Aging AND Cancer focuses on aging as a central component of cancer evolution and progression. We're proud to be an open access cancer journal sharing knowledge with biomedical researchers around the globe.
Our content spans basic, translational, and clinical findings, investigating the biology of and/or mechanisms via which age-associated deterioration of the individual, from macromolecules to tissues and organs - promotes the onset, progression and relapse of cancer, and impacts treatment options and outcomes.
Journal Metrics
- 4.5CiteScore
- 89%Acceptance rate
- 60 days Submission to first decision
Journal News
Aging AND Cancer is now indexed by the Directory of Open Access Journals, your work will be discoverable and widely distributed!
Articles
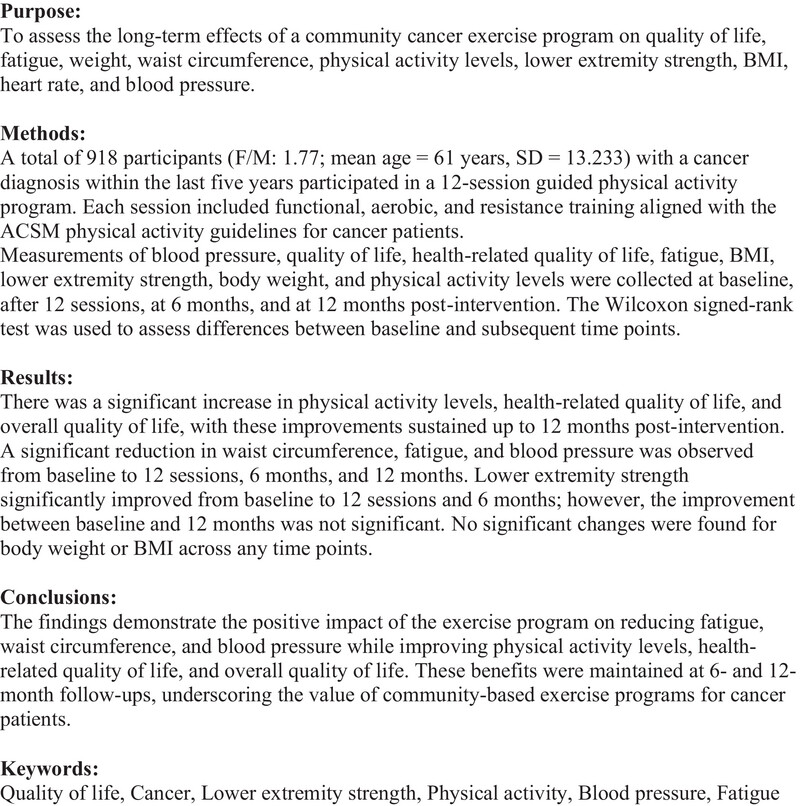
The Long Term Effects of a 12‐Session Community Exercise Program on Health Measures in Cancer Patients
- 54-68
- 3 May 2025
Aging‐Driven Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction and Its Impact on CNS Cancer Susceptibility: A Comprehensive Narrative Review
- 46-53
- 23 April 2025
Graphical Abstract
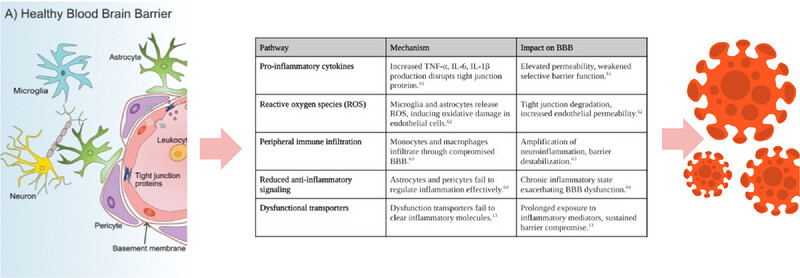
Aging weakens the blood–brain barrier (BBB), increasing susceptibility to CNS cancers and complicating treatment. This review examines BBB deterioration, its impact on drug delivery, and potential interventions like targeting neuroinflammation and advanced therapies. Understanding BBB aging is crucial for improving cancer treatment in older patients.
Understanding and Overcoming Immunotherapy Resistance in Skin Cancer: Mechanisms and Strategies
- 33-45
- 14 March 2025
Graphical Abstract
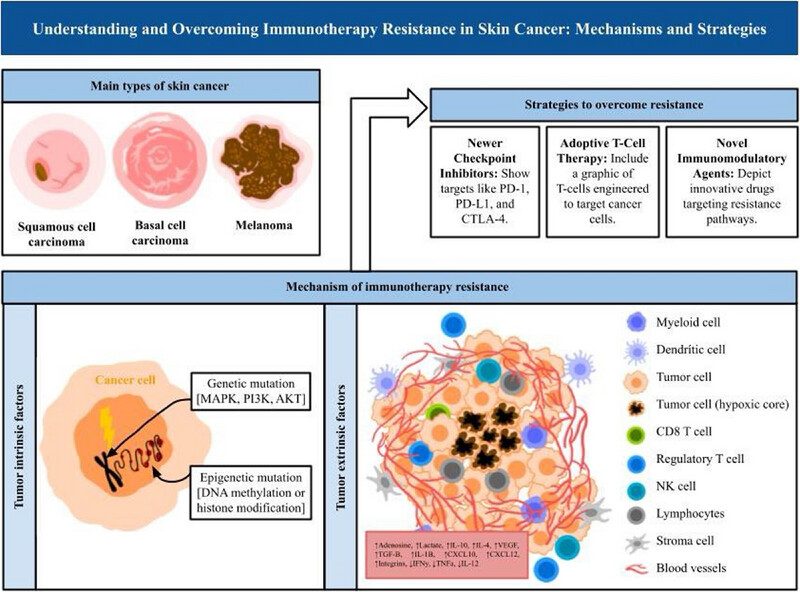
This narrative review explores the mechanisms driving immunotherapy resistance in skin cancer, including tumor microenvironment factors, genetic mutations, and immune evasion strategies. It highlights potential strategies to overcome resistance, offering insights for improving therapeutic outcomes and guiding future research in personalized immunotherapy.
Deciphering Aging, Genetic, and Epigenetic Heterogeneity in Cancer Evolution: Toward Personalized Precision Preventative Medicine
- 19-29
- 28 January 2025
Graphical Abstract
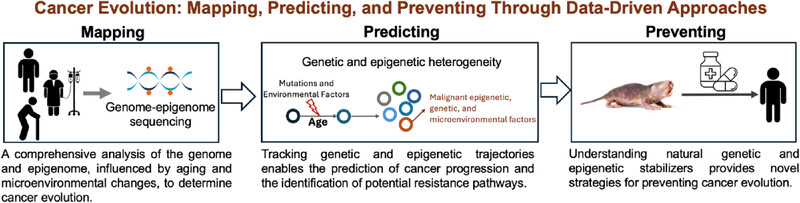
By integrating multi-omics dataincluding genomic and epigenomic profiles and microenvironmental exposures from both healthy individuals and patients, and performing intra-individual, inter-individual, and cross-species comparative analyses with advanced predictive models, we will uncover deeper insights into cancer evolution and identify potential strategies for individualized prevention.
Inflammation Promotes Aging‐Associated Oncogenesis in the Lung
- 3-18
- 30 October 2024
Graphical Abstract
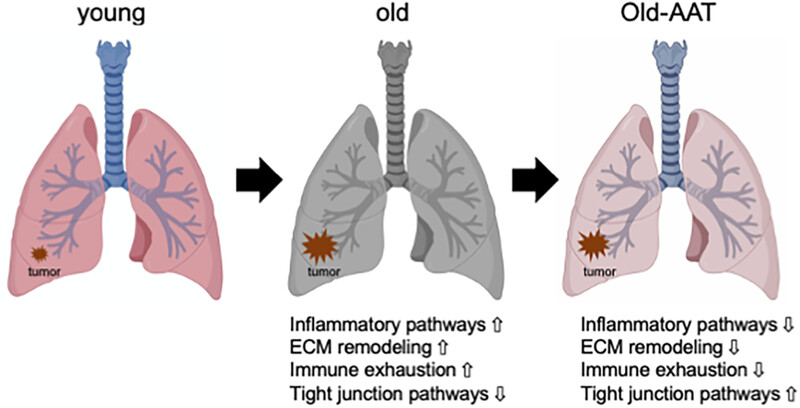
Aging lungs present an altered microenvironment, with increased inflammatory response, extracellular matrix remodeling, immune exhaustion, and decreased tight junctions, which contribute to increased tumor growth. This altered lung microenvironment is partially reversed to its youthful state with the overexpression of alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT).
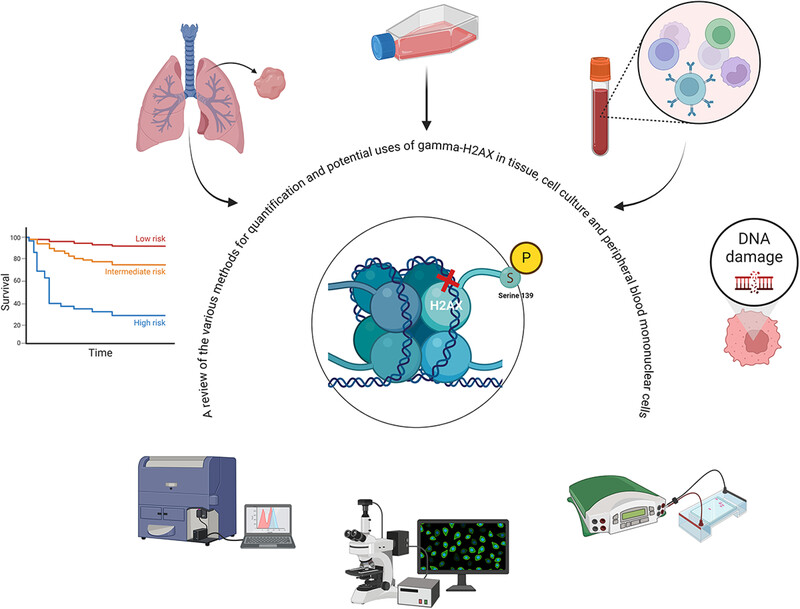
Considerations for the Use of the DNA Damage Marker γ‐H2AX in Disease Modeling, Detection, Diagnosis, and Prognosis
- 62-69
- 29 August 2024
From Hyperinsulinemia to Cancer Progression: How Diminishing Glucose Storage Capacity Fuels Insulin Resistance
- 51-61
- 27 August 2024
Graphical Abstract
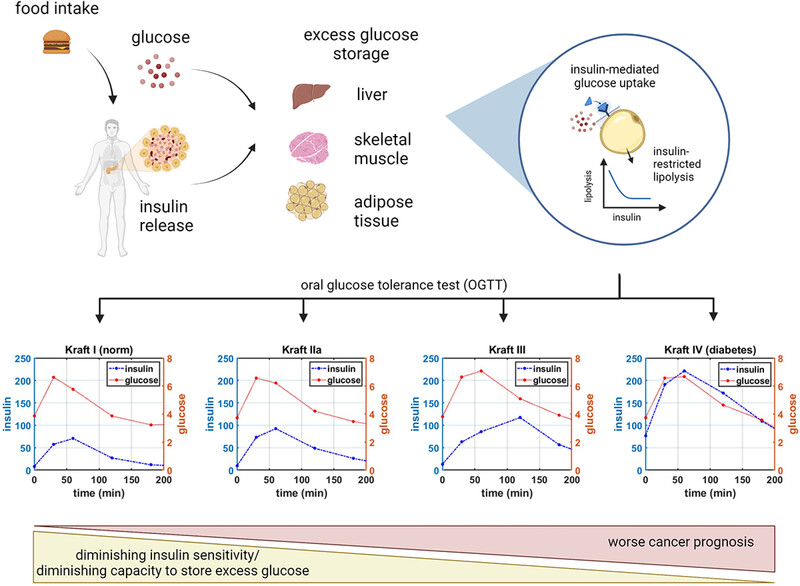
The key processes of glucose–insulin dynamics following glucose ingestion, including insulin-mediated intracellular glucose storage and insulin-restricted lipolysis, and the mechanistic connection between diminishing capacity to store excess glucose, decreased insulin sensitivity as reflected through the Kraft oral glucose tolerance test patterns, and cancer prognosis.
The Gut Microbiome in Aging and Ovarian Cancer
- 14-34
- 20 June 2024
Graphical Abstract
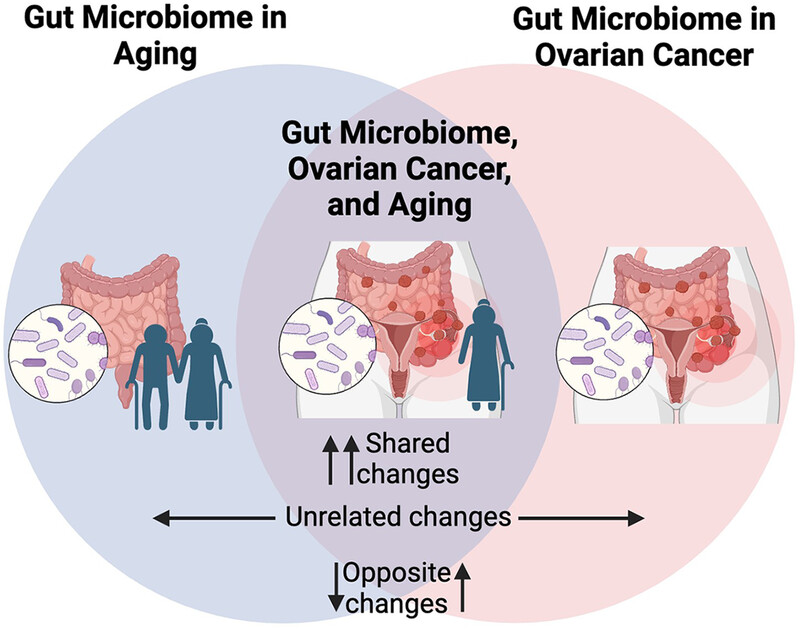
Changes in the gut microbiome accompany both aging and ovarian cancer. Despite that ovarian cancer primarily occurs in older women, there is a paucity of literature on the gut microbiome in ovarian cancer that specifically considers age of the host. This review highlights the changes in the gut microbiome that occur in ovarian cancer and aging, noting overlapping and contrasting trends and discussing the need for research that considers both age- and cancer-related changes in the gut microbiome of ovarian cancer patients.
Trending toward gero‐electroceuticals that target membrane potential for reprogramming aging and lifespan
- 3-13
- 8 June 2024
Graphical Abstract
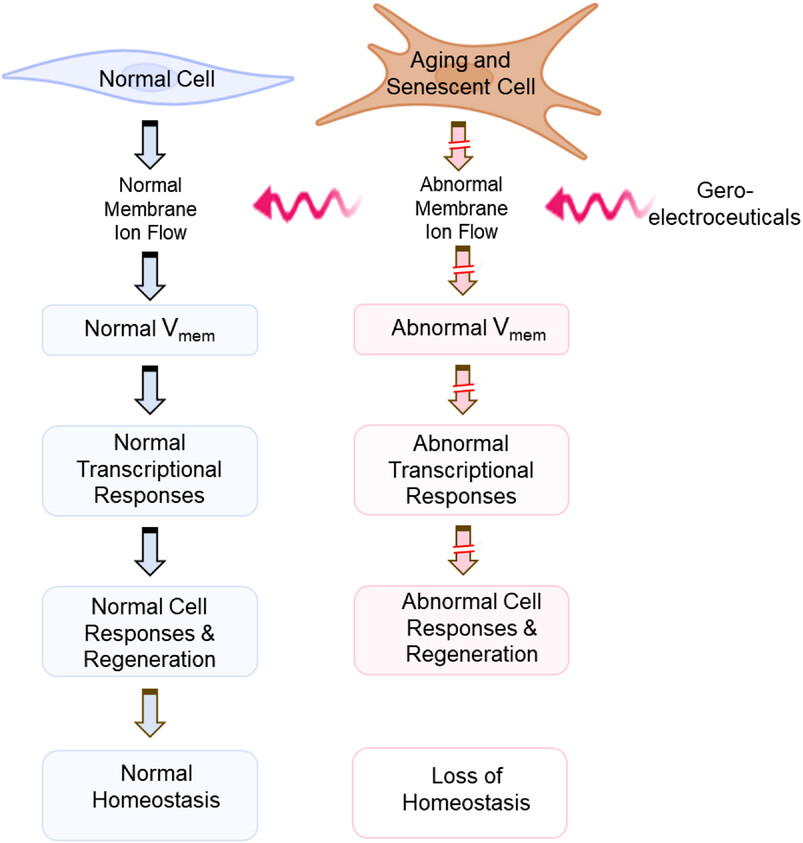
• Cells use ion flow in membranes to generate electric potential gradients (Vmem)
• Propagation of Vmem produces physiological tissue-wide bioelectric field gradients
• Bioelectric field gradients demarcate distinct gene expression domains within tissues
• Cells leverage bioelectricity for maintaining homeostasis and signal propagation
• Bioelectric field gradients direct or override the default genetic, epigenetic, or transcriptional responses
• Aging and senescence disrupt endogenous bioelectric dynamics and homeostasis
• Vmem deviations abrogate cellular functionality and regenerative capacity
• Bioelectric field gradients may be modified to regain lost function such as proliferation and regeneration
• Modifying the membrane potential can restore cell homeostasis and extend life-span.
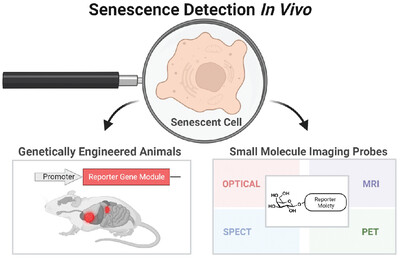
Detecting cellular senescence in vivo: Imagining imaging better
- Aging and Cancer
- 97-110
- 2 August 2023
Considerations for the Use of the DNA Damage Marker γ‐H2AX in Disease Modeling, Detection, Diagnosis, and Prognosis
- Aging and Cancer
- 62-69
- 29 August 2024
Trending toward gero‐electroceuticals that target membrane potential for reprogramming aging and lifespan
- Aging and Cancer
- 3-13
- 8 June 2024
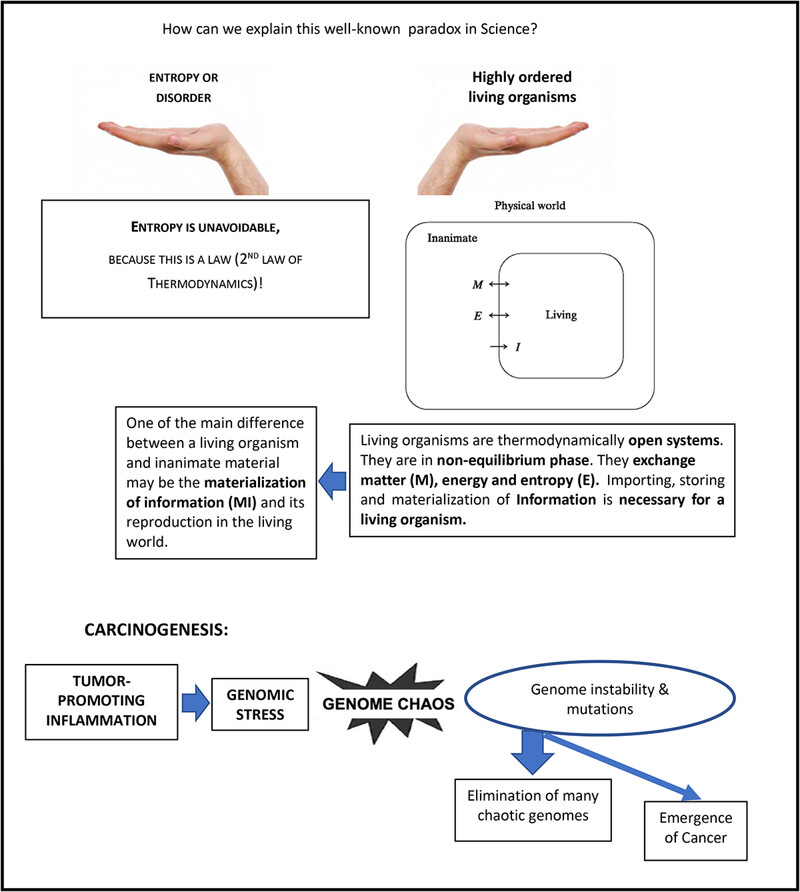
Biophysical Approach to Understand Life and Cancer
- Aging and Cancer
- 70-90
- 11 September 2024
Inflammation Promotes Aging‐Associated Oncogenesis in the Lung
- Aging and Cancer
- 3-18
- 30 October 2024
Deciphering Aging, Genetic, and Epigenetic Heterogeneity in Cancer Evolution: Toward Personalized Precision Preventative Medicine
- Aging and Cancer
- 19-29
- 28 January 2025
From Hyperinsulinemia to Cancer Progression: How Diminishing Glucose Storage Capacity Fuels Insulin Resistance
- Aging and Cancer
- 51-61
- 27 August 2024
Understanding and Overcoming Immunotherapy Resistance in Skin Cancer: Mechanisms and Strategies
- Aging and Cancer
- 33-45
- 14 March 2025