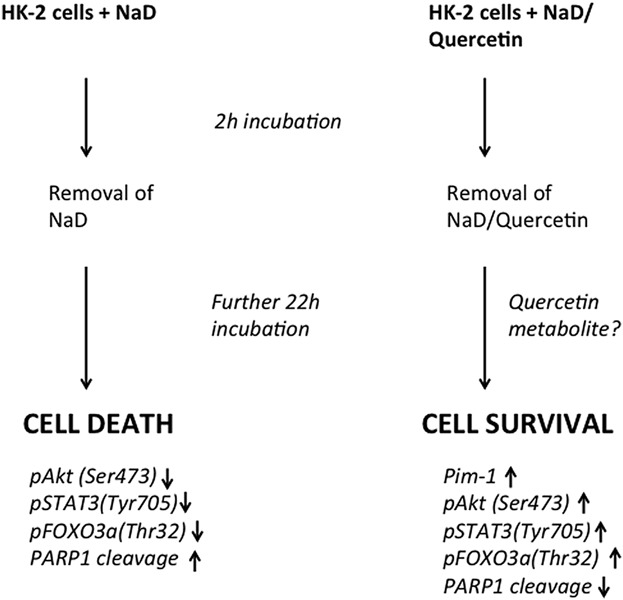
Quercetin protects against radiocontrast medium toxicity in human renal proximal tubular cells
- Pages: 4116-4125
- First Published: 16 October 2017
LncRNA DGCR5 promotes lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) progression via inhibiting hsa-mir-22-3p
- Pages: 4126-4136
- First Published: 14 October 2017
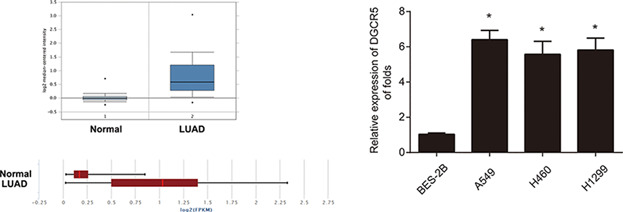
Our findings in LUAD cell lines and xenografts support the use of DGCR5 as an oncogene to promote LUAD development. This is the first reporting of a possible mechanism for a crosstalk between DGCR and hsa-mir-22-3p crosstalk in LUAD. These results suggest DGCR5 as a potential target for LUAD treatment.
Discovery and characterization of novel trans-spliced products of human polyoma JC virus late transcripts from PML patients
- Pages: 4137-4155
- First Published: 16 October 2017
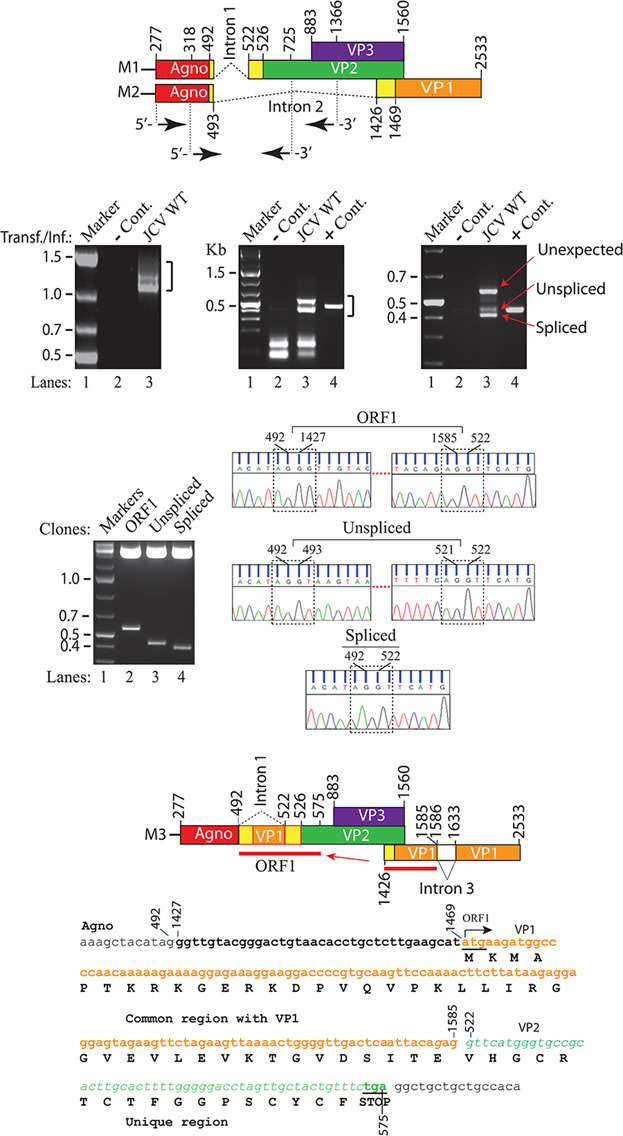
In this study, we have characterized the newly discovered trans-spliced products of the JC virus late transcripts, designated as new ORFs. We demonstrated that the 5′-coding region of the VP1 is trans-spliced between the coding regions of Agnoprotein and VP1 creating new open reading frames, ORF1 and ORF2, each of which is capable of encoding a 58 and 72 aa long, respectively. Each ORF protein shares a common coding region with VP1 and has a unique coding sequence of their own. When the expression of the unique coding regions of ORFs is blocked by a stop codon insertion in the viral background, the mutant virus replicates less efficiently when compared to wild-type, suggesting that the newly discovered ORFs play critical roles in the JCV life cycle.
Involvement of the Nrf2/HO-1/CO axis and therapeutic intervention with the CO-releasing molecule CORM-A1, in a murine model of autoimmune hepatitis
- Pages: 4156-4165
- First Published: 15 October 2017
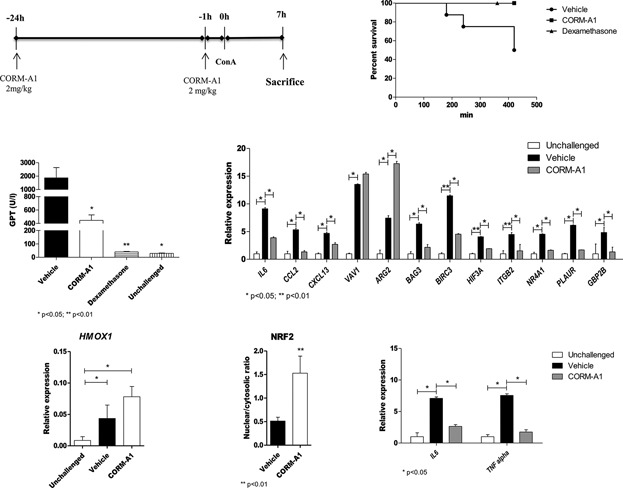
Concanavalin A (ConA)-induced hepatitis is an experimental model of human autoimmune hepatitis induced in rodents by i.v. injection of Con A. Our data indicate that the Nrf2/HO-1/CO pathway is involved in autoimmune hepatitis and that therapeutic intervention using the Carbon Monoxide releaser,CORM-A1, may represent a novel strategy to be considered for the treatment of autoimmune hepatitis in humans.
Annexin A1, Annexin A2, and Dyrk 1B are upregulated during GAS1-induced cell cycle arrest
- Pages: 4166-4182
- First Published: 14 October 2017
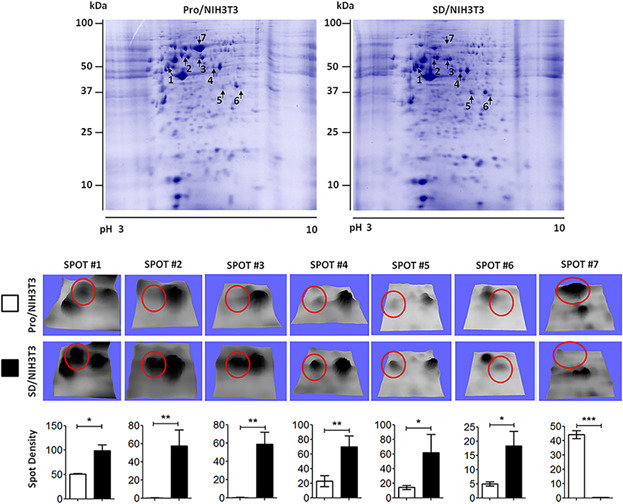
Two dimensional protein profiles in serum-deprived NIH3T3 cells revealed the upregulation of Gas1, Anxa1, Anxa 2, Dyrk 1B. Further experiments with GAS1-overexpressing cells demonstrated that GAS1 induces the upregulation of Anxa1, Anxa 2 and Dyrk 1B. Finally, we provide evidence showing that GAS1, through Dyrk 1B, leads not only NIH3T3 cells to cell arrest but also maintains cell viability.
NOD1 downregulates intestinal serotonin transporter and interacts with other pattern recognition receptors
- Pages: 4183-4193
- First Published: 14 October 2017
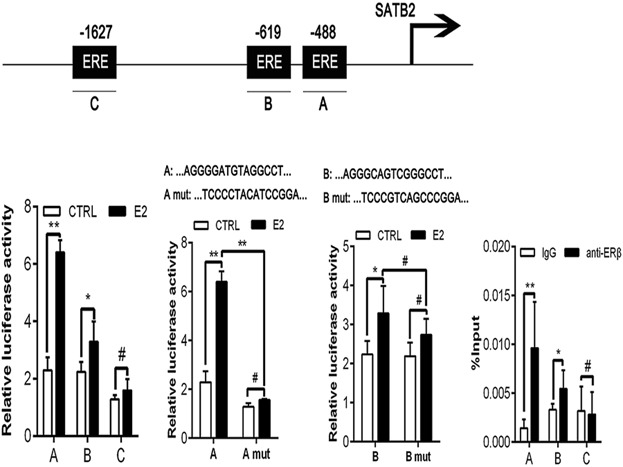
Estrogen regulates stemness and senescence of bone marrow stromal cells to prevent osteoporosis via ERβ-SATB2 pathway
- Pages: 4194-4204
- First Published: 14 October 2017
Transcription factor HMG box-containing protein 1 (HBP1) modulates mitotic clonal expansion (MCE) during adipocyte differentiation
- Pages: 4205-4215
- First Published: 14 October 2017
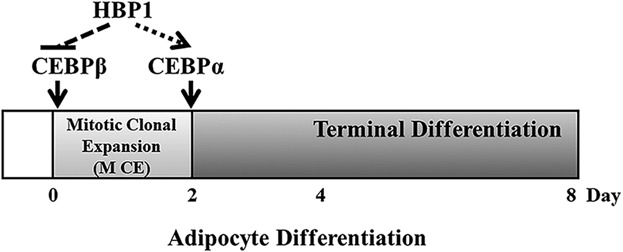
HBP1 regulates adipocyte differentiation. Upon MDI stimulation, HBP1 expression is down-regulated at the beginning of the MCE to ensure the up-regulation of C/EBPβ and allows the growth-arrested preadipocytes to reentry into postconfluent mitosis. However, HBP1 expression is up-regulated at the end of the MCE to ensure the up-regulation of C/EBPα and the termination of the MCE as well as the onset of terminal differentiation.
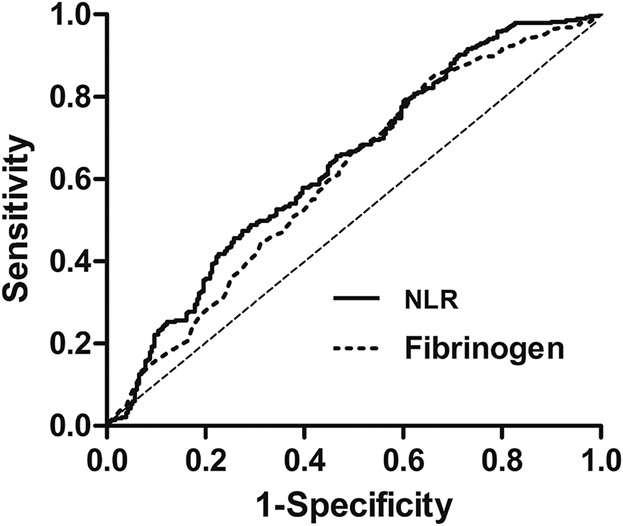
The combination of plasma fibrinogen and neutrophil lymphocyte ratio (F-NLR) is a predictive factor in patients with resectable non small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 4216-4224
- First Published: 23 October 2017
Fatty acid synthase knockout impairs early embryonic development via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress in pigs
- Pages: 4225-4234
- First Published: 23 October 2017
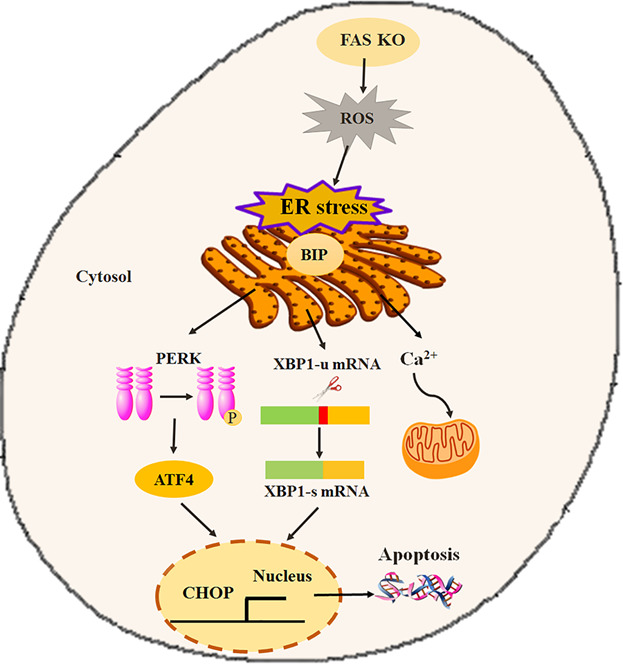
(1) FAS can be knocked out via the CRISPR/Cas9 system in porcine early embryonic development. (2) FAS knockout impaired the porcine embryonic development due to the induction of the endoplasmic reticulum stress. (3) FAS knockout induce the endoplasmic reticulum stress response displayed by the spliced XBP1 and phosphorylation of PERK.
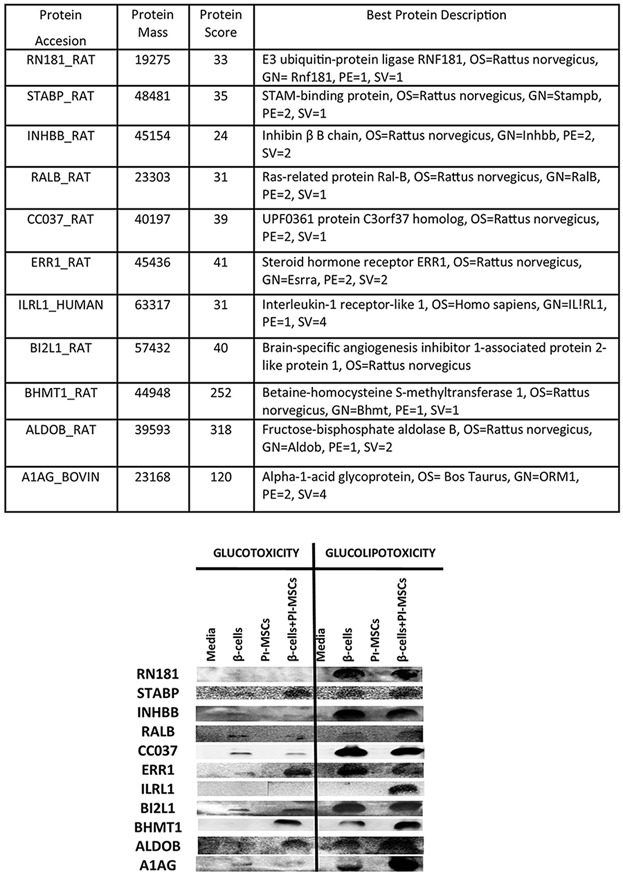
Involvement of dying beta cell originated messenger molecules in differentiation of pancreatic mesenchymal stem cells under glucotoxic and glucolipotoxic conditions
- Pages: 4235-4244
- First Published: 23 October 2017
CpG oligodeoxynucleotide preconditioning improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction via modulation of energy metabolism and angiogenesis
- Pages: 4245-4257
- First Published: 23 October 2017
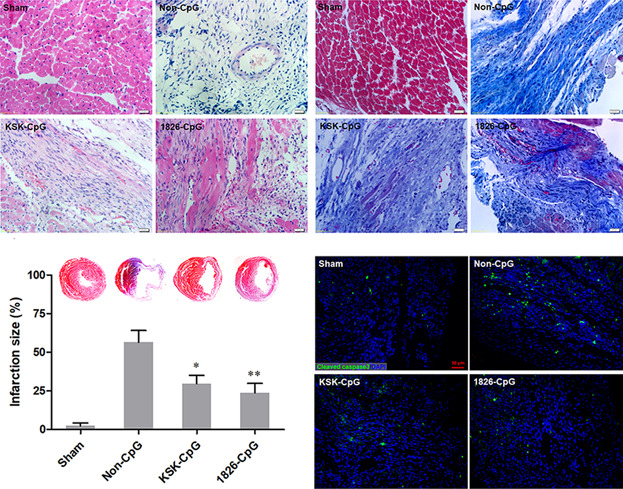
C57BL/6 mice were treated with CpG-ODN 2 hours prior to MI induction, and cardiac function and histology were analyzed 2 weeks after MI. We demonstratged that CpG-ODN preconditioning significantly protects cardiac function against MI by suppressing the energy metabolism of cardiomyocytes and promoting angiogenesis. Our data also indicate that CpG-ODN preconditioning may be useful in MI therapy.
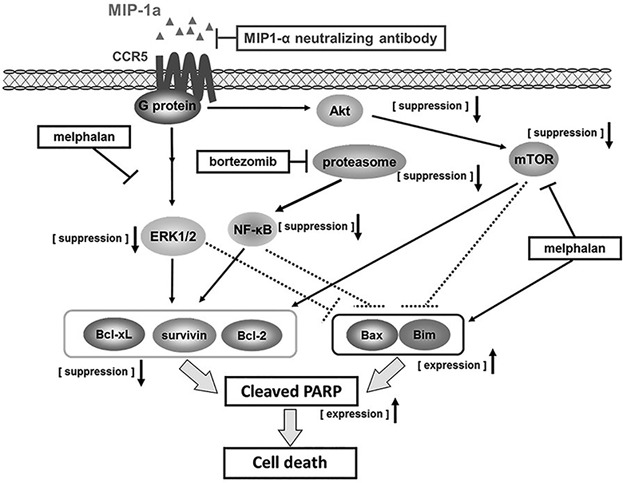
The MIP-1α autocrine loop contributes to decreased sensitivity to anticancer drugs
- Pages: 4258-4271
- First Published: 23 October 2017
Shear stress upregulates regeneration-related immediate early genes in liver progenitors in 3D ECM-like microenvironments
- Pages: 4272-4281
- First Published: 20 October 2017
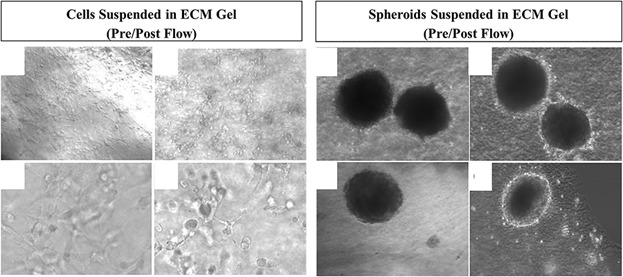
The role of fluid stresses in activating the hepatic stem/progenitor cell regenerative response is not well understood. This study hypothesized that immediate early genes (IEGs) with known links to liver regeneration will be upregulated in liver progenitor cells (LPCs) exposed to in vitro shear stresses on the order of those produced from elevated interstitial flow after partial hepatectomy. Two hours of shear stress exposure at ∼4 dyn/cm2 was applied to LPCs embedded individually or as 3D spheroids within a hyaluronic acid/collagen I hydrogel. Four IEGs (CFOS, IP10, MKP1, ALB) and three other regeneration-related genes (WNT, VEGF, EpCAM) were significantly upregulated in LPCs in response to fluid mechanical stress.
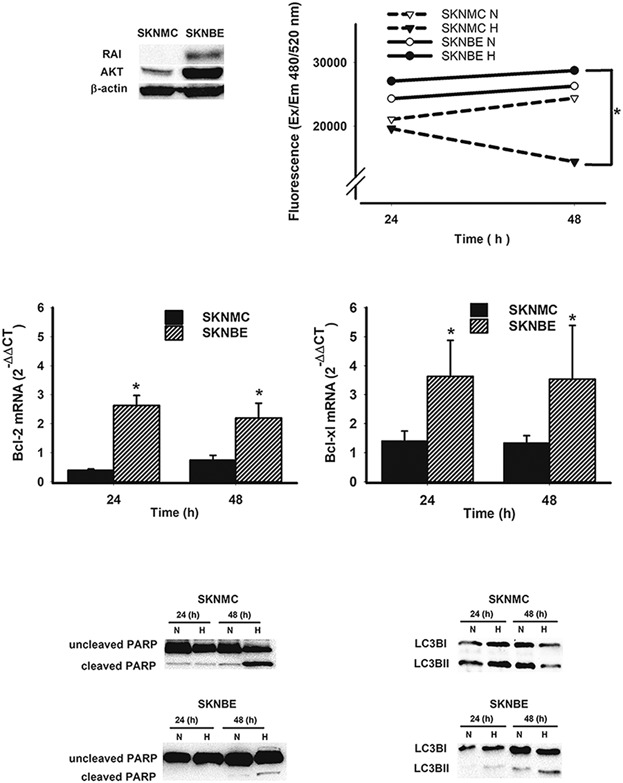
The Shc protein RAI promotes an adaptive cell survival program in hypoxic neuroblastoma cells
- Pages: 4282-4293
- First Published: 23 October 2017
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
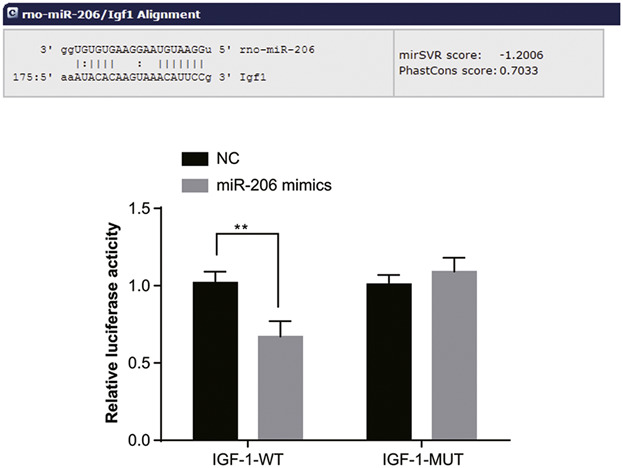
Retracted: Effects of microRNA-206 and its target gene IGF-1 on sevoflurane-induced activation of hippocampal astrocytes in aged rats through the PI3K/AKT/CREB signaling pathway
- Pages: 4294-4306
- First Published: 20 October 2017
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLES
Effects of XIST/miR-137 axis on neuropathic pain by targeting TNFAIP1 in a rat model
- Pages: 4307-4316
- First Published: 08 November 2017
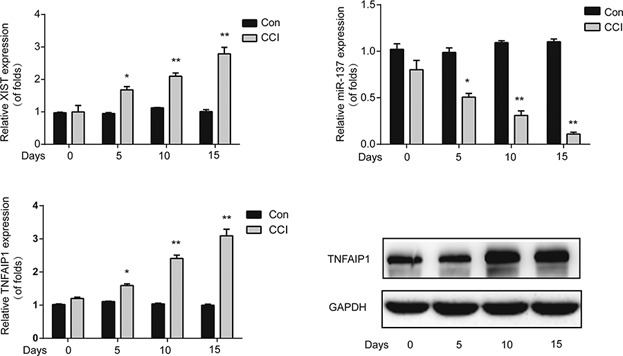
We exhibited that inhibition of XIST alleviated neuropathic pain development of CCI rats via upregulating miR-137 and downregulating TNFAIP1. Both in vitro and in vivo assays were carried out to elucidate the mechanisms of XIST/miR-137/TNFAIP1 axis in regulating neuropathic pain development. Our findings indicate that XIST can be identified as a novel therapeutic target for neuropathic pain treatment.
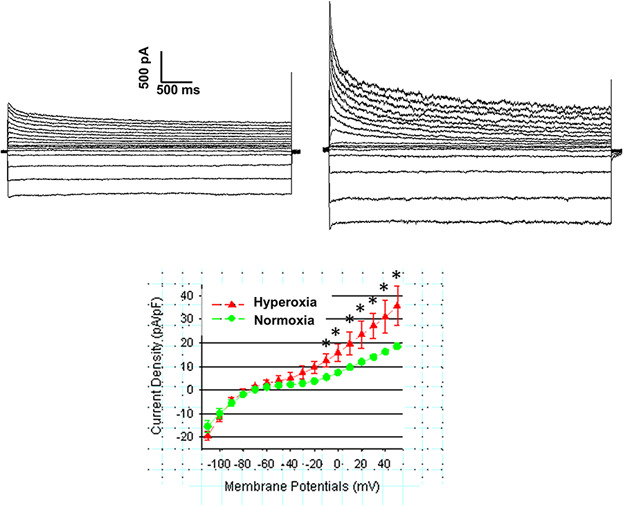
Elevated potassium outward currents in hyperoxia treated atrial cardiomyocytes
- Pages: 4317-4326
- First Published: 15 November 2017
Generation of insulin-producing cells from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on PVA scaffold by optimized differentiation protocol
- Pages: 4327-4337
- First Published: 18 November 2017
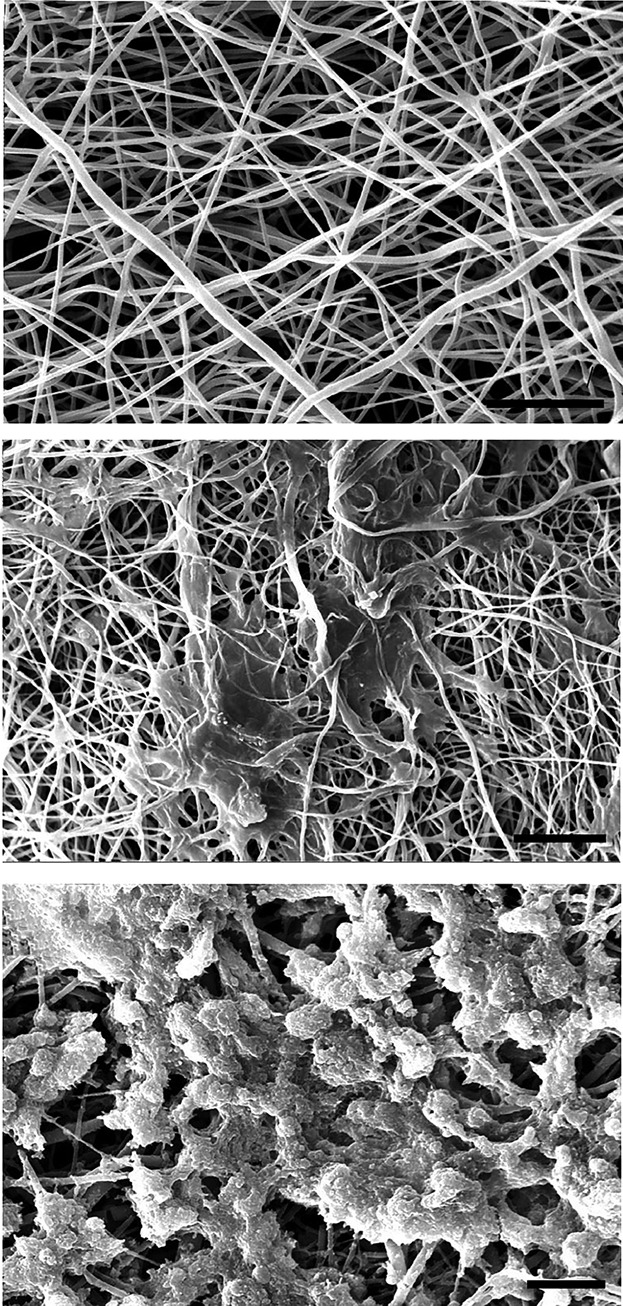
We established a polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) scaffold and a differentiation protocol by adding platelet-rich plasma (PRP) that induces the hADSCs into insulin-producing cells (IPCs). The results of our study for the first time demonstrated that the PVA nanofibrous scaffolds along with the optimized differentiation protocol with PRP can enhance the differentiation of IPCs from hADSCs. In conclusion, this study provides a new approach to the future pancreatic tissue engineering and beta cell replacement therapies for type 1 diabetes mellitus.
NONO ubiquitination is mediated by FBW7 and GSK3 β via a degron lost upon chromosomal rearrangement in cancer
- Pages: 4338-4344
- First Published: 18 November 2017
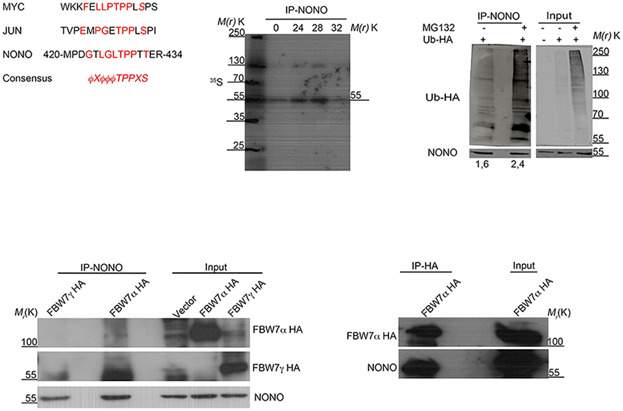
NONO is an RNA-binding protein involved in many cellular pathways. Its expression has been found altered in several tumor types and in papillary renal carcinoma, in which an X chromosome inversion generates a NONO-TFE3 fusion protein. We identified a degron motif in NONO protein adding another protein to the long list of FBW7 targets.
A novel epididymal quiescence factor inhibits sperm motility by modulating NOS activity and intracellular NO-cGMP pathway
- Pages: 4345-4359
- First Published: 18 November 2017
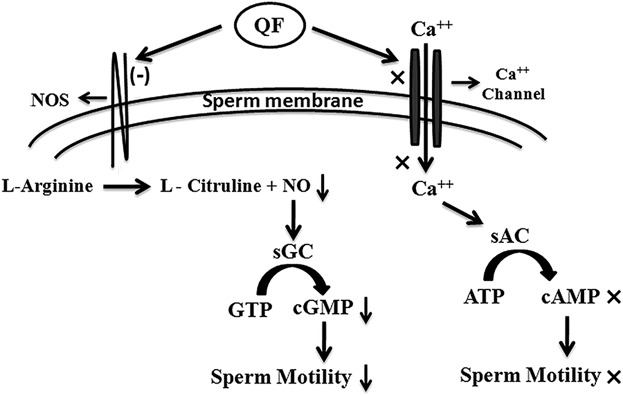
Newly identified 59 kDa monomeric quiescence factor (QF) is an α-helical globular protein which inhibits sperm progressive forward motility by decreasing NOS enzyme activity and subsequently reducing intracellular NO-cGMP concentration without modulating intracellular Ca++ and cAMP concentration. QF does not damage spermatozoa and its motility inhibitory efficacy is reversible. This study reveals the quiescence mechanism of mature spermatozoa and its energy saving strategy during storage and may help in understanding motility related idiopathic male infertility.
Muscle regeneration potential and satellite cell activation profile during recovery following hindlimb immobilization in mice
- Pages: 4360-4372
- First Published: 18 November 2017
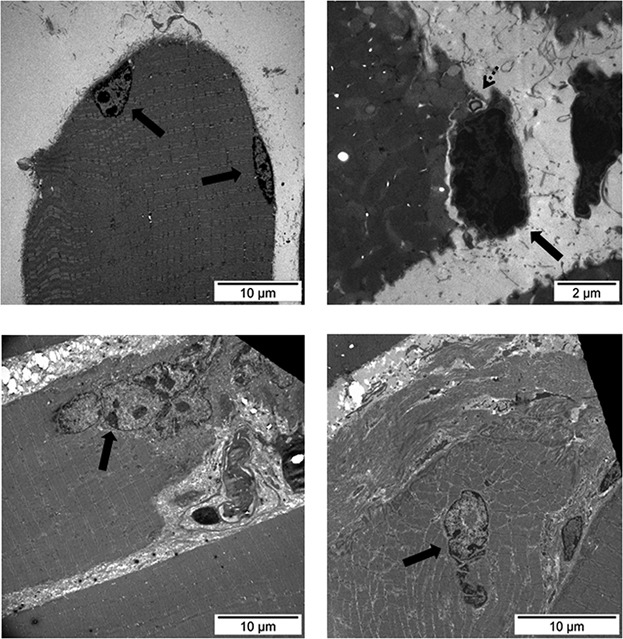
Hindlimb immobilization induced a decline in SCs together with an upregulation of markers of SC activation, suggesting that fusion to existing myofibers takes place during unloading. Muscle recovery induced a significant rise in muscle precursor cells and regeneration events along with reduced SC activation expression markers and a concomitant rise in terminal muscle differentiation expression. These are novel findings of potential applicability for the treatment of disuse muscle atrophy, which is commonly associated with severe chronic and acute conditions.