Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: Disorder Engineering in Monolayer Nanosheets Enabling Photothermic Catalysis for Full Solar Spectrum (250–2500 nm) Harvesting (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2019)
- Page: 2907
- First Published: 04 February 2019

Maximizing light harvesting while sustaining high photoredox capability is crucial for realizing high photocatalytic solar-to-chemical conversion. In their Communication on page 3077, G. W. Ho and co-workers report an order–disorder D-HNb3O8 monolayer structure to perform two disparate functions of photoexcitation to generate charge carriers and solar heating to thermally boost reaction kinetics. This solar thermal-mediated photocatalyst system fulfills full solar energy utilization from 250 to 2500 nm.
Inside Cover: EPR Spectroscopy Detects Various Active State Conformations of the Transcriptional Regulator CueR (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2019)
- Page: 2908
- First Published: 30 January 2019

CuII--NTA spin labeling of the transcription regulator CueR, an E. coli copper-sensing protein, enabled the high-resolution detection of its various conformational states, as described by S. Ruthstein and co-workers in their Communication on page 3053 ff. Two of the conformations, activators 1 and 2, represent CueR as it binds DNA and CuI ions. The computed structures suggest that one is more compressed on the DNA than the other and the transition between those states depends on CuI concentration in the bacterial cell.
Inside Back Cover: Multi-Light-Responsive Quantum Dot Sensitized Hybrid Micromotors with Dual-Mode Propulsion (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2019)
- Page: 3227
- First Published: 14 February 2019

The multi-light-controlled propulsion and on-the-fly chemical acceleration capabilities of micromotors based on Pt, Pd, and MnO2 catalysts is described by A. Escarpa, B. Jurado, R. M. Hormigos in their Communication on page 3128 ff. The built-in accelerating optical system allows for velocity control over the entire UV/Vis light spectrum for future on-demand operation, motion-based sensing, and beyond.
Back Cover: Reversible Hydrogen Uptake/Release over a Sodium Phenoxide–Cyclohexanolate Pair (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2019)
- Page: 3228
- First Published: 14 February 2019

Hydrogen uptake and release in arene–cycloalkane pairs is an attractive strategy for hydrogen storage but is hampered by the large enthalpy change associated with dehydrogenation. In their Communication on page 3102 ff., P. Chen, T. He, A. Wu, and co-workers describe how reversible hydrogen storage under moderate conditions is possible with a sodiated phenoxide–cyclohexanolate pair.
Frontispiece
Frontispiece: Design and Catalytic Asymmetric Construction of Axially Chiral 3,3′-Bisindole Skeletons
- First Published: 25 February 2019

Chiral Bisindole Skeletons. Organocatalytic asymmetric addition reactions of 2-substituted 3,3′-bisindoles and electrophiles create interesting structural skeletons, as described by F. Shi et al. in their Communication on page 3014 ff.
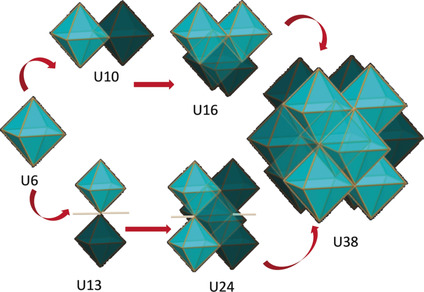
Frontispiece: Structural Snapshots of Cluster Growth from {U6} to {U38} During the Hydrolysis of UCl4
- First Published: 25 February 2019
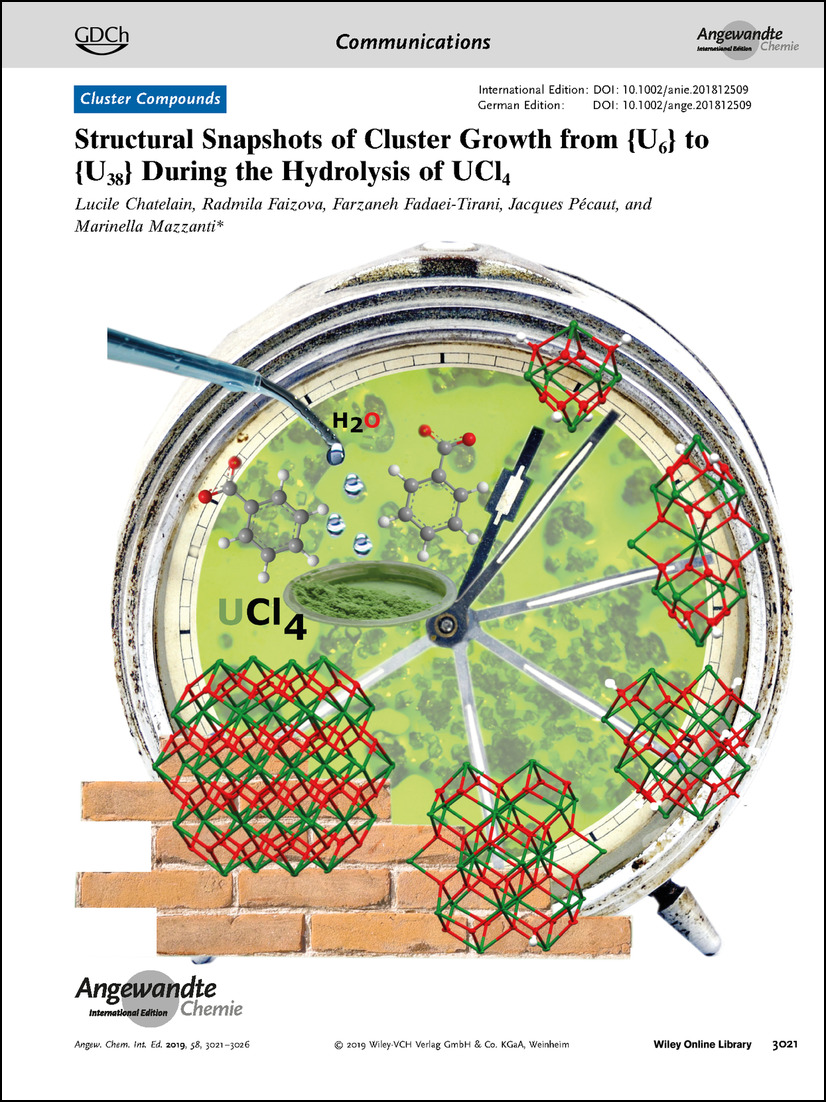
Uranium Clusters. Large UIV clusters slowly assemble upon controlled hydrolysis of UCl4. In their Communication on page 3021 ff., M. Mazzanti et al. show that the process is time-dependent.
Editorial
Chemistry for All: Advocating Gender Equality
- Pages: 2910-2911
- First Published: 25 February 2019

International Women's Day is celebrated every year on March 8, and this special issue of Angewandte Chemie focussing on Women in Chemistry coincides with International Women's Day 2019. The breadth and quality of content is testament to the excellent research being done in groups being successfully run by female researchers.
Guest Editorial
The Need for Cultural Competence in Science: A Practical Approach to Enhancing Equality, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Pages: 2912-2913
- First Published: 31 January 2019
Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2019
- Pages: 2915-2928
- First Published: 25 February 2019
News
Spotlights on our sister journals: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 10/2019
- Pages: 2930-2934
- First Published: 25 February 2019
Author Profile
News
Novartis Early Career Award: K. L. Hull / Leipziger Universitätsmedaille: E. Hey-Hawkins / Karl Ziegler Guest Professorship: K. Nozaki / Clara Immerwahr Award: M. Escudero-Escribano / Marion Milligan Mason Awards: V. E. Ferry, S. K. Fullerton, L. C. Hsiao, H. J. Kulik, C. S. Schindler
- Pages: 2940-2941
- First Published: 25 January 2019
Minireviews
DNA Nanotechnology
Chemical Regulation of DNA i-Motifs for Nanobiotechnology and Therapeutics
- Pages: 2942-2957
- First Published: 02 January 2019
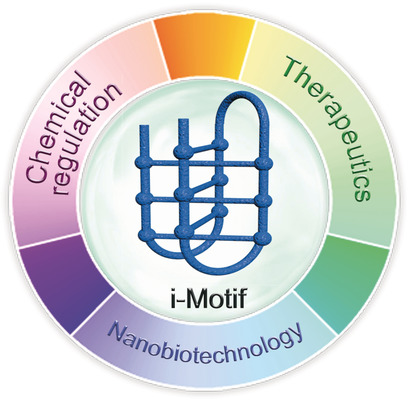
Non-canonical DNA structures: i-Motifs are four-stranded DNA structures formed by the folding of cytosine-rich sequences present in telomeres and gene promoters. Compared to complementary G-quadruplexes, i-motifs are less explored. This Minireview describes significant advances in chemically regulated i-motif-based functional nanostructures and small-molecule targeting of i-motifs for therapeutics.
Reviews
Cubosomes
Cubosomes: The Next Generation of Smart Lipid Nanoparticles?
- Pages: 2958-2978
- First Published: 21 June 2018
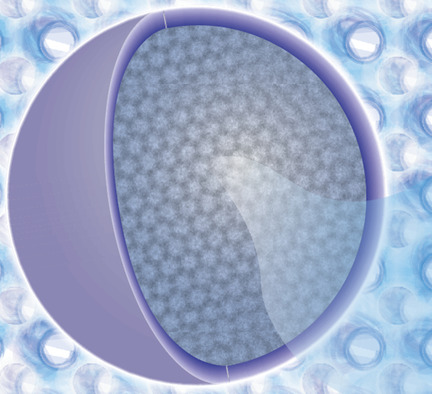
Cubosomes are nanoparticles with an internal periodic lipid membrane separated by two distinct water channels. The surface is stabilized by a polymer outer corona. Recent advances have enabled the rational design of cubosome systems. Key considerations are outlined for engineering cubosomes for tailor-made applications including delivery, biosensing, and medical applications.
Antitumor Agents
Polyoxometalates as Potential Next-Generation Metallodrugs in the Combat Against Cancer
- Pages: 2980-2999
- First Published: 12 June 2018
THz Spectroscopy
Ion Hydration and Ion Pairing as Probed by THz Spectroscopy
- Pages: 3000-3013
- First Published: 18 July 2018
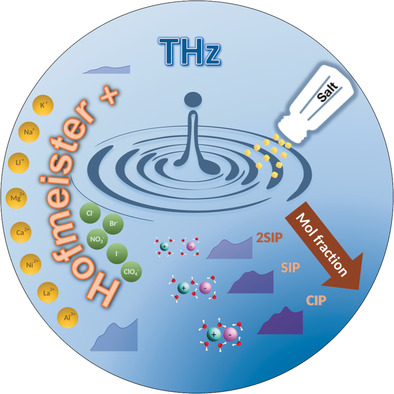
Testing the water: The microscopic interplay between cations, anions, and water can be understood by THz-FTIR spectroscopy. Dissection of the spectra shows that the full response of the solvating water when dissolving salts can not be explained from the individual properties (such as the ion radius, the ion–water interaction, the structural hydration shell size, etc.) alone; cooperativity effects need to be included.
Communications
Chirality | Hot Paper
Design and Catalytic Asymmetric Construction of Axially Chiral 3,3′-Bisindole Skeletons
- Pages: 3014-3020
- First Published: 20 November 2018
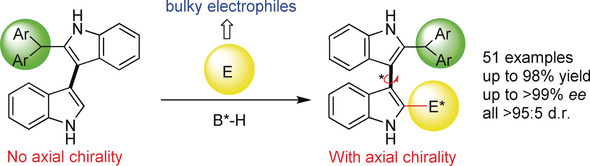
Bulk up: The first catalytic asymmetric construction of 3,3′-bisindole skeletons bearing axial and central chirality has been established by organocatalytic asymmetric addition reactions of 2-substituted 3,3′-bisindoles with electrophiles. This reaction also represents the first highly enantioselective construction of axially chiral 3,3′-bisindole skeletons, and utilizes the strategy of introducing a bulky group to the ortho-position of prochiral 3,3′-bisindoles.
Cluster Compounds
Structural Snapshots of Cluster Growth from {U6} to {U38} During the Hydrolysis of UCl4
- Pages: 3021-3026
- First Published: 02 January 2019
Multistimuli-Responsive Materials
Photochromic Benzo[b]phosphole Alkynylgold(I) Complexes with Mechanochromic Property to Serve as Multistimuli-Responsive Materials
- Pages: 3027-3031
- First Published: 15 August 2018
Photocatalyzed Water Splitting
Visible-Light-Driven Overall Water Splitting Boosted by Tetrahedrally Coordinated Blende Cobalt(II) Oxide Atomic Layers
- Pages: 3032-3036
- First Published: 23 August 2018
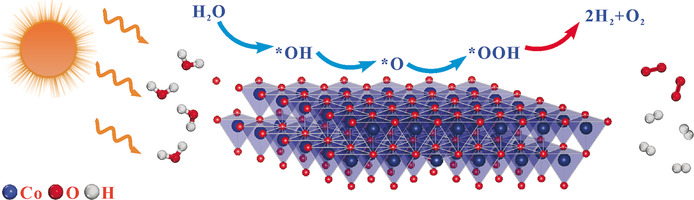
Tetrahedrally coordinated blende CoO and octahedrally coordinated rocksalt CoO atomic layers with similar thicknesses were synthesized. The blende CoO atomic layers achieve boosted visible-light-driven H2 and O2 formation rates that are roughly 3.7 times higher than those of the rocksalt CoO atomic layers.
Dioxygen Activation
Activating a Peroxo Ligand for C−O Bond Formation
- Pages: 3037-3041
- First Published: 27 December 2018
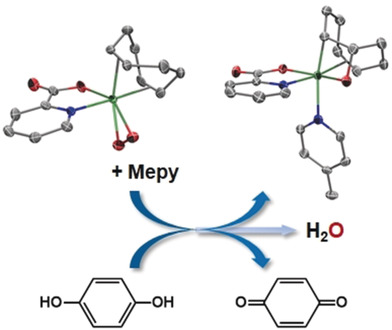
Taming oxygen for effective cleavage of the O−O bond and a further C−O bond formation has been achieved through proton transfer/electron transfer steps. A free radical mechanism accounts for the transformation of peroxide complexes into water and 2-iradaoxetane complexes (see scheme; C gray, Ir green, N blue, O red; Mepy=4-methylpyridine).
DNA Nanotechnology
“Printing” DNA Strand Patterns on Small Molecules with Control of Valency, Directionality, and Sequence
- Pages: 3042-3047
- First Published: 05 October 2018
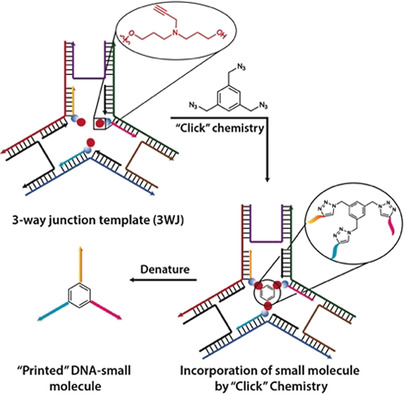
Breaking symmetry: A highly modular method to covalently transfer different DNA sequences with controllable directionality, length, and valency onto different synthetic molecules is reported. These DNA-imprinted small molecules can be elongated asymmetrically to different lengths in high yield using PCR and can be chemically replicated.
Bioelectronics
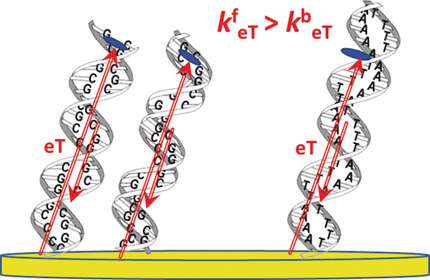
Directional Preference of DNA-Mediated Electron Transfer in Gold-Tethered DNA Duplexes: Is DNA a Molecular Rectifier?
- Pages: 3048-3052
- First Published: 14 November 2018
EPR Spectroscopy
EPR Spectroscopy Detects Various Active State Conformations of the Transcriptional Regulator CueR
- Pages: 3053-3056
- First Published: 19 December 2018
Porphyrinoid Complexes
Tetrahedral Pegs in Square Holes: Stereochemistry of Diboron Porphyrazines and Phthalocyanines
- Pages: 3057-3061
- First Published: 31 October 2018
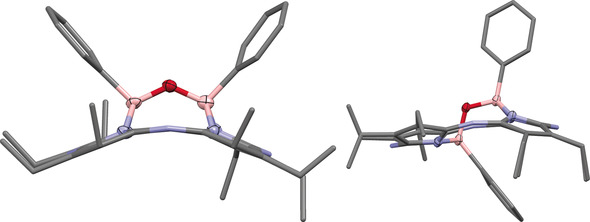
Fully characterised boron complexes of porphyrazine and phthalocyanine contain FBOBF and PhBOBPh moieties in both cisoid and transoid geometries. A DFT study, extended to include the previously reported FBOBF porphyrin, corrole, and calixphyrin complexes shows that the stereochemical preferences correlate with the ease with which each macrocycle can accommodate a rectangularly distorted N4 cavity.
Photooxidation
A Cross-linked Conjugated Polymer Photosensitizer Enables Efficient Sunlight-Induced Photooxidation
- Pages: 3062-3066
- First Published: 13 December 2018
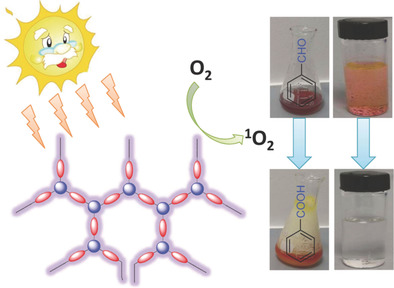
A sunny outlook: A cross-linked porous conjugated polymer photosensitizer CPTF is used for sunlight-induced photooxidation. Under simulated AM 1.5G irradiation, benzaldehyde can be oxidized to benzoic acid easily on a 10 g scale in the presence of CPTF. In addition, CPTF can also be used as photocatalyst for sunlight-induced organic waste decomposition and an antibacterial agent in water.
Cancer Therapy
Molecular Scaffolds as Double-Targeting Agents For the Diagnosis and Treatment of Neuroblastoma
- Pages: 3067-3072
- First Published: 10 December 2018
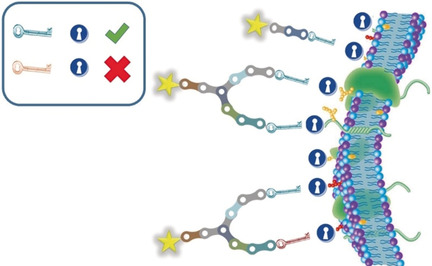
Double trouble: Novel Y-shaped scaffolds have been synthesized, with meta-iodobenzilguanidine analogues covalently attached at each end of the Y-structure, to deliver diagnostic and therapeutic agents to neuroblastoma cells. These double-targeting agents have a strong affinity for the norepinephrine transporter, usually overexpressed on the neuroblastoma cell membrane, and accumulate in cells at a higher level than single-targeting agents.
DNA Nanotechnology
Quantitative Mapping of Endosomal DNA Processing by Single Molecule Counting
- Pages: 3073-3076
- First Published: 22 January 2019
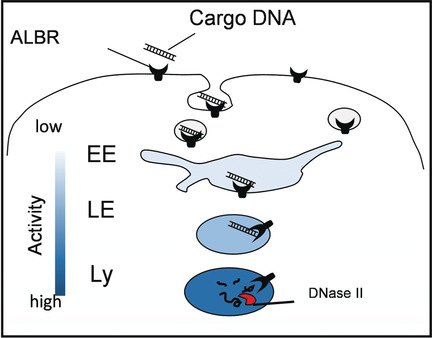
Elementary, my dear Watson: Organellar single-molecule, high-resolution localization and counting (oSHiRLoC), a fluorescence imaging method for the quantitative mapping of the endosomal processing of cargo DNA in innate immune cells with organelle-specific resolution, is reported. By using this method, it is shown that endosomal DNA degradation occurs mainly in lysosomes and is negligible in late endosomes.
Solar Energy Utilization
Disorder Engineering in Monolayer Nanosheets Enabling Photothermic Catalysis for Full Solar Spectrum (250–2500 nm) Harvesting
- Pages: 3077-3081
- First Published: 12 October 2018
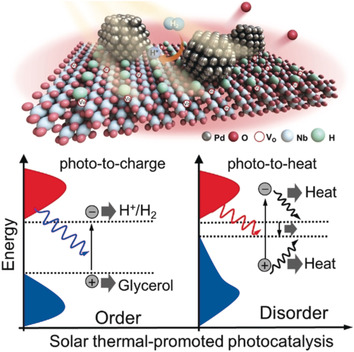
Let the sunshine in: Single-entity ordered–disordered monolayer D-HNb3O8 nanosheets were engineered to realize full solar spectrum (250–2500 nm) utilization. The crystalline domains absorb UV photons to generate charge carriers, while the disordered “nanoislands” capture the full spectrum for solar heating to thermally boost the reaction kinetics.
Luminescent Polymers
Multicolor Emission from Non-conjugated Polymers Based on a Single Switchable Boron Chromophore
- Pages: 3082-3086
- First Published: 21 November 2018
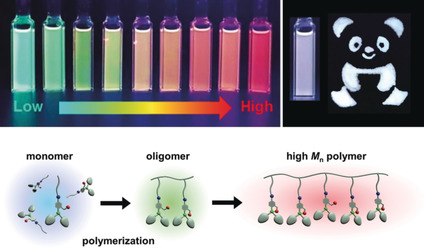
Multicolor emissive polymers: Multicolor emission was achieved in polymers that contain a switchable boron chromophore and a methacrylate backbone. The molecular weight and degree of polymerization provide the key driving force for the switching of three-coordinate boron units to four-coordinate ones in the polymer, and for the emission transition from blue to white and then red.
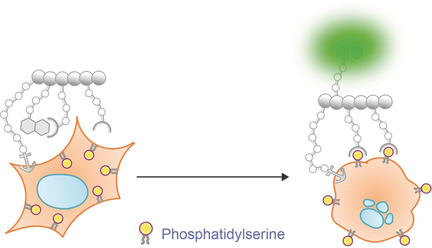
Imaging Agents | Hot Paper
A Fluorogenic Probe for Cell Surface Phosphatidylserine Using an Intramolecular Indicator Displacement Sensing Mechanism
- Pages: 3087-3091
- First Published: 22 November 2018
Electrochemistry
Lithiophilic Faceted Cu(100) Surfaces: High Utilization of Host Surface and Cavities for Lithium Metal Anodes
- Pages: 3092-3096
- First Published: 27 December 2018
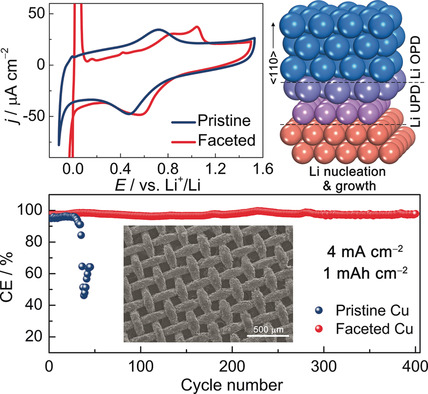
Get in touch with lithium: The generation of surface lithiophilicity on planar and 3D Cu hosts for Li metal anodes is reported. Enabled by a lattice matching of Cu(100) and Li(110), smooth deposition of Li thin films and the creation of ultra-smooth ultra-thin SEI on the Cu hosts is made possible. This allows a high utilization of not only the surface but also cavities of the Cu hosts.
Molecular Dynamics
Hidden Conformations in Aspergillus niger Monoamine Oxidase are Key for Catalytic Efficiency
- Pages: 3097-3101
- First Published: 02 January 2019
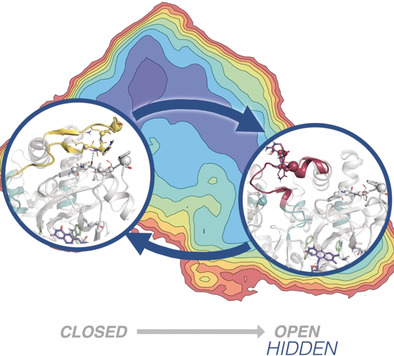
Hide and seek: Markov state models are used to unveil hidden conformational states of Monoamine Oxidase from Aspergillus niger (MAO-N). These hidden conformations, not previously observed by any other technique, play a crucial role in the enzyme activity and substrate binding. This reveals how distal mutations regulate MAO-N activity by stabilizing these hidden, catalytically important conformational states.
Hydrogen Storage Materials
Reversible Hydrogen Uptake/Release over a Sodium Phenoxide–Cyclohexanolate Pair
- Pages: 3102-3107
- First Published: 25 November 2018

Optimized storage: The metalation of the phenoxide–cyclohexanolate pair is a successful strategy to optimize the thermodynamic properties of this type of hydrogen storage material (see figure). In experiments the sodiated pair desorbed hydrogen at 413 K (373 K) in the solid state (aqueous solution), whereas hydrogenation could be accomplished at temperatures as low as 202 K.
Aromatic Dimers
Rotational Signatures of Dispersive Stacking in the Formation of Aromatic Dimers
- Pages: 3108-3113
- First Published: 23 January 2019
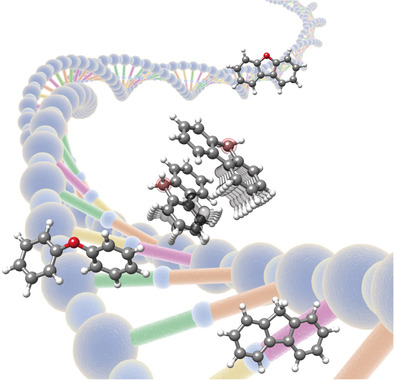
Use the force: A combined rotational spectroscopic and quantum-chemical study on diphenyl ether, dibenzofuran, and fluorene determined the influence of structural flexibility and the presence of heteroatoms on aromatic dimer formation. This furthers our understanding of the first steps of molecular aggregation in aromatic systems.
Mass Spectrometry
Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry Measures the Conformational Landscape of p27 and its Domains and how this is Modulated upon Interaction with Cdk2/cyclin A
- Pages: 3114-3118
- First Published: 20 December 2018
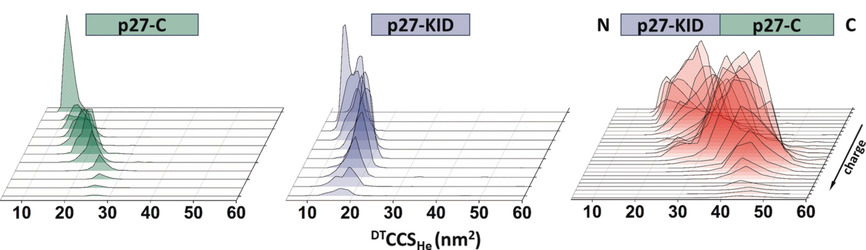
Order to disorder: Ion mobility mass spectrometry is employed to measure the intrinsic dynamic properties of p27, both in isolation and within the complex with Cdk2/cyclin A, and its individual domains. The findings support the formation of a fuzzy complex in which both the N- and C-termini of p27 interact with Cdk2/cyclin A in multiple states.
Fluorination
Copper-Mediated Aminoquinoline-Directed Radiofluorination of Aromatic C−H Bonds with K18F
- Pages: 3119-3122
- First Published: 03 January 2019
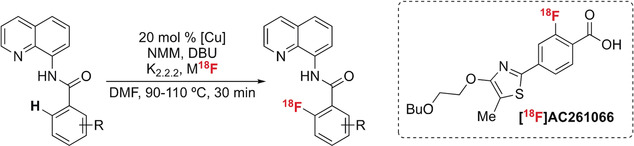
Late-stage fluorination: K18F is applied in a newly developed Cu-mediated ortho-C(sp2)−H radiofluorination of aromatic carboxylic acids that are protected as 8-aminoquinoline benzamides. Fluorination of 18 examples in up to 62 % radiochemical yield and high specific activity is reported, including the automated synthesis of [18F]AC261066.
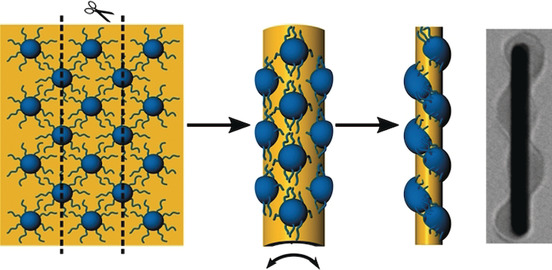
Nanorods | Very Important Paper
Helicoidal Patterning of Nanorods with Polymer Ligands
- Pages: 3123-3127
- First Published: 02 January 2019
Nanotechnology
Multi-Light-Responsive Quantum Dot Sensitized Hybrid Micromotors with Dual-Mode Propulsion
- Pages: 3128-3132
- First Published: 06 December 2018
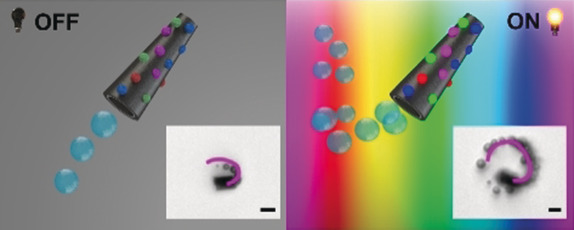
Light power: CdS quantum dots/C60 tubular micromotors with chemical/multi-light-controlled propulsion and “on-the-fly” chemical acceleration capabilities are described. The built-in accelerating optical system allows for the control of the velocity over the entire UV/Vis light spectrum by modulating the catalyst surface chemistry.
Zintl Ions
Elusive Zintl Ions [μ-HSi4]3− and [Si5]2− in Liquid Ammonia: Protonation States, Sites, and Bonding Situation Evaluated by NMR and Theory
- Pages: 3133-3137
- First Published: 08 January 2019
![Elusive Zintl Ions [μ-HSi4]3− and [Si5]2− in Liquid Ammonia: Protonation States, Sites, and Bonding Situation Evaluated by NMR and Theory](/cms/asset/41df39d2-f866-43ce-9c46-62feda72411a/anie201812955-toc-0001-m.jpg)
Long ago Zintlsized and now analyzed: 29Si and 1H NMR experiments confirm the existence of Zintl ions [μ-HSi4]3− and [Si5]2− in liquid ammonia. For [μ-HSi4]3−, NMR and theoretical calculations reveal a bridging hydrogen atom forming a 3c-2e-bond. Additionally, [Si5]2−, only known from solvate crystal structures so far, was characterized by 29Si NMR. Here, NBO analysis indicates the formation of three localized 3c-2e-bonds.
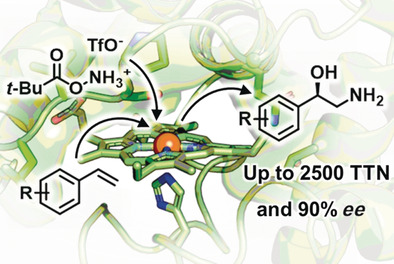
Directed Evolution | Very Important Paper
Enantioselective Aminohydroxylation of Styrenyl Olefins Catalyzed by an Engineered Hemoprotein
- Pages: 3138-3142
- First Published: 02 January 2019
Peptides
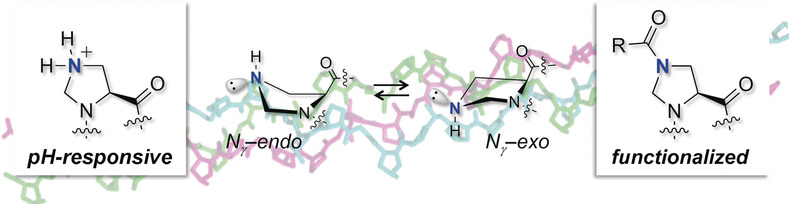
γ-Azaproline Confers pH Responsiveness and Functionalizability on Collagen Triple Helices
- Pages: 3143-3146
- First Published: 11 January 2019
Nanocrystals
Synthesis of Plasmonic Group-4 Nitride Nanocrystals by Solid-State Metathesis
- Pages: 3147-3150
- First Published: 15 January 2019
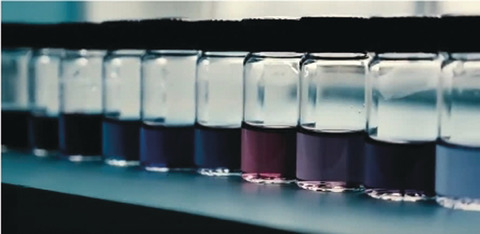
Ready to plassemble: The synthesis of TiN, ZrN, and HfN nanocrystals using solid-state metathesis is reported. The nanocrystals, which are dispersible in water, show localized surface plasmonic resonances in the near infrared (TiN) and visible region (ZrN, HfN) of light. This makes them ideal for applications like photothermal therapy or plasmon-enhanced sensing.
Biocatalysis
Biocatalytic Friedel–Crafts Alkylation Using a Promiscuous Biosynthetic Enzyme
- Pages: 3151-3155
- First Published: 01 February 2019
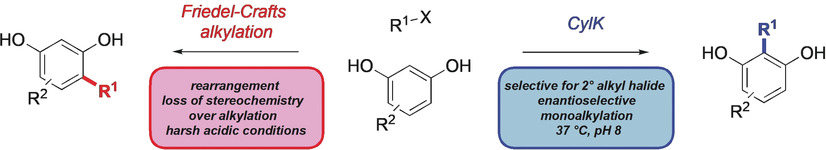
Enzymatic alkylation: The cylindrocyclophane biosynthetic enzyme CylK is identified as a promiscuous catalyst for Friedel–Crafts alkylation of resorcinol substrates with alkyl halide electrophiles. This transformation, which proceeds with exceptional regioselectivity and stereospecificity, highlights the promise of enzymatic catalysis for enabling mild and selective C−C bond-forming synthetic methodology.
Mass Spectrometry | Very Important Paper
Secondary-Ion Mass Spectrometry Images Cardiolipins and Phosphatidylethanolamines at the Subcellular Level
- Pages: 3156-3161
- First Published: 24 January 2019
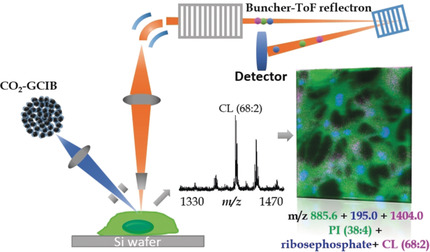
Beam me up: A high-energy gas-cluster ion beam (GCIB) with 1 μm lateral resolution was developed. This allowed single cell and subcellular mass spectrometry imaging of diverse phospholipids, including cardiolipin (CL) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). Coupling this with immunohistochemistry provided assessments in specific subcellular compartments.
Photoelectrochemistry
Aggregation-Induced Electrochemiluminescence of Carboranyl Carbazoles in Aqueous Media
- Pages: 3162-3166
- First Published: 30 January 2019
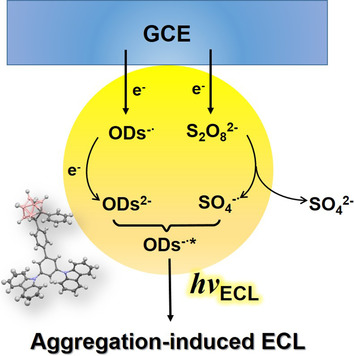
Carborane-based AIEgens: The reductive–oxidative aggregation-induced electrochemiluminescence (AIECL) of carboranyl carbazoles in air-saturated aqueous media was investigated. Mechanistic studies indicate that the carboranyl motif plays vital role in the high ECL intensity and stability of the aggregates.
Main Group Chemistry
The Diverse Reactivity of Disilenes Toward Isocyanides
- Pages: 3167-3172
- First Published: 17 September 2018
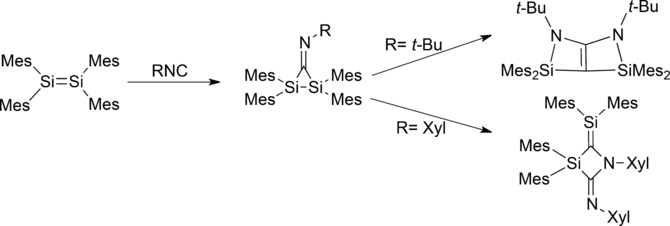
Twice the fun: In the addition of 2,6-dimethylphenyl isocyanide or tert-butyl isocyanide to tetramesityldisilene, the initially formed product is an iminodisilirane. These iminodisilirane intermediates react with a second equivalent of the isocyanide to give a 3-silaazetidine or a bicyclic double enamine, respectively.
Block Copolymer Nanofibers
Templated PISA: Driving Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly towards Fibre Morphology
- Pages: 3173-3177
- First Published: 23 November 2018
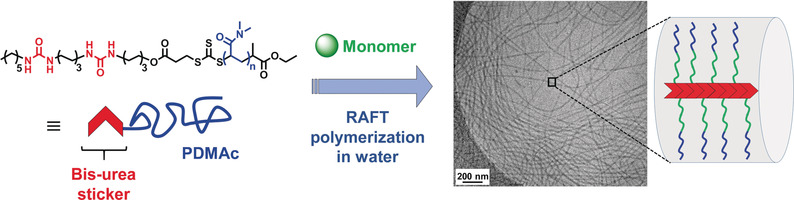
RAFT in water: Current limitations of polymerization-induced self-assembly (PISA) are overcome by combining reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization and supramolecular chemistry. The introduction of supramolecular stickers into PISA allows the robust synthesis of long nanofibres with tunable diameter.
Natural Products
Azetidine-Containing Alkaloids Produced by a Quorum-Sensing Regulated Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Pages: 3178-3182
- First Published: 11 December 2018
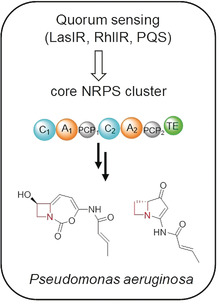
Ring constraints: The major opportunist human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces azetidine 2-carboxylic acid, a proline mimic, to be incorporated into a quorum-sensing controlled nonribosomal peptide synthetase assembly line, yielding constrained bicyclic alkaloids. These compounds play important functions in the physiology of P. aeruginosa.
Polymerizations
Precise Polymer Synthesis by Autonomous Self-Optimizing Flow Reactors
- Pages: 3183-3187
- First Published: 29 October 2018
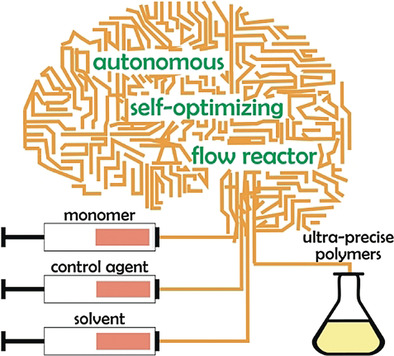
Polymers made by an artificial brain: An autonomous continuous flow system for polymerizations is presented. Reaction parameters (i.e., residence time, monomer and control agent/initiator concentrations) are dynamically and autonomously varied with a self-optimizing algorithm to obtain predefined molecular weights. This novel platform can target molecular weights with unprecedented accuracy in a reproducible manner.
Asymmetric Synthesis
Stereospecific Synthesis of α-Hydroxy-Cyclopropylboronates from Allylic Epoxides
- Pages: 3188-3192
- First Published: 02 January 2019

Rigid sp3 scaffolds: A catalytic and stereospecific method for the preparation of enantioenriched α-hydroxy cyclopropylboronates with control in four contiguous stereocenters is described. The reaction involves the borylation of readily available allylic epoxides using an inexpensive CuI salt and a commercially available phosphine ligand. High diastereocontrol is achieved and different diastereomers can be selectively prepared.
Enantioselective Aryl Transfer
Chiral Lithium Amido Aryl Zincates: Simple and Efficient Chemo- and Enantio-Selective Aryl Transfer Reagents
- Pages: 3193-3197
- First Published: 17 January 2019
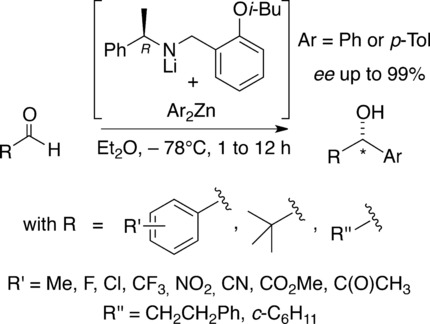
Chemo- and enantio-selective nucleophilic aryl transfer: The key reactant is a chiral tricoordinated lithium amido aryl zincate of which the chiral appendage is simply recovered and reused. The arylation leaves intact sensitive functions such as esters, nitriles, ketones or enolisable sites, while running with aldehyde groups in good yields and high ee values, this whatever the ortho, meta, or para substituent borne by the substrate if aromatic.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Nickel-Catalyzed Asymmetric Reductive Diarylation of Vinylarenes
- Pages: 3198-3202
- First Published: 25 January 2019
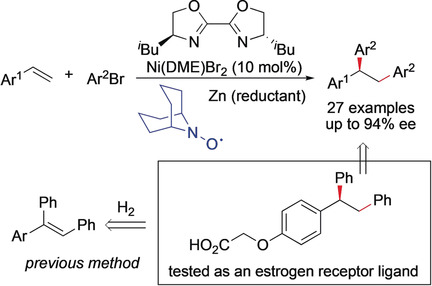
Under reducing conditions: A nickel-catalyzed asymmetric diarylation reaction of vinylarenes enables the preparation of chiral α,α,β-triarylated ethane scaffolds. The use of reducing conditions with aryl bromides as coupling partners obviates the need for stoichiometric organometallic reagents, and tolerates a broad range of functional groups.
Amination
A Highly Active Ylide-Functionalized Phosphine for Palladium-Catalyzed Aminations of Aryl Chlorides
- Pages: 3203-3207
- First Published: 19 November 2018
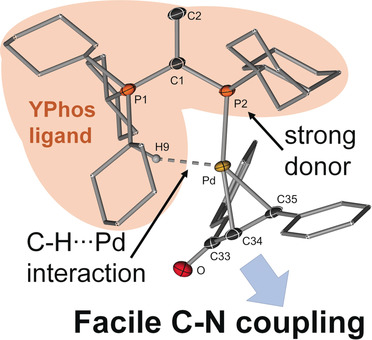
Give a little bit: The ylide-functionalized phosphine CyYMePCy2, which is easy to synthesize in few steps, shows excellent performance in a series of C−N cross coupling reactions at room temperature. This efficiency can be explained by the strong electron-donating properties of the ligand and its unique architecture, which allows stabilization of the active Pd species through a weak C−H⋅⋅⋅Pd interaction.
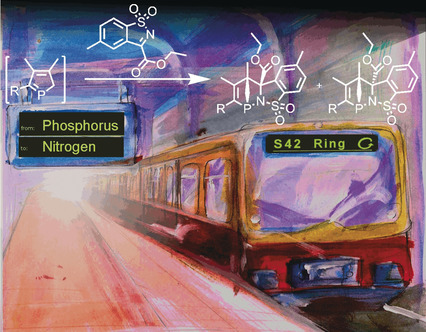
Phospha-aza-Diels–Alder Reaction
Access to 1-Phospha-2-azanorbornenes by Phospha-aza-Diels–Alder Reactions
- Pages: 3208-3211
- First Published: 29 October 2018
Clusters
Predicting Mole-Fraction-Dependent Dissociation for Weak Acids
- Pages: 3212-3216
- First Published: 27 December 2018
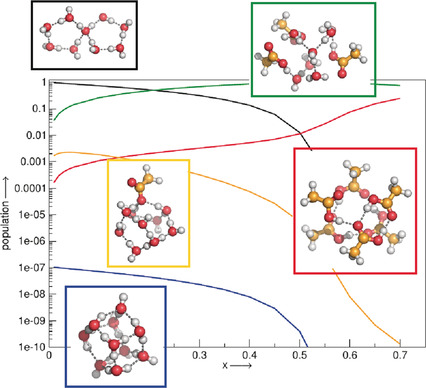
Binary quantum cluster equilibrium theory was applied to predict acid strengths over the complete concentration range through mole-fraction-depended populations of molecular and ionic clusters. It is shown for formic and acetic acid dissolved in water that the acid strength increases with increasing mole fraction in a complex way, reflecting the complex interplay between the dissociated hydronium ions.
Asymmetric Catalysis
Helical Multi-Coordination Anion-Binding Catalysts for the Highly Enantioselective Dearomatization of Pyrylium Derivatives
- Pages: 3217-3221
- First Published: 14 November 2018
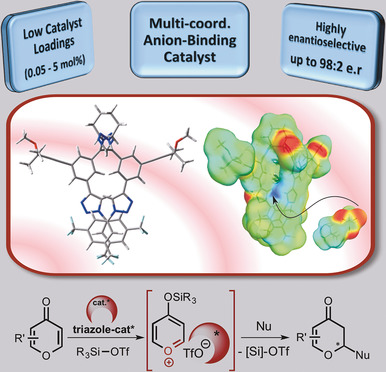
CApTive lock-key model: Oxygen heterocycles were synthesized in high enantioselectivities from pyrylium derivatives by embracing a multi-coordination approach with helical anion-binding tetrakistriazole catalysts. New insights into the hydrogen-donor ability and key binding interactions suggest the formation of a high-order host:guest complex.
Polybismuthides
Polybismuthide Anions as Ligands: The Homoleptic Complex [(Bi7)Cd(Bi7)]4− and the Ternary Cluster [(Bi6)Zn3(TlBi5)]4−
- Pages: 3222-3226
- First Published: 05 January 2019
![Polybismuthide Anions as Ligands: The Homoleptic Complex [(Bi7)Cd(Bi7)]4− and the Ternary Cluster [(Bi6)Zn3(TlBi5)]4−](/cms/asset/b93f47d9-88c8-49fc-a2da-98e29f536fa8/anie201812473-toc-0001-m.jpg)
A coordination compound with intact Bi73− ligands, namely the homoleptic complex [(Bi7)Cd(Bi7)]4−, and the ternary cluster [(Bi6)Zn3(TlBi5)]4− were prepared through in situ degradation of the binary Zintl anion (TlBi3)2−. The compounds provide a glimpse into a possible formation pathway of the polycyclic polybismuthide, the follow-up chemistry of which has been unprecedented to date. Both title compounds were further studied by means of DFT methods.









![Photochromic Benzo[b]phosphole Alkynylgold(I) Complexes with Mechanochromic Property to Serve as Multistimuli-Responsive Materials](/cms/asset/3c34e1b0-9803-4c3d-82cf-a0b89639896a/anie201806272-toc-0001-m.jpg)