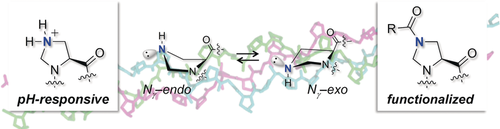
γ-Azaproline Confers pH Responsiveness and Functionalizability on Collagen Triple Helices
Dr. Matthew R. Aronoff
Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, ETH Zürich, Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 3, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJasmine Egli
Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, ETH Zürich, Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 3, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMassimiliano Menichelli
Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, ETH Zürich, Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 3, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Helma Wennemers
Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, ETH Zürich, Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 3, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Matthew R. Aronoff
Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, ETH Zürich, Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 3, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJasmine Egli
Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, ETH Zürich, Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 3, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorMassimiliano Menichelli
Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, ETH Zürich, Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 3, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Helma Wennemers
Laboratory of Organic Chemistry, ETH Zürich, Vladimir-Prelog-Weg 3, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to Professor Ronald Raines on the occasion of a special birthday
Graphical Abstract
Abstract
Proline derivatives bearing substituents at Cγ are valuable tools for biological and materials investigations. However, the stereochemistry at Cγ can produce undesired steric or stereoelectronic interactions. Here, we introduce γ-azaproline (γ-azPro), which lacks a stereogenic center at Cγ, as a pH-responsive and functionalizable proline analogue that can adapt to its environment. Conformational analyses by NMR spectroscopy and DFT calculations revealed that the imidazolidine ring of γ-azPro is flexible. Incorporation of γ-azPro into collagen model peptides (CMPs) produced pH-responsive triples helices and triple helices that can be easily functionalized.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201813048-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf8.4 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aP. Remuzon, Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 13803–13835;
- 1bA. K. Pandey, D. Naduthambi, K. M. Thomas, N. J. Zondlo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4333–4363.
- 2M. D. Shoulders, R. T. Raines, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958.
- 3For examples, see:
- 3aS. A. Lieblich, K. Y. Fang, J. K. B. Cahn, J. Rawson, J. LeBon, H. T. Ku, D. A. Tirrell, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8384–8387;
- 3bB. Holzberger, S. Obeid, W. Welte, K. Diederichs, A. Marx, Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 2924–2931;
- 3cM. D. Crespo, M. Rubini, PLoS One 2011, 5, e 19425;
- 3dT.-Y. Zheng, Y.-J. Lin, J.-C. Horng, Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4255–4263;
- 3eT. Steiner, P. Hess, J. H. Bae, B. Wiltschi, L. Moroder, N. Budisa, PLoS One 2008, 2, e 1680;
- 3fW. Kim, K. Hardcastle, V. P. Conticello, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 8141–8145; Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 8321–8325;
- 3gD. Naduthambi, N. J. Zondlo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12430–12431;
- 3hS. C. R. Lummis, D. L. Beene, L. W. Lee, H. A. Lester, R. W. Broadhurst, D. A. Dougherty, Nature 2005, 438, 248–252;
- 3iR. Golbik, C. Yu, E. Weyher-Stingl, R. Huber, L. Moroder, N. Budisa, C. Schiene-Fischer, Biochemistry 2005, 44, 16026–16034;
- 3jU. Arnold, M. P. Hinderaker, J. Köditz, R. Golbik, R. Ulbrich-Hofmann, R. T. Raines, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7500–7501;
- 3kC. Renner, S. Alefelder, J. H. Bae, N. Budisa, R. Huber, L. Moroder, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 923–925;
10.1002/1521-3773(20010302)40:5<923::AID-ANIE923>3.0.CO;2-# CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2001, 113, 949–951;
- 3lS. K. Holmgren, K. M. Taylor, L. E. Bretscher, R. T. Raines, Nature 1998, 392, 666–667.
- 4For examples, see:
- 4aL. E. Bretscher, C. L. Jenkins, K. M. Taylor, M. L. DeRider, R. T. Raines, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 777–778;
- 4bS. A. Cadamuro, R. Reichold, U. Kusebauch, H.-J. Musiol, C. Renner, P. Tavan, L. Moroder, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2143–2146; Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 2174–2177;
- 4cM. D. Shoulders, K. A. Satyshur, K. T. Forest, R. T. Raines, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 559–564;
- 4dL.-S. Sonntag, S. Schweizer, C. Ochsenfeld, H. Wennemers, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14697–14703.
- 5J. Bella, Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 1001–1025.
- 6
- 6aG. B. Fields, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 1237–1258;
- 6bS. Chattopadhyay, R. T. Raines, Biopolymers 2014, 101, 821–833;
- 6cK. Strauss, J. Chmielewski, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 34–41;
- 6dA. N. Moore, J. D. Hartgerink, Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 714–722.
- 7For examples, see:
- 7aF. W. Kotch, R. T. Raines, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3028–3033;
- 7bB. Sarkar, L. E. R. O'Leary, J. D. Hartgerink, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14417–14424;
- 7cI. C. Tanrikulu, A. Forticaux, S. Jin, R. T. Raines, Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 1008–1014.
- 8
- 8aJ. Bella, M. Eaton, B. Brodsky, H. M. Berman, Science 1994, 266, 75–81;
- 8bK. Okuyama, C. Hongo, R. Fukushima, G. G. Wu, H. Narita, K. Noguchi, Y. Tanaka, N. Nishino, Biopolymers 2004, 76, 367–377.
- 9R. S. Erdmann, H. Wennemers, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13957–13959.
- 10N. B. Hentzen, L. E. Smeenk, J. Witek, S. Riniker, H. Wennemers, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12815–12820.
- 11
- 11aC. Siebler, R. S. Erdmann, H. Wennemers, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10340–10344; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 10508–10512;
- 11bJ. Egli, C. Siebler, B. Maryasin, R. S. Erdmann, C. Bergande, C. Ochsenfeld, H. Wennemers, Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 7938–7944.
- 12
- 12aT. Jiang, C. Wu, Y. Liu, Z. Liu, J. S. Wall, X. Zuo, T. Lian, K. Salaita, C. Ni, D. Pochan, V. P. Conticello, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4300–4308;
- 12bI. R. Babu, K. N. Ganesh, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 2079–2080.
- 13
- 13aR. S. Erdmann, H. Wennemers, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6835–6838; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 6967–6970;
- 13bR. S. Erdmann, H. Wennemers, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17117–17124.
- 14
- 14aA. L. Bartuschat, K. Wicht, M. R. Heinrich, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10294–10298; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 10433–10437.
- 15
- 15aF. W. Kotch, I. A. Guzei, R. T. Raines, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2952–2953;
- 15bM. D. Shoulders, J. A. Hodges, R. T. Raines, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8112–8113;
- 15cJ. A. Hodges, R. T. Raines, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9262–9263.
- 16
- 16aP. Dumy, M. Keller, D. E. Ryan, B. Rohwedder, T. Wöhr, M. Mutter, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 918–925;
- 16bM. Keller, T. Wöhr, P. Dumy, L. Patiny, M. Mutter, Chem. Eur. J. 2000, 6, 4358–4363.
10.1002/1521-3765(20001201)6:23<4358::AID-CHEM4358>3.0.CO;2-W CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 17F. Lindahl, H. N. Hoang, D. P. Fairlie, M. A. Cooper, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 4496–4498.
- 18Note, whereas peptides containing the constitutional isomer with an N atom in place of the α-carbon atom, α-azPro, have been studied, γ-azPro has not been incorporated into peptides. For examples of α-azPro-containing peptides, see:
- 18aA. Lecoq, C. Boussard, M. Marraud, A. Aubry, Biopolymers 1993, 33, 1051–1059;
- 18bW.-J. Zhang, A. Berglund, J. L. F. Kao, J.-P. Couty, M. C. Gershengorn, G. R. Marshall, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 1221–1235;
- 18cY. Zhang, R. M. Malamakal, D. M. Chenoweth, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10826–10832; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 10976–10982.
- 19M. L. DeRider, S. J. Wilkens, M. J. Waddell, L. E. Bretscher, F. Weinhold, R. T. Raines, J. L. Markley, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 2497–2505.
- 20
- 20aM. Mutter, T. Wöhr, S. Gioria, M. Keller, Biopolymers 1999, 51, 121–128;
10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(1999)51:2<121::AID-BIP2>3.0.CO;2-O CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 20bY. K. Kang, J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 2074–2082.
- 21For details, see the Supporting Information.
- 22CMPs 4X and 5X are stable at room temperature and are stable upon heating at neutral and basic pH. At acidic pH (<2), the imidazolidine ring slowly opens at high temperatures as determined by MS (see the Supporting Information).
- 23Note, the γ-azPro residue destabilizes the collagen triple helix relative to a Pro residue, at both the Xaa and Yaa positions (Tm=40 °C for Ac-[ProHypGly]3-Pro-Pro-Gly-[ProHypGly]3-NH2 (CMP 7); see Ref. [13]), most likely because of the lower trans/cis ratio of γ-azPro- compared to Pro-containing peptides.
- 24The inductive effects from the electron-withdrawing groups in γ-azPro likely reduce the basicity of the γ-nitrogen atom far below the typical pKa value of secondary amines; see the Supporting Information for details.
- 25J. Huotari, A. Helenius, EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3481–3500.
- 26For another Pro derivative (4-ketoproline, Kep) with a sp2 character at the γ-position, see: A. Choudhary, K. J. Kramer, M. D. Shoulders, R. T. Raines, Pept. Sci. 2015, 104, 110–115.
- 27
- 27aN. Murthy, J. Campell, N. Fausto, A. S. Fausto, P. S. Stayton, J. Controlled Release 2003, 89, 365–374;
- 27bD. Neri, C. T. Supuran, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2011, 47, 8429–8432.