Editors-in-Chief: James Henderson Naismith, Guangping Gao and Yu-quan Wei
MedComm is a multidisciplinary open access journal publishing pioneering medical science advances that will improve human health. With a broad scope ranging from cell biology to clinical medicine, we emphasize original findings that advance knowledge of pathogenesis or improve the diagnosis and treatment of human disease.
We're particularly interested in interdisciplinary studies utilizing approaches of molecular biology, cell biology, chemistry, pharmacology or material science to address the issues of clinical, basic and translational medicine.
Journal Metrics
- 8.8CiteScore
- 10.7Journal Impact Factor
- 31%Acceptance rate
- 23 days Submission to first decision
Editor's Choice Articles
On the Cover
Articles
Long‐Term High‐Fat Diet Affected Bone Marrow Microenvironment During Aging at Single‐Cell Resolution
- MedComm
- 21 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
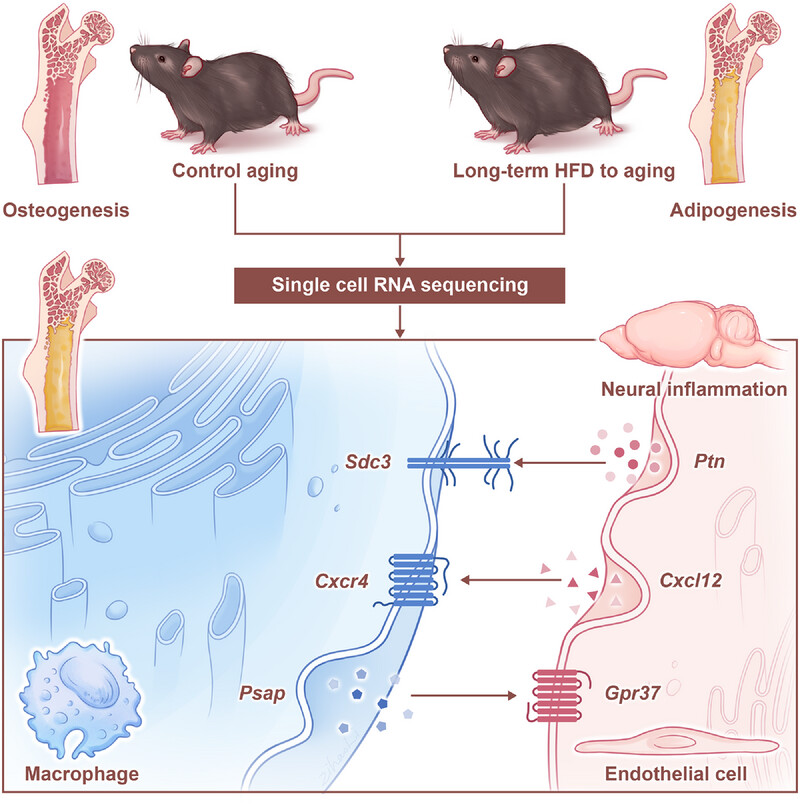
High-fat diet (HFD) promotes obesity and degenerative diseases. We established a long-term HFD to aging (LHA) mouse model, finding it induces a bone marrow shift from osteogenesis to adipogenesis and abnormal immune cell metabolic adaptations. Signaling axes were identified through single-cell RNA sequencing as potential bone marrow-brain crosstalk pathways, providing insights for treating related diseases.
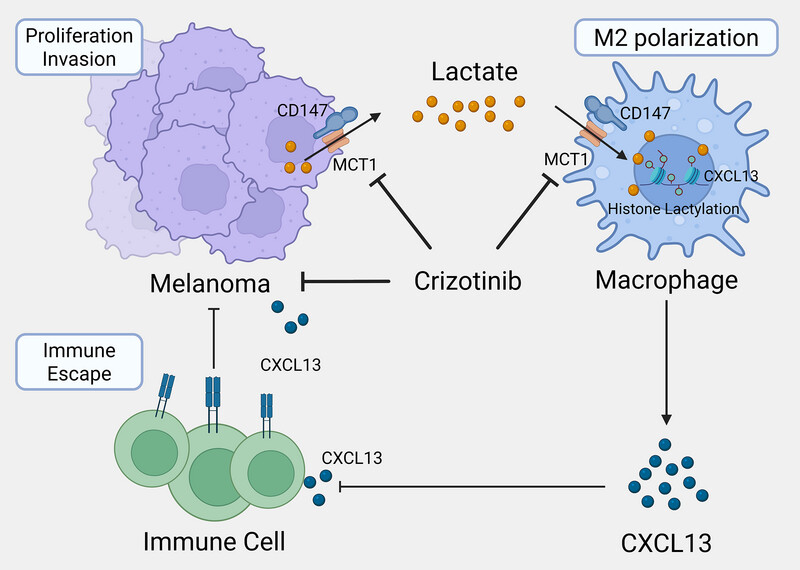
Crizotinib: A Novel Strategy to Reverse Immunosuppression in Melanoma by Targeting Lactate Transport
- MedComm
- 21 July 2025
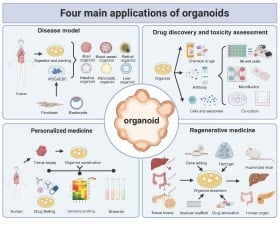
Extracellular Matrix Signaling Cues: Biological Functions, Diseases, and Therapeutic Targets
- MedComm
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
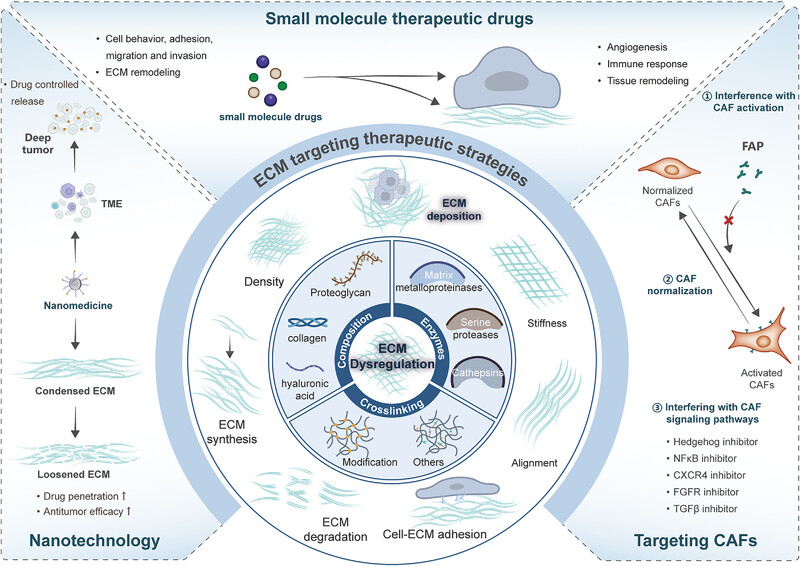
Targeting ECM dysregulation: therapeutic strategies for disease intervention. Dysregulated ECM composition and biomechanics contribute to disease pathogenesis in cancer and fibrotic disorders. Physical modulation: Nanomedicine-based strategies tune ECM physical properties (e.g., density, stiffness) to enhance drug penetration and therapeutic efficacy in the TME. Molecular targeting: Small-molecule drugs selectively modify ECM components to induce angiogenesis, immune response, and tissue remodeling. Cellular reprogramming: Pharmacological intervention of CAF signaling pathways promotes functional normalization, thereby restoring ECM homeostasis.
Astrocyte in Neurological Disease: Pathogenesis and Therapy
- MedComm
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
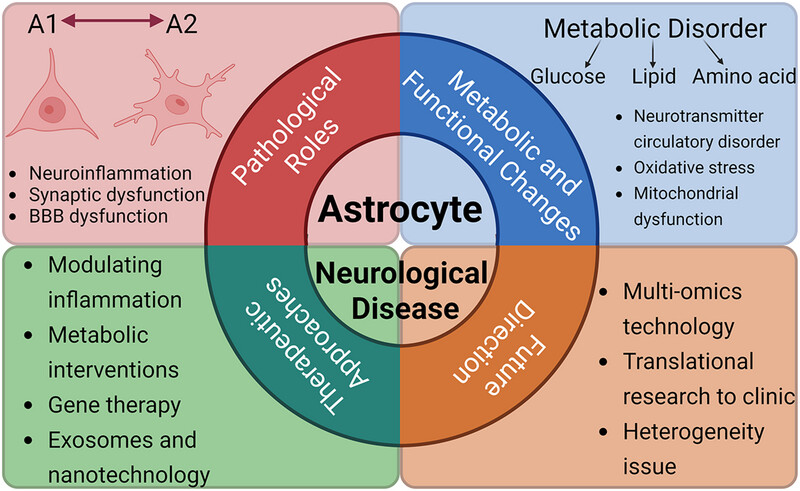
This review provides comprehensive overview of astrocytes in neurological disorders. Astrocytes contribute to neurological disorders via A1/A2 polarization, inducing neuroinflammation, synaptic, and BBB dysfunction. Metabolic disturbances in glucose, lipid, and amino acid pathways leading to oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage. Therapeutic targets include inflammation modulation, gene therapy, and nanotechnology. Future directions include multi-omics integration, clinical translation, and resolving astrocyte heterogeneity.
Association Between Preoperative Cognitive Performance and Postoperative Delirium in Older Patients: Results From a Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study, and a Mendelian Randomization Study
- MedComm
- 17 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
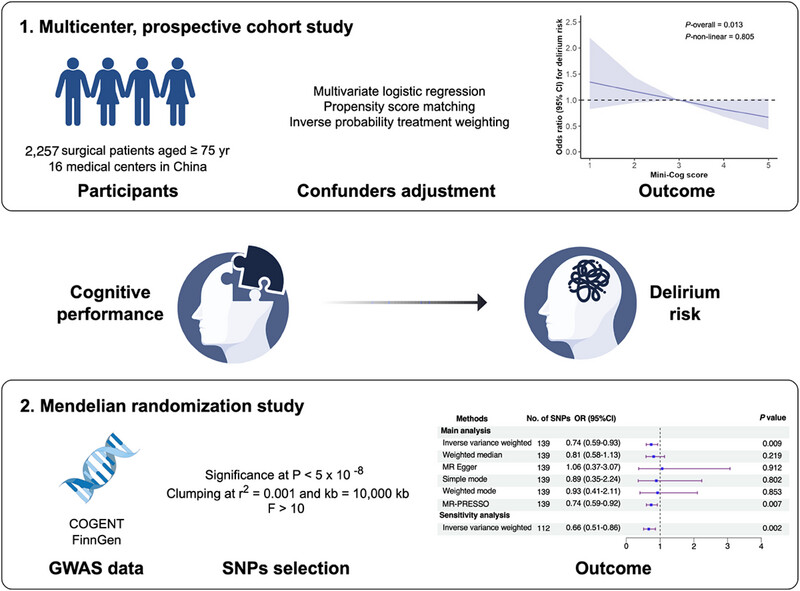
We analyzed population-based data from multicenter cohorts and found a nearly linear negative correlation between preoperative cognitive performance and postoperative delirium risk. In addition, our Mendelian randomization study provides genetic evidence supporting a causal relationship between cognitive performance and delirium risk.
Improvement of the Anticancer Efficacy of PD‐1/PD‐L1 Blockade: Advances in Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies
- MedComm
- 15 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
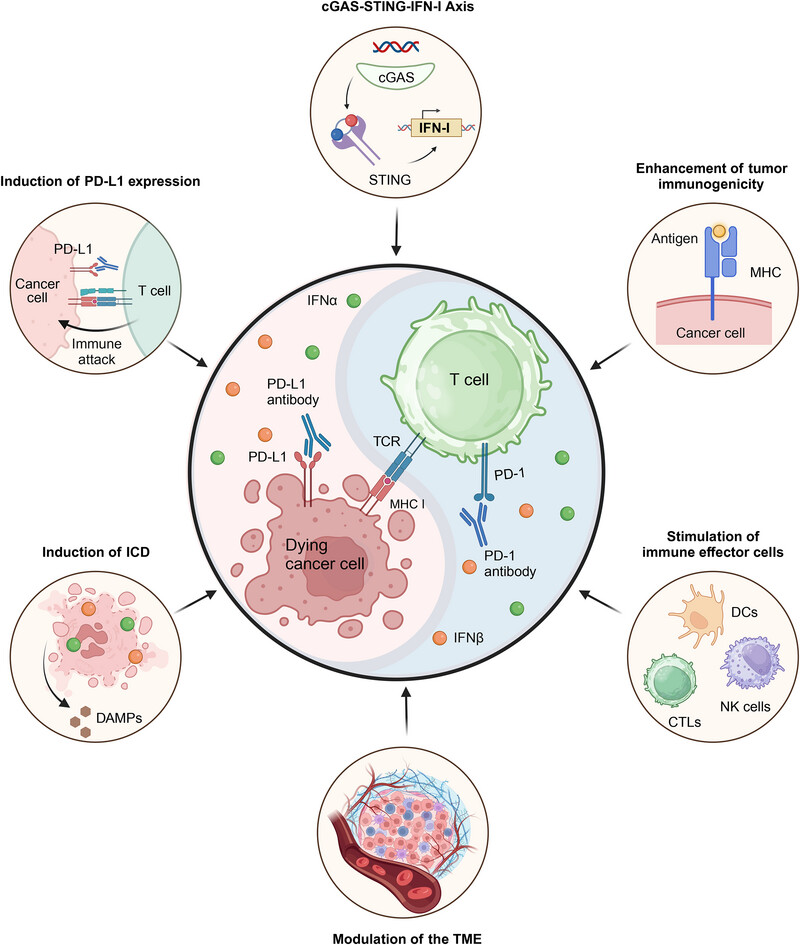
Mechanisms of alleviating resistance to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade by IFN-α and IFN-β. In these mechanisms, the “yin-yang balance” is disrupted, thus preventing T cells from attacking cancer cells. Restoring this balance may improve the efficacy of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy and reinvigorate T cells and other immune cells to target and destroy cancer cells.
Combining Intramuscular and Intranasal Immunization With the MF59‐Adjuvanted Respiratory Syncytial Virus Pre‐Fusion Protein Subunit Vaccine Induces Potent Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses in Mice
- MedComm
- 15 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
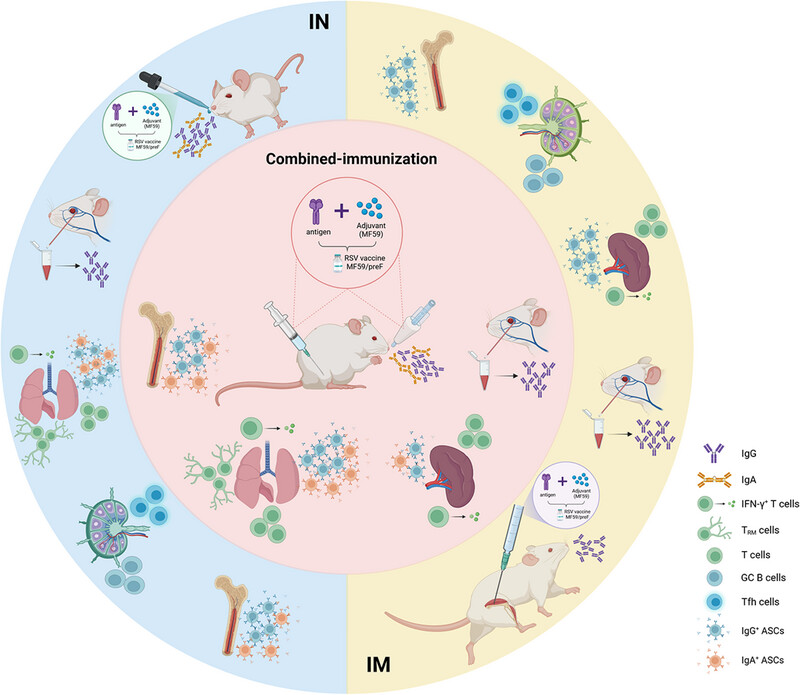
In our study, we formulated a protein-based vaccine known as MF59/preF, which contains RSV pre-fusion (preF) protein antigen in combination with an MF59-like oil-in-water adjuvant. Three-dose intramuscular (IM) administration of this vaccine induced robust humoral and cellular immunity against RSV F protein in systemic immune organs rather than at local sites. Intranasal (IN) immunization with MF59/preF demonstrated superior mucosal immunity, characterized by elevated levels of secretory IgA antibodies and an increased frequency of tissue-resident memory T (TRM) cells locally. We then optimized the MF59/preF vaccine by combining IM and IN immunization, which induced stronger systemic and mucosal immunity.
Microglial Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 2 Deficiency Accelerates Seizure Development via Increasing AMPAR‐Mediated Neuronal Excitability
- MedComm
- 14 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
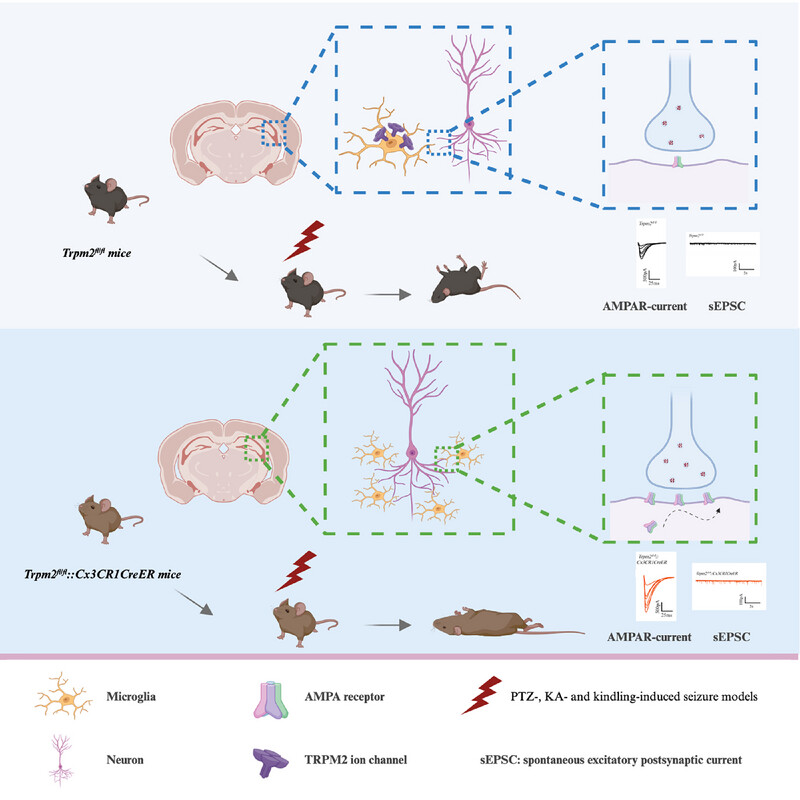
The deficiency of transient receptor potential melastatin type 2 (TRPM2) channel as a calcium permeable nonselective cation channel, accelerates seizure development in various mouse seizure models including PTZ-, KA-, and kindling-induced models, but does not affect seizure susceptibility in initial acute seizure. Interestingly, the deficiency of TRPM2 in microglia, but not CaMKIIα+ or PV+ neurons, is mainly responsible for seizure development. Moreover, microglial TRPM2 deficiency increases the excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons via enhancing the AMPAR-mediated excitatory synaptic transmission but does not influence the expression of inflammation cytokines.
Phage and Endolysin Therapy Against Antibiotics Resistant Bacteria: From Bench to Bedside
- MedComm
- 13 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
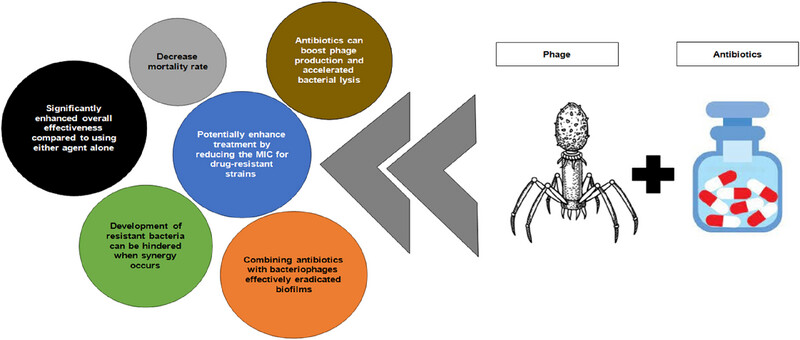
Synergistic effects of combining bacteriophages and antibiotics in antimicrobial therapy.
The diagram illustrates key advantages of phage-antibiotic synergy, including increased treatment effectiveness, reduced minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for drug-resistant strains, enhanced biofilm eradication, and inhibition of resistant bacteria development. Antibiotics can also promote phage production and accelerate bacterial lysis. These interactions suggest promising potential for combined therapies, particularly in overcoming antibiotic resistance. Figure created using Microsoft PowerPoint.
Novel Lysosomal‐Associated Transmembrane Protein 4B‐Positive Stem‐Like Cell Subpopulation Characterizes High‐Risk Colorectal Cancer Subtypes
- MedComm
- 13 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
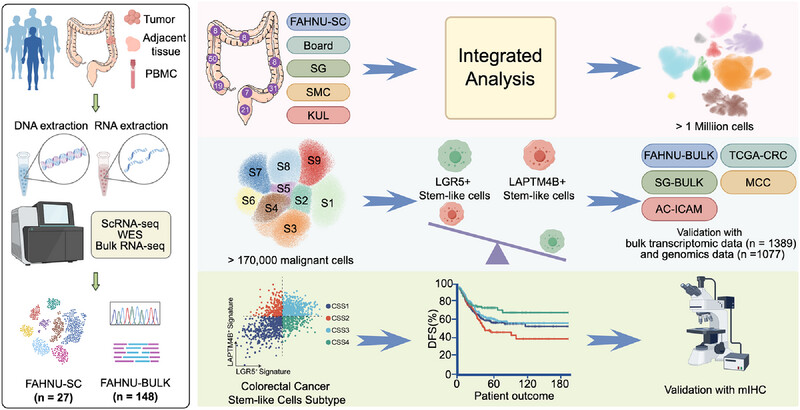
This study identified the existence of a novel population of LAPTM4B+ tumor stem-like cells in addition to the classical LGR5+ tumor stem-like cells in colorectal cancer (CRC). The combination of LGR5+ and LAPTM4B+ stem-like cells enable a more refined stratification of CRC, offering potential insights for targeted therapeutic strategies.
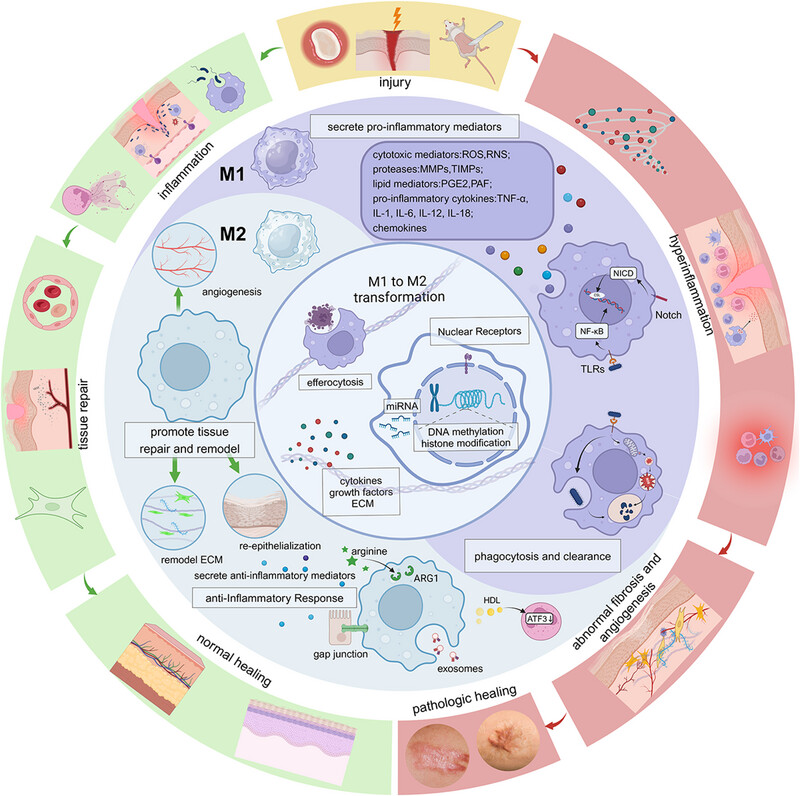
Macrophage plasticity: signaling pathways, tissue repair, and regeneration
- MedComm
- 1 August 2024
Rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenesis and therapeutic advances
- MedComm
- 10 March 2024
Graphical Abstract
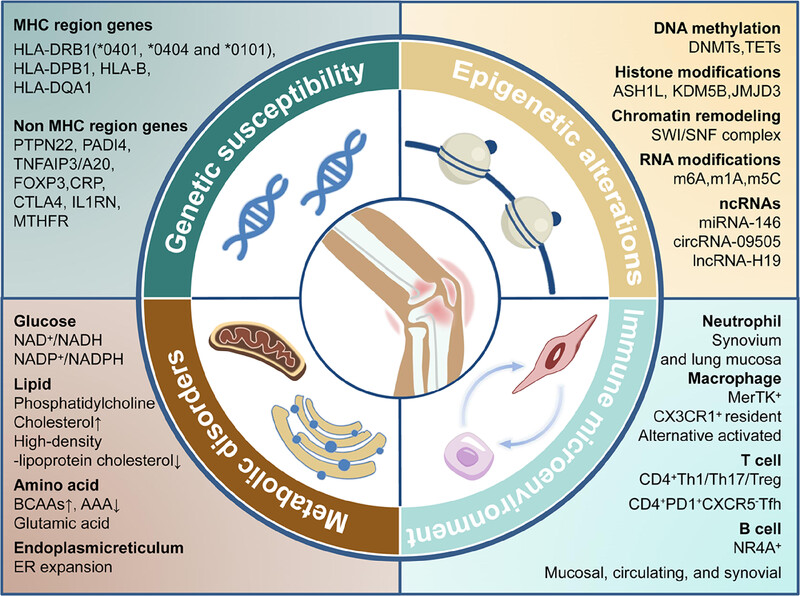
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory and autoimmune disease with multisystem involvement, including genetic, epigenetic, metabolic, and immune factors. This review focuses on the importance of recently identified epigenetic and metabolic risk factors for immune dysfunction and pathogenic tissue-remodeling programs in RA development. Moreover, this review depicts the therapeutic potential of these metabolite and epigenetic targets and their agents for clinical remission and treatment.
Endothelial dysfunction: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications
- MedComm
- 22 July 2024
Graphical Abstract
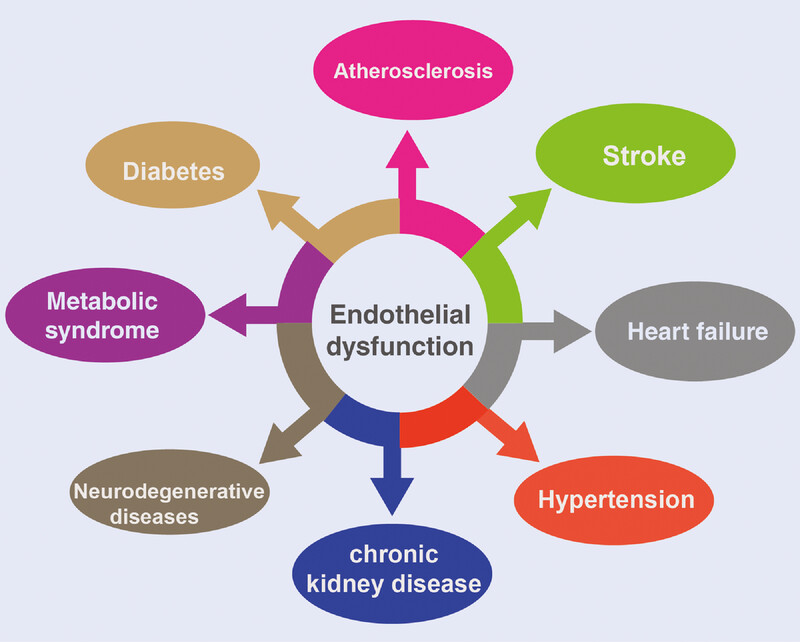
Endothelial dysfunction is commonly linked to various disease states resulting from an imbalance in the production of vasodilators and vasoconstrictors, among other factors. Human diseases associated with endothelial dysfunction include atherosclerosis, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, neurodegenerative diseases, chronic kidney disease, hypertension, heart failure, and stroke.
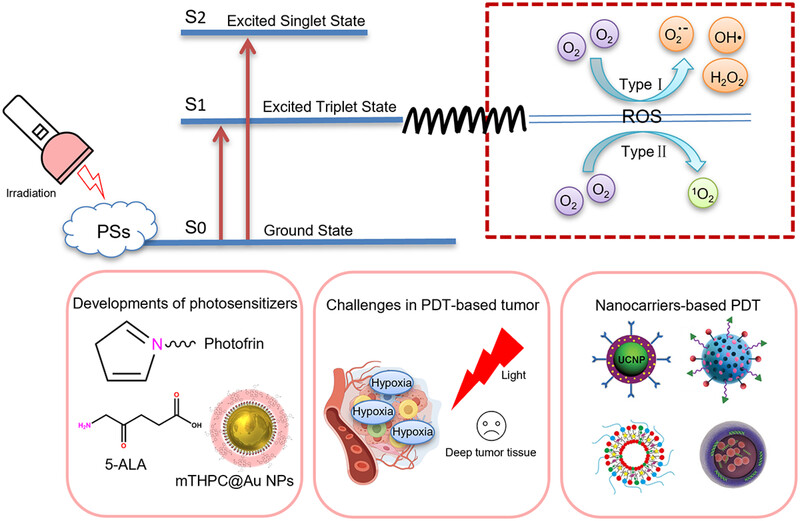
Photodynamic therapy for cancer: mechanisms, photosensitizers, nanocarriers, and clinical studies
- MedComm
- 22 June 2024
The interaction of innate immune and adaptive immune system
- MedComm
- 15 September 2024
Graphical Abstract
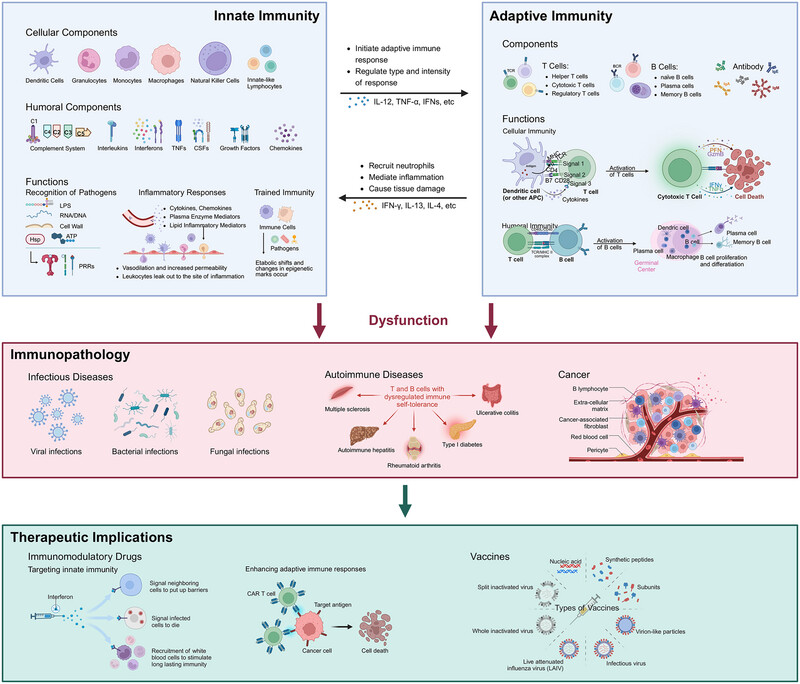
This review begins with a complete description of the composition and function of innate and acquired immunity. On this basis we summarize how the two systems interact and influence disease progression. The paper concludes with a review of therapeutic options and future directions for immune system research.
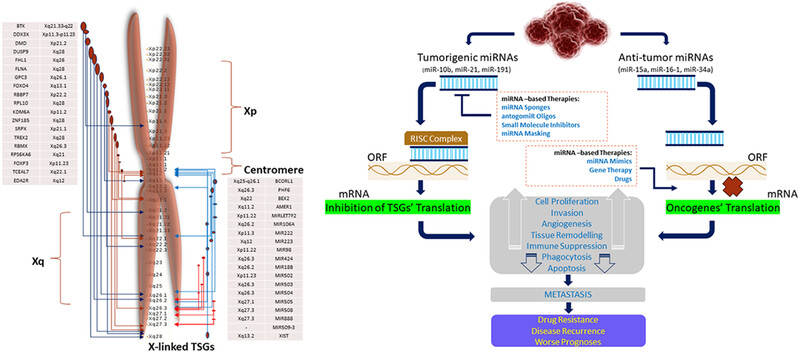
Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes: functions and roles in cancers
- MedComm
- 31 May 2024
Multi‐omics analysis of disulfidptosis regulators and therapeutic potential reveals glycogen synthase 1 as a disulfidptosis triggering target for triple‐negative breast cancer
- MedComm
- 28 February 2024
Graphical Abstract
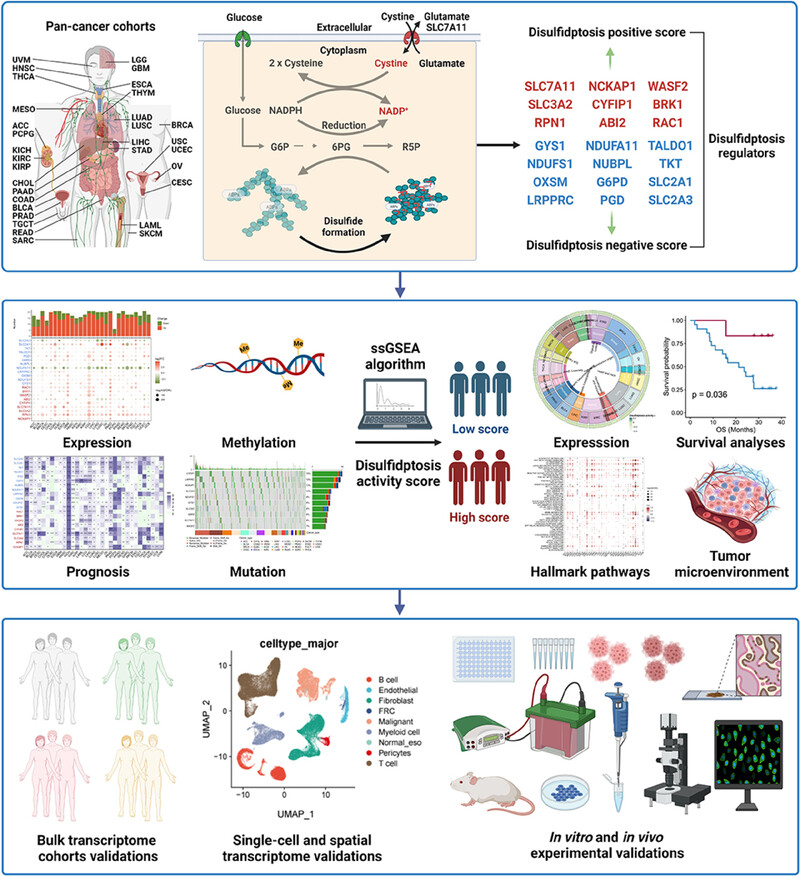
Flowchart of our study. By utilizing multi-omics pan-cancer cohorts, our study firstly offers a pan-cancer blueprint of the molecular and clinical characteristics of disulfidptosis regulators, as wells as disulfidptosis activity, which lay a solid foundation for the disulfidptosis-targeting strategy in precision cancer treatment.
Inflammation in diabetes complications: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions
- MedComm
- 12 April 2024
Graphical Abstract
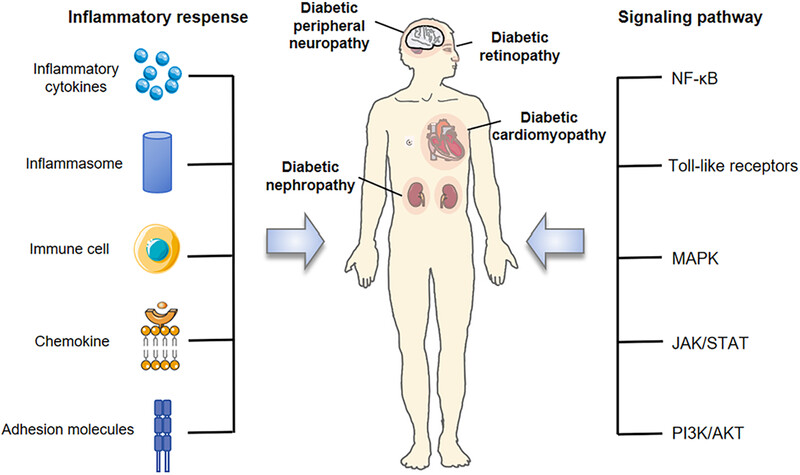
Inflammatory response and its related signaling pathways in diabetes complications. In the pathogenesis of diabetes complications, inflammatory factors, inflammasomes, immune cells, adhesion molecules, chemokine, and chemokine receptor are involved in the progression of diabetes complications through a series of inflammatory reactions. Related signaling pathways, including NF-κB, Toll-like receptors, MAPK, JAK/STAT, PI3K/Akt, mediate a series of inflammatory responses of diabetes complications.
Toll‐like receptors in health and disease
- MedComm
- 29 April 2024
Graphical Abstract
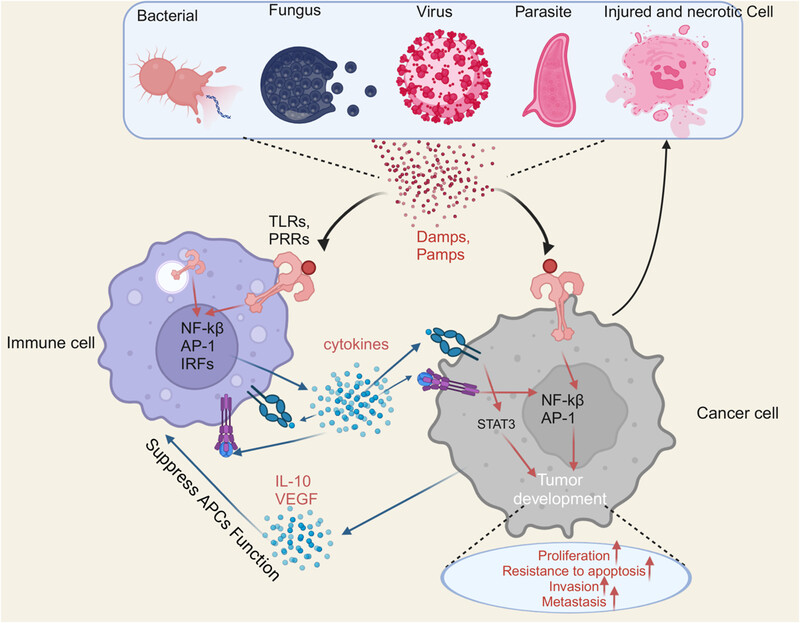
Interactions of TLRs with inflammation and tumor. TLRs are expressed on a variety of cells, including tumor cells and immune cells. TLRs signaling is involved in the carcinogenesis of the tumor microenvironment. TLRs expressed on immune cells and tumor cells are subjected to activation by pathogen-associated molecular patterns,damage-associated molecular patterns from microorganisms, viruses, parasites, injured and necrotic cancer cells. The release of cytokines and chemokines by these activated cells is an important part of the tumor microenvironment. Moreover, cytokine-activated infiltrating immune cells can subsequently induce additional cytokines that impair the function of antigen-presenting cells, leading to tumor immune tolerance.
Recent issues
- Volume 6, Issue 8August 2025
- Volume 6, Issue 7July 2025
- Volume 6, Issue 6June 2025
- Volume 6, Issue 5May 2025