Chiral Lithium Amido Aryl Zincates: Simple and Efficient Chemo- and Enantio-Selective Aryl Transfer Reagents
Dr. Pauline Chaumont-Olive
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Mathieu Rouen
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Gabriella Barozzino-Consiglio
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorAmel Ben Abdeladhim
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jacques Maddaluno
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Anne Harrison-Marchand
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Pauline Chaumont-Olive
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Mathieu Rouen
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Gabriella Barozzino-Consiglio
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorAmel Ben Abdeladhim
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Jacques Maddaluno
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Anne Harrison-Marchand
Normandie Univ, UNIROUEN, INSA de Rouen, CNRS, Laboratoire COBRA (UMR 6014 & FR 3038), 76000 Rouen, France
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
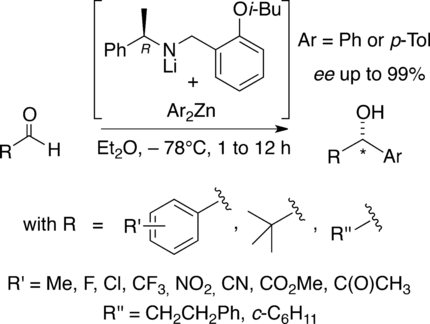
Chemo- and enantio-selective nucleophilic aryl transfer: The key reactant is a chiral tricoordinated lithium amido aryl zincate of which the chiral appendage is simply recovered and reused. The arylation leaves intact sensitive functions such as esters, nitriles, ketones or enolisable sites, while running with aldehyde groups in good yields and high ee values, this whatever the ortho, meta, or para substituent borne by the substrate if aromatic.
Abstract
An enantioselective aryl transfer is promoted using chiral tricoordinated lithium amido aryl zincates that are easily accessible reagents and whose chiral appendage is simply recovered for reuse. The arylation reaction is run in good yields (60 % average on twenty substrates) and high enantiomeric excesses (95 % ee average). This occurs whatever the ortho, meta, or para substituent borne by the substrate and a complete chemoselectivity is observed with respect to the aldehyde function. Sensitive groups such as nitriles, esters, ketones, and enolisable substrates resist to the action of the ate reagent, warranting a large scope to this methodology.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201813510-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf8.4 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aD. Ameen, T. J. Snape, MedChemComm 2013, 4, 893–907;
- 1bF. Schmidt, R. T. Stemmler, J. Rudolph, C. Bolm, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 454–470.
- 2For enantioselective aryl transfer reactions using homo(bi)metallic complexes, see with the [Ti,Ti] combination
- 2aK.-H. Wu, S. Zhou, C.-A. Chen, M. C. Yang, R.-T. Chiang, C.-R. Chena, H.-M. Gau, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11668–11670;
- 2bA. Uenishi, Y. Nakagawa, H. Osumi, T. Harada, Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 4896–4905;
- 2cS.-J. Chang, S. Zhou, H.-M. Gau, RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 9368–9373; with the [Zn-Zn] combination
- 2dP. I. Dosa, J. C. Ruble, G. C. Fu, J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 444–445;
- 2eW.-S. Huang, L. Pu, J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 4222–4223;
- 2fW.-S. Huang, L. Pu, Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 145–149;
- 2gC. Bolm, N. Hermanns, J. P. Hildebrand, K. Muñiz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3465–3467;
10.1002/1521-3773(20001002)39:19<3465::AID-ANIE3465>3.0.CO;2-4 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2000, 112, 3607–3609;
- 2hC. Bolm, M. Kesselgruber, N. Hermanns, J. P. Hildebrand, G. Raabe, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 1488–1490;
10.1002/1521-3773(20010417)40:8<1488::AID-ANIE1488>3.0.CO;2-B CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2001, 113, 1536–1538;
- 2iM. Fontes, X. Verdaguer, L. Solà, M. A. Pericàs, A. Riera, J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 2532–2543;
- 2jD. Castellnou, M. Fontes, C. Jimeno, D. Font, L. Solà, X. Verdaguer, M. A. Pericàs, Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 12111–12120;
- 2kY.-C. Qin, L. Pu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 273–277; Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 279–283;
- 2lY.-C. Qin, L. Liu, M. Sabat, L. Pu, Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 9335–9348;
- 2mJ. G. Kim, P. J. Walsh, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4175–4178; Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 4281–4284;
- 2nJ. Sedelmeier, C. Bolm, J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 8859–8862;
- 2oS. Rodríguez-Escrich, K. S. Reddy, C. Jimeno, G. Colet, C. Rodríguez-Escrich, L. Solà, A. Vidal-Ferran, M. A. Pericàs, J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 5340–5353;
- 2pL. Salvi, J. G. Kim, P. J. Walsh, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12483–12493;
- 2qK. Shimizu, H. Uetsu, T. Gotanda, K. Ito, Synlett 2015, 26, 1238–1242.
- 3For enantioselective aryl transfer reactions on imines using hetero(bi)metallic complexes see:
- 3aH.-F. Duan, Y.-X. Jia, L.-X. Wang, Q.-L. Zhou, Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 2567–2569;
- 3bH.-Y. Yanga, M.-H. Xu, Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 9223–9225;
- 3cZ. Cao, H. Du, Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 2602–2605;
- 3dZ. Cui, H.-J. Yu, R.-F. Yang, W.-Y. Gao, C.-G. Feng, G.-Q. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12394–12397.
- 4For enantioselective aryl transfer reactions on carbonyl substrates using hetero(bi)metallic complexes incorporating a transition metal (TM) see when TM=Cu
- 4aR. Shintani, K. Takatsu, T. Hayashi, Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6822–6824; when TM=Ni
- 4bT. Arao, K. Kondo, T. Aoyama, Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 4115–4117;
- 4cK. Yamamoto, K. Tsurumi, F. Sakurai, K. Kondo, T. Aoyama, Synthesis 2008, 3585–3590;
- 4dR. Kumar, Y. Hoshimoto, H. Yabuki, M. Ohashi, S. Ogoshi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11838–11845; when TM=Pd
- 4eR. Zhang, Q. Xu, X. Zhang, T. Zhang, M. Shi, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2010, 21, 1928–1935; when TM=Rh
- 4fH.-F. Duan, J.-H. Xie, W.-J. Shi, Q. Zhang, Q.-L. Zhou, Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 1479–1481;
- 4gT. Nishimura, H. Kumamoto, M. Nagaosa, T. Hayashi, Chem. Commun. 2009, 5713–5715;
- 4hV. R. Jumde, S. Facchetti, A. Iuliano, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2010, 21, 2775–2781;
- 4iJ. Chen, S. Yang, Z. Chen, C. Song, Y. Ma, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2015, 26, 288–295; when TM=Ru
- 4jY. Yamamoto, K. Kurihara, N. Miyaura, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4414–4416; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4478–4480; when TM=Ti
- 4kK.-H. Wu, H.-M. Gau, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14808–14809;
- 4lS.-H. Hsieh, C.-A. Chen, D.-W. Chuang, M.-C. Yang, H.-T. Yang, H.-M. Gau, Chirality 2008, 20, 924–929;
- 4mS. Zhou, D.-W. Chuang, S.-J. Chang, H.-M. Gau, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2009, 20, 1407–1412;
- 4nS. Zhou, K.-H. Wu, C.-A. Chen, H.-M. Gau, J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 3500–3505;
- 4oY. Muramatsu, T. Harada, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1088–1090; Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 1104–1106;
- 4pH. Takahashi, T. Tsubuki, K. Higashiyama, Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 260–265.
- 5For enantioselective aryl transfer reactions on carbonyl substrates using hetero(bi)metallic complexes incorporating the Zn post-transition metal element see
- 5aD. Glynn, J. Shannon, S. Woodward, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 1053–1060;
- 5bC. Bolm, J. Rudolph, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14850–14851;
- 5cO. Prieto, D. J. Ramón, M. Yus, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2003, 14, 1955–1957;
- 5dA. L. Braga, D. S. Lüdtke, F. Vargas, M. W. Paixão, Chem. Commun. 2005, 2512–2514;
- 5eA. L. Braga, D. S. Lüdtke, P. H. Schneider, F. Vargas, A. Schneider, L. A. Wessjohann, M. W. Paixão, Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 7827–7830;
- 5fJ.-X. Ji, J. Wu, T. T.-L. Au-Yeung, C.-W. Yip, R. K. Haynes, A. S. C. Chan, J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 1093–1095;
- 5gP.-Y. Wu, H.-L. Wu, B.-J. Uang, J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 833–835;
- 5hA. L. Braga, M. W. Paixão, B. Westermann, P. H. Schneider, L. A. Wessjohann, J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 2879–2882;
- 5iJ. Ruan, G. Lu, L. Xu, Y.-M. Li, A. S. C. Chan, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 76–84;
- 5jC. Jimeno, S. Sayalero, T. Fjermestad, G. Colet, F. Maseras, M. A. Pericàs, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1098–1101; Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 1114–1117;
- 5kM. Godoi, E. E. Alberto, M. W. Paixão, L. A. Soares, P. H. Schneider, A. L. Braga, Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 1341–1345;
- 5lR. S. Schwab, L. C. Soares, L. Dornelles, O. E. D. Rodrigues, M. W. Paixão, M. Godoi, A. L. Braga, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 3574–3578;
- 5mX.-B. Wang, K. Kodama, T. Hirose, X.-F. Yang, G.-Y. Zhang, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2010, 21, 75–80;
- 5nA. Dionéia Wouters, G. H. G. Trossini, H. A. Stefani, D. S. Lüdtke, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2351–2356;
- 5oA. Venturini Moro, E. R. T. Tiekink, J. Zukerman-Schpector, D. S. Lüdtke, C. R. D. Correia, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 3696–3703;
- 5pX. Jia, A. Lin, Z. Mao, C. Zhu, Y. Cheng, Molecules 2011, 16, 2971–2981;
- 5qR. Infante, J. Nieto, C. Andrés, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 6691–6699;
- 5rX. Song, Y.-Z. Hua, J.-G. Shi, P.-P. Sun, M.-C. Wang, J. Chang, J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 6087–6093;
- 5sS. Jarzyński, G. Utecht, S. Leśniak, M. Rachwalski, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2017, 28, 1774–1779;
- 5tY. Wang, H. Zong, H. Huang, L. Song, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2017, 28, 90–97.
- 6Among studies regarding enantioselective aryl transfers, only a few, that are [2l], [2m], [2p], [4i], [5a], [5g], and [5r–t], are punctually considering aromatic substrates and/or aryl nucleophiles substituted by a CN or a CO2R group, and even more rarely is encountered the possibility of engaging a ketone function only found in [2q], [4n], and [5c].
- 7For chemoselective aromatic deprotonative metalations with zincates, see
- 7aY. Kondo, M. Shilai, M. Uchiyama, T. Sakamoto, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 3539–3540;
- 7bK. Snégaroff, S. Komagawa, F. Chevallier, P. C. Gros, S. Golhen, T. Roisnel, M. Uchiyama, F. Mongin, Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8191–8201.
- 8For chemoselective aromatic deprotonative metalations with magnesates, see
- 8aC. J. Rohbogner, G. C. Clososki, P. Knochel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1503–1507; Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 1526–1530;
- 8bG. Bentabed-Ababsa, F. Blanco, A. Derdour, F. Mongin, F. Trécourt, G. Quéguiner, R. Ballesteros, B. Abarca, J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 163–169.
- 9For chemoselective aromatic deprotonative metalations with aluminates, see
- 9aH. Naka, M. Uchiyama, Y. Matsumoto, A. E. H. Wheatley, M. McPartlin, J. V. Morey, Y. Kondo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1921–1930;
- 9bS. H. Wunderlich, P. Knochel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1501–1504; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 1530–1533.
- 10
- 10aD. Catel, F. Chevallier, F. Mongin, P. C. Gros, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 53–57;
- 10bO. Payen, F. Chevallier, F. Mongin, P. C. Gros, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2012, 23, 1678–1682;
- 10cD. Catel, O. Payen, F. Chevallier, F. Mongin, P. C. Gros, Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 4018–4028;
- 10dD. Tilly, K. Snégaroff, G. Dayaker, F. Chevallier, P. C. Gros, F. Mongin, Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 8761–8766.
- 11M. Rouen, P. Chaumont, G. Barozzino-Consiglio, J. Maddaluno, A. Harrison-Marchand, Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 9238–9242.
- 12J. E. Fleckenstein, K. Koszinowski, Organometallics 2011, 30, 5018–5026.
- 13Both Ph2Zn and p-Tol2Zn synthesized following Koszinovski's procedure were contaminated by biaryl biproducts Ph-Ph and p-Tol-p-Tol, respectively. As the latter must not prevent the addition reaction of nucleophilic arylation studied, the two organozincs were reacted in the presence of these impurities.
- 14Study in progress.
- 15The arylation has been conducted adding LiCl after the formation of the zincate (before that of the aldehyde) or at the same time than the aldehyde. In both cases, no reaction was observed. Only starting material was recovered, a result interpreted in the hypothesis that LiCl and the lithium amide would form a strong dipole-dipole mixed aggregate letting unreactive free Ph2Zn in the medium. F. Paté, N. Duguet, H. Oulyadi, A. Harrison-Marchand, C. Fressigné, J.-Y. Valnot, M.-C. Lasne, J. Maddaluno, J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 6982–6991.