Lithiophilic Faceted Cu(100) Surfaces: High Utilization of Host Surface and Cavities for Lithium Metal Anodes
Yu Gu
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHong-Yu Xu
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXia-Guang Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWei-Wei Wang
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorJun-Wu He
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuai Tang
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Jia-Wei Yan
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. De-Yin Wu
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ming-Sen Zheng
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Quan-Feng Dong
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Bing-Wei Mao
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorYu Gu
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHong-Yu Xu
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXia-Guang Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorWei-Wei Wang
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorJun-Wu He
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuai Tang
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Jia-Wei Yan
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. De-Yin Wu
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ming-Sen Zheng
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Quan-Feng Dong
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Bing-Wei Mao
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
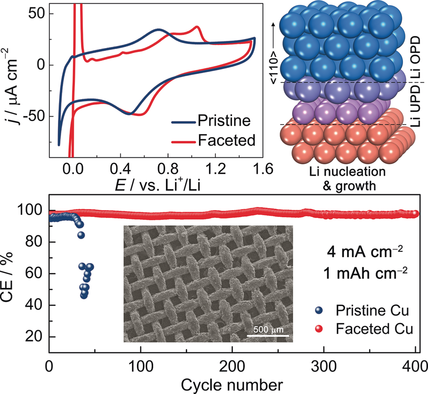
Get in touch with lithium: The generation of surface lithiophilicity on planar and 3D Cu hosts for Li metal anodes is reported. Enabled by a lattice matching of Cu(100) and Li(110), smooth deposition of Li thin films and the creation of ultra-smooth ultra-thin SEI on the Cu hosts is made possible. This allows a high utilization of not only the surface but also cavities of the Cu hosts.
Abstract
Lithium metal anodes suffer from poor cycling stability and potential safety hazards. To alleviate these problems, Li thin-film anodes prepared on current collectors (CCs) and Li-free types of anodes that involve direct Li plating on CCs have received increasing attention. In this study, the atomic-scale design of Cu-CC surface lithiophilicity based on surface lattice matching of the bcc Li(110) and fcc Cu(100) faces as well as electrochemical achievement of Cu(100)-preferred surfaces for smooth Li deposition with a low nucleation barrier is reported. Additionally, a purposely designed solid–electrolyte interphase is created for Li anodes prepared on CCs. Not only is a smooth planar Li thin film prepared, but a uniform Li plating/stripping on the skeleton of 3D CCs is achieved as well by high utilization of the surface and cavities of the 3D CCs. This work demonstrates surface electrochemistry approaches to construct stable Li metal–electrolyte interphases towards practical applications of Li anodes prepared on CCs.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201812523-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf45.8 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aD. Lin, Y. Liu, Y. Cui, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 194–206;
- 1bM. D. Tikekar, S. Choudhury, Z. Tu, L. A. Archer, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16114;
- 1cW. Xu, J. Wang, F. Ding, X. Chen, E. Nasybulin, Y. Zhang, J.-G. Zhang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 513;
- 1dD. Aurbach, B. D. McCloskey, L. F. Nazar, P. G. Bruce, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16128.
- 2
- 2aX.-B. Cheng, R. Zhang, C.-Z. Zhao, Q. Zhang, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10403–10473;
- 2bX. Yu, A. Manthiram, Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 527–543.
- 3
- 3aQ. Pang, X. Liang, I. R. Kochetkov, P. Hartmann, L. F. Nazar, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 9795–9798; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 9943–9946;
- 3bL. Li, S. Basu, Y. Wang, Z. Chen, P. Hundekar, B. Wang, J. Shi, Y. Shi, S. Narayanan, N. Koratkar, Science 2018, 359, 1513–1516;
- 3cH. J. Chang, A. J. Ilott, N. M. Trease, M. Mohammadi, A. Jerschow, C. P. Grey, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15209–15216.
- 4
- 4aY. Gu, W.-W. Wang, Y.-J. Li, Q.-H. Wu, S. Tang, J.-W. Yan, M.-S. Zheng, D.-Y. Wu, C.-H. Fan, W.-Q. Hu, Z.-B. Chen, Y. Fang, Q.-H. Zhang, Q.-F. Dong, B.-W. Mao, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1339;
- 4bY. Gu, W.-W. Wang, J.-W. He, S. Tang, H.-Y. Xu, J.-W. Yan, Q.-H. Wu, X.-B. Lian, M.-S. Zheng, Q.-F. Dong, B.-W. Mao, ChemElectroChem 2018, 6, 181–188;
- 4cX.-B. Cheng, C. Yan, X. Chen, C. Guan, J.-Q. Huang, H.-J. Peng, R. Zhang, S.-T. Yang, Q. Zhang, Chem 2017, 2, 258–270;
- 4dX. Xin, K. Ito, A. Dutta, Y. Kubo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13206–13210; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 13390–13394.
- 5
- 5aG. Zheng, S. W. Lee, Z. Liang, H.-W. Lee, K. Yan, H. Yao, H. Wang, W. Li, S. Chu, Y. Cui, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 618–623;
- 5bN. W. Li, Y. Shi, Y. X. Yin, X. X. Zeng, J. Y. Li, C. J. Li, L. J. Wan, R. Wen, Y. G. Guo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1505–1509; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 1521–1525;
- 5cZ. Zhang, X. Xu, S. Wang, Z. Peng, M. Liu, J. Zhou, C. Shen, D. Wang, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26801–26808.
- 6J. Zheng, P. Yan, D. Mei, M. H. Engelhard, S. S. Cartmell, B. J. Polzin, C. Wang, J.-G. Zhang, W. Xu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1502151.
- 7F. Ding, W. Xu, G. L. Graff, J. Zhang, M. L. Sushko, X. Chen, Y. Shao, M. H. Engelhard, Z. Nie, J. Xiao, X. Liu, P. V. Sushko, J. Liu, J.-G. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4450–4456.
- 8
- 8aJ. Qian, B. D. Adams, J. Zheng, W. Xu, W. A. Henderson, J. Wang, M. E. Bowden, S. Xu, J. Hu, J.-G. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7094–7102;
- 8bH. Porthault, C. Decaux, Electrochim. Acta 2016, 194, 330–337.
- 9
- 9aC. P. Yang, Y. X. Yin, S. F. Zhang, N. W. Li, Y. G. Guo, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8058;
- 9bY. Zhang, C. Wang, G. Pastel, Y. Kuang, H. Xie, Y. Li, B. Liu, W. Luo, C. Chen, L. Hu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800635;
- 9cH. Ye, S. Xin, Y. X. Yin, J. Y. Li, Y. G. Guo, L. J. Wan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5916–5922.
- 10A. M. Hafez, Y. Jiao, J. Shi, Y. Ma, D. Cao, Y. Liu, H. Zhu, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802156.
- 11
- 11aJ. Wang, H. Wang, J. Xie, A. Yang, A. Pei, C.-L. Wu, F. Shi, Y. Liu, D. Lin, Y. Gong, Y. Cui, Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 14, 345–350;
- 11bD. Lin, Y. Liu, A. Pei, Y. Cui, Nano Res. 2017, 10, 4003–4026.
- 12
- 12aC. Zhang, W. Lv, G. Zhou, Z. Huang, Y. Zhang, R. Lyu, H. Wu, Q. Yun, F. Kang, Q.-H. Yang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1703404;
- 12bZ. Liang, D. Lin, J. Zhao, Z. Lu, Y. Liu, C. Liu, Y. Lu, H. Wang, K. Yan, X. Tao, Y. Cui, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 2862–2867;
- 12cK. Yan, Z. Lu, H.-W. Lee, F. Xiong, P.-C. Hsu, Y. Li, J. Zhao, S. Chu, Y. Cui, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16010;
- 12dL. Qin, H. Xu, D. Wang, J. Zhu, J. Chen, W. Zhang, P. Zhang, Y. Zhang, W. Tian, Z. Sun, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27764–27770;
- 12eS. Wu, Z. Zhang, M. Lan, S. Yang, J. Cheng, J. Cai, J. Shen, Y. Zhu, K. Zhang, W. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705830.
- 13D. M. Kolb in Advances in Electrochemistry and Electrochemical Engineering, Vol. 11 (Eds.: ), Wiley-VCH, New York, 1978, p. 125.
- 14Y. Li, Y. Li, A. Pei, K. Yan, Y. Sun, C.-L. Wu, L.-M. Joubert, R. Chin, A. L. Koh, Y. Yu, J. Perrino, B. Butz, S. Chu, Y. Cui, Science 2017, 358, 506–510.
- 15Y. Xia, Y. Xiong, B. Lim, S. E. Skrabalak, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 60–103; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 62–108.
- 16During submission of the present work, a similar work was reported in the form of an online conference abstract: Y. J. Kim, H. Noh, S. Yuk, J. Lee, H. T. Kim, Americas International Meeting on Electrochemistry and Solid State Science, 2018, 309 (Sept. 30-Oct. 4,2018, Cancun).