Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Epithelial Atg5 Deficiency Intensifies Caspase-11 Activation, Fueling Extracellular mtDNA Release to Activate cGAS–STING–NLRP3 Axis in Macrophages During Pseudomonas Infection
- First Published: 15 June 2025
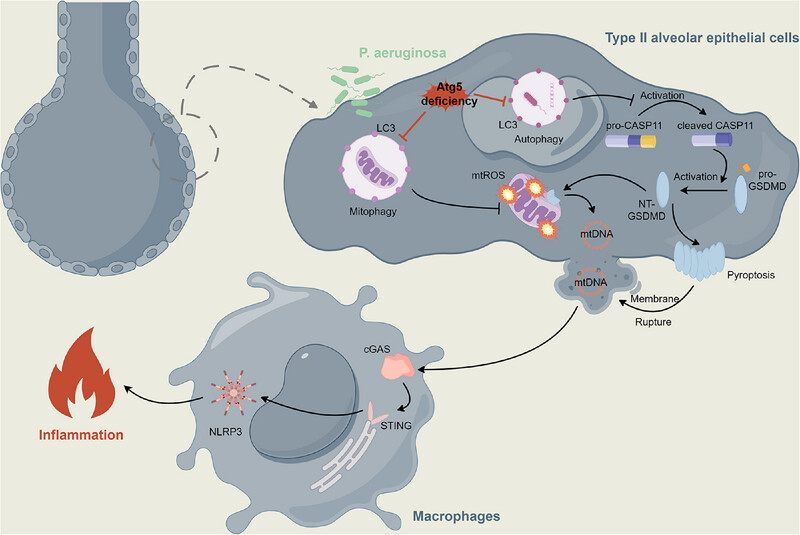
This work illuminates the essential role of epithelial ATG5 in defending against P. aeruginosa. Atg5 deficiency impairs bacterial clearance and aggravates inflammation via AKT/PI3K/NF-κB, inflammasome activation, and pyroptosis. Mechanistically, impaired mitophagy intensifies mitochondrial damage. This, combined with the enhanced activation of GSDMD mediated by the noncanonical caspase-11 inflammasome, amplifies the extracellular release of mtDNA, triggering cGAS–STING–NLRP3 signaling in macrophages and amplifying lung injury.
LETTER
HIGHLIGHT
Key Roles in the Process of Extravasation and Colonization: Acyl-coenzyme A Synthetase Long-chain Family Member 4 and Polyunsaturated Lipids
- First Published: 15 June 2025
REVIEW
The Interplay of Cross-Organ Immune Regulation in Inflammation and Cancer
- First Published: 15 June 2025
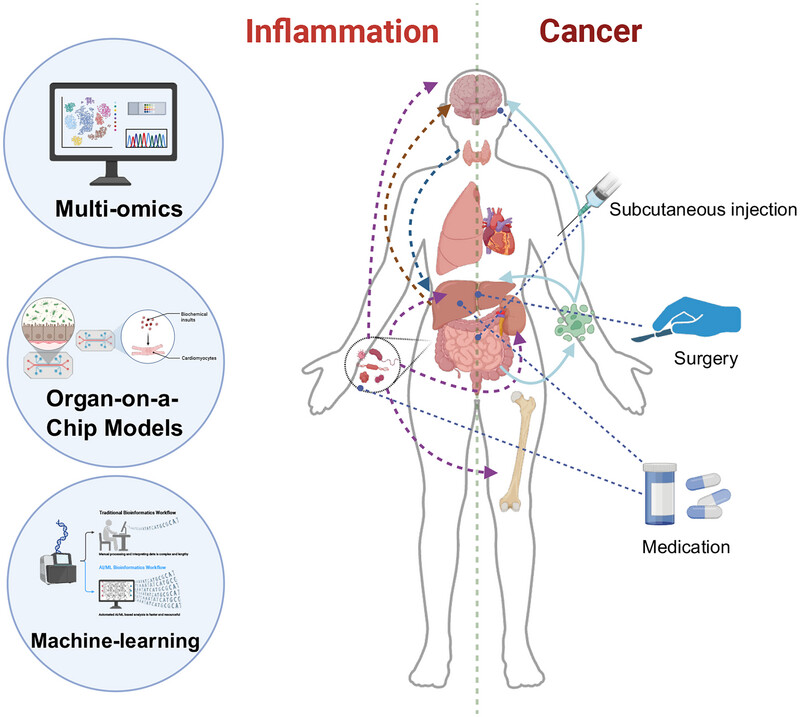
Organs interact dynamically through immune regulation, influencing systemic immune responses and disease progression. We review molecular and cellular mechanisms of cross-organ immune regulation in inflammation and cancer, focusing on gut, liver, and brain interactions with other organs. Advances in multiomics, machine learning, and organ-on-a-chip technologies provide new insights for precision medicine strategies.
Autoimmune Diseases: Molecular Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Targets
- First Published: 16 June 2025
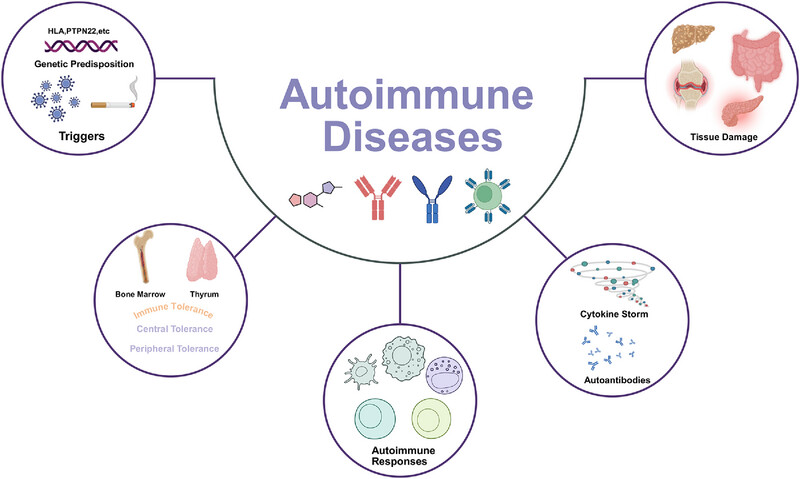
This review provides a comprehensive overview of common autoimmune diseases, details clinical manifestations and summarizes the pathogenesis, including the breakdown of immune tolerance, initiation of autoimmune responses, and their progressive amplification. We also explore current therapeutic strategies, including commonly used broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory drugs, recent molecular-targeted therapies, and emerging cellular therapies, aiming to propel future research and therapeutic breakthroughs in this field.
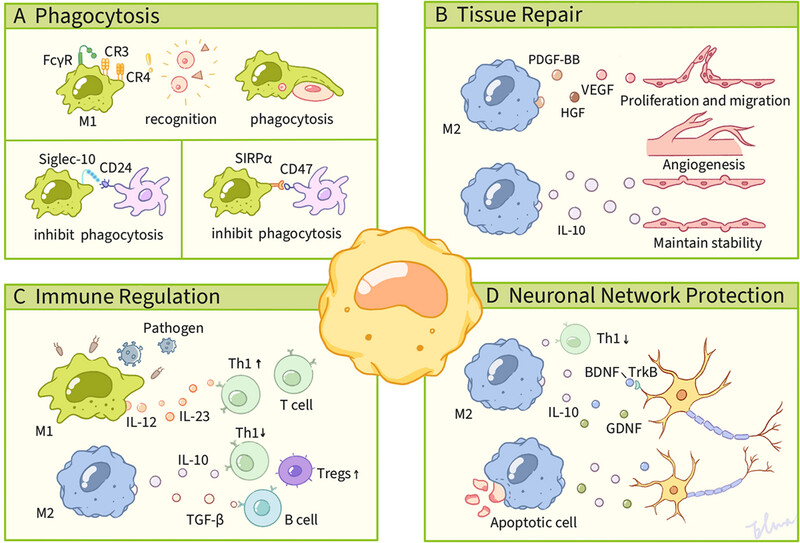
Macrophage Signaling Pathways in Health and Disease: From Bench to Bedside Applications
- First Published: 16 June 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
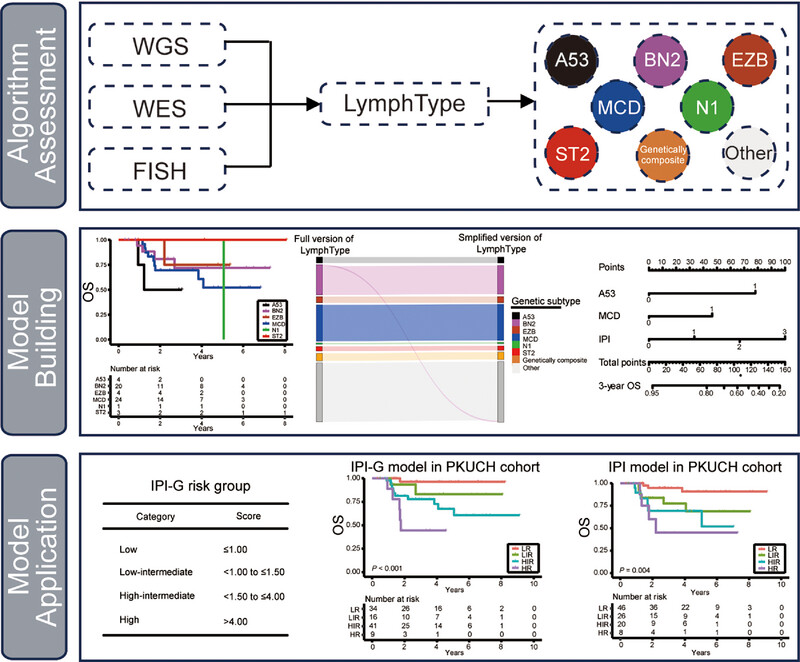
Genetic Subtype-Based International Prognostic Index Prognostic Model in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- First Published: 16 June 2025
Associations of Plasma and CSF Osteocalcin Levels With CSF ATN Biomarkers and Cognitive Functions in Alzheimer's Disease
- First Published: 19 June 2025
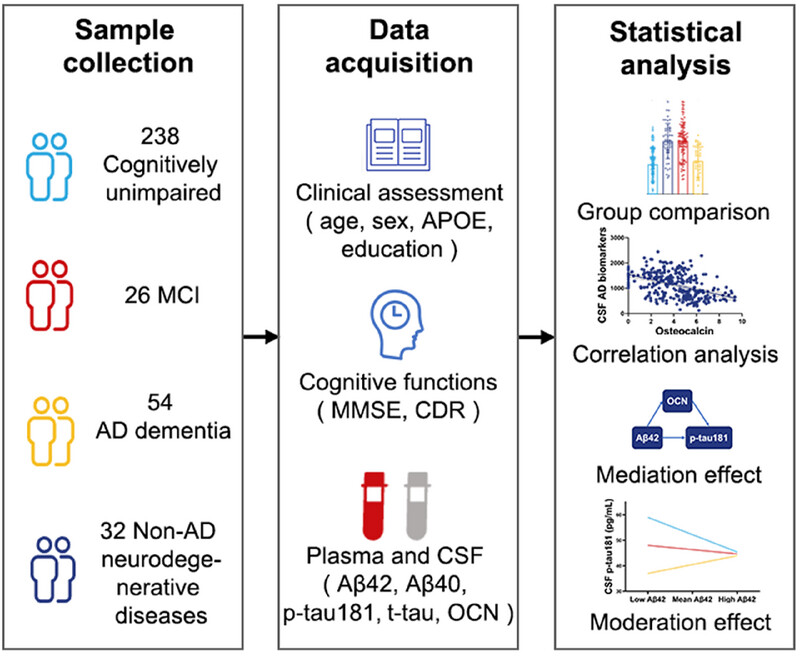
In this study, we observed elevated levels of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) osteocalcin (OCN) in patients with preclinical Alzheimer's disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment, and AD dementia. Both plasma and CSF OCN levels were correlated with brain amyloid-β (Aβ) deposition, tau hyperphosphorylation, neurodegeneration, and cognitive functions. Additionally, CSF OCN mediated the relationship between Aβ pathology and tau pathology. This study provides clinical evidence linking OCN to AD, suggesting that OCN may play a role in the pathogenesis of AD.
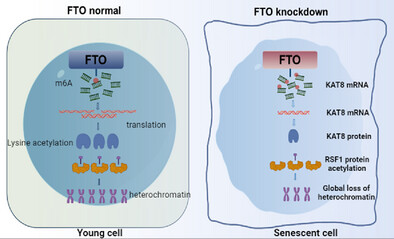
Tet Methylcytosine Dioxygenase 3 Promotes Cardiovascular Senescence by DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine-Mediated Sp1 Transcription Factor Expression
- First Published: 19 June 2025
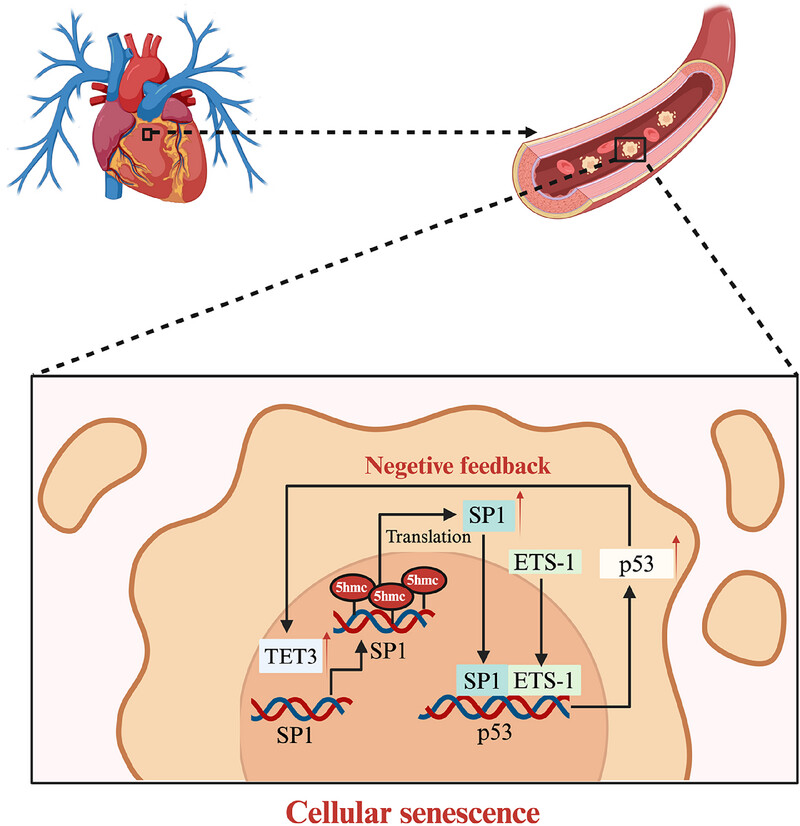
TET3 was identified to be a key DNA-active demethylase responsible for regulating cardiovascular senescence. TET3 facilitates the upregulation of SP1 through 5-hmC modification, leading to a synergistic interaction between SP1 and ETS-1 that further enhances p53 expression. Moreover, p53 not only promotes cellular senescence in vitro and in vivo but also reciprocally enhances TET3 and 5-hmC levels.
REVIEW
Interaction Between Microbiota and Immunity: Molecular Mechanisms, Biological Functions, Diseases, and New Therapeutic Opportunities
- First Published: 19 June 2025
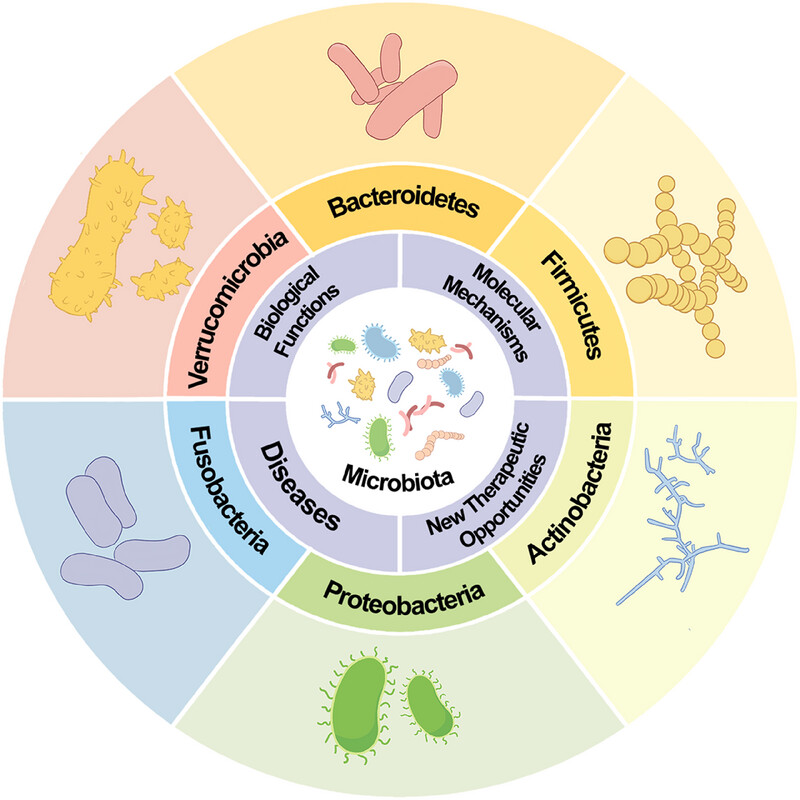
This review systematically concludes the interaction between microbiota and immunity. We introduce six phyla: Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, Fusobacteria, and Verrucomicrobia. We also elucidate molecular mechanisms, biological functions, diseases, and new therapeutic opportunities between microbiota and immunity. .
LETTER
The Mechanism of Omicron Variant-Associated Cardiac Injury in Rhesus Macaques Was Revealed by Proteomic and Phosphoproteomic Analyses
- First Published: 19 June 2025
REVIEW
Obesity Biomarkers: Exploring Factors, Ramification, Machine Learning, and AI-Unveiling Insights in Health Research
- First Published: 22 June 2025
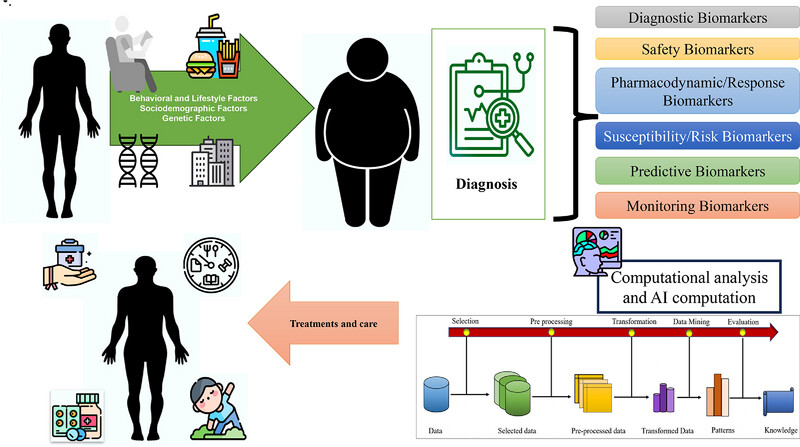
The graphical abstract emphasizes the complex nature of obesity, focusing on the interaction of behavioral, sociodemographic, genetic, and biomarker factors. It illustrates how lifestyle habits, demographics, and genetic predispositions influence obesity risk. Various biomarkers are used to detect and diagnose obesity, including diagnostic, safety, pharmacodynamic, monitoring, predictive, and susceptibility types. Advanced AI and programs analyze these biomarkers to provide personalized recommendations. These insights help individuals manage and overcome obesity by suggesting tailored lifestyle changes and medications, thus optimizing treatment and improving health outcomes.
Glutamine Metabolism: Molecular Regulation, Biological Functions, and Diseases
- First Published: 25 June 2025
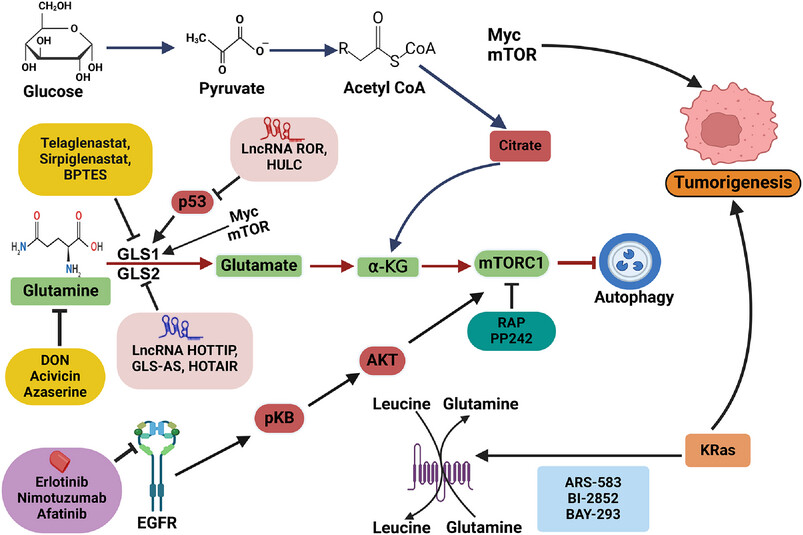
Tumor cells adapt to nutrient-poor environments by altering metabolism to acquire essential nutrients. They convert glutamine into glutamate and α-ketoglutarate, supporting mTOR activation and sugar biosynthesis. Disruption of mTORC1 signaling is linked to disease, while glutamine and leucine activation promotes cell growth and inhibits autophagy. Glutamine inhibitors are being explored for treatment.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Triplet Regimen of Metronomic Capecitabine Plus Antiangiogenic Drug and PD-1 Inhibitor as Later-Line Salvage Treatment for Patients With MSS/pMMR Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Retrospective Study
- First Published: 27 June 2025
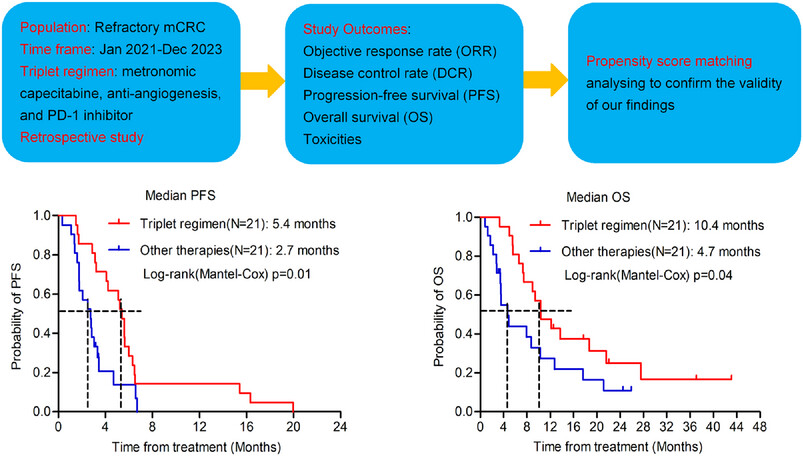
A retrospective propensity score-matched analysis demonstrated that the triplet regimen exhibited significantly improved antitumor efficacy compared to other later-line therapies in patients with microsatellite stable/mismatch repair proficient (MSS/pMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). The median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were significantly prolonged in the triplet regimen group compared to the other therapies group (PFS: 5.4 vs. 2.7 months, p = 0.01; OS: 10.4 vs. 4.7 months, p = 0.04).
REVIEW
Ten-Eleven Translocation Family Proteins: Structure, Biological Functions, Diseases, and Targeted Therapy
- First Published: 01 July 2025
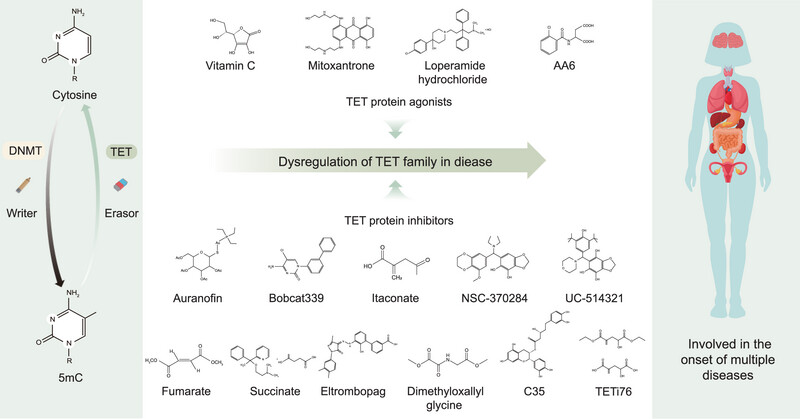
TET family proteins play a critical role in DNA demethylation, and their mutations and dysregulation contribute to the onset of multiple diseases. With a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms of TET involvement in disease, drug therapy targeting TET proteins shows great potential, which provides insights into new therapeutic strategies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Neobractatin and Trametinib Synergistically Induce Apoptosis and Gasdermin E-Dependent Pyroptosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells
- First Published: 01 July 2025
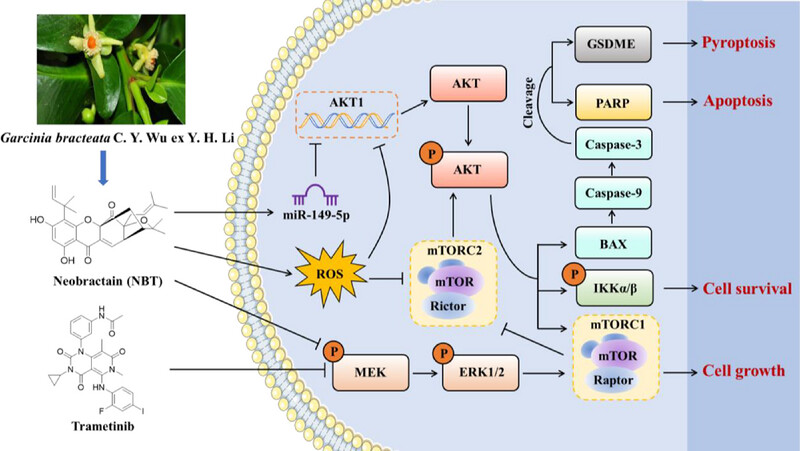
Neobractatin, a natural compound derived from Garcinia bracteata, significantly inhibited the growth of PDAC cells when used in combination with trametinib. This combination therapy promoted cell death through GSDME-mediated pyroptosis and apoptosis. Mechanistically, the combined treatment elevated levels of ROS, which in turn suppressed the AKT signaling pathway and its downstream targets, thereby enhancing the anti-tumor efficacy against PDAC cells.
REVIEW
Small Nucleolar RNAs: Biological Functions and Diseases
- First Published: 27 June 2025
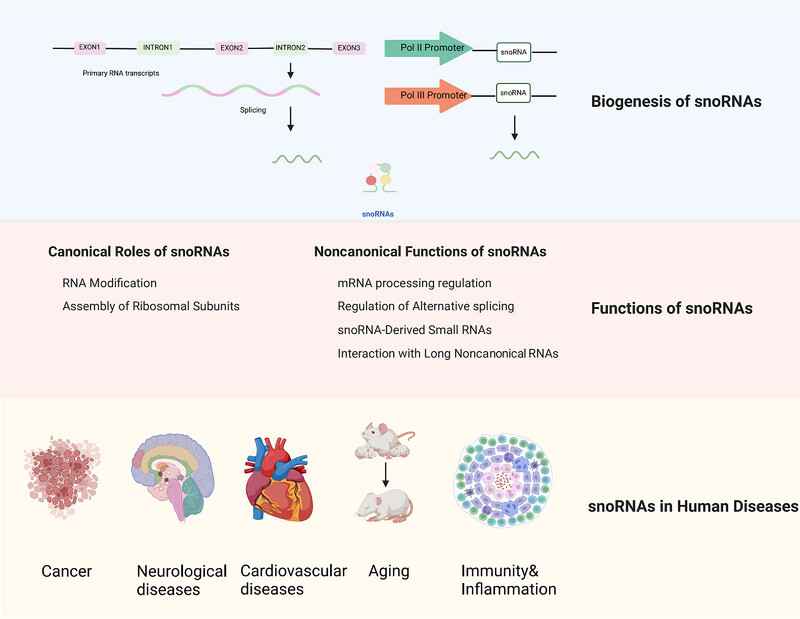
The majority of snoRNAs are derived from the intron region of genes, besides to intronic snoRNAs, some snoRNAs are transcribed as independent genes, often by Pol II or III, these snoRNAs are called intergenic snoRNAs. All of these play a role in the occurrence and progression of various diseases through multiple functions. Figures were created with biorender.com.
Advancing Design Strategy of PROTACs for Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 25 June 2025
Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membranes in Human Health and Diseases
- First Published: 27 June 2025
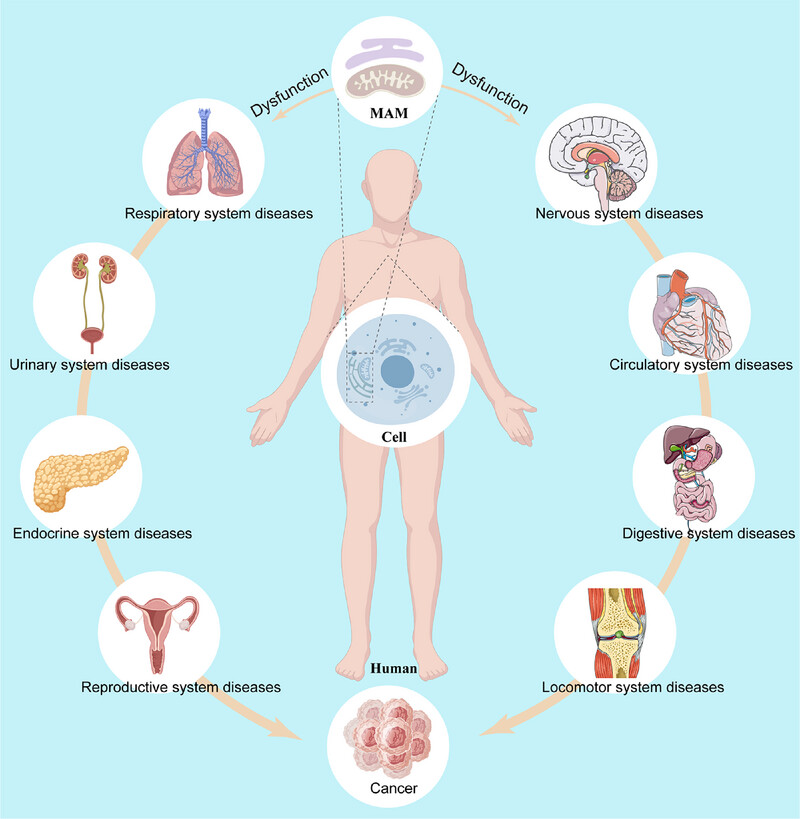
MAM dysfunction is considered as an initiator or contributor in the progression of various diseases such as nervous system diseases, circulatory system diseases, digestive system diseases, locomotor system diseases, reproductive system diseases, endocrine system diseases, urinary system diseases, respiratory system diseases and cancer.
Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Surgery: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions
- First Published: 25 June 2025
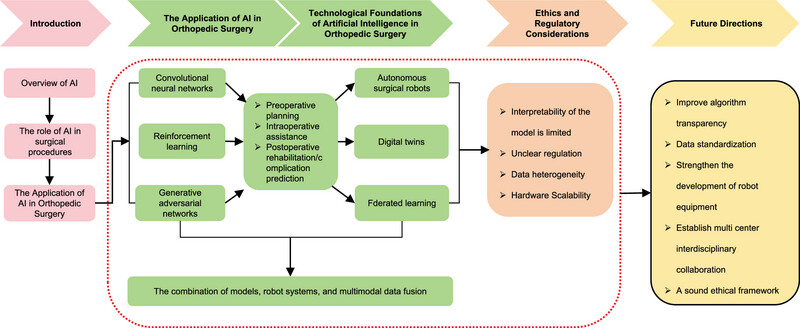
AI drives transformative changes in orthopedic surgery, steering it toward precision and personalization through intelligent applications in preoperative planning, intraoperative assistance, and postoperative rehabilitation/monitoring. Breakthroughs in deep learning, robotics, and multimodal data fusion have enabled AI to demonstrate significant advantages. Nonetheless, current applications face challenges such as limited real-time decision autonomy (reliance on static preoperative data), fragmented medical data silos, standardization gaps restricting model generalization, and ethical/regulatory frameworks lagging behind technological advancements. Therefore, a critical analysis of the current status of AI and the acceleration of its clinical translation is urgently required. This study systematically reviews the core advancements, challenges, and future directions of AI in orthopedic surgery from technical, clinical, and ethical perspectives. It elaborates on the “perceptual-decisional-executional” intelligent closed loop formed by algorithmic innovation and hardware upgrades, summarizes AI applications across the full surgical continuum, analyzes ethical and regulatory challenges, and explores emerging trajectories. This review integrates the end-to-end applications of AI in orthopedics, illustrating its evolution from assistive to semi-autonomous systems. It introduces an “algorithm-hardware-ethics trinity” framework for technical translation, providing methodological guidance for interdisciplinary collaboration. Additionally, it evaluates the combined efficacy of diverse algorithms and devices through practical cases and details of future research frontiers, aiming to inform researchers of current landscapes and guide subsequent investigations.
HIGHLIGHT
REVIEW
Oxidative Stress: Signaling Pathways, Biological Functions, and Disease
- First Published: 01 July 2025
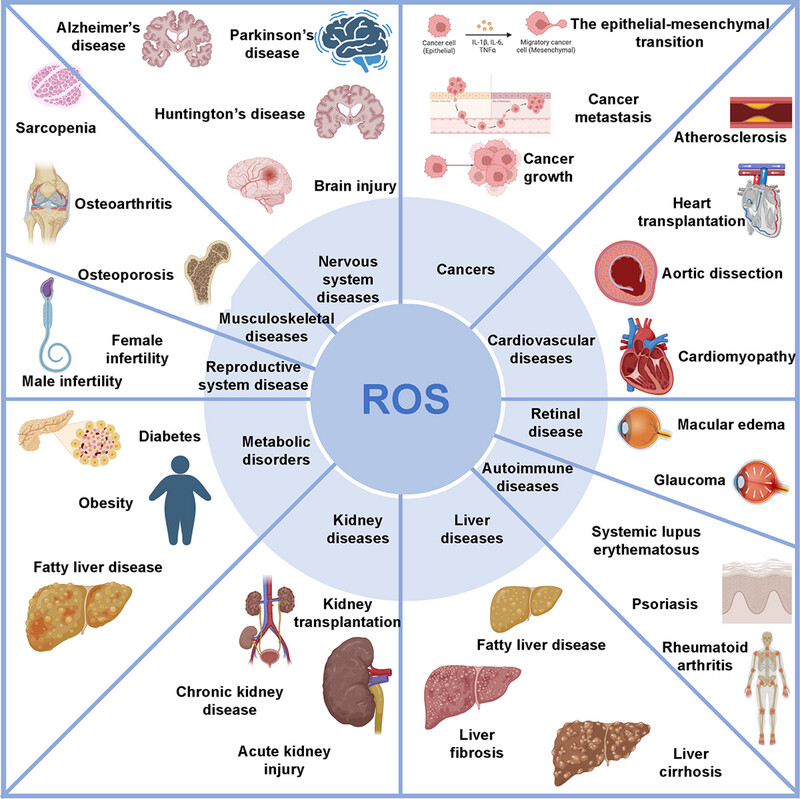
Oxidative stress causes cellular damage across multiple systems, contributing to neurodegeneration (Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Huntington's), cancer progression and resistance, cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis, heart failure), liver and kidney injury, metabolic disorders (diabetes, obesity), autoimmune diseases, musculoskeletal decline, retinal disorders, and reproductive infertility.
Lactate Metabolism and Lactylation Modification: New Opportunities and Challenges in Cardiovascular Disease
- First Published: 01 July 2025
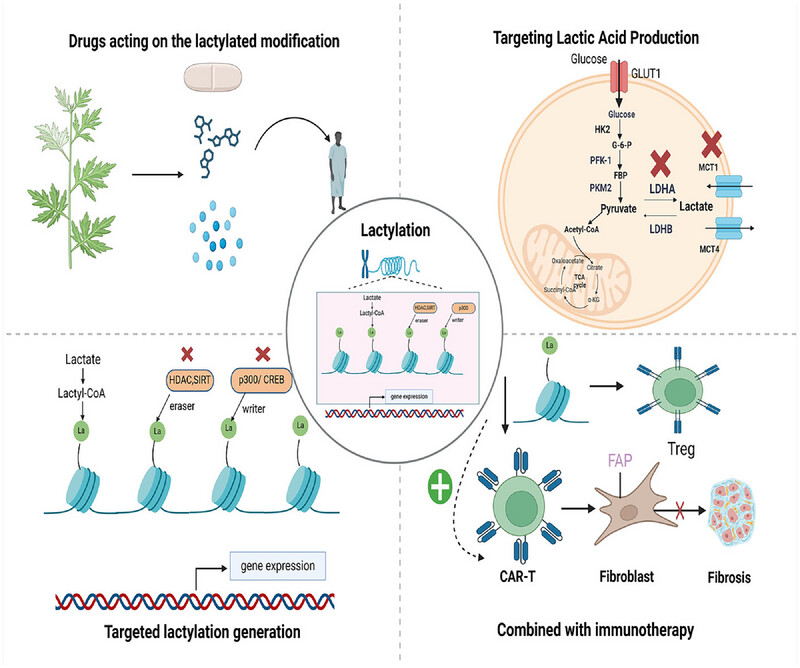
Lactate, beyond a metabolic byproduct, regulates immunity and inflammation, linked to cardiovascular diseases (CVD) via metabolic reprogramming. Lactylation, a lactate-driven epigenetic mark, modulates gene expression in fibrosis, lipid disorders, and CVD progression. Targeting lactylation (via GLUT1, HDACs, or CAR-T) and combining metabolic/immune therapies offer novel strategies to treat CVD, addressing unmet needs in current drug resistance.
Transforming Growth Factor-β Pathway: Biological Functions and Therapeutic Targets
- First Published: 27 June 2025
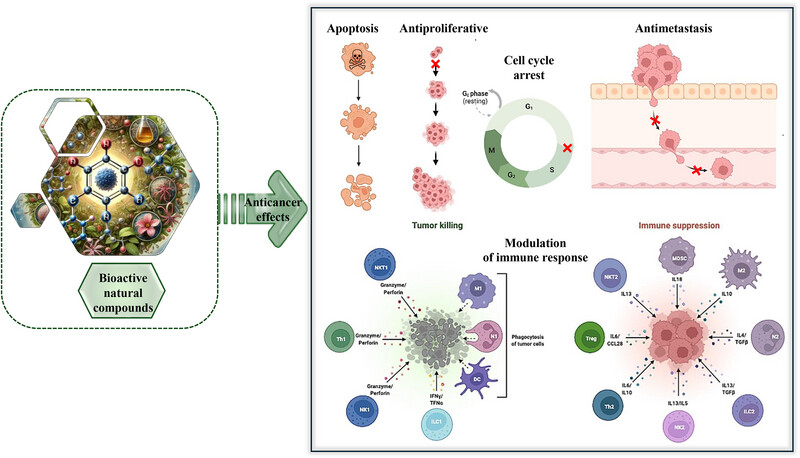
Natural compounds modulate the TGF-β pathway, which acts as both a tumor suppressor and promoter during cancer progression. Agents such as ginsenosides, halofuginone, and EGCG influence cell proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis. These bioactive molecules may complement standard therapies, highlighting the need for advanced formulations, mechanistic studies, and clinical validation.
Phase Separation Regulates Metabolism, Mitochondria, and Diseases
- First Published: 01 July 2025
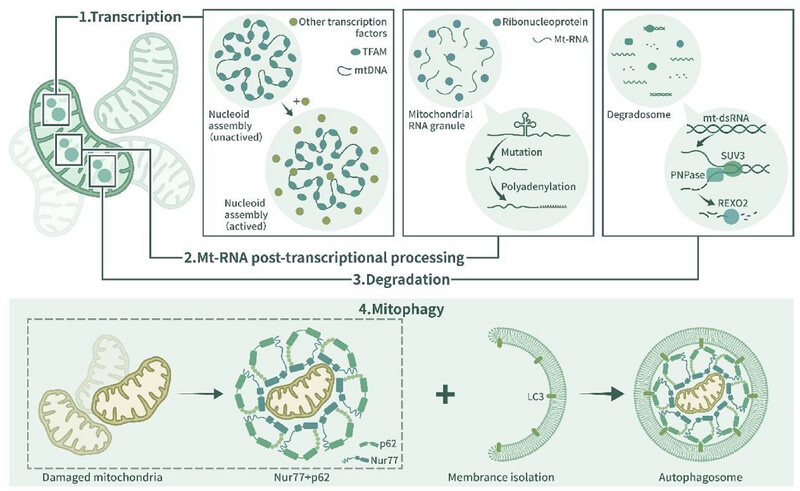
Mitochondrion-related liquid–liquid phase separation. (1) Phase separation mediates the self-assembly of mitochondrial nucleoids (mt-nucleoids). (2) Phase segregation mediates the formation of mitochondrial RNA granules (MRGs). (3) Phase separation mediates the formation of mitochondrial degradosomes. (4) Phase segregation is involved in mitophagy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A Novel Dual Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase/Janus Kinase 3 Inhibitor Wj1113 and its Therapeutic Effects on Rheumatoid Arthritis
- First Published: 07 July 2025
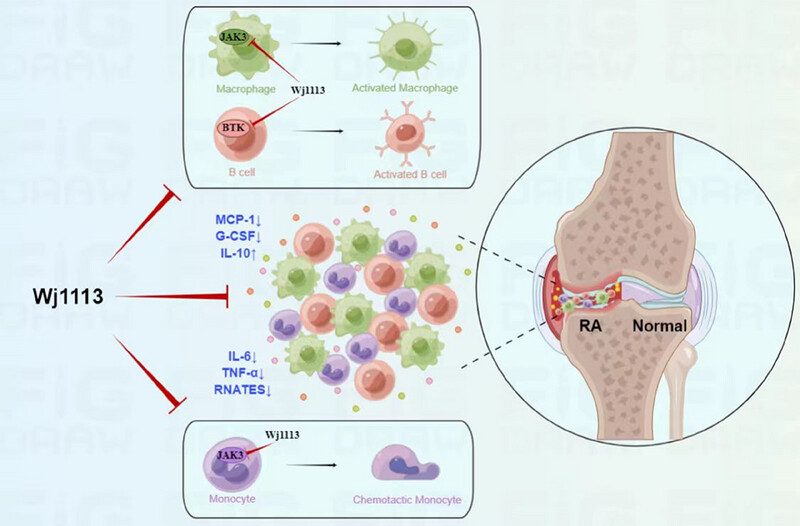
Wj1113 simultaneously inhibits the JAK3 and BTK pathways, impacting the activation of macrophages and B cells, as well as influencing monocyte chemotaxis. Consequently, this results in a decrease in proinflammatory factors such as MCP-1(monocyte chemoattractant protein-1), G-CSF(granulocyte colony-stimulating factor), IL-6, TNF-α, and RANTS(regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted) within the affected joints. Additionally, Wj1113 increases the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10. Therefore, Wj1113 has the potential to alleviate the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis.
A Dose-Tailored Anti-Plasma Cell Regimen Lowers the Mortality of Late-Stage Cardiac Amyloidosis
- First Published: 02 July 2025
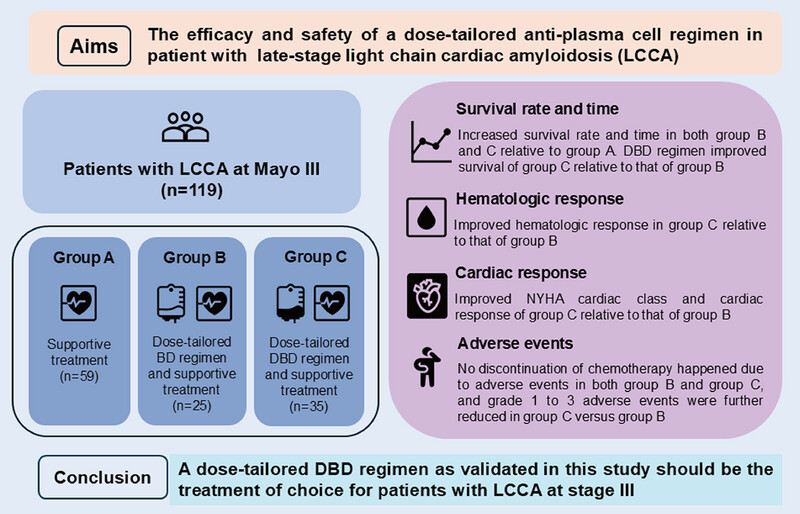
The present study was designed to assess the efficacy and safety of a dose-tailored BD regimen and a dose-tailored DBD regimen in patients with LCCA at Mayo Stage III. Both the two regimens markedly increased survival rate and time in those patients and the dose-tailored DBD regimen was superior to the dose-tailored BD regimen in both efficacy and safety. BD, bortezomib and dexamethasone; DBD, daratumumab, bortezomib, and dexamethasone; LCCA, light-chain cardiac amyloidosis.
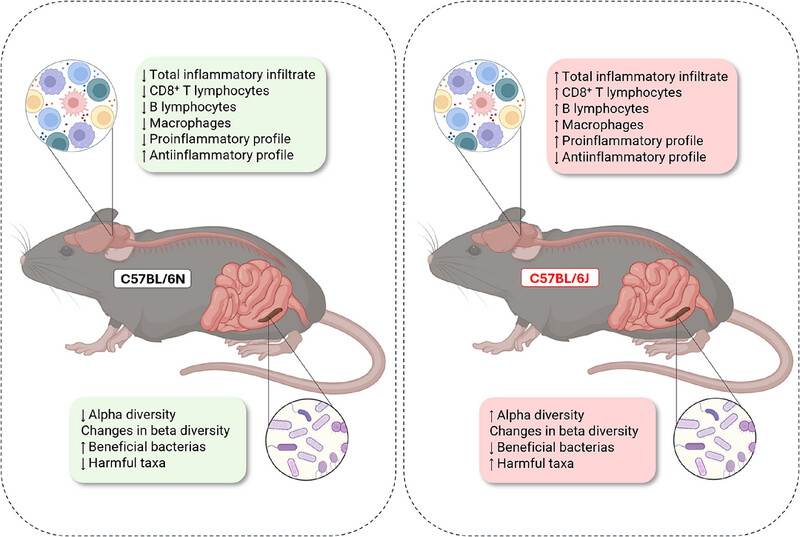
Differences of the 6N and 6J Substrains of C57BL/6 Mice in the Development of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
- First Published: 02 July 2025
Next-Generation HER-2 Tumor-Targeted Delivery of the STING Agonist Immune-Stimulating Antibody Conjugate (ISAC) Improves Anticancer Efficacy and Induces Immunological Memory
- First Published: 02 July 2025
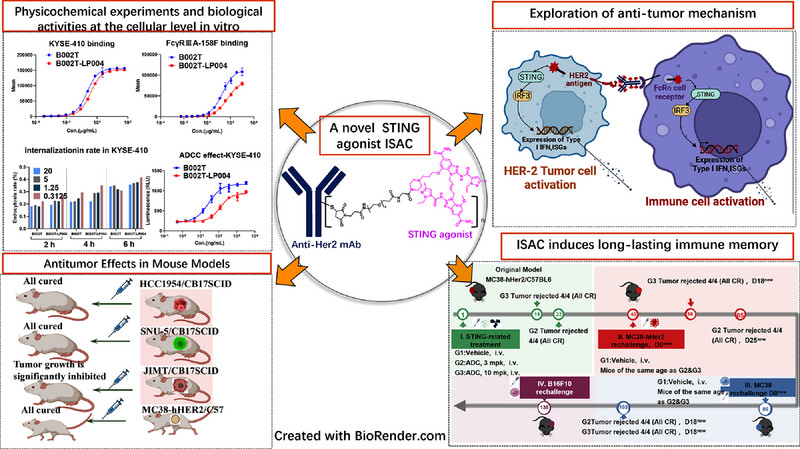
A novel immune-stimulating antibody-drug conjugate, which links STING agonists to anti-HER2 mAb through an optimized noncleavable Linker, remains highly stable at DAR = 5.7 and demonstrates superior efficacy over marketed HER2-targeted ADCs in multiple tumor models with high, low, and drug-resistant HER2 expression. And it shows good immune memory against HER2 tumors that have been killed before, thereby achieving rapid re-killing.
Hypomethylation-Triggered SERPINE1 (Serpin Family E Member 1) Exacerbates Polycystic Ovary Syndrome with Hyperandrogenism Induced by Circadian Disruption
- First Published: 04 July 2025
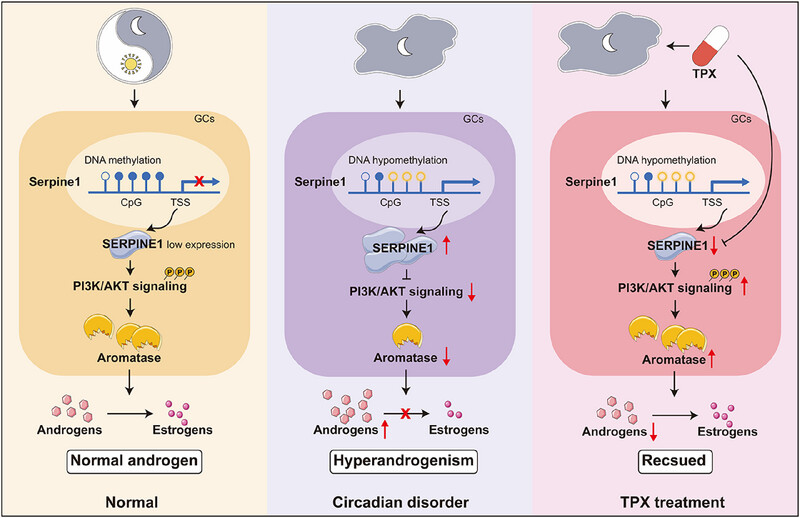
SERPINE1 shows CpG hypomethylation near its TSS of promoter region when exposed to circadian disruption, and its gene expression triggers hyperandrogenism through the PI3K/AKT pathway. SERPINE1 inhibitor TPX can significantly decrease serum SERPINE1 levels and reduce abnormally high testosterone levels in both continuous darkness-exposed rats and DHEA-treated rats.
LETTER
The Arming of Natural Killer Cells With Fc-Engineered Monoclonal Antibodies Confers Specificity Against Tumor B Cells
- First Published: 04 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Leveraged Vaccination to Alleviate Original Antigenic Sin for Enhancing Broad-Neutralizing Antibody Response against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Subvariants
- First Published: 07 July 2025
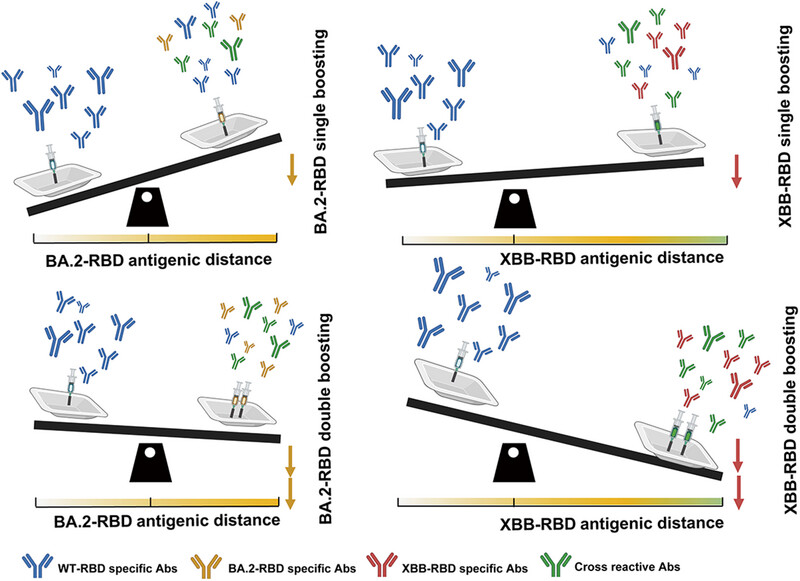
The leveraged vaccination strategy we proposed based on antigenic distance and boost frequence is effective to alleviate original antigen sin (OAS) or immune imprinting from prior exposure of the original SARS-CoV-2 antigen. We showed that boost twice with XBB–RBD vaccine having longer antigenic distance than BA.2–RBD is more effective to attenuate OAS than BA.2–RBD, suggesting that this leveraged vaccination strategy is feasible to alleviate OAS and enhance broad-neutralizing antibody (bnAb) response against Omicron subvariants.
Incidence and Immunopathology of Myositis in Rectal Cancer Patients Treated With Neoadjuvant Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Chemoradiotherapy: Findings From the CHINOREC Trial
- First Published: 07 July 2025
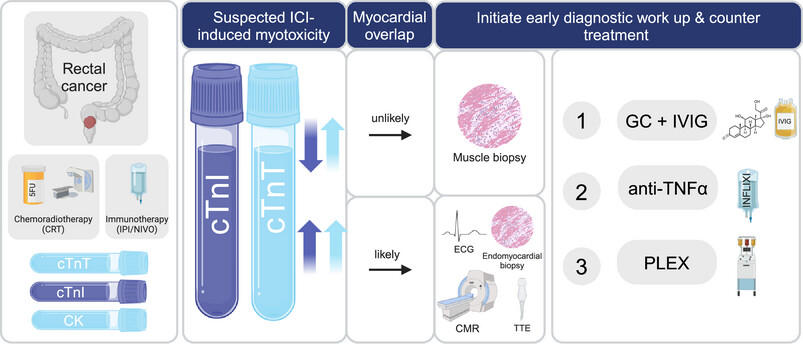
ICI-induced myositis occurred at a higher-than-expected rate (12%) in neoadjuvant-treated rectal cancer patients receiving CRT+ICI. Elevated cTnT, but not cTnI, differentiated skeletal from cardiac involvement. Immunopathology showed a predominant CD8+ T cell infiltrate, highlighting a T cell-mediated mechanism that necessitates early detection and targeted immunomodulation.
REVIEW
Current Bioinformatics Tools in Precision Oncology
- First Published: 09 July 2025
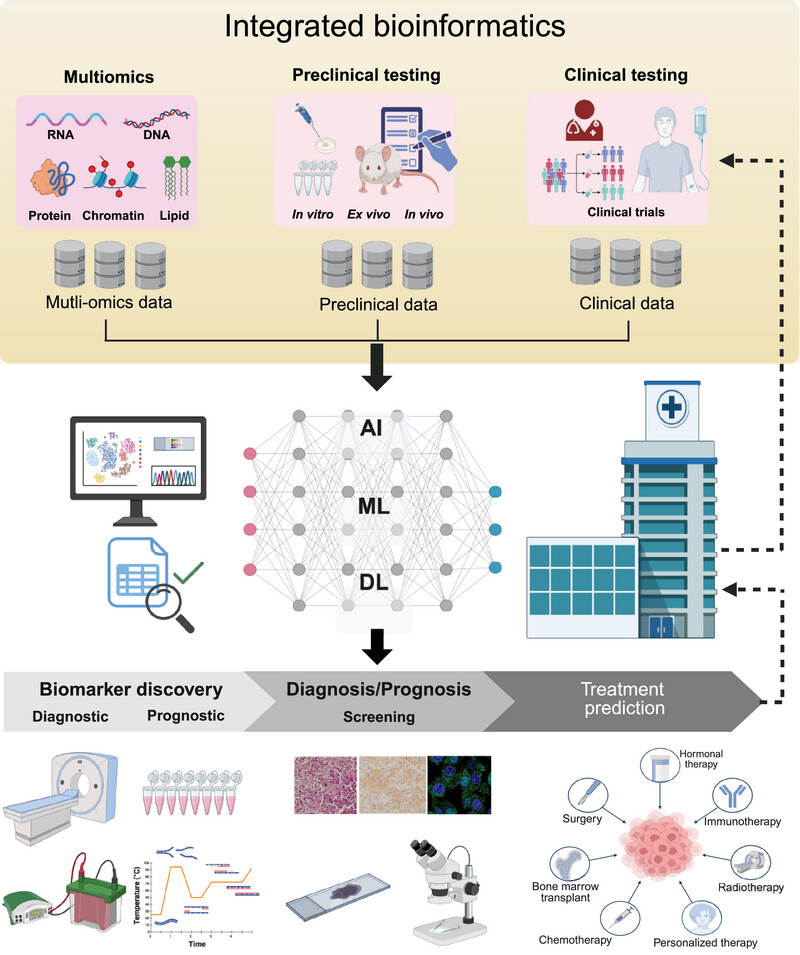
This framework illustrates the comprehensive integration of bioinformatics tools to enhance biomarker and therapeutic target discovery. It incorporates multiomics data—spanning RNA, DNA, proteins, lipids, and chromatin—alongside preclinical (in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo) and clinical (clinical trials) validation approaches. By leveraging advanced computational techniques, including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL), this workflow enables precise detection, classification, and prediction of disease-associated biomarkers. This integrative strategy supports diagnostic and prognostic screening, facilitates biomarker discovery, and aids in identifying potential therapeutic targets, ultimately advancing precision medicine and innovative treatment strategies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
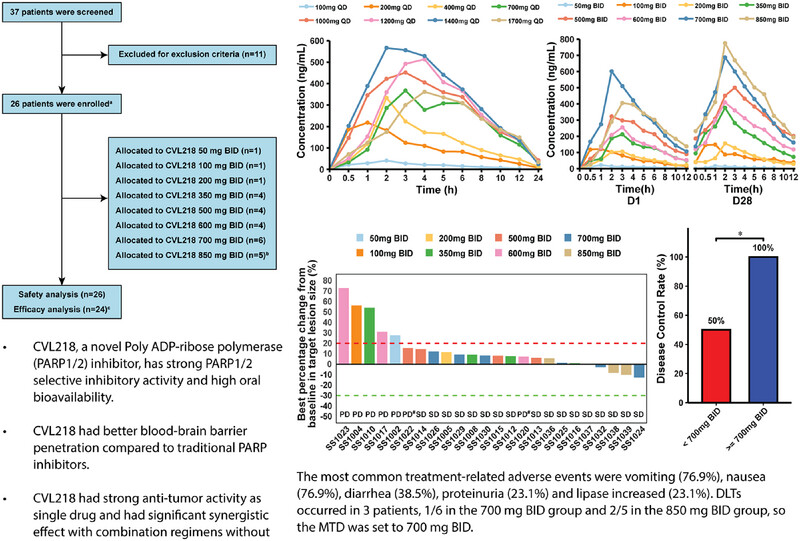
Phase I Clinical Trial of CVL218, a Novel PARP1/2 Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors
- First Published: 09 July 2025
Casein Kinase 2α Ablation Confers Protection Against Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Role of FUN14 Domain Containing 1-Dependent Regulation of Mitophagy and Ferroptosis
- First Published: 11 July 2025
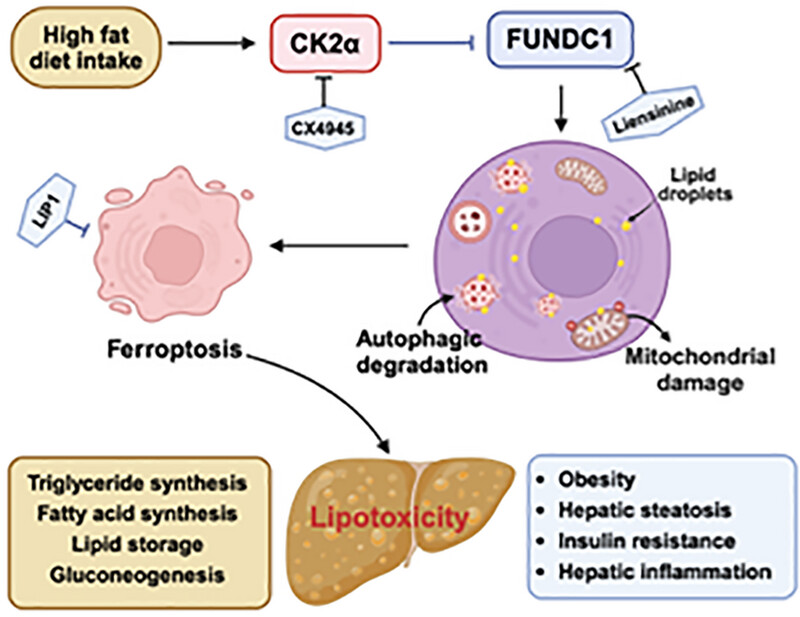
Schematic graph exhibiting possible mechanism(s) for the role of CK2α and FUNDC1 in high fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis. Long-term high fat diet insult dampens FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy through upregulation of CK2α, prompting disturbed lipid metabolism and lipid accumulation due to compromised mitophagy. Lipotoxicity subsequently promotes lipotoxic ferroptosis, imperiling hepatic steatosis.
Antiangiogenic Medications Impede the Oral Mucosal Microcirculation and Interfere with Oral Wound Healing: A Complication Deserving of Attention
- First Published: 11 July 2025
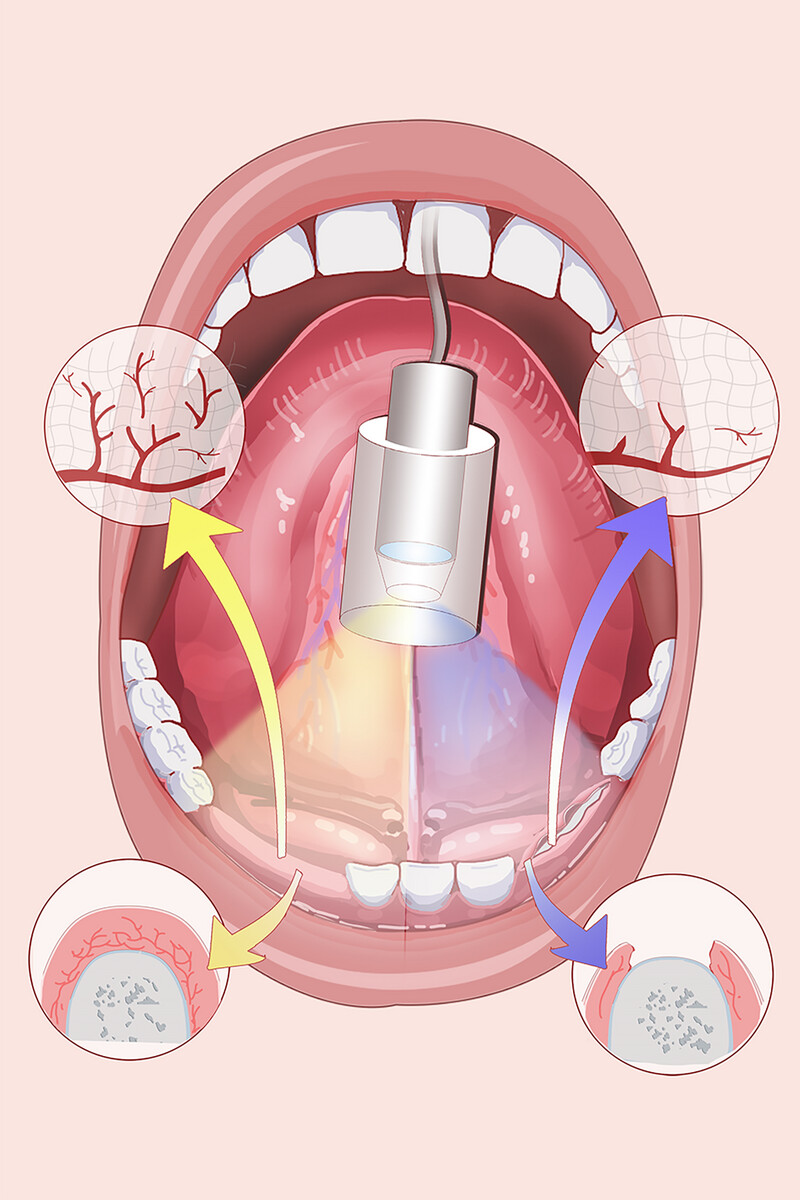
The combined use of antiangiogenic medication and antiresorptive medication aggravates the state of oral mucosal microcirculation. Antiangiogenic agents could affect postoperative wound healing in antiresorptive-drug-based MRONJ patients by the way of impairing the oral mucosa microcirculation. The HVM device provides an non-invasive and accurate way to detect oral mucosal microcirculation and therefore predict surgical prognosis.
REVIEW
Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Heterogeneity, Cancer Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic Targets
- First Published: 11 July 2025
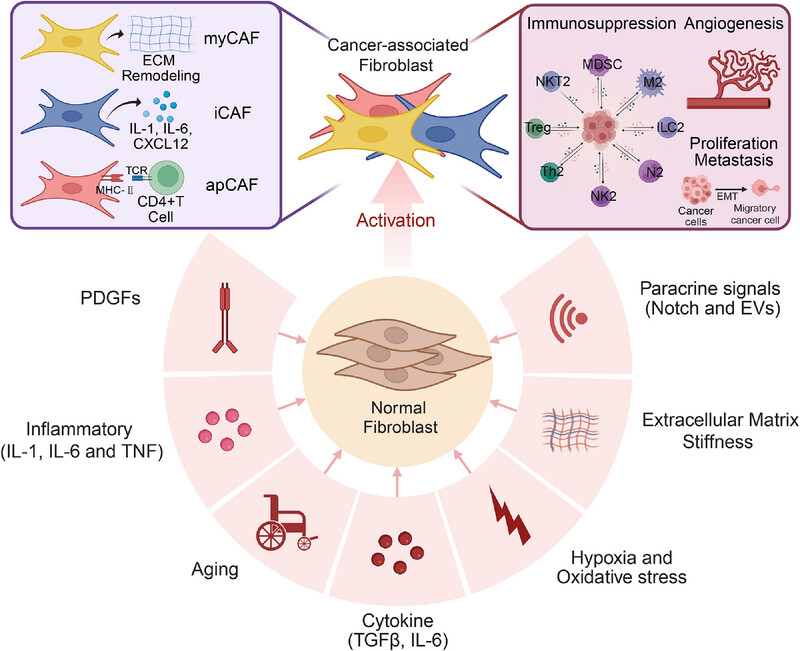
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) arise from normal fibroblasts in response to various tumor microenvironmental signals, including cytokines such as TGF-β and IL-6, paracrine factors like PDGFs, Notch signaling, extracellular vesicles, as well as aging, inflammation, hypoxia, oxidative stress, and increased extracellular matrix (ECM) stiffness. Upon activation, these fibroblasts differentiate into distinct subtypes—myofibroblastic CAFs (myCAFs), inflammatory CAFs (iCAFs), and antigen-presenting CAFs (apCAFs)—each contributing uniquely to tumor progression. CAFs remodel the ECM and secrete inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, and CXCL12, fostering an immunosuppressive environment by modulating immune cell populations. Through MHC-II-mediated interactions with CD4+ T cells and the recruitment or activation of immunosuppressive cells including MDSCs, Tregs, Th2 cells, ILC2s, NK2 cells, NKT2 cells, and M2 macrophages, CAFs blunt antitumor immunity. Collectively, these activities promote cancer cell proliferation, angiogenesis, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and metastasis, positioning CAFs as central orchestrators of tumor development and immune evasion (created with www.biorender.com).
Sjögren's Syndrome: Epidemiology, Classification Criteria, Molecular Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- First Published: 11 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Novel Lysosomal-Associated Transmembrane Protein 4B-Positive Stem-Like Cell Subpopulation Characterizes High-Risk Colorectal Cancer Subtypes
- First Published: 13 July 2025
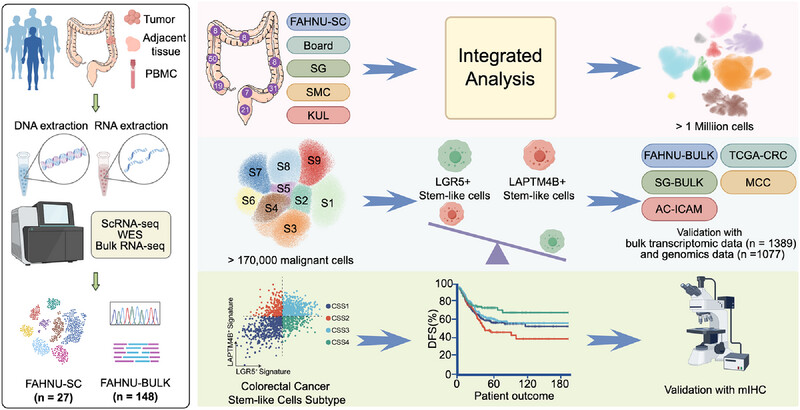
This study identified the existence of a novel population of LAPTM4B+ tumor stem-like cells in addition to the classical LGR5+ tumor stem-like cells in colorectal cancer (CRC). The combination of LGR5+ and LAPTM4B+ stem-like cells enable a more refined stratification of CRC, offering potential insights for targeted therapeutic strategies.
Sulfide Quinone Oxidoreductase Alleviates Acute Ulcerative Colitis by Regulating Mitochondrial Dysfunction
- First Published: 13 July 2025
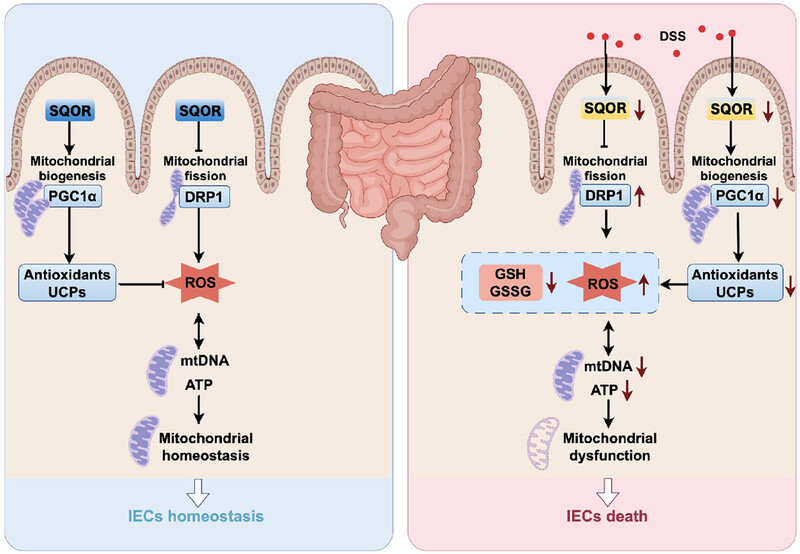
SQOR deficiency in intestinal epithelial cells aggravated DSS-induced acute colitis and disrupted the integrity of intestinal tight junctions. Moreover, SQOR plays a vital role in regulating the mitochondrial function of intestinal epithelial cells. Mechanistically, SQOR may rely on inhibiting excessive mitochondrial division and promoting mitochondrial biogenesis to regulate ROS levels in intestinal epithelial cells.
Intravesical Disitamab Vedotin (RC48) for HER2-Expressing High-Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Single-Arm, Dose–Escalation Phase I Trial Study
- First Published: 13 July 2025
REVIEW
Phosphate in Physiological and Pathological Mineralization: Important yet Often Unheeded
- First Published: 13 July 2025
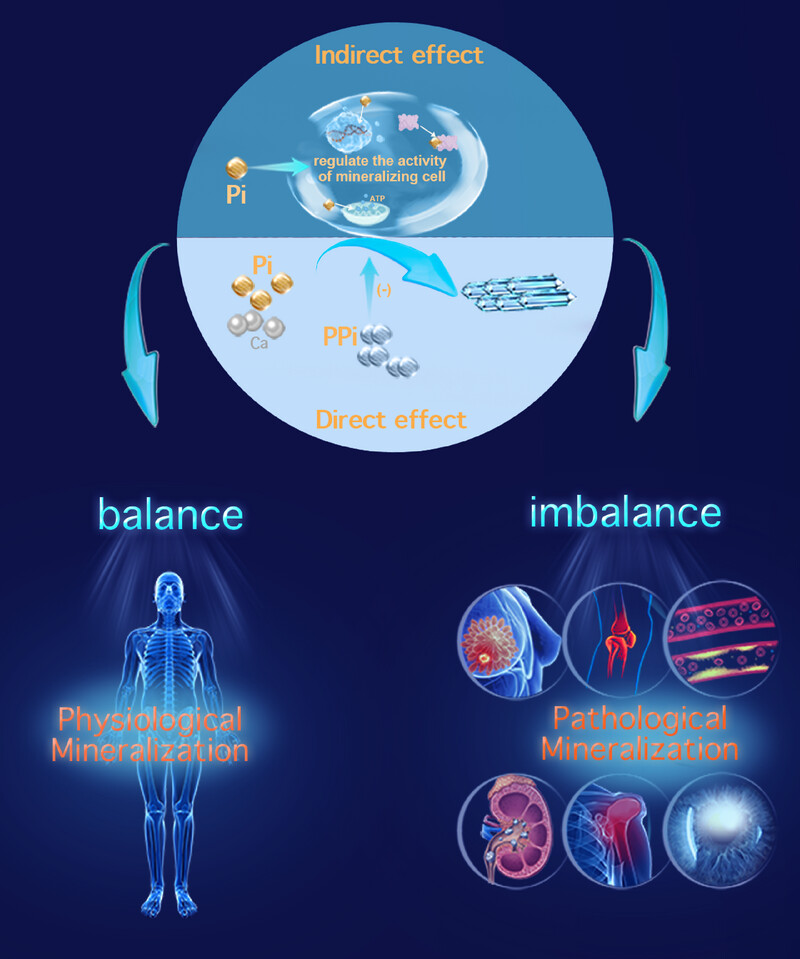
Phosphate serves as a building block for physiological mineralization, and as a signaling molecule that regulates the activity of mineralizing cells. The disturbance in these processes could induce a series of pathological mineralization, with abnormal mineralization of hard tissues and ectopic mineralization of soft tissues being the most representative.
Phage and Endolysin Therapy Against Antibiotics Resistant Bacteria: From Bench to Bedside
- First Published: 13 July 2025
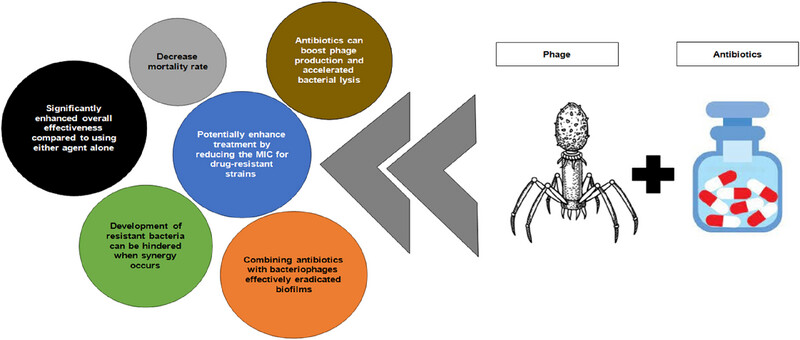
Synergistic effects of combining bacteriophages and antibiotics in antimicrobial therapy.
The diagram illustrates key advantages of phage-antibiotic synergy, including increased treatment effectiveness, reduced minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for drug-resistant strains, enhanced biofilm eradication, and inhibition of resistant bacteria development. Antibiotics can also promote phage production and accelerate bacterial lysis. These interactions suggest promising potential for combined therapies, particularly in overcoming antibiotic resistance. Figure created using Microsoft PowerPoint.