Editor-in-Chief: Fei Ma
Tsinghua University Press
Cancer Innovation is a high-quality, open access journal covering key topics in all aspects of cancer research, focusing on emerging interdisciplinary, strategic frontiers and key common technologies in oncology.
Journal Metrics
- 2CiteScore
- 2Journal Impact Factor
- 20%Acceptance rate
- 22 days Submission to first decision
A new frontier in innovative oncology solutions. Cancer Innovation provides timely updates on advances and unmet needs, bringing innovative oncology solutions to life.
Presenting a unique combination of oncology research, innovation, and data. Cancer Innovation bridges the gap between biological, medical, engineering, computational and data sciences. Its integrated, multidisciplinary coverage supports progress from basic research to clinical translation.
A hub for collaboration and communication across disciplines. Cancer Innovation unites researchers and clinicians from diverse medical subspecialities, providing opportunities to exchange, collaborate, and explore together.
A high-quality platform for guidelines on clinical decisions. Led by the China National Cancer Center, the editors ensure authentic statistics, consensus, and guidelines for clinical reference. Cancer Innovation combines professional resources to close the shortcomings in the management of oncological comorbidities.
News
We are glad to announce that Cancer Innovation has been indexed by Web of Science, Scopus, DOAJ, PMC (PubMed Center) and CAS: Chemical Abstract Service!
Articles
The Role of Multiparametric MRI Radiomics for Preoperative Prediction of Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Invasive Breast Cancer: A Comparative Study
- 13 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
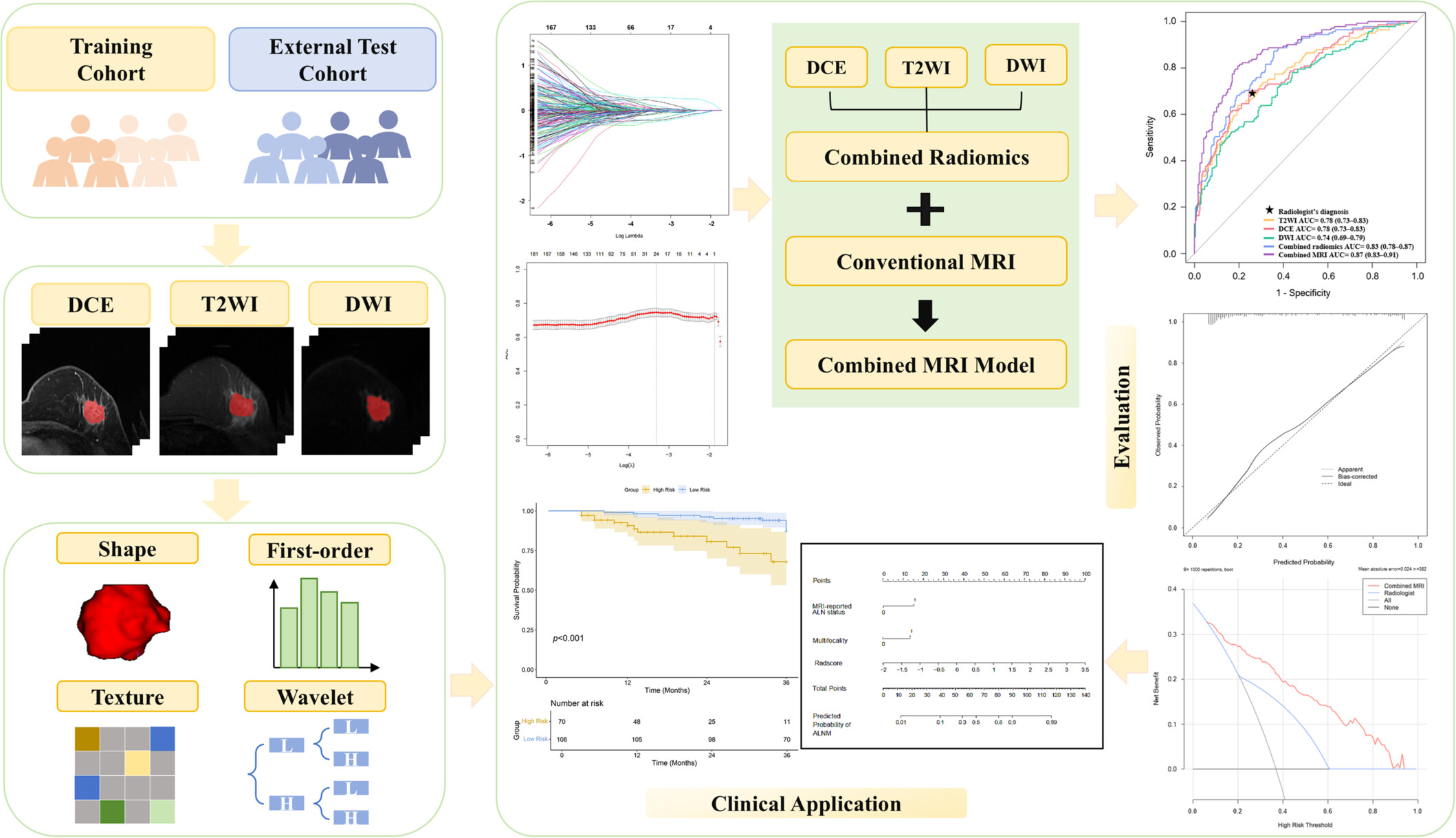
This study compared the preoperative noninvasive prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis in patients with invasive breast cancer using radiomics derived from single and multi-sequence MRI. The combined radiomics model outperformed the single-sequence models, with the DCE model performing better among the single-sequence models. The combined MRI model achieved the highest performance, improving diagnostic accuracy and showing potential for prognostic prediction.
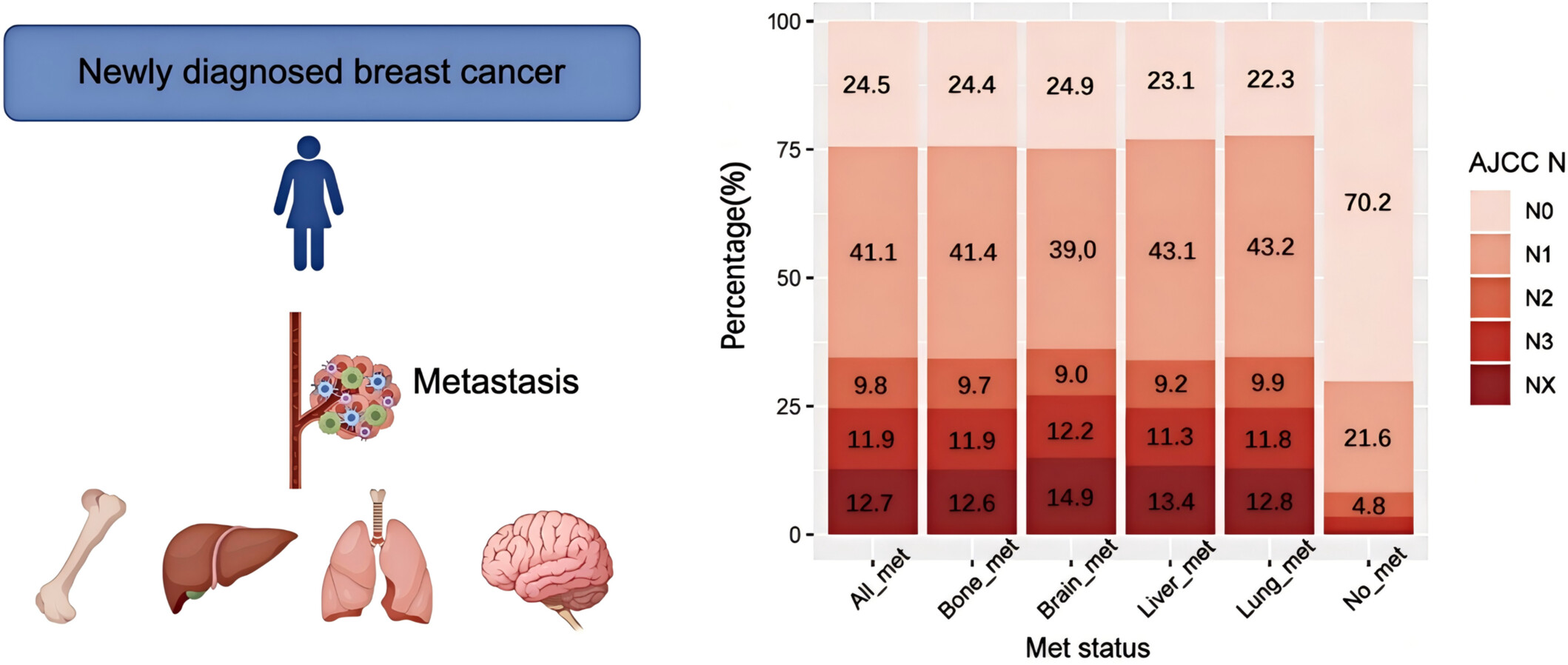
Mapping the Metastatic Landscape: A Population‐Based Cohort Study for Prognostic Insights Into Newly Diagnosed Stage IV Breast Cancer Cases
- 10 July 2025
Global Trajectories of Colorectal Cancer Burden From 1990 to 2021 and Projection to 2040
- 9 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
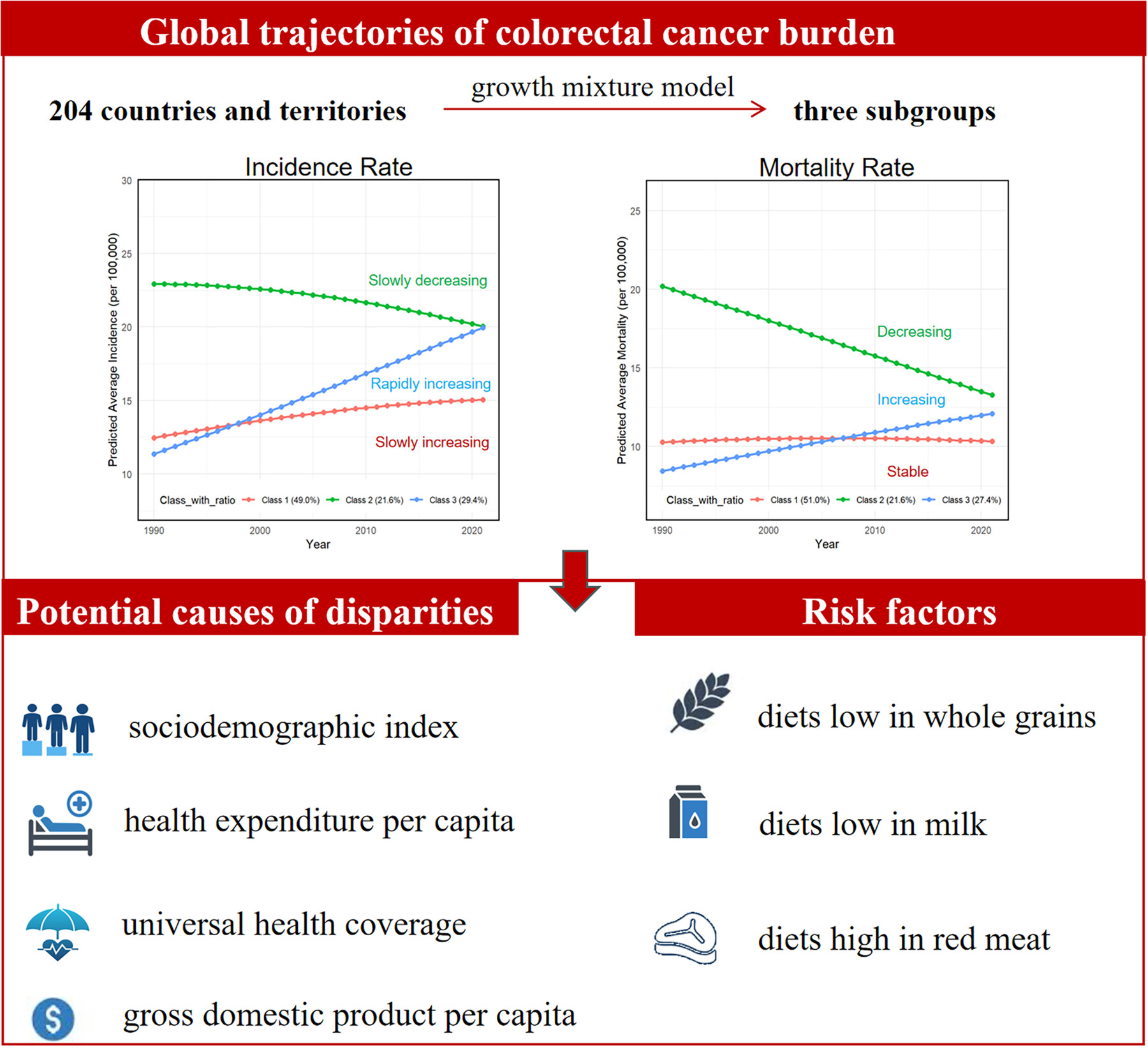
This study analyzes global colorectal cancer (CRC) burden trends, identifying three trajectories: slowly increasing, rapidly increasing, and slowly decreasing age-standardized incidence rate groups, with similar corresponding age-standardized mortality rate trends. Higher sociodemographic index, gross domestic product, health expenditure, and universal health coverage were associated with decreasing trends (all p < 0.05). Diets low in whole grains, milk, and high in red meat contributed significantly to CRC mortality. The findings highlight global disparities, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions to address dietary risks and health inequities.
Advances in Cellular Immune Theranostic Approaches for Glioblastoma: Current Trends and Future Directions
- 3 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
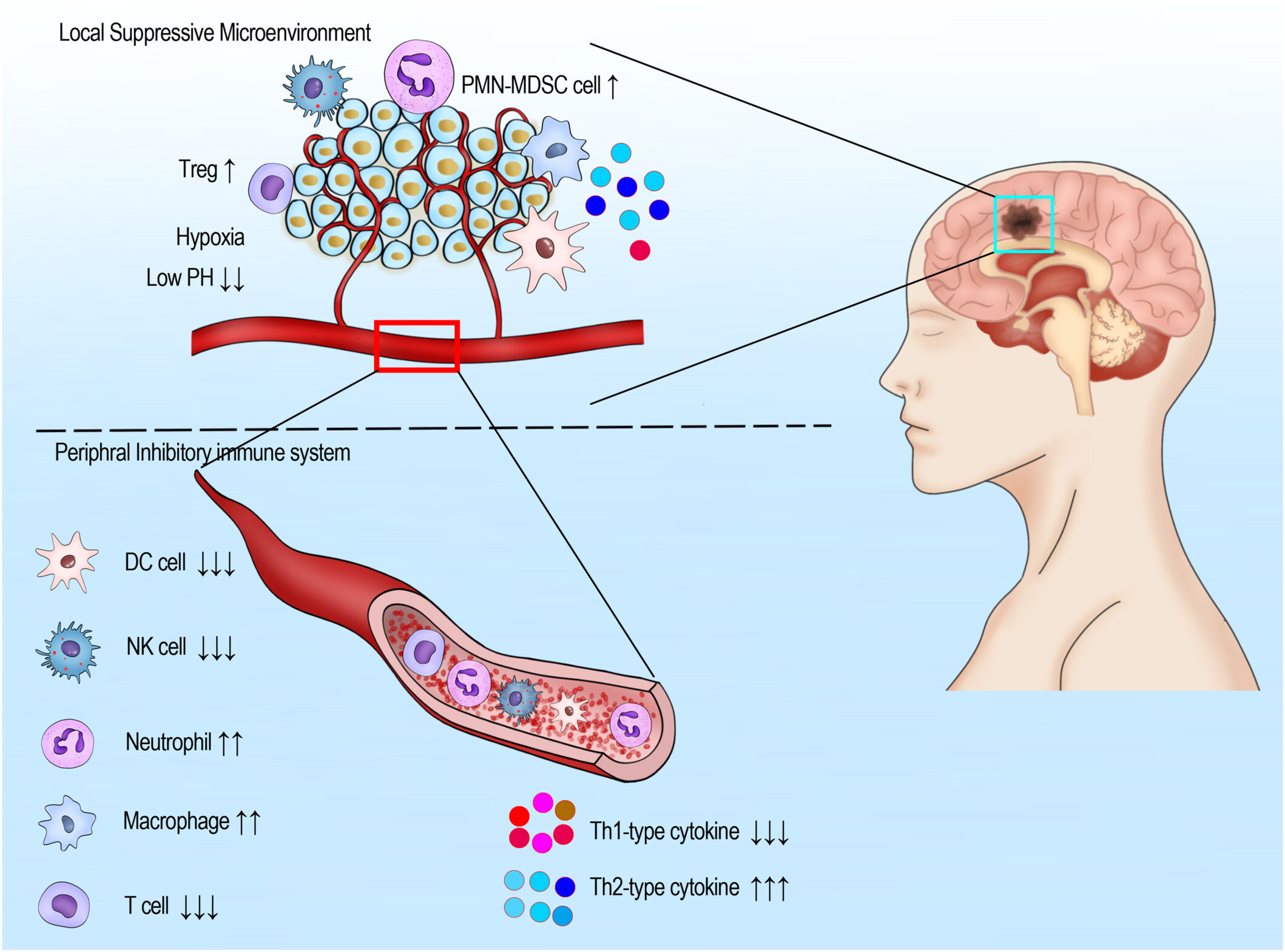
Glioblastoma (GBM) remains a highly malignant brain tumor with limited treatment efficacy, driving the need for innovative cellular immune theranostic strategies that integrate diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Recent advances in cellular immunotherapy for GBM include chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T/NK cells, macrophage-based therapies, oncolytic viruses, and personalized tumor vaccines, while advanced diagnostic tools like single-cell RNA sequencing and immune biomarkers enhance treatment monitoring. Key challenges in GBM immunotherapy involve overcoming the blood–brain barrier, addressing immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment, and optimizing the engineering of immune cells for durable clinical responses.
Explainable artificial intelligence in breast cancer detection and risk prediction: A systematic scoping review
- Cancer Innovation
- 3 July 2024
Graphical Abstract
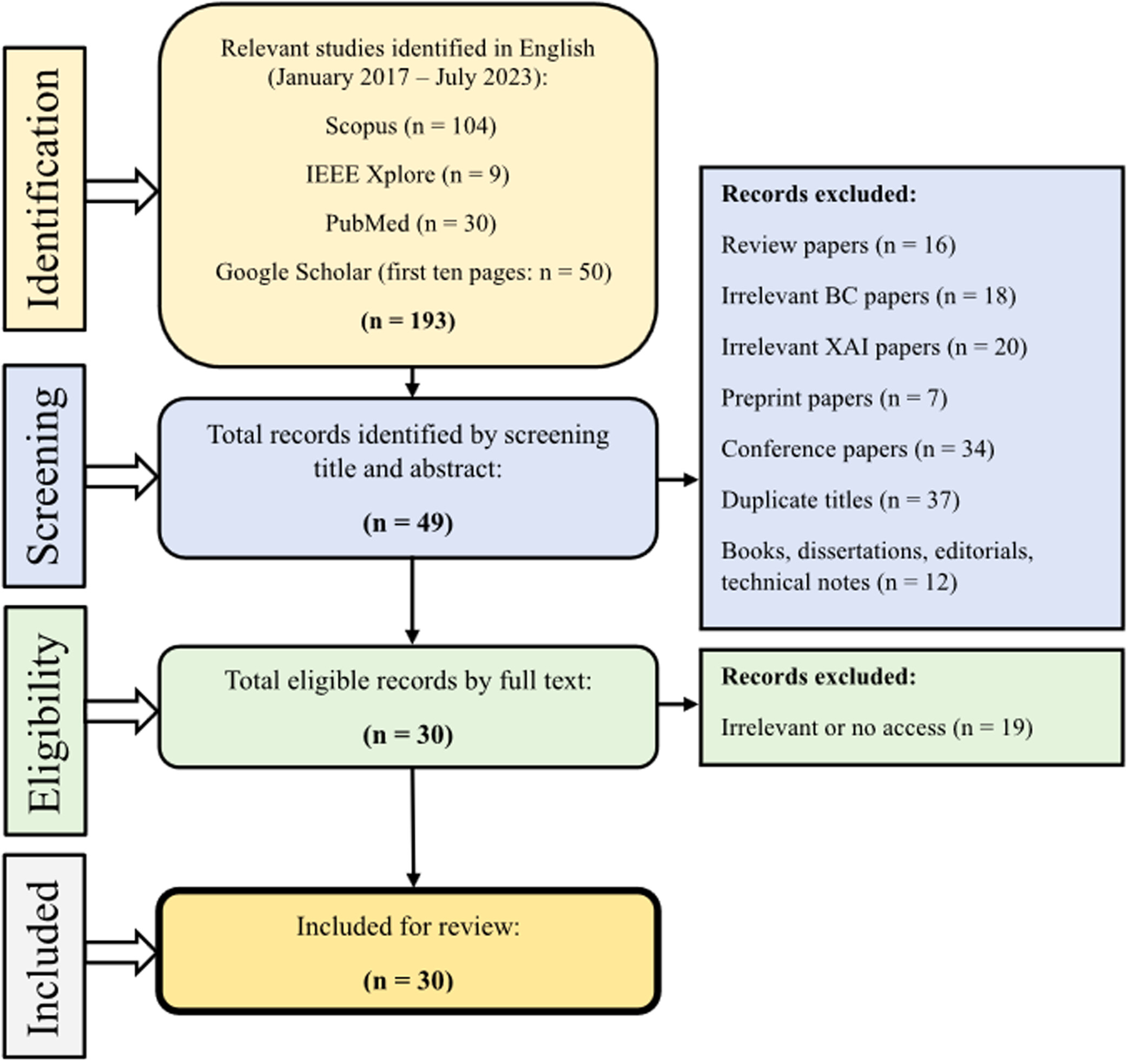
This systematic review is carried out using the preferred reporting items on systematic reviews and meta-analysis (PRISMA) guideline in three steps as follows:
Identifying studies (total of 193 studies were initially included). Selecting the studies (total of 30 articles met the inclusion criteria for our comprehensive review). Data extraction and summarization (A data extraction form was developed in Google Sheets, consisting of eight variables, including Authors, Year, the aim of the study (Objective), Data set(s), Data type, Important features, type of artificial intelligence (machine learning or deep learning), and the Explained model. Two reviewers (Amirehsan Ghasemi and Soheil Hashtarkhani) extracted data from all included articles, and any disagreement was resolved by consensus.
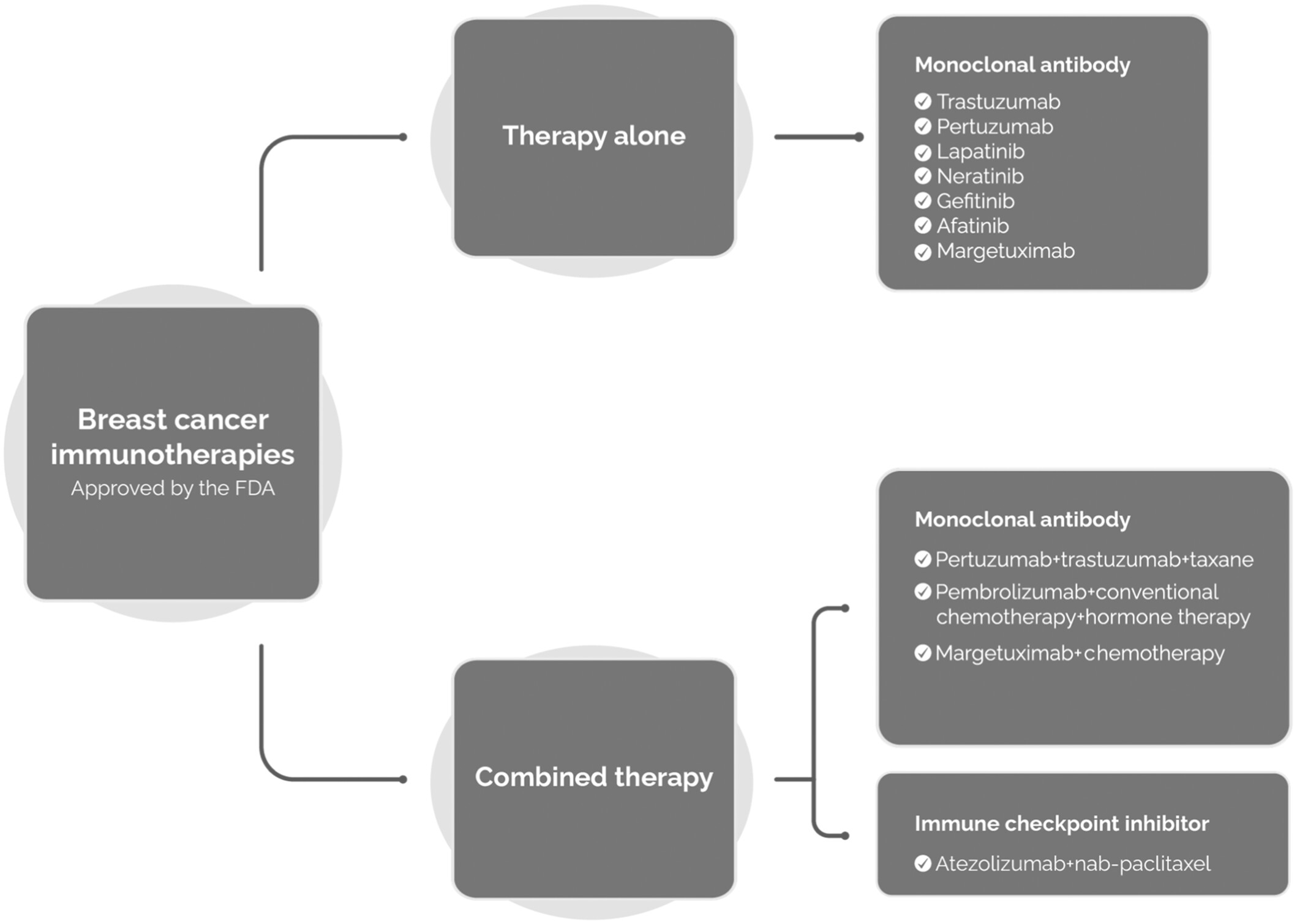
Breast cancer immunotherapy: Realities and advances
- Cancer Innovation
- 22 September 2024
Global trends of cancer: The role of diet, lifestyle, and environmental factors
- Cancer Innovation
- 290-301
- 25 July 2023
Graphical Abstract
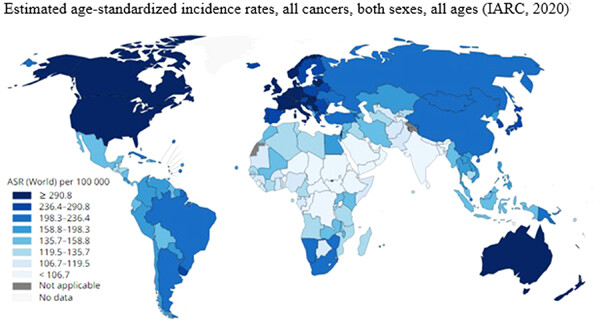
The age-standardized cancer incidence rate data for the selected countries indicate a great areal variation and different global trends for each type of cancer. Analysis of the worldwide statistical data regionally for cancer incidence rates for certain cancers meaningfully correlate with diet, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
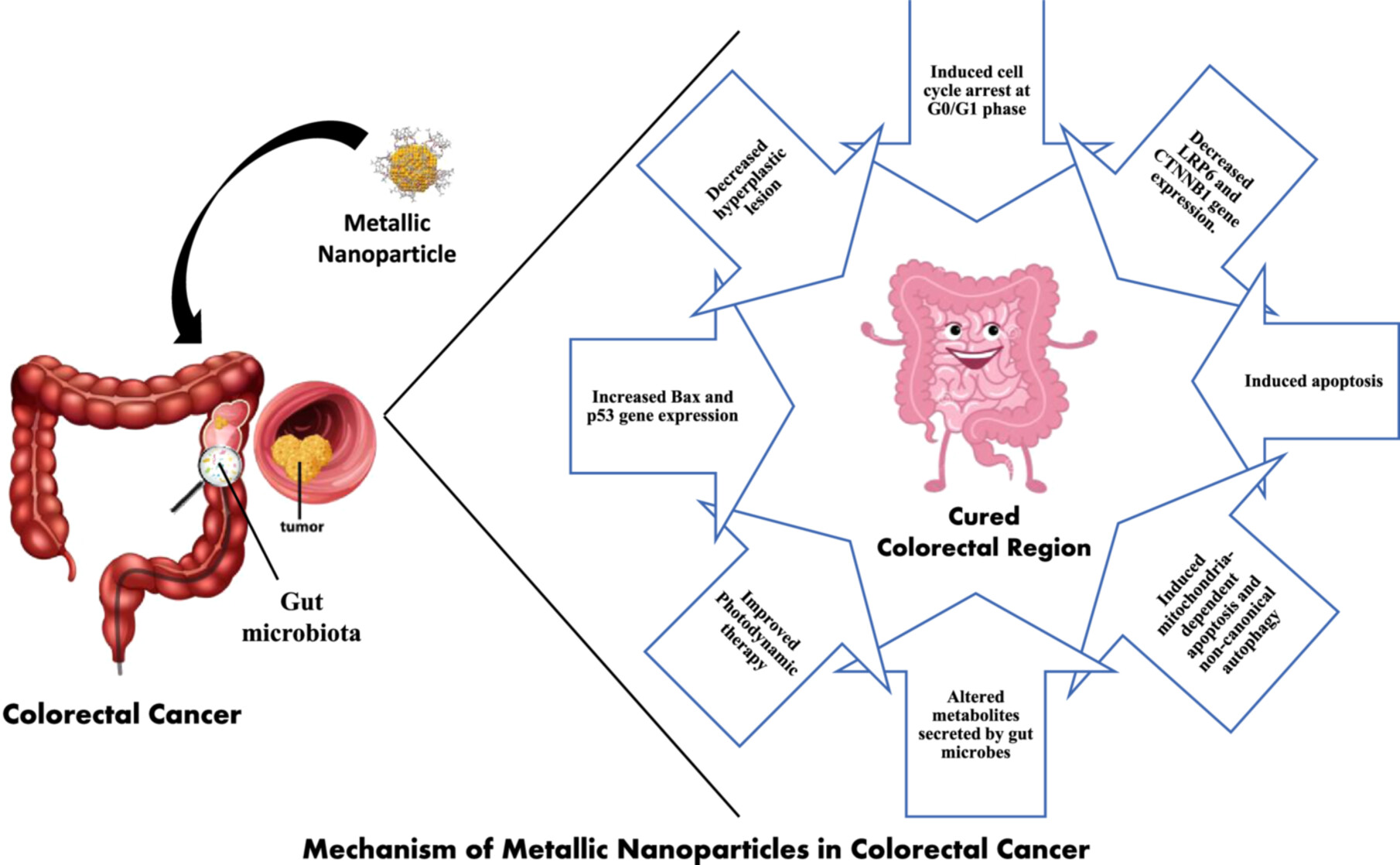
Impact of metallic nanoparticles on gut microbiota modulation in colorectal cancer: A review
- Cancer Innovation
- 11 October 2024
Prognostic nomograms for young breast cancer: A retrospective study based on the SEER and METABRIC databases
- Cancer Innovation
- 25 October 2024
Graphical Abstract
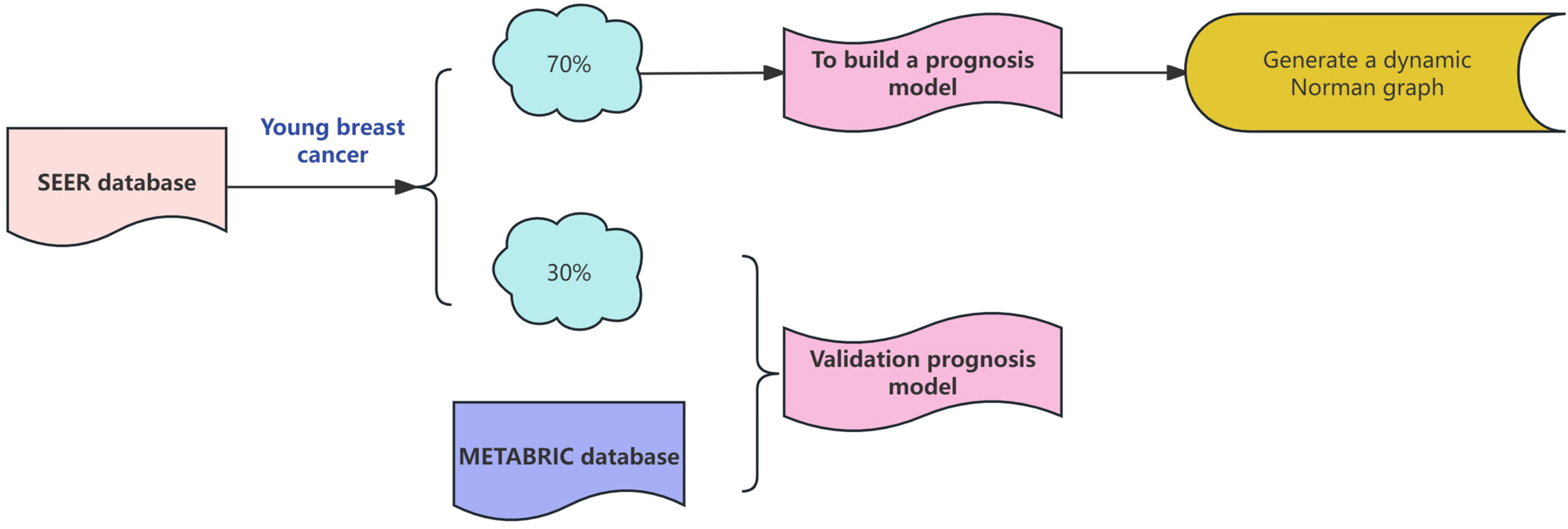
This study focuses on developing and validating prognostic nomograms for young breast cancer patients, integrating multiple clinical factors such as TNM stage, HER2 status, and pathological differentiation to predict overall survival and breast cancer-specific survival. Using data from the SEER and METABRIC databases, the nomograms provide accurate 3-, 5-, and 10-year survival estimates. Dynamic versions of these nomograms offer personalized, user-friendly tools to guide clinical decision-making, with the goal of improving prognosis and treatment outcomes for breast cancer with young patients.
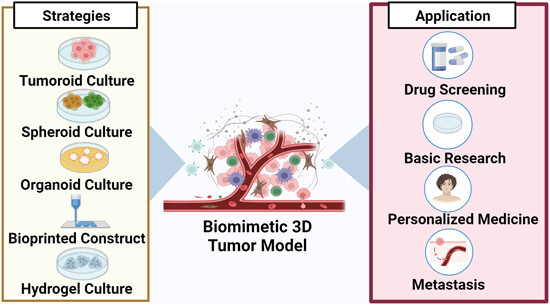
Organoid co‐culture models of the tumor microenvironment promote precision medicine
- Cancer Innovation
- 17 December 2023
Graphical Abstract
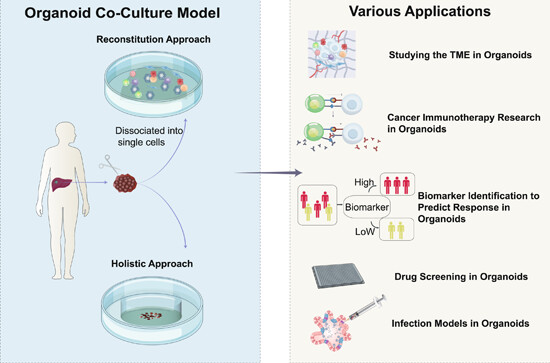
Three dimensional (3D) culture is a promising model for tumor research, replicating solid tumor characteristics. Advantages include high throughput and retention of heterogeneity. Traditional matrigel-submerged organoid culture requires exogenous cells to study the tumor microenvironment (TME). A holistic approach using patient-derived tumor fragments (PDTFs), air-liquid interface (ALI), suspension 3D culture, and microfluidic tumor-on-chip (ToC) models better mimic the tumor structure and composition. Organoid co-culture models are useful for studying the TME, immunotherapy, biomarkers, drug screening, and infections. These 3D systems aim to improve therapeutic approaches and patient outcomes.
Beyond clinical trials: CDK4/6 inhibitor efficacy predictors and nomogram model from real‐world evidence in metastatic breast cancer
- Cancer Innovation
- 25 October 2024
Graphical Abstract
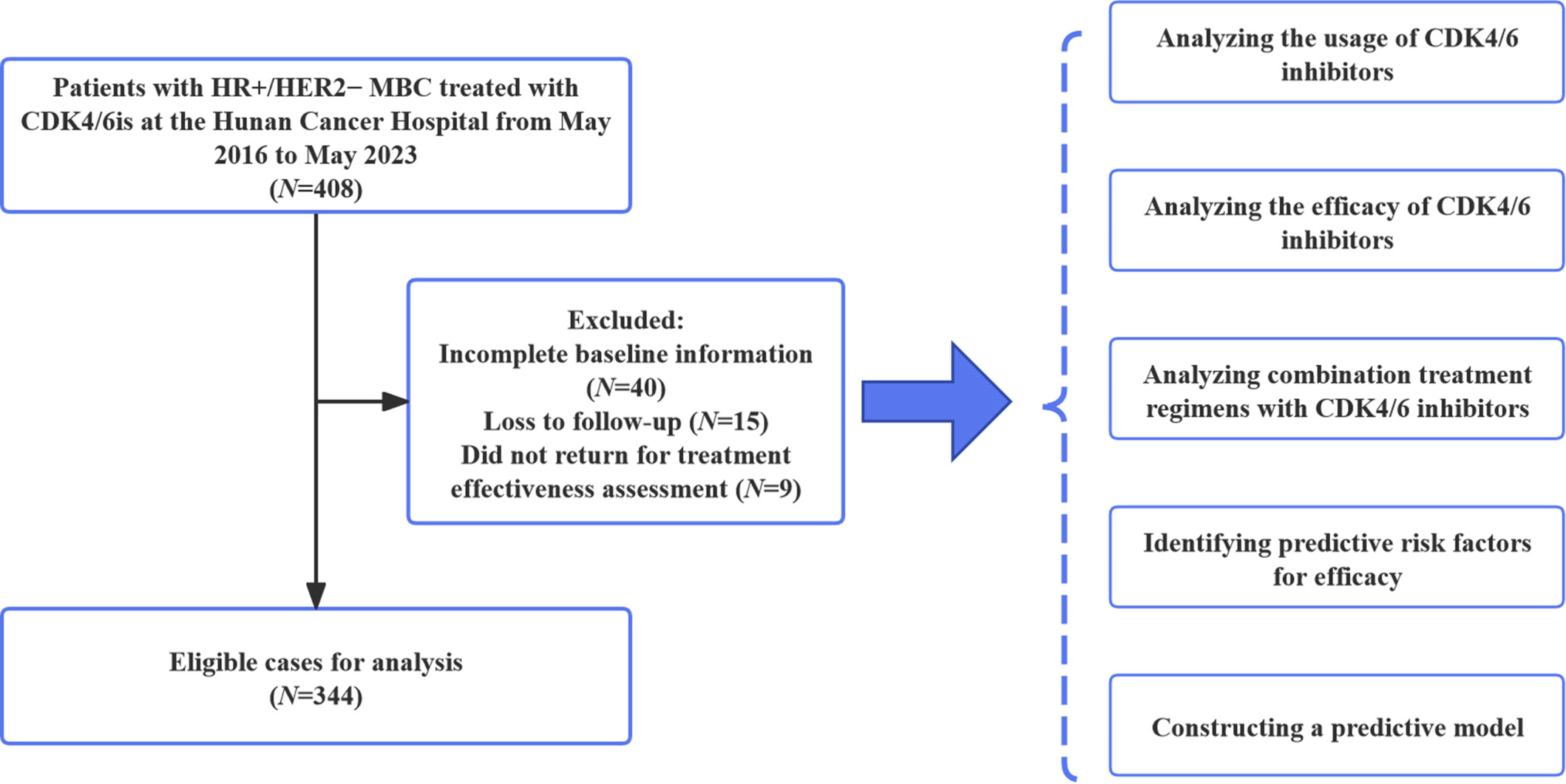
The graphical abstract summarizes a study evaluating CDK4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) combined with endocrine therapy in hormone receptorr-positive (HR+/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 metastatic breast cancer patients. It highlights a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 12.8 months, with significant factors reducing PFS including visceral metastasis, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status ≥ 1, low estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor levels, high Ki-67, and later-stage treatment. Adverse reactions such as neutropenia (29.1%), leukopenia (13.7%), and anemia (4.1%) were manageable. A prognostic nomogram showed good predictive performance (C-index 0.714), and a rechallenge of CDK4/6i demonstrated median PFS of 7.7 months, extending to 11.4 months for nonprogression discontinuation.
Inetetamab combined with sirolimus and chemotherapy for the treatment of HER2‐positive metastatic breast cancer patients with abnormal activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway after trastuzumab treatment
- Cancer Innovation
- 19 September 2024
Graphical Abstract
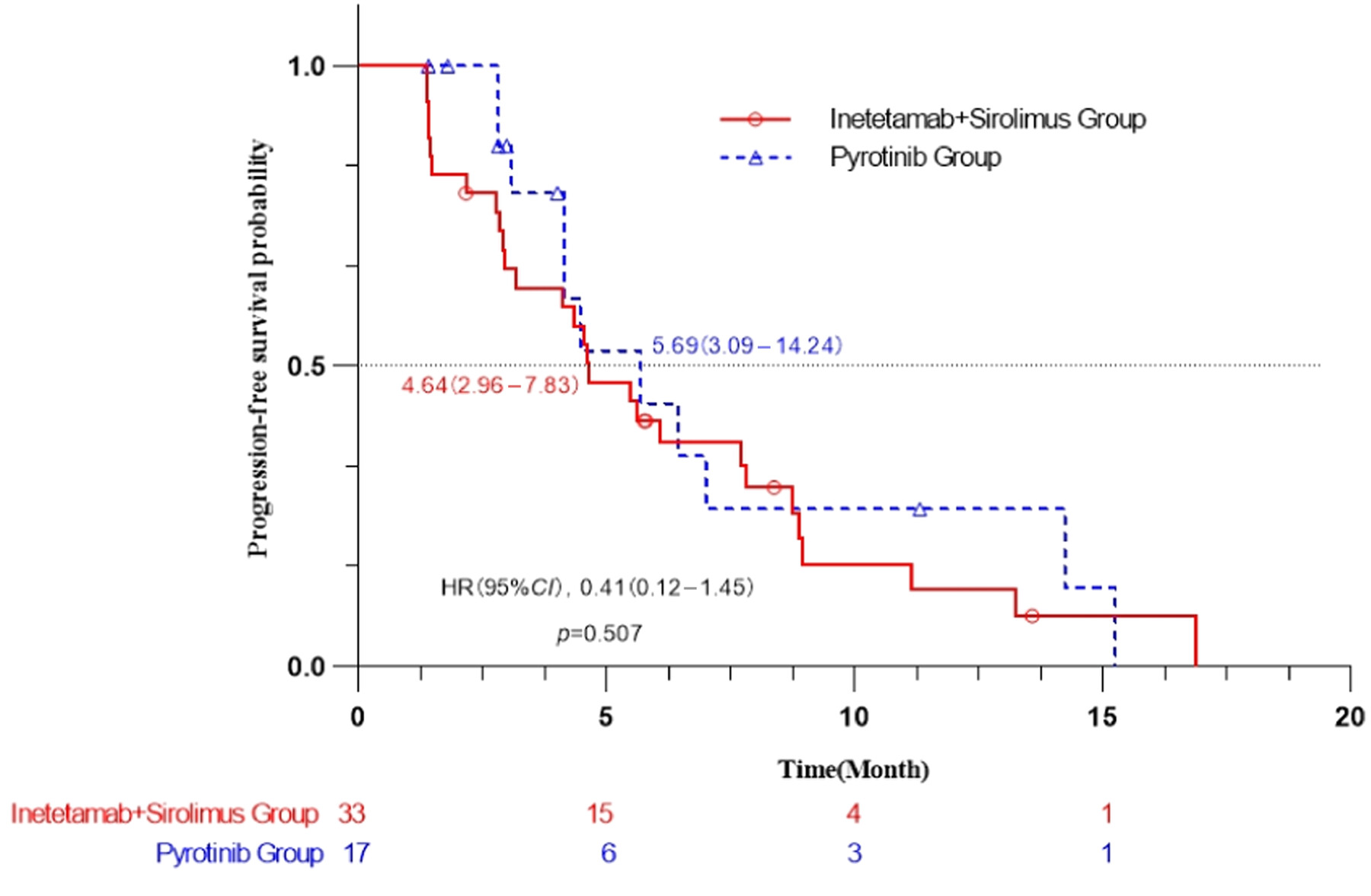
This prospective multicenter clinical study revealed that for metastatic Human epidermal factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer patients with abnormal activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR (PAM) pathway and previous trastuzumab treatment, the combination of inetetamab with sirolimus and chemotherapy is equivalent to the combination of pyrotinib and chemotherapy, and this regimen could be one of the treatment options for PAM pathway activated metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer patients.
Mitigating Ibrutinib‐Induced Ventricular Arrhythmia and Cardiac Dysfunction With Metformin
- Cancer Innovation
- 13 November 2024
Graphical Abstract
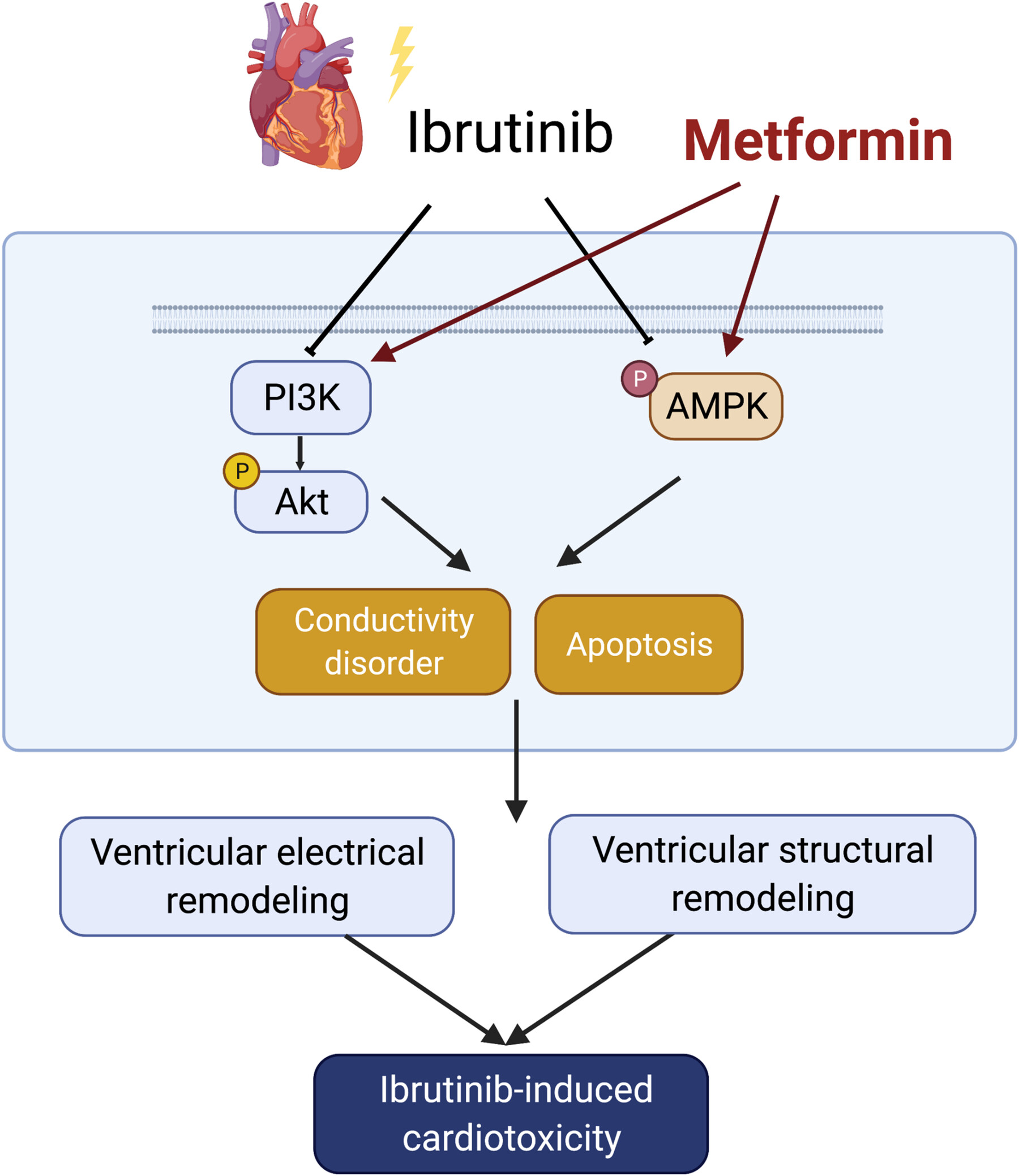
Ibrutinib, a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has been associated with a significant increase in the risk of ventricular arrhythmias. In our present study, we aimed to investigate the cardiotoxicity of ibrutinib and explore the potential protective effects of metformin in ibrutinib-treated mice. Our findings revealed that long-term exposure to ibrutinib triggered ventricular myocardial apoptosis and fibrosis, leading to alterations in cardiac electrophysiological properties and an increased potential for ventricular arrhythmia. In this ibrutinib-induced model of cardiac toxicity, metformin demonstrated the ability to upregulate the AMPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thereby mitigating the ibrutinib-induced cardiotoxicity. As a result, we have demonstrated the protective effects of metformin in counteracting ibrutinib-induced cardiotoxicity and propose it as a potential pharmaceutical therapeutic strategy for related diseases.
Leukocyte immunoglobulin‐like receptor B4: A keystone in immune modulation and therapeutic target in cancer and beyond
- Cancer Innovation
- 22 October 2024
Graphical Abstract
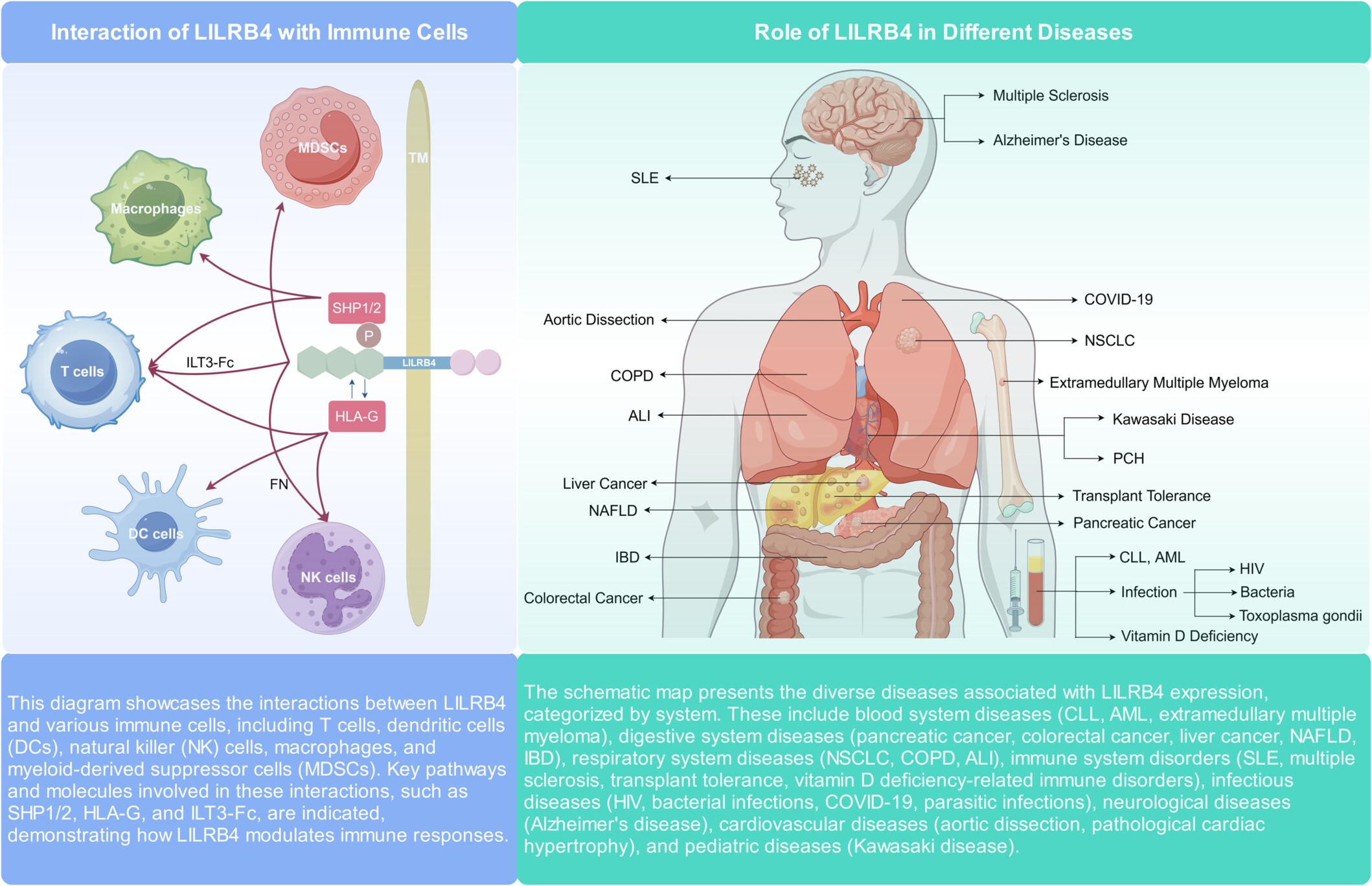
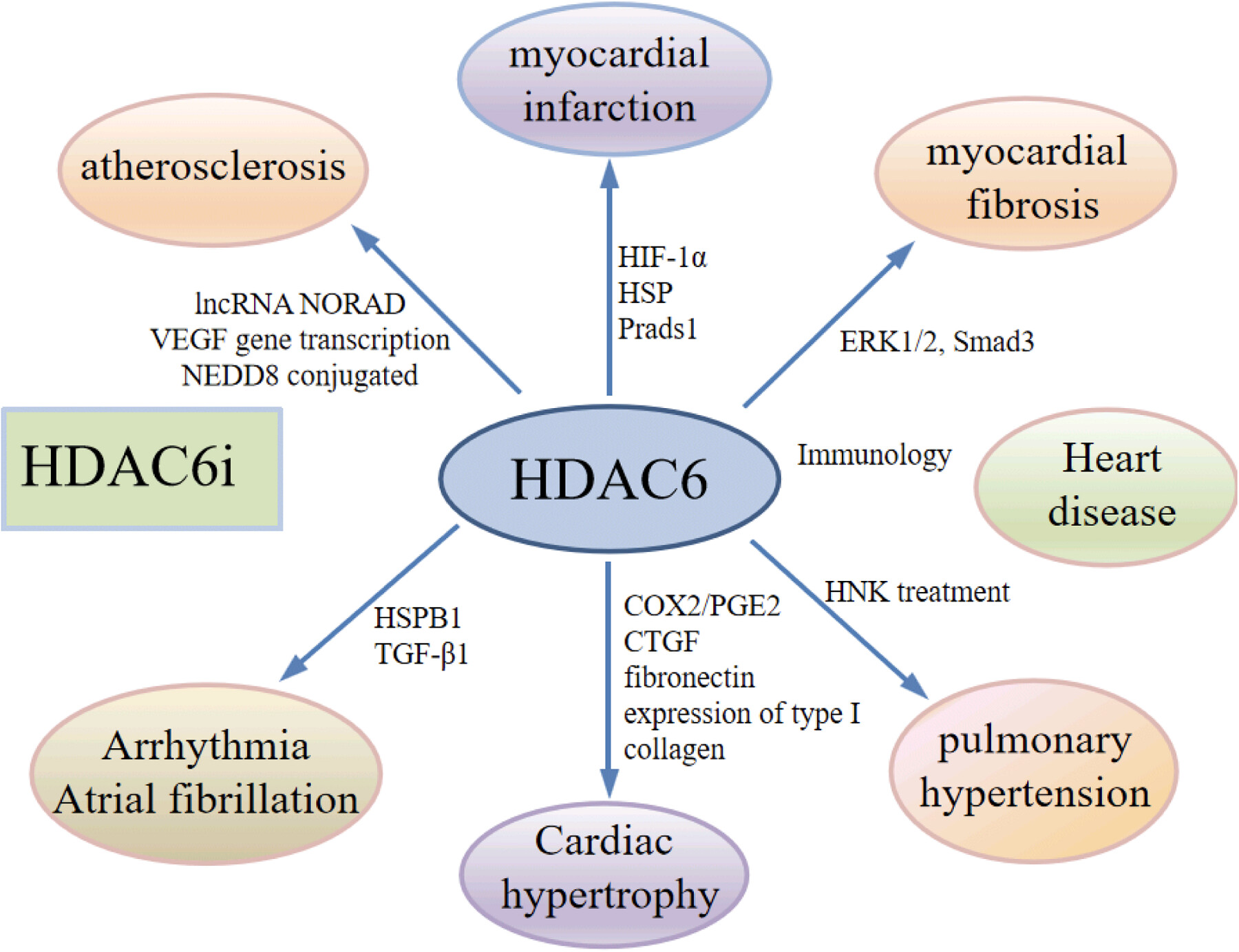
Interaction of LILRB4 with Immune Cells: This diagram showcases the interactions between LILRB4 and various immune cells, including T cells, dendritic cells (DCs), natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Key pathways and molecules involved in these interactions, such as SHP1/2, HLA-G, and ILT3-Fc, are indicated, demonstrating how LILRB4 modulates immune responses. Role of LILRB4 in Different Diseases: The schematic map presents the diverse diseases associated with LILRB4 expression, categorized by the system. These include blood system diseases (CLL, AML, extramedullary multiple myeloma), digestive system diseases (pancreatic cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer, NAFLD, and IBD), respiratory system diseases (NSCLC, COPD, and ALI), immune system disorders (SLE, multiple sclerosis, transplant tolerance, and vitamin D deficiency-related immune disorders), infectious diseases (HIV, bacterial infections, COVID-19, and parasitic infections), neurological diseases (Alzheimer's disease), cardiovascular diseases (aortic dissection, pathological cardiac hypertrophy), and pediatric diseases (Kawasaki disease).
Latest news
Recent issues
- Volume 4, Issue 5October 2025
- Volume 4, Issue 4August 2025
- Volume 4, Issue 3June 2025
- Volume 4, Issue 2April 2025