Secondary-Ion Mass Spectrometry Images Cardiolipins and Phosphatidylethanolamines at the Subcellular Level
Corresponding Author
Dr. Hua Tian
Department of Chemistry, Pennsylvania State University, 209 Chemistry Bldg., University Park, PA, 16802 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Louis J. Sparvero
Department of Environmental and Occupational Health and Center for Free Radical and Antioxidant Health, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Search for more papers by this authorPaul Blenkinsopp
Ionoptika Ltd., Unit B6, Millbrook Cl, Chandler's Ford, Eastleigh, SO53 4BZ UK
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Andrew A. Amoscato
Department of Environmental and Occupational Health and Center for Free Radical and Antioxidant Health, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Simon C. Watkins
Department of Cell Biology, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hülya Bayır
Department of Chemistry, Pennsylvania State University, 209 Chemistry Bldg., University Park, PA, 16802 USA
Departments of Environmental and Occupational Health, Radiation Oncology, Critical Care Medicine, Center for Free Radical and Antioxidant Health and Safar Center for Resuscitation Research, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Children's Neuroscience Institute, UPMC Children's Hospital, University of Pittsburgh, 4200 Fifth Ave, Pittsburgh, PA, 15260 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Valerian E. Kagan
Department of Chemistry, Pennsylvania State University, 209 Chemistry Bldg., University Park, PA, 16802 USA
Departments of Environmental and Occupational Health, Chemistry, Radiation Oncology, Center for Free Radical and Antioxidant Health, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Laboratory of Navigational Redox Lipidomics, IM Sechenov Moscow Medical State University, Russia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Nicholas Winograd
Department of Chemistry, Pennsylvania State University, 209 Chemistry Bldg., University Park, PA, 16802 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Hua Tian
Department of Chemistry, Pennsylvania State University, 209 Chemistry Bldg., University Park, PA, 16802 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Louis J. Sparvero
Department of Environmental and Occupational Health and Center for Free Radical and Antioxidant Health, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Search for more papers by this authorPaul Blenkinsopp
Ionoptika Ltd., Unit B6, Millbrook Cl, Chandler's Ford, Eastleigh, SO53 4BZ UK
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Andrew A. Amoscato
Department of Environmental and Occupational Health and Center for Free Radical and Antioxidant Health, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Simon C. Watkins
Department of Cell Biology, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hülya Bayır
Department of Chemistry, Pennsylvania State University, 209 Chemistry Bldg., University Park, PA, 16802 USA
Departments of Environmental and Occupational Health, Radiation Oncology, Critical Care Medicine, Center for Free Radical and Antioxidant Health and Safar Center for Resuscitation Research, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Children's Neuroscience Institute, UPMC Children's Hospital, University of Pittsburgh, 4200 Fifth Ave, Pittsburgh, PA, 15260 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Valerian E. Kagan
Department of Chemistry, Pennsylvania State University, 209 Chemistry Bldg., University Park, PA, 16802 USA
Departments of Environmental and Occupational Health, Chemistry, Radiation Oncology, Center for Free Radical and Antioxidant Health, University of Pittsburgh, USA
Laboratory of Navigational Redox Lipidomics, IM Sechenov Moscow Medical State University, Russia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Nicholas Winograd
Department of Chemistry, Pennsylvania State University, 209 Chemistry Bldg., University Park, PA, 16802 USA
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
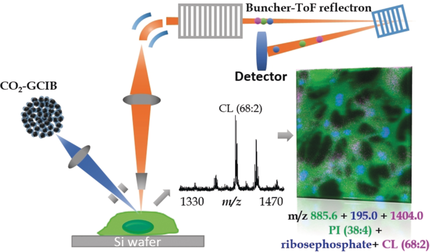
Beam me up: A high-energy gas-cluster ion beam (GCIB) with 1 μm lateral resolution was developed. This allowed single cell and subcellular mass spectrometry imaging of diverse phospholipids, including cardiolipin (CL) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE). Coupling this with immunohistochemistry provided assessments in specific subcellular compartments.
Abstract
Millions of diverse molecules constituting the lipidome act as important signals within cells. Of these, cardiolipin (CL) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) participate in apoptosis and ferroptosis, respectively. Their subcellular distribution is largely unknown. Imaging mass spectrometry is capable of deciphering the spatial distribution of multiple lipids at subcellular levels. Here we report the development of a unique 70 keV gas-cluster ion beam that consists of (CO2)n+(n>10 000) projectiles. Coupled with direct current beam buncher-time-of-flight secondary-ion mass spectrometry, it is optimized for sensitivity towards high-mass species (up to m/z 3000) at high spatial resolution (1 μm). In combination with immunohistochemistry, phospholipids, including PE and CL, have been assessed in subcellular compartments of mouse hippocampal neuronal cells and rat brain tissue.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201814256-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf6.9 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aB. R. Stockwell, J. P. Friedmann Angeli, H. Bayir, A. I. Bush, M. Conrad, S. J. Dixon, S. Fulda, S. Gascon, S. K. Hatzios, V. E. Kagan, K. Noel, X. Jiang, A. Linkermann, M. E. Murphy, M. Overholtzer, A. Oyagi, G. C. Pagnussat, J. Park, Q. Ran, C. S. Rosenfeld, K. Salnikow, D. Tang, F. M. Torti, S. V. Torti, S. Toyokuni, K. A. Woerpel, D. D. Zhang, Cell 2017, 171, 273–285;
- 1bY. Y. Tyurina, I. Shrivastava, V. A. Tyurin, G. Mao, H. H. Dar, S. Watkins, M. Epperly, I. Bahar, A. A. Shvedova, B. Pitt, S. E. Wenzel, R. K. Mallampalli, Y. Sadovsky, D. Gabrilovich, J. S. Greenberger, H. Bayir, V. E. Kagan, Antioxid. Redox Signaling 2017, 29, 1333–1358;
- 1cS. Neitemeier, A. Jelinek, V. Laino, L. Hoffmann, I. Eisenbach, R. Eying, G. K. Ganjam, A. M. Dolga, S. Oppermann, C. Culmsee, Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 558–570.
- 2
- 2aY. Y. Tyurina, V. A. Tyurin, A. M. Kaynar, V. I. Kapralova, K. Wasserloos, J. Li, M. Mosher, L. Wright, P. Wipf, S. Watkins, B. R. Pitt, V. E. Kagan, Am. J. Physiol.: Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 299, L73–L85;
- 2bJ. J. Maguire, Y. Y. Tyurina, D. Mohammadyani, A. A. Kapralov, T. S. Anthonymuthu, F. Qu, A. A. Amoscato, L. J. Sparvero, V. A. Tyurin, J. Planas-Iglesias, R.-R. He, J. Klein-Seetharaman, H. Bayır, V. E. Kagan, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 8–24.
- 3
- 3aJ. Ji, A. E. Kline, A. Amoscato, A. K. Samhan-Arias, L. J. Sparvero, V. A. Tyurin, Y. Y. Tyurina, B. Fink, M. D. Manole, A. M. Puccio, D. O. Okonkwo, J. P. Cheng, H. Alexander, R. S. B. Clark, P. M. Kochanek, P. Wipf, V. E. Kagan, H. Bayir, Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1407–1413;
- 3bV. E. Kagan, V. A. Tyurin, J. F. Jiang, Y. Y. Tyurina, V. B. Ritov, A. A. Amoscato, A. N. Osipov, N. A. Belikova, A. A. Kapralov, V. Kini, I. I. Vlasova, Q. Zhao, M. M. Zou, P. Di, D. A. Svistunenko, I. V. Kurnikov, G. G. Borisenko, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 223–232.
- 4
- 4aS. Doll, B. Proneth, Y. Y. Tyurina, E. Panzilius, S. Kobayashi, I. Ingold, M. Irmler, J. Beckers, M. Aichler, A. Walch, H. Prokisch, D. Trumbach, G. Mao, F. Qu, H. Bayir, J. Fullekrug, C. H. Scheel, W. Wurst, J. A. Schick, V. E. Kagan, J. P. Angeli, M. Conrad, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 91–98;
- 4bV. E. Kagan, G. Mao, F. Qu, J. P. Angeli, S. Doll, C. S. Croix, H. H. Dar, B. Liu, V. A. Tyurin, V. B. Ritov, A. A. Kapralov, A. A. Amoscato, J. Jiang, T. Anthonymuthu, D. Mohammadyani, Q. Yang, B. Proneth, J. Klein-Seetharaman, S. Watkins, I. Bahar, J. Greenberger, R. K. Mallampalli, B. R. Stockwell, Y. Y. Tyurina, M. Conrad, H. Bayir, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 81–90;
- 4cS. E. Wenzel, Y. Y. Tyurina, J. Zhao, C. M. St Croix, H. H. Dar, G. Mao, V. A. Tyurin, T. S. Anthonymuthu, A. A. Kapralov, A. A. Amoscato, K. Mikulska-Ruminska, I. H. Shrivastava, E. M. Kenny, Q. Yang, J. C. Rosenbaum, L. J. Sparvero, D. R. Emlet, X. Wen, Y. Minami, F. Qu, S. C. Watkins, T. R. Holman, A. P. VanDemark, J. A. Kellum, I. Bahar, H. Bayir, V. E. Kagan, Cell 2017, 171, 628–641.e626.
- 5
- 5aA. A. Amoscato, L. J. Sparvero, R. R. He, S. Watkins, H. Bayir, V. E. Kagan, Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 6587–6595;
- 5bL. J. Sparvero, A. A. Amoscato, A. B. Fink, T. Anthonymuthu, L. A. New, P. M. Kochanek, S. Watkins, V. E. Kagan, H. Bayir, J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 659–675.
- 6B. A. Boughton, B. Hamilton, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 965, 291–321.
- 7
- 7aM. Kompauer, S. Heiles, B. Spengler, Nat. Methods 2016, 14, 90;
- 7bA. Zavalin, E. M. Todd, P. D. Rawhouser, J. Yang, J. L. Norris, R. M. Caprioli, J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 1473–1481.
- 8B. Alberts, A. Johnson, J. Lewis, P. Walter, M. Raff, K. Roberts, Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed., Routledge, Abingdon-on-Thames, 2002.
- 9J. C. Vickerman, D. Briggs, ToF-SIMS: Surface Analysis by Mass Spectrometry, IM Publications, Chichester, 2001.
- 10
- 10aD. Touboul, F. Kollmer, E. Niehuis, A. Brunelle, O. Laprévote, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 1608–1618;
- 10bA. V. Steele, A. Schwarzkopf, J. J. McClelland, B. Knuffman, Nano Futures 2017, 1, 015005.
- 11J. S. Fletcher, R. Sadia, A. M. Barber, N. P. Lockyer, J. C. Vickerman, Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 273–276.
- 12H. Tian, L. J. Sparvero, A. A. Amoscato, A. Bloom, H. Bayır, V. E. Kagan, N. Winograd, Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4611–4619.
- 13T. B. Angerer, P. Blenkinsopp, J. S. Fletcher, Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 377, 591–598.
- 14
- 14aT. B. Angerer, A. S. Mohammadi, J. S. Fletcher, Biointerphases 2016, 11, 02A319;
- 14bP. M. Wehrli, T. B. Angerer, A. Farewell, J. S. Fletcher, J. Gottfries, Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8680–8688;
- 14cS. Sämfors, M. Ståhlman, M. Klevstig, J. Borén, J. S. Fletcher, Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 437, 77–86;
- 14dN. T. N. Phan, J. S. Fletcher, A. G. Ewing, Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 4063–4071.
- 15J. Matsuo, S. Torii, K. Yamauchi, K. Wakamoto, M. Kusakari, S. Nakagawa, M. Fujii, T. Aoki, T. Seki, Appl. Phys. Express 2014, 7, 056602.
- 16M. K. Passarelli, A. Pirkl, R. Moellers, D. Grinfeld, F. Kollmer, R. Havelund, C. F. Newman, P. S. Marshall, H. Arlinghaus, M. R. Alexander, A. West, S. Horning, E. Niehuis, A. Makarov, C. T. Dollery, I. S. Gilmore, Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 1175–1183.
- 17J. S. Fletcher, S. Rabbani, A. Henderson, P. Blenkinsopp, S. P. Thompson, N. P. Lockyer, J. C. Vickerman, Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9058–9064.
- 18
- 18aT. D. Do, T. J. Comi, S. J. B. Dunham, S. S. Rubakhin, J. V. Sweedler, Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3078–3086;
- 18bM. K. Passarelli, A. G. Ewing, N. Winograd, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 2231–2238;
- 18cJ. S. Fletcher, J. C. Vickerman, N. Winograd, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2011, 15, 733–740.
- 19D. Strzelecka, S. Chmielinski, S. Bednarek, J. Jemielity, J. Kowalska, Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8931.
- 20
- 20aH. Bayir, V. A. Tyurin, Y. Y. Tyurina, R. Viner, V. Ritov, A. A. Amoscato, Q. Zhao, X. J. Zhang, K. L. Janesko-Feldman, H. Alexander, L. V. Basova, R. S. B. Clark, P. M. Kochanek, V. E. Kagan, Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 154–169;
- 20bA. K. Samhan-Arias, J. Ji, O. M. Demidova, L. J. Sparvero, W. Feng, V. Tyurin, Y. Y. Tyurina, M. W. Epperly, A. A. Shvedova, J. S. Greenberger, H. Bayir, V. E. Kagan, A. A. Amoscato, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2012, 1818, 2413–2423.
- 21
- 21aA. M. Lavezzi, M. F. Corna, L. Matturri, J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 329, 45–50;
- 21bH. B. Sarnat, D. Nochlin, D. E. Born, Brain and Development 1998, 20, 88–94;
- 21cR. J. Mullen, C. R. Buck, A. M. Smith, Development 1992, 116, 201–211.