Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Intersectoral action for health
Economic and Humanistic Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results From the US National Survey Data 2018–2020
- First Published: 06 August 2024
Identification of Gaps in Quality of Care and Good Practice Interventions in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Insights From a Literature Review and Qualitative Study of Nine Centers in North America
- First Published: 27 June 2024
American College of Rheumatology White Paper: The Effects of Climate Change on Rheumatic Conditions—An Evolving Landscape and a Path Forward
- First Published: 15 May 2024
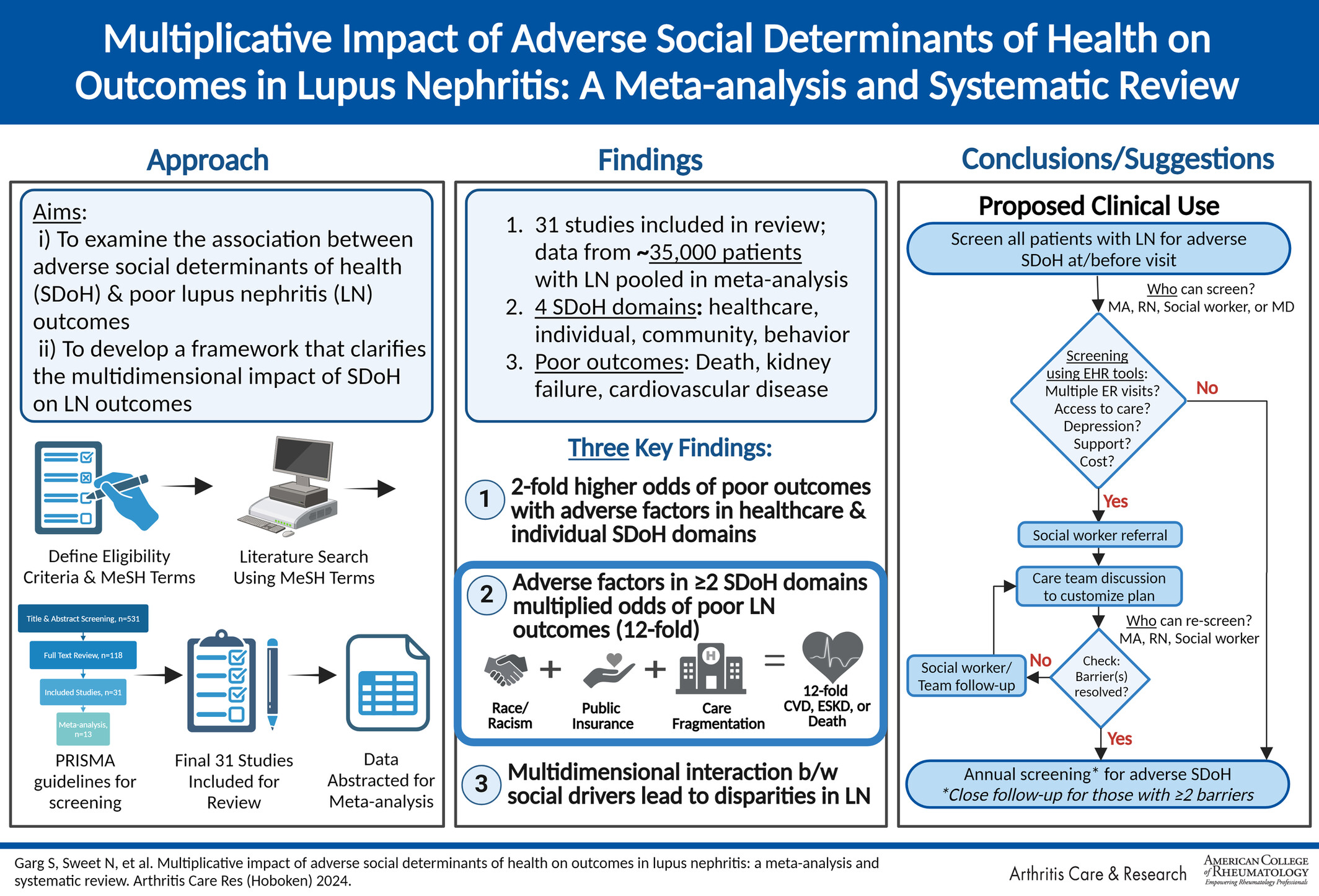
Multiplicative Impact of Adverse Social Determinants of Health on Outcomes in Lupus Nephritis: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review
- First Published: 01 May 2024
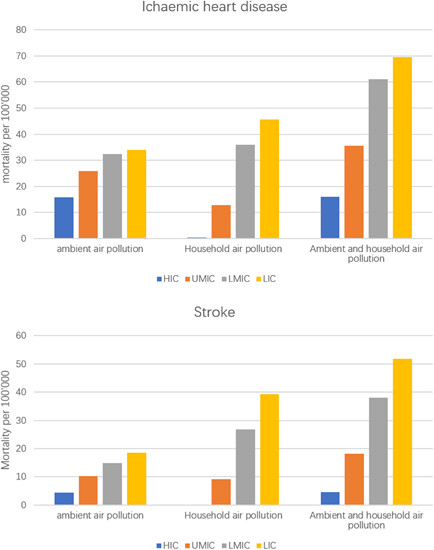
Cardiovascular disease mortality and air pollution in countries with different socioeconomic status
- First Published: 07 February 2024
Socioenvironmental sugar promotion and geographical inequalities in dental health of 5-year-old children in England
- First Published: 20 March 2024
Using Human Resources Data to Predict Turnover of Community Mental Health Employees: Prediction and Interpretation of Machine Learning Methods
- First Published: 03 July 2024
Commercial determinants of human rights: for-profit health care and housing
- First Published: 04 June 2023
How to … deconstruct the research paradigm: Supporting the non-social scientist researching in medical education
- First Published: 09 February 2024
Causality between COVID-19 and female reproductive function: A Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 07 August 2023
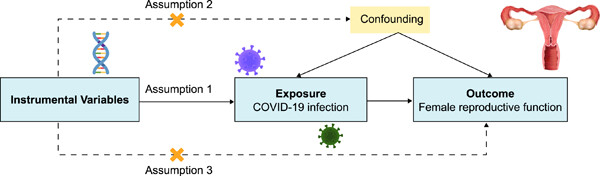
The two-sample Mendelian randomization and linkage disequilibrium score regression analyses revealed no association between coronavirus disease 2019 and estradiol levels, menstruation, and female infertility. However, the infection may causally influence sex hormone-binding globulin and total testosterone levels in females, while its impact on female reproductive function appears to be largely independent of the disease severity.
The International Association of Dental Traumatology (IADT) and the Academy for Sports Dentistry (ASD) guidelines for prevention of traumatic dental injuries: Part 1: General introduction
- First Published: 16 February 2024
The role of dental professionals in identifying, reporting, and supporting domestic violence victims
- First Published: 15 October 2023
International Association of Dental Traumatology guidelines for the management of traumatic dental injuries: General introduction
- First Published: 30 May 2020
World traumatic dental injury prevalence and incidence, a meta-analysis—One billion living people have had traumatic dental injuries
- First Published: 18 February 2018
Geriatric assessment for the practicing clinician: The why, what, and how
- First Published: 29 August 2024
Multidimensional structural racism and estimated cancer risk from traffic-related air pollution
- First Published: 26 August 2024
Significant associations were observed between high levels of structural racism and estimated cancer risk from traffic-related air pollution. These findings can inform policy interventions that address racial inequalities in exposure to traffic-related air pollution.
New and old technological and communication innovation
Association of optimism and social support with health-related quality of life among Australian women cancer survivors – A cohort study
- First Published: 21 May 2024
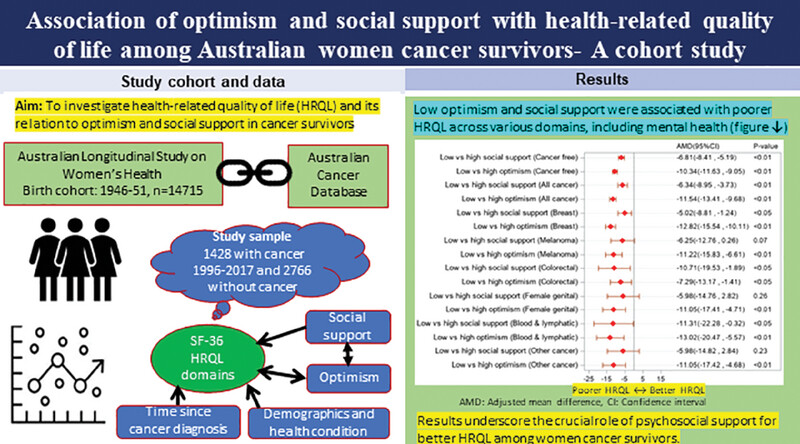
The study found that lower optimism was associated with poorer health-related quality of life (HRQL) across all domains. Social support and its interaction with optimism were significant in women with any cancer or breast cancer across various domains, highlighting the crucial role of psychosocial support for better HRQL.
eviQ Cancer Treatments Online: Providing evidence-based information to improve cancer patient outcomes
- First Published: 17 April 2024
eviQ Cancer Treatments Online (www.eviQ.org.au) is an Australian, open-access website providing evidence-based and consensus-driven cancer treatment protocols and information. This mixed method evaluation demonstrated eviQ is widely used and highly valued by Australian clinicians and that users agree eviQ contributes to improved patient health outcomes and quality of life.
Prediction of death rates for cardiovascular diseases and cancers
- First Published: 09 February 2023
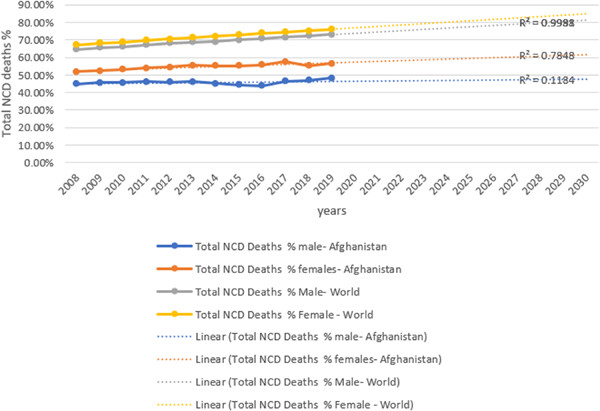
Trend analysis of noncommunicable diseases and their risk factors in Afghanistan
- First Published: 07 March 2023
The use of a large language model to create plain language summaries of evidence reviews in healthcare: A feasibility study
- First Published: 04 February 2024
The Man Van: A pilot study of using mobile targeted case-finding to address health inequalities in prostate cancer
- First Published: 04 September 2024

What's New?
Men from deprived groups are at increased risk of delayed prostate cancer diagnosis. To ease access to PSA blood testing and follow-up for ethnic minority men and men in deprived communities, the Royal Marsden Hospital and Institute of Cancer Research in the United Kingdom initiated Man Van. Here, comparison with health screening in general practice shows that the Man Van model yields higher levels of prostate cancer diagnosis at early stages. Other health conditions, including hypertension and erectile dysfunction, are also readily detected. The findings highlight the utility of the Man Van model in facilitating disease detection in hard-to-reach groups.
Quantitative imaging workshop XIX: Utilizing quantitative thoracic imaging to optimize population health final summary
- First Published: 29 December 2023
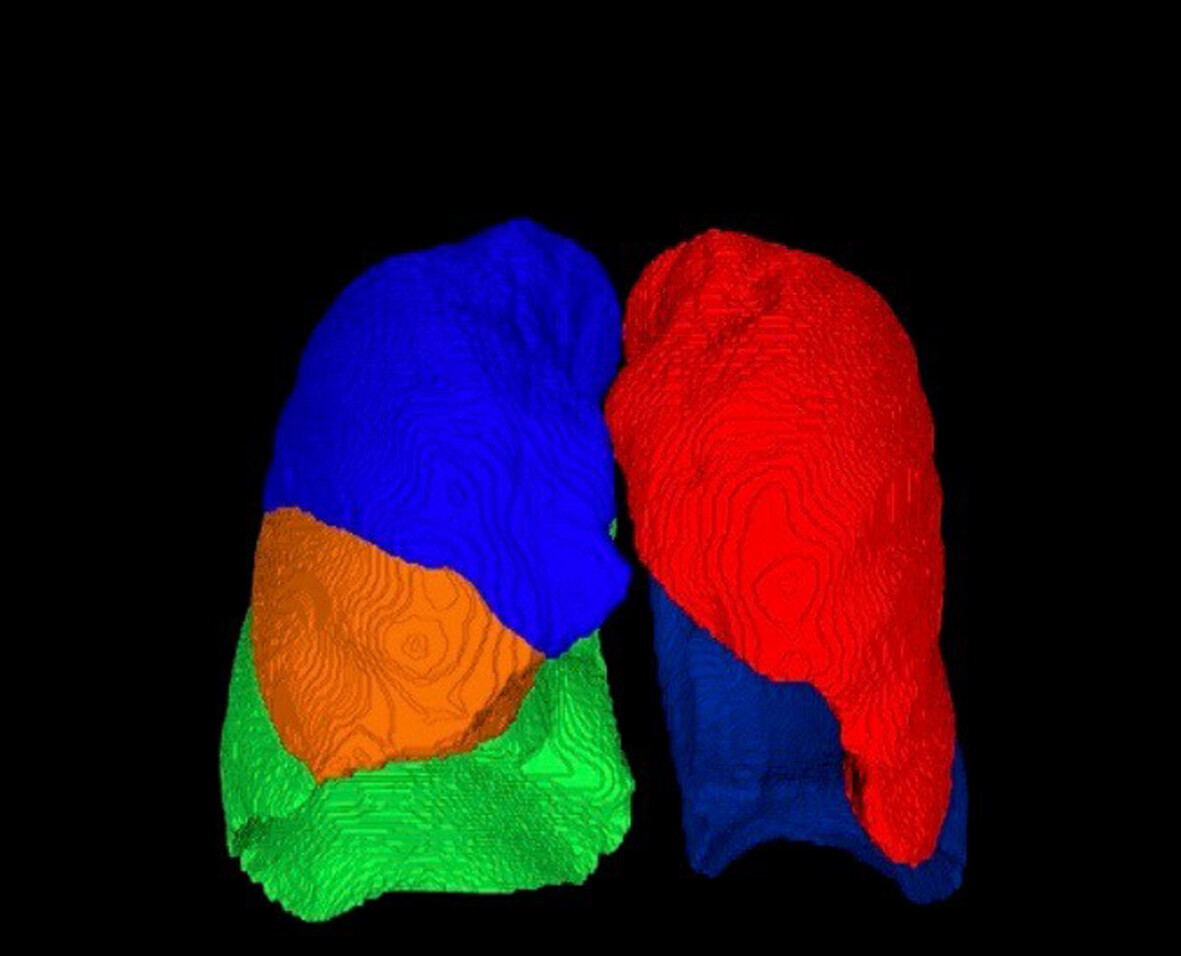
What's new?
Tobacco use is associated with the development of lung cancer, emphysema, and coronary artery disease. With these three thoracic diseases representing the three leading causes of premature death across the world, the potential of lung cancer screening to save lives is enormous. The specific goal of the 2022 Quantitative Imaging Workshop was to advance the use of quantitative CT imaging to detect not only lung cancer but other major thoracic, smoking-related diseases occurring in older individuals. A strategy is needed to ensure the development of carefully validated computational tools to responsibly advance the use of this important public health approach.
Emergence of Artificial Intelligence Art Therapies (AIATs) in Mental Health Care: A Systematic Review
- First Published: 17 July 2024
Artificial intelligence and digital health in improving primary health care service delivery in LMICs: A systematic review
- First Published: 10 September 2023
Nonviral vector system for cancer immunogene therapy
- First Published: 29 June 2022
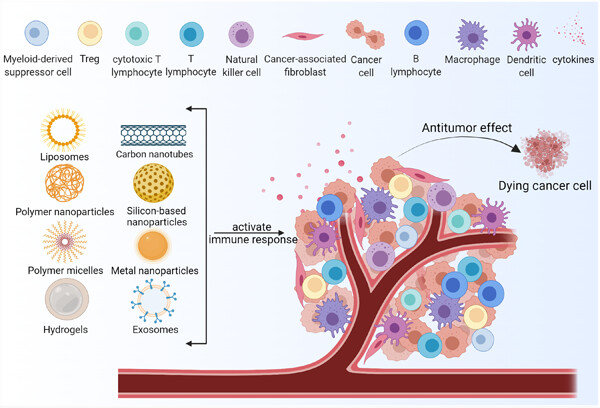
Immunogene therapy has become an effective and significant clinical strategy for cancer therapy. Enhancing the response rate to immunogene therapy is significant to controlling side effects and improving efficacy. Improved nonviral vectors combined with immunogene therapy efficiently deliver genes to the desired tumor cells and activate immune response to fight tumors while alleviating adverse reactions, which is a promising treatment approach for cancer.
New era for emerging therapeutic targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 (HER 3) in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer and metastatic breast cancer
- First Published: 15 December 2022
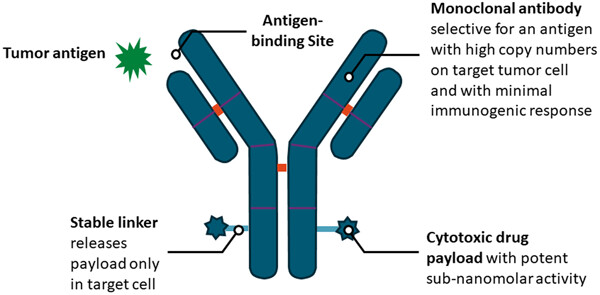
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 (HER3) overexpression represents a negative prognostic biomarker associated with poor survival. Targeting HER3 has shown some promise in early phase trials in both nonsmall cell lung cancer and metastatic breast cancer in heavily pretreated patients with varying degrees of response. Identifying a predictive biomarker will aid to better select patients that will respond to treatment.
Using improvisation to enhance communication skills in 4th year medical students
- First Published: 25 September 2024
Medical students experience science communication via moderating podcasts
- First Published: 22 September 2024
‘In their shoes now’—immersive video gameplay and design thinking for building grief literacy
- First Published: 10 September 2024
Supporting resident inbox management with screen-casted videos
- First Published: 05 September 2024
Beyond the planned and expected: the unintended consequences of telehealth in rural and remote Australia through a complexity lens
- First Published: 04 May 2024
Social media for learning: A qualitative exploration of the factors that impact clinical learners' attitudes and intentions
- First Published: 18 March 2024
What place for radiographers? The appropriateness of preliminary image evaluation in New Zealand emergency departments
- First Published: 26 August 2024
Meaningful consumer engagement in medical radiation sciences: enhancing quality improvement and research projects
- First Published: 20 December 2023
Accelerating the integration of ChatGPT and other large-scale AI models into biomedical research and healthcare
- First Published: 17 May 2023
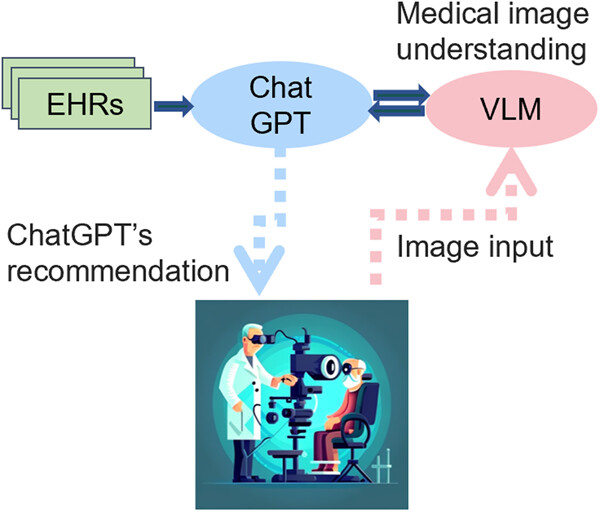
This review provides an overview of large-scale AI models, including language models (e.g., ChatGPT), vision-language models, and language-conditioned multiagent models, and discusses their potential applications in medicine, as well as their limitations and future trends. We also propose how large-scale AI models can be integrated into various scenarios of clinical applications.
A systematic review of the preferences of rural and remote youth for mental health service access: Telehealth versus face-to-face consultation
- First Published: 06 January 2023
Cancer screening with multicancer detection tests: A translational science review
- First Published: 22 March 2024
Tailoring language for genitourinary function in patients with newly diagnosed prostate cancer to facilitate discussions in diverse populations and overcome health literacy barriers
- First Published: 10 September 2024
Poor comprehension of common prostate cancer terms for genitourinary function creates health literacy barriers to treatment discussions. Tailoring medical terms with alternative colloquial words preferred by patients was helpful regardless of health literacy.
Generative artificial intelligence as a source of breast cancer information for patients: Proceed with caution
- First Published: 30 August 2024
Generative artificial intelligence large-language models like the chatbot interface generative pretrained transformer (ChatGPT) have gained rapid popularity. The authors evaluated the accuracy and appropriateness of ChatGPT as a source of breast cancer information for patients.
People, policy and power reimagined
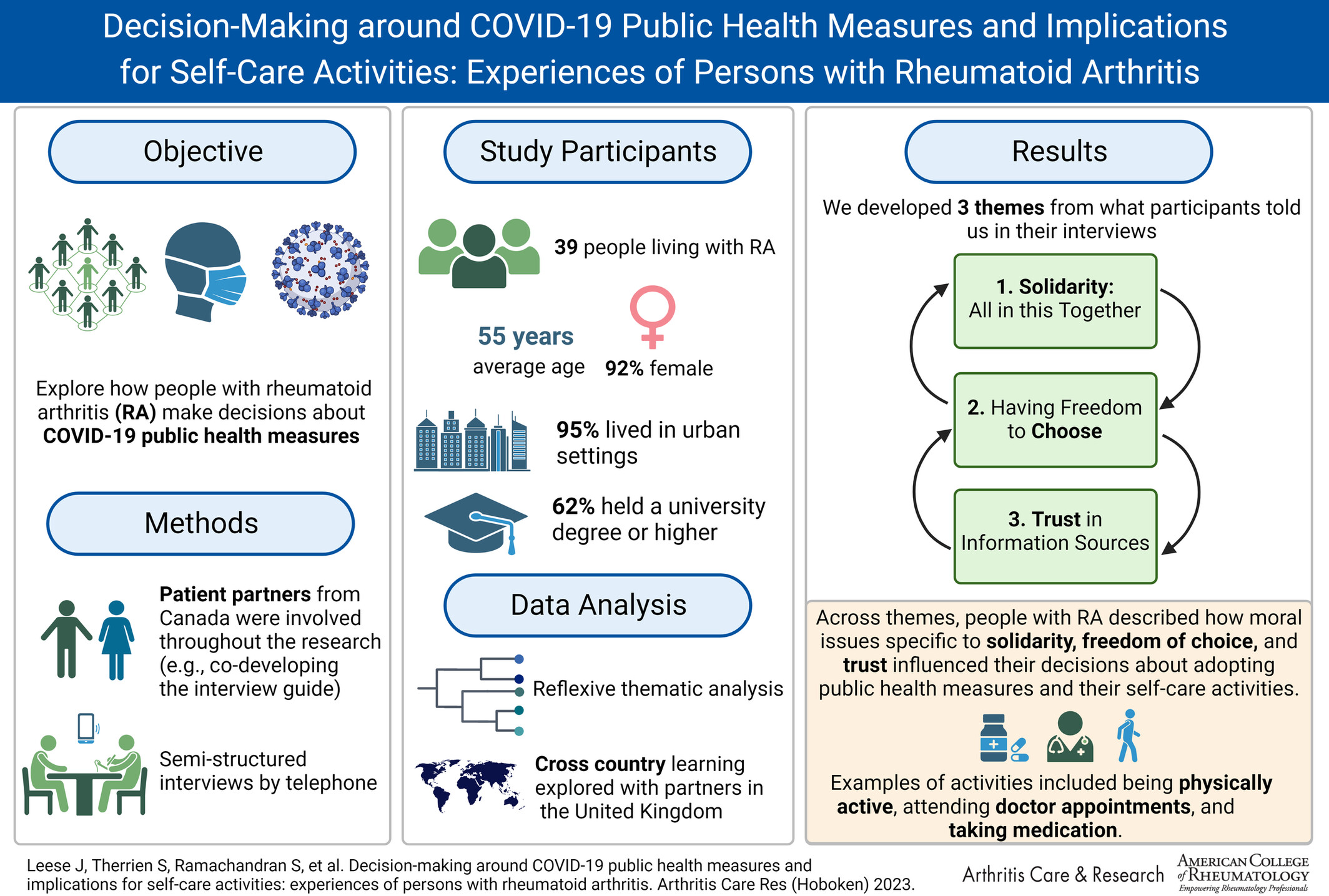
Decision-Making Around COVID-19 Public Health Measures and Implications for Self-Care Activities: Experiences of Persons With Rheumatoid Arthritis
- First Published: 23 October 2023
Exploring patient reported quality of life in lung cancer patients: A qualitative study of patient-reported outcome measures
- First Published: 23 March 2024
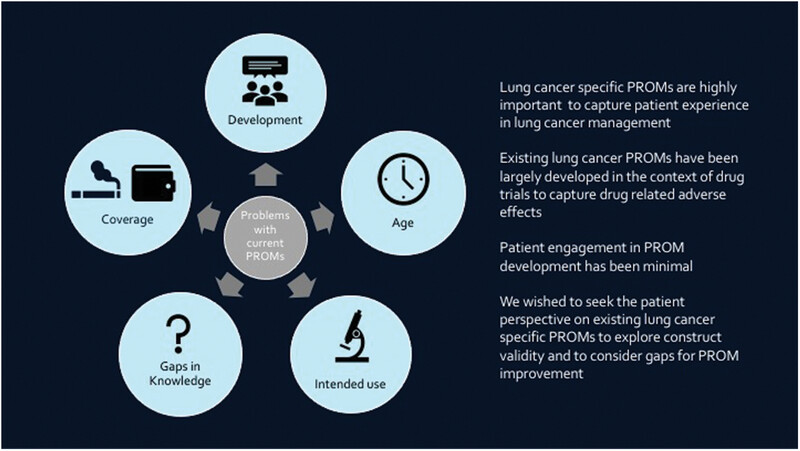
Much of what we know about QoL and PROMs in lung cancer care has been developed by researchers in the setting of drug trials aiming to identify symptoms reflective of drug-related adverse effects. These symptoms are important but may not fully reflect patient-defined experience and value in cancer care.
A NICE approach to addressing health inequalities in breast cancer guidance
- First Published: 24 April 2024
Is ‘too much medicine’ a guideline-driven phenomenon? Ten years' report and reflections of the Guidelines International Network Multimorbidity Working Group
- First Published: 03 June 2024
A protocol for adapting a clinical practice guideline for the treatment of paediatric asthma for the Egyptian Pediatric Clinical Practice Guidelines Committee
- First Published: 13 March 2024
Perspectives of vitamin C upregulating regulatory T cells in the era of thrombopoietin receptor agonists for immune thrombocytopenia
- First Published: 06 October 2022
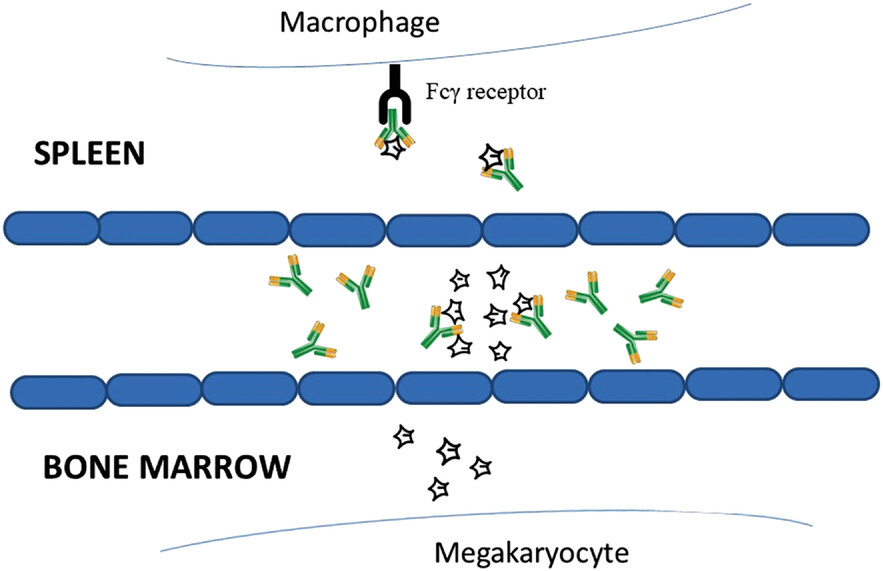
Gross platelet deficiency marks idiopathic thrombocytopenia's pathophysiology: normalization of the regulatory T cells (Tregs) through demethylation may well reverse the abnormal DNA methylation. Despite thrombopoietic receptor agonists’ recognized effectiveness, strongly demethylating (yet safe and affordable) ascorbate (e.g. with a plasma level of >1 mM several hours/week) could prevent their undesirable “rebound phenomenon” upon routine discontinuation, especially if abruptly mandated by refusal/adverse effects. [In Figure 1, star-shaped objects are platelets; Y-shaped objects are autoantibodies; in Figure 2, pro-inflammatory T helper 17 (Th17) cells are characterized by RORγt: a transcription factor (encoded by the gene Rorc) of the retinoic acid-receptor (RAR)-related orphan receptor (ROR) family. In ITP, Tregs expressing forkhead box P3 (Foxp3) are crucial for controlling ITP: in Figure 3, TET: ten-eleven translocation enzymes; 5mC; 5hmc: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (the initiating step of active DNA demethylation. A cofactor fostering this process is vitamin C which acts synergistically with retinoic acid (RA)].
Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients
- First Published: 12 October 2021
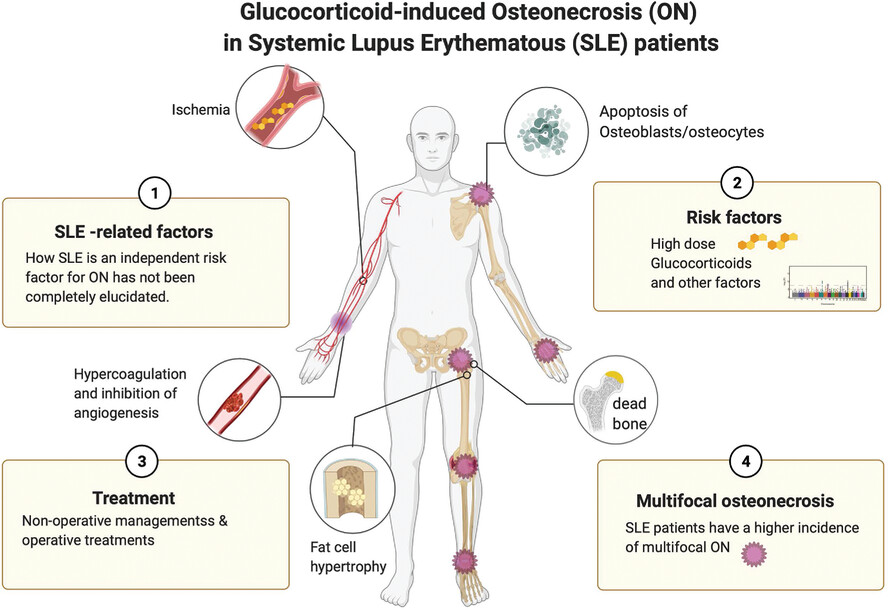
ON is a complex and multifactorial complication of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). However, the pathophysiology and risk factors for ON in patients with SLE have not been fully determined yet. Here, we review the epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options for glucocorticoid-induced ON, with a specific focus on patients with SLE
Trustworthiness assessment of published clinical trials: Literature review of domains and questions
- First Published: 20 August 2024
The effects of public health and social measures (PHSM) implemented during the COVID-19 pandemic: An overview of systematic reviews
- First Published: 29 April 2024
Menu labeling and portion size control to improve the out-of-home food environment: A scoping review
- First Published: 23 January 2024
Economic evaluation of a water fluoridation scheme in Cumbria, UK
- First Published: 25 March 2024
International Anal Neoplasia Society's consensus guidelines for anal cancer screening
- First Published: 31 January 2024
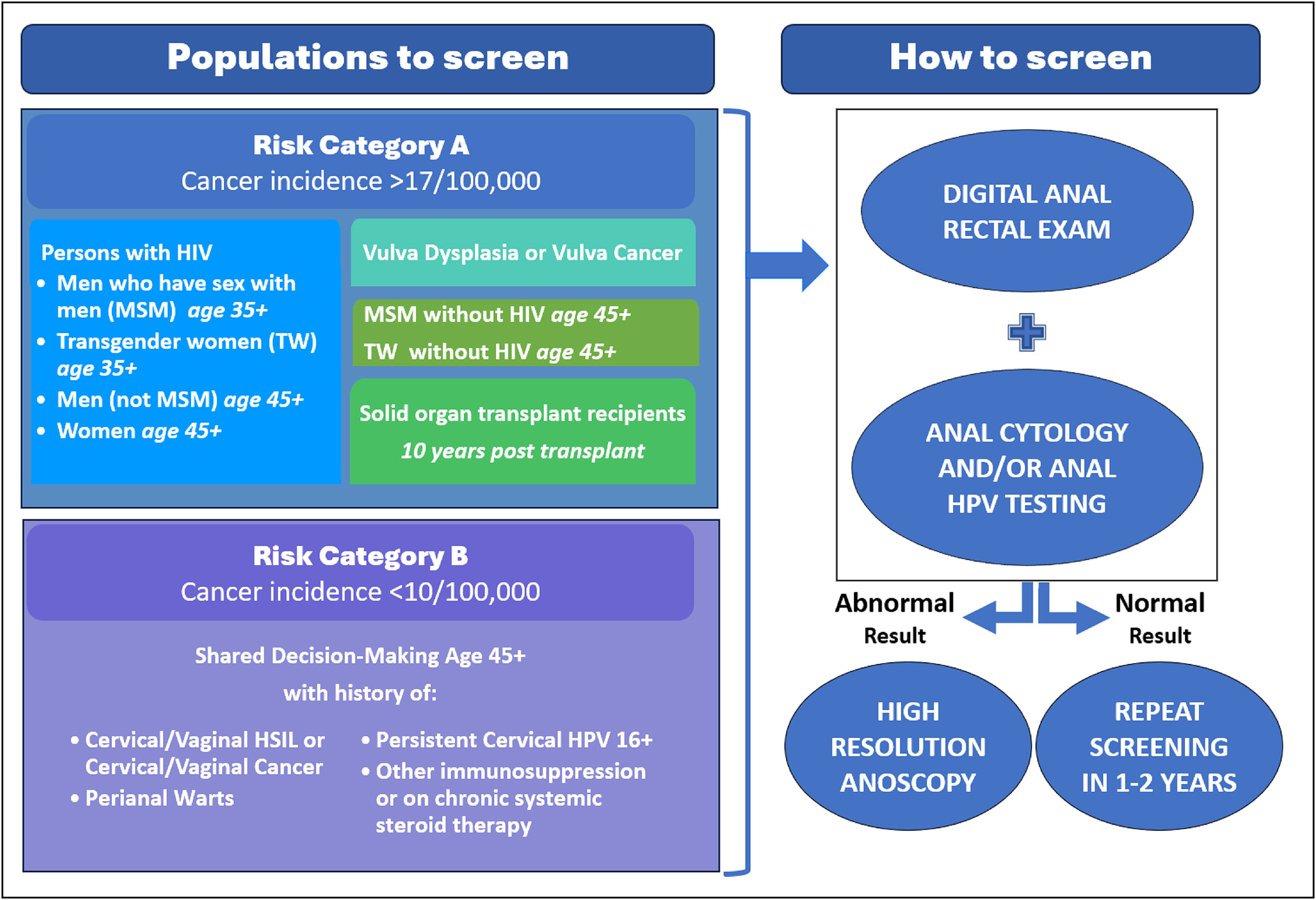
What's new?
Recently, treatment of anal high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL) was found to reduce anal cancer risk in people living with HIV. However, there are no current comprehensive anal cancer screening guidelines. The International Anal Neoplasia Society (IANS) recommendations provide evidence-based consensus guidance for which populations should be offered anal cancer screening and for management of abnormal screening results, considering currently available screening tools. The IANS guidelines provide a basis for expansion of anal cancer screening infrastructure to all at-risk populations.
Insights Towards Trauma-Informed Nursing Supervision: An Integrative Literature Review and Thematic Analysis
- First Published: 22 August 2024
Interviews with policymakers in Australian health policy: Understanding the process of policy development
- First Published: 24 March 2024
Perceived social status, socioeconomic status, and preventive dental utilization among a low-income Medicaid adult population
- First Published: 15 November 2023
Childhood caries is associated with poor health and a faster pace of aging by midlife
- First Published: 02 November 2023
Development and validation of a prognostic model incorporating tumor thrombus grading for nonmetastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma with tumor thrombus: A multicohort study
- First Published: 20 July 2023
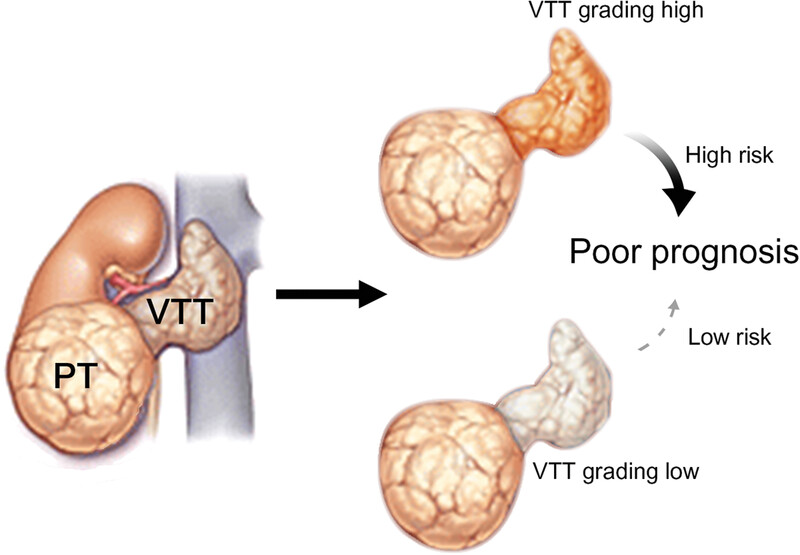
Inspired by the metastasis-seeding potential of VTT in ccRCC, we identified for the first time that pathological grading of VTT could serve as an unheeded prognostic factor. By incorporating VTT grading, TT-GPS score was constructed, displaying superior discriminatory ability for risk stratification in nonmetastatic ccRCC patients with VTT. This study highlights the significance of introducing VTT grading or TT-GPS score into routine pathological reports to improve the efficacy of risk assessment.
Chemoimmunotherapy for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma—Summary and discussion of recent clinical trials
- First Published: 14 August 2023
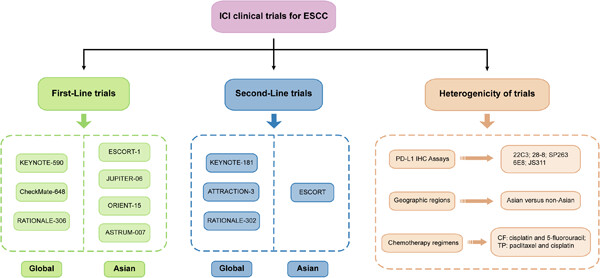
A large majority of clinical trials demonstrate the promising results of the addition of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) to the existing treatment strategy for patients with advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Therefore, this article aims to discuss the results of these trials and to highlight the changes and future of ESCC treatment.
Implementing the cultural determinants of health: our knowledges and cultures in a health system that is not free of racism
- First Published: 01 July 2024
Who holds power in decision making for young people's future?
- First Published: 19 November 2023
Baby steps in lobbying reform: opportunities and challenges in Queensland
- First Published: 27 December 2023
Barriers to routine dental care for children with special health care needs
- First Published: 26 July 2023
Does education in special care dentistry increase people's confidence to manage the care of a more diverse population?
- First Published: 26 September 2023
Proton therapy in Asia Pacific: current resources, international disparities and steps forward
- First Published: 29 February 2024

The burden of cancer in Asia Pacific, a region home to over four billion people, is growing. Because of sheer demographics alone, the Asia Pacific region arguably has the highest number of patients who can benefit from protons over conventional x-rays. However, only 39 out of 113 proton facilities globally are in Asia Pacific, and 11 of them are in low- and middle-income countries where 95% of the regional population reside. We draw attention to present resource distribution of proton therapy in Asia Pacific, highlight disparities in access, and suggest steps forward.
Public health policies in dental traumatology: A call for action!
- First Published: 14 May 2024
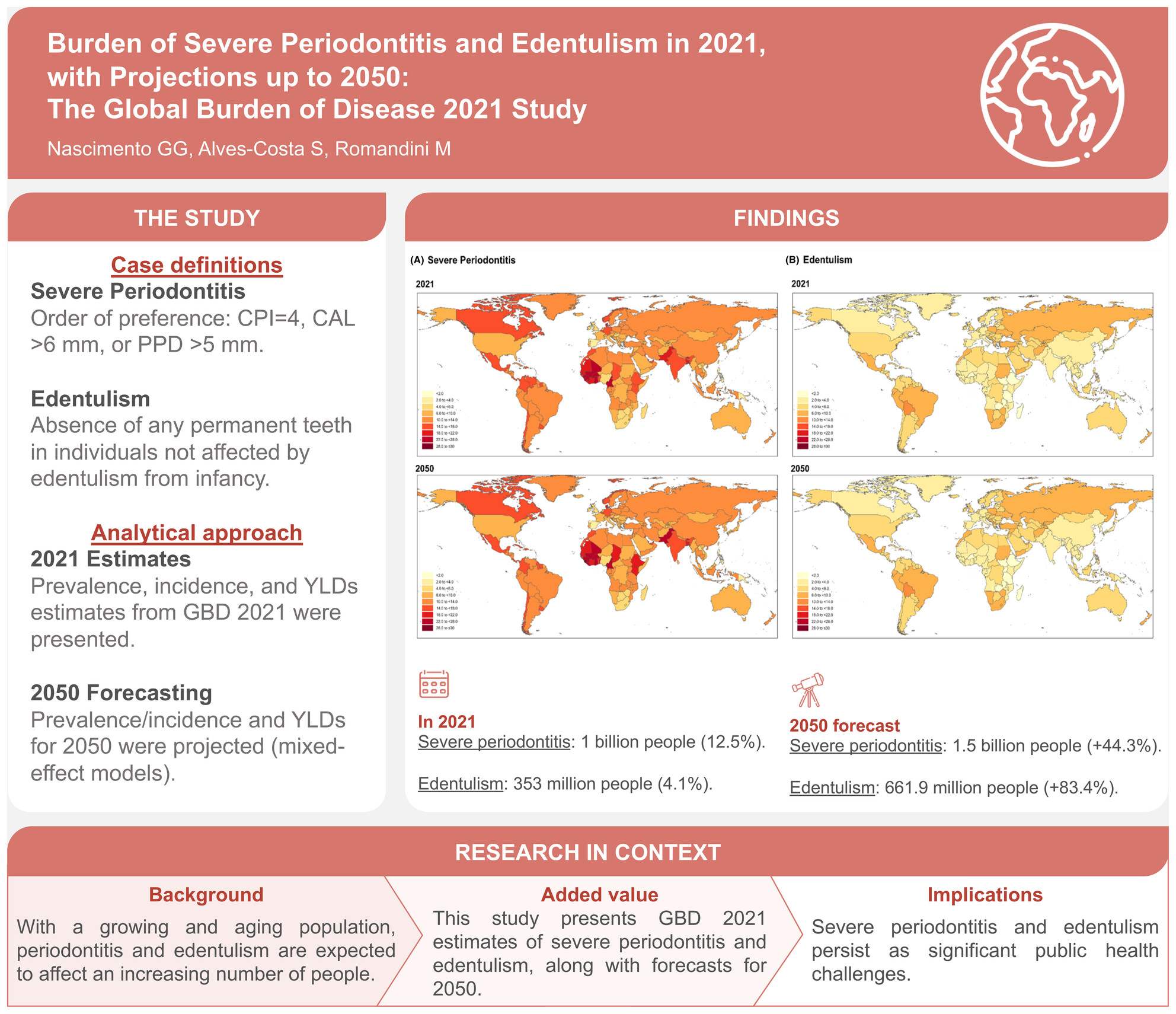
Burden of severe periodontitis and edentulism in 2021, with projections up to 2050: The Global Burden of Disease 2021 study
- First Published: 27 August 2024
Global prevalence of musculoskeletal pain in rural and urban populations. A systematic review with meta-analysis. Musculoskeletal pain in rural and urban populations
- First Published: 04 July 2024
Individuals of refugee background resettled in regional and rural Australia: A systematic review of mental health research
- First Published: 19 October 2021
Management of macular oedema due to retinal vein occlusion: An evidence-based systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 14 April 2023
Resources from the Cochrane Library
Undernutrition as a risk factor for tuberculosis disease
- Juan VA Franco et al.
- 11 June 2024
Exergaming for dementia and mild cognitive impairment
- Alexandra Voinescu et al.
- 25 September 2024
Healthcare workers’ informal uses of mobile phones and other mobile devices to support their work: a qualitative evidence synthesis
- Claire Glenton et al.
- 27 August 2024
Interventions for improving coverage of childhood immunisation in low‐ and middle‐income countries
- Angela Oyo-Ita et al.
- 06 December 2023
Antenatal magnesium sulphate reduces cerebral palsy after preterm birth, implementation into clinical practice needs to be accelerated globally to benefit preterm babies
- Karen Luyt
- 24 September 2024