Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
The rapid rise of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants with immune evasion properties: XBB.1.5 and BQ.1.1 subvariants
- First Published: 15 March 2023
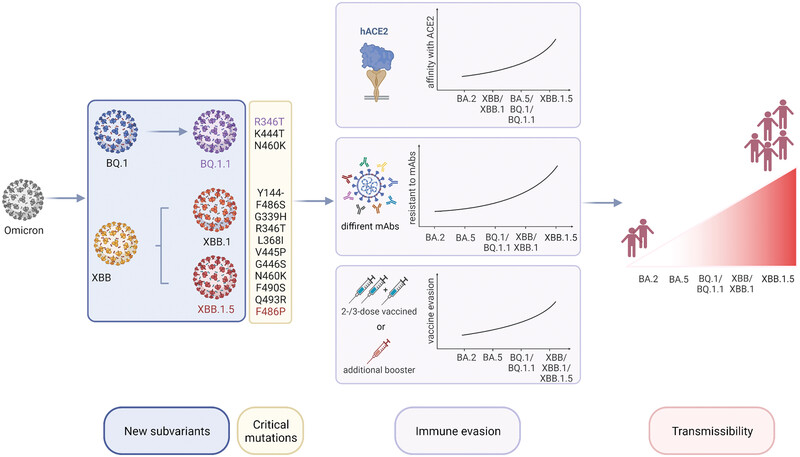
In the Omicron wave, two emerging subvariants, BQ.1 and XBB, have rapidly become a global public health concern. This diagram illustrates the critical spike mutations in these subvariants, which can lead to immune escape from prior COVID-19 vaccines, boosters, and therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Notably, XBB.1.5, which carries a rare F486P mutation, has demonstrated significantly higher receptor-binding domain (RBD)-ACE2 binding affinity and transmissibility compared to other subvariants, making it the dominant strain in several countries.
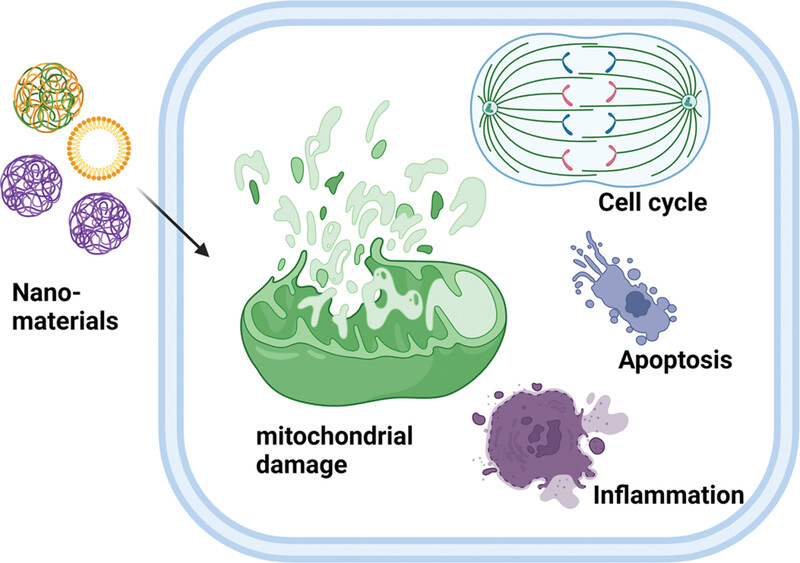
Nanoparticles-induced potential toxicity on human health: Applications, toxicity mechanisms, and evaluation models
- First Published: 14 July 2023
Applications of multi-omics analysis in human diseases
- First Published: 31 July 2023
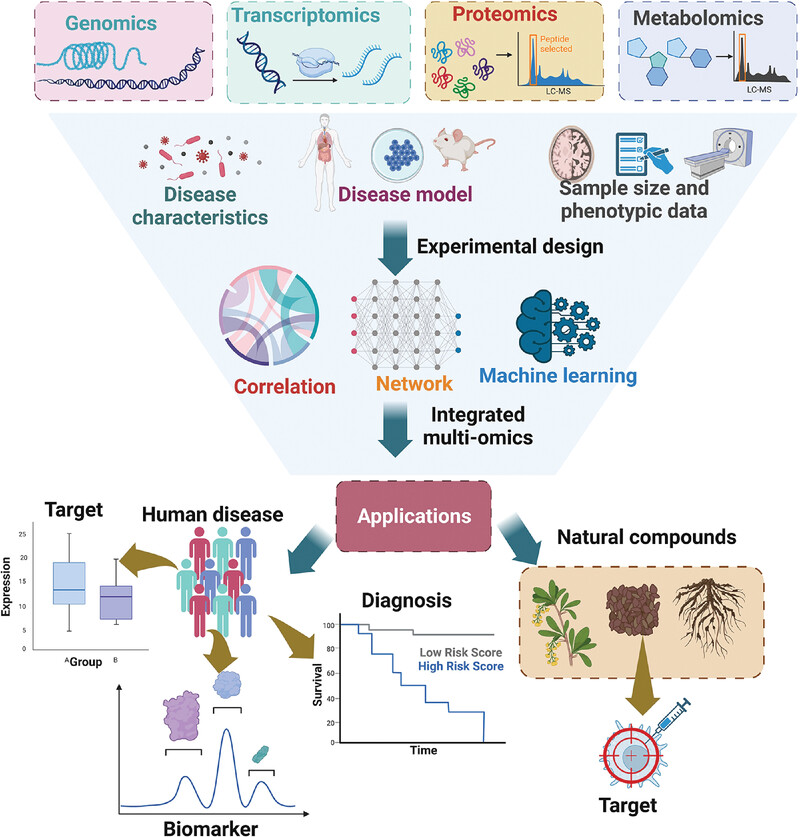
Multi-omics contains genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, etc. And the experimental design considers the disease characteristics, disease model, sample size and phenotypic data. After the data integration by the approach of correlation, network and machining learning, the multi-omics can be applied in diagnosis, biomarkers, targets of human disease and target discovery of natural compound.
Metabolic reprogramming in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutics
- First Published: 27 March 2023
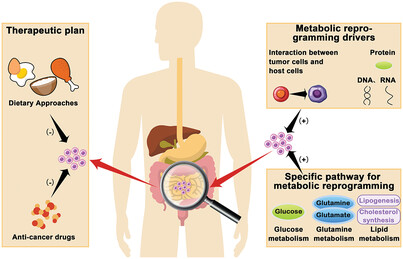
This article presented the metabolic reprogramming of tumor cells to adapt to their microenvironment distinct from normal cells. And this study reviewed the driving factors of metabolic reprogramming, the specific metabolic pathway changes affected, and the related treatment options, in order to provide some suggestions for future tumor treatment.
Organoids: The current status and biomedical applications
- First Published: 17 May 2023
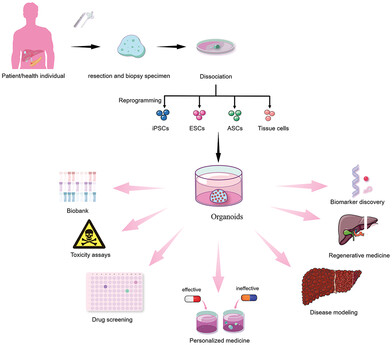
Organoids can be generated by inducing and culturing pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), embryonic stem cells (ESCs), adult stem cells (ASCs), and tumor cells from healthy donors or patients. The potential biomedical applications for organoids include disease modeling, drug screening, toxicity assays, personalized medicine, biobank, biomarker discovery, and regenerative medicine.
Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in cancer
- First Published: 22 May 2023
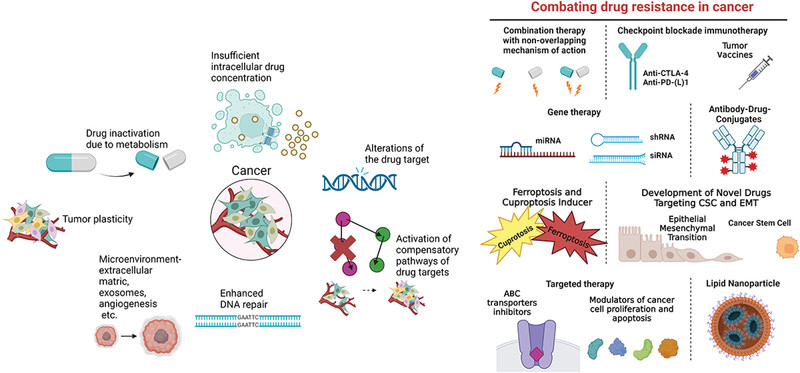
The reduced responsiveness of cancer cells can be associated with various mechanisms, including drug inactivation, reduced intracellular drug accumulation by reduced uptake or increased efflux, drug target alteration, activation of compensatory pathways for cell survival, regulation of DNA repair and cell death, tumor plasticity, and the regulation from tumor microenvironments. Various targeting strategies against different resistance mechanisms have been developed. The purpose of overcoming the drug resistance of cancer cells is to optimize the sensitivity of the therapy. This can be achieved by polytherapy using the combination of at least two drugs; immunotherapy using checkpoint inhibitors or monoclonal antibodies; antibody-drug conjugates improving the selectivity of cancer treatment; gene technology modifying the epigenetic sequence; targeted therapy targeting the overexpression of drug efflux transporter or vital proteins for the cancer cell apoptosis; and nanoparticle delivery system improving the efficacy of the drug and reducing the side effect.
Hot and cold tumors: Immunological features and the therapeutic strategies
- First Published: 26 August 2023
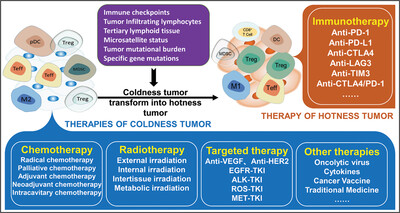
The characteristics of coldness and hotness tumors are determined by the information of cancer cells and tumor microenvironments, which significantly affects cancer patients’ clinical efficacy. Different therapeutic strategies for cold and hot tumors based on clinical efficacy were analyzed through clinical drug targets, tumor microenvironments, and tumor stages. Coldness tumors can transform into hotness tumors through chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and other therapies.
Probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics in health and disease
- First Published: 04 November 2023
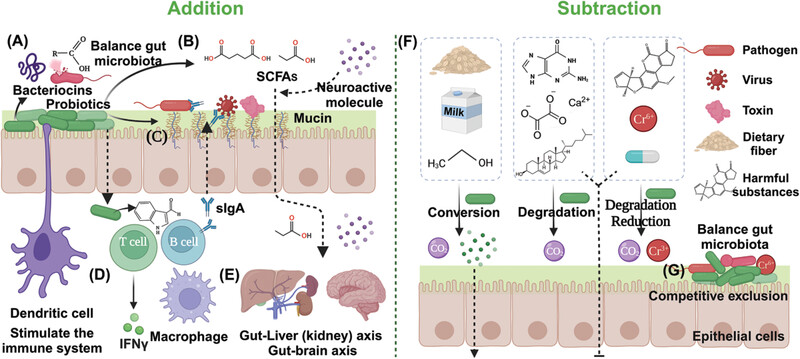
Extensive research and clinical evidence have demonstrated the mechanisms and effectiveness of probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics in restoring gut microbiota homeostasis and treating a variety of diseases. Prebiotics can promote the growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria, while probiotics produce postbiotics through “addition” to regulate the gut microbiota, and “subtraction” to remove harmful metabolites and exogenous substances to reduce their impact on the body, thereby alleviating or treating diseases. Probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics may represent the next generation of medicines, with the potential to revolutionize the way we treat and manage disease.
Protein posttranslational modifications in health and diseases: Functions, regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic implications
- First Published: 02 May 2023
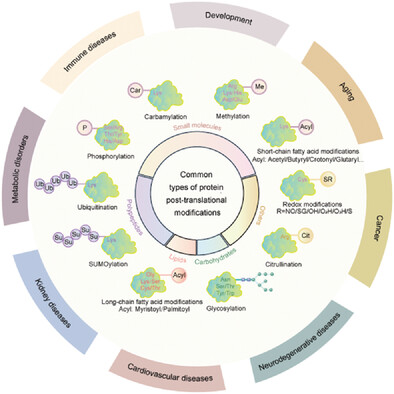
The reversible and irreversible protein posttranslational modifications, such as acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, glycosylation, SUMOylation, and redox modifications, are essential regulators in organisms and cells. This work systematically summarizes the features, regulatory mechanisms, substrates, functions, and related treatments of protein modifications and will deepen the understanding of protein modifications in health and diseases.
Post-translational modifications of histones: Mechanisms, biological functions, and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 20 May 2023
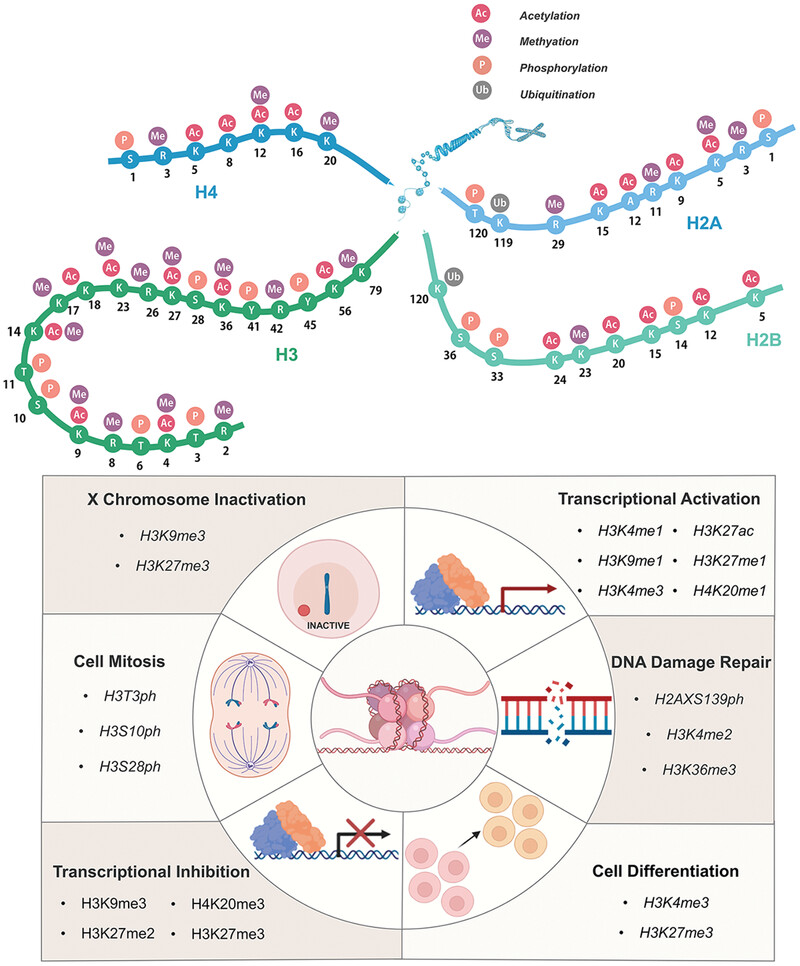
Histone tails are subject to a variety of post-translational modifications. We have introduced histone acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, malonylation, crotonylation, propionylation, butyrylation, and so forth. They participate in many life activities through different related histone sites.
3D bioprinting and its innovative approach for biomedical applications
- First Published: 24 December 2022
Hypoxia signaling in cancer: Implications for therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 23 January 2023
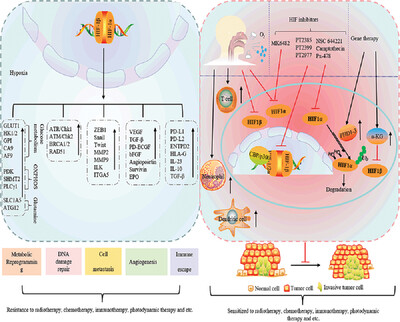
Solid tumors gradually form a hypoxic malignant microenvironment during growth, which promotes tumor proliferation and metastasis by affecting metabolism, angiogenesis, and immune escape, and finally leads to therapeutic resistance. In recent years, hypoxia-inducible factor inhibitors, direct targeting of hypoxic cells, and respiratory hyperoxia have been widely used to improve the hypoxic microenvironment of tumors and enhance the sensitivity of tumor therapy.
COVID-19 in early 2023: Structure, replication mechanism, variants of SARS-CoV-2, diagnostic tests, and vaccine & drug development studies
- First Published: 08 April 2023
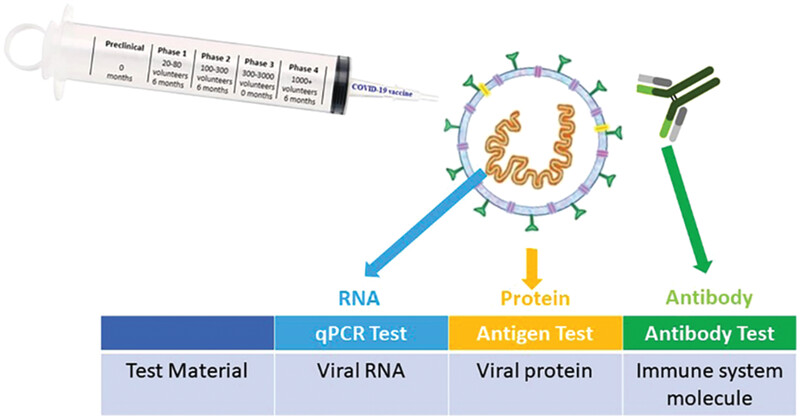
This paper reviews not only the structure, replication mechanism, and variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)-CoV-2 but also exposes all the details of the pandemic, such as how it came out, how it spread, what precautions should be taken, and prevention strategies in every aspect. It also compares the molecular and serological assays used for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis and lists the COVID-19 vaccines approved by the countries.
Arachidonic acid metabolism in health and disease
- First Published: 20 September 2023
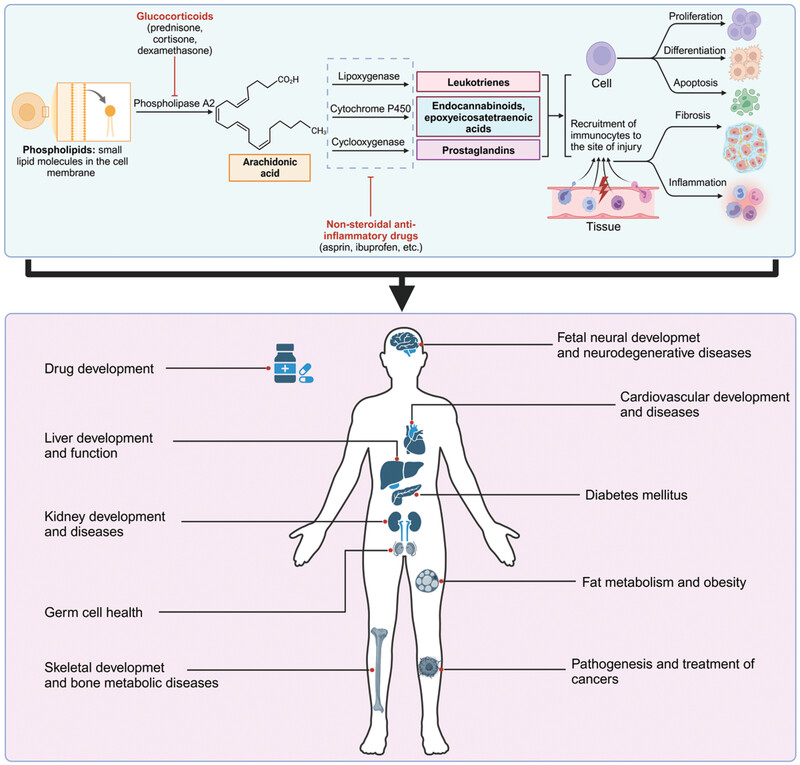
Arachidonic acid (AA) is released from phospholipids in the cell membrane by cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) and catabolized into different metabolites mainly through cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygenase (LOX), and cytochrome P450 (CYP-450) metabolic pathways. Arachidonic acid metabolites play important roles in cell fates, such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, as well as in fibrosis and inflammation caused by tissue injury. Accumulating evidence has proven that AA and its metabolites function in organ development and diseases, such as cardiovascular development, kidney development, liver development, skeletal development, diabetes, obesity, and cancers. Additionally, arachidonic acid metabolic pathways are important targets for drug development.